黄连味苦,性寒,归心、胃、肝、胆、大肠经,具有泻火解毒、清热燥湿的功效。黄连的炮制品有姜黄连、萸黄连、酒黄连、醋黄连、盐黄连和胆黄连等,其中胆黄连是以辅料猪胆汁浸制、炒制黄连而得,用猪胆汁的寒性进一步增强黄连的寒性,即“寒者益寒”,使炮制后胆黄连的寒性增强,主要用于肝胆实火之证。近年来对胆黄连的研究甚少,多是对胆黄连炮制前后的化学成分变化、炮制工艺及药效作用研究[1, 2, 3],关于胆黄连治疗实热证的药效作用与药代动力学的相关研究较少,急需深入系统研究。
黄连中主要化学成分是生物碱成分,包括小檗碱、药根碱和巴马汀等,这些生物碱成分具有广泛的药理作用,如抗炎[4]、抑菌[5]和解热[6]等作用,胆黄连是黄连的主要炮制品之一,胆黄连的主要化学成分亦是生物碱成分,因此,本实验以胆黄连为研究对象,对胆黄连中生物碱成分在实热证大鼠体内的整合药代动力学进行研究,并结合胆黄连对实热证大鼠的解热作用,分析胆黄连中生物碱成分在实热证大鼠体内血药浓度的变化情况与其药效作用的相关性,为胆黄连的药效物质基础及炮制机制的研究提供依据。
材料与方法 仪器MC-3B电脑数字式体温计 (欧姆龙大连有限公司); Agilent 6410 QQQ LC-MS分析系统,由美国Agilent LC液相色谱仪及Agilent 6410 QQQ三极杆质谱检测器组成,Masshunter version 4.0工作站。
药品与试剂小檗碱 (berberine,批号: 20130410); 药根碱 (jatrorrhizine,批号: 20121010); 巴马汀 (palmatine,批号: 20130508); 卡马西平 (carbamazepine,批号: 20130901) 均购自于中国食品药品检定研究院,纯度在98% 以上; 黄连饮片 (批号: 20130612)、干姜 (批号: 20140120)、肉桂 (批号: 20140426)、黑附子 (批号: 20140305) 均购自于大连权健中药饮片有限公司,干酵母 (安琪酵母有限公司)。色谱级甲醇、乙腈购于德国Merck INC; 甲酸 (色谱级,纯度大于98%) 购于美国Dikma technology INC; 超纯水由美国Milli-Q system制备。
动物雌性Wistar大鼠,(200± 20) g,由大连医科大学实验动物中心提供,合格证号SCXK (辽) 2010-0001。大鼠适应性喂养自由饮水,室温 (23 ± 2) ℃放置1周,预养期间测定大鼠肛温,两次测定时间间隔30 min,剔除体温波动大于0.5 ℃者。
胆黄连供试品溶液的制备取黄连饮片,加猪胆汁水溶液 (猪胆汁6 g,水40 mL) 拌匀,闷润1 h (每100 g黄连饮片,加猪胆汁水溶液40 mL),95 ℃下翻炒19 min,即得胆黄连饮片。取胆黄连饮片称重,加10倍量水浸泡0.5 h,煎煮1 h,绢布滤过,药渣再加8倍量水煎煮1 h,滤过,合并两次滤液,浓缩成0.1 g·mL-1。
动物分组与药物治疗30只Wistar雌性大鼠适应性饲养一周后,随机分为3组,每组10只。I组: 空白对照组; II组: 实热证模型组; III组: 胆黄连组。于每日早8:00,I组每只大鼠每日灌胃生理盐水4 mL,II、III组每鼠每日灌胃附子、干姜、肉桂的水煎液 (1∶1∶1,1 g·mL-1) 4 mL,持续造模15天,造模第16天时II、III组皮下注射20% 干酵母混悬液 (10 mL·kg-1),III组立即灌胃给予胆黄连供试品溶液2 g·kg-1,分别于给药后0、0.25、0.5、0.75、1、2、3、4、6、8、12和24 h眼眶取血0.2 mL,置于预先肝素化的离心管中,离心5 min (10 000 r·min-1),得血浆,在-80 ℃冰箱中保存、备用,血浆用于胆黄连整合药代动力学研究。造模第16天时,检测I组、II组在大鼠皮下注射干酵母混悬液后,III组在灌胃给予胆黄连供试品溶液后0、3、6和9 h的体温,数据用于胆黄连解热药效作用的研究。
血浆样品制备取血浆30 μL,加入内标溶液 (1 μg·mL-1卡马西平溶液) 10 μL,涡旋30 s,加入乙腈50 μL,振荡混匀3 min,离心 (4 ℃,13 000 r·min-1) 10 min,吸取上清液60 μL,经UPLC-MS/MS进样检测。
分析条件色谱柱为Waters acquity BEA C18 (50 mm × 2.1 mm,1.7 μm); 流动相A为含有10 mmol·L-1乙酸胺的0.1%甲酸水溶液,流动相B为0.1%甲酸的乙腈。梯度洗脱: 0~3 min,5%~50% B; 在3~4 min内,50%~95% B; 4~7 min,95% B; 7~7.1 min,95%~5% B; 7.1~10.0 min,5% B,共洗脱10 min。流速为0.3 mL·min-1,柱温箱温度为35 ℃。
质谱为三重四极杆; ESI离子源,扫描方式正离子扫描; 毛细管电压3 kV; 锥孔电压,30 V; 离子源温度,250 ℃; 去溶剂化温度,300 ℃; 锥孔气流,5 L·min-1; 去溶剂化温度气流,11 L·min-1; 数据的 采集及分析采用Masshunter Version 4.0软件。采用 质谱多反应监测技术 (multiple reaction monitoring,MRM) 对血浆样品进行分析和定量,小檗碱、药根碱、巴马汀和卡马西平 (内标物) 的MRM的主要参数如表 1所示。
|
|
Table 1 MS/MS transitions and parameters for the detection of the analytes and internal standards |
根据生物样品分析方法的要求,本实验对方法专属性、各分析物的标准曲线和最低定量限、提取回收率、基质效应、精密度、准确度和稳定性进行相应考察。
基于 AUC 自定义权重系数的胆黄连总生物碱整合药动学模型的建立根据胆黄连给药后测定的总生物碱血药浓度-时间数据,DAS软件计算药动学参数,得到胆黄连药根碱、巴马汀和小檗碱的AUC0-∞数据,根据各成分在3种成分总AUC0-∞中所占比值自定义各成分在综合浓度中的权重系数 (ωj),将每一时间点下3种生物碱成分的血药浓度赋以各自的权重系数,求算胆黄连总生物碱的综合浓度[7]。
胆黄连各成分自定义权重系数及综合浓度的计算公式如下:
| ${\omega _j} = \frac{{{\rm{AUC}}{j_{0 - \infty }}}}{{\sum\nolimits_1^3 {{\rm{AU}}{{\rm{C}}_{0 - \infty }}} }}$ | (1) |
| $\sum\limits_1^3 {{\rm{AU}}{{\rm{C}}_{0 - \infty }} = {\rm{AU}}{{\rm{C}}_{0 - \infty {\rm{Ber}}}} + {\rm{AU}}{{\rm{C}}_{0 - \infty {\rm{Jatr}}}} + {\rm{AU}}{{\rm{C}}_{0 - \infty {\rm{Pal}}}}} $ | (2) |
其中ω为权重系数,j分别代表药根碱 (Jatr)、巴马汀 (Pal) 和小檗碱 (Ber),ωj代表上述成分的AUC在3种成分总AUC中的比值。
整合浓度计算公式为:
| ${C_T} = {\omega _{Ber}} \times {C_{Ber}} + {\omega _{Jatr}} \times {C_{Jatr}} + {\omega _{Pal}} \times {C_{Pal}}$ | (3) |
CT为自定义权重系数校正后胆黄连总生物碱在大鼠体内的综合浓度。
数据处理方法质谱分析数据由质谱专业分析软件获得,所得质谱数据用药代动力学专业软件DAS进行运算。统计学分析使用SPSS软件,数据x±s表示,采用t检验分析,P < 0.05为具有显著差异。
结果 1 方法学确证 1.1 专属性UPLC-MS/MS方法血浆样品色谱图见图 1,图A为空白血浆色谱图,图B为空白血浆添加最低浓度小檗碱、药根碱和巴马汀以及内标物卡马西平 (1 μg·mL-1) 的色谱图,图C为大鼠灌胃胆黄连供试品溶液后1 h血浆样品的色谱图。结果表明,空白血浆中内源性物质不干扰小檗碱、药根碱和巴马汀在血浆中的测定。该UPLC-MS/MS方法的专属性较好。
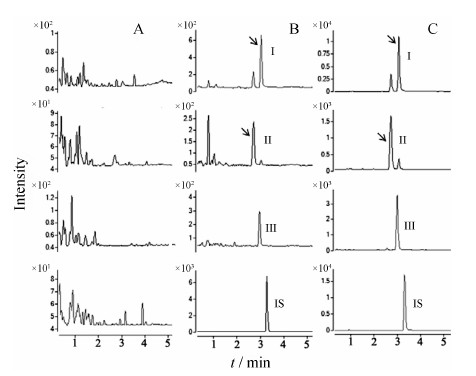 | Figure 1 UPLC-MS/MS chromatograms of (A) blank plasma, (B) blank plasma spiked with berberine (0.4 ng·mL−1), jatrorrhizine (0.4 ng·mL−1), palmatine (0.4 ng·mL−1) at LLOQ and carbamazepine (IS, 1μg·mL−1), (C) plasma sample after a single oral administration of bile processed Rhizoma Coptidis (BRC) extract. I: Berberine, II: Jatrorrhizine, III: Palmatine |
以对照品峰面积与内标峰面积的比值对浓度做线性回归,用最小二乘法考察其线性。最低定量限以信噪比的比值 (≥10) 为判断标准。结果见表 2。
|
|
Table 2 The regression equations and lower limit of quantification of the three analytes |
UPLC-MS/MS方法学的其他考察内容: 提取回收率为90%~98%,基质效应为98%~114%,血浆QC样品的日内精密度和日间精密度 (RSD) < 8%、准确度为98%~112%,稳定性 (RE) 为-8%~8%,均符合相关要求。
2 整合药代动力学研究 2.1 基于 AUC 自定义权重系数的胆黄连总生物碱整合药动学模型的建立由公式 (1)~(3) 可计算出胆黄连中3种生物碱成分的权重系数,结果见表 3。
|
|
Table 3 AUC0−∞ and self-defined weighting coefficients of three alkaloids of BRC in rats’ bodies |
将表 3中药根碱、巴马汀和小檗碱的自定义权重系数以及胆黄连给药后不同时间点3种生物碱成分的血药浓度代入公式 (3),计算出胆黄连的整合血药浓度,见图 2。胆黄连中药根碱、巴马汀和小檗碱的药动学参数及整合药动学参数见表 4。
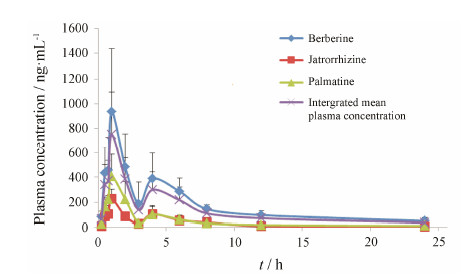 | Figure 2 Blood concentration-time curve before and after the integration of BRC |
|
|
Table 4 The pharmacokinetic parameters of alkaloids in BRC. |
各组大鼠不同时间点的体温结果见表 5,与空白组比较,在3 h时,模型组体温升高显著,胆黄连组无显著性变化,说明在3 h时,胆黄连对体温升高产生了较好的抑制作用; 在6 h时,模型组、胆黄连组体温升高均呈显著性; 在9 h时,模型组体温升高仍保持显著性,胆黄连组无显著性差异,说明体温开始有下降趋势。
|
|
Table 5 Results of the rectal temperature of rats in all the groups. n = 10, x±s. ***P < 0.001 vs normal group; △△△P < 0.001 vs model group |
与模型组比较,胆黄连组在3 h时有显著性差异,呈显著性降低,进一步说明了胆黄连可以很好地抑制发热,具有解热作用。
4 胆黄连对实热证大鼠的整合药代动力学与解热作用的相关分析将胆黄连生物碱的整合血药浓度-时间曲线与药效体温曲线进行比较,见图 3。胆黄连中生物碱的血药浓度的达峰时间是1.11 h,胆黄连对实热证模型大鼠的解热作用是在给药后3 h,与模型组的体温差值最大,胆黄连给药后3 h的解热作用最显著,药效作用的峰值明显滞后于血药浓度的峰值,这可能是由于胆黄连中的生物碱从血浆到效应室的分布、合成新的物质需要一定时间所造成[8],且胆黄连生物碱在肠道吸收很差,胆黄连的解热机制尚不清楚,应进一步深入研究。
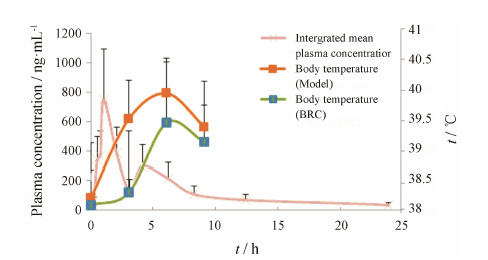 | Figure 3 Integrated plasma concentration-time profiles of alkaloids and the rectal temperature curve after oral administration of BRC in yeast-induced febrile rats |
胆黄连生物碱成分的整合药时曲线出现双峰现象,第二次达峰时间是4.82 h,胆黄连在3~6 h时仍有解热作用。胆黄连中生物碱成分的整合血药浓度在约5 h后开始逐渐降低,这与胆黄连6~9 h解热作用亦明显减弱的现象相符合。结果表明,胆黄连中的生物碱成分在体内的动态变化过程与其解热作用消长之间的相关性良好。
讨论本课题组曾采用HPLC法对胆黄连水煎液中的主要生物碱成分进行含量测定,结果表明胆黄连中小檗碱、药根碱和巴马汀的含量分别为36.50、12.24和10.73 mg·g-1(待发表)。但是胆黄连中生物碱成分在肠道吸收较差,导致血浆中药物浓度较低,因此对于检测方法的灵敏度要求较高。本实验采用UPLC-MS/MS方法检测血浆样品中小檗碱等成分的含量,不仅灵敏度高、检测速度快,而且对大鼠血样的采集量也明显降低,仅仅需要0.2 mL,能够保证实验中对大鼠进行多个时间点的血样采集工作。
本实验中的液相条件,经过多次考察[9, 10, 11, 12],最后确定采用流动相A为含有10 mmol·L-1乙酸胺和0.1%甲酸的水溶液,流动相B为含有0.1% 甲酸的乙腈,梯度洗脱,不仅3种生物碱成分基线分离,空白血浆无干扰,而且3种生物碱成分的峰形较好。关于内标物的选择曾考察延胡索乙素[13]、氯氮平[12]和卡马西平[14],结果发现卡马西平既能与3种生物碱成分完全分离,空白血浆又不干扰其测定,因此最后确定采用卡马西平作为内标物。
本实验研究了胆黄连在实热证大鼠的多效应成分整合药代动力学与解热作用的相关性,为胆黄连在临床的应用提供了实验基础,同时证明中药多成分整合药代动力学与药效作用相关研究的科学性和可行性。
| [1] | Shen XQ, Zhao F, Jian TZ. Studied on the antifebrile efficacy before and after Rhizoma Coptidis processed with bile [J]. Pharmacol Clin Chin Mater Clin Med (中药药理与临床), 2013, 29: 118-120. |
| [2] | Zhong LY, Yang JM, Xi QF, et al. Orthogonal experiment design in the optimization of processing technology for Rhizoma Coptidis with biles [J]. China Tradit Herb Drugs (中草药), 2010, 41: 1296-1298. |
| [3] | Zhao JY, Wang K, Zhang ZL. Comparison of contents of four alkaloids in different processed of Coptis chinensis with quantitative analysis multi-components by single marker method [J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form (中国实验方剂学杂志), 2012, 18: 11-13. |
| [4] | Li HM, Wang YY, Wang HD, et al. Berberine protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced intestinal injury in mice via alpha 2 adrenoceptor-independent mechanisms [J]. Acta Pharmacol Sin, 2011, 32: 1364-1372. |
| [5] | Kong WJ, Zhao YL, Shan LM, et al. Thermo-chemical investigation on the quantity-antibacterial effect relationship of five berberine alkaloids in Rhizoma Coptidis on Escherichia coli growth [J]. Pharmacogn Mag, 2008, 4: 241-248 |
| [6] | Zhao YN, Xing DM, Ding Y, et al. Comparison of berberine between normal and febrile rats-pharmacokinetic study of antifebrile complex YL2000 [J]. Chin Pharmacol Bull (中国药理学通报), 2003, 19: 1170-1173. |
| [7] | Dong LC, Zhang XH, Ma J, et al. The integrated pharmacokinetics of major rhodojaponins correlates with the cardiotoxicity after oral administration of Rhododendri Mollis Flos extract in rats [J]. J Ethnopharmacol, 2014, 157: 69-78. |
| [8] | Pérez-Urizar J, Granados-Soto V, Flores-Murrieta FJ, et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic modeling: why? [J]. Arch Med Res, 2000, 31: 539-545. |
| [9] | Li HL, Zhang WD, Liu RH, et al. Simultaneous determination of four active alkaloids from a traditional Chinese medicine Corydalis saxicola Bunting. (Yanhuanglian) in plasma and urine samples by LC-MS/MS [J]. J Chromatogr B, 2006, 831: 140- 146. |
| [10] | Lu T, Liang Y, Song J, et al. Simultaneous determination of berberine and palmatine in rat plasma by HPLC-ESI-MS after oral administration of traditional Chinese medicinal preparation Huang-Lian-Jie-Du decoction and the pharmacokinetic application of the method [J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2006, 40: 1218-1224. |
| [11] | Feng J, Xu W, Tao X, et al. Simultaneous determination of baicalin, baicalein, wogonin, berberine, palmatine and jatrorrhizine in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and application in pharmacokinetic studies after oral administration of traditional Chinese medicinal preparations containing Scutellaria-Coptis herb couple [J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2010, 53: 591-598. |
| [12] | Liu FQ, Li ZD, Shi XJ, et al. Determination of berberine, palmatine and jatrorrhizine in rabbit plasma by liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry [J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2011, 56: 1006-1015. |
| [13] | Deng YT, Liao QF, Li SH, et al. Simultaneous determination of berberine, palmatine and jatrorrhizine by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in rat plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Coptis- Evodia herb couple [J]. J Chromatogr B, 2008, 863: 195-205. |
| [14] | Yuan J, Wang Y, An R, et al. Simultaneous determination of six alkaloids and one monoterpene in rat plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of a Chinese medicine Wuji Pill [J]. J Chromatogr B, 2012, 895-896: 154-161. |
 2016, Vol. 51
2016, Vol. 51


