引用本文

侯学东, 刘正琦, 文涛. 铅暴露对大鼠脑海马mGluR5表达和学习记忆影响[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2014, 30(4): 451-453.

HOU Xue-dong, LIU Zheng-qi, WEN Tao. Effect of lead exposure on protein expression of mGluR5 in hippocampus and learning memory in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 2014, 30(4): 451-453.

铅暴露对大鼠脑海马mGluR5表达和学习记忆影响
1. 沈阳医学院附属中心医院耳鼻喉科, 辽宁 沈阳 110024;
2. 内蒙古医学院;
3. 辽宁省疾病预防控制中心
数字出版日期:2014-3-12 09:25.
基金项目:辽宁省博士科研启动基金(20071063)
作者简介:侯学东(1967- ),男,辽宁沈阳人,副主任医师,本科,主要从事耳鼻喉科临床工作。
摘要:目的 观察发育期慢性低浓度铅暴露对大鼠脑海马代谢型谷氨酸受体5(mGluR5)表达和学习记忆能力影响。方法 30只孕鼠按体重随机分成3组,分别给予双蒸水、0.05%、0.20%醋酸铅饮水,断乳后仔鼠自行饮用含铅水,至出生后28、56 d用水迷宫方法测试仔鼠学习记忆行为改变;蛋白印迹(Western blot)方法检测脑海马mGluR5蛋白表达。结果 发育期慢性低浓度铅暴露可导致仔鼠空间定位航行能力降低;与对照组比较,训练第3、5、7 d,0.05%、0.20%醋酸铅组大鼠寻找平台时间[分别为(40.13±9.20)、(32.82±6.45)、(26.83±7.12)和(61.50±13.84)、(54.51±9.65)、(19.81±4.92)s]明显延长,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);生后第7、14、21、28 d,0.05%,0.20%醋酸铅组脑海马mGluR5蛋白表达量分别为[(0.607±0.027)、(0.845±0.010)、(0.713±0.004)、(0.587±0.011)]和[(0.540±0.025)、(0.573±0.014)、(0.551±0.014)、(0.492±0.017)],均明显低于对照组(P<0.05)。结论 孕鼠低水平铅暴露可致仔鼠空间学习能力降低,其机制可能与脑海马mGluR5蛋白表达水平下降有关。
关键词:
海马
代谢型谷氨酸受体5(mGluR5)
学习记忆
Effect of lead exposure on protein expression of mGluR5 in hippocampus and learning memory in rats
HOU Xue-dong
1, LIU Zheng-qi
2, WEN Tao
3
Department of Otolaryngology, Fengtian Affiliated Hospital of Shenyang Medical University, Shenyang, Liaoning Province 110024, China
Abstract: Objective To observe effects of low level lead exposure during pregnant on expression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5(mGluR5)in hippocampus and learning and memory in rats.Methods Thirty pregnant rats were randomly divided into 3 groups,and the rats were fed with doubly distilled water in control group and 0.05%,0.2%lead acetate(PbAc)solution in treatment groups via drinking water during pregnancy and lactation.After weaning,the offspring rats were directly fed with drinking water as their dams.Western blot was used to detect the protein expression of mGluR5 in hippocampus of offspring rats at postnatal 7,14,21,and 28 days,respectively.The contents of lead in blood and hippocampus were determined with atomic absorption spectrophotometer at postnatal 28 days.Morris water maze test was used to observe the change of learning and memory at postnatal 56 days.Results Low level lead exposure during pregnancy resulted in the decreases of spatial positioning navigation in the offspring rats.The time of searching for the platform in the offsprings of the rats in 0.05%and 0.2%PbAc groups were 40.13±9.20,32.82±6.45,26.83±7.12 and 61.50±13.84,54.51±9.65,19.81±4.92 seconds at 3,5,and 7 day of training,compared to those of the control group,which exhibited a significant extension(P<0.05).The expression of mGluR5 in hippocampus of 0.05% and 0.2% PbAc group at postnatal 7,14,21,and 28 days were 0.607±0.027,0.845±0.010,0.713±0.004,and 0.587±0.011 and 0.540±0.025,0.573±0.014,0.551±0.014 and,0.492±0.017,with a decreased tendency compared to those of the control group(P<0.05).Conclusion Chronic lead exposure results in decrease of spatial learning and memory and its effect may relate to the decline of expression of mGluR5 in hippocampus in rats.
Key words:
hippocampus
mGluR5
learning and memory
代谢型谷氨酸受体5(metabotropic glutamate receptors,mGluR5)在脑内分布广泛,属于G蛋白偶联受体(G protein coupled receptor,GPCRs)超家族中成员。该受体及其介导的下游信号在调节神经系统正常生理功能中起着非常重要作用,参与学习、记忆和突触传递效率的可塑性变化等生理过程[1]。本研究通过建立发育期慢性低浓度铅暴露大鼠模型,观察仔鼠发育阶段脑海马mGluR5表达及空间学习记忆能力的变化,探讨铅影响学习记忆能力的机制,结果报告如下。
1 材料与方法
1.1 主要试剂与仪器
兔抗大鼠mGluR5单克隆抗体(美国Epitmics公司);辣根过氧化酶标记羊抗兔二抗(北京中山生物技术有限公司);ChemiImager5500自动电泳凝胶成像分析仪(美国Apha Innotech公司)。
1.2 实验动物与分组
体重250~300 g 健康Wistar大鼠(沈阳医学院实验动物中心),许可证号:SCXK(辽)2010-0002,60只,雌雄各半,按雄、雌1∶1自然交配,以次晨发现阴栓者确定为妊娠第0 d。将孕鼠随机分为3组,每组10只,分笼饲养。自怀孕第1 d起分别饲以双蒸水(对照组),0.05%,0.20%醋酸铅水溶液(低、高剂量醋酸铅组),仔鼠断乳前通过母乳接触铅,断乳(21 d)后自行饮用与其母鼠相同饮用水,暴露28 d后,改饮双蒸水。
1.3 指标与方法
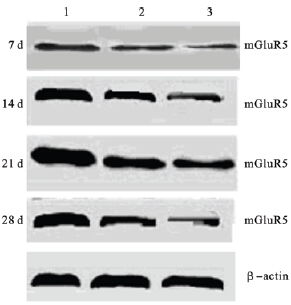
1.3.1 仔鼠脑海马mGluR5蛋白表达测定
采用蛋白免疫印迹法,各组分别随机选取出生后7、14、21、28 d仔鼠各10只,取海马组织,迅速置于液氮保存。将蛋白印迹显影图扫描,以mGluR5与相应内参(β-actin)的灰度值比值(mGluR5/βactin)代表相对蛋白含量。
1.3.2 血铅、海马铅测定
各组分别随机选取出生后28 d 仔鼠10只,微量注射器经眼眶采静脉血0.5 mL,肝素抗凝,200 μL静脉血,加0.1 mol/L稀硝酸2 500 μL及体积分数为10%的三氯醋酸
300 μL,3 000 r/min离心15 min,取上清待测;取仔
鼠双侧脑海马,称重后加纯硝酸5 mL 24 h 后,加热消化,冷却定容到25 mL,血清及脑海马铅含量均采用石墨炉原子吸收光谱法测定。
1.3.3 水迷宫实验
各组分别随机选取出生后56 d仔鼠8只,按文献[2]所示方法进行实验。
1.4 统计分析
数据采用x±s表示,应用SPSS 13 软件进行统计分析,多组间比较采用单因素方差分析,两两比较用SNK-q检验,P<0.05 为差异有统计学意义。
2 结 果
2.1 慢性铅暴露对仔鼠血铅和脑海马铅含量影响(表 1)
与对照组比较,醋酸铅组仔鼠血铅和脑海马铅含量均明显升高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
表 1
 表 1 铅暴露对仔鼠血铅和脑海马铅含量影响(x±s,n=10)
| 组别(%) | 血铅(μmol/L) | 脑海马铅(μg/g)
| | 对照组 | 0.74±0.11 | 0.06±0.004
| | 醋酸铅 0.05 | 5.71±1.28a | 0.296±0.054b
| | 0.20 | 15.19±2.14a | 6.680±0.921a
| | 注:与对照组比较,a P<0.01,b P<0.05。 |
| 表 1 铅暴露对仔鼠血铅和脑海马铅含量影响(x±s,n=10)
|
训练第1~3 d,醋酸铅组仔鼠寻找平台时间均略长于对照组;从第3 d开始,对照组所用时间明显缩短,而醋酸铅组所用时间虽减少,但减少幅度较慢;训练第5、7 d,醋酸铅组仔鼠寻找平台所用时间均明显长于对照组(P<0.05)。
表 2
 表 2 铅暴露对仔鼠寻找平台时间影响(s,x±s,n=8)
| 组别(%) |
训练天数 |
| 第1天 |
第3天 |
第5天 |
第7天 |
|
对照组 | 82.22±13.66 | 42.90±8.76 | 19.28±5.88 | 14.45±4.58
| | 醋酸铅 0.05 | 83.20±14.80 | 40.13±9.20 | 32.82±6.45a | 26.83±7.12a
| | 0.20 | 101.82±19.06 | 61.50±13.84b | 54.51±9.65b | 19.81±4.92a
| | 注:与对照组比较,a P<0.05,b P<0.01。 |
| 表 2 铅暴露对仔鼠寻找平台时间影响(s,x±s,n=8)
|
发育期脑海马mGluR5表达呈时间差异,生后14 d达高峰,而后表达逐渐下降。与对照组比较,醋酸铅组仔鼠脑海马mGluR5表达呈下降趋势,各时间点差异均有统计学意义(P<0.01)。
表 3
 表 3 铅暴露对仔鼠脑海马mGluR5 蛋白表达影响 (x±s,n=10)
| 组别(%) |
生后天数(d) |
| 7 |
14 |
21 |
28 |
|
对照组 | 1.012±0.083 | 1.267±0.012 | 0.927±0.015 | 0.837±0.012
| | 醋酸铅 0.05 | 0.607±0.027a | 0.845±0.010a | 0.713±0.004a | 0.587±0.011a
| | 0.20 | 0.540±0.025a | 0.573±0.014a | 0.551±0.014a | 0.492±0.017a
| | 注:与对照组比较,a P<0.01。 |
| 表 3 铅暴露对仔鼠脑海马mGluR5 蛋白表达影响 (x±s,n=10)
|
谷氨酸是中枢神经系统中一种主要的兴奋性递质,参与突触的兴奋性传递和长时程增强等生理及病理过程,在突触形成之前,谷氨酸对发育中的神经元发挥着营养作用。谷氨酸受体分为2类:离子型慢性铅暴露对仔鼠脑海马mGluR5表达影响
谷氨酸受体与代谢型谷氨酸受体(metabotropic glutamate receptors,mGluRs)。mGluRs是一个新的G2蛋白相关受体家族[3],至少有8个亚型,分为3组,第1组包括mGluR1a、b、c、d、g和mGluR5a、b;第2组包括mGluR2和mGluR3;第3组由mGluR4a、b,mGluR6,mGluR 7a、b和mGluR 8a、b组成[4]。mGluR5在神经系统中参与很多重要生理功能,如介导兴奋性神经信号传导和学习记忆过程中的突触传递。mGluR5的突触活化能诱发N-甲基-D-天冬氨酸受体(N-methyl D-aspartatereceptor,NMDAR)活化,藕联G蛋白,与磷脂酶C(phospholipase C,PLC)相结合。激活的PLC使磷脂酰肌醇4,5二磷酸(PIP2)水解产生1,4,5-三磷酸肌醇(IP3)和二酰基甘油(DG)2个第二信使,DG通过蛋白激酶C传递信号,IP3引起Ca2+动员,内质网内的Ca2+释放,
胞内Ca2+浓度增加;同时介导生长锥的改变,参与长时程增强的发生[5]。
据报道,mGluR5还可以激活纹状体培养神经元内细胞外调节蛋白激酶(extracellular regulatedprotein kinases,ERK),ERK的激活经由2条独立的胞内信号通路介导,三磷酸肌醇/Ca2+通路介导了一部分的 ERK激活,而mGluR5的C-端结合Homer蛋白则以Ca2+非依赖方式介导了主要的 ERK激活[6]。经2条通路激活的 ERK可以协同刺激转录因子 ETS(erythroblast transformation specific)相似基因1和环磷酸腺苷反应成分结合蛋白,从而促进ETS相似基因1和环磷酸腺苷反应成分结合蛋白敏感基因的表达[7]。本研究结果显示,围产期铅暴露使生后7、14、21、28 d仔鼠的脑海马中的mGluR5的表达量减少。提示mGluR5可能是铅影响学习记忆能力的靶点之一,mGluR5蛋白的发育期慢性低浓度铅暴露过程中是否与Homer蛋白及其他蛋白相互作用,还有待于进一步研究。
参考文献
| [1] |
SChlett K.Glutamate as a modulator of embryonic and adult neurogenesis[J].Curr Top Med Chem, 2006, 6(10):949-960.
|
| [2] |
胡前胜, 任铁玲, 傅洪军, 等.宫内铅暴露对大鼠神经行为发育的影响[J].中国公共卫生, 2005, 21(2):152-153.
|
| [3] |
Nicoletti F, Battaglia G, Storto M, et al.Metabotropic glutamate receptors:beyond the regulation of synaptic transmission[J].Psychoneuroendocrinology, 2007, 24:S40-S45.
|
| [4] |
Simonyi A, Ngomba RT, Storto M, et al.Expression of groups I and Ⅱ metabotropic glutamae receptors in the rat brain during aging[J].Brain Res, 2005, 1043 (1-2):95-106.
|
| [5] |
Yeh TH, Wang H.Global ischemia downregulates the function of metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype 5 in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons[J].Mol Cell Neurosci, 2005, 29(3):484-492.
|
| [6] |
Kinney GG, Burno M, Campbell UC, et al.Metabotropic glutamate subtype 5 receptors modulate locomotor activity and sensorimotor gating in rodents[J].J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2003, 306(1):116-123.
|
| [7] |
Castiglione M, Calafiore M, Costa L, et al.Group I metabotropic glutamate receptors control proliferation, survival and differentiation of cultured neural progenitor cells isolated from the subventricular zone of adult mice[J].Neuropharmacology, 2008, 55(4):560-567.
|
 2014, Vol. 30
2014, Vol. 30
