2. 中国石油大学 (华东)石油工程学院, 山东 青岛 266555
2. College of Petroleum Engineering, China University of Petroleum(East China), Qingdao 266555, Shandong, China
我国海上油田储层厚度大、含油层系多,层间和层内矛盾突出[1-4],同时海上油田开发又具有高风险、高投入的特点,因此,多采用强注强采的高效开发模式[5-6],而长期注水冲刷进一步加剧了储层非均质性,导致油井含水率上升快,产量递减迅速[7-10]。此外,由于海上油田注水水质差、强度高,使得水井注入压力高、近井地带污染严重[11-12]。
针对海上油田的储层特征以及开发特点,提出了集调剖、驱油、增注于一体的自生CO2调驱技术[13-15],该技术采用分段塞注入生气剂和释气剂方式,使二者直接在储层中反应并形成CO2泡沫体系,优先封堵高渗透层,扩大后续水驱波及体积[16-17],同时酸性的释气剂及反应产生的热量能够有效解除近井地带无机和有机堵塞,恢复储层渗透率[18]。结合海上油田的储层特征,采用物理模拟实验的手段弄清储层纵向非均质性对自生CO2调驱效果的影响规律,再通过矿场试验,考察自生CO2调驱技术的适用性及稳油控水效果[19-20],以期为该技术在海上油田的推广应用提供支持。
1 实验部分 1.1 材料与仪器表 1为海上某油田地层原油性质。自生CO2调驱体系,包括生气剂(碳酸氢钠,分析纯)、释气剂(盐酸,工业纯)和助剂(起泡剂、稳泡剂等);模拟油田地层水,矿化度为1万mg/L;层间和层内非均质岩心,3层等厚,人工压制,基本参数如表 2和表 3所列。实验装置如图 1所示。
|
|
下载CSV 表 1 渤海某油田地层原油性质(65 ℃) Table 1 Properties of crude oil in an oilfield in Bohai Sea |
|
|
下载CSV 表 2 层内非均质物理模型基本参数 Table 2 Basic parameters of in-layer heterogeneity model |
|
|
下载CSV 表 3 层间非均质物理模型基本参数 Table 3 Basic parameters of inter-layer heterogeneity model |
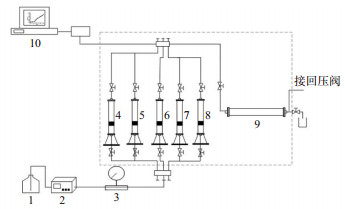
|
下载原图 图 1 实验装置流程 1.水罐;2.平流泵;3.压力表;4~8.中间容器罐;9.岩心夹持器;10.数据采集装置 Fig. 1 Flow chart of experiment |
实验步骤如下:①称量非均质岩心的质量,抽真空并饱和地层水后再次称取其质量;②向岩心饱和原油,通过计量油驱水的体积计算出原始含油饱和度;③对岩心进行水驱,至出口端含水率达到98%时停止;④对岩心进行自生CO2调驱,注入段塞组合如表 4所列,注入方式为4段塞式按顺序依次注入;⑤对岩心进行后续水驱,至出口端含水率达到98%时停止。记录驱替过程中油水的产量,并评价自生CO2调驱体系的驱油效果。实验时设定温度为65 ℃,手摇泵回压为10 MPa,岩心夹持器围压为15 MPa。
|
|
下载CSV 表 4 注入段塞组合设计 Table 4 Design of injection slug combination |
为了考察层内非均质性对自生CO2调驱效果的影响,分别选用1号、2号和3号岩心模型进行驱替实验,含水率、采收率以及驱替压力变化如图 2所示。
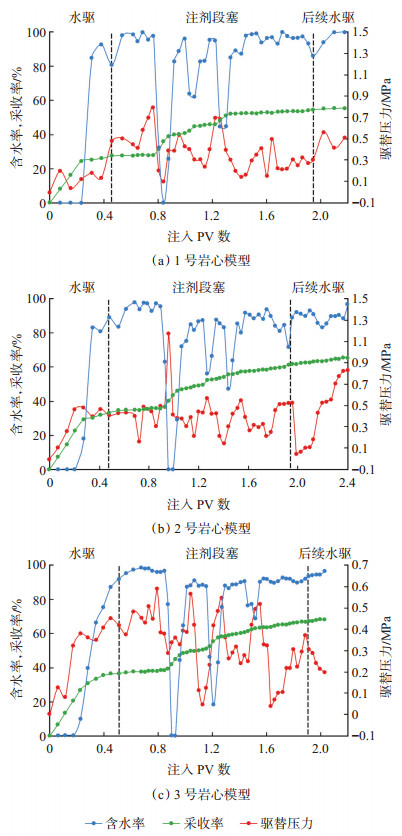
|
下载原图 图 2 层内非均模型驱替过程中含水率、采收率和驱替压力变化曲线 Fig. 2 Curves of water cut, recovery and displacement pressure during displacement in in-layer heterogeneity model |
为便于对实验结果进行分析,引入储层渗透率均值,即
| $ \bar k = \frac{{\sum\nolimits_{j = 1}^n {{k_i}} {h_i}}}{{\sum\nolimits_{j = 1}^n {{h_i}} }} $ | (1) |
式中:k为某小层渗透率,mD;h为某小层厚度,cm。
从图 2可以看出,水驱阶段1~3号岩心的采收率分别为27.69%,34.91%和37.38%,表明渗透率级差一定时,水驱采收率随储层渗透率均值k的增大而逐渐增大;注自生CO2调驱体系阶段,含水率急剧下降,产油量迅速增加,驱替压力波动明显,后续水驱后1~3号岩心的采收率分别提高了27.40%,30.60%和31.03%,说明自生CO2调驱技术对层内非均质模型提高采收率效果显著。
2.2 层间非均质性影响规律 2.2.1 储层渗透率均值为了考察层间非均质性对自生CO2调驱效果的影响,分别采用4~15号岩心模型进行驱替实验。首先通过4~6号岩心驱替实验研究了储层渗透率均值k对调驱效果的影响规律,实验结果如图 3和图 4所示。
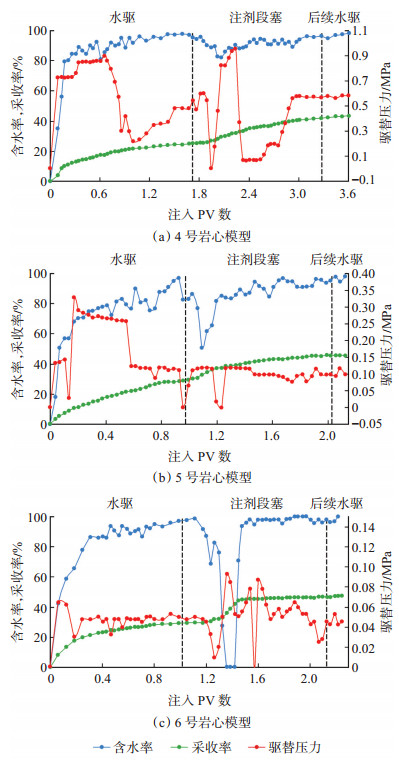
|
下载原图 图 3 层间非均质模型驱替过程中含水率、采收率和驱替压力变化曲线 Fig. 3 Curves of water cut, recovery and displacement pressure during displacement in inter-layer heterogeneity model |
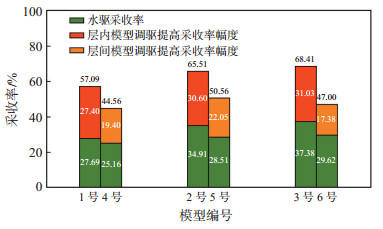
|
下载原图 图 4 层内、层间非均质模型调驱效果对比 Fig. 4 Comparison of profile control effects between in-layer and interlayer heterogeneity model |
由图 3和图 4可以看出,经自生CO2调驱后4~6号岩心的采收率分别增加了19.40%,22.05%和17.88%,说明自生CO2调驱技术对层间非均质模型也有很好的增油效果,但提高采收率幅度不及层内非均质模型。
2.2.2 渗透率级差实验还考察了层间非均质模型渗透率级差对自生CO2调驱效果的影响。选取7~15号层间非均质岩心模型进行驱替实验,实验结果如表 5所列。
|
|
下载CSV 表 5 不同渗透率级差下自生CO2调驱效果 Table 5 Effects of in-situ CO2 profile control and flooding under different permeability ratios |
将9块岩心分为3组(7~9号、10~12号、13~15号各为一组)进行对比,可以发现中、低渗透层相同的情况下,模型渗透率级差越大,自生CO2调驱提高采收率的幅度越大。这是由于自生CO2调驱的调剖效果有限,当液流无法发生转向时,渗透率级差越大,即高渗透层的渗透率越大,其孔隙体积越大,水驱后的可采油量越多,注入调驱体系时贡献的采油量也越多,高采收率幅度也随之增大。
为了进一步分析层间非均质模型渗透率对自生CO2调驱效果的影响,将4~15号岩心的自生CO2调驱采收率增值与其渗透率均值k的关系做图(图 5)。
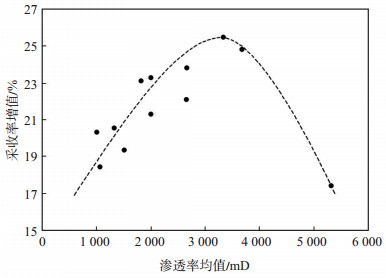
|
下载原图 图 5 采收率增值与渗透率均值的关系 Fig. 5 Relationship between recovery increment and permeability mean value |
从图 5可以看出,随着k值增大,岩心采收率提高幅度呈现出先增大后减小的变化规律。这主要是因为一方面随着k值增大,介质孔隙和喉道的直径均加大,有利于自生气体系反应的进行,但另一方面因体系的调剖能力有限,k值过大时易在岩心形成窜流通道,反而会中和掉部分有利的因素。因此,当渗透率均值高于4 000 mD时,提高采收率幅度会逐渐下降。该技术的k值适用于2 000~4000 mD,在该范围内自生CO2调驱技术提高采收率的增幅均高于20%。
3 矿场试验海上C油田存在的主要问题有注水强度大[水井平均注水强度为12.6 m3/(d·m),平均日注水量为867 m3]、储层渗透率级差大(渗透率级差为1.26~4.66)、各层吸水不均,致使周边油井注水突破,含水率上升迅速。为了缓解层间矛盾,减少无效注水,提高砂体采收率,2017—2018年先后对C油田5口注水井进行了自生CO2调驱矿场试验,累计注入药剂5 699 m3,措施实施后实现累计增油14 446 m3,取得了显著的稳油控水效果(表 6)。
|
|
下载CSV 表 6 措施实施效果 Table 6 Profile control and flooding effects |
(1)对于层内非均质模型,随着储层渗透率均值k的增大,自生CO2调驱在水驱基础上提高采收率幅度从27.4%增加到31.03%,表明k值对调驱效果的影响较小,自生CO2调驱可以很好地解决层内矛盾;对于层间非均质模型,随着k值的增大,自生CO2调驱在水驱基础上提高采收率幅度从17.38%增加到22.05%,表明k值对调驱效果的影响层间非均质模型大于层内非均质模型。
(2)对于层间非均质模型,当中—低渗透层渗透率一定时,自生CO2调驱提高采收率的效果随着渗透率级差的增大而变好。
(3)对于层间非均质模型,自生CO2调驱提高采收率幅度随k值的增大呈现出先增加后减小的趋势。自生CO2调驱技术的k值适用于2 000~4 000 mD,在该范围内自生CO2调驱提高采收率幅度大于20%。矿场试验结果表明,自生CO2调驱技术在海上油田具有良好的适用性。
| [1] |
梁爽, 刘义坤, 张玮, 等. 纵向非均质性对海上稠油油田水驱油开发效果的影响研究. 数学的实践与认识, 2017, 47(1): 128-134. LIANG S, LIU Y K, ZHANG W, et al. Influence of vertical heterogeneity on the water flooding development effect in offshore heavy oilfield. Mathematics in Practice and Theory, 2017, 47(1): 128-134. |
| [2] |
高尚, 张璐, 刘义刚, 等. 渤海油田聚驱受效井液气交注复合深部解堵工艺. 石油钻采工艺, 2017, 39(3): 375-381. GAO S, ZHANG L, LIU Y G, et al. In-depth combined blockage removing technology with liquid alternating gas injection for polymer flooding response wells in Bohai Oilfield. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2017, 39(3): 375-381. |
| [3] |
胡治华, 马奎前, 刘宗宾, 等. 海上S油田注水开发后期储层物性变化规律及应用. 科学技术与工程, 2014, 14(15): 164-168. HU Z H, MA K Q, LIU Z B, et al. Research and application of the properties variation regularity of water injection reservoirs in S offshore oilfield. Science Technology and Engineering, 2014, 14(15): 164-168. |
| [4] |
王婷婷, 卢祥国, 陈阳, 等. 渤海油田大尺寸优势通道封堵剂性能评价. 油气地质与采收率, 2017, 24(6): 103-107. WANG T T, LU X G, CHEN Y, et al. Performance evaluation of plugging agent for large-size preferential channels in Bohai Oilfield. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2017, 24(6): 103-107. |
| [5] |
周焱斌, 何逸凡, 章威, 等. 海上注水开发油田单井经济极限含水率分析. 岩性油气藏, 2019, 31(3): 130-134. ZHOU Y B, HE Y F, ZHANG W, et al. Economic limit water cut of single well in offshore waterflooding oilfield. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2019, 31(3): 130-134. |
| [6] |
李廷礼, 刘彦成, 于登飞, 等. 海上大型河流相稠油油田高含水期开发模式研究与实践. 地质科技情报, 2019, 38(3): 141-146. LI T L, LIU Y C, YU D F, et al. Innovation and practice of development mode in high water-cut stage of large offshore fluvial heavy oilfield. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2019, 38(3): 141-146. |
| [7] |
张保康, 徐国瑞, 铁磊磊, 等. "堵水+调剖"工艺参数优化和油藏适应性评价:以渤海SZ36-1油田为例. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(5): 155-161. ZHANG B K, XU G R, TIE L L, et al. Optimization of technological parameters and evaluation of reservoir adaptation by water plugging and profile control:a case from Bohai SZ36-1 oilfield. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2017, 29(5): 155-161. |
| [8] |
刘光普, 刘述忍, 李翔, 等. 淀粉胶体系调剖性能的影响因素. 石油钻采工艺, 2018, 40(1): 118-122. LIU G P, LIU S R, LI X, et al. Factors influencing the profile control performance of starch gel. Oil Drilling & Production Technology, 2018, 40(1): 118-122. |
| [9] |
张云宝, 薛宝庆, 卢祥国. 渤海油田多轮次凝胶调驱参数优化实验研究:以LD5-2油田A22井为例. 石油与天然气化工, 2015, 44(4): 87-92. ZHANG Y B, XUE B Q, LU X G. Experimental study of parameters optimization of rotational profile control operations in Bohai Oilfield:an example of A22 well in LD5-2 Oilfield. Chemical Engineering of Oil and Gas, 2015, 44(4): 87-92. |
| [10] |
耿艳宏. 海上油田注水开发效果评价. 石油地质与工程, 2018, 32(4): 83-86. GENG Y H. Effectiveness evaluation of water injection development in offshore oilfields. Petroleum Geology and Engineering, 2018, 32(4): 83-86. |
| [11] |
陈华兴, 高建崇, 唐晓旭, 等. 绥中36-1油田注聚井注入压力高原因分析及增注措施. 中国海上油气, 2011, 23(3): 189-192. CHEN H X, GAO J C, TANG X X, et al. Cause analysis of high injection pressure and measure of augmented injection in polymer injectors of SZ 36-1 oilfield. China Offshore Oil and Gas, 2011, 23(3): 189-192. |
| [12] |
靳国兴, 夏宏南. 海上油田注水井缓速酸深部酸化解堵增注技术研究. 当代化工, 2019, 48(2): 323-325. JIN G X, XIA H N. Research of retarded acid deep acidification blocking removal and augmented injection technology for water injection wells in offshore oilfields. Contemporary Chemical Industry, 2019, 48(2): 323-325. |
| [13] |
张博, 徐景亮, 李翔, 等. 层内生成CO2技术提高采收率机理研究及应用. 西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 32(3): 94-98. ZHANG B, XU J L, LI X, et al. Mechanism research and application of enhancing oil recovery by in-situ CO2 generating technology. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2017, 32(3): 94-98. |
| [14] |
张国萍, 肖良, 胡艳霞, 等. 层内生气提高采收率技术在中原断块油田的应用. 油气地质与采收率, 2004, 11(5): 60-61. ZHANG G P, XIAO L, HU Y X, et al. Applications of in situ gas generating for enhanced oil recovery to Zhongyuan faulted block oilfield. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency, 2004, 11(5): 60-61. |
| [15] |
林波, 蒲万芬, 赵金洲, 等. 利用就地CO2技术提高原油采收率. 石油学报, 2007, 28(2): 98-101. LIN B, PU W F, ZHAO J Z, et al. In-situ carbon dioxide-generation technology applied to enhance oil recovery. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2007, 28(2): 98-101. |
| [16] |
杨红, 王宏, 南宇峰, 等. 油藏CO2驱油提高采收率适宜性评价. 岩性油气藏, 2017, 29(3): 140-146. YANG H, WANG Y, NAN Y F, et al. Suitability evaluation of enhanced oil recovery by CO2 flooding. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2017, 29(3): 140-146. |
| [17] |
李友全, 孟凡坤, 阎燕, 等. 考虑流体非均质性的低渗透油藏CO2驱试井分析. 岩性油气藏, 2016, 28(4): 106-112. LI Y Q, MENG F K, YAN Y, et al. Pressure transient analysis on CO2 flooding in low permeability reservoirs considering fluid heterogeneity. Lithologic Reservoirs, 2016, 28(4): 106-112. |
| [18] |
何吉波, 陈蕾, 赵海涛, 等. 稠油油藏自生CO2吞吐油藏参数敏感性研究. 复杂油气藏, 2018, 11(2): 62-65. HE J B, CHEN L, ZHAO H T, et al. Parametric sensitivity research of heavy-oil reservoir by self-generating carbon dioxide huff-n-puff. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2018, 11(2): 62-65. |
| [19] |
汤勇, 汪勇, 邓建华, 等. 自生CO2结合表面活性剂复合吞吐数值模拟. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 35(4): 107-113. TANG Y, WANG Y, DENG J H, et al. Numerical simulation on increasing oil recovery by in-situ-generated CO2 compound surfactant huff-puff. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2013, 35(4): 107-113. |
| [20] |
张相春, 张军辉, 宋志学, 等. 绥中36-1油田泡沫凝胶调驱体系研究与性能评价. 石油与天然气化工, 2012, 41(4): 419-421. ZHANG X C, ZHANG J H, SONG Z X, et al. Performance evaluation control of foam gel and study of flooding in SZ36-1 oilfield. Chemical Engineering of Oil and Gas, 2012, 41(4): 419-421. |
 2020, Vol. 32
2020, Vol. 32



