页岩油是近年来油气勘探的新领域和研究热点[1-3]。阜四段(E1 f 4)是苏北盆地页岩油勘探和评价的主要目的层,区内多口探井在E1 f 4 段有不同级别的油气显示[4];显示类型主要以裂缝含油为主,裂缝是页岩油的储集空间和渗流通道[5]。开展泥页岩有效裂缝的成因类型和形成时间研究,对于深入分析页岩油富集规律、准确预测页岩油钻探甜点以及提高页岩油勘探成功率等方面具有重要理论及实际意义[6]。
本文在裂缝宏观、微观特征观察与描述的基础上,依据裂缝发育特征,划分了裂缝成因类型及期次。在裂缝之间相互限制切割关系分析的基础上, 运用裂缝充填物碳氧同位素分析,综合研究了裂缝发育时期,识别了有效裂缝的形成时间,以期为该区页岩油气勘探提供重要依据。
1 阜四段页岩沉积构造背景苏北盆地系苏北南黄海陆相中、新生代盆地的陆地部分,位于江苏省北部,包括安徽省天长县的部分地区。其南以江都如皋一线为界,北至滨海,西起泗洪、盱眙一带,东临黄海(图 1),面积3.5 km2[7];盆地基底为海相中、古生代沉积实体;盖层为陆相中、新生代断拗陷沉积体(图 2)。依据盖层发育程度将盆地划分为3 个二级构造单元、23 个三级构造单元[8] (图 1)。
E1 f 4 形成于苏北盆地拗陷演化阶段,为一套半深湖深湖相泥岩、页岩,云、灰质含量高;矿物组成以黏土矿物为主,次为石英和碳酸盐矿物,少量长石、黄铁矿和石膏;岩石相以纹层状灰质泥岩、 含灰泥岩、灰质泥岩相为主;TOC 在1%∼2%,油气显示丰富,是页岩油勘探和评价的主要目的层[9]。 主要分布于高邮凹陷和金湖凹陷,高邮凹陷深凹带厚度可达400 余米,金湖凹陷汊涧和龙岗次凹厚度可达300 余米,向凹陷边缘厚度逐渐变薄;海安、 盐城、阜宁凹陷仅在深凹带局部残存,厚度多小于100 m[10]。
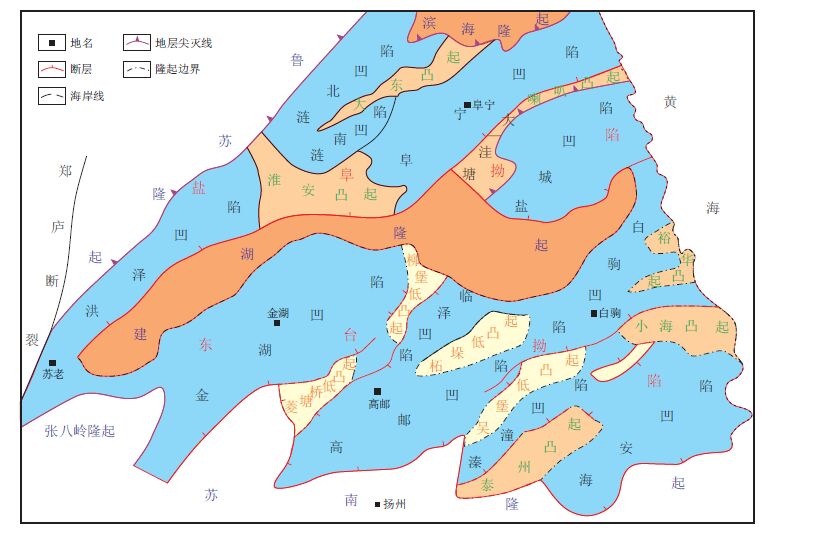 |
| 图1 苏北盆地中新生代构造区划图 Fig. 1 Mesozoic-Cenozoic tectonic division of the northern Jiangsu Basin |
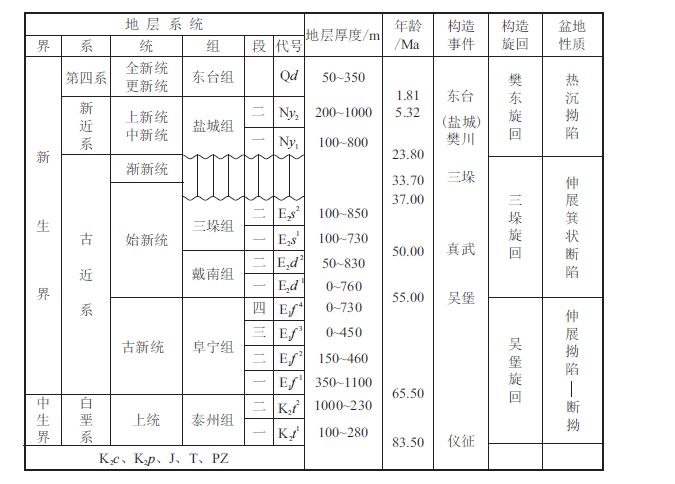 |
| 图2 苏北盆地构造演化特征 Fig. 2 Tectonic evolution characteristics of northern Jiangsu Basin |
E1 f 4 沉积后,盆地经历了吴堡、三垛、真武和盐城等多期构造运动[11-12]。其中,吴堡运动以南北向挤压为主,形成戴南组和阜宁组之间的不整合面;真武运动早期以伸展块陷为主,末期以抬升为主;三垛运动早期以伸展块陷为主,末期以抬升为主;盐城运动以抬升剥蚀为主,局部地区有火山活动[13]。这些构造运动的改造与叠加,在阜宁组页岩中形成了多期次、多方向、不同性质的构造裂缝(图 3)。
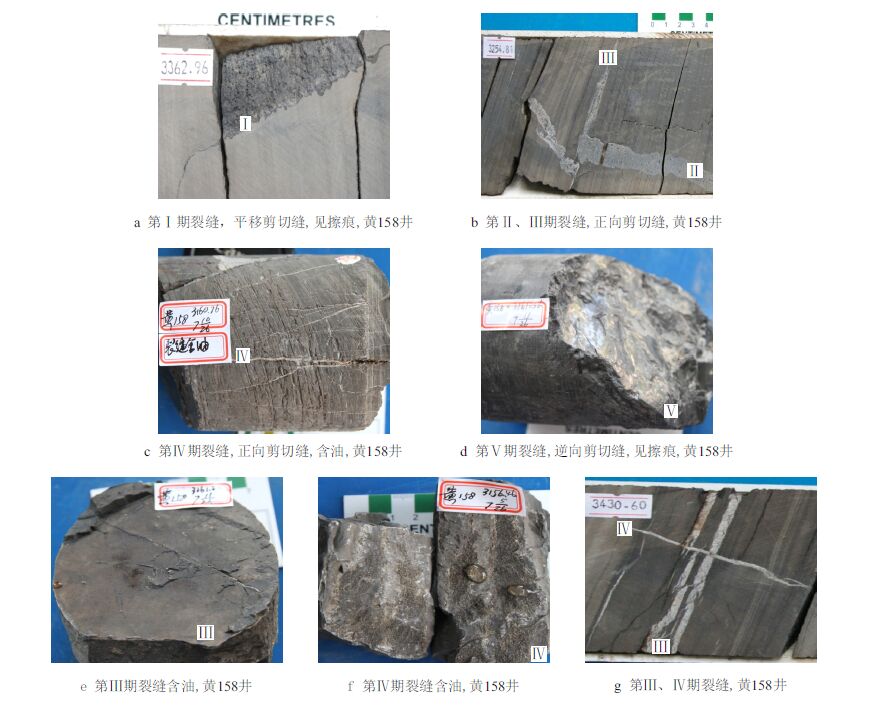 |
| 图3 苏北盆地E1 f 4 页岩裂缝成因类型及特征 Fig. 3 Fracture types and characteristics of shale of E1 f 4 in northern Jiangsu Basin |
在对区内33 口钻井岩芯裂缝参数精细观察描述与统计的基础上,依据裂缝成因、产状、几何形态、破裂性质等,将其划分为平移式剪切缝、正向剪切缝、逆向剪切缝、顺层缝等4 种成因类型。依据裂缝之间的相互限制切割关系、裂缝开度和充填情况等,识别出了5 期裂缝。
第I 期裂缝:为平移式剪切缝,多成组出现。一般垂直岩芯层面发育,倾角70◦∼90◦ ,缝面发育垂直岩芯长轴的擦痕(图 3a)。被暗色有机质充填或无充填,是在局部或区域应力场作用下形成的剪性缝。
第Ⅱ 期裂缝:为正向剪切缝。与层面呈高角度相交,倾角45◦∼70◦ 。裂缝开度较大,可达10 cm, 而且自岩芯顶部向底部逐渐变小。被方解石及泥砾等充填(图 3b),未见油气显示。裂缝充填方解石δ13C 为1.8‰,δ18O 为7.9‰。
第Ⅲ 期裂缝:为顺层缝,裂缝倾角小,多顺层发育,一般0◦∼20◦(图 3b,图 3e,图 3g);多被方解石充填,方解石脉顶底面光滑,多呈薄片页状,且多含油,气测异常明显。裂缝充填方解石δ13C 为4.0‰∼5.3‰,δ18O 为8.5‰∼ 9.2‰。切割被方解石和泥砾充填的正向剪切缝,被正向剪切缝和平移式剪切缝切割。
第Ⅳ 期裂缝:为正向剪切缝。与层面呈高角度相交,倾角60◦∼80◦(图 3c,图 3f,图 3g);裂缝开度较小,岩芯中多小于2 cm。无充填或被方解石半充填,多含油,裂缝发育段具明显气测异常。部分充填方解石自形程度较好,具粗晶结构。裂缝充填方解石δ13C 为2.8‰∼3.8‰,δ18O 为9.0‰∼ 10.0‰。 第Ⅴ 期裂缝:为逆向剪切缝,倾角20◦∼45◦ ,断面擦痕明显(图 3d),未见油气显示。属闭合缝,为局部或区域应力场作用下形成的剪性缝。
3 有效裂缝形成时间充填物碳氧同位素分析是目前国内裂缝型储层研究较为有效的手段[14-16]。对区内E1 f 4 页岩基质和第Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ 期裂缝充填方解石进行了碳氧同位素成分测试,获取了其形成时的温度及埋深等参数(表 1)。
| 表1 蜀南地区龙潭组煤层等温吸附参数表 Table 1 Isothermal adsorption parameters table of coal,Longtan Formation,in southern Sichuan Basin |
分析结果表明,区内E1 f 4 裂缝充填方解石和页岩基质碳氧同位素差异明显,而且第Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ 期裂缝充填方解石碳氧同位素也显著不同,同位素分布图上明显可划分为4 个区,反映它们的成因不同(图 4)。
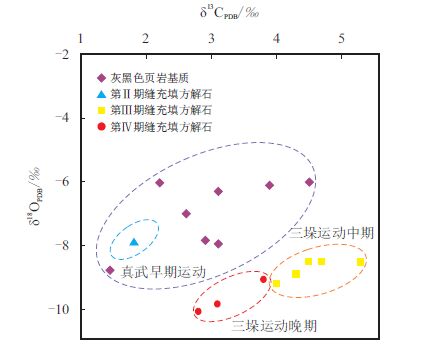 |
| 图4 苏北盆地E1 f 4 页岩和裂缝充填物碳氧同位素分布图 Fig. 4 Carbon and oxygen isotopes distribution diagrame of shaleand fracture infillings of E1 f 4 in northern Jiangsu Basin |
第Ⅱ 期裂缝充填方解石δ13C 为1.8‰,δ18O为9.2‰,与第Ⅲ、Ⅳ 期显著不同,而与页岩基质特征相似;其形成时温度为57.50 ◦C,E1 f 4 顶面埋深为782.9 m,对应于真武运动期。
第Ⅲ 期裂缝充填方解石δ18O 和δ13C 均较页岩基质偏大,表明方解石脉的δ13C 主要来源仍然是原来页岩中的碳酸盐(主要是骨骼碳酸盐),是原生碳酸盐中固有的,而不是来源于其他生物化学及化学作用的产物[17]。同时也说明了这些方解石脉的溶解和沉淀是发生于一个至少半封闭的体系内,与外来的溶解碳酸盐CO2 无关,更不是交代成因,应为钙质纹层页岩或富含碳酸盐岩页岩在晚成岩期随有机质的热演化经溶解和再沉淀作用的产物[18]。 通过对其形成温度和埋深与高邮凹陷埋藏史[10] 对比,认为其形成时间应为三垛中期(图 5)。
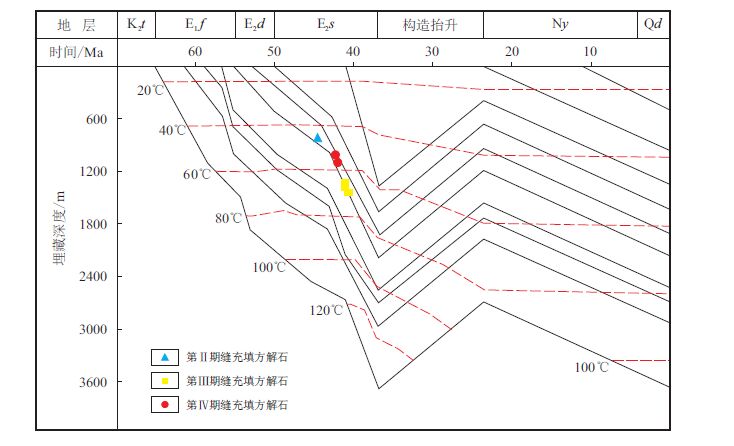 |
| 图5 形成温度与高邮凹陷埋藏史曲线判断裂缝形成时间图 Fig. 5 Determine fracture formation time with forming time and burial history curve in Gaoyou Sag |
第Ⅳ 期裂缝充填物δ13C 比页岩基质高,δ18O 明显比页岩基质偏负;其形成温度为63.49∼68.90 ◦C, E1 f 4 顶面埋深1 126.0∼1 235.0 m;其形成温度和埋深均略高于第Ⅲ 期裂缝,推测其形成时间略晚于第Ⅲ 期裂缝形成时间,为三垛中晚期。该结论与岩芯中上述两套裂缝之间的相互限制切割关系吻合。
结合苏北盆地构造背景及裂缝之间相互限制切割关系,推算第I 期裂缝应形成于吴堡运动右行走滑期,第Ⅴ 期裂缝形成应于三垛运动末期(三垛事件)。
综上所述,第Ⅲ 期顺层缝和第Ⅳ 期正向剪切缝均形成于三垛运动期,即三垛中晚期,与阜四段大规模生排烃期(E2 s1 晚期E2 s2) [19-20] 匹配较好,而且油气显示丰富,气测异常明显,为有效裂缝。而第I 期和第Ⅱ 期裂缝由于形成时间与大规模生排烃期匹配较差,且未见油气显示,属于无效缝; 第Ⅴ 期缝属压性缝,断面闭合,且与油气形成时间匹配不好,亦属无效缝。该认识与区内E1 f 2 页岩裂缝含油显示等认识一致,如盐城朱家墩地区E1 f 2 含油裂缝均为高角度张裂缝。
4 结论(1)苏北盆地E1 f 4 页岩发育4 类5 期构造裂缝,其中第I 期缝为平移式剪裂缝,形成于吴堡运动;第Ⅱ 期缝为正向剪切缝,形成于真武运动;第Ⅲ 期裂缝为顺层缝,形成于三垛运动中期;第Ⅳ 期缝为正向剪切缝,形成于三垛运动晚期;第Ⅴ 期缝为逆向剪切缝,形成于三垛运动末期。
(2)三垛运动中期和晚期形成的顺层缝和正向剪切缝,油气显示丰富,与E1 f 4 大规模生排烃期匹配较好,为有效裂缝。
| [1] |
李隽, 汤达祯, 薛华庆, 等. 中国油页岩原位开采可行性初探[J].
西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 36 (1) : 58 –64.
LI Jun, TANG Dazhen, XUE Huaqing, et al. Discission of oil shale in-situ conversion process in China[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2014, 36 (1) : 58 –64. |
| [2] |
李德生. 中国多旋回叠合油气盆地的理论与勘探实践[J].
新疆石油地质, 2013, 34 (5) : 497 –503.
LI Desheng. China's multicycle superimposed petroliferous basins:Theory and explorative practices[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2013, 34 (5) : 497 –503. |
| [3] |
邹才能, 杨智, 崔景伟, 等. 页岩油形成机制、地质特征及发展对策[J].
石油勘探与开发, 2013, 40 (1) : 14 –25.
ZOU Caineng, YANG Zhi, CUI Jingwei, et al. Formation mechanism,geological characteristics and development strategy of nonmarine shale oil in China[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 2013, 40 (1) : 14 –25. |
| [4] |
段宏亮, 何禹斌. 高邮凹陷阜四段页岩可压裂性分析[J].
复杂油气藏, 2014, 7 (1) : 1 –3.
DUAN Hongliang, HE Yubin. Analysis on shale fracability of the fourth member in Funing Formation,Gaoyou Depression[J]. Complex Hydrocarbon Reservoirs, 2014, 7 (1) : 1 –3. |
| [5] |
刘之的, 赵靖舟. 鄂尔多斯盆地长7段油页岩裂缝测井定量识别[J].
天然气地球科学, 2014, 25 (2) : 259 –265.
LIU Zhidi, ZHAO Jingzhou. Recognizing oil shale fracture of Chang7 Member in Ordos Basin using logging data[J]. Natural Gas Geoscience, 2014, 25 (2) : 259 –265. |
| [6] |
刘红岐, 刘诗琼, 刘静. 复杂致密储层裂缝特征研究[J].
西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 34 (4) : 62 –68.
LIU Hongqi, LIU Shiqiong, LIU Jing. Study on the fracture characteristics of complex tight formation[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2012, 34 (4) : 62 –68. |
| [7] | 介霖, 朱儒勋, 陈瑞庚, 等. 中国石油地质志(卷八)[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社, 1992 : 215 . |
| [8] |
刘平, 陈书平, 刘世丽, 等. 苏北盆地阜宁组泥页岩裂缝类型及形成期次[J].
西安石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 29 (6) : 13 –20.
LIU Ping, CHEN Shuping, LIU Shili, et al. Types and forming epochs of the fractures in the shale of Funing Formation of Subei Basin[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University(Natural Science Edition), 2014, 29 (6) : 13 –20. |
| [9] |
杨玉平, 钟建华, 段宏亮, 等. 高邮凹陷吴堡断裂带南段古近系剥蚀量计算及地质意义[J].
新疆石油地质, 2012, 33 (4) : 453 –455.
YANG Yuping, ZHONG Jianhua, DUAN Hongliang, et al. Recovery and geologic significance of paleogene eroded thickness in south of Wubao fault zone in Gaoyou Sag[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2012, 33 (4) : 453 –455. |
| [10] |
傅强, 李益, 张国栋, 等. 苏北盆地晚白垩世-古新世海侵湖泊的证据及其地质意义[J].
沉积学报, 2007, 25 (3) : 380 –384.
FU Qiang, LI Yi, ZHANG Guodong, et al. Evidence of transgression lake of Subei Basin during late Cretaceous and Paleocene epoch and its geological significance[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25 (3) : 380 –384. |
| [11] |
陈安定, 郭彤楼, 万景林. 裂变径迹、同位素年龄研究苏皖周边隆起构造抬升[J].
大地构造与成矿学, 2004, 28 (4) : 379 –387.
CHEN Anding, GUO Tonglou, WAN Jinglin. Study on the tectonic uplift of the peipheral upheaval in Jiangsu and Anhui by using fisson track and isotopes dating methods[J]. Geotectonica Et Metallogenia, 2004, 28 (4) : 379 –387. |
| [12] |
张沛, 周祖翼, 许长海. 苏皖下扬子区晚白垩世以来的构造-热历史:浦口组砂岩磷灰石裂变径迹证据[J].
海洋石油, 2009, 29 (4) : 26 –32.
ZHANG Pei, ZHOU Zuyi, XU Changhai. Thermotectonic history of the lower Yangtze area since late Cretaceous:Evidence from apatite fission track analysis of sandstones from Pukou Formation[J]. Offshore Oil, 2009, 29 (4) : 26 –32. |
| [13] |
鲁雪松, 马淑芳, 杨贵丽. 苏北盆地金湖凹陷三垛组剥蚀厚度恢复及意义[J].
西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 31 (4) : 13 –17.
LU Xuesong, MA Shufang, YANG Guili. Erosion thickness reconstruction of Sanduo Formation and its significance in Jinhu Sag,Subei Basin[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University(Science & Technology Edition), 2009, 31 (4) : 13 –17. |
| [14] |
刘德良, 孙先如, 李振生, 等. 鄂尔多斯盆地奥陶系白云岩碳氧同位素分析[J].
石油实验地质, 2006, 28 (2) : 155 –161.
LIU Deliang, SUN Xianru, LI Zhensheng, et al. Analysis of carbon and oxygen isotope on the ordovician dolostones in the Ordos Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2006, 28 (2) : 155 –161. |
| [15] |
张云峰, 王清晨. 济阳坳陷奥陶系碳酸盐岩及缝洞充填方解石C、O同位素特征及其意义[J].
地质科学, 2007, 42 (3) : 570 –578.
ZHANG Yunfeng, WANG Qingchen. Characters and implications of C,O isotopes in the Ordovician carbonate rocks and calcite filled in porosties/fissures in the Jiyang Depression[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology (Scientia Geologica Sinica), 2007, 42 (3) : 570 –578. |
| [16] |
任丽华, 林承焰. 构造裂缝发育期次划分方法研究与应用——以海拉尔盆地布达特群为例[J].
沉积学报, 2007, 25 (2) : 253 –260.
REN Lihua, LIN Chengyan. Classification methods for development period of fractures and its application:A case study from Budate Group of Hailaer Basin[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2007, 25 (2) : 253 –260. |
| [17] |
段宏亮, 王红伟. 苏南地区下三叠统青龙组灰岩有效裂缝的厘定[J].
西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 32 (1) : 59 –63.
DUAN Hongliang, WANG Hongwei. Dating the effective fractures of Qinglong Formation (T1) limestone in southern Jiangsu Area[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 2012, 32 (1) : 59 –63. |
| [18] |
王冠民, 任拥军, 钟建华, 等. 济阳坳陷古近系黑色页岩中纹层状方解石脉的成因探讨[J].
地质学报, 2005, 79 (6) : 834 –838.
WANG Guanmin, REN Yongjun, ZHONG Jianhua, et al. Genetic analysis on lamellar calcite veins in Paleogene black shale of the Jiyang Depression[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2005, 79 (6) : 834 –838. |
| [19] |
刘玉瑞. 苏北盆地与南黄海盆地中-新生界成烃对比浅析[J].
石油实验地质, 2010, 32 (6) : 541 –552.
LIU Yurui. Comparison analysis of Meso-Cenozoic hydrocarbon generation between the north Jiangsu Basin and the South Yellow Sea Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2010, 32 (6) : 541 –552. |
| [20] |
纪亚琴, 刘义梅, 冯武军. 苏北盆地盐城凹陷阜宁组烃源岩研究与成藏模式[J].
石油实验地质, 2013, 35 (4) : 449 –452.
JI Yaqin, LIU Yimei, FENG Wujun. Source rock study and accumulation pattern of Funing Formation in Yancheng Sag,northern Jiangsu Basin[J]. Petroleum Geology & Experiment, 2013, 35 (4) : 449 –452. |
 2016, Vol. 38
2016, Vol. 38


