2. 中国石化胜利油田分公司胜利采油厂, 山东 东营 257051
2. Shengli Oil Recovery Plant, Shengli Oilfield Company, SINOPEC, Dongying, Shandong 257051, China
陆相沉积储层中,由于沉积环境、水动力条件、成岩作用等因素的变化,层内夹层比较发育。按照夹层岩、电特征的差异,通常可分为3种类型:泥质夹层、物性夹层和钙质夹层。钙质夹层指钙质胶结的致密砂岩,作为储层中的渗流屏障,钙质夹层增强了储层的非均质性,复杂化了油水运动规律,是油田开发后期剩余油分布的重要控制因素[1-4]。研究钙质夹层成因及分布能够为建立储层内部建筑结构模型、定量分析剩余油分布规律提供依据。
当前,对于钙质夹层成因方面的研究主要以“无机成因机制”为主[5-11],认为钙质胶结物来源于砂岩周围的烃源岩(泥岩),随着有机质成熟,富含有机酸的孔隙流体与泥岩中的碳酸盐、长石、岩屑作用形成富Ca2+、Mg2+、HCO${_3^-}$的流体,与油气一起进入临近砂岩体,在砂岩与泥岩界面处发生CaCO3沉淀,形成钙质夹层。在钙质夹层分布规律研究方面,目前以“随机分布模式”为主[12-14],认为钙质夹层的分布与沉积微相和断层的分布有关,总体比较零散,连续性差,具有较强的随机性。
胜坨油田三角洲前缘储层中,钙质夹层主要分布在砂体内部,其空间分布规律具有明显的选择性特征。钙质夹层的“无机成因机制”和“随机分布模式”难以合理解释这种现象。鉴于上述问题,本文利用老油田开发后期丰富的岩芯、密井网测井资料,在精细地层对比的基础上,系统地总结胜坨油田沙二段8砂组三角洲前缘储层中钙质夹层的岩电特征,揭示其在高分辨率层序地层格架中的分布特征,提出钙质夹层的生物成因机制,明确了钙质夹层成因与分布特征之间的内在关系。
1 钙质夹层岩电特征胜坨油田位于济阳拗陷东营凹陷北部,北为陈家庄凸起,东临青坨子凸起,主要发育古近系[17]。其中,古近系沙二段为河流——三角洲沉积体系,沿东营湖盆长轴方向从东至西发展。河流的流域面积大、物源广泛,所形成的三角洲规模也较大,整个沙二段下油组都以三角洲前缘和前三角洲沉积为主,沙二段8砂组是沉积最完整、沉积序列最典型的一套三角洲前缘地层,其岩性以细砂岩、粉砂岩、粉砂质泥岩、泥质粉砂岩、泥岩为主,地层的岩性及电性组合具有明显的反旋回特征,砂体厚度大,钙质夹层主要发育在砂体内部(图 1)。
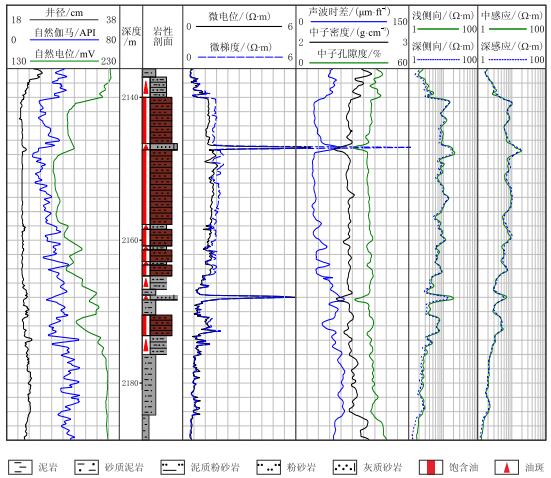 |
| 图1 胜坨油田沙二段8砂组三角洲前缘储层中钙质夹层岩电特征 Fig. 1 The lithology and log responses of calcareous intercalation in delta front reservoir in the E$s^2$(8) sand sets of Shengtuo Oilfield |
钙质夹层具有独特的测井响应特征,但不同测井系列对钙质夹层的识别能力存在差异。其中,微电极曲线在钙质胶结段呈刺刀状尖峰,是指示钙质夹层的最敏感的曲线;中子密度、中子孔隙度、声波时差曲线在钙质夹层段变化剧烈,也能较好地指示钙质夹层的存在;自然电位、自然伽马、井径以及电阻率测井对钙质夹层的响应与其他岩性地层相比不具有特异性。因此,微电极测井和三孔隙度测井是三角洲前缘储层识别钙质夹层最有效的方法。
岩芯观察表明,钙质夹层主要为钙质胶结的中细砂岩,胶结物成分为方解石和少量白云石,含量大于15%,胶结方式以基底式胶结为主,其断面上可见玻璃光泽的碳酸盐矿物晶体。钙质夹层非常致密,孔隙度、渗透率极低,是稳定的渗流屏障。
2 钙质夹层空间分布特征利用三角洲前缘钙质夹层的岩电特征,在高分辨率层序地层格架中明确了钙质夹层的空间分布特征(图 2)。
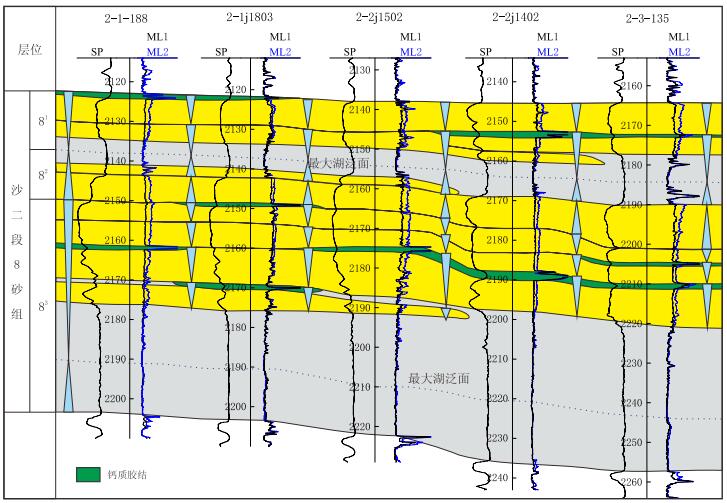 |
| 图2 胜坨油田沙二段8砂组三角洲前缘高分辨率层序地层格架中钙质夹层分布特征 Fig. 2 Sectional distribution of calcareous intercalation in high-resolution sequence stratigraphic framework of delta front reservoir in the E$s^2$(8) sand sets of Shengtuo Oilfield |
胜坨油田沙二段8砂组三角洲前缘地层由2个完整的中期基准面旋回组成,并可进一步识别出8个短期基准面半旋回。钙质夹层主要分布在中期基准面下降半旋回所形成的复合砂体中,并且在每一个短期基准面下降半旋回所形成的砂体中都有分布。纵向上看,钙质夹层只分布在短期基准面下降半旋回砂体的顶部,厚度为0.5~2.5 m;横向上看,钙质夹层的延伸规模小,只在局部井点分布,常过渡为泥质或粉砂质沉积界面。因此,钙质夹层是三角洲前缘地层中良好的层序界面和复合砂体的分期界面。
平面上同一沉积单元中,钙质夹层的分布与沉积微相的类型有关,仅分布在河口坝微相带,规模不大,范围局限在与水下分流河道注入方向对应的河口坝局部区域,形态呈相互独立的团块状(图 3)。
总体上看,三角洲前缘储层中钙质夹层分布具有明显的选择性,纵向上在短期基准面下降半旋回的砂体顶部,平面上在与水下分流河道相对应的河口坝局部。这种选择性分布特征难以用钙质夹层的无机成因机制来解释。
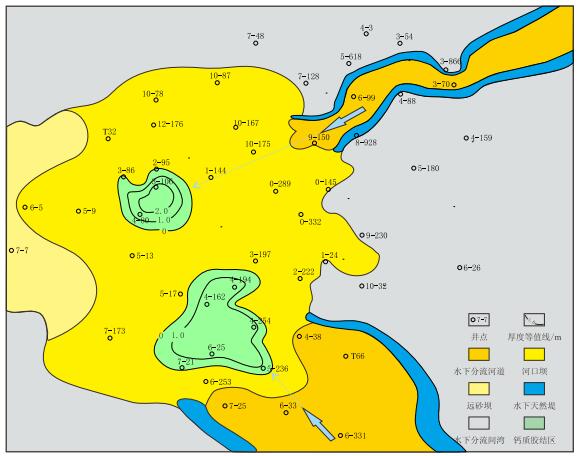 |
| 图3 胜坨油田沙二段8$^{3{\twodash}1}$沉积单元中钙质夹层平面分布特征 Fig. 3 Areal distribution of calcareous intercalation in the E$s^2$(8$^{3{\twodash}1}$) depositional unit of Shengtuo Oilfield |
钙质夹层的主要成分为碳酸钙(CaCO3),因此,对于钙质夹层成因研究的关键是要确定Ca2+的来源。除了烃源岩可以提供无机成因的Ca2+外,生物成因的Ca2+也是重要的来源。
在对研究区取芯井的岩芯观察中,发现在部分钙质胶结层段存在比较密集的腹足类化石(图 4),其种属确定为Tulotomoides terrassa(阶状似瘤田螺)。该种属是渤海湾盆地古近系沙河街组特有的腹足类化石,沉积环境主要为三角洲前缘亚相[15]。阶状似瘤田螺壳厚、坚固、近卵锥形,具螺旋型口盖,适于在水动力较强的浅水环境中生活,因此其主要生活环境是淡水湖泊的河口地带。河口地带水体深浅适中,并且水下河道携带的微生物及养分含量较高,容易成为阶状似瘤田螺大量聚集和繁殖的区域。因此,区域性的密集成层出现是阶状似瘤田螺的重要分布特征[16]。
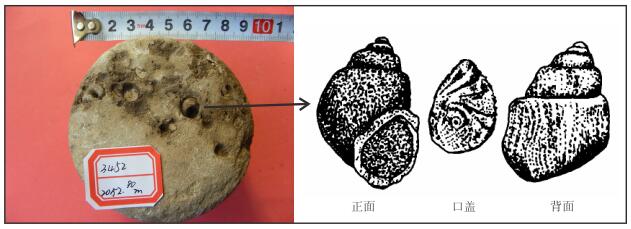 |
| 图4 胜坨油田三角洲前缘钙质夹层中的阶状似瘤田螺 Fig. 4 Tulotomoides terrassa in the calcareous intercalation in delta front reservoir of Shengtuo Oilfield |
阶状似瘤田螺的介壳成分主要为CaCO3,在其大量聚集、埋藏后,地层中的孔隙水可以逐渐溶解介壳中的CaCO3,所形成的Ca2+、HCO${_3^-}$离子在成岩期就近沉淀、胶结,从而形成钙质胶结的夹层。阶状似瘤田螺的密集分布可以为钙质夹层的形成、分布提供丰富的Ca2+来源。
阶状似瘤田螺对于生存环境有着明显的选择性,由此决定了钙质夹层在三角洲前缘地层中的分布规律。首先,对浅水环境的需求,决定了河口坝区域是阶状似瘤田螺的最佳聚集区,特别是在中期基准面下降半旋回背景中,由短期基准面下降半旋回控制形成的单期河口坝沉积末期(河口坝顶部),水体相对较浅,沉积环境比较稳定,更加适合阶状似瘤田螺的生存,而在中期基准面上升半旋回中,由于水体不断变深,不适合阶状似瘤田螺的生存和大量聚集,也难以形成生物成因的钙质夹层。其次,为满足捕食和繁殖的需求,决定了平面上与水下分流河道直接对应的河口坝局部区域,由于微生物及养分含量更高,更适合阶状似瘤田螺的大量聚集和繁殖。
4 结 论胜坨油田三角洲前缘储层中的钙质夹层主要为钙质胶结的中细砂岩,微电极测井以及三孔隙度测井是识别钙质夹层的最有效的方法。胜坨油田三角洲前缘储层中钙质夹层的分布具有选择性,纵向上分布在短期基准面下降半旋回所形成的河口坝砂体的顶部,平面上分布在与水下分流河道对应的河口坝局部区域,其分布规律与阶状似瘤田螺的生存、聚集规律高度吻合,指示了钙质夹层的生物成因机制。
| [1] |
刘睿, 姜汉桥, 刘同敬, 等. 夹层对厚油层采收率影响研究[J].
西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2009, 31 (4) : 103–106.
Liu Rui, Jiang Hanqiao, Liu Tongjing, et al. Study on the influence of interlayer on the recovery of thick reservoir[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University:Science & Technology Edition, 2009, 31 (4) : 103–106. |
| [2] |
薛永超, 梁卫, 耿传林. 夹层对底水油藏油水运动的控制作用[J].
西安石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 26 (1) : 14–17.
Xue Yongchao, Liang Wei, Geng Chuanlin. Control effect of interlayers on the migration of oil and water in bottom-water reservoirs[J]. Journal of Xi'an Shiyou University:Natural Science Edition, 2011, 26 (1) : 14–17. |
| [3] |
余成林, 国殿斌, 熊运斌, 等. 厚油层内部夹层特征及在剩余油挖潜中的应用[J].
地球科学与环境学报, 2012, 34 (1) : 35–39.
Yu Chenglin, Guo Dianbin, Xiong Yunbin, et al. Characteristics of interbeds in thick reservoir and application in potential tapping of residual oil[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2012, 34 (1) : 35–39. |
| [4] |
辛治国, 冯伟光, 郭士博, 等. 夹层自动识别方法[J].
新疆石油地质, 2010, 31 (3) : 307–310.
Xin Zhiguo, Feng Weiguang, Guo Shibo, et al. A method for automatic identification of interbed[J]. Xinjiang Petroleum Geology, 2010, 31 (3) : 307–310. |
| [5] |
黄东, 戴鸿鸣, 杨跃明, 等. 邛西地区须家河组二段钙质夹层特征与成因[J].
天然气工业, 2009, 29 (6) : 31–32.
Huang Dong, Dai Hongming, Yang Yueming, et al. Features and genesis of calcite-cement intercalations in the second member of Xujiahe Formation in Qiongxi Area[J]. Natural Gas Industry, 2009, 29 (6) : 31–32. |
| [6] |
田洋, 卢宗盛, 权英哲, 等. 辽河盆地大民屯凹陷沈95区块砂岩储层中钙质夹层研究[J].
岩石矿物学杂志, 2009, 28 (2) : 152–160.
Tian Yang, Lu Zongsheng, Quan Yingzhe, et al. Calcareous interbeds in the sandstone reservoir of Shen 95 Block within Damintun Sag, Liaohe Basin[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 2009, 28 (2) : 152–160. |
| [7] |
孙思敏, 罗家群. 南襄盆地南阳凹陷核桃园组储层中碳酸盐胶结物富集规律[J].
石油与天然气地质, 2007, 28 (3) : 384–389.
Sun Simin, Luo Jiaqun. Enrichment pattern of carbonate cements in reservoirs of the Hetaoyuan Formation in Nanyang Sag, Nanxiang Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 2007, 28 (3) : 384–389. |
| [8] |
郭宏莉, 王大锐. 塔里木油气区砂岩储集层碳酸盐胶结物的同位素组成与成因分析[J].
石油勘探与开发, 1999, 26 (3) : 31–33.
Guo Hongli, Wang Darui. Stable isotopic composition and origin analysis of the carbonate cements within sandstone reservoirs of Tarim oil-gas bearing area[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 1999, 26 (3) : 31–33. |
| [9] |
张吉, 张烈辉, 胡书勇, 等. 陆相碎屑岩储层隔夹层成因、特征及其识别[J].
测井技术, 2003, 27 (3) : 221–224.
Zhang Ji, Zhang Liehui, Hu Shuyong, et al. The genesis and characteristics and identification of intercalations in non-marine reservoir with clastic rock[J]. Well Logging Technology, 2003, 27 (3) : 221–224. |
| [10] |
曾溅辉. 东营凹陷第三系水-盐作用对储层孔隙发育的影响[J].
石油学报, 2001, 22 (4) : 39–43.
Zeng Jianhui. Effect of fluid-rock interaction on porosity of reservoir rocks in tertiary system, Dongying Sag[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2001, 22 (4) : 39–43. |
| [11] |
张敏强, 黄思静, 吴志轩, 等. 东海盆地丽水凹陷古近系储层砂岩中碳酸盐胶结物及形成机制[J].
成都理工大学学报:自然科学版, 2007, 34 (3) : 259–266.
Zhang Minqiang, Huang Sijing, Wu Zhixuan, et al. Carbonate cements and their formation mechanism in Palaeogene sandstones of Lishui Sag, east China Sea Basin[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology:Science & Technology Edition, 2007, 34 (3) : 259–266. |
| [12] |
林承焰, 侯连华, 董春梅, 等. 辽河西部凹陷沙三段浊积岩储层中钙质夹层研究[J].
沉积学报, 1996, 14 (3) : 72–81.
Lin Chengyan, Hou Lianhua, Dong Chunmei, et al. Study on calcareous interbeds in turbidite reservoir of Sha-3 Member of the Liaohe western Depression[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 1996, 14 (3) : 72–81. |
| [13] |
谢寅符, 李洪奇. 准噶尔盆地钙质夹层成因及层序地层学意义[J].
石油学报, 2005, 26 (5) : 24–27.
Xie Yinfu, Li Hongqi. Origin of calcareous interbeds and its significance of sequence stratigraphy in Junggar Basin[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2005, 26 (5) : 24–27. |
| [14] |
束青林. 孤岛油田馆陶组河流相储层隔夹层成因研究[J].
石油学报, 2006, 27 (3) : 100–103.
Shu Qinglin. Interlayer characterization of fluvial reservoir in Guantao Formation of Gudao Oilfield[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2006, 27 (3) : 100–103. |
| [15] |
严科, 赵红兵. 断背斜油藏油水界面的差异分布及成因探讨[J].
西南石油大学学报:自然科学版, 2013, 35 (2) : 28–34.
Yan Ke, Zhao Hongbing. Discussion on the differential distribution of WOC and its mechanism in the faulted anticline reservoir[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University:Science & Technology Edition, 2013, 35 (2) : 28–34. |
| [16] | 赵鸥. 阶状似瘤田螺与油气聚集[J]. 石油学报, 1992, 13 (2) : 47–50. |
| [17] |
毛秀兰. 东营凹陷北部沙河街组二段腹足类的生活环境[J].
石油学报, 1983, 4 (1) : 29–35.
Mao Xiulan. Habitat of gastropoda in 2nd member of Shahejie Formation in northern part of Dongying Depression[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 1983, 4 (1) : 29–35. |
 2014, Vol. 36
2014, Vol. 36

