文章信息
- 于宏, 邱芳, 顾玺, 边小博
- YU Hong, QIU Fang, GU Xi, BIAN Xiaobo
- HER-2低表达的三阴性乳腺癌患者的临床特征和预后分析
- Clinical features and prognosis of patients with triple negative breast cancer with low expression of HER-2
- 中国医科大学学报, 2022, 51(8): 721-724
- Journal of China Medical University, 2022, 51(8): 721-724
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2022-02-12
- 网络出版时间:2022-07-13 13:46
乳腺癌是女性最常见的恶性肿瘤,其发病率逐年上升,研究[1]显示2021年乳腺癌发病率已超过肺癌,成为发病率最高的恶性肿瘤。三阴性[雌激素受体(estrogen receptor,ER)、孕激素受体(progesterone receptor,PR)、人表皮生长因子受体2(human epidermal growth factor receptor 2,HER-2)均阴性]乳腺癌是乳腺癌的常见类型,复发和死亡率较高[2-4]。研究[5-7]发现HER-2过表达与肿瘤侵袭性生长及较差预后直接相关,约15%~20%乳腺癌患者中HER-2过表达或HER-2基因扩增。到目前为止,未发现与HER-2受体结合的配体,HER-2分子主要通过与表皮生长因子(epidermal growth factor,EGF)家族的其他受体形成异二聚体,进一步激活MAPK、JAK、PI3K、STAT3等通路,促进肿瘤的发生和进展。HER-2在正常上皮细胞中低表达,在30%以上的人类肿瘤(乳腺癌、胃癌、肺癌等)中扩增/过表达。
HER-2是一种酪氨酸激酶受体,通过形成同源二聚体或与人表皮受体家族其他成员形成异二聚体而活化,激活下游酪氨酸激酶级联信号,从而触发细胞的增殖、迁移、侵袭和存活机制。根据美国临床肿瘤学会(American Society of Clinical Oncology,ASCO)和美国病理学家学会(College of American Pathologists,CAP)指南(ASCO/CAP指南)[8],免疫组化检测到HER-2(3+)或(2+)且原位杂交(in situ hybridization,ISH)阳性可以判定为HER-2过表达,否则为HER-2阴性。在某些HER-2阴性乳腺癌细胞表面也有不同程度的HER-2蛋白的表达。在HER-2(1+)和HER-2(2+)的乳腺癌细胞膜上存在50万~ 100万个HER-2受体分子,约30%早期乳腺癌患者HER-2低表达[9]。HER-2低表达的乳腺癌患者不同于HER-2(0)的患者,HER-2低表达时肿瘤具有特定的生物学特性,并且在治疗和预后方面表现出差异,这与治疗耐药、激素受体阴性的肿瘤尤其相关[10]。HER-2低表达三阴性乳腺癌患者的临床特征及预后的研究尚未见报道,本研究探讨HER-2低表达的三阴性乳腺癌患者的临床特征和预后,旨在为改善HER-2低表达乳腺癌患者预后提供参考。
1 材料与方法 1.1 临床资料及分组收集2015年1月至2019年1月我院收治的三阴性乳腺癌患者的临床资料。纳入标准:(1)确诊为三阴性乳腺癌;(2)术前未接受新辅助化疗、内分泌治疗;(3)直接行手术治疗;(4)病历资料完整;(5)年龄18~75岁;(6)术后接受规范的辅助治疗。排除标准:(1)特殊类型乳腺癌(化生性乳腺癌等);(2)合并其他恶性肿瘤;(3)远处转移;(4)肝、肾、心、脑、肺等重要脏器功能不全;(5)未能获得随访;(6)炎性乳腺癌、双侧乳腺癌。共纳入498例。本研究获得医院伦理委员会批准。根据患者HER-2表达状态,分为阴性组[免疫组化:HER-2(0),n = 350]和低表达组[免疫组化HER-2(1+),或者HER-2(2+)但ISH检测显示HER-2基因未扩增,n = 148]。
1.2 分组标准术中取患者乳腺癌组织,行免疫组化染色。根据CerbB2蛋白在细胞膜上的染色比例和着色强度,将HER-2表达水平定义为阴性(-)、1+、2+、3+。-,表示无染色或≤10%的肿瘤细胞上存在不完整、微弱的细胞膜染色;1+,表示 > 10%的肿瘤细胞上存在完整的、微弱的细胞膜染色;2+,表示 > 10%的肿瘤细胞上存在弱~中强度的、完整细胞膜染色或≤10%的肿瘤细胞上存在强而完整的细胞膜染色;3+,表示 > 10%的肿瘤细胞上存在强、完整、均匀的细胞膜染色。HER-2(2+)患者需进行ISH检测,明确HER-2基因有无扩增。
1.3 观察指标观察指标包括患者一般临床指标[年龄、发病部位、体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)、家族史],病理特征[Ki-67(%)、T分期、N分期、组织学分级、脉管癌栓形成],乳房切除方式(保乳或全切、是否行腋窝淋巴结清扫),术后3年内复发或转移率、无病生存率。
1.4 统计学分析利用SPSS 26.0软件进行数据分析。计量资料采用x±s表示,组间比较采用t检验;计数资料采用率(%)表示,组间比较采用χ2检验。采用多因素logistic回归分析三阴性乳腺癌患者术后复发或转移的危险因素。2组患者无病生存率比较采用生存曲线分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 2组患者各项临床指标比较结果显示,与阴性组比较,低表达组患者Ki-67显著增高(P < 0.001);T分期为T3的患者比例显著增高(P < 0.001);淋巴结转移率显著增高(P = 0.033);腋窝淋巴结清扫率显著增高(P = 0.001);术后3年内复发或转移率显著增高(P = 0.022)。见表 1。
| Item | HER-2-low group(n = 148) | HER-2-zero group(n = 350) | t/χ2 | P |
| Age(year) | 56.37±6.74 | 56.12±7.08 | 0.365 | 0.715 |
| Location[n(%)] | 0.788 | 0.375 | ||
| Left breast | 88(59.46) | 193(55.14) | ||
| Right breast | 60(40.54) | 157(44.86) | ||
| BMI(kg/m2) | 23.57±2.77 | 23.80±2.82 | 0.836 | 0.403 |
| Family history[n(%)] | 12(8.11) | 20(5.71) | 0.991 | 0.319 |
| Ki-67(%) | 66.47±16.38 | 54.37±15.82 | 7.719 | < 0.001 |
| T stage[n(%)] | 12.419 | < 0.001 | ||
| T1-2 | 106(71.62) | 298(85.14) | ||
| T3 | 42(28.38) | 52(14.86) | ||
| N stage[n(%)] | 4.529 | 0.033 | ||
| N0 | 96(64.86) | 260(74.29) | ||
| N1-3 | 52(35.14) | 90(25.71) | ||
| Grading[n(%)] | 1.444 | 0.229 | ||
| Ⅰ-Ⅱ | 132(89.19) | 298(85.14) | ||
| Ⅲ | 16(10.81) | 52(14.86) | ||
| Vessel carcinoma embolus[n(%)] | 61(41.22) | 160(45.71) | 0.853 | 0.356 |
| Operation[n(%)] | 0.015 | 0.903 | ||
| Breast-conserving | 35(23.65) | 81(23.14) | ||
| Mastectomy | 113(76.35) | 269(76.86) | ||
| Axillary lymph node dissection[n(%)] | 78(52.70) | 126(36.00) | 11.999 | 0.001 |
| Recurrence or metastasis[n(%)] | 16(10.81) | 18(5.14) | 5.253 | 0.022 |
2.2 三阴性乳腺癌患者术后3年复发或转移的危险因素分析
logistic回归分析显示,HER-2低表达、淋巴结转移、T分期为T3是三阴性乳腺癌患者术后3年复发或转移的危险因素(均P < 0.05)。见表 2。
| Variable | B | SD | Wald | P | OR | 95% CI |
| HER-2 low expression | 0.663 | 0.352 | 3.912 | 0.047 | 1.453 | 1.008-2.912 |
| Lymphatic metastasis | 0.901 | 0.488 | 3.521 | 0.008 | 2.461 | 1.253-6.412 |
| T3 | -1.232 | 0.577 | 4.558 | 0.033 | 0.292 | 0.094-0.904 |
2.3 2组患者无病生存率比较
生存曲线分析结果显示,与阴性组比较,低表达组患者无病生存率显著降低(P = 0.019)。见图 1。
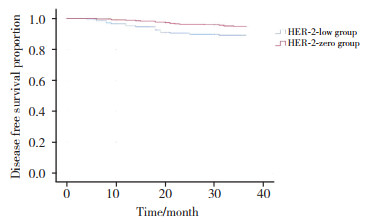
|
| 图 1 2组患者术后3年无病生存率比较 Fig.1 Comparison of disease-free survival between two group |
3 讨论
中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范[11]表明,目前对于三阴性乳腺癌的治疗并未区分HER-2不表达或HER-2低表达。本研究探讨了HER-2低表达的三阴性乳腺癌患者的临床特征和预后,结果发现HER-2低表达的三阴性乳腺癌患者临床特征与HER-2不表达患者显著不同,HER-2低表达是三阴性乳腺癌患者术后复发或转移的危险因素,而且HER-2低表达患者术后无病生存率显著降低。
目前已有学者[12]关注HER-2低表达在乳腺癌患者中的作用。美国一项研究[13]显示在淋巴结阳性患者中,HER-2低表达可能与患者预后不良有关,表明HER-2(0)和HER-2(1+),或者HER-2(2+)但ISH检测显示HER-2基因未扩增的乳腺癌患者临床特征和预后存在不同。早期乳腺癌患者研究[14]显示了HER-2低表达状态可能是可手术治疗乳腺癌患者预后不良的危险因素,而且与HER-2(0)或(1+)的患者比较,HER-2(2+)且ISH阳性的患者在首诊时肿瘤体积更大、淋巴结累及更多、临床分期更严重、Ki-67表达更高;生存分析显示HER-2(2+)且ISH阴性患者无病生存率较HER-2(0)或(1+)的患者、HER-2阳性但接受曲妥珠单抗治疗的患者降低。在激素受体阳性的乳腺癌患者中,也证实了HER-2低表达状态的乳腺癌患者临床特征和预后与HER-2(0)或(1+)的患者显著不同[15],与本研究结果一致。
综上所述,HER-2低表达的三阴性乳腺癌患者临床特征与HER-2不表达患者显著不同,HER-2低表达是三阴性乳腺癌患者术后复发或转移的危险因素。本研究的不足之处:样本量较小,病例来源仅为一家医院;随访时间较短,且仅对无病生存期、复发率或转移率进行统计,未对患者死亡率做进一步分析,今后将扩大样本量,延长随访时间来进一步论证。
| [1] |
SIEGEL RL, MILLER KD, FUCHS HE, et al. Cancer statistics, 2021[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2021, 71(1): 7-33. DOI:10.3322/caac.21654 |
| [2] |
NIERENGARTEN MB. Higher mortality risk in African American women with triple-negative breast cancer[J]. Cancer, 2021, 127(20): 3712-3713. DOI:10.1002/cncr.33924 |
| [3] |
NWAGU GC, BHATTARAI S, SWAHN M, et al. Prevalence and mortality of triple-negative breast cancer in west Africa: biologic and sociocultural factors[J]. JCO Glob Oncol, 2021, 7: 1129-1140. DOI:10.1200/GO.21.00082 |
| [4] |
CHO B, HAN YN, LIAN M, et al. Evaluation of racial/ethnic differences in treatment and mortality among women with triple-negative breast cancer[J]. JAMA Oncol, 2021, 7(7): 1016-1023. DOI:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.1254 |
| [5] |
SLAMON DJ, CLARK GM, WONG SG, et al. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene[J]. Science, 1987, 235(4785): 177-182. DOI:10.1126/science.3798106 |
| [6] |
SAPINO A, GOIA M, RECUPERO D, et al. Current challenges for HER2 testing in diagnostic pathology: state of the art and controversial issues[J]. Front Oncol, 2013, 3: 129. DOI:10.3389/fonc.2013.00129 |
| [7] |
CHOONG GM, CULLEN GD, O'SULLIVAN CC. Evolving standards of care and new challenges in the management of HER2-positive breast cancer[J]. CA A Cancer J Clin, 2020, 70(5): 355-374. DOI:10.3322/caac.21634 |
| [8] |
WOLFF AC, HAMMOND MEH, SCHWARTZ JN, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer[J]. Arch Pathol Lab Med, 2007, 131(1): 18-43. DOI:10.5858/2007-131-18-ASOCCO |
| [9] |
XIN L, WU Q, ZHAN CM, et al. Multicenter study of the clinicopathological features and recurrence risk prediction model of earlystage breast cancer with low-positive human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 expression in China (Chinese Society of Breast Surgery 021)[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2022, 135(6): 697-706. DOI:10.1097/CM9.0000000000002056 |
| [10] |
DENKERT C, SEITHER F, SCHNEEWEISS A, et al. Clinical and molecular characteristics of HER2-low-positive breast cancer: pooled analysis of individual patient data from four prospective, neoadjuvant clinical trials[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2021, 22(8): 1151-1161. DOI:10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00301-6 |
| [11] |
中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会. 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2019年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2019, 29(8): 609-680. DOI:10.19401/j.cnki.1007-3639.2019.08.009 |
| [12] |
袁芃, 徐兵河. 人表皮生长因子受体2低表达乳腺癌及其相关药物治疗的研究进展[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2021, 43(9): 901-905. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112152-20210220-00149 |
| [13] |
GILCREASE MZ, WOODWARD WA, NICOLAS MM, et al. Even low-level HER2 expression may be associated with worse outcome in node-positive breast cancer[J]. Am J Surg Pathol, 2009, 33(5): 759-767. DOI:10.1097/PAS.0b013e31819437f9 |
| [14] |
ROSSI V, SAROTTO I, MAGGIOROTTO F, et al. Moderate immunohistochemical expression ofHER-2(2+) without HER-2 gene amplification is a negative prognostic factor in early breast cancer[J]. Oncologist, 2012, 17(11): 1418-1425. DOI:10.1634/theoncologist.2012-0194 |
| [15] |
EGGEMANN H, IGNATOV T, BURGER E, et al. Moderate HER2 expression as a prognostic factor in hormone receptor positive breast cancer[J]. Endocr Relat Cancer, 2015, 22(5): 725-733. DOI:10.1530/ERC-15-0335 |
 2022, Vol. 51
2022, Vol. 51




