2. 中国医科大学公共卫生学院劳动卫生教研室
饮水型砷中毒是中国主要地方病之一〔1〕。无机砷(inorganicarsenic,iAs)进入人体后,被甲基化代谢形成一甲基胂(monomethylarsonicacid,MMA)和二甲基胂(dimethylarsenicacid,DMA)〔2〕。蛋氨酸(methionine,Met)在砷甲基化代谢中起重要作用〔3〕。一氧化氮(nitricoxide,NO)是中枢神经系统中的重要信使分子〔4〕。砷对脑中NO水平及相关代谢酶活性的影响可能是砷对中枢神经系统毒作用的重要途径之一。本研究通过给予砷暴露小鼠不同剂量Me,t探讨其对小鼠脑中砷形态及NO代谢影响,为砷中毒防治提供理论依据。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试剂与仪器亚砷酸钠(NaAsO2)(上海分析试剂厂),分析纯,Met(美国Sigma公司),优级纯;一氧化氮合酶(NOS)与NO试剂盒(南京建成生物工程研究所);分光光度计(上海凤凰光学仪器公司)。
1.2 实验动物健康雌性清洁级昆明种小鼠(中国医科大学实验动物中心)40只,体重(25.0±2.0)g。动物室温度(20±2)℃,相对湿度为50%~60%,适应性喂养1周。
1.3 分组与处理将小鼠随机分为5组,分别为对照、染砷组及低、中、高剂量Met干预组,每组8只小鼠。对照组小鼠饮蒸馏水,其余各组小鼠自由饮用含砷水(50mg/L),连续4周。在第4周,低、中、高Met干预组分别腹腔注射100,200,400mg/kgMet溶液(生理盐水配制),对照与染砷组腹腔注射生理盐水,共7d。末次注射24h后,处死小鼠,取血和脑组织,保存于-40℃冰箱待测。
1.4 砷含量测定取50mg脑组织,加入1.0mL三蒸水,制成组织匀浆,并与2.0mL1.5mol/LH2SO4混合;取0.1mL全血与2.0mL1.0mol/LH2SO4混合。超声消化10min。采用氢化物发生-超低温捕集-原子吸收分光光度法(HG-AAS)测定消化液中iAs、MMA和DMA含量。并计算血和脑组织中总砷含量(TAs=iAs+MMA+DMA)。
1.5 NOS活性及NO含量测定按试剂盒说明书进行。
1.6 统计分析采用SPSS 13.0进行统计分析。多组间比较采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA),组间两两比较采用q检验(SNK),以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
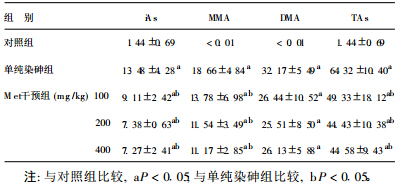
2 结 果 2.1 各组小鼠血中不同形态砷含量比较 (表 1)| 表 1 各组小鼠血中不同形态砷含量比较 ( x± s, ng /mL, n= 8) |
单纯染砷组及各Met干预组小鼠血中iAs、MMA、DMA和TAs含量均明显高于对照组(P<0.05)。各Met干预组小鼠血中iAs、MMA和TAs含量与单纯染砷组比较均明显降低(P<0.05)。对照组小鼠血中MMA和DMA含量未检出。
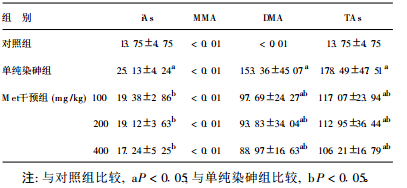
2.2 各组小鼠脑中不同形态砷含量比较 (表 2)| 表 2 各组小鼠脑中不同形态砷含量的比较 ( x± s, ng /mL, n= 8) |
单纯染砷组小鼠脑中iAs、DMA和TAs含量均明显高于对照组(P<0.05)。各剂量Met干预组小鼠脑中iAs、DMA和TAs含量与单纯染砷组比较均明显降低(P<0.05)。各组小鼠脑中MMA含量及对照组小鼠脑中DMA均未检出。
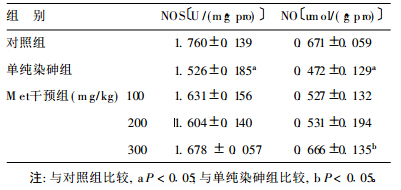
2.3 各组小鼠脑组织NOS活性和NO含量比较 (表 3)| 表 3 各组小鼠脑组织NOS活性与NO含量的比较 ( x± s , n= 8) |
单纯染砷组小鼠脑组织NOS活性和NO含量与对照组比较明显降低;各Met干预组小鼠脑组织NOS活性和NO含量与单纯染砷组比较均有升高,并与对照组比较差异无统计学意义,高剂量Met干预组小鼠脑中NO含量与单纯染砷组比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。
3 讨 论iAs与其甲基代谢物由肝脏入血后,随血液循环进入机体其他组织器官。研究表明,某些肝外组织也具有砷甲基化代谢能力〔5〕。本研究结果表明,Met干预可明显降低小鼠血中iAs、MMA及TAs的含量,提示Met通过促进iAs在体内的甲基化代谢过程,有效降低了血液中的砷负荷。NO在中枢神经系统中起重要生理调节作用,NO含量变化会严重影响脑组织功能。本研究发现,单纯染砷组小鼠脑中NOS活性和NO含量明显低于对照组,与SergioZ等〔6〕研究结果一致,进一步证明砷暴露可明显干扰脑组织NO代谢。给予Met可有效降低进入脑中的iAs、DMA及TAs含量,从而减少了脑组织的砷暴露水平,可能与Met有效降低血中各形态砷的含量有关。Met干预可提升小鼠脑组织NOS活性和NO含量,明显改善砷对脑组织NO代谢的影响,可能与外源性Met降低了脑中的砷负荷有关。
| 〔1〕 | Sun G F,Sun G,Xu Y,et al.Urinary arsenic metabolites in children and adults exposed to arsenic in drinking water in Inner Mongolia,China[J].Environ Health Perspect,2007,115(4):648-652. |
| 〔2〕 | 徐苑苑,李昕,梁秀芬,等.内蒙古不同浓度砷暴露人群尿砷代谢产物研究[J].中国公共卫生,2006,22(8):956-957. |
| 〔3〕 | Craig S,Kenichi C,DaveK,et al.Dietary in take and arsenicm ethylation in a U.S.population[J].Environ Health Perspec,t 2005,113:1153-1159. |
| 〔4〕 | Koesling D,Russwurm M,Merdia E,et al.Nitricoxide sensitive guanylyl cyclase:structure and regulation[J].Neurochem Int,2004,45(6):813-819. |
| 〔5〕 | Rodr guez VM,Del Razo LM.Glutathione reductase inhibition and methylated arsenic distribution in Cd1 mice brain and liver[J].Toxicol Sci,2005,84:157-166. |
| 〔6〕 | Sergio Z,Fran cisca PS,Juan M D,et al.Decreased nitric oxide production in the rat brain after chronic arsenic exposure[J].Neuro chem Res,2006,31:1069-1077. |
 2010, Vol. 26
2010, Vol. 26