O1 /O139 群霍乱弧菌产毒株是引起霍乱流行的主要病原体,其致病性依赖于多种致病因子的协同作用。近年来发现,一些O1 /O139 群霍乱弧菌非产毒株也可以引起霍乱样腹泻[1, 2]。外环境水体是霍乱弧菌的自然滋生地,存在大量非产毒O1 /O139 群霍乱弧菌,分析外环境中非产毒O1 /O139 群霍乱弧菌的毒力基因携带情况对于人群健康危险评估有重要意义。本研究通过对2008—2009 年广东省外环境水体和水产品O1 /O139 群霍乱弧菌分离株进行毒力基因PCR 检测和毒力基因分型分析,为霍乱防控提供科学依据。
1 材料和方法 1.1 菌株来源2008—2009 年广东省外环境水体和水产品监测以及同期霍乱疫情常规监测的90 株 O1 /O139 群霍乱弧菌。其中,外环境水体分离株69 株( 稻叶型41 株,小川型18 株,O139 群10 株) ,水产品分离株16 株( 稻叶型5 株,小型11 株) ,病例菌株5 株( 稻叶型2 株,小川型2 株,O139 群1 株) 。 阳性对照菌株采用O1 群霍乱弧菌标准株N16961。
1.2 主要仪器与试剂Biometra TGradient PCR 扩增仪( 德国Biometra 公司) ; 电泳仪( 日本Cosmo 公司) ; Gel Doc EQ 自动凝胶成像系统( 美国Bio-Rad 公司) 。DL2000 Marker ( 大连宝生物公司) ; Taq Premix( 大连宝生物公司) ; 细菌染色体DNA 提取试剂盒( 北京天根公司) 。
1.3 基因组DNA 提取参照试剂盒说明书采用 DNA 提取试剂盒提取细菌基因组DNA。
1.4 毒力基因的多重PCR 测定用多重PCR 扩增ctxA,tcpA,zot,toxR,ompU,ace,tcpI 和hlyA 等8 种毒力基因[3]。各毒力基因引物序列参考文献 [3],并由上海生工生物工程公司合成。PCR 反应体系为25 μL,内含12.5 μL Taq Premix( 2 × ) ,上、 下游各1 μL,模板DNA 2 μL。设立空白对照( 试剂) 和阳性对照( N 16 961) 。扩增条件: 94 ℃预变性2 min,94 ℃,1 min; 56 ℃,1 min; 72 ℃,1 min; 25 个循环,最后72 ℃,4 min。扩增产物用0.5 × Trisborate-EDTA ( TBE) 配制的1%的琼脂糖凝胶中电泳,以DL 2000 Marker 为参照,电泳后的胶块在1% 的溴化乙锭染液染色5 min 后于自动凝胶成像系统中观察记录结果。
2 结果 2.1 毒力基因的多重PCR 测定图谱特征( 图 1)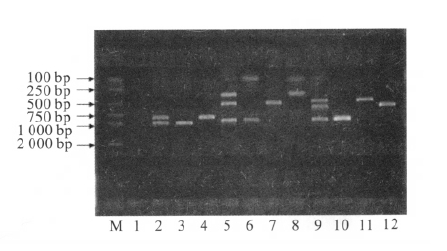 |
注: M: Marker; 1: H2O; 2: toxR + zot; 3: zot; 4: toxR; 5: ace + hlyA + tcpI; 6: tcpI; 7: hlyA; 8: ace; 9: ctxA + tcpA + ompU; 10: ompU; 11: tcpA; 12: ctxA。图 1 霍乱弧菌毒力基因PCR 扩增产物电泳图 |
多重PCR 扩增霍乱弧菌毒力基因得到特异性的阳性扩增带,分别为ctxA ( 564 bp) ,tcpA ( 451 bp) 和 ompU( 896 bp) ; ace ( 289 bp) ,tcpI( 862 bp) 和hlyA ( 481 bp) ; zot( 947 bp) 和toxR( 779 bp) 。
2.2 菌株毒力基因多重PCR 检测所有被检菌株均含有hlyA 和toxR 基因。5 株病例来源菌株中有3株( 2 株稻叶,1 株O139) 8 种毒力基因全部阳性,另外2 株小川菌株未检出ctxA 基因。18 株水体来源小川型菌株有2 株分别检出ace,zot 和/或tcpA 阳性 ( 11.11%) ,5 株检出tcpI 阳性( 27.78%) ,6 株检出 ompU 阳性( 33.33%) 。11 株水产品来源小川型菌株有4 株检出ace 阳性( 36.36%) ,5 株检出zot 阳性( 45.45%) ,7 株分别检出tcpA 和/或tcpI 阳性 ( 63.64%) ,10 株检出ompU 阳性( 90.91%) 。41 株水体来源稻叶型菌株均未检出ctxA 和tcpA,其中,22 株检出ace 阳性( 53.66%) ,23 株分别检出zot 和/ 或tcpI 阳性( 56.10%) ,39 株检出ompU 阳性 ( 95.12%) 。5 株水产品来源稻叶型菌株均未检出 ctxA、ace、zot 和tcpA,4 株分别检出tcpI 和ompU 阳性 ( 80%) 。10 株O139 群菌株均分离自水体标本,毒力基因检测均未检出ctxA、ace 和tcpA,其中,2 株检出zot 阳性( 20%) ,1 株分别检出tcpI 和/或ompU 阳性( 10%) 。
2.3 霍乱弧菌毒力基因分型69 株水体来源的菌株中,18 株为小川型,41 株为稻叶型,10 株为O139 群菌株。根据不同来源菌株携带毒力基因不同,可将69 株外环境水体来源的霍乱弧菌分成9 个基因型。稻叶型菌株可分为6 种型别,其中14 株为 hlyA+ toxR+ ompU+ ace + zot + tcpI + 型( 34.15%) ,9 株为hlyA+ toxR+ ompU+ tcpI + 型( 21.95%) ,8 株为 hlyA+ toxR+ ompU+ ace + zot + 型( 19.51%) ,7 株为 hlyA + toxR + ompU +型( 17.07%) ,2 株为hlyA + toxR + 型( 4.88%) 以及1 株为hlyA + toxR + ompU + zot + 型 ( 2.44%) 。18 株小川型菌株可分为5 种型别,12 株为hlyA + toxR + 型( 66.67%) ,3 株为hlyA + toxR + ompU + tcpI + 型( 16.67%) ,另外各有1 株( 5.56%) 为hlyA + toxR + ompU + ace + zot + tcpI + tcpA + 型、hlyA + toxR + ompU + ace + zot + 型和hlyA + toxR + ompU + tcpI + tcpA +型。10 株O139 群菌株可分为3 种型别,7 株为hlyA + toxR + 型( 70%) ,2 株为hlyA + toxR + zot + 型 ( 20%) ,1 株为hlyA + toxR + ompU + tcpI +型。
16 株水产品来源的菌株中,11 株为小川型,4 株为稻叶型,1 株为O139 群菌株。11 株小川型菌株中,各有2 株为hlyA + toxR + ompU + ace + zot + tcpA + tcpI + 型,hlyA + toxR + ompU + ace + zot + tcpA + 型,hlyA + toxR + ompU + tcpA + 型和hlyA + toxR + ompU + tcpI + 型,另外,各有1 株为hlyA + toxR + ompU + zot + tcpI + 型、 hlyA + toxR + ompU + tcpA + tcpI + 型和hlyA + toxR + tcpI + 型。4 株稻叶型菌株中3 株为hlyA + toxR + ompU + tcpI +型( 75.00%) ,1 株为hlyA + toxR + tcpI + 型。1 株 O139 群菌株为hlyA + toxR + ompU + tcpI + 型。同期病例分离株中,2 株稻叶型和1 株O139 群菌株为产毒株,含ctxA 在内的8 种所测毒力基因。1 株小川型菌株基因型为hlyA + toxR + ompU + zot + tcpA + tcpI + 型,另外1 株为hlyA + toxR + tcpA +型。
3 讨论外环境中大多数非致病性的霍乱弧菌,经过复杂的进化和变异,某些特定的菌株可通过获得毒力而有效定殖在人类小肠并释放肠毒素致病,其过程涉及多个毒力因子的协调作用[4]。本研究发现,外环境来源的O1 /O139 群霍乱弧菌毒力基因携带和分型呈多样性。其中,有28 株( 31.11%) 毒力基因型别为ctxA-、ace +、zot +,全部为外环境菌株。有5 株( 5.56%) 菌株的毒力基因型别为ctxA -,ace-,zot +,包括1 株病例来源的小川型菌株,与芮勇宇等[5]的研究结果一致,表明CTX 元件上存在着至少 1 种基因的缺失,尤其是外环境霍乱弧菌菌株。对于tcpA 基因的检测发现,tcpA +,ctxA + /ace + /zot + 的菌株有9 株( 10%) ,而tcpA-,ctxA + /ace + /zot + 的菌株有27 株( 30%) ,与Heilpern 等[6]的结果一致,提示噬菌体CTXФ 在霍乱弧菌间的水平转移可能存在毒素共调协菌毛( Toxin-Coregulated Pilus,TCP) 以外的途径。此外,在所有菌株中均检测出toxR 和hlyA 基因,44 株( 48.89%) 霍乱弧菌含有tcpI 基因,64 株 ( 71.11%) 霍乱菌株携带ompU 基因,提示其不仅仅有病理学意义,还有更重要的生理学意义[7]。
| [1] | Faruque SM,Chowdhury N,Kamruzzaman M,et al.Genetic diversity and virulence potential of environmental Vibrio cholerae population in a cholera-endemic area[J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2004,101(7):2123-2128. |
| [2] | 严寒秋,李伟,吴疆,等.一起由非产毒霍乱弧菌引发腹泻暴发的调查[J].中华流行病学杂志,2006,27(10):918-919. |
| [3] | Singh DV,Matte MH,Matte GR,et al.Molecular analysis of Vibrio cholerae O1,O139,non-O1,and non-O139 strains:clonal relationships between clinical and environmental isolates[J].Appl Environ Microbiol,2001,67:910-921. |
| [4] | Bakhshi B,Pourshafie MR,Navabakbar F,et al.Comparison of distribution of virulence determinants in clinical and environmental isolates of Vibrio cholera[J].Iranian Biomedical Journal,2008,12(3):159-165. |
| [5] | 芮勇宇,阚飙,高守一,等.霍乱弧菌新类型溶源性噬菌体基因组结构研究[J].中国公共卫生,2007,23(4):406-408. |
| [6] | Heilpern AJ,Waldor MK.CTXphi infection of Vibrio cholerae requires the tolQRA gene products[J].J Bacteriol,2000,182(6):1739-1747. |
| [7] | Karunasagar I,Rivera I,Joseph B,et al.ompU genes in non-toxigenic Vibrio cholerae associated with aquaculture[J].J Appl Microbiol,2003,95:338-343. |
 2012, Vol. 28
2012, Vol. 28
