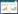文章信息
- 张明慧, 李彦姝
- ZHANG Minghui, LI Yanshu
- 利用生物信息学分析LMO2在乳腺癌中的表达和功能
- Bioinformatics approach to analyze LMO2 expression and function in breast cancer
- 中国医科大学学报, 2021, 50(5): 390-397
- Journal of China Medical University, 2021, 50(5): 390-397
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2020-10-29
- 网络出版时间:2021-05-17 9:08
2. 中国医科大学 生命科学学院分子细胞生物学教研室, 教育部医学细胞生物学重点实验室暨卫健委细胞生物学重点实验室, 沈阳 110122
2. Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Key Laboratory of Medical Cell Biology of Ministry of Education, Key Laboratory of Cell Biology of Public Health Ministry, School of Life Sciences, China Medical University, Shenyang 110122, China
LMO2基因首次发现于急性T淋巴细胞白血病(acute T lymphoblastic leukemia,T-ALL)患者[1],作为核转录因子促进胚胎造血与血管的生成[2]。研究[3]表明,LMO2可在多种实体组织和肿瘤中的细胞质和细胞核表达。LMO2蛋白仅由2个串联的LIM结构域组成,在LDB1、GATA1、TAL1和E47构成的转录复合物中起桥梁作用[4]。乳腺癌是全世界女性癌症死亡的主要原因[5],也是目前中国女性最常见的癌症。2014年中国新增乳腺癌病例估计数约为28万例,因乳腺癌死亡人数约为6.6万[6]。
无论在正常的乳腺导管上皮还是乳腺癌细胞中,LMO2均主要表达在胞质中。通过阻断LIMK1介导的CFL1磷酸化,LMO2促进板状足/丝足的组装形成,进而增加基底型乳腺癌细胞的侵袭和转移[7-8]。此外,LMO2通过与DVL-1/2蛋白结合,减弱Wnt信号通路中β-catenin激活,因此,LMO2在乳腺癌细胞中的表达下调可促进细胞增殖,减少凋亡[9]。
本研究通过生物信息学分析LMO2在乳腺癌中的表达以及LMO2及其共表达基因在乳腺癌中的生物学作用,有望为临床以LMO2基因为靶点的乳腺癌治疗提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 数据来源本研究数据来源于Oncomine数据(http://www.oncomine.org/resource), 基因表达谱数据动态分析(gene expression profiling interactive analysis, GEPIA)数据库(http://gepia.cancer-pku.cn), 人类蛋白质图谱(human protein atlas, HPA)数据库(http://www.proteinatlas.org/), KM plotter数据库(http://kmplot.com/analysis/), Coexpedia数据库(http://www.coexpedia.org/)和FunRich 3.1.3.软件。
1.2 数据提取 1.2.1 Oncomine数据库肿瘤基因芯片数据库与集成数据挖掘平台,包含65个基因表达数据集,可提供肿瘤和正常组织的基因差异表达分析[10]。筛选条件为(1)gene:LMO2;(2)cancer type:breast cancer;(3)data type:mRNA;(4)analysis type:cancer vs normal analysis;(5)临界值设定为P < 0.01,fold change > 2,gene rank=top10%。
1.2.2 HPA数据库免疫组织化学数据的公共存储库,该数据库测定了蛋白在正常组织、细胞以及肿瘤病理组织的表达。筛选条件为(1)search:LMO2;(2)type:tissue atlas:breast caner;(3)分别选择“tissue”“pathology”,组织来源为“female organs:breast”。
1.2.3 GEPIA数据库分析来自TCGA和GTEx的数据,提供关键的交互式和可定制的功能,包括差异表达分析、剖面绘制、相关性分析、患者生存分析、相似基因检测和降维分析[11],分析LMO2在乳腺癌与正常组织中表达的水平。筛选条件为(1)Expression DIY:Box plot;(2)gene:LMO2;(3)data selection:BRCA。其他设为默认值。
1.2.3.1 LMO2基因在肿瘤组织中的表达差异分析(1)cancer type analysis:differential genes analysis;(2)dataset:BRCA;(3)differential methods:LIMMA。
1.2.3.2 相关性分析筛选条件为(1)correlation analysis;(2)gene A:LMO2,gene B:GIMAP6、TGFBR2、LHFP、PTPRB、CAV1;(3)Dataset selection:BRCA Tumor。
1.2.4 KM plotter数据库采用包括乳腺癌在内多种癌症的基因表达和生存数据构建的在线数据库,评估LMO2在乳腺癌患者中的预后价值。筛选条件为(1)选择:Breast cancer;(2)gene:LMO2;(3)Split patients by:Auto select best cutoff;(4)Survival:分别选择“OS”“PPS”“RFS”。
1.2.5 Coexpedia数据库通过功能关联进行评估的共表达[12],对LMO2进行在乳腺癌中的分子调控网络分析。筛选条件为(1)Submit:Human LMO2;(2)MeSH incl. Neoplasms:Breast Neoplasms。
1.2.6 FunRich 3.1.3.软件进行基因注释分析,分别显示LMO2及共表达基因的细胞组成(cellular component,CC)、分子功能(molecular function,MF)、生物学过程(biological process,BP)、信号通路(biological pathway,BPA)。筛选条件:(1)Add dataset:输入LMO2和通过Coexpedia获得的Score > 3的14个基因;(2)gene enrichment:analysis:Cellular component、Molecular function、Biological process、Biological pathway;(3)临界值设定为P < 0.05。
1.2.7 R包clusterProfiler用作LMO2及其共表达的关键基因京都基因与基因组百科全书(kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes,KEGG)通路富集分析。富集显著性的阈值设定为P < 0.05。
1.3 统计学分析采用数据库默认的统计学分析方法。乳腺癌与正常乳腺组织中LMO2表达的比较采用单因素方差分析;LMO2与其关键基因的表达相关性采用Pearson分析;Kaplan-Meier法绘制生存曲线,LMO2高、低表达组生存率的比较采用log-rank检验。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 LMO2基因在常见肿瘤组织中的基因表达对Oncomine数据库进行检索分析后共纳入涉及LMO2基因相关性研究结果453项,挑选出高表达7项和低表达41项差异有统计学意义的结果进一步分析。脑和中枢神经系统肿瘤中高表达2项;乳腺癌中低表达4项;结直肠癌中低表达6项;食管癌中低表达2项;头颈癌中低表达2项;白血病中低表达6项;肺癌中低表达14项;淋巴瘤中低表达2项;黑色素瘤中低表达2项。见图 1。
|
| 图 1 LMO2基因在多种肿瘤中的表达 Fig.1 LMO2 gene expression in multiple tumors |
2.2 LMO2在乳腺癌中的表达
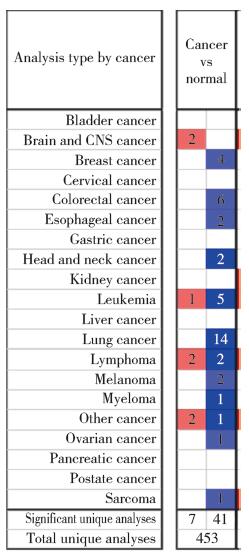
在GEPIA数据库中对乳腺癌(1 197例),乳腺癌组织(1 085例)及正常组织(112例)在mRNA水平上的表达情况进行比较,结果表明,LMO2在乳腺癌组织中的转录水平明显低于正常组织,且差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见图 2。
|
| 图 2 LMO2基因表达水平在乳腺癌中明显低于正常乳腺组织 Fig.2 LMO2 gene expression levels are significantly lower in breast cancer than in normal breast tissue |
2.3 LMO2蛋白在正常乳腺组织与乳腺癌组织中的表达
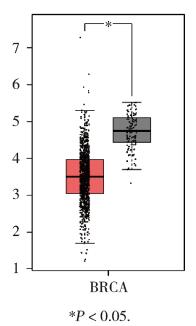
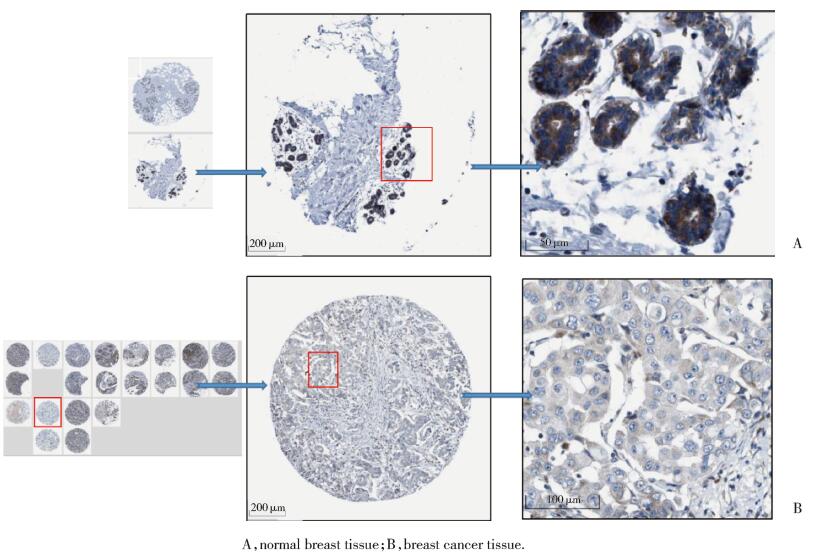
HPA数据库中的免疫组化染色结果证实,LMO2蛋白在乳腺癌组织中的表达明显低于正常乳腺组织。且乳腺癌患者病理组织中LMO2主要定位于细胞质或细胞膜。见图 3。
|
| 图 3 乳腺癌中LMO2蛋白表达水平低于正常乳腺组织 Fig.3 LMO2 protein expression levels are lower in breast cancer than in normal breast tissue |
2.4 LMO2在乳腺癌中的临床预后价值
采用KM plotter数据库评估LMO2的表达水平对肿瘤患者总生存期(overall survival,OS)的影响,提示低表达水平的LMO2在乳腺癌中预示更差的总生存期(P = 0.002 2)。进一步分析结果显示,LMO2低表达同样预示着乳腺癌患者更差的后进展生存期(post progression survival,PPS)(P = 0.045)和更差的无复发生存期(release free survival,RFS)(P < 0.001)。见图 4。
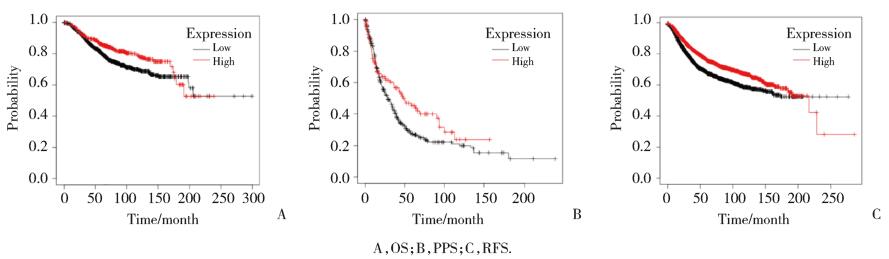
|
| 图 4 LMO2在乳腺癌患者中的预后价值 Fig.4 The prognostic value of LMO2 in breast cancer patients |
2.5 LMO2在乳腺癌中的分子调控网络
本研究利用Coexpedia数据库筛选出LMO2基因在乳腺癌中调控的分子调控网络,得到LMO2的共表达基因共47个。其中score > 3的共表达基因有14个:ADGRL4、GIMAP6、PECAM1、TGFBR2、MEF2C、CD93、S1PR1、LHFP、GMFG、A2M、LDB2、KCTD12、PTPRB和CAV1。见图 5。
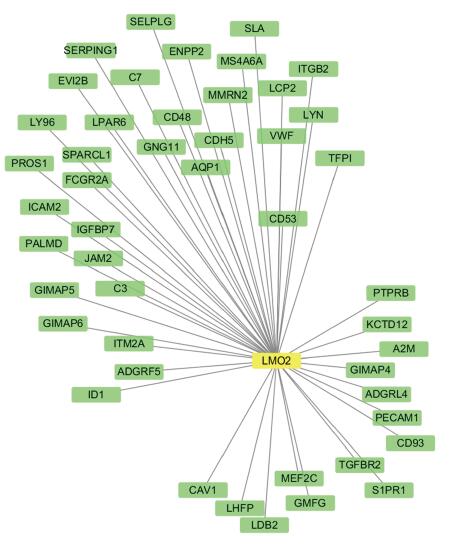
|
| 图 5 LMO2在乳腺癌中的共表达分子网络 Fig.5 Network of LMO2 co-expressed molecules in breast cancer |
2.6 LMO2及其共表达基因的注释分析
采用Funrich软件进行基因注释分析,细胞组成方面,8个基因主要分布在细胞膜,基因占比57.14%(P < 0.010)。分子功能方面分别在受体信号蛋白丝氨酸/苏氨酸激酶活性、补体活性、受体信号蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶活性起着重要作用。生物学过程方面,7个基因在信号传导方面起着重要作用,基因占比46.67%(P = 0.028)。信号通路方面,可能参与转化生长因子-β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)受体信号转导、激活蛋白-1(activator protein-1,AP-1)转录因子网络)、上皮-间质转换等多种通路。见表 1~4。
| Cellular component | P | Genes mapped |
| Plasma membrane | < 0.010 | ADGRL4; PECAM1; TGFBR2; CD93; S1PR1 LHFP; PTPRB; CAV1 |
| Receptor complex | 0.010 | TGFBR2 |
| Nuclear speck | 0.029 | MEF2C |
| Apical plasma membrane | 0.040 | CAV1 |
| Platelet alpha granule lumen | 0.033 | A2M |
| Caveola | < 0.010 | TGFBR2; CAV1 |
| Membrane raft | 0.034 | CAV1 |
| External side of plasma membrane | 0.033 | TGFBR2 |
| Basolateral plasma membrane | 0.038 | CAV1 |
| Platelet alpha granule membrane | 0.011 | PECAM1 |
| Lipid particle | 0.004 | CAV1 |
| Molecular function | P | Genes mapped |
| Receptor signaling protein serine/threonine kinase activity | 0.012 | TGFBR2 |
| Complement activity | 0.023 | CD93 |
| Receptor signaling protein tyrosine phosphatase activity | 0.013 | PTPRB |
| Biological process | P | Genes mapped |
| Signal transduction | 0.028 | ADGRL4; GIMAP6; PECAM1; TGFBR2; S1PR1; GMFG; PTPRB |
| Regulation of cell proliferation | 0.019 | TGFBR2 |
| Regulation of immune response | 0.007 | TGFBR2 |
| Biological pathway | P | Genes mapped |
| CTLA4 inhibitory signaling | 0.006 | PECAM1 |
| Regulation of cytoplasmic and nuclear SMAD2/3 signaling | 0.005 | TGFBR2; MEF2C; CAV1 |
| CDC42 signaling events | 0.010 | TGFBR2; MEF2C; A2M; CAV1 |
| Integrin family cell surface interactions | 0.002 | PECAM1; TGFBR2; MEF2C; S1PR1; A2M; CAV1 |
| TGF-β receptor signaling | 0.005 | TGFBR2; MEF2C; CAV1 |
| Beta3 integrin cell surface interactions | 0.001 | PECAM1; TGFBR2 |
| AP-1 transcription factor network | 0.005 | TGFBR2; MEF2C; A2M; CAV1 |
| ALK1 pathway | 0.006 | TGFBR2; MEF2C; CAV1 |
| Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition | 0.001 | GIMAP6; LHFP; CAV1 |
2.7 关键基因的差异性分析、相关性分析与KEGG富集分析
为了验证上述14个关键基因是否在乳腺癌中存在差异性表达,采用GEPIA进行差异基因筛选,筛选出在乳腺癌与正常组织之间有显著差异表达的基因3 559个,见图 6。
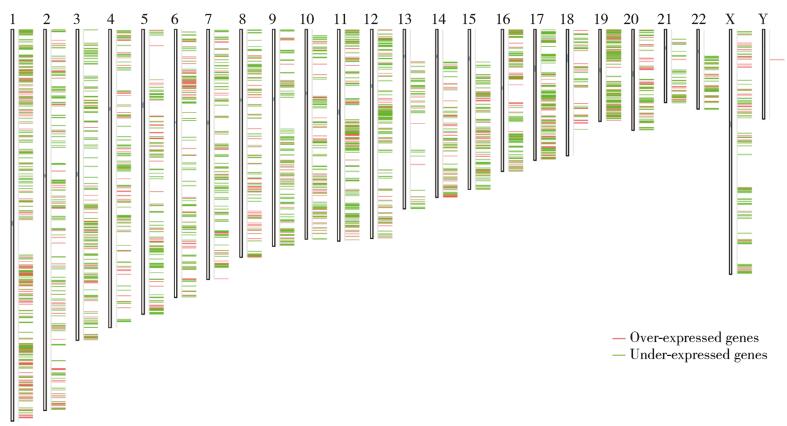
|
| 图 6 染色体上乳腺癌差异性表达基因 Fig.6 Differentially expressed genes in breast cancer mapped to chromosomes |
14个基因中,表达显著上调的基因为CAV1(FC=1.008,P < 0.001),表达显著下调的基因有GIMAP6(FC=-1.142,P < 0.001)、TGFBR2(FC=-1.373,P < 0.001)、LHFP(FC=-1.075,P < 0.001)和PTPRB(FC=-1.537,P < 0.001)。见表 5。
| Gene symbol | Median (tumor) | Median (normal) | Log2(fold change) | P |
| aGIMAP6 | 2.190 | 6.040 | -1.142 | < 0.001 |
| TGFBR2 | 15.220 | 41.019 | -1.373 | < 0.001 |
| LHFP | 12.970 | 28.425 | -1.075 | < 0.001 |
| PTPRB | 1.200 | 5.385 | -1.537 | < 0.001 |
| CAV1 | 10.090 | 4.515 | 1.008 | < 0.001 |
通过GEPIA进一步相关性分析发现,LMO2在mRNA的表达水平与GIMAP6、TGFBR2、LHFP、PTPRB和CAV1等基因的mRNA表达呈显著正相关,其相关性系数r分别为0.51、0.46、0.52、0.48、0.43。见图 7。
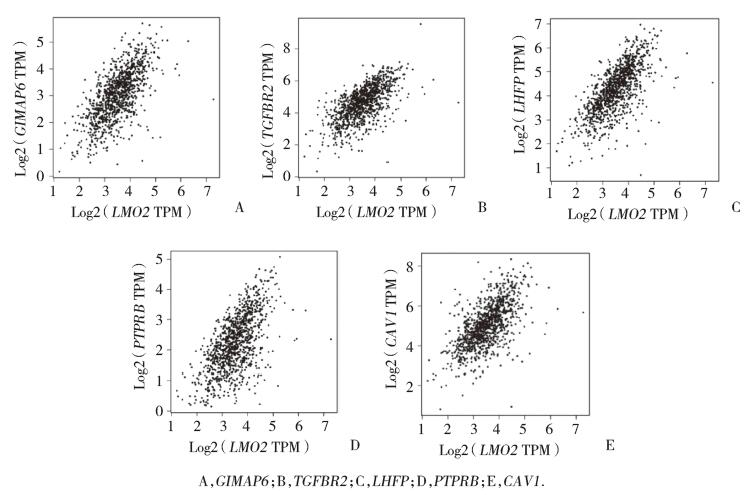
|
| 图 7 LMO2与核心基因表达的相关性 Fig.7 Correlation between LMO2 and expression of core genes |
对LMO2、GIMAP6、TGFBR2、LHFP、PTPRB和CAV1进行KEGG通路富集分析,结果显示,上述6个基因富集于黏附连接、肿瘤内转录调控失调、细胞内吞等通路。见图 8。
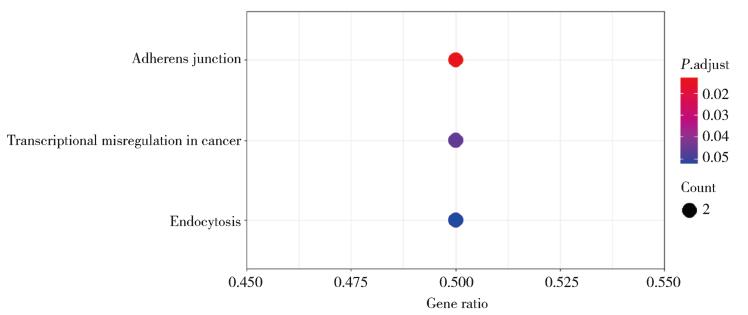
|
| 图 8 LMO2与核心基因的KEGG富集分析 Fig.8 KEGG pathways enriched with LMO2 and core genes |
3 讨论
过去LMO2被认为在胚胎造血以及血管生成中起着重要作用,并通过不同的致癌机制驱动T-ALL形成[13]。在造血细胞和内皮细胞中,LMO2主要分布在细胞核内,而在上皮细胞和实体瘤细胞中则分布在细胞质内[9]。无论是在细胞核还是细胞质中,LMO2都发挥着复杂的功能。作为转录调节因子时,LMO2主要通过与多种转录因子相互作用并定位到DNA的结构域上,参与下游靶基因的调控[14]。而存在于细胞质时,LMO2作为癌基因或肿瘤抑制因子,与其他蛋白结合参与肿瘤的发病过程[15]。
本研究通过Oncomine分析LMO2在各肿瘤中的表达情况。在有统计学意义的4项乳腺癌的研究中,LMO2集中表达高、低均有报道,可能与乳腺癌的不同亚型及样本量大小有关。利用GEPIA及HPA数据库,发现LMO2在乳腺癌组织中转录水平及蛋白表达水平均低于正常组织。此外,低表达LMO2预示着乳腺癌患者更差的OS。这些进一步提示LMO2可能在乳腺癌的发病过程中作为肿瘤抑制因子发挥作用,同时可以作为预后指标预测乳腺癌患者生存。
为了清楚LMO2参与调控哪些分子生物学网络,采用Coexpedia数据库挖掘,并应用FunRich 3.1.3.软件着重分析score > 3的LMO2共表达基因,分析其中的分子功能和生物学过程作用。如ADGRL4、GIMAP6和PECAM等基因参与信号转导通路的建立,TGFBR2参与细胞增殖的调节,这些基因均可能在乳腺癌细胞增殖、侵袭、转移过程中与LMO2基因发挥重要作用。
进一步探究这些与LMO2关系密切的基因在乳腺癌和正常人群中是否呈差异性表达,结果显示,GIMAP6、TGFBR2、LHFP和PTPRB 4个基因与LMO2相同,在乳腺癌中呈低表达,而CAV1基因则相反,呈高表达。其中GIMAP6、LHFP和CAV1参与上皮细胞向间质细胞转化(epithelial-mensenchymal transition,EMT),EMT是肿瘤发生发展的重要驱动因素,研究[16]已证明EMT的激活是产生癌症干细胞的主要机制。此外,TGFBR2与CAV1共同参与TGF-β受体信号通路,TGF-β在乳腺癌早期起增殖抑制和凋亡诱导作用,在晚期可促进肿瘤的侵袭[17]。相关性分析结果显示,LMO2与GIMAP6、TGFBR2、LHFP、PTPRB和CAV1的表达均有明显的相关性。KEGG分析表明,这些基因富集于黏附连接、肿瘤内转录调控失调等通路,表明LMO2很可能与这些基因相互作用,共同参与乳腺癌的癌变、侵袭、转移。
乳腺癌是一种多因素、异质性疾病,需要临床敏锐性和多学科的诊断和治疗方法。本研究对多个肿瘤数据库进行挖掘,明确了LMO2基因在乳腺癌中转录水平及蛋白表达水平均下降。通过生物信息分析学技术发掘在乳腺癌发病过程中有潜在研究价值的重要基因,以及乳腺癌与正常组织间的差异表达基因,并对这些关键基因进行细胞组成、分子功能、生物学过程及信号通路等方面的注释,能够为临床上乳腺癌的治疗提供新靶点。
| [1] |
CHAMBERS J, RABBITTS TH. LMO2 at 25 years: a paradigm of chromosomal translocation proteins[J]. Open Biol, 2015, 5(6): 150062. DOI:10.1098/rsob.150062 |
| [2] |
MATRONE G, MENG S, GU QL, et al. LMO2(LIM-domain-only 2) modulates Sphk1(sphingosine kinase) and promotes endothelial cell migration[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2017, 37(10): 1860-1868. DOI:10.1161/atvbaha.117.309609 |
| [3] |
AGOSTINELLI C, PATERSON JC, GUPTA R, et al. Detection of LIM domain only 2(LMO2) in normal human tissues and haematopoietic and non-haematopoietic tumours using a newly developed rabbit monoclonal antibody[J]. Histopathology, 2012, 61(1): 33-46. DOI:10.1111/j.1365-2559.2012.04198.x |
| [4] |
WADMAN IA. The LIM-only protein LMO2 is a bridging molecule assembling an erythroid, DNA-binding complex which includes the TAL1, E47, GATA-1 and Ldb1/NLI proteins[J]. EMBO J, 1997, 16(11): 3145-3157. DOI:10.1093/emboj/16.11.3145 |
| [5] |
ARNOLD M, PANDEYA N, BYRNES G, et al. Global burden of cancer attributable to high body-mass index in 2012:a population-based study[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2015, 16(1): 36-46. DOI:10.1016/S1470-2045(14)71123-4 |
| [6] |
ZENG HM, ZHENG RS, ZHANG SW, et al. Incidence and mortality of female breast cancer in China, 2009[J]. Thorac Cancer, 2013, 4(4): 400-404. DOI:10.1111/1759-7714.12037 |
| [7] |
LIU Y, WANG ZY, HUANG D, et al. LMO2 promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis in basal-type breast cancer by altering actin cytoskeleton remodeling[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(6): 9513-9524. DOI:10.18632/oncotarget.13434 |
| [8] |
LIU Y, WU C, ZHU TH, et al. LMO2 enhances lamellipodia/filopodia formation in basal-type breast cancer cells by mediating ARP3-Profilin1 interaction[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2017, 23: 695-703. DOI:10.12659/msm.903261 |
| [9] |
LIU Y, HUANG D, WANG ZY, et al. LMO2 attenuates tumor growth by targeting the Wnt signaling pathway in breast and colorectal cancer[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6(1): 1-11. DOI:10.1038/srep36050 |
| [10] |
RHODES DR, KALYANA-SUNDARAM S, MAHAVISNO V, et al. Oncomine 3.0:genes, pathways, and networks in a collection of 18, 000 cancer gene expression profiles[J]. Neoplasia, 2007, 9(2): 166-180. DOI:10.1593/neo.07112 |
| [11] |
TANG Z, LI C, KANG B, et al. GEPIA: a web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(w1): W98-W102. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkx247 |
| [12] |
YANG SM, KIM CY, HWANG S, et al. COEXPEDIA: exploring biomedical hypotheses via co-expressions associated with medical subject headings (MeSH)[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2017, 45(D1): D389-D396. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkw868 |
| [13] |
GOOSSENS S, WANG JQ, TREMBLAY CS, et al. ZEB2 and LMO2 drive immature T-cell lymphoblastic leukemia via distinct oncogenic mechanisms[J]. Haematologica, 2019, 104(8): 1608-1616. DOI:10.3324/haematol.2018.207837 |
| [14] |
SUN W, SHEN WW, YANG S, et al. Homo-binding character of LMO2 isoforms and their both synergic and antagonistic functions in regulating hematopoietic-related target genes[J]. J Biomed Sci, 2010, 17(1): 1-10. DOI:10.1186/1423-0127-17-22 |
| [15] |
WU C, LIU Y, GU X, et al. LMO2 blocks the UBA6-USE1 interaction and downstream FAT10ylation by targeting the ubiquitin fold domain of UBA6[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2016, 478(3): 1442-1448. DOI:10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.143 |
| [16] |
YE X, WEINBERG RA. Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity: a central regulator of cancer progression[J]. Trends Cell Biol, 2015, 25(11): 675-686. DOI:10.1016/j.tcb.2015.07.012 |
| [17] |
ZHAO YY, MA J, FAN YL, et al. TGF-β transactivates EGFR and facilitates breast cancer migration and invasion through canonical Smad3 and ERK/Sp1 signaling pathways[J]. Mol Oncol, 2018, 12(3): 305-321. DOI:10.1002/1878-0261.12162 |
 2021, Vol. 50
2021, Vol. 50