文章信息
- 郝相楠, 李亚, 王冬冬, 栾军军, 周华
- HAO Xiangnan, LI Ya, WANG Dongdong, LUAN Junjun, ZHOU Hua
- 血浆纤维蛋白原水平在特发性膜性肾病中的临床意义
- Clinical significance of plasma fibrinogen level in idiopathic membranous nephropathy
- 中国医科大学学报, 2021, 50(11): 961-965
- Journal of China Medical University, 2021, 50(11): 961-965
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2021-01-26
- 网络出版时间:2021-11-03 14:08
2. 保定市第二中心医院肾内科, 河北 保定 072750;
3. 南京医科大学第四附属医院肾内科, 南京 210000
2. Department of Nephrology, Baoding second central hospital, Baoding 072750, China;
3. Department of Nephrology, The Fourth Affiliated Hospital of Nanjing Medical University, Nanjing 210000, China
膜性肾病(membranous nephropathy,MN)是肾病综合征常见的病理类型之一[1-2],病因未明者称为特发性膜性肾病(idiopathic membranous nephropathy,IMN),其病理改变主要发生于肾小球基底膜(glomerular basement membrane,GBM),光镜下表现为GBM早期可见空泡样改变,病变明显时弥漫增厚,钉突形成,免疫荧光下可见以IgG和C3为主的沿毛细血管壁的颗粒样沉积,电镜表现为GBM增厚、上皮细胞足突融合以及上皮下颗粒状电子致密物沉积[3-5]。IMN的发病机制复杂,病情隐匿,临床进展缓慢,病程长,迁延难愈易复发,对于IMN的治疗方案目前尚无统一定论[6]。免疫抑制治疗为主要治疗方案,包括应用糖皮质激素联合细胞毒药物或者采用其他免疫抑制剂治疗。研究[7-9]证明激素联合环磷酰胺治疗IMN安全有效。本研究回顾性分析了应用激素及环磷酰胺治疗IMN患者的临床疗效。肾病综合征引起的高凝、血栓形成及肾小球进行性硬化与血浆纤维蛋白原(fibrinogen,Fg)升高有关[10]。本研究还探讨了治疗前血浆Fg水平对IMN预后的预测作用,旨在为IMN的治疗提供指导。
1 材料与方法 1.1 研究对象选取2013年1月至2015年3月中国医科大学附属盛京医院肾内科病房住院确诊为IMN的137例患者。其中,男89例,女48例,年龄16~77岁,平均年龄为(49.20±1.17)岁,均应用以血管紧张素Ⅱ受体阻滞剂(angiotensin receptor blocker,ARB)为基础治疗,激素联合环磷酰胺的治疗方案。纳入标准:经肾活检及临床诊断为IMN的患者。排除标准:乙型肝炎病毒相关肾炎、糖尿病肾病(diabetic nephropathy,DN)、其他免疫相关肾炎;存在血栓的患者;单独应用雷公藤、来氟米特、他克莫司、吗替麦考酚酯等治疗的患者。
1.2 研究分组 1.2.1 随访9个月后分组按照2020年KDIGO指南,尿蛋白(urinary total protein,UTP)定量 < 0.3 g/24 h者定义为完全缓解(complete remission,CR);UTP定量0.3 g/24 h~3.5 g/24 h,或UTP比初始值至少减少50%,且 < 3.5 g/24 h者,定义为部分缓解(partial remission,PR);UTP定量降低 < 50%者定义为不缓解(no response,NR)[11]。
1.2.2 治疗前UTP定量分组< 3.5 g/24 h组,3.5 g/24 h~8.0 g/24 h组,> 8.0 g/24 h~ 12 g/24 h组和 > 12 g/24 h组[9, 12-14]。
1.2.3 治疗前血白蛋白水平分组< 20 g/L组,20 g/L~ 25 g/L组,> 25 g/L~ 30 g/L组和 > 30 g/L组[15]。
1.2.4 肾脏病理免疫荧光下有无纤维蛋白沉积(-)为无沉积组,(+)为有沉积组。
1.3 观察临床生化指标观察IMN患者治疗前、治疗后3、6、9、12、24个月24 h UTP定量、血白蛋白(serum albumin,sAlb)、甘油三酯(triglyceride,TG)、总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、低密度脂蛋白(low-density lipoprotein,LDL-C)、血钙(serum calcium,Ca)、25-羟维生素D3(25-hydroxyvitamin D3,25-OH-VitD3)、Fg(g/L)。随访患者于检测指标前1 d 22时之后禁食水,次日抽取血液进行检测,留取早6时至次日早6时的24 h尿液进行检测。
1.4 统计学分析采用Graphpad prism 8.0统计软件对数据进行分析,符合正态分布计量资料以x±s表示,多组间差异采用one way-ANOVA检验,相关性分析采用Pearson检验,受试者工作特征曲线,2组间差异采用独立样本t检验,P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 激素联合环磷酰胺治疗效果激素联合环磷酰胺治疗IMN临床有效,随访24个月后uTP水平明显降低(P < 0.01),sAlb水平显著升高(P < 0.01),血脂和Ca、25-OH-VitD3水平也得到纠正,Fg水平恢复到正常。见表 1。
| Item | Pre-treatment | 3 months | 6 months | 9 months | 12 months | 24 months | P |
| sAlb(g/L) | 22.25±0.44 | 28.01±0.54 | 31.80±0.80 | 34.35±0.78 | 35.36±0.9 | 35.48±1.47 | < 0.001 |
| 24 h UTP(g) | 7.08±0.29 | 5.38±0.53 | 2.89±0.31 | 2.50±0.42 | 1.29±0.24 | 2.14±0.77 | < 0.001 |
| TC(mmol/L) | 8.56±0.22 | 7.31±0.19 | 6.69±0.21 | 6.48±0.25 | 6.03±0.30 | 5.77±0.26 | < 0.001 |
| LDL(mmol/L) | 6.08±0.22 | 4.50±0.16 | 4.19±0.18 | 4.15±0.20 | 3.75±0.23 | 3.68±0.24 | < 0.001 |
| Ca(mmol/L) | 1.95±0.01 | 2.08±0.01 | 2.16±0.02 | 2.22±0.02 | 2.24±0.02 | 2.26±0.06 | < 0.001 |
| 25-OH-VitD(ng/mL) | 4.38±0.29 | 6.62±0.55 | 7.77±0.64 | 9.8±1.15 | 11.30±1.66 | - | < 0.001 |
| Fg(g/L) | 5.76±0.17 | 4.14±0.14 | 3.89±0.13 | 3.59±0.12 | 3.80±0.36 | - | < 0.001 |
2.2 治疗前Fg水平与临床活动指标的相关性
UTP为 < 3.5 g/d,3.5~8 g/d,> 8~12 g/d和 > 12 g/d时,Fg分别为(4.746±1.082)g/L,(5.593±2.488)g/L,(6.009±2.488)g/L和(7.295±2.578)g/L。治疗前Fg水平随着UTP增多而增高(P = 0.006)。sAlb为 < 20 g/L,20~25 g/L,> 25~30 g/L和 > 30 g/L时,Fg分别为(6.616±2.167)g/L,(5.780±1.771)g/L,(4.816±1.306)g/L和(4.135±0.922)g/L。Fg水平随着sAlb水平升高而降低(P < 0.000 1)。治疗前Fg与治疗前(r = 0.311 5,P = 0.001 2)及治疗后3个月(r = 0.271 1,P = 0.004 9)、6个月(r = 0.270 6,P = 0.009 9)、9个月(r = 0.359 3,P = 0.001 7)uTP定量呈正相关,与治疗前(r = -0.436,P < 0.000 1)及治疗后3个月(r = -0.239 6,P = 0.008 7)、6个月(r = -0.205 4,P = 0.048 3)、9个月(r = -0.230 9,P = 0.044 8)sAlb呈负相关;治疗前Fg与初治(r = 0.501 2,P < 0.000 1)、治疗后3个月(r = 0.312 5,P = 0.001 4)、6个月(r = 0.311 5,P = 0.003 1)TC及初治(r = 0.552 9,P < 0.000 1)、治疗后3个月(r = 0.314 3,P = 0.001 3)、6个月(r = 0.312 3,P = 0.001 3)LDL-C均呈正相关。由于随访到治疗后9个月、12个月时,患者失访 > 50 %,所以只分析了初治、治疗后3个月和6个月时的相关性。见图 1。
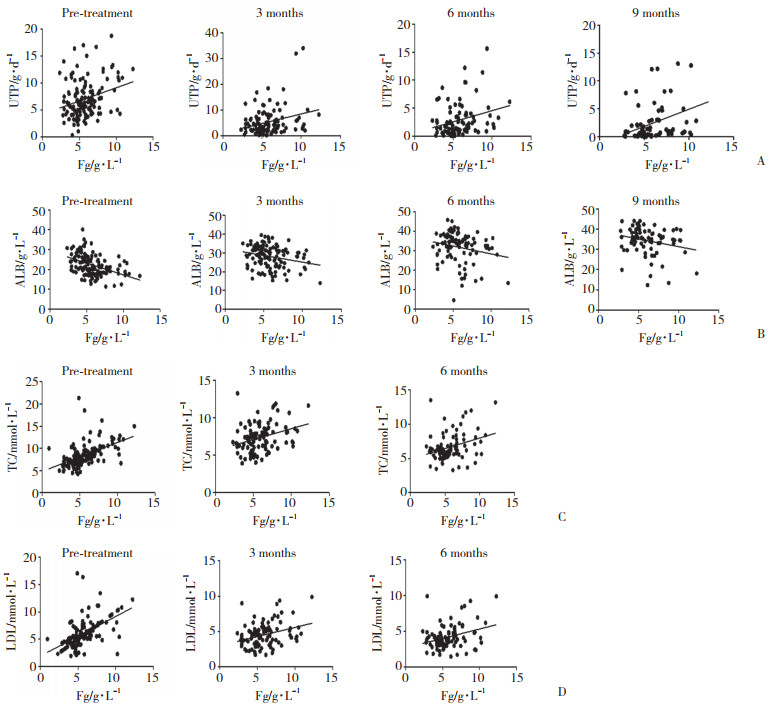
|
| A, pre-treatment Fg level was correlated with UTP; B, correlation between Fg and ALB levels before treatment and 3, 6, and 9 months after treatment; C, pre-treatment Fg level was correlated with TC level; D, correlation between Fg and LDL-C before treatment and 3 and 6 months after treatment. 图 1 治疗前Fg水平与临床活动指标的相关性 Fig.1 The correlation between Fg levels and clinical activity indicators before treatment |
2.3 治疗前Fg水平预测治疗9个月后临床疗效的准确性分析
随访9个月时,NR组与CR组初始Fg水平间有统计学差异(P = 0.018 98),曲线下面积为0.726 5,PR组与CR组初始Fg水平组间有统计学差异(P = 0.032 66),曲线下面积为0.680 1。在随访的77例患者中,治疗前Fg水平 > 9.4 g/L共9例,uTP为(7.178±3.339)g/L,ALB为(24.725±4.652)g/L,治疗灵敏度为100 %,治疗9个月后只有20 %达到CR;治疗前Fg水平 < 4.0 g/L共21例,治疗灵敏度为17.5 %,治疗9个月后有85 %会达到CR。
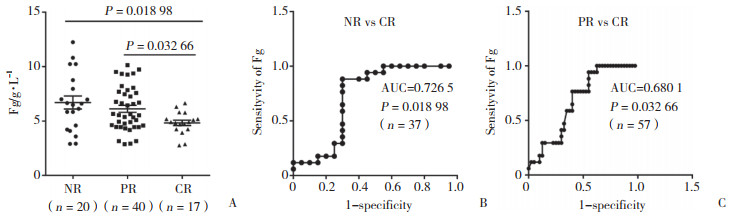
|
| A, distribution of Fg levels among the three prognostic groups; B, ROC curve analysis of the pre-treatment Fg levels in the NR and CR groups; C, ROC curve ana lysis of the pre treatment Fg levels in the PR and CR groups. 图 2 治疗前Fg水平预测治疗9个月后临床疗效 Fig.2 Pre-treatment Fg level as a predictor of efficacy of 9-month clinical treatment |
2.4 Fg与肾脏病理
在肾脏病理免疫荧光纤维蛋白有无沉积2组间Fg无统计学差异(P > 0.05),治疗前Fg水平高低与纤维蛋白有无沉积无相关性。见图 3。
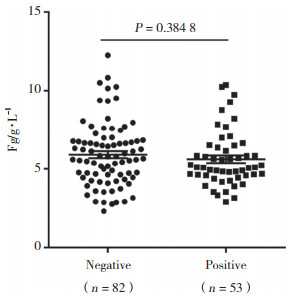
|
| 图 3 Fg与肾脏病理纤维蛋白沉积 Fig.3 Relationship between plasma Fg levels and renal pathological fibrin deposition |
3 讨论
我国IMN的检出率呈日益增高趋势[16],而其自然病程、预后及转归存在较大差异。目前,IMN的治疗中免疫抑制剂的应用国际上尚无统一标准,但已达成共识的是单独应用糖皮质激素治疗方案对临床缓解率及控制病情无效,应用激素联合细胞毒药物治疗或钙调蛋白拮抗剂治疗在缓解蛋白尿及保护肾功能方面有效,各中心仍在开展采用不同药物剂量和联合治疗方案临床试验[17]。本研究中,对我院诊断IMN的患者采用激素联合环磷酰胺治疗方案,从临床疗效看,随访2年时uTP水平明显降低,sAlb水平明显升高,Ca和25-OH-VitD3水平同样明显升高,TC和LDL-C水平明显降低,与其他临床研究结果一致。
肾病患者病理免疫荧光最常见的变化为纤维蛋白沉积于肾小球[18]。Fg由肝脏产生,是纤维蛋白的前体,在凝血的最后阶段起作用,也是决定血小板聚集性和血液黏度的重要因素之一。肾病综合征患者存在凝血及纤溶系统失衡,呈不同程度的高凝状态,容易导致血栓形成与血栓栓塞等并发症,由于肾小球局部凝血障碍及纤维素沉淀,促进肾小球进行性损伤,从而影响治疗效果和预后[19]。Fg参与肾脏纤维化的进展,在慢性肾功能不全患者中Fg水平增高,Fg水平较高与肾功能快速降低有关。Fg水平是慢性肾脏病(chronic kidney disease,CKD)3~4期、终末期肾病(end-stage renal disease,ESRD)患者全因死率的危险因素。IMN大多表现为肾病综合征。本研究结果显示,Fg水平与sAlb降低程度及uTP升高程度均有关,初始血浆Fg与初始、治疗后3个月、6个月、9个月uTP呈正相关,与sAlb呈负相关;与初始、治疗后3个月、6个月TC、LDL-C呈正相关。9个月uTP未缓解与部分缓解、未缓解与完全缓解患者治疗前Fg水平均有差异,受试者工作特征曲线下面积分别为0.680 1和0.726 5。治疗前Fg水平较高时治疗灵敏度高,CR率较低,治疗前Fg水平较低者CR率较高,但治疗灵敏度较低。在IMN病理免疫荧光中无论有无纤维蛋白沉积,初始Fg水平并无差异。有研究[10]表明,Fg水平与DN发展为ERSD的风险相关。本研究具有一定的局限性,首先由于本研究是回顾性研究设计,选择偏差不可避免,样本量较为有限,且随访时间较长,失访率略高,在进一步的研究中将加大研究样本量;其次,抗磷脂酶A2受体抗体(phospholipase A2 receptor antibody,PLA2Rab)为可高准确率确诊MN的指标[11],因收集标本时PLA2Rab尚未纳入医院检测指标中,故未有提及,下一步研究中将加入此指标。
综上所述,Fg可作为判断激素联合环磷酰胺治疗IMN的预后的良好指标。早期干预Fg的水平可能对改善IMN的预后大有益处。
| [1] |
ONWUZULIGBO O, HENDRICKS AR, HASSLER J, et al. Mercury intoxication as a rare cause of membranous nephropathy in a child[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2018, 72(4): 601-605. DOI:10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.05.013 |
| [2] |
YANG L, WU Y, LIN S, et al. sPLA2-IB and PLA2R mediate insufficient autophagy and contribute to podocyte injury in idiopathic membranous nephropathy by activation of the p38MAPK/mTOR/ULK1 ser757 signaling pathway[J]. Faseb J, 2021, 35(2): e21170. DOI:10.1096/fj.202001143r |
| [3] |
LIU W, GAO C, DAI H, et al. Immunological pathogenesis of membranous nephropathy: focus on PLA2R1 and its role[J]. Front Immunol, 2019, 10: 1809. DOI:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01809 |
| [4] |
WANG J, WANG M, CUI Z, et al. Epitope mapping of human α3(IV) NC1-induced membranous nephropathy in mice[J]. Am J Nephrol, 2020, 51(2): 99-107. DOI:10.1159/000505443 |
| [5] |
HUI M, UPPIN MS, PRAYAGA AK, et al. C4d immunohistochemistry in membranous nephropathy[J]. J Lab Physicians, 2014, 6(2): 76-79. DOI:10.4103/0974-2727.141500 |
| [6] |
ROJAS-RIVERA JE, CARRIAZO S, ORTIZ A. Treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults: kdigo 2012, cyclophosphamide and cyclosporine A are out, rituximab is the new normal[J]. Clin Kidney J, 2019, 12(5): 629-638. DOI:10.1093/ckj/sfz127 |
| [7] |
LIN W, LI HY, LIN S, et al. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus vs cyclophosphamide in the therapy of patients with idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a meta-analysis[J]. Drug Des Devel Ther, 2019, 13: 2179-2186. DOI:10.2147/dddt.s209211 |
| [8] |
LIU D, YANG Y, KUANG F, et al. Risk of infection with different immunosuppressive drugs combined with glucocorticoids for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy: a pairwise and network meta-analysis[J]. Int Immunopharmacol, 2019, 70: 354-361. DOI:10.1016/j.intimp.2019.03.002 |
| [9] |
KÖNIGSHAUSEN E, SELLIN L. Recent treatment advances and new trials in adult nephrotic syndrome[J]. Biomed Res Int, 2017, 2017: 7689254. DOI:10.1155/2017/7689254 |
| [10] |
ZHANG JL, WANG YT, ZHANG R, et al. Serum fibrinogen predicts diabetic ESRD in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J]. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 2018, 141: 1-9. DOI:10.1016/j.diabres.2018.04.025 |
| [11] |
NO A. KDIGO 2020 clinical practice guideline for diabetes management in chronic kidney disease[J]. KIDNEYS, 2020, 9(4): 221-233. DOI:10.22141/2307-1257.9.4.2020.218237 |
| [12] |
HAN WW, TANG LJ, KONG XL, et al. Clinical significance of autoantibodies in the assessment and treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2019, 17(3): 1825-1830. DOI:10.3892/etm.2018.7108 |
| [13] |
POLANCO N, GUTIÉRREZ E, COVARSÍ A, et al. Spontaneous remission of nephrotic syndrome in idiopathic membranous nephropathy[J]. J Am Soc Nephrol, 2010, 21(4): 697-704. DOI:10.1681/asn.2009080861 |
| [14] |
李敏侠, 邱强, 魏日胞, 等. 成人特发性膜性肾病的预后分析[J]. 军事医学, 2012, 36(5): 392-394. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-9960.2012.05.019 |
| [15] |
GUPTA K, ISKANDAR SS, DAEIHAGH P, et al. Distribution of pathologic findings in individuals with nephrotic proteinuria according to serum albumin[J]. Nephrol Dial Transplant, 2008, 23(5): 1595-1599. DOI:10.1093/ndt/gfm833 |
| [16] |
YANG Y, ZHANG Z, ZHUO L, et al. The spectrum of biopsy-proven glomerular disease in China: a systematic review[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2018, 131(6): 731-735. DOI:10.4103/0366-6999.226906 |
| [17] |
HOGAN J, MOHAN P, APPEL GB. Diagnostic tests and treatment options in glomerular disease: 2014 update[J]. Am J Kidney Dis, 2014, 63(4): 656-666. DOI:10.1053/j.ajkd.2013.09.019 |
| [18] |
KATAFUCHI R, NAGAE H, MASUTANI K, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the significance of immunofluorescent findings on clinicopathological features in IgA nephropathy[J]. Clin Exp Nephrol, 2019, 23(2): 169-181. DOI:10.1007/s10157-018-1619-6 |
| [19] |
HUANG MJ, WEI RB, WANG ZC, et al. Mechanisms of hypercoagulability in nephrotic syndrome associated with membranous nephropathy as assessed by thromboelastography[J]. Thromb Res, 2015, 136(3): 663-668. DOI:10.1016/j.thromres.2015.06.031 |
 2021, Vol. 50
2021, Vol. 50




