文章信息
- 多种药物预防铂类和紫杉烷类致慢性周围神经病变有效性的网状Meta分析
- Efficacy of Multiple Drugs in Preventing Chronic Peripheral Neuropathy Induced by Platinum and Taxane: A Network Meta-analysis
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2022, 49(2): 128-140
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2022, 49(2): 128-140
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2022.21.0675
- 收稿日期: 2021-06-11
- 修回日期: 2021-11-30
2. 362000 泉州,福建医科大学第二临床医学部
2. Second Clinical Medicine College, Fujian Medical University, Quanzhou 362000, China
各种铂类和紫杉烷类药物是癌症治疗中广泛使用的化疗药物,常单独或联合用于各种肿瘤的治疗,而周围神经病变是常见不良反应。周围神经病变主要分为急性和慢性两种类型。急性周围神经病变具有可逆性,发生率达到68.1%,对周围神经系统不会造成严重损害[1],但超过30%的患者可发展为慢性周围神经病变[2],不仅长期遭受症状折磨、影响生活质量,对于细小物体的感觉、扣扣子、走路会有困难,甚至可引起步态不稳,摔倒风险增加[3],即使有望治愈,症状可能也不会消失。现如今随着癌症存活率的不断提高,慢性周围神经病变的长期疾病负担越来越受到重视。
目前,为预防铂类和紫杉烷类引起的慢性周围神经病变(chronic peripheral neuropathy induced by platinum and taxane, PTIPN)的发生已进行了大量药物临床试验[4],但无指南推荐药物用于预防,有些药物临床试验证明无受益,不良反应显著(乙酰-L-左旋肉碱、尼莫地平等);有些药物仅初步试验有效,临床研究证据不足(多种中药、锰福地吡钙等);有些药物研究结果不一,疗效具有争议性(钙镁输注、谷氨酰胺、维生素E等)。同时各药物间头对头的直接比较试验也较为缺乏,无法确定各个药物的相对疗效。因此,本研究使用网状Meta分析方法,对预防PTIPN发生的各个药物进行汇总后实施定量化统计分析比较,确定拥有最佳疗效的预防药物,旨在为临床合理用药提供更多参考。
1 资料与方法 1.1 检索策略计算机检索PubMed、Cochrane library、Embase、中国知网(CNKI)、万方数据库和维普数据库,检索时限定义为建库至2021年2月。英文检索词包括“peripheral neuropathy”、“peripheral neurotoxicity”、“neuroprotective effect”、“neuroprotection”、“neuropathy”、“neurotoxicity”、“taxane”、“oxaliplatin”、“cisplatin”、“paclitaxel”、“chemotherapy”、“carboplatin”、“docetaxel”、“platinum”、“randomized controlled trial”等,中文检索词包括周围神经病变、周围神经毒性、神经毒性、预防、防治、治疗、奥沙利铂、卡铂、顺铂、紫杉醇、多西、紫杉烷等,采用主题词搭配自由词,并运用相应布尔逻辑运算符连接进行检索。此外,进行手工检索对纳入文献和研究药物已发表的系统评价和Meta分析的参考文献进行追溯。
1.2 纳排标准 1.2.1 研究类型已发表的随机对照试验(randomized controlled trial, RCT),语种限定为中文或者英文。
1.2.2 研究对象患者在细胞学或组织学诊断为癌症,在临床试验期间使用含铂类或紫杉烷类为基础的化疗方案,因慢性周围神经病变为剂量累积性,患者化疗周期≥4周期。
1.2.3 干预措施至少包含两种药物之间的成对比较,干预组和对照组的药物均为单药,且在预防期间,干预组和对照组除研究药物和对照药物外,不加用其他可能对预防PTIPN发生具有疗效药物。
1.2.4 结局指标包含有周围神经毒性的发生率,评价标准都是以等级方式报道,由正常、轻微、中度、重度、完全丧失逐步升级,其中发生2级及以上的PTIPN定义为严重的PTIPN。
1.2.5 排除标准(1)非随机对照试验;(2)研究对象纳入前存在周围神经病变;(3)正在接受除铂类和紫杉烷类外其他可能导致周围神经病变的药物;(4)药物无临床试验证明对PTIPN预防有效;(5)试验数据提供不足无法提取,数据出现明显错误;(6)药物仅进行初步试验和Ⅱ期临床试验,药物各个试验总例数加合小于200例;(7)患者试验期间同步放化疗。
1.3 文献质量评价与数据提取两位研究者独立审查通过搜索获得的文章列表,依据纳排标准选择符合条件的文章,并使用EXCEL软件制作文献数据提取表,提取内容包括:第一作者、发表年份;患者数量、癌症类型、预防引起PTIPN药物种类;干预措施和结局指标(疗效性结局指标PTIPN总发生率、严重PTIPN发生率)。分别对纳入研究采用Jadad评分量表和Cochrane偏倚风险评估工具进行方法学质量评价并交叉核对,若发生讨论未解决的分歧由第三者协助裁定。
1.4 统计学方法Stata 14.0软件进行统计分析,将各个试验拆分成成对比较,绘制各预防措施比较的证据网络图;计算不一致因子(inconsistency factors, IF)及其95%CI来评价各闭环是否一致,95%CI包含0视为一致性较好;绘制SUCRA曲线图,预测各预防措施疗效排序,曲线下面积越小,表明预防措施越好;并通过漏斗图识别发表偏倚。其次使用ADDIS1.16.6软件运用贝叶斯马尔科夫链-蒙特卡罗(Markov Chain Monte Carlo, MCMC)法对数据进行先验评估与处理,4条链进行模拟,调整迭代次数设置为20 000次,模拟迭代次数设置为50 000次,计算各预防措施有效性比较的OR值及95%CI,绘制出在稳定模型中各干预措施的网状Meta分析结果和对干预措施疗效排序的等级概率图,而直接与间接比较的不一致性通过点分法模型衡量,若P < 0.05认为不一致性是明显的。
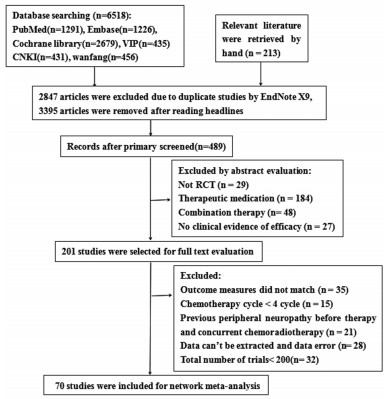
2 结果 2.1 文献检索结果共检索出6 731篇文献。排除重复文献和阅读题目后剩余489篇,阅读摘要后排除288篇,对余下文献进行通读全文后最终纳入70篇研究[5-74],其中中文文献36篇,英文文献34篇,依据纳排标准,排除无临床试验证明对PTIPN预防有效的药物,如乙酰-L-左旋肉碱、尼莫地平等和仅进行初步试验和Ⅱ期试验的药物,总例数 < 200人,如锰福地吡钙,参麦注射液,补阳还五汤等,共纳入11种药物,排除检索流程与结果,见图 1。
|
| 图 1 网状Meta分析的检索流程图 Figure 1 Retrieval flow chart of network Meta-analysis |
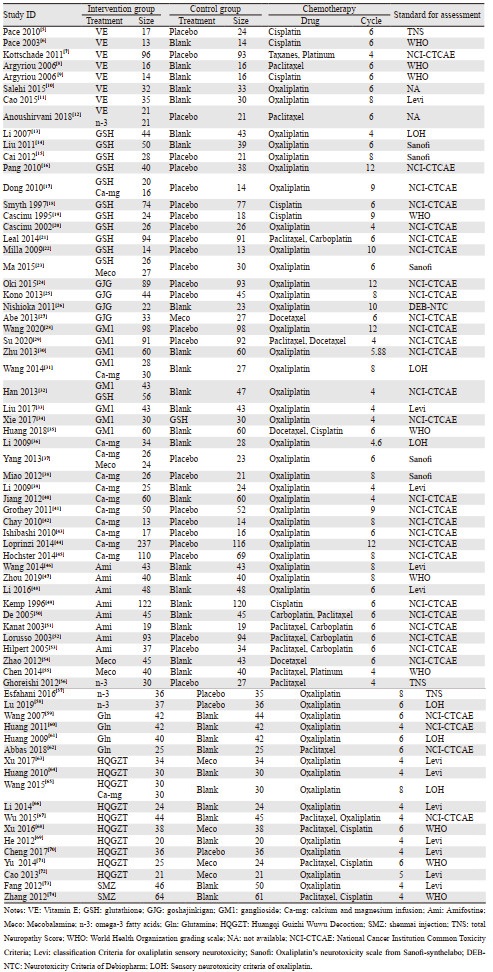
纳入的70项RCTs中,7项是三臂试验,其余均为二臂试验。共纳入11种干预药物,8项研究为维生素E(Vitamin E, VE),13项为谷胱甘肽(glutathione, GSH),4项为goshajinkigan(GJG),8项为神经节苷酯(ganglioside, GM1),13项为钙镁输注(calcium and magnesium infusion, ca-mg),8项为氨磷汀(amifostine, Ami),9项为甲钴胺(mecobalamine, Meco),4项为omega-3脂肪酸(omega-3 fatty acids, n-3),4项为谷氨酰胺(glutamine, Gln),10项为黄芪桂枝五物汤(huangqi guizhi wuwu decoction, HQGZT),两项为参麦注射液(shenmai injection, SMZ);在预防引起PTIPN的化疗药物中,51项试验预防的是铂类,7项试验预防的是紫杉烷类,12项预防的是二者联合;癌症类型绝大部分都为实体瘤,多集中于胃肠道肿瘤、乳腺癌、卵巢癌和肺癌;化疗周期4~7周期的研究有50项,≥8周期的有20项;55项研究比较了总的PTIPN发生率,而66项研究有报道了严重的PTIPN的发生情况,见表 1。
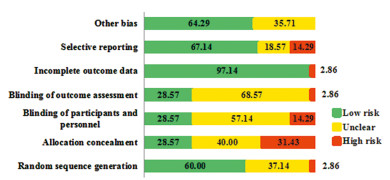
所有的研究均有描述其随机分组,42项研究有具体描述由通过“随机数字表法”、“计算机随机”等随机方法产生随机序列;20项研究[5, 7-9, 16, 19-20, 24-26, 29, 43, 45, 50, 52, 56-58, 62, 70]提及通过“密闭信封”、“中心分配”等实现分配隐藏,26项研究[5, 7, 10, 17-22, 24-25, 28-30, 37, 41-45, 49, 53, 56-58, 70]实施了“盲法”,20项研究[5, 7, 10, 17-21, 23, 25, 28-30, 43-45, 49, 56-57, 70]提及了对受试者、研究人员和分析者设盲,其他研究均未提及。Cochrane风险偏倚评估结果显示,随机方法、分配隐藏、盲法、分析者设盲、结局数据的完整性、选择性报告及其他偏倚的低偏倚风险比例占60.0%、28.57%、28.57%、28.57%、97.14%、67.14%、64.29%,见图 2。采用满分为7分的改良Jadad量表对纳入研究进行评分,45项研究得分≥4分,视为高质量研究,25项研究得分 < 4分,视为低质量研究,见表 1。
|
| 图 2 纳入研究的偏倚风险评价 Figure 2 Risk of bias in included literatures |
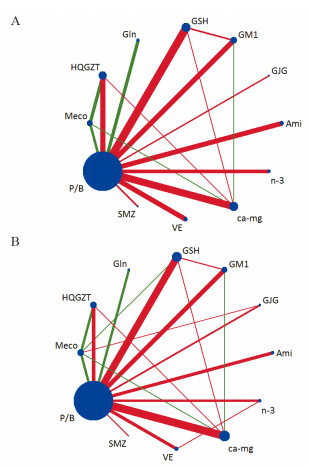
由图 3可见,每个圆点代表一种药物,2点之间有线段直接相连表明两种药物之间存在直接比较,使用Jadad量表对各研究进行评分后给线段上色,红色线段为高质量,绿色为低质量。其中钙镁输注总样本量最大,参麦注射液最小;钙镁输注与5种干预措施都有直接比较,甲钴胺、神经节苷脂、谷胱甘肽、黄芪桂枝五物汤都有与3种以上干预措施直接的研究;甲钴胺、谷氨酰胺与安慰剂或空白(placebo or blank, P/B)之间的比较,甲钴胺、神经节苷酯与钙镁输注之间的比较,甲钴胺与黄芪桂枝五物汤之间的比较在两个证据网络图中总体证据质量都偏低,甲钴胺与谷胱甘肽之间的比较在严重PTIPN的证据网络图中总体证据质量偏低,其余比较总体证据质量都偏高。
|
| P/B: Placebo or Blank. 图 3 11种药物预防总的PTPIN(A)和严重PTPIN(B)发生率的证据网络图 Figure 3 Network diagram for prevention of total PTPIN(A) and severe PTPIN(B) incidence with 11 drugs |
此次研究的预防措施之间在结局指标总的PTIPN发生率形成了8个三边形环,在严重PTIPN发生率形成了12个三边形环,对各个闭环研究结论的一致性进行检测,结果显示总的和严重PTIPN发生率的IF界分别0.23~1.03,0.00~2.20,二者95%CI下限均为0,表明各闭环一致性都较好,见图 4。
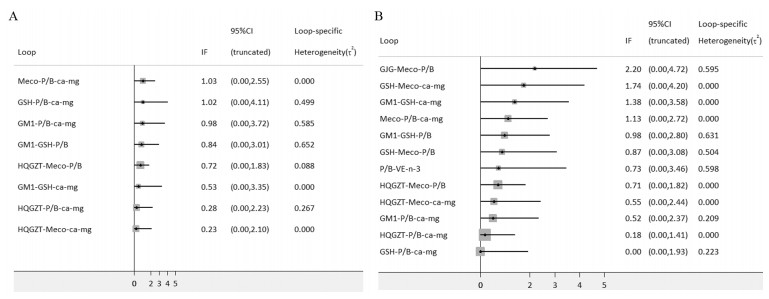
|
| 图 4 11种药物预防总的PTIPN(A)和严重PTIPN(B)发生率的不一致性检测图 Figure 4 Inconsistency test results for prevention of total PTPIN(A) and severe PTPIN(B) incidence with 11 drugs |
对纳入的研究绘制比较-校正漏斗图识别干预网络中是否可能存在小样本效应,若漏斗图是对称的,则说明不存在明显小样本效应或发表偏倚。从图 5的漏斗图可以看出在预防总的和严重PTIPN发生率指标方面各研究分布较为对称,说明研究间可能不存在小样本效应或发表偏倚。
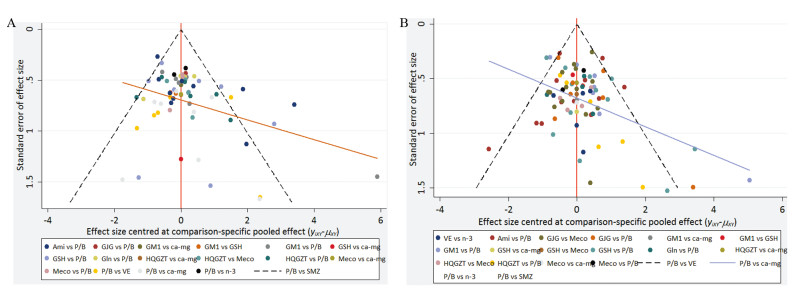
|
| 图 5 11种药物预防总的PTIPN(A)和严重PTIPN(B)发生率的比较-校正漏斗图 Figure 5 A comparison-adjusted funnel plot for prevention of total PTPIN(A) and severe PTPIN(B) incidence with 11 drugs |
使用一致性模型针对总的和严重PTIPN发生率指标进行网状Meta分析,各项药物头对头比较的网状分析结果见图 6,红色区域代表的是总的PTIPN发生率指标,蓝色区域代表的是严重PTIPN发生率指标,各个单元格内的数据代表是对应列与行预防措施疗效比较的OR(95%CI);若95%CI不包含1表明差异有统计学意义,OR值小于1,表明列预防措施疗效优于行预防措施;OR值大于1,表明列预防措施疗效劣于行预防措施;若95%CI包含1则表明差异无统计学意义,尚不能认为两种预防措施的疗效具有差异性。从图中可以看出,在降低总的PTIPN发生率指标方面,氨磷汀优于goshajinkigan、甲钴胺、P/B,黄芪桂枝五物汤优于甲钴胺、P/B,神经节苷脂,谷胱甘肽、维生素E、钙镁输注、omega-3脂肪酸优于P/B,其余比较均无统计学意义;在降低严重PTIPN发生率指标方面,黄芪桂枝五物汤优于甲钴胺,氨磷汀、神经节苷酯、谷胱甘肽、谷氨酰胺、黄芪桂枝五物汤、参麦注射液、维生素E、钙镁输注、omega-3脂肪酸优于P/B,神经节苷脂、黄芪桂枝五物汤优于钙镁输注,其余比较均无统计学意义。而从等级概率图中可以看出,无论是总的还是严重的PTIPN发生方面,安慰剂或者空白发生率为最高的概率都是最大的,黄芪桂枝五物汤发生率为最小的概率可能性较大,见图 7。
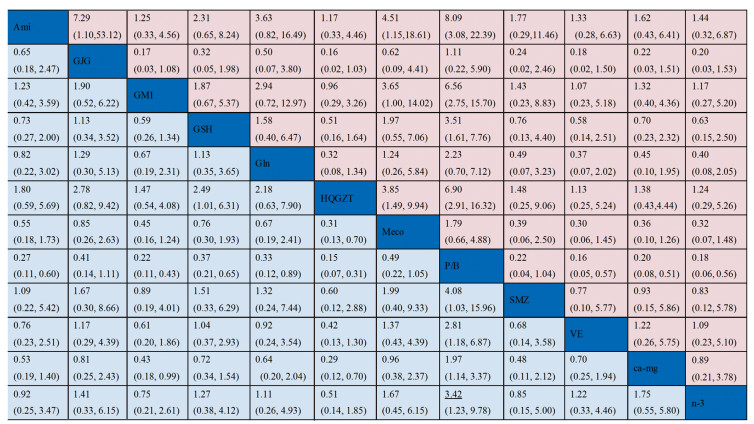
|
| 图 6 网状Meta分析结果 Figure 6 Network Meta-analysis result |
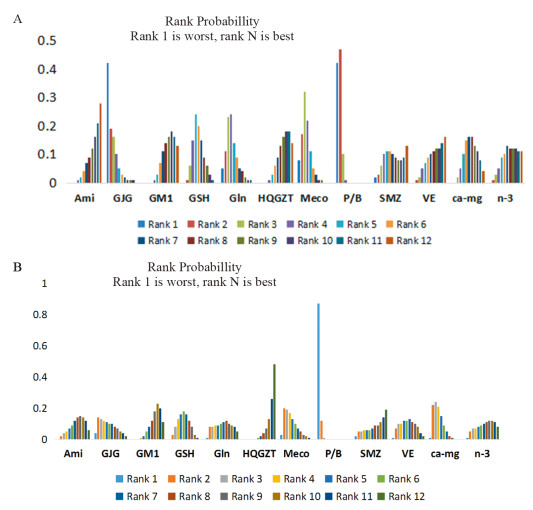
|
| 图 7 11种药物预防总的PTIPN(A)和严重PTIPN(B)发生率的等级概率图 Figure 7 Rank probability plot for prevention of total PTPIN(A) and severe PTPIN(B) incidence with 11 drugs |
使用点分法检验纳入的文献数据是否具有稳定性,由表 2和表 3提供的直接比较、间接比较和合并结果可以看出,无论是总的还是严重的PTIPN发生率指标Z检验求得所有均P > 0.05,说明直接比较证据与间接比较证据之间的结果一致,不存在统计学不一致性。
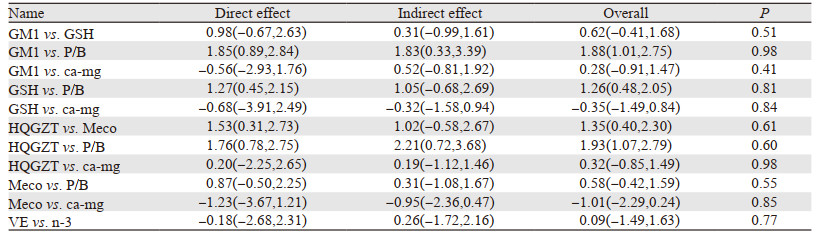
|
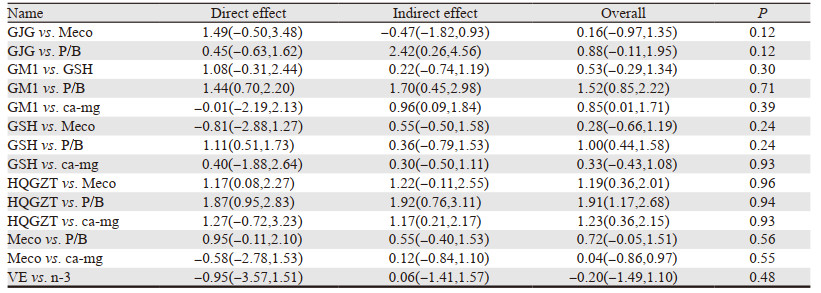
|
根据绘制SUCRA曲线图结果,曲线下面积小预测疗效排序越前,因此在预防总的PTIPN发生方面,11种预防措施由优到劣排序结果为:氨磷汀 > 黄芪桂枝五物汤 > 维生素E > omega-3脂肪酸 > 参麦注射液 > 钙镁输注 > 神经节苷脂 > 谷胱甘肽 > 谷氨酰胺 > 甲钴胺 > goshajinkigan > P/B;在预防严重PTIPN发生方面:黄芪桂枝五物汤 > 参麦注射液 > 氨磷汀 > 神经节苷脂 > omega-3脂肪酸 > 谷氨酰胺 > 维生素E > 谷胱甘肽 > 钙镁输注 > 甲钴胺 > goshajinkigan > P/B。从排序中可以看出11种药物在降低总的和严重PTIPN发生都优于P/B,而氨磷汀、黄芪桂枝五物汤、omega-3脂肪酸、神经节苷脂在预防总的或严重的PTIPN发生都有较好疗效(图请扫描本文OSID码)。
2.4.7 森林图同时绘制总的和严重的PTIPN发生率的网状分析森林图,蓝色为各项研究的直接比较,绿色为间接比较合并效应量,红色为合并直接与间接比较的效应量,从图中可以看出,各个两组药物之间的成对比较在间接比较合并效应量与直接与间接比较合并总效应量之间差异性较小(图请扫描本文OSID码)。
2.4.8 不良反应发生情况共有29篇文献报告各个药物在预防PTIPN试验过程中发生的不良反应发生情况,维生素E有3篇[7-9]都显示与P/B对比差异无统计学意义;谷胱甘肽有4篇,2篇[20-21]显示与安慰剂对比差异无统计学意义,2篇[17, 19]显示与安慰剂对比患者贫血程度有降低的趋势,需要输血量减少;goshajinkigan有4篇[24-27]显示与安慰剂、空白、甲钴胺对比差异无统计学意义;神经节苷脂有4篇,2篇[28, 34]显示与安慰剂、谷胱甘肽对比差异无统计学意义,1篇[29]显示与安慰剂对比2级以上疲劳的发生率更低,1篇[35]显示与空白对比各个化疗毒性反应发生率明显降低;钙镁输注有4篇[40-41, 44-45]都显示与P/B对比差异无统计学意义;谷氨酰胺有2篇,1篇[59]显示与P/B对比无差异,1篇[60]显示与空白对比腹泻发生率明显减少;黄芪桂枝五物汤有1篇[70]显示与安慰剂对比差异无统计学意义;氨磷汀有7篇,2篇[47, 49]显示与空白对比能降低中性粒细胞减少,1篇[52]显示与安慰剂对比对患者黏膜炎有改善,但有2篇[50, 53]显示与P/B对比恶心呕吐更为常见,同时有2项研究[51-52]报告接受氨磷汀都有5个患者出现低血压。由此,可看出11种除氨磷汀报道低血压和加重恶心呕吐外,其余药物与P/B对比差异均无统计学意义。
3 讨论铂类和紫杉烷类药物作为各种肿瘤化疗的基石,其引起CIPN的不良反应影响患者的治疗和生活质量。在防治CIPN的药物中,度洛西汀是指南唯一推荐的治疗药物,对于预防目前尚未有其他药物推荐,本研究依据循证相关研究原则及方法,首次针对预防PTIPN这一临床问题,通过全面搜索各大英文和中文数据库和手工追溯参考文献,并对中文期刊的质量进行筛选,遴选出具有代表性的11种药物共70项RCTs合计6201例患者,以严重和总的PTIPN发生率为结局指标进行网状Meta分析。旨在比较不同药物之间的疗效差异,解决原始研究中缺乏各个药物头对头直接比较,难以判断相对疗效差异的问题,同时结合考虑纳入研究的不良反应报告情况,以此排选出疗效和安全性兼顾的最佳选择。
在降低总的PTIPN发生率方面,氨磷汀、神经节苷脂、黄芪桂枝五物汤、谷胱甘肽、维生素E、钙镁输注、omega-3脂肪酸均优于P/B,氨磷汀优于goshajinkigan和甲钴胺,黄芪桂枝五物汤优于甲钴胺;SUCRA曲线图和等级概率图显示氨磷汀、黄芪桂枝五物汤、维生素E、omega-3脂肪酸排序在前,甲钴胺、goshajinkigan、P/B排序在后;但同时文献报道氨磷汀可引起低血压,并比P/B对比能加重恶心呕吐,因此,推荐黄芪桂枝五物汤为预防总的PTIPN发生的最佳选择,维生素E、omega-3脂肪酸、神经节苷酯、钙镁输注、谷胱甘肽为次要选择。在降低严重PTIPN发生率方面,氨磷汀、神经节苷酯、谷胱甘肽、黄芪桂枝五物汤、维生素E、钙镁输注、omega-3脂肪酸、谷氨酰胺、参麦注射液优于P/B,神经节苷脂、黄芪桂枝五物汤优于钙镁输注;黄芪桂枝五物汤优于甲钴胺;SUCRA曲线图和等级概率图显示黄芪桂枝五物汤、氨磷汀、神经节苷脂、omega-3脂肪酸排序在前,甲钴胺、goshajinkigan、P/B排序在后,但同时考虑到氨磷汀的不良反应,因此,推荐黄芪桂枝五物汤为预防严重PTIPN发生的最佳选择,神经节苷脂、谷胱甘肽、维生素E、钙镁输注、omega-3脂肪酸为次要选择,由于谷氨酰胺、参麦注射液OR至上下限接近1,不作推荐。点分法显示直接比较与间接比较证据结果一致,IF、95%CI下限均为0,各闭环一致性较好,结果具有稳定性。因此,推荐黄芪桂枝五物汤为最佳选择,次要可选神经节苷酯、维生素E、omega-3脂肪酸、钙镁输注、谷胱甘肽都能预防总的和严重PTIPN的发生。目前关于PTIPN的发病机制尚不十分明确,但大量实验证据表明,化疗药物诱导的表皮神经纤维损伤、氧化应激损伤、异常自发放电、离子通道激活、各种促炎细胞因子的上调和神经免疫系统的激活与其发生和发展密切相关[75]。黄芪桂枝五物汤是《金匮要略》记载的中药方剂,用于改善肢体麻木和疼痛;神经节苷脂是一类主要位于神经元细胞膜表面的糖脂,对神经系统发育再生和损伤修复起重要作用[29];omega-3脂肪酸作为一种长链脂肪酸,能提高机体的免疫力,具有营养保护周围神经的作用[58];三者都可通过减少背根神经节组织中炎性反应来保护周围神经,增强免疫调控,修复神经损伤[30-32, 70, 76]。谷胱甘肽和维生素E都是抗氧化剂,影响生物能量代谢,能够对抗自由基的破坏,减轻氧化应激损伤[6, 14],谷胱甘肽还能防止铂化合物在脊神经节中的蓄积,而钙镁输注利用镁的膜稳定特性,同时增加细胞内Ca2+的浓度来影响细胞膜的超极化,促进Na+通道的关闭[75],从而减少周围神经病变的发生。
此次研究存在以下不足:(1)纳入文献质量不够高,虽然已经对中文期刊进行了筛选,纳入的都为RCT,但有一半以上研究在分配隐藏和盲法实施方面偏倚较大,26项研究Jadad量表评分较低,可能会对研究结论产生一定影响。(2)研究结论显示为最佳选择的黄芪桂枝五物汤仅在中国使用广泛,能否进行推广至其他国家存疑。(3)研究只关注了单一用药预防PTIPN疗效,并未评价联合用药或联合其他非药物干预手段的疗效,同时未将不同药物使用的成本纳入考虑。
综上所述,本研究通过网状Meta分析对药物预防PTIPN有效性进行了较系统、客观的评价,对临床治疗选药具有一定参考价值。研究结果黄芪桂枝五物汤最能有效预防PTIPN的发生,其次可选神经节苷酯、维生素E、omega-3脂肪酸、钙镁输注、谷胱甘肽,不推荐谷氨酰胺、参麦注射液、甲钴胺、goshajinkigan进行预防。本研究仍存在着局限性,尚有待更多研究设计严谨,方法得当,尤其是在高加索人群中开展的RCT来给予证实。
作者贡献:
梁翠绿:论文构思、设计及撰写、数据的收集、整理及分析
张吟:提出研究、对研究结果进行分析与解释、审校论文
陈琪莹、卓萍萍:数据的收集、整理及分析、审校论文
| [1] |
Colvin LA. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: where are we now?[J]. Pain, 2019, 160(suppl 1): S1-S10. |
| [2] |
Ibrahim EY, Ehrlich BE. Prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A review of recent findings[J]. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol, 2020, 145: 102831. DOI:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2019.102831 |
| [3] |
Kolb NA, Smith AG, Singleton JR, et al. The Association of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy Symptoms and the Risk of Falling[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2016, 73(7): 860-866. DOI:10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.0383 |
| [4] |
Loprinzi CL, Lacchetti C, Bleeker J, et al. Prevention and management of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in survivors of adult cancers: ASCO Guideline Update[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2020, 38(28): 3325-3348. DOI:10.1200/JCO.20.01399 |
| [5] |
Pace A, Giannarelli D, Galiè E, et al. Vitamin E neuroprotection for cisplatin neuropathy: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Neurology, 2010, 74(9): 762-766. DOI:10.1212/WNL.0b013e3181d5279e |
| [6] |
Pace A, Savarese A, Picardo M, et al. Neuroprotective effect of vitamin E supplementation in patients treated with cisplatin chemotherapy[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2003, 21(5): 927-931. DOI:10.1200/JCO.2003.05.139 |
| [7] |
Kottschade LA, Sloan JA, Mazurczak MA, et al. The use of vitamin E for the prevention of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: results of a randomized phase Ⅲ clinical trial[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2011, 19(11): 1769-1777. DOI:10.1007/s00520-010-1018-3 |
| [8] |
Argyriou AA, Chroni E, Koutras A, et al. Preventing paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase Ⅱ trial of vitamin E supplementation[J]. J Pain Symptom Manage, 2006, 32(3): 237-244. DOI:10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2006.03.013 |
| [9] |
Argyriou AA, Chroni E, Koutras A, et al. A randomized controlled trial evaluating the efficacy and safety of vitamin E supplementation for protection against cisplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: final results[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2006, 14(11): 1134-1140. DOI:10.1007/s00520-006-0072-3 |
| [10] |
Salehi Z, Roayaei M. Effect of vitamin E on oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy prevention: a randomized Controlled trial[J]. Int J Prev Med, 2015, 6: 104. DOI:10.4103/2008-7802.169021 |
| [11] |
曹宇华, 朱州, 冯国生, 等. 维生素E预防草酸铂周围神经毒性的临床研究[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 2015, 32(5): 761-763. [Cao YH, Zhu Z, Feng GS, et al. Clinical study of vitamin E in prevention of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity[J]. Gaungxi Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao, 2015, 32(5): 761-763.] |
| [12] |
Anoushirvani AA, Poorsaadat L, Aghabozorgi R, et al. Comparison of the effects of omega 3 and vitamin E on palcitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy[J]. Open Access Maced J Med Sci, 2018, 6(10): 1857-1861. DOI:10.3889/oamjms.2018.333 |
| [13] |
李海金, 董良, 李英. 还原型谷胱甘肽预防奥沙利铂神经毒性疗效观察[J]. 全科医学临床与教育, 2007, 5(5): 387-388, 398. [Li HJ, Dong L, Li Y. Observation on preventive effect of reduced glutathione on oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity[J]. Quan Ke Yi Xue Lin Chuang Yu Jiao Yu, 2007, 5(5): 387-388, 398. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-3686.2007.05.013] |
| [14] |
刘淑红, 魏萍, 张灵智, 等. 还原型谷胱甘肽预防奥沙利铂慢性神经毒性的临床研究[J]. 中国实用医药, 2011, 6(2): 5-6. [Liu SH, Wei P, Zhang LZ, et al. Clinical study of the protective effect of reduced glutathion on oxaliplatin-induced chronic neurotoxicity[J]. Zhongguo Shi Yong Yi Yao, 2011, 6(2): 5-6. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-7555.2011.02.003] |
| [15] |
蔡典琨, 缪继东. 谷胱甘肽预防奥沙利铂相关神经毒性的随机对照研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2012, 39(2): 482-483. [Cai DK, Miao JD. Randomized controlled trial of glutathione infusions in prevention of oxaliplatin-related neurotoxicity[J]. Xian Dai Yu Fang Yi Xue, 2012, 39(2): 482-483.] |
| [16] |
庞丹梅, 邓燕明, 蓝晓珊, 等. 还原型谷胱甘肽用于预防和降低奥沙利铂周围神经毒性的研究[J]. 中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2010, 17(24): 2057-2059, 2069. [Pang DM, Deng YM, Lan XS, et al. Efficacy of reduced glutathione in preventing and reducing neurotoxicity of oxaliplatin[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Za Zhi, 2010, 17(24): 2057-2059, 2069.] |
| [17] |
董梅, 邢镨元, 刘鹏, 等. 钙镁制剂和谷胱甘肽预防奥沙利铂所致神经毒性的效果观察[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2010, 32(3): 208-211. [Dong M, Xing PY, Liu P, et al. Assessment of the protective effect of calcium-magnesium infusion and glutathione on oxaliplatin-induced neurotocixity[J]. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi, 2010, 32(3): 208-211.] |
| [18] |
Smyth JF, Bowman A, Perren T, et al. Glutathione reduces the toxicity and improves quality of life of women diagnosed with ovarian cancer treated with cisplatin: results of a double-blind, randomised trial[J]. Ann Oncol, 1997, 8(6): 569-573. DOI:10.1023/A:1008211226339 |
| [19] |
Cascinu S, Cordella L, Del Ferro E, et al. Neuroprotective effect of reduced glutathione on cisplatin-based chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer: a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 1995, 13(1): 26-32. DOI:10.1200/JCO.1995.13.1.26 |
| [20] |
Cascinu S, Catalano V, Cordella L, et al. Neuroprotective effect of reduced glutathione on oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in advanced colorectal cancer: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2002, 20(16): 3478-3483. DOI:10.1200/JCO.2002.07.061 |
| [21] |
Leal AD, Qin R, Atherton PJ, et al. North central cancer treatment group/alliance trial N08CA-the use of glutathione for prevention of paclitaxel/carboplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy: a phase 3 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study[J]. Cancer, 2014, 120(12): 1890-1897. DOI:10.1002/cncr.28654 |
| [22] |
Milla P, Airoldi M, Weber G, et al. Administration of reduced glutathione in FOLFOX4 adjuvant treatment for colorectal cancer: effect on oxaliplatin pharmacokinetics, Pt-DNA adduct formation, and neurotoxicity[J]. Anticancer Drugs, 2009, 20(5): 396-402. DOI:10.1097/CAD.0b013e32832a2dc1 |
| [23] |
马金国, 张冰, 常晓静. 奥沙利铂致神经毒性患者应用甲钴胺和谷胱甘肽治疗临床研究[J]. 中国实用神经疾病杂志, 2015, 18(23): 77-79. [Ma JG, Zhang B, Chang XJ. Oxaliplatin induced neurotoxicity in patients treated with Mecobalamin and Glutathione[J]. Zhongguo Shi Yong Shen Jing Ji Bing Za Zhi, 2015, 18(23): 77-79. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5110.2015.23.048] |
| [24] |
Oki E, Emi Y, Kojima H, et al. Preventive effect of Goshajinkigan on peripheral neurotoxicity of FOLFOX therapy (GENIUS trial): a placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized phase Ⅲ study[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2015, 20(4): 767-775. DOI:10.1007/s10147-015-0784-9 |
| [25] |
Kono T, Hata T, Morita S, et al. Goshajinkigan oxaliplatin neurotoxicity evaluation (GONE): a phase 2, multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of goshajinkigan to prevent oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy[J]. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol, 2013, 72(6): 1283-1290. DOI:10.1007/s00280-013-2306-7 |
| [26] |
Nishioka M, Shimada M, Kurita N, et al. The kampo medicine, goshajinkigan, prevents neuropathy in patients treated by FOLFOX regimen[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2011, 16(4): 322-327. DOI:10.1007/s10147-010-0183-1 |
| [27] |
Abe H, Kawai Y, Mori T, et al. The Kampo medicine goshajinkigan prevents neuropathy in breast cancer patients treated with docetaxel[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2013, 14(11): 6351-6356. DOI:10.7314/APJCP.2013.14.11.6351 |
| [28] |
Wang DS, Wang ZQ, Chen G, et al. Phase Ⅲ randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of monosialotetrahexosylganglioside for the prevention of oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in stage Ⅱ/Ⅲ colorectal cancer[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(1): 151-159. DOI:10.1002/cam4.2693 |
| [29] |
Su YH, Huang JJ, Wang SS, et al. The effects of ganglioside-monosialic acid in taxane-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in patients with breast cancer: a randomized trial[J]. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2020, 112(1): 55-62. |
| [30] |
Zhu YY, Yang JL, Jiao SC, et al. Ganglioside-monosialic acid (GM1) prevents oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in patients with gastrointestinal tumors[J]. World J Surg Oncol, 2013, 11: 19. DOI:10.1186/1477-7819-11-19 |
| [31] |
王南瑶, 王琼, 费燕华, 等. 神经节苷脂预防奥沙利铂致末梢神经毒性30例临床研究[J]. 中国药业, 2014, 23(23): 28-29. [Wang NY, Wang Q, Fei YH, et al. Clinical Study on Gangliosides for Preventing Oxaliplatin Induced Peripheral Neurotoxicity in 30 Cases[J]. Zhongguo Yao Ye, 2014, 23(23): 28-29.] |
| [32] |
韩灵敏, 曲申, 杜利力, 等. 单唾液酸四己糖神经节苷脂防治奥沙利铂周围神经毒性疗效观察[J]. 中华实用诊断与治疗杂志, 2013, 27(5): 483-485. [Han LM, Qu S, Du LL, et al. Efficacy of monosialotetrahexose Ganglioside in the prevention and treatment of Oxaliplatin- peripheral neurotoxicity[J]. Zhonghua Shi Yong Zhen Duan Yu Zhi Liao Za Zhi, 2013, 27(5): 483-485.] |
| [33] |
刘颖, 尹磊, 张伟杰. 神经节苷脂对奥沙利铂所致周围神经毒性的预防作用[J]. 肿瘤基础与临床, 2017, 30(4): 307-309. [Liu Y, Yin L, Zhang WJ. Protective effect of Ganglioside on the peripheral neurotoxicity of Oxaliplatin[J]. Zhong Liu Ji Chu Yu Lin Chuang, 2017, 30(4): 307-309. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-5412.2017.04.011] |
| [34] |
谢建立, 冯丽娟. 神经节苷脂对结肠癌患者含奥沙利铂化疗方案致周围神经毒性的疗效观察[J]. 中国医院用药评价与分析, 2017, 17(11): 1496-1498. [Xie JL, Feng LJ. Observation on Efficacy of Gangliosides in Application of Chemotherapy Regimen of Oxaliplatin in Treatment of Peripheral Neurotoxicity Among Patients with Colon Cancer[J]. Zhongguo Yi Yuan Yong Yao Ping Jia Yu Fen Xi, 2017, 17(11): 1496-1498.] |
| [35] |
黄作超, 曾春生, 刘怡, 等. 单唾液酸四己糖神经节苷脂钠预防多西他赛联合顺铂方案神经毒性的效果观察[J]. 中国医院用药评价与分析, 2018, 18(9): 84-86. [Huang ZC, Zeng CS, Liu Y, et al. Observation on Preventive Effects of Monosialate Tetrahexose Ganglioside Sodium on Neurotoxicity of Docetaxel Combined with Cisplatin[J]. Zhongguo Yi Yuan Yong Yao Ping Jia Yu Fen Xi, 2018, 18(9): 84-86.] |
| [36] |
李明颖, 徐建明, 宋三泰, 等. 钙镁合剂防治草酸铂神经毒性的临床研究[J]. 肿瘤学杂志, 2009, 15(5): 450-452. [Li MY, Xu JM, Song ST, et al. A Clinical Trial of Ca and Mg Mixture for Preventing Oxaliplatin-Induced Neurotoxicity[J]. Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2009, 15(5): 450-452.] |
| [37] |
杨武, 喻永龙, 王新帅, 等. 钙镁合剂和甲钴胺预防奥沙利铂所致神经毒性疗效比较[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报, 2013, 38(1): 37-40. [Yang W, Yu YL, Wang XS, et al. Efficacy comparison of calcium-magnesium infusion and mecobalamin to prevent the neurotoxicity induced by oxaliplatin[J]. Bengbu Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao, 2013, 38(1): 37-40. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-2200.2013.01.011] |
| [38] |
缪继东, 蔡典琨. 钙镁合剂预防奥沙利铂相关神经毒性的随机对照研究[J]. 现代预防医学, 2012, 39(18): 4756-4757. [Miao JD, Cai DK. A randomized controlled study on the Preventive effect of Calcium/magnesium infusions for Oxaliplatin-Related Neurotoxicity[J]. Xian Dai Yu Fang Yi Xue, 2012, 39(18): 4756-4757.] |
| [39] |
李杨, 李艳华, 樊青霞, 等. 硫酸镁联合葡萄糖酸钙预防奥沙利铂神经毒性25例[J]. 郑州大学学报(医学版), 2009, 44(4): 897-898. [Li Y, Li YH, Fan QX, et al. Prevention of oxaliplatin-induced neurotoxicity by magnesium sulfate in combination with calcium gluconate[J]. Zhengzhou Da Xue Xue Bao(Yi Xue Ban), 2009, 44(4): 897-898. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-6825.2009.04.084] |
| [40] |
蒋一玲, 陆帅. 葡萄糖酸钙和硫酸镁预防奥沙利铂对晚期结直肠癌患者的神经毒性[J]. 肿瘤学杂志, 2012, 18(12): 960-963. [Jiang YL, Lu S. Calcium gluconate and magnesium sulfate prevent Oxaliplatin-neurotoxicity in patients with advanced colorectal cancer[J]. Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2012, 18(12): 960-963.] |
| [41] |
Grothey A, Nikcevich DA, Sloan JA, et al. Intravenous calcium and magnesium for oxaliplatin-induced sensory neurotoxicity in adjuvant colon cancer: NCCTG N04C7[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2011, 29(4): 421-427. DOI:10.1200/JCO.2010.31.5911 |
| [42] |
Chay WY, Tan SH, LO YL, et al. Use of calcium and magnesium infusions in prevention of oxaliplatin induced sensory neuropathy[J]. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol, 2010, 6(4): 270-277. DOI:10.1111/j.1743-7563.2010.01344.x |
| [43] |
Ishibashi K, Okada N, Miyazaki T, et al. Effect of calcium and magnesium on neurotoxicity and blood platinum concentrations in patients receiving mFOLFOX6 therapy: a prospective randomized study[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2010, 15(1): 82-87. DOI:10.1007/s10147-009-0015-3 |
| [44] |
Loprinzi CL, Qin R, Dakhil SR, et al. Phase Ⅲ randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of intravenous calcium and magnesium to prevent oxaliplatin-induced sensory neurotoxicity (N08CB/Alliance)[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2014, 32(10): 997-1005. DOI:10.1200/JCO.2013.52.0536 |
| [45] |
Hochster HS, Grothey A, Hart L, et al. Improved time to treatment failure with an intermittent oxaliplatin strategy: results of CONcePT[J]. Ann Oncol, 2014, 25(6): 1172-1178. DOI:10.1093/annonc/mdu107 |
| [46] |
王芬, 王树滨, 申东兰, 等. 氨磷汀对奥沙利铂所致周围神经毒性的改善作用的病例对照研究[J]. 癌症进展, 2014, 12(6): 571-575. [Wang F, Wang SB, Shen DG, et al. The randomized controlled trial of amifostine in improving neurotoxicity induced by oxaliplatin on gastroenteric tumor patients[J]. Ai Zheng Jin Zhan, 2014, 12(6): 571-575.] |
| [47] |
周锋, 黄万钟, 夏瑜, 等. 氨磷汀对消化道肿瘤化疗患者周围神经毒性的预防效果分析[J]. 中国综合临床, 2019, 35(3): 246-249. [Zhou F, Huang WZ, Xia Y, et al. Analysis on the preventive effect of amifostine on peripheral neurotoxicity in patients with gastrointestinal cancer undergoing chemotherapy[J]. Zhongguo Zong He Lin Chuang, 2019, 35(3): 246-249. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-6315.2019.03.012] |
| [48] |
李涛, 朱慧娟. 氨磷汀改善奥沙利铂药物神经毒性疗效观察[J]. 中国中西医结合外科杂志, 2016, 22(3): 246-248. [Li T, Zhu HJ. The Observation on the Effects of Amifostine on Improving Neurotoxicity induced by Oxaliplatin[J]. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Wai Ke Za Zhi, 2016, 22(3): 246-248. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6948.2016.03.010] |
| [49] |
Kemp G, Rose P, Lurain J, et al. Amifostine pretreatment for protection against cyclophosphamide-induced and cisplatin-induced toxicities: results of a randomized control trial in patients with advanced ovarian cancer[J]. J Clin Oncol, 1996, 14(7): 2101-2112. DOI:10.1200/JCO.1996.14.7.2101 |
| [50] |
De Vos FY, Bos AM, Schaapveld M, et al. A randomized phase Ⅱ study of paclitaxel with carboplatin +/- amifostine as first line treatment in advanced ovarian carcinoma[J]. Gynecol Oncol, 2005, 97(1): 60-67. DOI:10.1016/j.ygyno.2004.11.052 |
| [51] |
Kanat O, Evrensel T, Baran I, et al. Protective effect of amifostine against toxicity of paclitaxel and carboplatin in non-small cell lung cancer: a single center randomized study[J]. Med Oncol, 2003, 20(3): 237-245. DOI:10.1385/MO:20:3:237 |
| [52] |
Lorusso D, Ferrandina G, Greggi S, et al. Phase Ⅲ multicenter randomized trial of amifostine as cytoprotectant in first-line chemotherapy in ovarian cancer patients[J]. Ann Oncol, 2003, 14(7): 1086-1093. DOI:10.1093/annonc/mdg301 |
| [53] |
Hilpert F, Stähle A, Tomé O, et al. Neuroprotection with amifostine in the first-line treatment of advanced ovarian cancer with carboplatin/paclitaxel-based chemotherapy-a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized phase Ⅱ study from the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Gynäkologische Onkologie (AGO) Ovarian Cancer Study Group[J]. Support Care Cancer, 2005, 13(10): 797-805. DOI:10.1007/s00520-005-0782-y |
| [54] |
赵艳霞, 程晶, 朱芳, 等. 甲钴胺预防乳腺癌患者多西紫杉醇化疗导致外周神经毒性的研究[J]. 肿瘤防治研究, 2012, 39(12): 1487-1490. [Zhao YX, Cheng J, Zhu F, et al. Mecobalamin prevents peripheral neurotoxicity induced by docetaxel in breast cancer patients[J]. Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Yan Jiu, 2012, 39(12): 1487-1490. DOI:10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2012.12.019] |
| [55] |
陈婵娟, 陈昌南, 潘岐作, 等. 甲钴胺预防紫杉醇神经毒性疗效观察[J]. 中国热带医学, 2014, 14(4): 508-509. [Chen CJ, Chen CN, Pan QZ, et al. Effect of mecobalamin in preventing paclitaxe-induced peripheral neurotoxicity in cancer patients[J]. Zhongguo Re Dai Yi Xue, 2014, 14(4): 508-509.] |
| [56] |
Ghoreishi Z, Esfahani A, Djazayeri A, et al. Omega-3 fatty acids are protective against paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy: A randomized double-blind placebo controlled trial[J]. BMC Cancer, 2012, 12: 355. DOI:10.1186/1471-2407-12-355 |
| [57] |
Esfahani A, Somi MH, Ayromlou H, et al. The effect of n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids on incidence and severity of oxaliplatin induced peripheral neuropathy: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Biomark Res, 2016, 4: 13. DOI:10.1186/s40364-016-0066-3 |
| [58] |
陆怡, 张波, 蔡鹄, 等. ω-3 PUFAs防治奥沙利铂联合卡培他滨治疗所致周围神经毒性的临床研究[J]. 肿瘤学杂志, 2019, 25(9): 817-821. [Lu Y, Zhang B, Cai H, et al. Prevention of Peripheral Neurotoxicity Caused by Oxaliplatin and Capecitabine with ω-3 PUFAs in Colon Cancer Patients[J]. Zhong Liu Xue Za Zhi, 2019, 25(9): 817-821.] |
| [59] |
Wang WS, Lin JK, Lin TC, et al. Oral glutamine is effective for preventing oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy in colorectal cancer patients[J]. Oncologist, 2007, 12(3): 312-319. DOI:10.1634/theoncologist.12-3-312 |
| [60] |
黄沂, 张志锋, 施烯, 等. 静滴丙氨酰谷氨酰胺减少FOLFOX4方案的不良反应[J]. 中国生化药物杂志, 2011, 32(6): 486-488. [Huang Y, Zhang ZF, Shi X, et al. Application of parenteral supplemented with Ala-Gln in patients with gastrointestinal neoplasms could reduce the side effects induced by FOLFOX4[J]. Zhongguo Sheng Hua Yao Wu Za Zhi, 2011, 32(6): 486-488.] |
| [61] |
黄世锋, 陈德伦, 宋学民. 口服谷氨酰胺预防奥沙利铂神经毒性的疗效观察[J]. 中国全科医学, 2009, 12(18): 1716-1718. [Huang SF, Chen DL, Song XM. Effect of Oral Glutamine on Oxaliplatin-induced Neurotoxicity[J]. Zhongguo Quan Ke Yi Xue, 2009, 12(18): 1716-1718. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2009.18.025] |
| [62] |
Abbas W. Incidence of neuropathy with weekly paclitaxel and role of oral glutamine supplementation for prevention of paclitaxel induced peripheral neuropathy randomized controlled trial[J]. Indian J Med Paediatr Oncol, 2018, 39(3): 339-348. DOI:10.4103/ijmpo.ijmpo_38_17 |
| [63] |
徐成兴, 胡新民, 徐森华. 加味黄芪桂枝五物汤防治奥沙利铂致周围神经毒性的临床观察[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2017, 51(1): 53-54, 63. [Xu CX, Hu XM, Xu SH. Clinical observation of modified Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction in the prevention and treatment of peripheral neurotoxicity induced by oxaliplatin[J]. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi, 2017, 51(1): 53-54, 63.] |
| [64] |
黄振步, 黄兆明, 陈光群, 等. 黄芪桂枝五物汤熏洗防治奥沙利铂外周神经毒性的临床研究[J]. 上海中医药杂志, 2010, 44(5): 40-42. [Huang ZB, Huang ZM, Chen GQ, et al. Clinical study on external bath of "Huangqi Guizhi Decoction" in relieving peripheral neurotoxicity induced by Oxaliplatin[J]. Shanghai Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi, 2010, 44(5): 40-42.] |
| [65] |
王强. 黄芪桂枝五物汤手足浴联合钙镁合剂防治奥沙利铂神经毒性的临床观察[J]. 现代中西医结合杂志, 2015, 24(3): 318-320. [Wang Q. Clinical observation on Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction hand foot bath combined with calcium magnesium mixture for prevention and treatment of oxaliplatin neurotoxicity[J]. Xian Dai Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi, 2015, 24(3): 318-320. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2015.03.038] |
| [66] |
李道明, 王蓉, 谢菁. 黄芪桂枝五物汤治疗奥沙利铂化疗后周围神经毒性24例[J]. 南京中医药大学学报, 2014, 30(2): 186-188. [Li DM, Wang R, Xie J. Clinical Study on Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu Decoction Treating the Neuro-sensory Toxicity Caused by Oxaliplatin[J]. Nanjing Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao, 2014, 30(2): 186-188.] |
| [67] |
吴冠楠, 姚学权, 吴晓宇, 等. 黄芪桂枝五物汤加减防治术后化疗所致周围神经毒性疗效观察[J]. 四川中医, 2015, 33(12): 132-133. [Wu GN, Yao XQ, Wu XY, et al. Effect of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction on prevention and treatment of postoperative chemotherapy induced peripheral neurotoxicity[J]. Sichuan Zhong Yi, 2015, 33(12): 132-133.] |
| [68] |
徐先容. 黄芪桂枝五物汤加减对卵巢癌TP方案化疗引起神经毒性的防治效果[J]. 陕西中医, 2016, 37(4): 396-397. [Xu XR. Control effect of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction on neurotoxicity which caused by TP chemotherapy regimen of ovarian cancer[J]. Shaanxi Zhong Yi, 2016, 37(4): 396-397. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2016.04.005] |
| [69] |
何映月. 黄芪桂枝五物汤加味防治奥沙利铂外周神经毒性临床观察[J]. 山东中医药大学学报, 2012, 36(1): 42-43. [He YY. Clinical observation of Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction on prevention and treatment of oxaliplatin peripheral neurotoxicity[J]. Shandong Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao, 2012, 36(1): 42-43.] |
| [70] |
Cheng XL, Huo J, Wang D, et al. Herbal medicine AC591 prevents oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy in animal model and cancer patients[J]. Front Pharmacol, 2017, 8: 344. DOI:10.3389/fphar.2017.00344 |
| [71] |
于滨, 苏智祥, 袁媛, 等. 黄芪桂枝五物汤加减防治TP方案化疗引起神经毒性的疗效观察[J]. 成都中医药大学学报, 2014, 37(2): 18-20. [Yu B, Su ZX, Yuan Y, et al. Clinical Observation of Efficacy Jia-Wei-Huang-Qi-Gui-Zhi-Wu-Wu Decoction in Prevention and Treatment of Neurotoxicity Caused by TP Regimen[J]. Chengdu Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao, 2014, 37(2): 18-20.] |
| [72] |
曹顺金. 黄芪桂枝五物汤加味防治奥沙利铂所致外周神经毒性疗效观察[J]. 光明中医, 2013, 28(1): 88-89. [Cho SJ. Effect of modified Huangqi Guizhi Wuwu decoction on prevention and treatment of peripheral neurotoxicity induced by Oxaliplatin[J]. Guang Ming Zhong Yi, 2013, 28(1): 88-89. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1003-8914.2013.01.041] |
| [73] |
方凤奇, 张洁, 于佩瑶. 参麦注射液防治含奥沙利铂化疗方案所致神经毒性效果的临床观察[J]. 中国医院药学杂志, 2012, 32(12): 965-967. [Fang FQ, Zhang J, Yu PY. Clinical observation on the efficacy of Shenmai injection in prevention and treatment of neuro-toxicity induced by oxaliplatin-containing chemotherapy regimen[J]. Zhongguo Yi Yuan Yao Xue Za Zhi, 2012, 32(12): 965-967.] |
| [74] |
张洁, 董岩, 张春霞. 参麦注射液防治含紫杉醇化疗方案所致神经毒性的临床观察[J]. 中国药房, 2012, 23(8): 700-702. [Zhang J, Dong Y, Zhang CX. Clinical Observation of Shenmai Injection in the Treatment and Prevention of Neurotoxicity Induced by Chemotherapy Regimen Containing Taxtol[J]. Zhongguo Yao Fang, 2012, 23(8): 700-702. DOI:10.6039/j.issn.1001-0408.2012.08.11] |
| [75] |
Hu LY, Mi WL, Wu GC, et al. Prevention and Treatment for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Therapies Based on CIPN Mechanisms[J]. Curr Neuropharmacol, 2019, 17(2): 184-196. DOI:10.2174/1570159X15666170915143217 |
| [76] |
Wu YQ, Dang RL, Tang MM, et al. Long chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation alleviates doxorubicin-induced depressive-like behaviors and neurotoxicity in rats: involvement of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation[J]. Nutrients, 2016, 8(4): 243. DOI:10.3390/nu8040243 |
 2022, Vol. 49
2022, Vol. 49