文章信息
- 陈颖, 于月新, 张倩, 张宁
- CHEN Ying, YU Yuexin, ZHANG Qian, ZHANG Ning
- 体外受精胚胎移植不同时点雌二醇水平及其日上升率与助孕结局的关系
- Relationship between the estradiol level and its daily change rate and pregnancy outcomes at different time points in in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer
- 中国医科大学学报, 2021, 50(10): 920-924
- Journal of China Medical University, 2021, 50(10): 920-924
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期:2020-12-07
- 网络出版时间:2021-09-29 19:29
2. 北部战区总医院生殖医学科, 沈阳 110015
2. Department of Reproductive Medicine, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110015, China
辅助生殖技术广泛用于临床,探索有效的医学指标来预测临床妊娠十分重要。目前,尚无研究分析取卵(oocyte pick-up,OPU)日和移植日血清雌二醇(estradiol,E2)上升幅度对体外受精胚胎移植术(in vitro fertilization and embryo transfer,IVF-ET)临床妊娠结局的影响。本研究通过回顾性分析,探讨新鲜胚胎移植周期不同时点的E2水平及其日上升率与助孕结局的关系,为临床预测助孕结局提供依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 研究对象和分组选取2018年1月至2019年12月在我院生殖医学科行IVF-ET新鲜胚胎移植患者的临床资料,共192个新鲜胚胎移植周期。根据IVF-ET的助孕结局,分为临床妊娠组(74个周期)和未妊娠组(118个周期)。本研究设计符合人体试验伦理学标准,通过北部战区总医院和平院区伦理委员会审批(批号:202H2019PJ005)。
纳入标准:(1)行新鲜胚胎移植周期者;(2)移植至少1枚形态学评分良好的D3胚胎者;(3)患者年龄 < 40岁,体质量指数(body mass index,BMI)18.5~25 kg/m2;(4)基础卵泡刺激素 < 10 IU/L者。排除标准:(1)夫妇任何一方存在染色体异常;(2)女性生殖道畸形或患有明确影响胚胎着床的疾病,如子宫内膜息肉,宫腔镜检查发现宫腔粘连,慢性子宫内膜炎等;(3)移植日或者OPU日E2水平下降者;(4)临床数据记录缺失者;(5)取消移植者,如预防卵巢过度刺激综合征,注射人绒毛膜促性腺激素(human chorionic gonadotropin,HCG)当日血清孕酮≥1 ng/mL,输卵管积水等。
1.2 临床指标收集患者的一般临床资料、获取卵泡情况、容受期子宫内膜参数和助孕结局等指标。
计算指标:(1)OPU日E2日上升率(%)=(OPU日E2水平-HCG日E2水平)/OPU日E2水平×100;(2)移植日E2日上升率(%)=(移植日E2水平-移植前1 d的E2水平)/移植日E2水平×100;(3)胚胎着床率(%)=(孕囊数/移植胚胎总数)×100;(4)临床妊娠率(%)=(临床妊娠周期数/移植周期数)×100。
OPU日和移植日E2日上升率中位数(范围)分别为16.12%(1.41%~72.95%)和41.23%(13.28%~ 67.13%)。根据OPU日和移植日E2日上升率各分为3层:OPU日E2日上升率 < 12%为A1组,12%~ < 24%为B1组,≥24%为C1组;移植日E2日上升率 < 30%为A2组,30%~ < 50%为B2组,≥50%为C2组。
1.3 统计学分析采用SPSS 22.0软件进行统计分析,计量资料以x±s表示,采用t检验进行比较。计数资料用率(%)表示,采用χ2检验进行比较。采用MedCalc软件绘制受试者操作特征(receiver operator characteristic,ROC)曲线。相关影响因素分析采用logistic回归分析。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果 2.1 不同妊娠结局患者临床资料的比较临床妊娠组和未妊娠组比较,患者年龄、BMI、基础卵泡刺激素、容受期子宫内膜厚度、促性腺激素用药总天数和总剂量、OPU日E2日上升率、获取卵泡数和成熟卵泡数、HCG日血清孕酮水平均无统计学差异(P > 0.05)。与未妊娠组相比,临床妊娠组患者的不孕年限时间更短,容受期子宫内膜内穿支血管数目增多,移植日E2日上升率幅度下降,HCG日、OPU日、移植前1 d和移植日E2水平升高(均P < 0.05)。见表 1。临床妊娠组和未妊娠组比较,患者受精方式、超促排卵方案和不孕因素均无统计学差异(P > 0.05)。见表 2。
| Item | No-pregnancy group(n = 118) | Clinical pregnancy group(n = 74) | P |
| Age(year) | 33.10±2.67 | 32.89±3.50 | 0.167 |
| BMI(kg/m2) | 24.55±3.22 | 24.23±3.18 | 0.509 |
| Infertility duration(year) | 5.04±2.88 | 4.14±2.28 | 0.024 |
| bFSH(10 IU/L) | 6.79±1.76 | 6.62±2.39 | 0.574 |
| Endometrial receptive period | |||
| Number of blood vessels | 7.81±1.19 | 8.16±1.12 | 0.040 |
| Endometrial thickness(cm) | 1.13±0.29 | 1.18±0.23 | 0.234 |
| Total time of Gn(d) | 10.50±3.30 | 11.39±3.06 | 0.063 |
| Total dose of Gn(U) | 2 674.19±1 327.88 | 2 776.01±897.64 | 0.562 |
| Daily increase rate of estradiol(%) | |||
| OPU day | 17.64±10.93 | 19.95±11.72 | 0.167 |
| Embryo transfer day | 42.07±16.45 | 37.58±11.98 | 0.033 |
| Total number of follicles | 6.16±3.92 | 6.82±3.83 | 0.251 |
| Number of mature follicles | 5.32±3.53 | 6.01±3.61 | 0.192 |
| Estradiol level(pg/mL) | |||
| HCG day | 1 234.21±561.76 | 1 557.78±470.8 | < 0.001 |
| OPU day | 1 461.21±730.71 | 1 935.85±563.17 | < 0.001 |
| Embryo transfer day | 794.40±549.78 | 1 157.20±529.01 | < 0.001 |
| 1 day before embryo transfer | 503.65±415.26 | 762.56±400.16 | < 0.001 |
| Progesterone level on HCG day(nmol/L) | 2.87±1.76 | 2.73±1.64 | 0.577 |
| bFSH,basal follicle-stimulating hormone;Gn,gonadotropin;OPU,oocyte pick-up. | |||
| Item | No-pregnancy group(n = 118) | Clinical pregnancy group(n = 74) | χ2 | P |
| Fertilization method | 1.503 | 0.472 | ||
| IVF | 94(79.66) | 64(86.49) | ||
| ICSI | 19(16.10) | 8(10.81) | ||
| IVF and ICSI | 5(4.24) | 2(2.70) | ||
| Controlled ovarian hyperstimulation | 2.156 | 0.142 | ||
| GnRH agonist long protocol | 81(68.64) | 58(78.38) | ||
| GnRH antagonist protocol | 37(31.36) | 16(21.62) | ||
| Infertility factor | 3.047 | 0.550 | ||
| Male factor | 6(5.08) | 4(5.41) | ||
| Pelvic or fallopian tube factor | 81(68.64) | 58(78.38) | ||
| Endometriosis | 13(11.02) | 4(5.41) | ||
| Reasons for both spouses | 12(10.17) | 6(8.11) | ||
| Unknown reason | 6(5.08) | 2(2.70) | ||
| IVF,in vitro fertilization;ICIS,intracytoplasmic sperm injection;GnRH,gonadotropin-releasing hormone. | ||||
2.2 E2水平及其日变化率预测临床妊娠的ROC曲线分析
对不同时点E2水平和临床妊娠进行ROC曲线分析(图 1),结果显示,HCG日曲线下面积(area under the curve,AUC)为0.661(95%CI:0.583~0.739,P < 0.05),OPU日AUC为0.671(95%CI:0.595~0.747,P < 0.05),移植前1 d AUC为0.721(95%CI:0.649~0.794,P < 0.05),移植日AUC为0.706(95%CI:0.632~0.780,P < 0.05)。结果表明,新鲜胚胎移植周期的HCG日、OPU日、移植前1 d和移植日E2均可以预测临床妊娠(P < 0.05)。
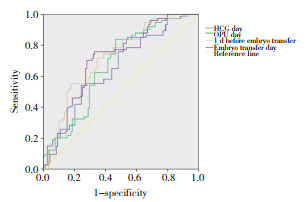
|
| 图 1 E2水平和临床妊娠的ROC曲线 Fig.1 ROC curve of the estradiol level and clinical pregnancy |
对不同时点E2日上升率和临床妊娠进行ROC曲线分析,结果显示,OPU日AUC为0.573(95%CI:0.494~0.653,P > 0.05),移植日AUC为0.437(95%CI:0.358~0.515,P > 0.05)。结果表明,新鲜胚胎移植周期OPU日和移植日E2日上升率不能预测临床妊娠。
2.3 临床妊娠影响因素的logistic回归分析将OPU日和移植日E2日上升率进行分层后,同年龄、BMI、不孕年限作为协变量,助孕结局情况作为因变量(1=临床妊娠,0=未妊娠),校正其他基本资料的影响并构建多元回归模型。结果表明,年龄与临床妊娠相关(P < 0.05),BMI和不孕年限与临床妊娠无关(P > 0.05)。将A1组作为参照,B1组临床妊娠率是A1组的6.70倍(P < 0.05),C1组是A1组的1.36倍(P > 0.05);将A2组作为参照,B2组临床妊娠率是A2组的0.28倍(P > 0.05),C2组是A2组的0.31倍(P < 0.05)。结果表明,OPU日E2日上升率在12%~ < 24%时临床妊娠率最高(P < 0.05),移植日E2日上升率≥50%时临床妊娠率最低(P < 0.05)。见表 3。
| Variable | β | P | OR | 95% CI |
| Stratification based on the daily increase rate of estradiol on the OPU day | ||||
| Age | -0.18 | 0.00 | 0.83 | 0.75-0.94 |
| BMI | 0.01 | 0.89 | 1.01 | 0.91-1.12 |
| Infertility duration | -0.10 | 0.16 | 0.90 | 0.77-1.04 |
| Daily increase rate of estradiol on the OPU day | ||||
| A1(< 12%) | - | |||
| B1(12%- < 24%) | 1.90 | 0.00 | 6.70 | 2.93-5.29 |
| C1(≥24%) | 0.30 | 0.50 | 1.36 | 0.56-3.31 |
| Stratification based on the daily increase rate of estradiol on the embryo transfer day | ||||
| Age | -0.18 | 0.00 | 0.83 | 0.75-0.93 |
| BMI | -0.03 | 0.52 | 0.97 | 0.88-1.07 |
| Infertility duration | 0.82 | 0.21 | 0.92 | 0.81-1.05 |
| Daily increase rate of estradiol on the transplant day | ||||
| A2(< 30%) | - | |||
| B2(30%- < 50%) | -0.54 | 0.15 | 0.28 | 0.28-1.22 |
| C2(≥50%) | -1.17 | 0.01 | 0.31 | 0.14-0.71 |
| -,for reference. | ||||
3 讨论
E2水平对于女性生殖系统至关重要,增生期参与卵泡的发育和成熟,分泌期参与胚胎植入和着床[1-2]。子宫内膜种植窗期外周血E2水平过高会导致种植窗开放缩短[3-4],高水平E2明显影响子宫内膜的胞饮突形成数量[5],而胚胎通常种植在子宫内膜胞饮突大量表达的区域,缺乏胞饮突作用会导致胚胎着床失败。在新鲜胚胎移植周期中,E2水平与临床妊娠的关系十分密切。以往的研究多是对于IVF-ET周期中HCG日或移植日E2水平进行分析[6-9]。本研究对新鲜胚胎移植周期中多个时点E2水平及其日上升率与临床妊娠的关系进行分析。
本研究结果提示,HCG日、OPU日和移植日E2水平可以预判新鲜胚胎移植的妊娠结局。与未妊娠组相比,临床妊娠组HCG日、OPU日和移植日E2水平升高。低水平E2可能影响子宫内膜腺体的发育和成熟,最终降低临床妊娠率。新鲜胚胎移植周期中,影响子宫内膜容受性良好状态的E2水平范围有待进一步研究。
本研究进一步将OPU日和移植日E2日上升率进行分层,进行logistic回归分析。结果显示,OPU日E2日上升率12%~ < 24%时临床妊娠率最高,移植日E2日上升率 < 30%时临床妊娠率最高。提示OPU日E2日上升率在适合范围内可以获得良好的临床妊娠,同时移植日E2日上升率过高可能降低临床妊娠率。这可能是增生期E2水平上升速度加快,影响子宫内膜腺体发育加速,影响子宫内膜容受性,进一步影响胚胎种植。目前研究[10]已证实,孕酮刺激胞饮突的出现和成熟,E2导致其萎缩和限制其发育。增生期E2水平上升速度加快,可能限制子宫内膜胞饮突的数量,影响胚胎着床。E2日变化率对胚胎着床和持续妊娠的影响有待进一步研究。此外,IVF-ET后通过E2水平评估助孕结局,越来越受到国内外学者的重视[11-12]。
综上所述,在IVF-ET新鲜胚胎移植周期中,不同时点的E2水平可以预判新鲜胚胎移植的妊娠结局。虽然在新鲜胚胎移植周期中E2日变化率不能够预测助孕结局,但是在适宜的上升幅度内将会有良好的助孕结局。未来需要进行大样本和前瞻性随机对照研究明确本研究结果,以进一步探索高效评估助孕结局的指标。
| [1] |
刘曼曼, 刘艳丽, 管一春, 等. 早卵泡期长方案控制性促排卵E2水平下降对IVF-ET助孕结局的影响[J]. 中国计划生育学杂志, 2019, 27(5): 636-639. |
| [2] |
ULLAH K, RAHMAN TU, PAN HT, et al. Serum estradiol levels in controlled ovarian stimulation directly affect the endometrium[J]. J Mol Endocrinol, 2017, 59(2): 105-119. DOI:10.1530/JME-17-0036 |
| [3] |
MOBERG C, BOURLEV V, ILYASOVA N, et al. Endometrial expression of LIF and its receptor and peritoneal fluid levels of IL-1α and IL-6 in women with endometriosis are associated with the probability of pregnancy[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2015, 292(2): 429-437. DOI:10.1007/s00404-015-3626-0 |
| [4] |
KOBAYASHI R, TERAKAWA J, OMATSU T, et al. The window of implantation is closed by estrogen via insulin-like growth factor 1 pathway[J]. J Reprod Infertil, 2017, 18(2): 231-241. |
| [5] |
CAI H, LI H, HE YL. Interceed and estrogen reduce uterine adhesions and fibrosis and improve endometrial receptivity in a rabbit model of intrauterine adhesions[J]. Reprod Sci, 2016, 23(9): 1208-1216. DOI:10.1177/1933719116632923 |
| [6] |
黄帅, 张亚男, 李佳阳, 等. 雌激素及雌激素日变化值对妊娠结局的预测研究[J]. 中华妇产科杂志, 2020, 55(1): 49-50. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0529-567X.2020.01.009 |
| [7] |
连方, 郑玫, 孙振高. 超促排卵周期HCG日与取卵日雌激素水平与妊娠的相关性研究[J]. 现代妇产科进展, 2013, 22(8): 641-643. DOI:10.13283/j.cnki.xdfckjz.2013.08.013 |
| [8] |
王柏菊. 促排卵早期血清雌激素水平的临床意义[J]. 中国城乡企业卫生, 2018, 33(3): 73-75. DOI:10.16286/j.1003-5052.2018.03.028 |
| [9] |
严思思, 丁锦丽, 张怡, 等. 三种不同促排卵方案HCG日雌二醇水平和获卵数与妊娠结局的相关性分析[J]. 生殖医学杂志, 2020, 29(2): 169-175. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-3845.2020.02.005 |
| [10] |
刘琴, 李佩玲, 刘梅梅. 胞饮突的相关研究进展[J]. 中国优生与遗传杂志, 2012, 20(1): 3-4. DOI:10.13404/j.cnki.cjbhh.2012.01.039 |
| [11] |
叶菁华, 陈以勒, 叶亦巍, 等. 妊娠早期雌二醇监测对妊娠结局预测价值的探讨[J]. 实用预防医学, 2019, 26(2): 170-172. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-3110.2019.02.012 |
| [12] |
MORALOĞLU Ö, TONGUC EA, ÖZEL M, et al. The effects of peak and mid-luteal estradiol levels on in vitro fertilization outcome[J]. Arch Gynecol Obstet, 2012, 285(3): 857-862. DOI:10.1007/s00404-011-2090-8 |
 2021, Vol. 50
2021, Vol. 50




