文章信息
- RNA干扰沉默IQGAP1表达可提高食管鳞癌细胞KYSE150对顺铂的化疗敏感度
- Sensitivity of Esophageal Squamous Carcinoma Cell Line KYSE150 to Cisplatin Can Be Improved by RNA-interfered Expression of IQGAP1
- 肿瘤防治研究, 2017, 44(6): 387-391
- Cancer Research on Prevention and Treatment, 2017, 44(6): 387-391
- http://www.zlfzyj.com/CN/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2017.16.1210
- 收稿日期: 2016-10-17
- 修回日期: 2017-03-21
2. 450008 郑州,郑州大学附属肿瘤医院病理科
2. Department of Pathology, Affiliated Tumor Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou 450008, China
具有IQ结构域的GTP激酶活化蛋白(IQ motif containing GTPase activating protein 1, IQGAP1)是一种分子量为189 kDa、包含多种结构域的支架蛋白,通过与肌动蛋白、钙调蛋白、血管内皮生长因子受体2、表皮生长因子等多种蛋白相结合参与调控细胞黏附、细胞迁移、基因转录和信号转导等多种细胞生物学行为[1],目前研究发现IQGAP1蛋白在食管鳞癌细胞及组织中异常表达并与食管鳞癌的发生、发展、侵袭、转移密切相关[2],然而IQGAP1基因对食管鳞癌化疗耐药方面的影响目前还鲜有报道,本研究通过构建针对IQGAP1的siRNA并转染食管鳞癌细胞KYSE150,研究沉默IQGAP1基因对食管鳞癌细胞顺铂化疗敏感度的影响及可能的作用机制。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料及主要试剂人食管鳞癌细胞株KYSE150购自上海博谷生物公司并保存于河南省人民医院中心实验室。胎牛血清(FBS)、RPMI1640、碘化丙锭(PI)及Annexin V-FICT/PI双染细胞凋亡检测试剂盒均购自美国Gibco公司;顺铂、四甲基噻唑蓝(MTT)、二甲基亚砜(DMSO)购自美国Sigma-Aldrich公司;Nrf2蛋白、MRP1蛋白、IQGAP1蛋白及内参GAPDH蛋白一抗均购自美国Santa Cruz公司;TRIzol试剂、反转录聚合酶链反应(RT-PCR)试剂盒和转染试剂LipofectamineTM2000均购自美国Invitrogen公司。
1.2 siRNA序列构建与细胞转染IQGAP1基因三条阳性干扰序列和阴性对照序列均由上海吉凯基因化学技术有限公司设计合成。序列信息分别为:IQGAP1-siRNA1(5'-GGCACAUGCAGAGAAUAAUTT-3'),IQGAP1-siRNA2(5'-GCCCACUUAAGCAUCAUUATT-3'),IQGAP1-siRNA3(5'-GCAGGUGGAUUACUAUAAATT-3'),IQGAP1-阴性对照序列(5'-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3')。实验细胞分为空白对照组、阴性对照组、IQGAP1-siRNA1干扰组、IQGAP1-siRNA2干扰组和IQGAP1-siRNA3干扰组。转染前一天,按5×104个/毫升细胞接种在6孔板上,每孔加入2 ml含FBS的基础培养液,待细胞融合率达到70%后,将siRNA-LipofectamineTM2000复合物(每500 μl Opti-MEM®Ⅰ低血清培养液加入5 μl的LipofectamineTM2000和7.5 μl的siRNA)加入到每一个包含细胞和培养液的孔中。轻摇均匀,培养6 h后,将孔中含siRNA转染试剂弃去并更换新鲜培养液,将培养板置于37℃、CO2培养箱孵育24~72 h,在转染率最高的时间点通过荧光显微镜观察细胞转染数量,采用Western blot和RT-PCR检测转染细胞中IQGAP1 mRNA和蛋白表达水平,筛选具有最佳沉默效果的阳性干扰序列用于后续实验。
1.3 RT-PCR法检测各组细胞中IQGAP1 mRNA的表达利用Primer 5.0软件设计引物,IQGAP1基因上游引物序列:5'-GGTGGAGTTGGCATGAACTT-3',下游:5'-CACTCAACTGGAGGTCAGCA-3';内参基因β-actin上游引物序列:5'-TCCTGTGGCATCCACGA AACT-3',下游:5'-GAAGCATTTGCGGTGGACGAT-3'。根据TRIzol操作说明书对细胞株进行总RNA提取。按照反转录试剂盒说明书,在PCR扩增仪上反转录成cDNA,以此为模板,采用实时荧光定量PCR检测IQGAP1 mRNA表达水平。IQGAP1反应条件为:95℃ 5 min,94℃ 20 s,72℃ 20 s,共计40个循环,循环结束后进行融点曲线分析,于60℃~95℃之间进行测定,条件设置为升温幅度每次0.5℃ 5 s。采用2-ΔΔCt(RQ)法处理荧光定量PCR数据。
1.4 MTT法检测IQGAP1对细胞顺铂敏感度的影响调节细胞浓度至5×104个/毫升,按每孔200 μl接种于96孔板,培养4 h待细胞贴壁后,分别用1、5、10、20 μmol/L顺铂干预24 h,每孔加入5 mg/ml的MTT 20 μl,继续培养4 h后弃上清液,加入DMSO 200 μl,振荡10 min使结晶充分溶解,酶标仪测定490 nm处OD值。实验重复3次。
1.5 流式细胞仪测定细胞周期将细胞以2×106个/毫升的浓度接种在培养皿中,待细胞贴壁生长后加入顺铂干预24 h,收集细胞,PBS洗涤,预冷75%乙醇固定,4℃孵育过夜,重悬细胞于800 μl(1×PBS+1% BSA)溶液中,加入100 μl PI染液及100 μl RNA酶,37℃避光孵育30 min,流式细胞仪检测细胞周期,以未做任何处理的KYSE150细胞作对照。实验重复3次。
1.6 Annexin V-FICT/PI双染检测细胞凋亡细胞的培养、干预及收集步骤同1.5,每份细胞标本加入100 μl Annexin V标记液(10 μl 10×Binding Buffer, 5 μl Annexin V-FITC, 85 μl去离子水),于暗处室温下孵育15 min,再向每个标本加入10 μl PI和400 μl预冷的1×Binding Buffer稀释,15 min内进行细胞凋亡检测。实验重复3次。
1.7 Western blot检测IQGAP1、Nrf21和MRP1蛋白的表达收集细胞并用细胞裂解液裂解提取细胞总蛋白,取50 μg蛋白进行SDS聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳1.5 h,然后将蛋白转移至PVDF膜上,1% BSA封闭过夜,加入Nrf2、MRP1、IQGAP1及内参GAPDH蛋白一抗37℃孵育2 h,TBST漂洗,加入羊抗鼠二抗(1:5000稀释)37℃孵育1 h,将PVDF膜浸于1 ml显色液中避光约10 min后观察结果,用凝胶图像处理系统分析目标条带的相对分子质量和净吸光度值。
1.8 统计学方法应用SPSS17.0软件进行统计学分析,计量资料以均数±标准差(x± s)表示,两样本比较采用t检验,多组间均数差异的比较采用单因素方差分析,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 siRNA对IQGAP1 mRNA及蛋白表达的影响Western blot显示IQGAP1蛋白在空白对照组和阴性对照组的表达水平无显著差异(P=0.492),3条阳性干扰序列均有效下调KYSE150细胞中的IQGAP1蛋白表达量,其中以IQGAP1-siRNA2阳性干扰序列的抑制效果最强(与对照组相比较,IQGAP1蛋白表达量下降85.39%),见图 1A。RT-PCR检测进一步显示阳性干扰组的IQGAP1 mRNA表达水平较空白对照组和阴性对照组均有不同程度的下降,尤以IQGAP1-siRNA2组下降最为明显(P=0.002, P=0.006),两对照组间差异无统计学意义(P=0.412),见图 1B。结果表明siRNA可有效抑制食管癌细胞KYSE150中IQGAP1 mRNA和蛋白的表达水平,同时选取IQGAP1-siRNA2阳性干扰序列(干扰组)用于后续实验。
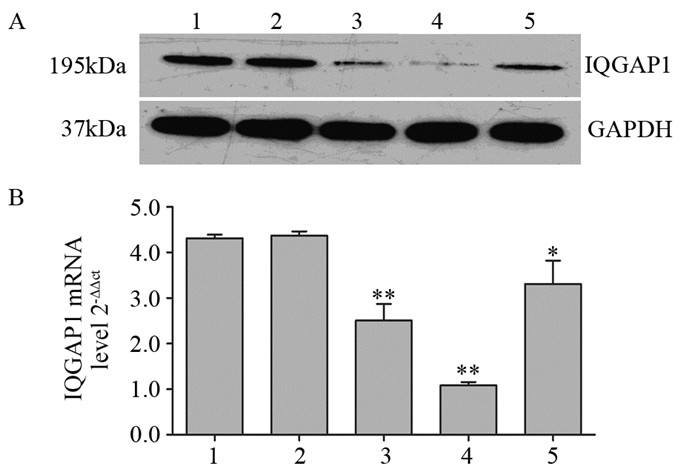
|
| A: the protein expression of IQGAP1 detected by Western blot; B: the mRNA expression of IQGAP1 detected by RT-PCR; *: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, compared with blank control group and negative control group; 1: Blank control; 2: Negative control; 3: IQGAP1-siRNA1; 4: IQGAP1-siRNA2; 5: IQGAP1-siRNA3 图 1 siRNA对IQGAP1 mRNA及蛋白表达的影响 Figure 1 Effect of siRNA on IQGAP1 mRNA and protein expression |
经(1、5、10、20)μmol/L顺铂处理各组细胞24 h后,干扰组细胞生存率均明显低于阴性对照组和空白对照组(均P=0.000),并且随着化疗药物浓度的增加,细胞生存率降低的越明显,而阴性对照组与空白对照组之间差异无统计学意义(P=0.971, P=0.889, P=0.926, P=0.895),见表 1。结果表明IQGAP1-siRNA可明显提高KYSE150细胞对化疗药物顺铂的敏感度。
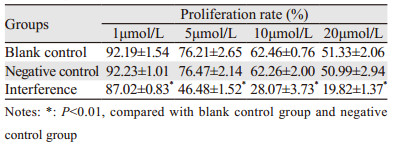 |
流式细胞仪检测显示,干扰组在顺铂处理后的G0/G1期细胞比例(68.89±1.73)%明显高于空白对照组(54.81±3.15)%和阴性对照组(54.35±1.54)%(P=0.002, P=0.005),阴性对照组与空白对照组之间差异无统计学意义(P=0.809);干扰组在顺铂处理后的细胞凋亡率(26.70±2.21)%明显高于空白对照组(12.15±1.40)%和阴性对照组(12.32±1.65)%(P=0.001, P=0.001),阴性对照组与空白对照组之间差异无统计学意义(P=0.909),见图 2。结果表明siRNA沉默IQGAP1可增强顺铂对食管鳞癌细胞的周期阻滞作用,使细胞阻滞于G0/G1期,细胞凋亡率增加。
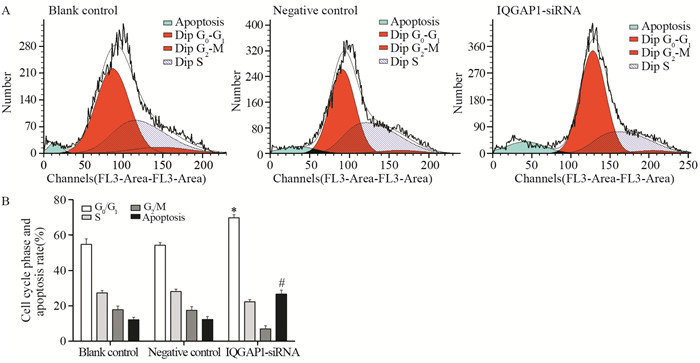
|
| A: the cell cycle distribution and apoptosis rate of KYSE150 cells detected by flow cytometry; B: the average percentage of cell cycle and apoptosis of KYSE150 cells; *: P < 0.05, compared with the G0/G1 phase in control groups; #: P < 0.05, compared with the apoptosis rate in control groups 图 2 沉默IQGAP1对顺铂作用下细胞周期及凋亡的影响 Figure 2 Effect of IQGAP1 silencing on cell cycle phase and apoptosis of KYSE150 after cisplatin treatment |
干扰组Nrf2蛋白的相对表达水平(0.18±0.05)明显低于阴性对照组(0.67±0.11)和空白对照组(0.65±0.05)(P=0.001, P=0.001),两对照组间差异无统计学意义(P=0.793);干扰组MRP1蛋白的相对表达水平(0.14±0.03)明显低于阴性对照组(0.83±0.06)和空白对照组(0.80±0.10)(P=0.000, P=0.000),两对照组间差异无统计学意义(P=0.844),见图 3。结果表明沉默IQGAP1基因可引起Nrf2蛋白及其下游靶件MRP1蛋白的表达下调。
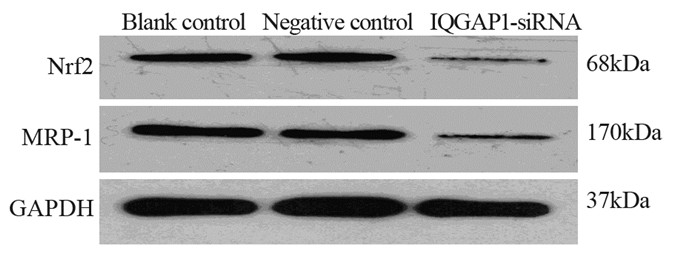
|
| 图 3 IQGAP1基因沉默对Nrf2和MRP1蛋白表达水平的影响 Figure 3 Effect of IQGAP1 silencing on expression of Nrf2 and MRP1 proteins |
手术治疗结合化疗药物顺铂的使用是临床上针对中晚期食管鳞癌患者的一种有效治疗手段,它可以降低食管鳞癌患者术后复发转移的风险,提高预后效果。然而随着顺铂在临床的广泛使用,越来越多的研究发现食管鳞癌细胞对顺铂的敏感度降低甚至产生耐药性[3-5]。顺铂耐药机制十分复杂,任何发生在细胞生长、细胞凋亡、DNA损伤修复、药物分解代谢及药物转运过程中的改变都可能导致化疗耐药性的产生,过去的研究已经发现多种基因表达异常参与了顺铂耐药[6-8]。White等[9]研究发现IQGAP1在HER2阳性乳腺癌细胞中过表达并能与表皮生长因子受体2(HER2)结合抑制乳腺癌细胞对曲妥单抗的药物敏感度,Holck等[10]也发现IQGAP1过表达通过上调丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAKP)组件介导直肠腺癌对5-氟尿嘧啶的耐药,说明IQGAP1的异常表达与肿瘤的化疗耐药相关。
为了研究IQGAP1表达水平与食管鳞癌顺铂化疗敏感度的相关性,本研究首先通过RNA干扰技术沉默食管鳞癌细胞KYSE150中IQGAP1基因的表达,并通过MTT实验检测IQGAP1基因沉默前后KYSE150细胞增殖率的变化,结果显示沉默IQGAP1表达可明显改善KYSE150细胞对顺铂的抵抗作用,干扰组细胞生存率较对照组发生明显下降。其次,通过流式细胞仪检测细胞周期比例和凋亡率发现,siRNA沉默IQGAP1可增强顺铂对食管鳞癌细胞的周期阻滞作用,使大部分细胞阻滞于G0/G1期,并有效增加顺铂对细胞的杀伤作用,促进食管鳞癌细胞凋亡。以上结果均证明IQGAP1-siRNA可有效提高食管鳞癌细胞KYSE150对顺铂的化疗敏感度。在肝细胞癌的研究中发现,siRNA沉默IQGAP1表达可通过抑制mTOR信号通路促进DNA合成前期细胞比例升高,抑制细胞增殖,IQGAP1还可通过调控RAS基因家族及多种凋亡蛋白表达介导HepG2细胞凋亡[11-12]。另有研究表明IQGAP1与增殖相关的ERK信号通路有关,在MEK-ERK信号通路中,IQGAP1作为支架蛋白与ERK2连接,通过调节ERK2活性在细胞增殖的信号网络中发挥关键作用[13-14]。推测IQGAP1基因可能通过上述信号通路参与调节KYSE150细胞的增殖和凋亡。MRP1是一种能量依赖性的跨膜转运蛋白,主要定位于细胞膜,负责主动转运脂质、氨基酸、多糖、药物或其他外源性物质[15]。研究发现MRP1高表达时,转运负电荷药物能力增强导致进入肿瘤细胞内的顺铂浓度降低,顺铂-DNA复合物形成量减少引起肿瘤细胞耐药性增强[16]。在食管癌研究领域目前已经发现转录因子4(ATF4),微囊蛋白1(Caveolin-1)等基因通过调控MRP1表达参与食管鳞癌的多重化疗耐药[17-18]。另有研究发现Nrf2信号通路可通过调控下游靶件MRP1参与肿瘤细胞对顺铂化疗耐药[19],而IQGAP1蛋白作为Nrf2相互作用蛋白,可通过激活MEK-ERK信号通路上调Nrf2蛋白表达[20]。为进一步揭示IQGAP1参与调节食管鳞癌细胞化疗敏感度的机制,我们通过Western blot实验检测KYSE150细胞中Nrf2和MRP1蛋白表达水平变化,结果显示沉默IQGAP1可引起Nrf2和MRP1蛋白表达水平明显减低,提示IQGAP1可能通过调控Nrf2/MRP1的表达参与介导食管鳞癌细胞对顺铂的化疗敏感度。
综上所述,本研究成功构建有效沉默食管鳞癌KYSE150细胞IQGAP1表达的siRNA,与化疗药物顺铂联合作用时能够促进细胞周期阻滞、介导细胞凋亡,并提高肿瘤细胞化疗敏感度。提示IQGAP1可能作为食管鳞癌治疗的一个潜在靶点,并能在一定意义上用于改善顺铂的耐药性。
| [1] | 王夏炜, 曹永倩, 张芮. 支架蛋白IQGAP1与肿瘤研究现状[J].中华肿瘤防治杂志, 2014, 21(20): 1657–61. [Wang XW, Cao YQ, Zhang R. Scaffold protein IQGAP1 and tumor research status[J].Zhonghua Zhong Liu Fang Zhi Za Zhi, 2014, 21(20): 1657–61. ] |
| [2] | Wang XX, Wang K, Li XZ, et al. Targeted knockdown of IQGAP1 inhibits the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo[J].PLoS One, 2014, 9(5): e96501. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0096501 |
| [3] | Cheng Y, Li K, Diao D, et al. Expression of KIAA0101 protein is associated with poor survival of esophageal cancer patients and resistance to cisplatin treatment in vitro[J].Lab Invest, 2013, 93(12): 1276–87. DOI:10.1038/labinvest.2013.124 |
| [4] | Ajani JA, Wang X, Song S, et al. ALDH-1 expression levels predict response or resistance to preoperative chemoradiation in resectable esophageal cancer patients[J].Mol Oncol, 2014, 8(1): 142–9. DOI:10.1016/j.molonc.2013.10.007 |
| [5] | Shen DW, Pouliot LM, Hall MD, et al. Cisplatin resistance: a cellular self-defense mechanism resulting from multiple epigenetic and genetic changes[J].Pharmacol Rev, 2012, 64(3): 706–21. DOI:10.1124/pr.111.005637 |
| [6] | Xu J, Hu Z. Y-box-binding protein 1 promotes tumor progression and inhibits cisplatin chemosensitivity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma[J].Biomed Pharmacother, 2016, 79: 17–22. DOI:10.1016/j.biopha.2016.01.037 |
| [7] | Cao B, Shi Q, Wang W. Higher expression of SIRT1 induced resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells to cisplatin[J].J Thorac Dis, 2015, 7(4): 711–9. |
| [8] | Lai KK, Chan KT, Choi MY, et al. 14-3-3sigma confers cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells via regulating DNA repair molecules[J].Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(2): 2127–36. DOI:10.1007/s13277-015-4018-6 |
| [9] | White CD, Li Z, Dillon DA, et al. IQGAP1 protein binds human epidermal growth factor receptor 2(HER2) and modulates trastuzumab resistance[J].J Biol Chem, 2011, 286(34): 29734–47. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M111.220939 |
| [10] | Holck S, Nielsen HJ, Hammer E, et al. IQGAP1 in rectal adenocarcinomas: localization and protein expression before and after radiochemotherapy[J].Cancer Lett, 2015, 356(2 Pt B): 556–60. |
| [11] | Chen F, Zhu HH, Chen Z, et al. IQGAP1 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation by Akt activation[J].Exp Mol Med, 2010, 42(7): 477–83. DOI:10.3858/emm.2010.42.7.049 |
| [12] | Ma Y, Jin Z, Huang J, et al. IQGAP1 plays an important role in the cell proliferation of multiple myeloma via the MAP kinase (ERK) pathway[J].Oncol Rep, 2013, 30(6): 3032–8. |
| [13] | Ma Y, Jin Z, Huang J, et al. Quercetin suppresses the proliferation of multiple myeloma cells by down-regulating IQ motif-containing GTPase activating protein 1 expression and extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation[J].Leuk Lymphoma, 2014, 55(11): 2597–604. DOI:10.3109/10428194.2013.879128 |
| [14] | Ji L, Li H, Gao P, et al. Nrf2 pathway regulates multidrug-resistance-associated protein 1 in small cell lung cancer[J].PLoS One, 2013, 8(5): e63404. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0063404 |
| [15] | He SM, Li R, Kanwar JR, et al. Structural and functional properties of human multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1/ABCC1)[J].Curr Med Chem, 2011, 18(3): 439–81. DOI:10.2174/092986711794839197 |
| [16] | Lu JF, Pokharel D, Bebawy M. MRP1 and its role in anticancer drug resistance[J].Drug Metab Rev, 2015, 47(4): 406–19. DOI:10.3109/03602532.2015.1105253 |
| [17] | Zhang S, Cao W, Yue M, et al. Caveolin-1 affects tumor drug resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating expressions of P-gp and MRP1[J].Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(7): 9189–96. DOI:10.1007/s13277-015-4778-z |
| [18] | Zhu H, Chen X, Chen B, et al. Activating transcription factor 4 mediates a multidrug resistance phenotype of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells through transactivation of STAT3 expression[J].Cancer Lett, 2014, 354(1): 142–52. DOI:10.1016/j.canlet.2014.07.044 |
| [19] | Zoheir KM, Abd-Rabou AA, Harisa G I, et al. IQGAP1 gene silencing induces apoptosis and decreases the invasive capacity of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells[J].Tumour Biol, 2016, 37(10): 13927–39. DOI:10.1007/s13277-016-5283-8 |
| [20] | Cheung KL, Lee JH, Shu L, et al. The Ras GTPase-activating-like protein IQGAP1 mediates Nrf2 protein activation via the mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase (MEK)-ERK pathway[J].J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(31): 22378–86. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M112.444182 |
 2017, Vol. 44
2017, Vol. 44


