固体药物的溶解度在制药行业中起着重要作用,常常会直接影响到药物的生物活性,溶解度数据可以为药物制剂的配伍变化研究提供一定的理论依据,并作为筛选新药的标准[1],有助于解决药物研究和生产过程中的许多问题。
目前,测定溶解度的方法主要有通过配制饱和溶液,利用不同的分析手段分析体系固液平衡后上清液组成的平衡法[2, 3],以及在预先精确称量样品中溶质和溶剂的条件下,不断改变温度或加入定量的溶质或溶剂,观察体系中固体的产生或消失来确定溶解度的动态法[4, 5]等。平衡法因其设备简单、易操作、对体系平衡速率没有限制,是较常用的溶解度测定方法。然而该方法耗时长[6],在高温或一定压力下取样困难,对不同药物需采用特定的分析手段,如化学滴定法、分光光度法[7]和HPLC法等,故当测定药物种类较多、数量较少时,会造成分析方法各异,操作繁琐,资源浪费,为实际的科研工作带来不便。动态法通常由组合的激光监测系统代替人眼观察固体的溶解状况,并判断测定终点,平衡时间相对较短,不易达到真正的平衡,需要加强搅拌,严格控制升温速度。对于溶解过程缓慢的药物,不易使用此法。
针对上述方法的局限性,作者提出了一种对大多数药物普遍适用的溶解度测定方法。采用湿度传感器直接测定与药物饱和溶液呈平衡的空气的相对湿度[8],避免了平衡法中对饱和溶液的取样分析过程,大大简化了测定步骤。作者用空气湿度法测定了NaCl在20~50 ℃内的溶解度,并与重量分析法及文献报道值进行了比较。
原理 1 空气湿度法根据物理化学基本原理,与溶液呈平衡的空气的相对湿度 (Hr) 即为溶液中水的活度 (
| ${\alpha _{{H_2}O}} = {x_{{H_2}O}}{\gamma _{{H_2}O}}$ | (1) |
故可得:
| ${x_{{H_2}O}} = {{{H_r}} \over {{\gamma _{{H_2}O}}}}$ | (2) |
其中,
目前有多种物理化学理论模型可用于计算
在Extended-NRTL模型中,
| $In{\gamma _{{H_2}O}} = In\gamma _{_{{H_2}O}}^{LR} + In\gamma _{_{{H_2}O}}^{SR}$ | (3) |
在水溶液中,
| $\eqalign{ & In\gamma _{{H_2}O}^{LR} = - 7.4494 \cdot \left\{ - \right.61.4453\exp \left[ {\left( {T - 273.15} \right)/273.15} \right] + \cr & 2.864468\left( {\exp {{\left[ {\left( {T - 273.15} \right)/273.15} \right]}^2}} \right) + 183.5379 \cr & In\left( {T - 273.15} \right) - 0.6282022\left( {T - 273.15} \right) + 0.00078756 \cr & \left( {{T^2} - {{273.15}^2}} \right) + 58.95788\left. {\left( {273.15/T} \right)} \right\} \cdot {{I_x^{1.5}} \over {1 + 14.9I_x^{0.5}}} \cr} $ | (4) |
| $\eqalign{ & In\gamma _{{H_2}O}^{SR} = {{ - 3.094In\left[ {{{{x_{{H_2}O}} + 4.805\left( {{z_ + }{x_ + } + {z_ - }{x_ - }} \right)} \over {{x_{{H_2}O}} + {z_ + }{x_ + } + {z_ - }{x_ - }}}} \right]} \over {RT}} + \cr & {{ - 3.094{x_{{H_2}O}}\left[ {1 - {{{x_{{H_2}O}} + 4.805\left( {{z_ + }{x_ + } + {z_ - }{x_ - }} \right)} \over {{x_{{H_2}O}} + {z_ + }{x_ + } + {z_ - }{x_ - }}}} \right]} \over {RT\left[ {{x_{{H_2}O}} + 4.805\left( {{z_ + }{x_ + } + {z_ - }{x_ - }} \right)} \right]}} + \cr & {{ - 10.245{z_ - }{x_ - }\left( {0.106 - {{{z_ + }{x_ + } + 0.106{x_{{H_2}O}}} \over {{x_{{H_2}O}} + {z_ + }{x_ + }}}} \right)} \over {RT\left( {{z_ + }{x_ + } + 0.106{x_{{H_2}O}}} \right)}} + \cr & {{22.968{x_{{H_2}O}}} \over {RT}}\left[ {{{{z_ + }{x_ + }} \over {{{\left( {{z_ + }{x_ + } + {x_{{H_2}O}}} \right)}^2}}} + {{{z_ - }{x_ - }} \over {{{\left( {{z_ + }{x_ + } + {x_{{H_2}O}}} \right)}^2}}}} \right] + \cr & {{ - 10.245{z_ + }{x_ + }\left( {0.106 - {{{z_ - }{x_ - } + 0.106{x_{{H_2}O}}} \over {{x_{{H_2}O}} + {z_ - }{x_ - }}}} \right)} \over {RT\left( {{z_ - }{x_ - } + 0.106{x_{{H_2}O}}} \right)}} - \cr & {{22.968{x_{{H_2}O}}} \over {RT}}\left( {{{{z_ + }{x_ + }} \over {{z_ - }{x_ - } + {x_{{H_2}O}}}} + {{{z_ - }{x_ - }} \over {{z_ + }{x_ + } + {x_{{H_2}O}}}}} \right) \cr} $ | (5) |
式中,
仪器与试剂 Rotronic湿度计 (HydroPalm Hp22),探头型号: HygroClip HC2-S。相对湿度和温度的测 定范围分别为0~1和−50~100 ℃; 准确度分别为 ± 0.008和 ± 0.1 ℃,输出结果的时间间隔为1 s。FA2004型分析天平 (上海良平仪器仪表有限公司)。SDH401型恒温恒湿箱 (重庆试验设备厂)。NaCl为分析纯 (≥99.5 %,天津市瑞金特化学品有限公司)。
空气湿度法测定溶解度 取一定量的NaCl于锥形瓶中,加水,搅拌,使成饱和溶液。密闭插入湿度传感器于锥形瓶上方的空间 (图 1)。在测定温度下恒温2 h后,读取相对湿度值,根据式 (2)~(5) 计算溶解度值。
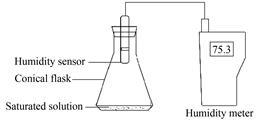
|
Figure 1 Assembly used in the determination of the relative air humidity in equilibrium with the solution |
重量法测定溶解度 取上述已达固液平衡的NaCl饱和溶液适量,精密称定,在105 ℃下烘干至恒重后,再精密称定残留的溶质质量,计算出NaCl的溶解度[13]。
结果 1 空气湿度法测定溶解度值用空气湿度法和重量法测定的溶解度值及文 献[14]报道的溶解度值见表 1和图 2,结果表明三者基本一致。
| Table 1 Solubility of NaCl determined by air humidity solubility assay,gravimetry and reported by literature within the temperature range 20−50 ℃. n = 3,x± s |
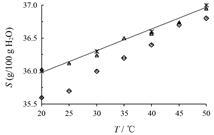
|
Figure 2 Comparison of NaCl solubility (S) determined by air humidity solubility assay (◇),gravimetriy (△) and reported by literature (错误!未指定书签。错误!未指定书签。) within the temperature range 20−50 ℃. n = 3,x± s |
为了解相对湿度测定值对溶解度计算值的影响,进行误差分析。以25 ℃时NaCl饱和溶液的相对湿度值0.754为例,用空气湿度法测得的溶解度为35.70 g/ 100 g H2O,若湿度测定值因误差而增加至0.764 (ΔHr = 0.01),则溶解度的计算值将减少为34.51 g/100 g H2O,由此得相对湿度测定误差 (DHr) 对溶解度计算值误差 (DS) 的影响为
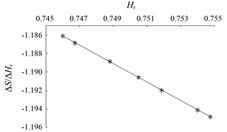
|
Figure 3 The impact of relative humidity (Hr) measurement error (ΔHr) on the calculated value for solubility (ΔS) |
本实验中使用的湿度计用标准溶液标定后,在相对湿度0~1内湿度测定的绝对误差≤0.008,由此造成的溶解度计算值的绝对误差≤0.85 g/100 g H2O,相对误差≤2%。
讨论在本实验中,空气湿度法测定的相对误差≤2%,虽然其准确度不及重量分析法,但操作简便、条件易控,对大多数药物普遍适用,弥补了现有的溶解度测定方法的局限性。
众所周知,高分子化合物由于黏度很大且难以结晶,又缺乏简便易行的含量分析方法,其溶解度是很难测定的。目前常用极性相似的原则[15]或通过比较高分子化合物与溶剂的“溶度参数”[16]来判断其溶解的难易程度。而作者提出的新方法只需测定在平衡条件下的空气相对湿度,避免了上述困难,因而具有潜在的测定高分子化合物溶解度的能力。在后续研究工作中,将对此进行验证。
| [1] | Hu CY, Huang P. Recent research and development on determination of solid solubility[J]. Chin J Pharm Anal (药物分析杂志) , 2010, 30 :761–766. |
| [2] | Joly J, Nicolau I, Armand M. Solubility of a-HgI2 in dimethylsulfoxide-methanol and dimethylsulfoxide-ethyl acetate mixtures[J]. J Chem Eng Data , 1979, 24 :283–285. DOI:10.1021/je60083a015 |
| [3] | Yan H, Li RY, Li Q, et al. Solubility of minoxidil in methanol, ethanol, 1-propanol, 2-propanol, 1-butanol, and water from (278.15 to 333.15) K[J]. J Chem Eng Data , 2011, 56 :2720–2722. DOI:10.1021/je1012839 |
| [4] | Yu OS, Black S, Wei HY. Solubility of butanedioic acid in different solvents at temperatures between 283 K and 333 K[J]. J Chem Eng Data , 2009, 54 :2123–2125. DOI:10.1021/je900021g |
| [5] | Lin HM, Tien HY, Hone YT, et al. Solubility of selected dibasic carboxylic acids in water, in ionic liquid of[J]. Fluid Phase Equilib , 2007, 253 :130–136. DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2007.02.011 |
| [6] | Chen ZG, Yang WG, Hu YH, et al. Measurement and correlation for the solubility of dimethyl 1,4-cyclohex-anedione-2,5-dicarboxylate in different solvents at tempera-tures from (278.15 to 323.15) K[J]. J Chem Eng Data , 2011, 56 :2726–2729. DOI:10.1021/je2000292 |
| [7] | Hou GY, Yin QX, Zhang MJ, et al. Solubility of indinavir sulfate in different solvents from (278.35 to 314.15) K[J]. J Chem Eng Data , 2009, 54 :2106–2108. DOI:10.1021/je800689a |
| [8] | Zhan XC, Wang YL, Cao L, et al. Determining critical relative humidity by measuring air humidity in equilibrium directly[J]. Eur J Pharm Sci , 2010, 41 :383–387. DOI:10.1016/j.ejps.2010.07.002 |
| [9] | Zhan XC, Li H, Yu L, et al. Determining osmotic pressure of drug solutions by air humidity in equilibrium method[J]. Drug Dev Ind Pharm , 2014, 40 :758–761. DOI:10.3109/03639045.2013.782555 |
| [10] | Zhan XC, Xu A, Fu Q, et al. Air humidity cryoscopy[J]. Acta Pharm Sin (药学学报) , 2016, 51 :668–671. |
| [11] | Sadeghi R. Simultaneous correlation of mean ionic activity coefficient and osmotic coefficient of electrolyte solutions by a new local composition model[J]. Fluid Phase Equilib , 2006, 243 :92–100. DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2006.02.019 |
| [12] | Jaime-Leal JE, Bomlla-Petriciolet A, Bhargava V, et al. Nonlinear parameter estimation of e-NRTL model for quarter-nary ammonium ionic liquids using Cuckoo Search[J]. Chem Eng Res Des , 2015, 93 :464–472. DOI:10.1016/j.cherd.2014.06.014 |
| [13] | Ferreira LA, Macedo EA, Pinho SP. KCl effect on the solubility of five different amino acids in water[J]. Fluid Phase Equilib , 2007, 255 :131–137. DOI:10.1016/j.fluid.2007.04.004 |
| [14] | Liu GQ, Ma LX, Liu J. Handbook of Chemistry Data Physical Properties Inorganic Chemistry (化学化工数据物性手册: 无机卷)[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2002 : 477 . |
| [15] | Miller-Chou BA, Koenig JL. A review of polymer dissolu-tion[J]. Prog Polym Sci , 2003, 28 :1223–1270. DOI:10.1016/S0079-6700(03)00045-5 |
| [16] | Wu SS. Study on solution parameter of styrene-butadiene rubber[J]. Polymer Mater Sci Eng (高分子材料科学与工程) , 2002, 18 :185–187. |
 2016, Vol. 51
2016, Vol. 51


