2. 中国海洋大学海洋环境与生态教育部重点实验室,山东 青岛 266100
水质基准是制定水质标准的基础,是进行环境质量评价、环境风险评估、环境损害鉴定和应急事故管理的重要参考依据。自上世纪60年代起,美国、欧盟、加拿大、荷兰等国家在水质基准方面已经开展了大量研究,建立了较为完善的淡水、海水水质基准技术体系,并颁布了一批典型污染物的水质基准值。中国水质基准研究起步较晚,直到本世纪初,我国的水质基准研究基本以零散的技术探讨为主。2017年环保部才颁布了符合我国水体区系和生态系统特征的《淡水水生生物水质基准制定技术指南》(HJ 831—2017)、《湖泊营养物基准制定技术指南》(HJ 838—2017)和《人体健康水质基准制定技术指南》(HJ 837—2017),旨在保护淡水生物、生态和人体健康。而对于海水水质基准,我国尚缺乏系统性研究。目前,仅有少数学者借鉴国外的方法理论,结合我国海洋生物毒理数据对我国海水水质基准的构建进行了探讨,并推导了一些营养盐[1]、重金属[2]、有机物[3]等典型污染物的海水水质基准值。目前,推导水质基准的主流方法是物种敏感度分布法(Species Sensitivity Distribution,SSD),推导的基准值往往以双值(长期水质基准和短期水质基准)表示,以期在污染物长期或短期暴露情况下对生物及其生态功能给予恰当的保护。
汞是一种全球性污染物,其天然来源主要有火山喷发、地质沉积、森林火灾等,人为来源主要有石化、金属冶炼、燃煤发电、氯碱、水泥、PVC、医疗等涉汞行业废水废气的排放。汞可以通过海气交换以及入海河流进入海洋中,其中大气干、湿沉降占据了海洋汞输入的70%以上[4]。汞在海洋中主要有四种存在形态:溶解态或颗粒态的Hg2+、溶解态Hg0、溶解态或颗粒态甲基汞(CH3Hg+)、溶解态二甲基汞((CH3)2Hg),其中Hg2+可以在硫酸盐还原菌等微生物的作用下转化为毒性更强的甲基汞[5]。在淡水中甲基汞光解速率很快,但Zhang等[6]的研究表明,作为海洋中甲基汞主要存在形式的氯化甲基汞则难以光解,因此汞在海洋中的危害更大。在我国,由于涉汞行业污染物的排放,每年会有大量的汞进入海洋。根据国家海洋局《中国海洋环境质量状况公报2016》,2016年我国主要入海河流中汞的排海量为39 t,是我国近岸海域中主要的重金属类污染物。研究表明,低浓度的汞即可对海洋生物的生长、发育、繁殖等产生不利影响,而且其残留时间长,容易通过食物链在生物体内富集,富集系数可高达4.6×105[7]。因此,中国、美国、欧盟等国家已将汞列为优先控制污染物。2013年,联合国环境规划署通过了由128个国家签署的《关于汞的水俣公约》,旨在控制和减少全球汞的排放。
目前,美国、加拿大等国家已经颁布了汞的淡水和海水基准值。但在中国仅有汞淡水基准的研究,对于汞海水基准的研究尚未见报道[8]。本研究以汞对我国海洋生物的毒性数据为基础,采用SSD法对海水中汞的水质基准进行探讨。在此基础上利用商值法对我国近海环境中的汞进行初步生态风险评价。研究结果可为我国海洋环境质量评价、生态风险评估及海水水质标准的修订提供参考。
1 材料与方法 1.1 毒性数据的搜集与筛选本文搜集和筛选的海洋生物毒性数据主要来源于中国知网(http://www.cnki.net/)、美国环保署ECOTOX毒性数据库(http://cfpub.epa.gov/ecotox/)和其他公开发表的相关文献。为保证推导出的水质基准值更符合我国海洋水体区系特征和生态系统特征,本文所选用的物种皆在我国沿海地区广泛分布。本文所选用的毒性数据来自于Hg2+的毒性试验,使用的汞化合物主要为氯化汞(HgCl2)、醋酸汞(Hg(CH2COOH)2)、硫酸汞(HgSO4)和硝酸汞(Hg(NO3)2)。
本文中毒性数据的筛选原则为:急性毒性数据采用暴露时间不大于96 h且毒性效应终点为死亡、生长、发育和繁殖的LC50或EC50(半数致死浓度或半数效应浓度);慢性毒性数据选择暴露时间≥14 d且毒性效应终点为生长、发育和繁殖的NOEC(无观察效应浓度)或LOEC(最低可观察效应浓度),若同一物种有多个毒性数据,则采用暴露时间最长者。若同一物种、毒性终点和暴露时间有多个毒理数据,则采用这些数据的几何平均值。同一物种同一毒性终点的毒理数据间若相差10倍以上,则剔除离群值。
1.2 SSD曲线的拟合以及海水水质基准的推导目前,用于拟合SSD曲线的模型众多(如Log-normal、Log-logistic、BurrⅢ等),但Wheer等[9]研究表明,没有任何一个模型适用于所有物质的毒性数据拟合,我国学者在研究不同化学物质的水质基准时采用的模型也不尽相同。本文利用由中国环境科学研究院推出的用于淡水水生生物水质基准的模型预测软件China-WQC V1.0对所搜集筛选的毒性数据进行处理。该软件内置Normal、Log-normal、Logistic、Log-logistic和Extreme value五种模型,用于拟合污染物毒性数据的概率分布。该软件以化学物质毒性浓度的对数值为X轴,累积概率为Y轴绘制SSD曲线,并计算出累积概率5%条件下的污染物危害浓度(Hazardous Concentration, HC5),输出检验模型拟合优度的参数:决定系数(R2)、均方根(RMSE)、残差平方和(SSE)、K-S检验值。其中R2越接近1,模型拟合优度越高;RMSE越接近0,模型拟合精确度越高;SSE越接近0,模型拟合的随机误差效应越低;当K-S检验P>0.05时,表明模型符合理论分布。最终,依据毒性数据的HC5值进行水质基准值的计算。短期水质基准(Short-term Water Quality Criteria, SWQC)和长期水质基准(Long-term Water Quality Criteria, LWQC)的计算公式分别为:
| $ SWQC = H{C_{{\rm{5}}急性}}~~~/AF, $ | (1) |
| $ LWQC = H{C_{{\rm{5慢性}}}}~~~/AF。$ | (2) |
式中AF为评价因子,通常取值范围为2~5。当有效数据量大于15并涵盖足够的营养级(至少涵盖水生植物、无脊椎动物、脊椎动物三个营养级)时,AF取2。由于慢性毒性实验方法、条件等的限制,在水质基准推导过程中常存在慢性毒性数据不足的情况,对此US EPA提出用急慢性比率法(Acute to Chronic Ratio, ACR)来推导长期基准,计算公式为:
| $ LWQC = SWQC/FACR。$ | (3) |
式中FACR为最终急慢性比率(Final Acute to Chronic Ratio,FACR),是所有物种ACR的几何平均值。
1.3 生态风险评估本文采用商值法(Risk Quotient,RQ)对我国近海典型水体中汞的生态风险进行初步表征。急性风险商以环境暴露浓度的最大值与短期基准值的商表示,慢性风险商以环境暴露浓度的平均值与长期基准值的商表示。风险等级判断标准为:RQ<0.1,水体存在低生态风险;1≥RQ≥0.1,水体存在中等生态风险;RQ>1,水体存在高生态风险,风险程度随RQ值的增加而增加[3]。
2 结果与讨论 2.1 毒性数据本文搜集筛选的汞的急性毒性数据涵盖了藻类、环节、棘皮、脊索、节肢、腔肠、软体、星虫、螠虫等13门52科74种海水生物(见表 1)。其中主要为软体动物,占总物种数的31.1%;其次为节肢动物、脊椎动物、藻类等,分别占总物种数的23.0%、17.6%、14.9%。从单一物种敏感性来看,最敏感的为诸氏鲻虾虎鱼(Mugilogobius chulae),96 h LC50为1.30 μg·L-1,最不敏感的为斧文蛤(Meretrix lamarckii),96 h LC50为12 027 μg·L-1。
|
|
表 1 汞对海水生物的急性毒性数据 Table 1 Acute toxicity of mercury to marine species |
本研究运用China-WQC V1.0对不同类别生物的毒性数据分别进行了拟合(由于部分门类生物毒性数据量较少无法进行拟合,故暂不讨论),根据最优模型拟合结果藻类、脊椎动物、软体动物和节肢动物的HC5分别为5.781、3.443、3.483和3.350 μg·L-1。对比可知,节肢动物对汞最为敏感,藻类最不敏感。这一方面可能是因为用作毒性实验的节肢动物多处于生命早期阶段,对毒物比较敏感,得出的LC50或EC50偏小;另一方面可能是因为节肢动物中尤其是浮游甲壳类所处营养级较低,相对于鱼类、贝类等高营养级生物,解毒机制不够完善。有研究表明,鱼类体内可能存在某种修复机制能够恢复Hg2+引起的组织损伤,因此对Hg2+具有较大的耐受性,但甲壳类未见类似报道[8]。
本文运用China-WQC V1.0对所搜集筛选的所有急性毒性数据进行处理,并构建SSD曲线。通过对比表 3中数据可知,用Normal模型拟合急性毒性数据得到的R2最大,均方根和残差平方和最小,K-S检验结果大于0.05,故Normal模型为最优拟合模型。图 1为应用Normal模型所构建的SSD曲线。由表 1、3可知,所有物种的急性HC5为3.318 9 μg·L-1,且急性毒性数据大于15个并涵盖了足够的营养级,故AF取2,则短期水质基准值为1.659 μg·L-1。由于符合要求的慢性毒性数据不足,本文采用US EPA推荐的ACR法进行长期水质基准的推导。由表 2知FACR为3.831,则长期水质基准值为0.433 μg·L-1。
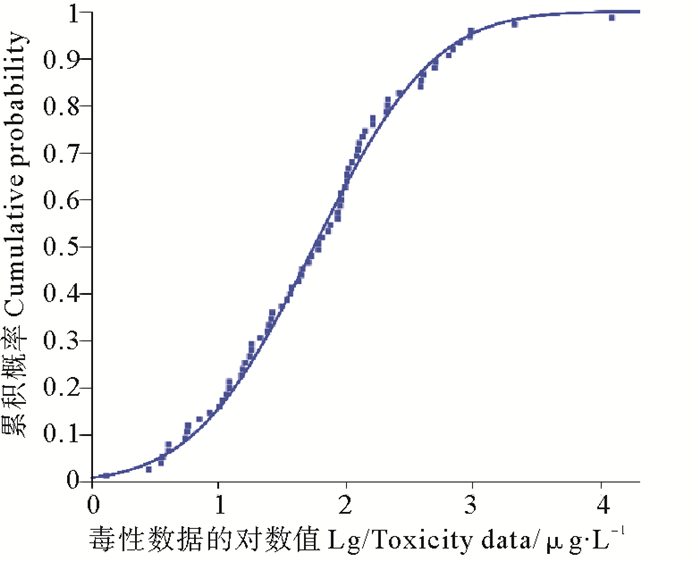
|
图 1 汞对海洋生物急性毒性的物种敏感度分布曲线 Fig. 1 The acute toxicity species sensitivity distribution curve of mercury to marine organisms |
|
|
表 2 用于推导汞急慢性毒性比(ACR)的毒性数据 Table 2 All the toxicity data for deriving the acute to chronic ratio of mercury |
|
|
表 3 汞急性毒性数据的不同分布模型拟合结果 Table 3 Fitting results of acute toxicity data of mercury by different distribution models |
本文基准值是以Hg2+的毒性数据为基础得出,但汞在水体中形态多样,毒性也存在差异,尤其是有机态的甲基汞毒性较强。如果水中汞的主要形态是甲基汞,则本基准值能否为生物提供足够的保护有待进一步探讨。故将本研究推导的基准值与已报道的不同形态汞的急、慢性毒性数据进行对比,以验证本基准的适用性。根据文献报道,当暴露于甲基汞时,美丽羽枝藻(Plumaria elegans)的18 h LC50为44 μg·L-1[73],岩虾(Palaemon elegans)96 h LC50为31 μg·L-1[74],草虾(Palaemonetes vulgaris)24 h LC50为125 μg·L-1[75],4-8细胞阶段的底鳉胚胎(Fundulus heteroclitus)48 h LC50为50 μg·L-1[76],这些急性毒性值皆高于短期基准值;草虾(Palaemonetes pugio)幼体21 d LOEC为12.5 μg·L-1[77],高于短期基准值。因此,本文推导的基准值对于以甲基汞为主的水体中的生物也能提供一定的保护。当暴露于Hg2+中时,草虾(Palaemonetes pugio)的21 d LOEC为10 μg·L-1[78];黑点青鳉(Oryzias melastigma)胚胎的14 d LOEC为24 μg·L-1[26],慢性毒性值皆高于长期基准值。故综上所述,本研究所得的基准值能够保护我国大部分海水生物免受突发性污染事件中汞的短期暴露以及低浓度长期暴露产生的不可接受的影响。
此外,Branco等[79]发现硒能够通过恢复生物体内被汞抑制的重要酶的活性,如硫氧还原蛋白酶和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶等,从而降低汞的毒性;Denton等[45]研究显示,在相同温度下汞对墨吉对虾(Penaeus merguiensis)的毒性随温度的增加而增加;Chin等[49]研究表明,在相同温度下盐度的增加会使汞对丽文蛤(Meretrix lusoria)的毒性增强,这在一程度上表明汞的毒性会受到温度、盐度和硒含量等因素的影响。但是,目前尚缺乏足够的数据来建立这些因素和汞基准值之间的定量关系,故本研究暂未考虑其对汞基准值的影响。
如表 4所示,与美国汞基准(基于Hg2+)相比,本研究中的短期基准值略低于美国;慢性基准值明显低于美国。笔者认为产生这种差异的原因可能有以下三个方面:(1)在推导慢性基准值时,美国采用的也是ACR法,但缺乏鱼类数据;(2)中国和美国推导基准时所采用的物种不同,而这些物种由于生理构造、生活环境、地理分布等的不同对同一化学物质的敏感性存在一定差异;(3)美国推导基准时未采用藻类数据[80]。由本文搜集到的数据显示,一些藻类对汞也具有较高的敏感性,且藻类是海洋中重要的初级生产者,藻类数据的缺乏可能会对最终基准值产生一定影响。与加拿大的基准值相比,本研究的结果明显较高,这是因为加拿大采取的是评价因子法,以所有毒性数据中最敏感的一种藻类(Emiliania huxleyi)的LOAEL(Lowest Observed Adverse Effect Level)与安全系数10的商作为最终基准值,产生过保护的可能性较大[81]。本文所得海水基准值较张瑞卿等[8]推导的无机汞淡水基准值低,这在一定程度上表明,海洋生物对汞比淡水生物更为敏感,为充分保护海洋生物,制定相应的海水基准十分必要。此外,本文推导的慢性基准值低于我国渔业水质标准和四类海水水质标准,高于一、二、三类海水水质标准,可见借鉴国外水质标准所制定的海水水质标准,并不完全符合我国国情,存在过保护现象,需要进一步修订。
|
|
表 4 不同国家汞水质基准及标准值 Table 4 The water quality criteria or standards of mercury in different countries |
本文从已公开发表的文献中搜集了27个中国沿海典型水体(河口、海湾、近海养殖区、码头等)中汞的环境暴露数据[84-105],站点分布覆盖了我国大部分近岸海域,可在一定程度上代表我国沿海水体中汞的整体分布情况。汞的浓度范围从低于检测限至4.33 μg·L-1,平均值为0.146 μg·L-1,其中以珠江口红树林湿地海水中的汞浓度最高为4.33 μg/L。如图 2所示,在研究区域内,水体的急性风险商的范围为0.010~2.61,平均值为0.171;慢性风险商的范围为0.032~5.35,平均值为0.337。存在急性高风险的水体占所有研究水体的3.70%,急性中度风险的水体占18.5%,急性低风险的水体占77.8%;存在慢性高风险的水体占3.70%,慢性中度风险的水体占55.6%,慢性低风险的水体占40.7%。在所有调查水体中,仅珠江口红树林湿地海水存在急、慢性高生态风险。据徐颂军等[90]调查研究,珠江口红树林保护区的周围存在餐饮业、以养殖生蚝和鱼虾为主的养殖业以及密集生活区等,它们所产生的废水和污水经过各种明渠暗渠排放到湿地内,这可能是导致红树林湿地海水汞污染严重,存在高生态风险的主要原因。其他水体皆处于不同程度的中度风险状态或低风险状态。处于中度风险状态的水体对生物具有潜在的危害,其生态风险需进一步关注。从保护海洋水生生物的角度出发,如果不发生泄漏事故或者有集中排放的情况,整体上我国近海汞的生态风险相对较低。
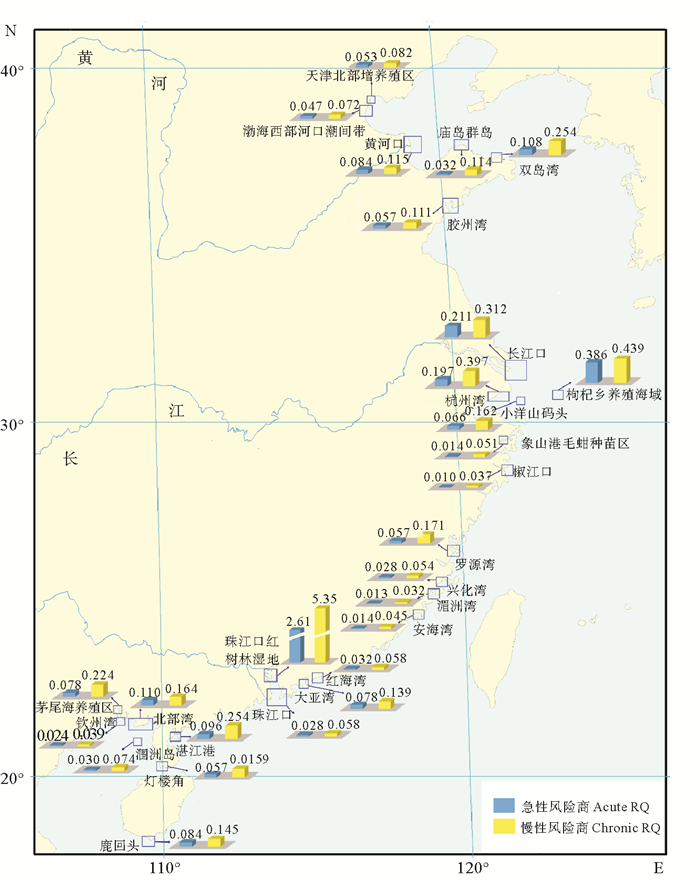
|
图 2 中国近海水体汞的生态风险商值分布 Fig. 2 Risk quotient values of mercury in coastal waters of China |
(1) 在本研究所搜集的毒性数据范围内,中国海洋生物对汞的敏感性为:节肢动物>脊椎动物>软体动物>藻类。
(2) 本研究以物种敏感度分布法为基础,采用Normal、Log-normal、Logistic、Log-logistic和Extreme value五种模型对汞的急性毒性数据进行拟合,其中Normal模型拟合效果最佳,在此基础上得到我国汞的长期和短期海水水质基准值分别为0.433和1.659 μg·L-1。
(3) 本研究根据推导出的基准值,采用商值法对中国近海水环境中汞的生态风险进行了初步评估。结果显示,整体上中国近海环境中汞的生态风险相对较低。但个别海域,如珠江口红树林湿地,处于较高风险水平,应引起相关部门的重视。
| [1] |
郑磊, 张娟, 闫振广, 等. 我国氨氮海水质量基准的探讨[J]. 海洋学报, 2016(4): 109-119. Zheng L, Zhang J, Yan Z G, et al. Development of seawater aquatic life criteria for ammonia in China[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinia, 2016(4): 109-119. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2016.04.010 (  0) 0) |
| [2] |
穆景利, 王莹, 张志锋, 等. 我国近海镉的水质基准及生态风险研究[J]. 海洋学报, 2013, 35(3): 137-146. Mu J L, Wang Y, Zhang Z F, et al. Marine water quality criteria for cadmium with a view to protecting aquatic life in China and ecological risk assessment[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinia, 2013, 35(3): 137-146. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0253-4193.2013.03.016 (  0) 0) |
| [3] |
张京京, 管博, 范家诚, 等. 中国近海环境中三丁基锡水质基准推导与生态风险初步评价[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 47(1): 32-42. Zhang J J, Guan B, Fan J C, et al. Derivation of marine water quality criteria and preliminary ecological risk assessment for tributyltin in coastal waters of China[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(1): 32-42. (  0) 0) |
| [4] |
Mason R P, Hammerschmidt C R, Lamborg C H, et al. The air-sea exchange of mercury in the low latitude Pacific and Atlantic[J]. Deep Sea Research Part Ⅰ: Oceanographic Research Papers, 2017, 122: 17-28. DOI:10.1016/j.dsr.2017.01.015
(  0) 0) |
| [5] |
Lamborg C H, Yiiterhan O, Fitzgerald W F, et al. Vertical distribution of mercury species at two sites in the western Black Sea[J]. Marine Chemistry, 2008, 111(1-2): 77-89. DOI:10.1016/j.marchem.2007.01.011
(  0) 0) |
| [6] |
Zhang T, Hsu-Kim H. Photolytic degradation of methylmercury enhanced by binding to natural organic ligands[J]. Nature Geoscience, 2010, 3(7): 473-476. DOI:10.1038/ngeo892
(  0) 0) |
| [7] |
Hirota R, Asada J, Tajima S, et al. Accumulation of mercury by the marine copepod Acartia clausi[J]. Bulletin of the Japanese Society of Scientific Fisheries, 1983, 49(8): 1249-1251. DOI:10.2331/suisan.49.1249
(  0) 0) |
| [8] |
张瑞卿, 吴丰昌, 李会仙, 等. 应用物种敏感度分布法研究中国无机汞的水生生物水质基准[J]. 环境科学学报, 2012, 32(2): 440-449. Zhang R Q, Wu F C, Li H X, et al. Deriving aquatic water quality criteria for inorganic mercury in China by species sensitivity distributions[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2012, 32(2): 440-449. (  0) 0) |
| [9] |
Wheer J R, Grist E P M. Species sensitivity distributions: Data and model choice[J]. Marine Pollution Bulletin, 2002, 45(1): 192-202.
(  0) 0) |
| [10] |
战玉杰, 杨茹君, 王修林, 等. Hg(Ⅱ)和Pb(Ⅱ)对海洋单细胞藻的急性毒性效应[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2011, 6(5): 523-531. Zhan Y J, Yang J R, Wang X L, et al. Acute toxic effect of Hg(Ⅱ) and Pb(Ⅱ) on marine unicellular algae[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2011, 6(5): 523-531. (  0) 0) |
| [11] |
欧泽奎, 刘东超, 谢恩义, 等. 海水环境中Hg2+、Cd2+、Pb2+对张氏马尾藻幼孢子体的生物毒性研究[J]. 南方水产科学, 2016, 12(5): 43-52. Ou Z K, Liu D C, Xie E Y, et al. Biotoxicity of Hg2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ in germlings of Sargassum zhangii Tseng et Lu in seawater[J]. South China Fisheries Science, 2016, 12(5): 43-52. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.2095-0780.2016.05.006 (  0) 0) |
| [12] |
Okamoto O K, Shao L, Hastings J W, Colepicolo P. Acute and chronic effects of toxic metals on viability, encystment and bioluminescence in the dinoflagellate Gonyaulax polyedra[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Pharmacology, Toxicology and Endocrinology, 1999, 123(1): 75-83. DOI:10.1016/S0742-8413(99)00013-4
(  0) 0) |
| [13] |
Han Y S, Kumar A S, Han T. Comparison of metal toxicity bioassays based on inhibition of sporulation and spore release in Ulva pertusa[J]. Toxicology and Environmental Health Sciences, 2009, 1(1): 24-31. DOI:10.1007/BF03216460
(  0) 0) |
| [14] |
Reish D J, Martin J M, Piltz F M, et al. The effect of heavy metals on laboratory populations of two polychaetes with comparisons to the water quality conditions and standards in southern California marine waters[J]. Water Research, 1976, 10: 299-302. DOI:10.1016/0043-1354(76)90170-6
(  0) 0) |
| [15] |
Reish D J. The effects of heavy metals on polychaetous annelids[J]. Rev Int Oceanogr Med, 1978, 49(3): 99-104.
(  0) 0) |
| [16] |
Reish D J, Lemay J A. Toxicity and bioconcentration of metals and organic compounds by polychaeta[J]. Ophelia, 1991, 5: 653-660.
(  0) 0) |
| [17] |
Gopalakrishnan S, Thilagam H, Raja P V. Comparison of heavy metal toxicity in life stages (spermiotoxicity, egg toxicity, embryotoxicity and larval toxicity) of Hydroides elegans[J]. Chemosphere, 2008, 71(3): 515-528. DOI:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2007.09.062
(  0) 0) |
| [18] |
Sadripour E, Mortazavi M S, Shahri N M. Effects of mercury on embryonic development and larval growth of the sea urchin Echinometra mathaei from the Persian Gulf[J]. Iranian Journal of Fisheries Sciences, 2013, 12(4): 898-907.
(  0) 0) |
| [19] |
秦华伟, 刘爱英, 谷伟丽, 等. 6种重金属对3种海水养殖生物的急性毒性效应[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2015, 10(6): 287-296. Qin H W, Liu A Y, Gu W L, et al. Acute toxicity of six heavy metals on three aquaculture organisms[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2015, 10(6): 287-296. (  0) 0) |
| [20] |
李建军, 林忠婷, 陈小曲, 等. 四种重金属离子对诸氏鲻虾虎鱼的单一和联合毒性[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2014, 33(2): 236-241. Li J J, Lin Z T, Chen X Q, et al. Single and joint toxicity of four heavy metal ions on Mugilogobius chulae[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2014, 33(2): 236-241. (  0) 0) |
| [21] |
蓝伟光, 陈霓. Hg、Cu、Cd、Zn对真鲷仔鱼的急性毒性研究[J]. 海洋科学, 1991, 15(5): 56-60. Lan W G, Chen N. Acute toxicity of Hg, Cu, Cd, Zn to larva of red sea bream, Chrysophrys major[J]. Marine Sciences, 1991, 15(5): 56-60. (  0) 0) |
| [22] |
柳学周, 徐永江, 兰功刚. 几种重金属离子对半滑舌鳎胚胎发育和仔稚鱼的毒性效应[J]. 海洋水产研究, 2006, 27(2): 33-42. Liu X Z, Xu Y J, Lan G G. Toxic effects of several heavy metals on the embryos, larvae of Cynoglossus semilaevis Günther[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 2006, 27(2): 33-42. (  0) 0) |
| [23] |
Yasunaga Y. The influence of some pollutants on the survival of eggs and larvae of two species of flatfish, Limanda yokohamae and Paralichtys olivaceus[J]. Bulletin of Tokai Regional Fisheries Research Laboratory, 1976, 86: 81-111.
(  0) 0) |
| [24] |
Krishnakumari L, Varshney P K, Gajbhiye S N, et al. Toxicity of some metals on the fish Therapon jarbua (Forsskal, 1775)[J]. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 1983, 12(1): 64-66.
(  0) 0) |
| [25] |
吕敢堂, 王志铮, 邵国洱, 等. 4种重金属离子对黑鲷幼鱼的急性毒性研究[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2010, 29(3): 206-210. Lv G T, Wang Z Z, Shao G E, et al. Acute toxicity of four kinds of heavy metal on Juveniles Sparus macrocephalus[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University, 2010, 29(3): 206-210. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2010.03.002 (  0) 0) |
| [26] |
穆景利, 王莹, 王新红, 等. Cd2+、Hg2+、Cr6+和Pb2+对黑点青鳉( Oryzias melastigma)早期生活阶段的毒性效应研究[J]. 生态毒理学报, 2011, 6(4): 352-360. Mu J L, Wang Y, Wang X H, et al. Toxic effects of cadmium, mercury, chromium and lead on the early life stage of marine medaka (Oryzias melastigma)[J]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology, 2011, 6(4): 352-360. (  0) 0) |
| [27] |
Krishnani K K, Azad I S, et al. Acute Toxicity of some heavy metals to Lates calcarifer fry with a note on its histopathological manifestations[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part A: Environmental Science and Engineering & Toxic and Hazardous Substance Control, 2003, 38(4): 645-655.
(  0) 0) |
| [28] |
Choi M S, Kinae N. Toxic effect of micropollutants on coastal organisms 1. Toxicity on some marine fishes[J]. Korean Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences, 1994, 27(6): 529-534.
(  0) 0) |
| [29] |
Helmy M M, Lemke A E, Jacob P G, et al. Haematological changes in Kuwait mullet, Liza macrolepis (smith), induced by heavy metals[J]. Indian Journal of Marine Sciences, 1979, 8(4): 278-281.
(  0) 0) |
| [30] |
王志铮, 刘祖毅, 吕敢堂, 等. Hg2+、Zn2+、Cr6+对黄姑鱼幼鱼的急性致毒效应[J]. 中国水产科学, 2005, 12(6): 745-750. Wang Z Z, Liu Z Y, Lv G T, et al. Acute toxic effects of Hg2+, Zn2+ and Cr6+ on Nibea albiflora juvenile[J]. Journal of Fishery Sciences of China, 2005, 12(6): 745-750. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-8737.2005.06.013 (  0) 0) |
| [31] |
许章程, 洪丽卿, 郑邦定. 重金属对几种海洋双壳类和甲壳类生物的毒性[J]. 台湾海峡, 1994, 13(4): 381-386. Xu Z C, Hong L Q, Zheng B D. Toxicity effects of heavy metals on several marine bivalve and crustacean[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 1994, 13(4): 381-386. (  0) 0) |
| [32] |
高淑英, 邹栋梁. 铜、汞和铬对长毛对虾幼体的急性毒性[J]. 海洋通报, 1994, 13(2): 28-32. Gao S Y, Zou D L. Acute toxicity of copper, mercury and chromium to larva of Penaeus penicillatus[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1994, 13(2): 28-32. (  0) 0) |
| [33] |
梁军辉, 王睿睿, 闫启仑, 等. Cd2+、Cr6+ 、Hg2+三种金属对河蜾蠃蜚(Corophium acherusicum)的急性毒性[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2013, 32(4): 551-555. Liang J H, Wang R R, Yan Q L, et al. Acute toxic effects of cadmium, chromium, mercury on Corophium acherusicum[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2013, 32(4): 551-555. (  0) 0) |
| [34] |
陈志鑫. Hg2+、Pb2+、Cd2+对中华哲水蚤(Calanus sinicus)总超氧歧化酶(T-SOD)及线粒体COI基因影响的初步研究[D].青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2010. Chen Z X. Effect of Hg2+, Pb2+, Cd2+ on the T-SOD Activity and Mitochondrial COI Gene of Calanus sinicus[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10423-1011029227.htm (  0) 0) |
| [35] |
高淑英, 邹栋梁, 厉红梅. 汞、镉、锌和锰对日本对虾仔虾的急性毒性[J]. 海洋通报, 1999, 18(2): 93-96. Gao S Y, Zou D L, Li H M. Acute toxicity of Hg, Cd, Zn and Mn to post larvae of Penaeus japonicus Bate[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 1999, 18(2): 93-96. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.1999.02.014 (  0) 0) |
| [36] |
张语克, 冯丹青, 刘万民, 等. 5种重金属对白脊藤壶无节幼体的急性毒性研究[J]. 台湾海峡, 2007, 26(1): 133-141. Zhang Y K, Feng D Q, Liu W M, et al. Acute toxic effects of five heavy metals on nauplii of Balanus albicostatus[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2007, 26(1): 133-141. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8160.2007.01.018 (  0) 0) |
| [37] |
Mc Clurg T P. Effects of fluoride, cadmium and mercury on the estuarine prawn Penaeus indicus[J]. Water Sa, 1984, 10(1): 40-45.
(  0) 0) |
| [38] |
Wu Z, Chen G. Studies of Acute intoxication by some harmful substances on Penaeus orientalis[J]. Marine Sciences, 1988, 4: 36-40.
(  0) 0) |
| [39] |
Das S, Sahu B K. Toxicity of Hg (Ⅱ) to prawns Penaeus monodon and Penaeus indicus (crustacea: penaeidae) from Rushikulya Estuary, Bay of Bengal[J]. Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 2002, 31(4): 337-339.
(  0) 0) |
| [40] |
Selvakumar S, Khan S A, Kumaraguru A K. Acute toxicity of some heavy metals, pesticides and water soluble fractions of diesel oil to the larvae of some brachyuran crabs[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 1996, 17(3): 221-226.
(  0) 0) |
| [41] |
包坚敏, 王志铮, 杨阳, 等. 4种重金属离子对三疣梭子蟹大眼幼体的急性毒性[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 26(4): 395-398. Bao J M, Wang Z Z, Yang Y, et al. Acute toxicity of four heavy metals on megalopa larvaes of Portunus trituberculatus[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2007, 26(4): 395-398. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2007.04.006 (  0) 0) |
| [42] |
俞佳锋.洋山港海域挠足类对重金属的富集及急性毒性分析[D].上海: 上海海洋大学, 2014. Yu J F. Heavy Metal Concentrating and Acute Toxic Analysis of Copepoda in Yangshan Port[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2014. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10264-1014051732.htm (  0) 0) |
| [43] |
Curtis M W, Ward C H. Aquatic toxicity of forty industrial chemicals: testing in support of hazardous substance spill prevention regulation[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 1981, 51(1-4): 359-367. DOI:10.1016/0022-1694(81)90144-X
(  0) 0) |
| [44] |
Devi V U. Heavy metal toxicity to fiddler crabs, Uca annulipes latreille and Uca triangularis (Milne Edwards): tolerance to copper, mercury, cadmium[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination & Toxicology, 1987, 39(6): 1020-1027.
(  0) 0) |
| [45] |
Denton R W, Burdon-Jones C. The influence of temperature and salinity upon the acute toxicity of heavy metals to the banana prawn (Penaeus merguiensis de Man)[J]. Chemistry and Ecology, 1982, 1(2): 131-143. DOI:10.1080/02757548208070795
(  0) 0) |
| [46] |
王志铮, 吕敢堂, 许俊, 等. Cr6+、Zn2+、Hg2+对凡纳滨对虾幼虾急性毒性和联合毒性研究[J]. 海洋水产研究, 2005, 26(2): 6-12. Wang Z Z, Lv G T, Xu J, et al. Study on the acute toxicity and joint toxicity of Cr6+, Zn2+, Hg2+acting on Litopenaeus vannamei juvenile[J]. Marine Fisheries Research, 2005, 26(2): 6-12. (  0) 0) |
| [47] |
Krishnaja A P, Rege M S, Joshi A G. Toxic effects of certain heavy metals (Hg, Cd, Pb, As and Se) on the intertidal crab Scylla serrata[J]. Marine Environmental Research, 1987, 21(2): 109-119. DOI:10.1016/0141-1136(87)90045-6
(  0) 0) |
| [48] |
Pavicic J, Skreblin M, Kregar I, et al. Embryo-larval tolerance of Mytilus galloprovincialis, exposed to the elevated sea water metal concentrations—Ⅰ. toxic effects of Cd, Zn and Hg in relation to the metallothionein level[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Pharmacology, Toxicology and Endocrinology, 1994, 107(2): 249-257. DOI:10.1016/1367-8280(94)90048-5
(  0) 0) |
| [49] |
Chin T S, Chen H C. Toxic effects of mercury on the hard clam, Meretrix lusoria, in various salinities[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C: Pharmacology, Toxicology and Endocrinology, 1993, 105(3): 501-507. DOI:10.1016/0742-8413(93)90092-Y
(  0) 0) |
| [50] |
Wang Q, Liu B, Yang H, et al. Toxicity of lead, cadmium and mercury on embryogenesis, survival, growth and metamorphosis of Meretrix meretrix larvae[J]. Ecotoxicology, 2009, 18(7): 829-837. DOI:10.1007/s10646-009-0326-1
(  0) 0) |
| [51] |
Ramakritinan C M, Chandurvelan R, Kumaraguru A K. Acute toxicity of metals: Cu, Pb, Cd, Hg and Zn on marine molluscs, Cerithedia cingulata G, and Modiolus philippinarum H[J]. Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences, 2012, 41(2): 141-145.
(  0) 0) |
| [52] |
陈金堤, 王文雄. 重金属对褶牡蛎胚胎及幼体发育的毒性效应[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 1985(1): 96-101. Chen J D, Wang W X. The toxic effects of the heavy metals on the embryonic and larvae developments of the oyster[J]. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 1985(1): 96-101. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0438-0479.1985.01.013 (  0) 0) |
| [53] |
Calabrese A, Collier R S, Nelson D A, et al. The toxicity of heavy metals to embryos of the American oyster Crassostrea virginica[J]. Marine Biology, 1973, 18(3): 162-166. DOI:10.1007/BF00367984
(  0) 0) |
| [54] |
周光锋, 王志铮. 4种重金属离子对厚壳贻贝幼贝的急性毒性[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 26(4): 391-394. Zhou G F, Wang Z Z. Acute toxic effects of four heavy metalson juveniles of Mytilus coruscus Gould[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science), 2007, 26(4): 391-394. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2007.04.005 (  0) 0) |
| [55] |
Mohan C V, Gupta T R C, Shetty H P C, et al. Combined toxicity of mercury and cadmium to the tropical green mussel Perna viridis[J]. Diseases of Aquatic Organisms, 1986, 2(1): 65-72.
(  0) 0) |
| [56] |
Beiras R, His E. Effects of dissolved mercury on embryogenesis, survival, growth and metamorphosis of Crassostrea gigas oyster larvae[J]. Marine Ecology Progress, 1994, 113(1-2): 95-103.
(  0) 0) |
| [57] |
Nelson D A, Calabrese A, Nelson B A, et al. Biological effects of heavy metals on juvenile bay scallops, Argopecten irradians, in short-term exposures[J]. Bulletin of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1976, 16(3): 275-282. DOI:10.1007/BF01685889
(  0) 0) |
| [58] |
王志铮, 王伟定, 杨阳, 等. 4种重金属离子对彩虹明樱蛤(Moerella iridescens)的急性致毒效应[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2007, 38(4): 373-378. Wang Z Z, Wang W D, Yang Y, et al. Acute toxic effects of four heavy metals on Goerella iridescens[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2007, 38(4): 373-378. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0029-814X.2007.04.013 (  0) 0) |
| [59] |
隋国斌, 杨凤, 孙丕海, 等. 铅、镉、汞对皱纹盘鲍幼鲍的急性毒性试验[J]. 大连水产学院学报, 1999, 14(1): 22-26. Sui G B, Yang F, Sun P H, et al. The acute toxicity tests of Pb, Hg and Cd to larvae of Haliotis discus hannai Ino[J]. Journal of Dalian Fisheries University, 1999, 14(1): 22-26. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-9957.1999.01.004 (  0) 0) |
| [60] |
Nelson D A, Miller J E, Calabrese A. Effect of heavy metals on bay scallops, surf clams, and blue mussels in acute and long-term exposures[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1988, 17(5): 595-600. DOI:10.1007/BF01055828
(  0) 0) |
| [61] |
王晓宇, 王清, 杨红生. 镉和汞两种重金属离子对四角蛤蜊的急性毒性[J]. 海洋科学, 2009, 33(12): 24-29. Wang X Y, Wang Q, Yang H S. Acute toxicities of Cd2+ and Hg2+ on Mactra veneriformis Reeve[J]. Marine Sciences, 2009, 33(12): 24-29. (  0) 0) |
| [62] |
Devi V U. Changes in oxygen consumption and biochemical composition of the marine fouling dreissinid bivalve Mytilopsis sallei (Recluz) exposed to mercury[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 1996, 33(1): 168-174.
(  0) 0) |
| [63] |
Eisler R, Hennekey R J. Acute toxicities of Cd2+, Cr+6, Hg2+, Ni2+ and Zn2+ to estuarine macrofauna[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1977, 6(1): 315-323.
(  0) 0) |
| [64] |
Devi V U. Heavy metal toxicity to an intertidal gastropod Morula granulata (duclos): tolerance to copper, mercury, cadmium and zinc[J]. Journal of Environmental Biology, 1997, 18(3): 287-290.
(  0) 0) |
| [65] |
包坚敏, 王志铮, 陈启恒, 等. 4种重金属对泥螺的急性毒性和联合毒性研究[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版), 2007, 26(3): 252-256. Bao J M, Wang Z Z, Chen Q H, et al. Acute toxic effects of four heavy metals on Bullacta exarata[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University(Natural Science), 2007, 26(3): 252-256. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1008-830X.2007.03.003 (  0) 0) |
| [66] |
张艳红, 郭旭东. 重金属Hg2+对毛蚶的急性毒性及肝脏组织结构的影响[J]. 河北渔业, 2016(8): 13-15. Zhang Y H, Guo V D. The acute toxicity and effects to hepatic tissue structure of Hg2+ to Scapharca subcrenata[J]. Hebei Fisheries, 2016(8): 13-15. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1004-6755.2016.08.003 (  0) 0) |
| [67] |
蒋国萍.海洋酸化条件下重金属Cd2+、Hg2+对斧文蛤生态毒理效应研究[D].上海: 上海海洋大学, 2016. Jiang G P. Ecotoxicological Effects of Cd2+, Hg2+ on Meretrix lamarckii Under the Ocean Acidification Conditions[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2016. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10264-1016912249.htm (  0) 0) |
| [68] |
严俊贤, 李铭垚, 李有宁, 等. 重金属Hg2+、Cd2+对凸加夫蛤的急性毒性效应[J]. 广东海洋大学学报, 2014, 34(1): 66-70. Yan J X, Li M Y, Li Y N. Acute toxic effect of Hg2+ and Cd2+ on Gafrarium tumidum[J]. Journal of Guangdong Ocean University, 2014, 34(1): 66-70. (  0) 0) |
| [69] |
高业田.重金属Cd和Hg对可口革囊星虫(Phascolosoma esculenta)的毒理学效应[D].上海: 上海海洋大学, 2012. Gao Y T. Toxic effects of Cd and Hg Exposure on Phascolosoma esculenta [J]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2012. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D366347 (  0) 0) |
| [70] |
唐永政, 宋祥利, 翟传阳, 等. 3种重金属离子对单环刺螠幼螠的急性毒性研究[J]. 烟台大学学报(自然科学与工程版), 2017, 30(1): 31-35. Tang Y Z, Song X L, Zhai C Y, et al. Acute toxicity of three heavy metal ions to Urechis unicinctus juveniles[J]. Journal of Yantai University, 2017, 30(1): 31-35. (  0) 0) |
| [71] |
郭平, 刘春洋, 鲁男. 重金属对海蜇螅状体的急性毒性试验[J]. 水产科学, 1986(4): 10-12. Gon P, Liu C Y, Lu N. The acute toxicity test of heavy metals to jellyfish scyphistoma[J]. Fisheries Science, 1986(4): 10-12. (  0) 0) |
| [72] |
US EPA. Ambient Water Quality Criteria for Mercury[R]. Washington DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency, 1984.
(  0) 0) |
| [73] |
Boney A D, Corner E D S, Sparrow B W P. The effects of various poisons on the growth and viability of sporelings of the red alga Plumaria elegans (bonnem.) schm[J]. Biochemical Pharmacology, 1959, 2(1): 37-49. DOI:10.1016/0006-2952(59)90055-3
(  0) 0) |
| [74] |
Lucu C, Obersnel V, Jelisavcic O. Transport and toxicity of metal pollutants to marine organisms[J]. Map Technology Reports Series, 1991, 52: 55-62.
(  0) 0) |
| [75] |
Ray G L, Tripp M R. The uptake of mercury from water by the grass shrimp, Palaemonetes vulgaris (say)[J]. Journal of Environmental Quality, 1976, 5(2): 193-196.
(  0) 0) |
| [76] |
Sharp J R, Neff J M. The toxicity of mercuric chloride and methylmercuric chloride to Fundulus heteroclitus embryos in relation to exposure conditions[J]. Environmental Biology of Fishes, 1982, 7(3): 277-284. DOI:10.1007/BF00002502
(  0) 0) |
| [77] |
Kraus M L, Weis J S, Weis P. Effects of mercury on larval and adult grass shrimp (Palaemonetes pugio)[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1988, 17(3): 355-363. DOI:10.1007/BF01055173
(  0) 0) |
| [78] |
Kraus M L, Weis J S. Differences in the effects of mercury on telson regeneration in two populations of the grass shrimp Palaemonetes pugio[J]. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology, 1988, 17(1): 115-120. DOI:10.1007/BF01055161
(  0) 0) |
| [79] |
Branco V, Canario J, Lu J, et al. Mercury and selenium interaction in vivo: effects on thioredoxin reductase and glutathione peroxidase[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine, 2012, 52(4): 781-793. DOI:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.12.002
(  0) 0) |
| [80] |
US EPA. 1995 Updates: Water Quality Criteria Documents for the Protection of Aquatic Life in Ambient Water[R]. Washington D C: United States Environmental Protection Agency, 1995.
(  0) 0) |
| [81] |
CCME. Canadian Water Guidelines for the Protection of Aquatic Life: Mercury[R]. Canada: Canadian Council of Ministers of the Environment, 2003.
(  0) 0) |
| [82] |
中华人民共和国环境保护部. GB11607—89渔业水质标准[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 1989. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. GB11607—89 Water Quality for Fisheries[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1989. (  0) 0) |
| [83] |
中华人民共和国环境保护部. GB3097-1997海水水质标准[S].北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2004. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People's Republic of China. GB3097-1997 Sea Water Quality Standard[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 2004. (  0) 0) |
| [84] |
张亚南.黄河口、长江口、珠江口及其邻近海域重金属的河口过程和沉积物污染风险评价[D].厦门: 国家海洋局第三海洋研究所, 2013. Zhang Y N. Heavy Metals Process in Water and Pollution Risk Assessment in Surface Sediments of the Yellow River Estuary, Yangzi Estuary Pearl River Estuary[D]. Xiamen: Third Institute of Oceanography, State Oceanic Administration, 2013. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=D472415 (  0) 0) |
| [85] |
孙维萍, 于培松, 潘建明. 灰色聚类法评价长江口、杭州湾海域表层海水中的重金属污染程度[J]. 海洋学报, 2009, 31(1): 79-84. Sun W P, Yu P S, Pan J M. Assessment of dissolved trace metals in nearshore area of Changjiang Estuary and Hangzhou Bay with gray cluster method[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2009, 31(1): 79-84. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2009.01.010 (  0) 0) |
| [86] |
李玉.胶州湾主要重金属和有机污染物的分布及特征研究[D].北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2005. Li Y. Study on the Distribution and Characteristics of Main Heavy Metals and Organic Pollutants of Jiaozhou Bay[D]. Beijing: Graduate University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2005. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=degree&id=Y844613 (  0) 0) |
| [87] |
江锦花, 江正玲, 陈希方, 等. 椒江口海域重金属含量分布及在沉积物和生物体中的富集[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2007, 26(1): 58-62. Jing J H, Wang Z L, Chen X F, et al. Distribution of heavy metals and enrichment of it in sediment and organisms in Jiaojiang Estuary[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2007, 26(1): 58-62. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-6336.2007.01.014 (  0) 0) |
| [88] |
张效龙, 丁德文, 徐家声, 等. 渤海西部河口潮间带区海水及沉积物中重金属研究[J]. 东华理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 33(3): 276-280. Zhang X L, Ding D W, Xv J S, et al. Heavy metal in seawater and sediment investigation at Bohai Sea Western Estuary tidal Zone[J]. Journal of East China Institute of Technology, 2010, 33(3): 276-280. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3504.2010.03.10 (  0) 0) |
| [89] |
李壮伟, 罗荣真, 陈鸿生, 等. 广东红海湾表层海水重金属含量的时空变化特征与污染水平评价[J]. 台湾海峡, 2012, 31(1): 21-27. Li Z W, Luo R Z, Chen H S, et al. Characteristics of temporal-spatial variation and evaluated pollution level of heavy metals in surface seawater of Honghai Bay[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2012, 31(1): 21-27. (  0) 0) |
| [90] |
姜发军, 尹闯, 张荣灿, 等. 2010年冬季广西北部湾近岸海域表层海水和沉积物中重金属污染现状及评价[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2013, 32(6): 824-830. Jiang F J, Yin C, Zhang R C, et al. Pollution assessment and evaluation of heavy metals in the sea water and surface sediments of Guangxi Beibu Gulf coast in winter 2010[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2013, 32(6): 824-830. (  0) 0) |
| [91] |
徐颂军, 许观嫦, 廖宝文. 珠江口红树林湿地海水重金属污染评价及分析[J]. 华南师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 48(5): 44-51. Xu S J, Xu G C, Liao B W. Evaluation and analysis on heavy metals' pollution in mangrove wetland's seawater of the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Journal of South China Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 48(5): 44-51. (  0) 0) |
| [92] |
杨华, 王少鹏, 余克服, 等. 南海北部珊瑚生长区海水重金属污染特征[J]. 生态环境学报, 2017, 26(2): 253-260. Yang H, Wang S P, Yu K F, et al. Pollution characteristics of heavy metals in seawater of coral growing regions in the Northern South China Sea[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2017, 26(2): 253-260. (  0) 0) |
| [93] |
刘芳文, 颜文, 苗莉, 等. 湛江港海域海水和表层沉积物重金属分布特征及其污染评价[J]. 海洋技术学报, 2015, 34(2): 74-82. Liu F W, Yan W, Miao L, et al. Distribution characteristics and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the seawater and surface sediments from the Zhanjiang Harbor[J]. Journal of Ocean Technology, 2015, 34(2): 74-82. (  0) 0) |
| [94] |
何荣, 刘洋. 天津北部近岸增养殖区重金属污染的调查与评价[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2015(4): 149-154. He R, Liu Y. Investigation and assessment of heavy metal pollution in the nearshore aquaculture area of northern Tianjin[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2015(4): 149-154. (  0) 0) |
| [95] |
郑程, 朱亮, 穆卫华, 等. 枸杞乡养殖海域贻贝和海水中重金属含量研究[J]. 广州化工, 2016, 44(1): 133-135. Zheng C, Zhu L, Mu W H, et al. Determination and evaluation of heavy metals in mytilus elulis and sea water in Gouqi Inland of Shengsi[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2016, 44(1): 133-135. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2016.01.051 (  0) 0) |
| [96] |
朱文娟, 黄祥娟, 张栋, 等. 茅尾海养殖区重金属污染调查与评价[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2016, 33(2): 36-38. Zhu W J, Huang X J, Zhang D, et al. The investigation and assessment of heavy metal pollution in the aquiculture area of Maowei Sea[J]. Ocean Development and Management, 2016, 33(2): 36-38. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2016.02.007 (  0) 0) |
| [97] |
李娟英, 崔昱, 曹宏宇, 等. 小洋山码头潮间带地区海水及生物体内重金属污染特征的分析与评价[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2014(1): 48-55. Li J Y, Cui Y, Cao H Y, et al. Evaluation and analysis on pollution characteristic of heavy metal in seawater and intertidal marine animals from Xiaoyangshan[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2014(1): 48-55. (  0) 0) |
| [98] |
徐艳东, 王茂剑, 马建新, 等. 庙岛群岛南部海域海水和表层沉积物重金属分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 海洋湖沼通报, 2016(2): 30-39. Xu Y D, Wang M J, Ma J X, et al. spatial distribution and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in seawater and in surface sediments of southern Miaodao Archipelago[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology, 2016(2): 30-39. (  0) 0) |
| [99] |
席英玉, 杨妙峰. 湄洲湾水域海水、沉积物中砷及重金属的含量分析[J]. 福建水产, 2011, 33(4): 9-13. Xi Y Y, Yang M F. Contents analysis of arsenic and heavy metals in seawater and sediment in Meizhou Bay[J]. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, 2011, 33(4): 9-13. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5601.2011.04.003 (  0) 0) |
| [100] |
吴烨飞. 罗源湾表层海水中重金属含量的分布特征分析[J]. 福建水产, 2012, 34(5): 387-391. Wu Y F. Distribution of heavy metals in the surface water of Luoyuan Bay[J]. Journal of Fujian Fisheries, 2012, 34(5): 387-391. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-5601.2012.05.007 (  0) 0) |
| [101] |
杨斌, 钟秋平, 李宗活, 等. 钦州湾表层海水重金属分布特征及其污染评价[J]. 广州化工, 2012, 40(11): 146-148. Yang B, Zhong Q P, Li Z H, et al. Distribution and pollution evaluation of heavy metals in the surface seawaters of Qinzhou Bay[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2012, 40(11): 146-148. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2012.11.058 (  0) 0) |
| [102] |
蔡榕硕, 白娅舒. 兴化湾表层海水和沉积物中重金属含量的时空变化特征[J]. 台湾海峡, 2011, 30(3): 316-323. Cai R S, Bai Y S. Spatio-temporal variation characteristics of heavy metal contents in the surface seawater and marine sediments of Xinghua Bay[J]. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2011, 30(3): 316-323. DOI:10.3969/J.ISSN.1000-8160.2011.03.003 (  0) 0) |
| [103] |
陈艳梅, 黄智伟, 陈凯, 等. 福建安海湾五种重金属和砷在不同介质中的分布特征研究[J]. 渔业研究, 2016, 38(3): 219-229. Chen Y M, Huang Z W, Chen K, et al. Study on distribution characteristics of 5 heavy metals and As concentration in different medium of Anhai Bay[J]. Journal of Fisheries Research, 2016, 38(3): 219-229. (  0) 0) |
| [104] |
徐国锋, 何东海, 毛伟宏, 等. 象山港毛蚶种苗区重金属的含量分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 应用海洋学报, 2016, 35(3): 348-355. Xu G F, He D H, Mao W H, et al. Distribution of heavy metals in seeding area of Scapharca subcrenata in Xiangshan Bay and its potential ecological risk assessment[J]. Journal of Applied Oceanography, 2016, 35(3): 348-355. (  0) 0) |
| [105] |
张学超, 刘营, 宋吉德, 等. 威海双岛湾海域重金属的分布特征及生态风险评价[J]. 海洋学研究, 2014, 32(2): 85-90. Zhang X C, Liu Y, Song J D, et al. distributions and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in Shuangdao Bay of Weihai[J]. Journal of Marine Sciences, 2014, 32(2): 85-90. (  0) 0) |
2. Key Laboratory of Marine Environmental Science and Ecology, Ministry of Education, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
 2019, Vol. 49
2019, Vol. 49


