奶牛乳腺上皮细胞(BMECs)在奶牛乳腺发育与泌乳中发挥着重要作用[1-3],也是乳汁合成与分泌的重要场所,对于乳品质、乳成分及产乳量具有重要影响[4-5]。长链非编码RNA(long non-coding RNAs, lncRNAs)是长度超过200 nt的转录本,具有重编程基因表达,影响细胞命运决定,细胞周期进展、凋亡和衰老等功能[6]。
已有的研究表明,lncRNA参与乳腺发育、泌乳和乳腺炎等过程[7-8]。lncRNA NEAT1缺失型小鼠的乳腺上皮细胞增殖能力下降,并导致小鼠乳腺导管形态及泌乳功能发生退化[9]。lncRNA ROR使乳腺干细胞的自我更新能力增强,并且提高乳腺干细胞对雌激素毒性的防御能力[10]。lncRNA MALAT1、AWPPH和CASC9等在乳腺癌组织和细胞中高表达,下调其表达可抑制乳腺癌细胞的增殖和侵袭,抑制肿瘤的生长[11-13]。
PI3K-AKT信号通路对乳腺中乳脂和乳蛋白的合成、BMECs的增殖和凋亡等过程发挥重要作用[14-15]。JAK-STAT信号通路中,Jak2磷酸化转录因子信号转导和转录激活因子5a(STAT5a),而STAT5a激活β-酪蛋白(Csn2)等乳蛋白编码基因的转录[16-18]。ErbB3与磷脂酰肌醇-3激酶(PI3K)的PIK3R1(p85调节亚基)有6个结合位点,当磷酸化后,ErbB3与PIK3R1相互作用促进PI3K的活性,激活AKT[19]。也有研究发现,ErbB3敲除小鼠乳腺中表达p-STAT5a/b的aMEC(alveolar mammary epithelial cells)很少,ErbB3可能作为ErbB4的异二聚体伴侣参与了信号级联,激活STAT5a的表达和磷酸化[20]。
本课题组前期对荷斯坦奶牛乳腺组织的lncRNA-seq分析结果表明,lncRNA EPB41L4A-AS(erythrocyte membrane protein band 4.1 like 4A antisense RNA)在干奶期及泌乳期差异表达,生物信息学分析表明其参与调控生长因子连接及蛋白质磷酸化等过程[21]。因此,本研究干扰EPB41L4A-AS后检测其对BMECs增殖及PI3K-AKT和JAK-STAT信号通路相关基因表达的影响,为阐释lncRNA调控奶牛乳腺发育与泌乳的分子机理及奶牛的分子育种等工作提供理论基础。
1 材料与方法 1.1 BMECs培养和转染奶牛乳腺上皮细胞(BMECs)系由西北农林科技大学赵辛教授实验室提供,用SV40大T抗原转染BMECs获得。BMECs在DMEM培养基(10%胎牛血清、1%青-链霉素、5 μg·mL-1胰岛素和1 μg·mL-1地塞米松)中于37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养。当细胞培养至60%~70%汇合时,转染EPB41L4A-AS siRNA(序列为5′-CTGCTTGTATGAAACTACT-3′)和NC-siRNA(广州锐博),培养箱中孵育48 h,每组设置3个重复。
1.2 BMECs RNA核质分离按照细胞核蛋白/浆蛋白抽提试剂盒(C510001,生工)分离BMECs细胞质与细胞核;Trizol法分别提取细胞核与细胞质RNA。
1.3 MTT检测BMECs活力将BMECs按每孔5 × 103细胞接种于96孔板。转染EPB41L4A-AS siRNA和NC-siRNA 48 h,每组设置6个重复,添加20 μL无菌MTT,培养箱中孵育4 h。每孔加入150 μL二甲基亚砜(DMSO)后置于摇床孵育10 min,直到紫色晶体完全溶解。利用酶标仪检测波长570 nm处的吸光度(A)值,计算细胞活力。
1.4 EdU检测BMECs增殖将BMECs按每孔5 × 103细胞接种于96孔板,每组设置3个重复。转染EPB41L4A-AS siRNA和NC-siRNA 48 h后,按照EdU细胞增殖检测试剂盒(c10310-1,广州锐博)进行操作,在荧光显微镜下观察并拍照。
1.5 Quantitative real-time PCR(qPCR)检测BMECs中基因表达水平TRIzol法提取组织和细胞中总RNA,使用PrimerScript RT试剂盒(TaKaRa,大连)反转录获得cDNA。引物采用Primer 6.0设计,由上海生工合成(表 1)。反应体系参考PerfectStartⓇ Green qPCR SuperMix (AQ601-01,TRANS)试剂盒说明书,反应程序: 95 ℃ 3 min; 95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃(或最适温度) 30 s,40个循环。
|
|
表 1 EPB41L4A-AS等基因的qPCR引物信息 Table 1 Real-time PCR primers information for EPB41L4A-AS and genes |
转染48 h后,使用RIPA(radioimmunoprecipitation assay)细胞裂解液(Applygen,北京)从BMECs中提取总蛋白。利用10% SDS-PAGE凝胶分离蛋白样品(20 μg)并转移到聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)膜上。室温下用5%脱脂奶粉溶液封闭1 h后,在4 ℃下用兔单克隆抗体ErbB3 (Abcam,1∶1 000稀释)、鼠单克隆抗体PIK3R1(proteintech,1∶2 000稀释)、兔多克隆抗体AKT(碧云天,1∶2 000稀释)、鼠单克隆抗体p-AKT(proteintech,1∶2 000稀释)和鼠单克隆抗体STAT5a(SANTA CRUZ,1∶500稀释),孵育过夜,然后山羊抗兔IgG和山羊抗小鼠IgG孵育(中山生物,北京)。利用ACTIN (Abcam,1∶5 000稀释)作为内参,通过Super ECL Plus(Apply-GEN)对蛋白条带可视化。
1.7 数据分析qPCR结果以内参基因β-actin为对照,采用2-△△CT的方法进行数据处理;MTT试验,根据不同处理组490 nm波长下OD值,分析试验组与对照组的相对比值;Western blot数据用软件ImageJ进行灰度分析,用GraphPad Prism 9软件对数据采用t检验进行差异显著性分析并作图。差异显著性用*P<0.05、**P<0.01、***P<0.001表示。
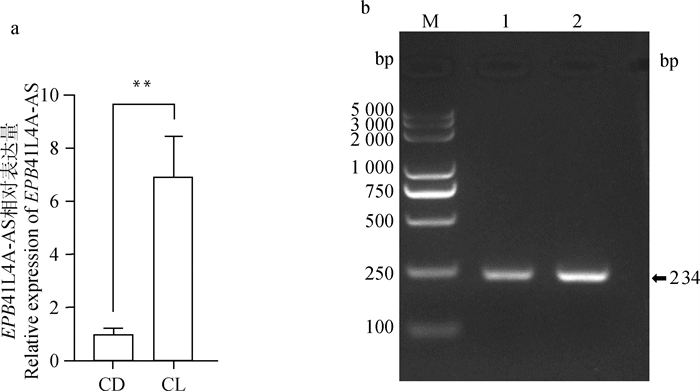
2 结果 2.1 EPB41L4A-AS在奶牛乳腺组织中的表达前期的测序发现EPB41L4A-AS(NC-037337.1,位于奶牛10号染色体,逆向转录,因此将其命名为EPB41L4A-AS)在泌乳早期的表达量显著高于干奶期[21],因此,通过qPCR对EPB41L4A-AS在奶牛乳腺组织中的表达量进行了验证。结果表明,EPB41L4A-AS在泌乳期表达量极显著高于干奶期(图 1a,P < 0.01),与测序结果一致。亚细胞定位结果表明,EPB41L4A-AS在BMECs细胞核和细胞质中均有分布,且主要存在于细胞质中(图 1b)。
|
a. EPB41L4A-AS在干奶期(CD)和泌乳期(CL)奶牛乳腺组织中的相对表达量,**P < 0.01,下同。b. EPB41L4A-AS的亚细胞定位:1.细胞核;2.细胞质;M. DNA相对分子质量标准 a. Relative expression of EPB41L4A-AS in mammary gland tissue of dry (CD) and lactation (CL) stages, **P < 0.01, the same as below. b. Subcellular localization of EPB41L4A-AS: 1. Nucleus; 2. Cytoplasm; M. DNA marker 图 1 EPB41L4A-AS在奶牛乳腺组织中的表达和亚细胞定位 Fig. 1 Expression and subcellular localization of EPB41L4A-AS in bovine mammary gland tissue |
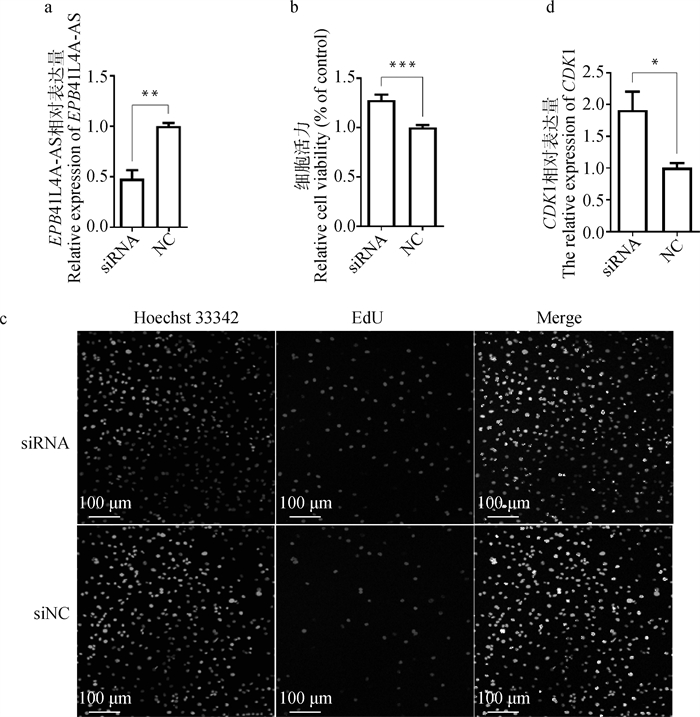
向BMECs中转染150 nmol·L-1 EPB41L4A-AS siRNA 48 h后,EPB41L4A-AS的相对表达量极显著低于对照组(图 2a,P < 0.01)。MTT结果表明,与对照组相比,降低EPB41L4A-AS的表达后奶牛乳腺上皮细胞的活力极显著提高(图 2b,P < 0.001)。EdU试验进一步表明,降低EPB41L4A-AS的表达后EdU阳性细胞数目明显增多(图 2c),而且细胞增殖相关基因CDK1的相对表达量显著高于对照组(图 2d,P < 0.05)。
|
a. siRNA对BMECs的干扰效率;b. siRNA对BMECs活力的影响;c. siRNA对BMECs增殖的影响; d. siRNA对BMECs中CDK1相对表达量的影响。*. P < 0.05;***.P < 0.001,下同 a. Interference efficiency of siRNA on BMECs; b. Effect of siRNA on BMECs activity; c. Effect of siRNA on proliferation of BMECs; d. Effects of siRNA on the relative expression of CDK1 in BMECs. *. P < 0.05; ***. P < 0.001, the same as below 图 2 EPB41L4A-AS对BMECs活力和增殖的影响 Fig. 2 Effects of EPB41L4A-AS on the activity and proliferation of BMECs |
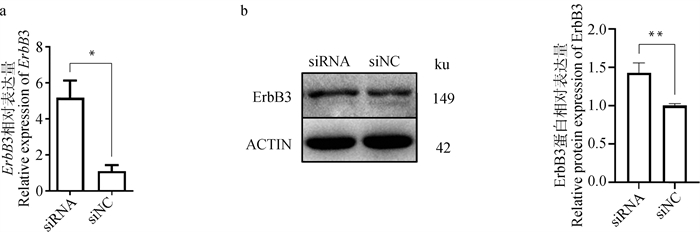
由于ErbB3基因能够促进乳腺的发育和分化[20],因此本研究在降低EPB41L4A-AS的表达后,在转录和翻译水平分别检测了ErbB3基因的表达量情况。qPCR结果表明,降低EPB41L4A-AS的表达后,ErbB3基因的相对表达量显著高于对照组(图 3a,P < 0.05),Western blot结果进一步表明,ErbB3基因在蛋白水平的表达量也极显著增加(图 3b,P < 0.01)。
|
a.siRNA对ErbB3基因相对表达量的影响;b. siRNA对ErbB3蛋白相对表达量的影响 a.Effect of siRNA on relative mRNA expression of ErbB3 gene; b.Effect of siRNA on relative protein expression of ErbB3 图 3 EPB41L4A-AS调控BMECs中ErbB3的表达 Fig. 3 EPB41L4A-AS regulates the expression of ErbB3 in BMECs |
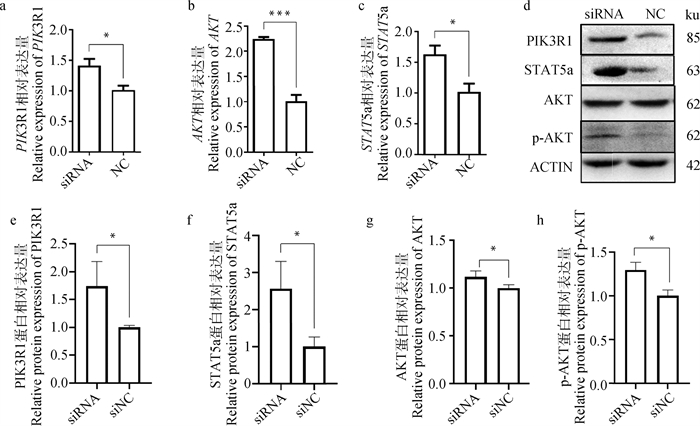
PI3K-AKT和JAK-STAT信号通路在奶牛乳腺中乳脂和乳蛋白的合成、BMECs的增殖和凋亡等过程中发挥重要作用,而ErbB3是它们的上游基因[19-20],因此本研究对这两个信号通路中PIK3R1、AKT和STAT5a基因也进行了检测。结果表明,降低EPB41L4A-AS的表达后,PIK3R1、AKT和STAT5a基因的相对表达量都显著高于对照组(图 4a、4b和4c,P < 0.05)。Western blot结果进一步表明,PIK3R1、AKT和STAT5a在蛋白水平的相对表达量显著升高(图 4d、4e、4f和4g,P < 0.05)。由于AKT发生磷酸化后才具有活性,才可以激活下游因子进而起到调节细胞的功能,因此检测了磷酸化AKT的表达量,发现降低EPB41L4A-AS的表达后磷酸化AKT(p-AKT)的表达量显著升高(图 4d和4h,P < 0.05)。
|
a~c. siRNA对PIK3R1、AKT和STAT5a基因相对表达量的影响; d~h. siRNA对PIK3R1、AKT、p-AKT和STAT5a蛋白相对表达量的影响 a-c. Effects of siRNA on the relative mRNA expression levels of PIK3R1, AKT and STAT5a genes; d-h. Effects of siRNA on the relative protein expression levels of PIK3R1, AKT, p-AKT and STAT5a 图 4 EPB41L4A-AS对BMECs中PI3K-AKT和JAK-STAT信号通路的影响 Fig. 4 Effects of EPB41L4A-AS on PI3K-AKT and JAK-STAT signaling pathways in BMECs |
lncRNA是一类长度大于200 nt的非编码RNA分子,通过表观遗传、转录以及转录后调控等多个层面调控基因的表达[22-24],参与乳腺的发育、泌乳和乳腺炎等过程[25-26]。已有研究证明,lncRNA可以抑制乳腺上皮细胞增殖,如lncRNA Zfas1在乳腺组织中高表达,敲低lncRNA Zfas1会导致乳腺上皮细胞增殖,且较正常者而言,三阴性乳腺癌(TNBC)患者血液中lncRNA Zfas1的表达明显下调,表明其可能是一种肿瘤抑制lncRNA[27-28]。课题组前期对奶牛泌乳期和干奶期乳腺组织进行lncRNA测序发现,EPB41L4A-AS在泌乳早期高表达,提示EPB41L4A-AS可能在控制上皮细胞生长和增殖中发挥重要作用。因此,本研究首先利用qPCR技术验证了EPB41L4A-AS在干奶期和泌乳期乳腺组织中相对表达量,结果与测序相一致。进一步对EPB41L4A-AS的功能研究发现,降低EPB41L4A-AS的表达后EdU阳性细胞数目和细胞活力明显增加,表明EPB41L4A-AS在泌乳期作为乳腺上皮细胞增殖的抑制因子,维持乳腺上皮细胞的稳定。
已有的研究表明,ErbB3能够促进乳腺增生和乳腺癌细胞增殖[29-30]。本研究发现,干扰EPB41L4A-AS后显著增加了BMECs中ErbB3的相对表达量,并且促进BMECs的增殖,这与已有的研究结果相符。ErbB3在妊娠中期乳腺中参与了PI3K/AKT和JAK-STAT信号通路,PI3K/AKT信号对于妊娠期间迅速扩大的aMEC群体的生存是必需的,而STAT5a信号是ErbB3下游MEC分化的关键驱动因素[19]。STAT5a可以通过信号转导途径调节乳蛋白合成和妊娠期乳腺上皮细胞的分化,维持乳腺上皮细胞的存活,促进酪蛋白合成[31-32]。不同的AKT1、AKT2和AKT3敲除小鼠表明,AKT对STAT5a的激活和乳腺细胞增殖是必要的[33]。因此,本研究干扰EPB41L4A-AS后检测了PI3K-AKT和JAK-STAT信号通路中相关基因的表达是否受到影响,发现PIK3R1、AKT和STAT5a基因在转录和翻译水平均受EPB41L4A-AS的调控,干扰EPB41L4A-AS表达后,显著增加了PIK3R1、AKT和STAT5a在mRNA水平的相对表达量。PIK3R1、AKT和STAT5a蛋白的相对表达量显著升高,且磷酸化AKT(p-AKT)蛋白的表达量也显著升高。这些结果表明,干扰EPB41L4A-AS表达后显著增加了BMECs中ErbB3的相对表达量,从而促进PI3K/AKT和JAK-STAT信号通路关键基因的表达。
有研究证明,lncRNAs能直接与信号蛋白的功能域相互作用,NF-κB可以上调lncRNA NKILA的表达量,同时NKILA与NF-κB/IκB结合,直接掩盖了IκB的磷酸化基序,从而抑制IKK诱导的IκB磷酸化和NF-κB激活,影响乳腺癌的转移和预后[34]。在hESCs中,定位细胞质的lncRNA hFAST结合到E3泛素连接酶β-TrCP的WD40结构域,并阻断其与磷酸化β-catenin的相互作用以防止降解,导致WNT信号通路激活,从而实现多能性[35]。lncRNA DANCR与RXRA结合,通过GSK3β增加其丝氨酸49/78磷酸化,从而激活PIK3CA转录,进而增强PI3K/AKT信号通路和TNBC肿瘤的发生[36]。因此推测,EPB41L4A-AS可能与ErbB3蛋白的功能域存在潜在的相互作用,但这需要更深入的研究证明。
4 结论本研究结果表明,降低EPB41L4A-AS表达后能够促进ErbB3的表达,激活PI3K/AKT和JAK-STAT信号通路从而促进BMECs的增殖。
| [1] |
华丽萍, 刘双行, 赵鑫哲, 等. DDR1对奶牛乳腺上皮细胞增殖与凋亡的调控作用[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2020, 51(9): 2109-2119. HUA L P, LIU S X, ZHAO X Z, et al. Effects of interference and overexpression of DDR1 on proliferation and apoptosis of mammary epithelial cells in dairy cows[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2020, 51(9): 2109-2119. (in Chinese) |
| [2] |
LAPORTA J, DADO-SENN B, SKIBIEL A L. Late gestation hyperthermia: epigenetic programming of daughter's mammary development and function[J]. Domest Anim Endocrinol, 2022, 78: 106681. DOI:10.1016/j.domaniend.2021.106681 |
| [3] |
HUO N, YU M M, LI X Y, et al. PURB is a positive regulator of amino acid-induced milk synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2019, 234(5): 6992-7003. DOI:10.1002/jcp.27452 |
| [4] |
ZHAO Y L, YAN S M, CHEN L, et al. Effect of interaction between leucine and acetate on the milk protein synthesis in bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Anim Sci J, 2019, 90(1): 81-89. DOI:10.1111/asj.13125 |
| [5] |
YU M M, WANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Taurine promotes milk synthesis via the GPR87-PI3K-SETD1A signaling in BMECs[J]. J Agric Food Chem, 2019, 67(7): 1927-1936. DOI:10.1021/acs.jafc.8b06532 |
| [6] |
BRIDGES M C, DAULAGALA A C, KOURTIDIS A. LNCcation: lncRNA localization and function[J]. J Cell Biol, 2021, 220(2): e202009045. DOI:10.1083/jcb.202009045 |
| [7] |
MA M R, PEI Y F, WANG X X, et al. LncRNA XIST mediates bovine mammary epithelial cell inflammatory response via NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammasome pathway[J]. Cell Prolif, 2019, 52(1): e12525. DOI:10.1111/cpr.12525 |
| [8] |
WANG X X, WANG H, ZHANG R Q, et al. LRRC75A antisense lncRNA1 knockout attenuates inflammatory responses of bovine mammary epithelial cells[J]. Int J Biol Sci, 2020, 16(2): 251-263. DOI:10.7150/ijbs.38214 |
| [9] |
STANDAERT L, ADRIAENS C, RADAELLI E, et al. The long noncoding RNA Neat1 is required for mammary gland development and lactation[J]. RNA, 2014, 20(12): 1844-1849. DOI:10.1261/rna.047332.114 |
| [10] |
ZHANG Y S, XIA J X, LI Q L, et al. NRF2/long noncoding RNA ROR signaling regulates mammary stem cell expansion and protects against estrogen genotoxicity[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289(45): 31310-31318. DOI:10.1074/jbc.M114.604868 |
| [11] |
LI X L, CHEN N F, ZHOU L, et al. Genome-wide target interactome profiling reveals a novel EEF1A1 epigenetic pathway for oncogenic lncRNA MALAT1 in breast cancer[J]. Am J Cancer Res, 2019, 9(4): 714-729. |
| [12] |
LIU A N, QU H J, GONG W J, et al. lncRNA AWPPH and miRNA-21 regulates cancer cell proliferation and chemosensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer by interacting with each other[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(9): 14860-14866. DOI:10.1002/jcb.28747 |
| [13] |
SHAO G L, WANG M C, FAN X L, et al. lncRNA CASC9 positively regulates CHK1 to promote breast cancer cell proliferation and survival through sponging the miR-195/497 cluster[J]. Int J Oncol, 2019, 54(5): 1665-1675. |
| [14] |
YANG W, LI X Z, QI S P, et al. lncRNA H19 is involved in TGF-β1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in bovine epithelial cells through PI3K/AKT signaling pathway[J]. PeerJ, 2017, 5: e3950. DOI:10.7717/peerj.3950 |
| [15] |
ZHU C, JIANG Y, ZHU J R, et al. CircRNA8220 sponges MiR-8516 to regulate cell viability and milk synthesis via Ras/MEK/ERK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways in goat mammary epithelial cells[J]. Animals (Basel), 2020, 10(8): 1347. |
| [16] |
刘晓飞, 高学军, 李庆章, 等. stat5高效表达对奶牛乳腺上皮细胞泌乳能力的影响[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2011, 42(4): 508-512. LIU X F, GAO X J, LI Q Z, et al. Effects on lactation ability of dairy cow mammary gland epithelial cells by stat5 high expression[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2011, 42(4): 508-512. (in Chinese) |
| [17] |
KHAN M Z, KHAN A, XIAO J X, et al. Role of the JAK-STAT pathway in bovine mastitis and milk production[J]. Animals (Basel), 2020, 10(11): 2107. |
| [18] |
LEE H K, WILLI M, KUHNS T, et al. Redundant and non-redundant cytokine-activated enhancers control Csn1 s2b expression in the lactating mouse mammary gland[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 2239. DOI:10.1038/s41467-021-22500-w |
| [19] |
KIM K, LEE D. ERBB3-dependent AKT and ERK pathways are essential for atrioventricular cushion development in mouse embryos[J]. PLoS One, 2021, 16(10): e0259426. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0259426 |
| [20] |
WILLIAMS M M, VAUGHT D B, JOLY M M, et al. ErbB3 drives mammary epithelial survival and differentiation during pregnancy and lactation[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2017, 19(1): 105. DOI:10.1186/s13058-017-0893-7 |
| [21] |
YANG B, JIAO B L, GE W, et al. Transcriptome sequencing to detect the potential role of long non-coding RNAs in bovine mammary gland during the dry and lactation period[J]. BMC Genomics, 2018, 19(1): 605. DOI:10.1186/s12864-018-4974-5 |
| [22] |
杨兵, 李晓凤, 王昕. 长链非编码RNA在畜禽经济性状中的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2018, 49(10): 2063-2069. YANG B, LI X F, WANG X. Research progress of long noncoding RNA in economic traits of livestock[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2018, 49(10): 2063-2069. DOI:10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2018.10.001 (in Chinese) |
| [23] |
YANG M Y, LU H F, LIU J J, et al. lncRNAfunc: A knowledgebase of lncRNA function in human cancer[J]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2022, 50(D1): D1295-D1306. DOI:10.1093/nar/gkab1035 |
| [24] |
YADAV G, KULSHRESHTHA R. Metastasis associated long noncoding RNAs in glioblastoma: Biomarkers and therapeutic targets[J]. J Cell Physiol, 2022, 237(1): 401-420. DOI:10.1002/jcp.30577 |
| [25] |
JI Z B, CHAO T L, LIU Z H, et al. Genome-wide integrated analysis demonstrates widespread functions of lncRNAs in mammary gland development and lactation in dairy goats[J]. BMC Genomics, 2020, 21(1): 254. DOI:10.1186/s12864-020-6656-3 |
| [26] |
MU T, HU H H, FENG X F, et al. Screening and conjoint analysis of key lncRNAs for milk fat metabolism in dairy cows[J]. Front Genet, 2022, 13: 772115. DOI:10.3389/fgene.2022.772115 |
| [27] |
ASKARIAN-AMIRI M E, CRAWFORD J, FRENCH J D, et al. SNORD-host RNA Zfas1 is a regulator of mammary development and a potential marker for breast cancer[J]. RNA, 2011, 17(5): 878-891. DOI:10.1261/rna.2528811 |
| [28] |
SHARMA U, BARWAL T S, KHANDELWAL A, et al. LncRNA ZFAS1 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer by targeting STAT3[J]. Biochimie, 2021, 182: 99-107. DOI:10.1016/j.biochi.2020.12.026 |
| [29] |
YOUNG C D, PFEFFERLE A D, OWENS P, et al. Conditional loss of ErbB3 delays mammary gland hyperplasia induced by mutant PIK3CA without affecting mammary tumor latency, gene expression, or signaling[J]. Cancer Res, 2013, 73(13): 4075-4085. DOI:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4579 |
| [30] |
JI Z C, HAN S H, XING Y F. Overexpression of miR-3196 suppresses cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis through targeting ERBB3 in breast cancer[J]. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, 2018, 22(23): 8383-8390. |
| [31] |
FARACI-ORF E C, MCFADDEN C, VOGEL W F. DDR1 signaling is essential to sustain stat5 function during lactogenesis[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2006, 97(1): 109-121. DOI:10.1002/jcb.20618 |
| [32] |
BUSER A C, GASS-HANDEL E K, WYSZOMIERSKI S L, et al. Progesterone receptor repression of prolactin/signal transducer and activator of transcription 5-mediated transcription of the β-casein gene in mammary epithelial cells[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2007, 21(1): 106-125. DOI:10.1210/me.2006-0297 |
| [33] |
CHEN C C, BOXER R B, STAIRS D B, et al. Akt is required for Stat5 activation and mammary differentiation[J]. Breast Cancer Res, 2010, 12(5): R72. DOI:10.1186/bcr2640 |
| [34] |
LIU B D, SUN L J, LIU Q, et al. A cytoplasmic NF-κB interacting long noncoding RNA blocks IκB phosphorylation and suppresses breast cancer metastasis[J]. Cancer Cell, 2015, 27(3): 370-381. DOI:10.1016/j.ccell.2015.02.004 |
| [35] |
GUO C J, MA X K, XING Y H, et al. Distinct processing of lncRNAs contributes to non-conserved functions in stem cells[J]. Cell, 2020, 181(3): 621-636. DOI:10.1016/j.cell.2020.03.006 |
| [36] |
TANG J M, ZHONG G S, ZHANG H B, et al. LncRNA DANCR upregulates PI3K/AKT signaling through activating serine phosphorylation of RXRA[J]. Cell Death Dis, 2018, 9(12): 1167. DOI:10.1038/s41419-018-1220-7 |
(编辑 郭云雁)



