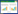文章信息
- 张弘扬, 李思嘉, 李巍
- ZHANG Hongyang, LI Sijia, LI Wei
- 基于缺氧相关基因甲状腺癌预后模型的研究
- Prognostic model of thyroid cancer based on hypoxia-related genes
- 中国医科大学学报, 2022, 51(4): 306-312
- Journal of China Medical University, 2022, 51(4): 306-312
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2021-10-22
- 网络出版时间:2022-04-29 11:19
甲状腺癌是一种常见的肿瘤,可发生于所有年龄段[1]。目前,针对甲状腺癌的诊断主要依靠超声和经皮细针穿刺,治疗手段上则以手术和I131放射治疗为主。虽然,这种成熟的诊断和治疗方案得到了广泛的认可,但是,关于甲状腺癌的预后分析仍然是学者们探讨的热点。
众所周知,肿瘤细胞内微环境的紊乱多由供氧不足导致。缺氧可使基因和蛋白质的表达发生异常,也可能在遗传不稳定性、肿瘤发生和进展中发挥作用。已有研究[2]表明,缺氧引起肿瘤微环境的变化,促进炎症发生、免疫抑制和治疗抵抗,从而诱发肺癌。
近年来,研究者们致力于利用缺氧相关标志物评估肿瘤的预后。例如,3个缺氧相关基因(PDSS1、CDCA8和SLC7A11)被用于构建肝细胞癌的预后、复发和诊断模型[3]。基于缺氧相关基因,开发了缺氧风险模型来评估胶质瘤患者的预后[4]。这些缺氧相关预后独立模型的建立对癌症患者的综合治疗做出了重大贡献。本研究旨在为甲状腺癌患者的综合治疗提供新的、可靠的预后标志物。
1 材料与方法 1.1 缺氧相关基因的获得甲状腺癌样本的转录组数据和临床数据从肿瘤与癌症基因组图谱(the cancer genome atlas,TCGA)网站下载,其中,包括510份甲状腺癌样本数据和58份癌旁样本数据,以供进一步分析。根据错误发现率(false discovery rate,FDR) < 0.05和| log2FC | > 1,获得2 215个差异表达基因,结合从hypoxiaDB数据库(此数据库为人类缺氧相关调节蛋白的研究提供了一个完整的最新数据库)下载的差异表达基因,共获得了373个差异表达的缺氧相关基因。
1.2 功能分析为进一步了解基因本身的功能,以及基因可能参与的通路,采用clusterProfiler进行基因本体(gene ontology,GO)分析及京都基因和基因组百科全书(Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)分析,以研究差异表达的缺氧相关基因之间的功能相关性。
1.3 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络的构建将缺氧相关基因映射至STRING数据库,以创建一个交互网络来阐明差异表达基因之间的关联。随后,采用Cytoscape软件对蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络进行了可视化处理。
1.4 缺氧相关标志物预测模型的构建与验证用Cox单因素回归分析鉴定与总生存时间相关的差异表达缺氧相关基因,并结合每个基因特定回归系数(β),构建患者的风险评分公式。风险评分= β(基因1)×表达量(基因1)+ β(基因2)×表达量(基因2)+……+β(基因n)×表达量(基因n)。
从整个甲状腺癌TCGA数据库中随机选择50%甲状腺癌样本(n = 255)作为实验组,其余50%甲状腺癌样本(n = 255)作为验证组,在2组根据风险评分公式,以中位风险评分为临界点,将患者分为低危组和高危组。用Kaplan-Meier分析评估2组的生存差异,并用log-rank统计方法进行比较。受试者操作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线和Harrell一致性指数用于评估模型预测的准确性。最后,采用单变量Cox回归分析来确定风险评分、年龄、肿瘤TNM分期以及性别之间的独立预后功能。
1.5 预测模型的内部验证为了进一步验证该模型的预测能力,从整个甲状腺癌TCGA数据库中随机选择了50%甲状腺癌样本作为内部验证数据集(n = 255)。采用C指数评估所建立模型的性能。
1.6 统计学分析采用R语言分析TCGA数据库。绘制Kaplan-Meier生存曲线,并通过log-rank检验进行比较。多因素Cox回归分析用于建立缺氧相关基因的预后预测模型。所有统计分析均使用R语言进行。所有统计检验均为双侧检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 差异表达缺氧相关基因的鉴定从TCGA数据库中获得2 215个差异表达的甲状腺癌基因,结合hypoxiaDB数据库,共获得373个差异表达的缺氧相关基因。图 1A、1B所示为373个差异表达的缺氧相关基因中的前30个基因。其中,只有1个上调基因(CCND1),而下调基因有29个。采用箱氏图来总结甲状腺癌和癌旁组织之间30个差异表达的缺氧相关基因的表达模式,见图 1C。
|
| A, volcano map showing differentially expressed hypoxia-related genes between thyroid cancer and paracancerous tissues. Red dots indicate significantly upregulated genes, and green dots represent significantly downregulated genes; B, heatmaps show cluster analysis of the top 30 differentially expressed hypoxia-related genes; C, box plot of 30 hypoxia-related genes in thyroid cancer tissues and paired paracancerous tissues. Each red box represents a hypoxia-related gene differentially expressed in thyroid cancer tissues, and each blue box represents a hypoxia-related gene differentially expressed in paracancerous tissues. 图 1 缺氧相关基因的差异表达 Fig.1 Differentially expressed hypoxia-related genes |
2.2 差异表达的缺氧相关基因的功能富集分析
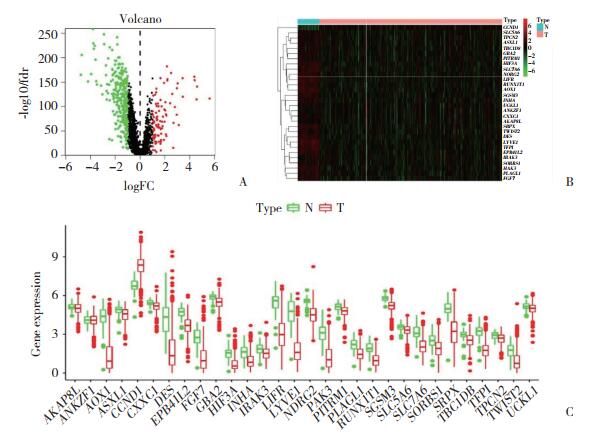
对差异表达的缺氧相关基因进行功能富集分析有助于理解其生物学作用。GO富集分析的前10个生物学过程和KEGG富集分析的前10个通路分析如图 2所示。差异基因的生物学过程主要涉及“细胞外结构组织”“含有胶原的细胞外基质”和“细胞外基质结构成分”(图 2A)。而差异基因的通路分析主要涉及“PI3K-Akt信号通路”“细胞因子-细胞因子-受体相互作用”和“MAPK信号通路”(图 2B)。
|
| A, biological processes; B, cell components; C, molecular functions; D, KEGG enrichment to show the signaling pathways involved in differentially expressed hypoxia-related genes. 图 2 差异表达的缺氧相关基因的功能富集分析 Fig.2 Functional enrichment of differentially expressed hypoxia-related genes |
2.3 蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络的构建与重要基因模块
为了充分了解缺氧相关基因的差异表达,利用Cytoscape软件构建了一个交互式蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用网络。采用cytoscape软件中的分子复合物检测(MCODE)工具来识别重要的基因模块(hub genes),并筛选出3个重要的基因模块。
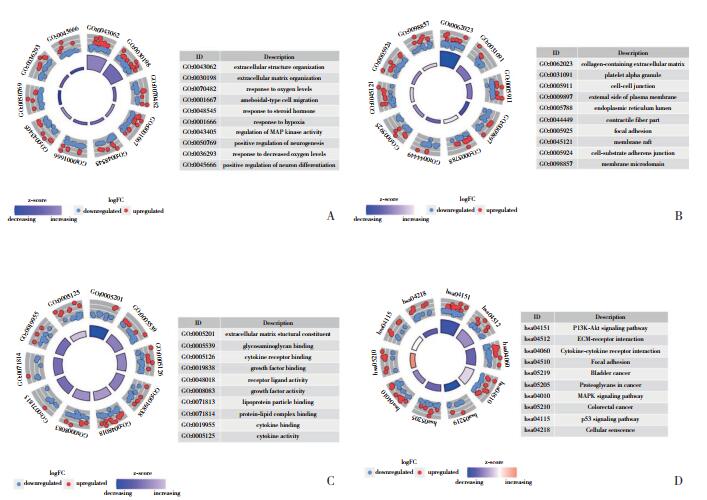
2.4 缺氧相关基因的鉴定与预后采用单变量Cox回归分析确定与甲状腺癌患者预后相关的缺氧相关基因。森林图显示有23个基因在甲状腺癌患者中具有显著的预后价值(P < 0.05,图 3A)。进一步的多变量Cox回归分析共鉴定出11个基因(P < 0.05,图 3B)。
|
| A, univariate analysis revealed that 23 hypoxia-related genes were significantly associated with overall survival. Red represents upregulated genes, and green represents downregulated genes; B, multivariate analysis revealed a total of 11 hypoxia-related genes, which were significantly associated with overall survival. 图 3 差异表达基因的单因素和多因素分析 Fig.3 Univariate and multivariate analysis of differentially expressed genes |
2.5 多因素Cox回归分析预测公式的建立
根据以下公式建立基因风险评分:遗传风险评分=0.792 6×SLC6A8+0.806 4×STC1+0.7867×PTGIS-1.057×SLC24A3-0.349 2×DPP4-0.749 2×ANK2-1.204 0×APOE+0.521 1×PIM1+3.085 0×PHKG1+0.547 3×AKR1C3+1.171 4×NDRG1。根据缺氧相关基因的预后公式,在实验组和验证组中分别确定了这些基因在不同风险人群中的分布以及患者的生存率。为了确定11个缺氧相关基因在预测甲状腺癌患者临床预后中的作用,进一步绘制了Kaplan-Meier生存曲线,以分析实验组和对照组中高危组和低危组的不同生存时间。Kaplan-Meier分析结果显示,高危组患者的生存率明显低于低危组,见图 4。
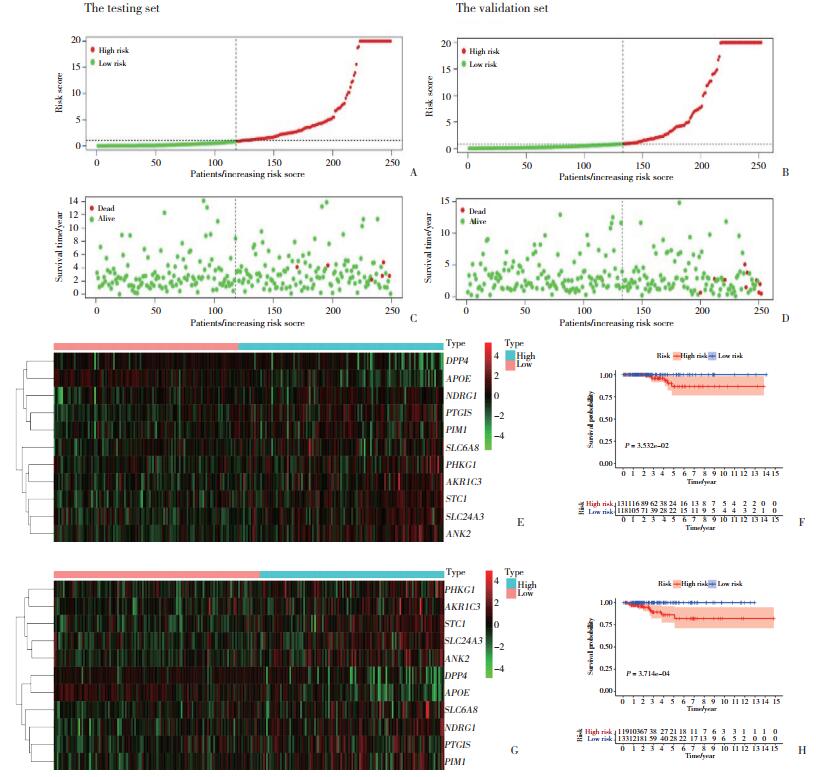
|
| A, distribution of different risk groups in the testing set; B, survival status of patients in different groups, wherein the red dots indicate dead patients and the blue dots represent surviving patients in the testing set; C, heat maps of hypoxia-related gene expression profiles from 11 multivariate analyses in the testing set; D, high-risk patients exhibited a shorter overall survival in the testing set; E, distribution of different risk groups in the validation set; F, survival status of patients in different groups, wherein the red dots indicate dead patients and the blue dots represent surviving patients in the validation set; G, heat maps of hypoxia-related gene expression profiles from 11 multivariate analyses in the validation set; H, High-risk patients exhibited a shorter overall survival in the validation set. 图 4 基于缺氧相关基因的甲状腺癌预后指标验证 Fig.4 Verification of prognostic indicators for thyroid cancer based on hypoxia-related genes |
采用11个与缺氧相关的基因构建了2组甲状腺癌患者1年、3年和5年生存率的ROC曲线,来评估模型的预测性能(图 5)。在实验组中,ROC曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)分别为0.943(1年)、0.897(3年)和0.831(5年)。而在验证组中,AUC分别为0.944(1年)、0.964(3年)和0.992(5年)。
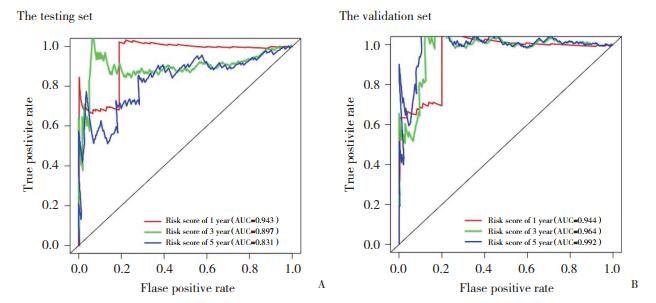
|
| A, ROC analysis of overall survival after 1, 3, and 5 year for 11 gene markers in the testing set; B, ROC analysis of overall survival after 1, 3, and 5 year for 11 gene markers in the validation set. 图 5 基于缺氧相关基因的预后指标显示出良好的预测性能 Fig.5 Prognostic indicators based on hypoxia-related genes showed good predictive performance |
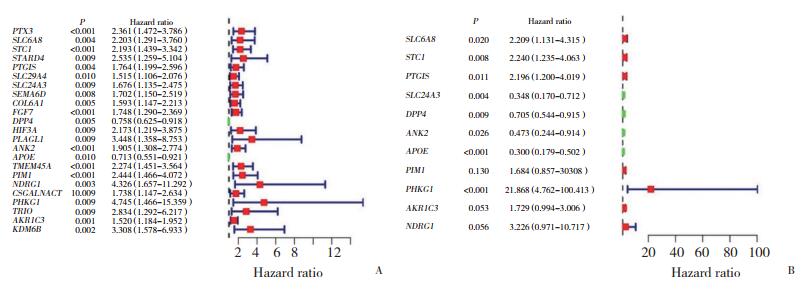
对甲状腺癌患者的临床数据(包括风险评分)的预后价值进行单因素Cox回归分析(表 1),结果显示,构建的风险评分在预后评估中具有较高的预测价值。
| Item | HR(95%CI) | P |
| Age | 1.155(1.080-1.235) | < 0.001 |
| Gender | 0.087(0.180-4.187) | 0.086 |
| T | 2.443(1.100-5.427) | 0.028 |
| N | 2.087(0.521-8.358) | 0.299 |
| M | 2.561(0.314-20.855) | 0.380 |
| Stage | 2.730(1.411-5.283) | 0.003 |
| Rick score | 1.003(1.002-1.004) | < 0.001 |
3 讨论
近年来,甲状腺癌的发病率呈上升趋势,对人类健康构成了重大威胁。在美国,男性和女性甲状腺癌的检出率均有所上升,从1975年的每10万人中可检出4.9例上升至2014年的每10万人中14.3例[4]。同时,由于5年特异性生存率差的低分化甲状腺癌的存在[5],对甲状腺癌的预后研究更为关键。
随着对缺氧引起的肿瘤微环境变化的深入了解以及TCGA和hypoxiaDB数据库的完善,学者们将更多的目光放在了通过缺氧相关基因来预测肿瘤的预后[6-7],近来新兴的证据都在强调免疫及炎症微环境在甲状腺癌中的重要性[8-9]。然而,还没有一项研究致力于通过缺氧相关基因来对甲状腺癌患者进行预后分析。
目前,对甲状腺癌缺氧微环境的研究大多集中在单个基因上[10-12]。本研究中鉴定的11个缺氧相关基因中,部分基因已被证实与肿瘤的预后密切相关。研究[13]显示,CrT(SLC6A8)基因的敲除导致肌酸摄取不足,同时损害抗肿瘤T细胞的免疫功能。补充肌酸可显著抑制肿瘤生长,并与PD-1/PD-L1阻滞剂协同抑制肿瘤生长[14]。载脂蛋白E作为高脂血症的主要病因,被证明在高脂血症模型中,可通过运动改善肿瘤的缺氧微环境,同时减缓原发性和继发性EO771乳腺肿瘤的形成[15]。
此外,PTGIS和DPP4在生物信息学研究中也得到了证实。在先前与肝细胞肝癌相关的新生物标志物研究中,PTGIS是通过mRNA表达网络分析确定的21个核心基因之一,可能是抑制肝细胞肝癌的潜在治疗靶点[16],而DPP4也被证明是NF-κB 15的靶基因[17]。
STC1、PIM1和NDRG1这3种基因在癌症中的研究更加成熟。由于STC1可能通过Bcl-2的失调在缺氧性胃癌中发挥致癌作用,因此被视为可能的胃癌潜在治疗靶点[18]。在缺氧微环境下,miR-124和miR-144的下调可通过减弱PIM1的抑制作用使细胞发生缺氧,而增加患前列腺癌的风险[19]。NDRG1作为调节脂质代谢的关键基因可促进乳腺癌的侵袭性。因NDRG1与乳腺癌预后不良之间的关系密切,故NDRG1成为了乳腺癌中一种有前途的治疗靶点[20]。
总之,本研究基于对差异表达的缺氧相关基因表达谱和相应临床特征的综合分析,确定了多种甲状腺癌的预后标志物。并通过构建一个新的风险评分模型,以有效地评估甲状腺癌患者的预后。本研究的局限性在于其为回顾性研究,今后应该进行更多的前瞻性研究,以验证缺氧相关基因的预后功能。当然,这也需要多中心数据来证实本研究的发现。
| [1] |
LUZÓN-TORO B, FERNÁNDEZ R, VILLALBA-BENITO L, et al. Influencers on thyroid cancer onset: molecular genetic basis[J]. Genes, 2019, 10(11): 913. DOI:10.3390/genes10110913 |
| [2] |
MITTAL V, EL RAYES T, NARULA N, et al. The microenvironment of lung cancer and therapeutic implications[J]. Adv Exp Med Biol, 2016, 890: 75-110. DOI:10.1007/978-3-319-24932-2_5 |
| [3] |
ZHANG B, TANG B, GAO J, et al. A hypoxia-related signature for clinically predicting diagnosis, prognosis and immune microenvironment of hepatocellular carcinoma patients[J]. J Transl Med, 2020, 18(1): 342. DOI:10.1186/s12967-020-02492-9 |
| [4] |
LIN W, WU S, CHEN X, et al. Characterization of hypoxia signature to evaluate the tumor immune microenvironment and predict prognosis in glioma groups[J]. Front Oncol, 2020, 10: 796. DOI:10.3389/fonc.2020.00796 |
| [5] |
KITAHARA CM, SOSA JA. The changing incidence of thyroid cancer[J]. Nat Rev Endocrinol, 2016, 12(11): 646-653. DOI:10.1038/nrendo.2016.110 |
| [6] |
DAVIES L, WELCH HG. Current thyroid cancer trends in the United States[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 140(4): 317-322. DOI:10.1001/jamaoto.2014.1 |
| [7] |
IBRAHIMPASIC T, GHOSSEIN R, SHAH JP, et al. Poorly differentiated carcinoma of the thyroid gland: current status and future prospects[J]. Thyroid, 2019, 29(3): 311-321. DOI:10.1089/thy.2018.0509 |
| [8] |
WANG J, WANG Y, XING P, et al. Development and validation of a hypoxia-related prognostic signature for breast cancer[J]. Oncol Lett, 2020, 20(2): 1906-1914. DOI:10.3892/ol.2020.11733 |
| [9] |
YANG L, ROBERTS D, TAKHAR M, et al. Development and validation of a 28-gene hypoxia-related prognostic signature for localized prostate cancer[J]. E Bio Medicine, 2018, 31: 182-189. DOI:10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.04.019 |
| [10] |
FERRARI SM, FALLAHI P, GALDIERO MR, et al. Immune and inflammatory cells in thyroid cancer microenvironment[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2019, 20(18): 4413. DOI:10.3390/ijms20184413 |
| [11] |
张廓. nm23-H1和HBME-1在乳头状甲状腺癌中的表达及其临床意义[J]. 中国实用医药, 2021, 16(12): 64-66. DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2021.12.022 |
| [12] |
XING M, HAUGEN BR, SCHLUMBERGER M. Progress in molecular-based management of differentiated thyroid cancer[J]. Lancet, 2013, 381(9871): 1058-1069. DOI:10.1016/s0140-6736(13)60109-9 |
| [13] |
LIN P, GUO YN, SHI L, et al. Development of a prognostic index based on an immunogenomic landscape analysis of papillary thyroid cancer[J]. Aging (Albany NY), 2019, 11(2): 480-500. DOI:10.18632/aging.101754 |
| [14] |
DI BIASE S, MA X, WANG X, et al. Creatine uptake regulates CD8 T cell antitumor immunity[J]. J Exp Med, 2019, 216(12): 2869-2882. DOI:10.1084/jem.20182044 |
| [15] |
BUSS LA, DACHS GU. Voluntary exercise slows breast tumor establishment and reduces tumor hypoxia in ApoE-/- mice[J]. J Appl Physiol, 2018, 124(4): 938-949. DOI:10.1152/japplphysiol.00738.2017 |
| [16] |
BAI KH, HE SY, SHU LL, et al. Identification of cancer stem cell characteristics in liver hepatocellular carcinoma by WGCNA analysis of transcriptome stemness index[J]. Cancer Med, 2020, 9(12): 4290-4298. DOI:10.1002/cam4.3047 |
| [17] |
LI Y, YANG L, DONG L, et al. Crosstalk between the Akt/mTORC1 and NF-κB signaling pathways promotes hypoxia-induced pulmonary hypertension by increasing DPP4 expression in PASMCs[J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2019, 40(10): 1322-1333. DOI:10.1038/s41401-019-0272-2 |
| [18] |
WANG Y, QI Z, ZHOU M, et al. Stanniocalcin-1 promotes cell proliferation, chemoresistance and metastasis in hypoxic gastric cancer cells via Bcl-2[J]. Oncol Rep, 2019, 41(3): 1998-2008. DOI:10.3892/or.2019.6980 |
| [19] |
GU H, LIU M, DING C, et al. Hypoxia-responsive miR-124 and miR-144 reduce hypoxia-induced autophagy and enhance radiosensitivity of prostate cancer cells via suppressing PIM1[J]. Cancer Med, 2016, 5(6): 1174-1182. DOI:10.1002/cam4.664 |
| [20] |
SEVINSKY CJ, KHAN F, KOKABEE L, et al. NDRG1 regulates neutral lipid metabolism in breast cancer cells[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2018, 20(1): 1-17. DOI:10.1186/s13058-018-0980-4 |
 2022, Vol. 51
2022, Vol. 51