文章信息
- L-精氨酸抑制人肺腺癌A549细胞增殖及对PI3K/AKt信号通路的影响
- L-Arginine Inhibites Proliferation of Human Lung Adenocarcinoma A549 Cells and Expression of PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2017, 44(9): 585-589
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2017, 44(9): 585-589
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2017.16.1574
- 收稿日期: 2016-12-19
- 修回日期: 2017-04-16
2. 400700 重庆,重庆市第九人民医院呼吸内科;
3. 646000 泸州,西南医科大学附属医院胸心外科
2. Department of Respiratory, The Ninth People's Hospital of Chongqing, Chongqing 400700, China;
3. Department of Thoracic Surgery, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou 646000, China
肺癌是目前发病率及死亡率极高的恶性肿瘤之一,严重不良反应、靶向治疗费用昂贵且适应人群少,限制了化疗在临床中的广泛运用,因此进一步探寻高效、低毒、价廉的肺癌抗肿瘤药物具有重要的临床价值。L-Arg是哺乳动物中一种非必需氨基酸,不仅参与体内重要生理过程,还具有抗肿瘤效应,但其具体机制尚不明确[1]。磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶-蛋白激酶B(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase B, PI3K)家族作为原癌基因的组成部分,是一类重要激酶,而Akt被称为蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B, PKB),是PI3K信号通路的核心靶点。PI3K/Akt信号通路与恶性肿瘤的发生发展密切相关,它可以通过磷酸化或去磷酸化Akt来影响肿瘤细胞周期,或调控下游凋亡蛋白表达,如Bad和Cleaved Caspase-3来影响细胞增殖,调节细胞凋亡。目前发现肺癌的增殖与PI3K/Akt信号通路有着密切联系,因此本研究探讨L-Arg对A549细胞增殖及凋亡效应,筛选出适宜浓度,通过检测PI3K/Akt信号通路活化状态,以明确L-Arg的抗肿瘤机制,为临床提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料与试剂人肺腺癌A549细胞(西南医科大学附属医院病理科培养);胎牛血清、HyClone改良型RPMI1640培养液、Western blot marker(美国赛默飞公司),MTT、兔抗人Bad一抗、Cleaved Caspase-3一抗、内参GAPDH抗体、山羊抗兔二抗、Western凝胶试剂盒、蛋白裂解液、PMSF、BCA试剂盒(碧云天研究所);L-Arg(美国Sigma-Aldrich公司);兔抗人Akt一抗、p-Akt serine473一抗(美国Cell Signaling公司);CO2恒温培养箱(日本SANYO MCO-18AIC),流式细胞仪(美国BD公司),酶标仪(济南奥诺公司)。
1.2 实验方法 1.2.1 A549细胞培养采用含10%胎牛血清的RPMI1640培养液培养A549细胞,于37℃、5%CO2恒温培养箱中孵育,贴壁85%时按1:3传代。
1.2.2 MTT法检测L-Arg作用后A549细胞的存活率将A549细胞按照每孔4×104个接种于96孔板,贴壁后,按分组每孔加试剂100 μl:无细胞空白组(无血清培养液+L-Arg),阴性对照组(无血清培养液)、实验组(无血清培养液+16、32、64、96、128 mmol/L L-Arg),设置复孔,放入恒温培养箱中培养24、36、48 h;每孔加入10 μl MTT溶液培养4 h,弃上清液,每孔加入100 μl甲瓒溶解液,再培养4 h,酶标仪检测570 nm吸光度值,实验重复3次。
1.2.3 显微镜观察细胞形态变化实验分为对照组L-Arg(0 mmol/L)、L-Arg处理组(16、32、64、96、128 mmol/L),处理时间为48 h;常规胰酶消化处理、离心、计数后按每毫升5×104个接种于12孔板,每组设三个复孔;显微镜检查,DAPI染色,PBS缓冲液漂洗细胞三次;在避光条件下,于12孔板中,每孔加入DAPI染液500 μl,室温下染核3 min;吸出DAPI染液,PBS缓冲液漂洗细胞5 min×3次;荧光显微镜观察细胞核数目及形态。
1.2.4 流式细胞检测仪检测L-Arg作用后A549细胞的凋亡率将A549细胞按照每毫升1×105个接种于6孔板,实验分为对照组(无药干预组,即L-Arg:0 mmol/L)、实验组采用不同浓度L-Arg(16、32、64、96 mmol/L)干预A549细胞48 h后,离心收集细胞,PBS洗涤3次,加入预冷的70%乙醇溶液,4℃固定过夜,离心后PBS洗涤2次,然后按照AnnexinV-FITC/PI凋亡试剂盒操作步骤操作,试验重复3次。
1.2.5 流式细胞检测仪检测L-Arg作用后A549细胞的细胞周期将A549细胞按照每毫升1×105个接种于6孔板,实验分组同1.2.4。采用不同浓度L-Arg干预A549细胞48 h后,离心收集细胞,PBS洗涤3次,取100 μl,加入RNase A酶(1 mg/m1)5 μl,37℃水浴1 h,加入PI染液(100 μg/m1),避光30 min,上机检测。
1.2.6 Westernblot检测Akt、p-Akt、Bad、Cleaved Caspase-3蛋白表达水平实验分组同1.2.4。不同浓度L-Arg处理细胞48 h,裂解细胞后行蛋白提取,BCA法测蛋白含量后各取样本50 μg进行SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳,切取目标蛋白,电转至PVDF膜后5%脱脂奶粉封闭2 h,加入一抗培养,抗体稀释比例:Akt(1:1 000),p-Akt(1:1 000),Bad(1:500),Cleaved Caspase-3(1:500),GAPDH(1:800)。4℃过夜,洗膜,加二抗,洗膜,再与ECL发光剂反应显影,Quantity One软件计算条带灰度值,GAPDH作为内参作标准对照,实验重复3次。
1.3 统计学方法采用SPSS17.0软件进行统计分析,计量资料采用均数±标准差(x±s);正态性检验,Levene法检测方差齐性,各组之间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两间比较采用LSD-t检验,α=0.05为检验水准,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 L-Arg对人肺腺癌A549细胞生长增殖的影响在同一浓度不同时间点条件下,L-Arg浓度≥64 mmol/L时,均能降低A549细胞存活率(P < 0.05),且随着时间延长,存活率越低(P < 0.05);在同一时间点不同浓度条件下,时间≥36 h时,A549细胞生存率随L-Arg浓度升高而下降(P < 0.05),见表 1、图 1。
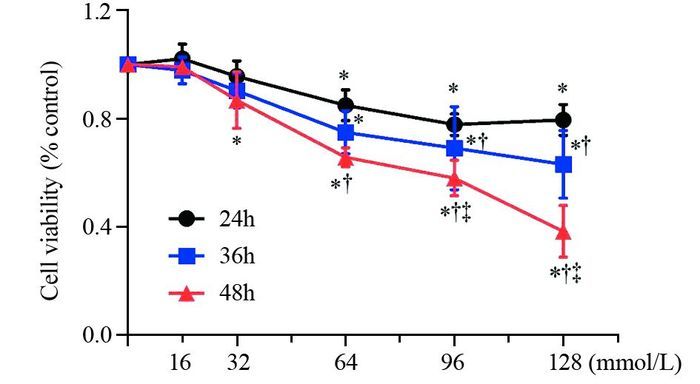
|
| *: all P < 0.05, vs. control group, P(24h)=0.005, P(36h)=0.000, P(48h)=0.001; †: all P < 0.05, vs. 24h group, P(64mmol/L)=0.033, P(96mmol/L)=0.029, P(128mmol/L)=0.012; ‡: all P < 0.05, vs. 36h group, P(96mmol/L)=0.011, P(128mmol/L)=0.001 图 1 MTT检测L-精氨酸对人肺腺癌A549细胞增殖的影响 Figure 1 Effect of L-Arg on proliferation of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells detected by MTT |
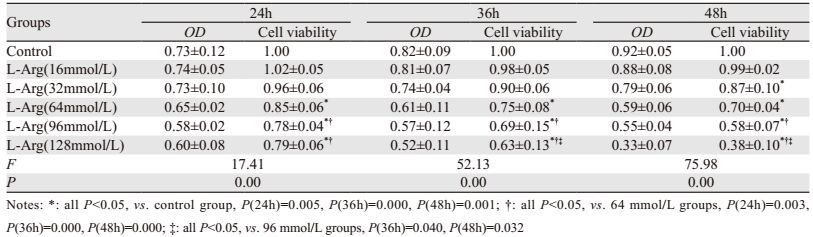 |
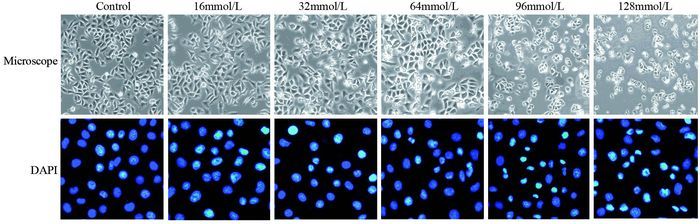
随着L-Arg浓度的增加,肺腺癌A549细胞数目减少,当L-Arg浓度为128 mmol/L时,细胞完全失去细胞形态,反映出高浓度的L-Arg对细胞有明显的毒性,A549细胞增殖受到影响;而低浓度的L-Arg对细胞的形态未见明显的改变;DAPI细胞核染色同样显示出,高浓度的L-Arg(96、128 mmol/L)可显著改变细胞核形态,细胞核不规则、皱缩。因此后续的细胞处理时,L-精氨酸浓度应≤96 mmol/L,见图 2。
|
| The morphology of human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells treated with different concentrations of L-Arg(control, 16, 32, 64, 96, 128mmol/L) for 48h was observed by microscope. Then fluorescence microscope was used to evaluate the status of nucleus stained by DAPI 图 2 L-精氨酸对人肺腺癌A549细胞形态的影响 Figure 2 Effect of L-Arg on morphology of A549 cells |
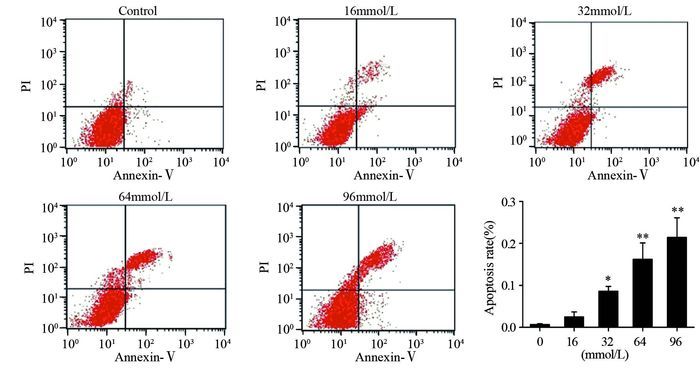
48 h条件下,随着浓度(32、64、96 mmol/L)增加,L-Arg能促进A549细胞凋亡(P < 0.05),且96 mmol/L时,晚期凋亡率最高(P < 0.01),见图 3。
|
| *: P=0.019, compared with control group; **: all P=0.031, compared with control group 图 3 L-Arg对A549细胞凋亡率凋亡的影响 Figure 3 Effect of L-Arg on apoptosis of A549 cells |
48 h条件下,随着L-Arg浓度(32、64、96 mmol/L)增加,A549细胞G0/G1期比例增加,S期比例降低,DNA合成较少(P < 0.05),见表 2。
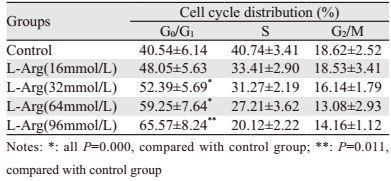 |
48 h条件下,随着L-Arg浓度递增,Cleaved Caspase-3、Bad蛋白表达增强(P < 0.05);随着L-Arg(≥32 mmol/L)浓度递增,p-Akt s473位点磷酸化水平降低(P < 0.05),而非磷酸化蛋白Akt含量没有明显的改变(P > 0.05),见图 4。
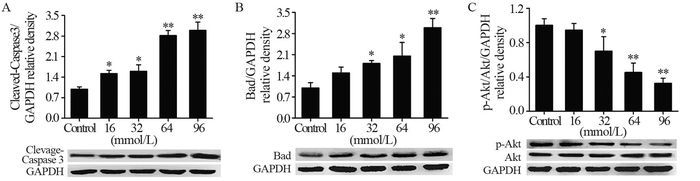
|
| *: all P=0.002, compared with control group; **: all P=0.010, compared with control group 图 4 Western blot检测A549细胞Cleaved Caspase-3、Bad、Akt、p-Akt蛋白表达水平 Figure 4 Protein expression of Cleaved Caspase-3, Bad, Akt, p-Akt in A549 cells detected by Western blot |
L-Arg为人体内的非必需氨基酸,不仅参与能量代谢和蛋白质合成,在营养平衡、组织修复等生理过程中也具有重要作用。近年来,大量基础研究报道L-Arg还具有抗肿瘤作用[2-4],其机制或许与鸟氨酸脱羧酶活性受到抑制、肿瘤细胞DNA合成受阻、细胞增殖受限有关。动物实验表明,在饮水或饲料中添加L-Arg,对肿瘤的形成和生长有显著的抑制作用[5]。Lee等[6]研究表明肺癌细胞A549、CRL-2081、MAK9经Arg处理后,肿瘤细胞生长及增殖均受到明显抑制。本实验结果与上述文献报道吻合,L-Arg处理A549细胞后,其细胞生长增殖受到抑制,且作用48 h时,随着L-Arg浓度升高,细胞增殖抑制越明显,细胞存活率越低。
细胞凋亡是细胞在相关基因控制下应对内外环境变化时细胞的稳态[7]。当细胞凋亡受阻或减少时,肿瘤细胞恶性生长,参与肿瘤发生发展。以相关药物诱导肿瘤细胞发生凋亡是抗肿瘤的重要方法。L-Arg不仅具有抑制肿瘤细胞增殖作用,还可以通过调节凋亡及迁移蛋白表达促进细胞凋亡。本实验采用L-Arg处理人肺腺癌A549细胞,结果显示48 h时,随着干预浓度(32、64、96 mmol/L)递增,细胞凋亡越明显。相关研究报道[8],PI3K/Akt信号通路可参与细胞增殖及凋亡调控。PI3K通过Akt将细胞分裂信号向下游传递,调控细胞周期素D,促进有丝分裂G1期进展,使细胞周期加速,从而达到抑制细胞凋亡,参与肿瘤发生进展[9-10]。细胞周期异常调控及细胞凋亡受阻是肿瘤细胞生长不受控制的主要原因。本实验采用流式细胞仪技术检测L-Arg处理细胞后的细胞周期,结果显示:48 h时,随着药物浓度递增,细胞G0/G1期比例越高,且在96 mmol/L时,细胞周期抑制作用越明显。进一步阐明L-Arg对A549细胞的增殖凋亡机制与提高G0/G1期细胞比例、DNA合成受阻有关。
PI3K/Akt信号通路可通过磷酸化或去磷酸化下游效应分子,改变活化状态,激活生长信号,从而促进肿瘤细胞增殖,抑制细胞凋亡[11-12]。人体肿瘤细胞内PI3K/Akt信号通路均处于活化状态,当其失调时,对肺癌形成具有重要意义。Akt作为PI3K下游信号通路的核心靶点主要作用于肿瘤细胞抗凋亡通路,维持细胞存活,在绝大多数肺癌中也呈现活化形式。NSCLC患者标本检测发现,磷酸化Akt呈高水平表达趋势,提示Akt的活化与NSCLC患者疾病发展直接相关[13]。Bcl-2家族的促凋亡Bad蛋白与Caspase家族的Caspase-3均是PI3K/Akt信号通路凋亡调控中的重要蛋白。Akt可激活Bad蛋白Serine136位点发生磷酸化,阻碍其与抗凋亡蛋白Bcl-2或Bcl-xL形成异源二聚物,抑制Bad发挥促凋亡效应。而Caspase-3是PI3K/Akt下游线粒体凋亡信号通路的重要组成部分,在诱导细胞凋亡过程中起着重要作用,其表达可反映细胞凋亡程度[14],通过剪切多种凋亡相关蛋白,从而促进凋亡的进展[15-16]。本实验采用Western blot检测L-Arg处理A549细胞后Bad、Cleaved caspase-3、p-Akt/Akt蛋白表达情况发现,48 h时,随着浓度递增,Bad蛋白及Cleaved caspase-3蛋白表达均增加,而p-Akt/Akt表达降低,且当L-Arg浓度为96 mmol/L时,抑制作用最明显,由此可得出:L-Arg可以通过抑制PI3K/Akt信号通路活性来促进A549细胞凋亡,其具体机制与上调Cleaved Caspase-3、Bad蛋白表达有关。因此,抑制该信号通路转导将为L-Arg治疗肺癌提供新的理论依据。
| [1] | Roy S, Reddy BS, Sudhakar G, et al. 17β-estradiol-linked nitro-L-arginine as simulataneous inducer of apoptosis in melanoma and tumor-angiogenic vascular endothelial cells[J]. Mol Pharm, 2011, 8(2): 350–9. DOI:10.1021/mp2000346 |
| [2] | Winter G, Todd CD, Trovato M, et al. Physiological implications of arginine metabolism in plants[J]. Front Plant Sci, 2015, 6: 534. |
| [3] | Qiu F, Huang J, Sui M. Targeting arginine metabolism pathway to treat arginine-dependent cancers[J]. Cancer Lett, 2015, 364(1): 1–7. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2015.04.020 |
| [4] | Morettin A, Baldwin RM, Côté J. Arginine methyltransferases as novel therapeutic targets for breast cancer[J]. Mutagenesis, 2015, 30(2): 177–89. DOI:10.1093/mutage/geu039 |
| [5] | Pawlikowski M, Pisarek H, Fryczak J, et al. Effects of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on diethylstilbestrol-induced hyperprolactinaemia and pituitary tumourigenesis in rats[J]. Endokrynol Pol, 2012, 63(2): 115–8. |
| [6] | Lee HY, Mohammed KA, Goldberg EP, et al. Arginine-conjugated albumin microspheres inhibits proliferation and migration in lung cancer cells[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2013, 3(3): 266–77. |
| [7] | Fiandalo MV, Kyprianou N. Caspase control: protagonists of cancer cell apoptosis[J]. Exp Oncol, 2012, 34(3): 165–75. |
| [8] | Spring L, Bardia A, Modi S. Targeting the cyclin D-cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) 4/6-retinoblastoma pathway with selective CDK 4/6 inhibitors in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer: rationale, current status, and future directions[J]. Discov Med, 2016, 21(113): 65–74. |
| [9] | Li J, Lai Y, Cao Y, et al. SHARPIN overexpression induces tumorigenesis in human prostate cancer LNCaP, DU145 and PC-3 cells via NF-κB/ERK/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Med Oncol, 2015, 32(2): 444. |
| [10] | Liu Y, Chen YY, Cao JY, et al. Oxidative stress, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest are induced in primary fetal alveolar type Ⅱ epithelial cells exposed to fine particulate matter from cooking oil fumes[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int, 2015, 22(13): 9728–41. DOI:10.1007/s11356-015-4140-4 |
| [11] | Shukla S, Bhaskaran N, Babcook MA, et al. Apigenin inhibits prostate cancer progression in TRAMP mice via targeting PI3K/Akt/FoxO pathway[J]. Carcinogenesis, 2014, 35(2): 452–60. DOI:10.1093/carcin/bgt316 |
| [12] | Henderson V, Smith B, Burton LJ, et al. Snail promotes cell migration through PI3K/AKT-dependent Rac1 activation as well as PI3K/AKT-independent pathways during prostate cancer progression[J]. Cell Adh Migr, 2015, 9(4): 255–64. DOI:10.1080/19336918.2015.1013383 |
| [13] | David O, Jett J, LeBeau H, et al. Phospho-Akt overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer confers significant stage-independent survival disadvantage[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2004, 10(20): 6865–71. DOI:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-0174 |
| [14] | Horwacik I, Rokita H. Targeting of tumor-associated gangliosides with antibodies affects signaling pathways and leads to cell death including apoptosis[J]. Apoptosis, 2015, 20(5): 679–88. DOI:10.1007/s10495-015-1103-7 |
| [15] | Soto-Nuñez M, Díaz-Morales KA, Cuautle-Rodríguez P, et al. Single-cell microinjection assay indicates that 7-hydroxycoumarin induces rapid activation of caspase-3 in A549 cancer cells[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2015, 10(5): 1789–95. DOI:10.3892/etm.2015.2765 |
| [16] | Gu J, Ren L, Wang X, et al. Expression of livin, survivin and caspase-3 in prostatic cancer and their clinical significance[J]. Int J Clin Exp Pathol, 2015, 8(11): 14034–9. |
 2017, Vol. 44
2017, Vol. 44


