2. 天津中医药大学第一附属医院分子生物学实验室, 天津 300193
2. Laboratory of Molecular Biology, First Teaching Hospital of Tianjin University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Tianjin 300193, China
阿尔茨海默病(Alzheimer's disease, AD)是老年人中最常见的中枢神经系统退行性疾病, 全世界超过3 700万人罹患AD[1]。阿尔茨海默病中β-淀粉样蛋白(β-amyloid, Aβ)理论在过去的20年一直受到科学界的认可和关注, 不断开发出许多的药物来消除Aβ斑块, 抑制Aβ聚集和沉积, 或通过抑制γ-分泌酶和β-分泌酶来降低脑内Aβ的生成, 但这些治疗策略在临床试验中均以失败而告终[2]。目前, 以拮抗tau蛋白磷酸化为靶点的药物研究越来越引起关注[3-5]。
Tau蛋白是脑内一种微管相关蛋白, 其磷酸化受蛋白激酶和蛋白磷酸酯酶的调节维持平衡。蛋白磷酸酯酶2A (protein phosphatase 2A, PP2A)是促进tau蛋白去磷酸化的主要调节酶, 在抑制AD患者脑中tau蛋白过度磷酸化方面起关键作用, 研究发现, 在AD患者脑中PP2A活性明显下降[6, 7]。研究PP2A激活剂成为目前AD药物研究的新策略[8, 9]。
山茱萸环烯醚萜苷(cornel iridoid glycoside, CIG)是我室从山茱萸中提取的主要有效部位。在前期研究中发现, CIG能够改善拟AD大鼠模型的学习记忆功能[10, 11], 并且在PP2A抑制剂冈田酸(okadaic acid, OA)拟AD细胞模型上能够抑制tau蛋白过度磷酸化, 保护微管结构, 减少细胞凋亡, 能够通过抑制PP2A催化亚基C (PP2Ac)的去甲基化而恢复PP2A的活性[12, 13]。
有研究报告, PP2Ac的翻译后修饰除了甲基化以外, 还包括磷酸化[14]。酪氨酸激酶Src的活化能够促进PP2Ac的磷酸化[15]。本实验的目的是研究CIG对OA拟AD细胞模型PP2Ac磷酸化及其调节酶Src的影响, 以进一步明确CIG恢复PP2A活性的机制。
材料与方法药物 CIG由本室自行研制。山茱萸为市售(产地:浙江), 经提取和分离获得CIG, 纯度为70% (其中主要成分为莫诺苷和马钱苷), 达到国家中药、天然药物5类新药的要求。CIG为棕黄色粉末, 水溶性好。实验中采用干粉剂量, 溶解于蒸馏水, 制成药液应用。
试剂 OA、aprotinin、leupeptin、多聚赖氨酸和Triton X-100 (美国Sigma-Aldrich公司); DMEM基础培养液、胎牛血清(FBS)和胰蛋白酶(美国Gibco BRL公司); Opti-MEM (美国Invitrogen公司); RC-DC蛋白测定试剂盒(500-0122-MSDS, 美国Bio-Rad公司); PP2A活性测定试剂盒(美国Promega公司)。主要抗体详见表 1。
| Table 1 Primary antibodies used in this study. Poly-: Polyclonal; Mono-: Monoclonal; PP2Ac: Protein phosphatases 2A catalytic subunit C; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
主要仪器 二氧化碳培养箱(Tc2323型, 美国SHELL/JB公司); 全波长酶标仪(Multiskan Spectrum, 法国巴德斯公司); 低温高速台式离心机(Beckman 22R, 美国Beckman公司); 电泳仪、垂直型电泳槽、转膜仪和凝胶电泳分析系统(美国Bio-Rad公司)。
细胞培养 人神经母细胞瘤细胞株(SK-N-SH细胞)在5% CO2、37 ℃培养箱内进行培养, 每2~3天更换1次培养基。细胞生长至60%~70%丰度时, 传代或用于实验。细胞接种于12孔、24孔或96孔培养板中, 备用。
细胞模型的制备及药物处理 将不同浓度CIG (50、100、200 μg·mL-1)与SK-N-SH细胞预孵育24 h后弃去药液, 加入OA (20 nmol·L-1)处理6 h后, 收集细胞并进行裂解。
Western blot法检测蛋白质表达 SDS-PAGE电泳分离蛋白, 溴酚蓝到达分离胶底部时, 结束电泳。安装湿转装置, 在转移槽的阴极铺2层滤纸, 小心将胶平铺于滤纸上, 并在胶上铺硝酸纤维素膜, 将剩余2层滤纸铺在膜的上方。接通电源, 设定100 V, 90 min。转膜后, 硝酸纤维素膜用Tris buffered saline with Tween 20 (TBST)轻轻漂洗, 然后置于5%脱脂奶粉封闭液中, 4 ℃过夜; 弃去封闭液, TBST洗膜1次。加入适当浓度的第一抗体(抗特异蛋白质的抗体, 表 1), 置于摇床上摇动, 室温下2 h; 倾去一抗, TBST洗膜3次。加入相应的二抗, 置于摇床上摇动, 室温下1 h; 弃去二抗, TBST洗膜3次。在暗室将荧光剂A液和B液等量混合, 立即加到膜上, 每张膜1 mL, 滚匀液体, 反应1 min, 然后吸去多余荧光剂, 采用化学发光仪进行图像采集及分析。
PP2A活性测定 按照PP2A活性测定试剂盒说明书进行操作。在含有40 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl (pH 8.5)、20 mmol·L-1 β-巯基乙醇(β-mercaptoethanol, β-ME)、0.2 mmol·L-1 CaCl2和15 mmol·L-1 MgCl2的缓冲液中, 用磷酸化酶b中和0.5 mmol·L-1 [γ-32P] ATP和10 mg·L-1磷酸化酶激酶, 经30 min孵育, 一部分被γ-32P ATP标记的、由磷酸化酶b转变的磷酸化酶a, 经Sephadex G-50柱层析出, 收集含γ-32P ATP标记的磷酸化酶a (标记率 > 70%), 作为PP2A底物, 根据PP2A催化的、γ-32P标记的磷酸化酶a所释放γ-32P的释放量, 判定PP2A的活性。反应总体积为20 μL, 含50 mmol·L-1 Tris-HCl (pH 7.0)、10 mmol·L-1 β-ME、0.1 mmol·L-1 EDTA、7.5 mmol·L-1 cafreine、7.5 mg·L-1 [γ-32P]磷酸化酶a、0.06 g·L-1细胞提取物和抑制因子-1 (PP-1的特异性抑制剂), 用20%三氯乙酸终止反应, 取7 μL反应混合物至层析纸上, 释放出γ-32P在5%三氯乙酸(0.2 mol·L-1 NaCl溶解)层析液中通过上行色谱法与底物分离, 经Cerenkov闪烁液进行闪烁计数分析。
统计学方法 用SPSS16.0软件分析实验数据, 数据以均数±标准误(x± s)表示, 组间样本比较应用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA), 以P < 0.05为差异有显著统计学意义。用Origin 8将数据转换为图表。
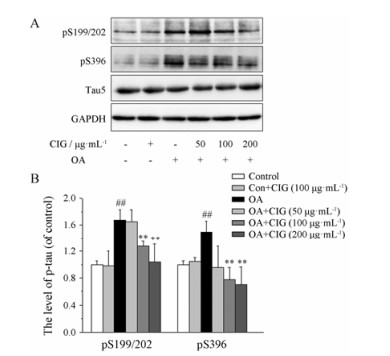
结果 1 CIG对OA拟AD细胞模型tau蛋白过度磷酸化的影响OA是PP2A的特异性抑制剂。本实验将CIG与人神经母细胞瘤细胞株(SK-N-SH细胞)预孵育24 h后换液, 加入OA处理, 6 h后收集细胞, 应用Western blot法检测tau蛋白的磷酸化水平。结果显示, OA能够显著增高细胞内tau蛋白在Ser 199/Ser 202 (S 199/202)位点及Ser 396 (S 396)位点的磷酸化(P < 0.01); CIG (100和200 μg·mL-1)能够明显降低模型细胞内tau蛋白在S 199/202位点及S 396位点的磷酸化水平(P < 0.01); CIG (100 μg·mL-1)对正常细胞无明显影响(图 1)。
|
Figure 1 Effect of cornel iridoid glycoside (CIG) on tau hyper- phosphorylation in okadaic acid (OA)-induced cells, cells were exposed to OA for 6 h after incubation with CIG (50, 100, 200 μg·mL-1). A: The levels of tau phosphorylation at different sites were detected by Western blot. pS 199/202: Tau phosphorylation at Ser 199/Ser 202; pS 396: Tau phosphorylation at Ser 396; Tau 5: Total 5. B: Quantitative analysis of tau phosphorylation. n = 3, x± s. ##P < 0.01 vs control group; **P < 0.01 vs model group |
采用试剂盒检测各组细胞内PP2A活性。结果显示, OA与SK-N-SH细胞孵育6 h后, 细胞内PP2A活性显著降低(P < 0.05); CIG (50和100 μg·mL-1)预孵育24 h能够明显恢复OA模型细胞内PP2A活性(P < 0.05); CIG对正常对照细胞PP2A活性无影响(表 2)。
| Table 2 The effect of CIG on protein phosphatases 2A (PP2A) activity. The PP2A activity of control group was set as 100%. n = 3, x± s. #P < 0.05 vs control group; *P < 0.05 vs model group |
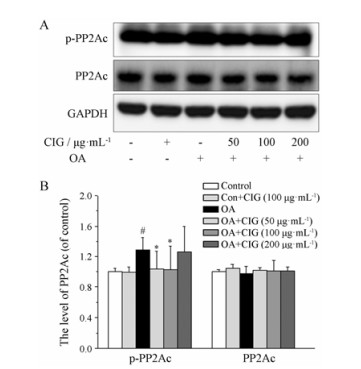
PP2Ac在Tyr 307位点的磷酸化水平增高能降低PP2A的活性[15-18]。为了明确CIG恢复PP2A活性的机制, 本实验采用Western blot方法检测磷酸化PP2Ac (p-PP2Ac)和总PP2Ac的表达。结果显示, SK-N-SH细胞经OA处理后, 细胞内PP2Ac在Tyr 307位点的磷酸化水平明显增高(P < 0.05); CIG (50和100 μg·mL-1)预孵育24 h能显著降低模型细胞PP2Ac的磷酸化水平(P < 0.05, 图 2)。
|
Figure 2 The effect of CIG on phosphorylation of PP2Ac in OA-induced cells, cells were exposed to OA for 6 h after the incubation with CIG (50, 100, 200 mg·mL-1). A: The levels of PP2Ac and phosphorylated PP2Ac (p-PP2Ac) at Tyr 307 site were detected by Western blot; B: Quantitative analysis of PP2Ac and p-PP2Ac. n = 3, x± s. #P < 0.05 vs control group; *P < 0.05 vs model group |
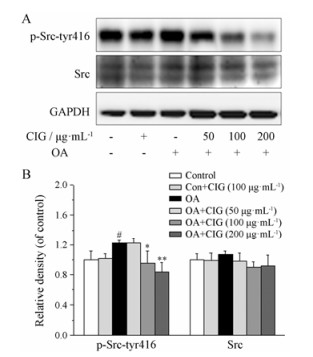
酪氨酸激酶Src在Tyr 416位点的磷酸化能够使酶激活, 从而促进PP2Ac的磷酸化[14]。为了进一步探讨CIG抑制PP2Ac磷酸化的作用机制, 本实验采用Western blot方法测定细胞内Src在Tyr 416位点的磷酸化(p-Src-tyr 416)及总Src的表达。结果显示, SK-N-SH细胞经OA处理后, Src在Tyr 416位点的磷酸化水平明显增高(P < 0.05); CIG (100和200 μg·mL-1)预孵育24 h能够显著降低模型细胞Src在Tyr 416位点的磷酸化水平(P < 0.05, P < 0.01), 见图 3。
|
Figure 3 The effect of CIG on phosphorylation of Src in OA-induced cells, cells were exposed to OA for 6 h after the incubation with CIG (50, 100, 200 mg·mL-1). A: The levels of Src and phosphorylated Src (p-Src) at Ser 416 site were detected by Western blot; B: Quantitative analysis of Src and p-Src. n = 3, x± s. #P < 0.05 vs control group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs model group |
AD患者主要病理特征之一是在脑中出现大量由过度磷酸化tau蛋白聚集形成的神经原纤维缠结, 其含量与AD患者的痴呆严重程度密切相关[19], 表明过度磷酸化的tau蛋白在AD的发病机制中起重要作用。正常微管相关蛋白tau主要分布于细胞轴突及树突中, 具有促进管蛋白聚集成微管和维持微管结构的功能[20, 21]。本实验发现, CIG能够抑制OA诱导的tau蛋白过度磷酸化, 提示CIG可能通过保护微管而起到改善AD认知障碍的作用。
PP2A能够很大程度地使tau蛋白去磷酸化, 并能恢复tau蛋白促进微管组装的能力[22, 23]。为了明确CIG拮抗tau蛋白过度磷酸化的机制, 本实验采用PP2A特异性抑制剂OA制备拟AD细胞模型[24-26], 观察CIG对PP2A的影响。结果发现, CIG能够明显恢复OA模型细胞内PP2A的活性, 这可能是CIG拮抗tau蛋白异常过度磷酸化的重要机制。
PP2A由结构亚基A、调节亚基B及催化亚基C构成, C亚基独具PP2A的催化活性[27]。PP2Ac翻译后修饰异常可造成PP2A活性下降, PP2Ac的翻译后修饰主要包括磷酸化和甲基化[14]。作者前期研究发现, CIG能通过抑制PP2Ac的去甲基化而恢复PP2A的活性, 进而拮抗tau蛋白异常过度磷酸化[13]。本实验通过研究CIG对PP2Ac的磷酸化影响进一步揭示CIG恢复PP2A活性的机制。有研究报告, PP2Ac在Tyr 307位点的磷酸化增高能够抑制PP2A的活性[18]。AD脑中PP2Ac在Tyr 307位点的磷酸化明显增高, 且在皮层及海马的神经原纤维缠结中有大量磷酸化PP2Ac存在[16], 提示PP2Ac的磷酸化和tau蛋白磷酸化与AD密切关系。本实验发现, OA诱导PP2Ac在Tyr 307位点的磷酸化水平增高, 而CIG能够抑制模型细胞内PP2Ac在Tyr 307位点的过度磷酸化, 这可能是CIG增高PP2A活性的另一机制。
Src是一种位于细胞质的非受体酪氨酸蛋白激酶, 是Src家族中的一员[17, 28, 29]。Src在Tyr 416位点的磷酸化能够增加Src的活性, 从而促进PP2Ac的磷酸化[15]。本实验结果显示, OA诱导Src在Tyr 416位点的磷酸化水平增高, 而CIG能够抑制模型细胞内Src在Tyr 416位点的过度磷酸化, 提示可能减低Src的活性, 这可能是CIG抑制PP2Ac磷酸化的机制。
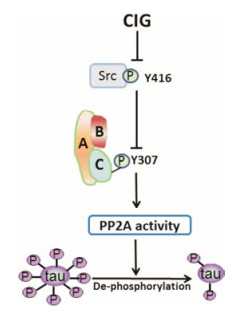
综上所述, CIG能够抑制OA诱导的tau蛋白异常过度磷酸化; 其作用机制为CIG通过抑制Src在Tyr 416位点的磷酸化减低其活性而降低PP2Ac的磷酸化, 从而恢复PP2A活性, 促进tau蛋白的去磷酸化(图 4)。本研究进一步阐明了CIG拮抗tau蛋白过度磷酸化的作用机制, 也为研发有效治疗AD的药物提供了实验数据。
|
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of CIG inhibiting tau hyper-phosphorylation. PP2A consists of a dimeric core enzyme composed of the structure A and catalytic subunit C, and a regulatory subunit B |
| [1] | Mullane K, Williams M. Alzheimer's therapeutics:continued clinical failures question the validity of the amyloid hypothesis-but what lies beyond?[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2013, 85: 289–305. DOI:10.1016/j.bcp.2012.11.014 |
| [2] | Yin M. Full-scale setback and thinking in R & D of Alzheimer's disease drug[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报), 2014, 49: 757–763. |
| [3] | Del Carmen Cárdenas-Aguayo M, Gómez-Virgilio L, DeRosa S, et al. The role of tau oligomers in the onset of Alzheimer's disease neuropathology[J]. ACS Chem Neurosci, 2014, 5: 1178–1191. DOI:10.1021/cn500148z |
| [4] | Mullard A. BACE inhibitor bust in Alzheimer trial[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2017, 16: 155. |
| [5] | Wischik CM, Harrington CR, Storey JM. Tau-aggregation inhibitor therapy for Alzheimer's disease[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2014, 88: 529–539. DOI:10.1016/j.bcp.2013.12.008 |
| [6] | Avila J, Pallas N, Bolós M, et al. Intracellular and extracellular microtubule associated protein tau as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer disease and other tauopathies[J]. Expert Opin Ther Targets, 2016, 20: 653–661. DOI:10.1517/14728222.2016.1131269 |
| [7] | Pachima YI, Zhou LY, Lei P, et al. Microtubule-tau interaction as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease[J]. J Mol Neurosci, 2016, 58: 145–152. DOI:10.1007/s12031-016-0715-x |
| [8] | Suzuki K, Iwata A, Iwatsubo T. The past, present, and future of disease-modifying therapies for Alzheimer's disease[J]. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B, 2017, 93: 757–771. DOI:10.2183/pjab.93.048 |
| [9] | Wu XL, Piña-Crespo J, Zhang YW, et al. Tau-mediated neurodegeneration and potential implications in diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer's disease[J]. Chin Med J, 2017, 130: 2978–2990. DOI:10.4103/0366-6999.220313 |
| [10] | Ding YX, Zhang L, Ye CF, et al. Effect of cornel iridoid glycoside on learning-memory ability and synaptophysin in fimbria-fornix transacted rats[J]. Chin J New Drugs (中国新药杂志), 2010, 19: 133–138. |
| [11] | Ma D, Zhu Y, Li Y, et al. Beneficial effects of cornel iridoid glycoside on behavioral impairment and senescence status in SAMP8 mice at different ages[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2016, 312: 20–29. DOI:10.1016/j.bbr.2016.06.008 |
| [12] | Chu YQ, Li W, Zhang L, et al. Effects of cornus officinalis iridoid glycoside on cellular model of Alzheimer disease induced by protein phosphatase inhibitor okadaic acid[J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull (中国药理学通报), 2006, 22: 960–963. |
| [13] | Yang CC, Kuai XX, Li YL, et al. Cornel iridoid glycoside attenuates tau hyperphosphorylation by inhibition of PP2A demethylation[J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med, 2013. DOI:10.1155/2013/108486 |
| [14] | Hoffman A, Taleski G, Sontag E. The protein serine/threonine phosphatases PP2A, PP1 and calcineurin:a triple threat in the regulation of the neuronal cytoskeleton[J]. Mol Cell Neurosci, 2017, 84: 119–131. DOI:10.1016/j.mcn.2017.01.005 |
| [15] | Yang W, Wang X, Duan C, et al. Alpha-synuclein overexpression increases phospho-protein phosphatase 2A levels via formation of calmodulin/Src complex[J]. Neurochem Int, 2013, 63: 180–194. DOI:10.1016/j.neuint.2013.06.010 |
| [16] | Liu R, Zhou XW, Tanila H, et al. Phosphorylated PP2A (tyrosine 307) is associated with Alzheimer neurofibrillary pathology[J]. J Cell Mol Med, 2008, 12: 241–257. |
| [17] | Liu R, Zhou XW, Wang JZ. Effect of blocking tyrosine kinase Src expression on protein phosphatase 2A and tau phosphorylation[J]. Neural Injury Funct Reconstr (神经损伤与功能重建), 2007, 2: 203–206. |
| [18] | Xiong Y, Jing XP, Liu R, et al. Zinc ions inhibits PP2A and promotes tau protein hyperphosphorylation by regulating the SRC[J]. Chin J Phathopysiol (中国病理生理杂志), 2010, 26: 2052. |
| [19] | Yang X, Yang Y, Luo Y, et al. Hyperphosphorylation and accumulation of neurofilament proteins in transgenic mice with Alzheimer presenilin 1 mutation[J]. Cell Mol Neurobiol, 2009, 29: 497–501. DOI:10.1007/s10571-008-9341-7 |
| [20] | Haass C, Mandelkow E. Fyn-tau-amyloid:a toxic triad[J]. Cell, 2010, 142: 356–358. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2010.07.032 |
| [21] | Ittner LM, Ke YD, Delerue F, et al. Dendritic function of tau mediates amyloid-β toxicity in Alzheimer's disease mouse models[J]. Cell, 2010, 142: 387–397. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2010.06.036 |
| [22] | Martin L, Latypova X, Wilson CM, et al. Tau protein phosphatases in Alzheimer's disease:the leading role of PP2A[J]. Ageing Res Rev, 2013, 12: 39–49. DOI:10.1016/j.arr.2012.06.008 |
| [23] | Taleski G, Sontag E. Protein phosphatase 2A and tau:an orchestrated 'Pas de Deux'[J]. FEBS Lett, 2018, 592: 1079–1095. DOI:10.1002/feb2.2018.592.issue-7 |
| [24] | Ikehara T, Imamura S, Yoshino A, et al. PP2A inhibition assay using recombinant enzyme for rapid detection of okadaic acid and its analogs in shellfish[J]. Toxins (Basel), 2010, 2: 195–204. DOI:10.3390/toxins2010195 |
| [25] | Messner DJ, Romeo C, Boynton A, et al. Inhibition of PP2A, but not PP5, mediates p53 activation by low levels of okadaic acid in rat liver epithelial cells[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2006, 99: 241–255. DOI:10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4644 |
| [26] | Rahman MM, Rumzhum NN, Morris JC, et al. Basal protein phosphatase 2A activity restrains cytokine expression:role for MAPKs and tristetraprolin[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 10063. DOI:10.1038/srep10063 |
| [27] | Hu Y, Guo J. PP2A regulation subunits and their substrates[J]. J Med Mol Biol (医学分子生物学杂志), 2008, 5: 169–173. |
| [28] | Ding MQ. Advances in research of non-receptor tyrosine kinase Src in brain ischemia[J]. Chin Contin Med Edu (中国继续医学教育), 2015, 7: 169–170. |
| [29] | Liu R, Zhou XW, Wang JZ. Effect of Blocking Tyrosine Kinase Src Expression on Protein Phosphatase 2A and Tau Phosphorylation[C]//Proceedings of Hubei province and Wuhan pathophysiological association's 14th annual seminar. Wuhan: Hubei Science and Technology Association, 2008. |
 2018, Vol. 53
2018, Vol. 53


