2. 山东省农业科学院 畜牧兽医研究所, 济南 250100;
3. 山东师范大学, 济南 250014
2. Institute of Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, Shandong Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Jinan 250100, China;
3. Shandong Normal University, Jinan 250014, China
猪支原体肺炎(Mycoplasma pneumonia of swine, Mps)是由猪肺炎支原体(Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae, Mhp)引起的一种呼吸道疾病[1-2],又名喘气病,具有慢性、可接触性、高传染性的特征,通过呼吸道和直接接触传播,该病主要影响育肥猪,主要病症表现为咳嗽、气喘和患猪生长速度降低[3-4]。该病在1956年由Mare等[5]发现,至今在世界范围内广泛流行,而且猪肺炎支原体很难净化,易于受其他病原影响。支原体是介于细菌与病毒之间的特殊微生物,无细胞壁,通过黏附到猪呼吸道细胞上皮纤毛上,而导致上皮细胞的坏死、纤毛脱落和游走性改变,影响纤毛的清除功能,从而导致病猪生长发育不良、饲料转化率下降等,给规模化养殖场的健康发展造成严重危害[6-9]。
目前,对于猪肺炎支原体的诊断,主要有临床诊断(屠宰)、分离培养、血清学和分子生物学试验等方法。临床诊断不能保证准确性,分离培养需要的周期长[10-11],血清学检测易与其他支原体之间存在交叉污染[12]。随着分子生物学技术的飞速发展,PCR技术已成为实验室的常规技术[3]。环介导等温扩增技术是一种新型的基因扩增技术,Notomi等[13]在2000年首次应用。针对目的基因设计两对引物:1对外引物和1对内引物,目的基因可在恒温下短时间内得到大量扩增,通常采用琼脂糖凝胶电泳的方法对其结果进行判断,电泳条带呈阶梯状[14-16],亦或在反应管中加入荧光染料SYBR Green Ⅰ,在紫外分析仪下观察颜色变化,阳性会显现黄绿色,阴性为橘色。本研究使用横向流动试纸条检测LAMP反应结果,可通过肉眼快速准确灵敏地判断结果[17],无需紫外分析仪,更加简便、快捷、经济,更适于基层检测[18]。
1 材料与方法 1.1 试验菌株与试剂猪肺炎支原体Q株、猪圆环病毒(porcine circovirus PCV)(1、2、3型)、猪输血性传播病毒(transfusion transmitted virus, TTV)、猪伪狂犬病病毒(pseudorabies virus,PRV)、猪繁殖与呼吸综合征病毒(porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome virus, PRRSV)、猪鼻支原体(Mycoplasma hyorhinis, Mhr)、猪胸膜肺炎放线杆菌(Actinobacillus pleuropneumoniae, App)、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus, S. aureus)和大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli, E. coli)均由山东省农业科学院畜牧兽医研究所猪病研究室保存。
88份病料组织取自山东某规模化生猪养殖场。
Bst DNA聚合酶(大片段)购自美国New England Biolabs公司。甜菜碱(Betaine)购自美国Sigma-Aldrich公司。MgSO4购自美国Amresco公司。Taq DNA聚合酶购自Fermentas中国公司。SYBR Green Ⅰ核酸染料购自北京索莱宝科技有限公司。dNTP、DL2000 DNA Marker、TaqⅠ酶均购自宝生物工程(大连)有限公司。其他试剂均为进口或国产分析纯。Milenia GenLine HybriDetect侧向流检测试纸条试剂盒(含tris-buffered saline)购自Milenia Biotec GmbH公司。
1.2 方法1.2.1 DNA的提取 水煮法提取DNA。取2 mL猪肺炎支原体菌液,12 000 r·min-1离心30 min,弃上清,取50 μL ddH2O重悬沉淀,沸水煮10 min,置于-20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.2 引物设计 根据NCBI中GenBank公布的猪肺炎支原体P36基因(AY312243),利用Meg Align分析其保守区序列,应用Primer 5设计普通PCR引物,上游:5′-CCCGGCGAGAAACTGGATAC-3′,下游:5′-CCTTACAGCGGGAAGACCAC-3′。用Primer Explorer V 4设计出5套LAMP引物,如表 1,包括1对外引物FIP、BIP,1对内引物F3、B3。针对LAMP扩增出的目的片段区域,通过Primer5设计探针CATAACGGGAGACACT,BIP标记生物素,探针标记FITC。以上引物均由TaKaRa公司合成并标记。
|
|
表 1 5套Mhp的LAMP引物 Table 1 Five sets of primers for detcetion of Mhp in the LAMP |
1.2.3 普通PCR 参考文献[19]优化了PCR体系(20 μL):上、下游引物各1 μL,Taq酶10 μL,猪肺炎支原体DNA模板1 μL,双蒸水7 μL。反应条件:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃变性40 s,53 ℃退火40 s,72 ℃延伸1 min,35个循环;72 ℃终延伸5 min。反应结束取5 μL扩增产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定,同时以标准品为模板检测普通PCR敏感性。
1.2.4 LAMP反应体系及优化 参考文献[10]建立LAMP反应体系(25 μL):Bst DNA聚合酶1 μL,10×Buffer 2.5 μL,MgSO4 1 μL,甜菜碱2 μL,dNTP 2 μL,FIP 1 μL,BIP 1 μL,F3 0.25 μL,B3 0.25 μL,DNA 2 μL,双蒸水6 μL。以Mhp基因组DNA作为模板,对LAMP的温度与时间进行优化。阴性对照以水作为模板,分别在50、55、60、65、70 ℃条件下扩增40 min,取5 μL扩增产物置于1.5%琼脂糖中做凝胶电泳,依据扩增效果确立最佳反应温度。再以在最佳反应温度下优化反应时间,分别反应5、10、15、20、25、30、35、40 min,取5 μL扩增产物置于1.5%琼脂糖中做凝胶电泳,同时在反应管中加入SYBR Green Ⅰ,在紫外分析仪下观察颜色变化,依据扩增效果确立可行引物与最佳反应时间。
1.2.4.1 LAMP特异性 分别以PCV(1、2、3型),TTV、PRV、PRRSV基因组DNA或cDNA和Mhr、App、S.aureus和E.coli DNA为模板,经优化好的反应温度与时间检验LAMP的特异性。扩增产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测。
1.2.4.2 LAMP敏感性试验 利用普通PCR扩增产物经电泳后,电泳产物切胶回收,纯化,定量,克隆至pMD18-T载体中,转化DH5感受态细胞,挑取阳性菌落做PCR鉴定,用加入氨苄青霉素的LB培养基摇菌12 h,并提取质粒,测定质粒浓度,计算拷贝数,使用灭菌水将质粒稀释一定倍数,使每微升溶液中含有的质粒拷贝数数量级为10-3~1011,作为标准品待用。分别以标准品作为模板,阴性对照以水替代DNA模板,进行LAMP敏感性试验。
1.2.5 LAMP-LFD1.2.5.1 LFD检测 向LAMP反应管中加入2 μL探针,反应结束后,取5 μL加入含有100 μL Tris-buffered saline的1.5 mL EP管中,插入试纸条,静置2 min,观察结果。
1.2.5.2 LAMP-LFD方法的特异性分析 分别以PCV(1、2、3型)、TTV、PRV、PRRSV基因组DNA和Mhr、App、S.aureus、E.coli的DNA为模板,按优化的条件检测该方法的特异性,同时以Mhp DNA作为阳性对照。
1.2.5.3 LAMP-LFD敏感性分析 以10-3~104ng·μL-1DNA作为模板,经优化好的反应时间、温度反应后,结果用试纸条检测,以此分析LAMP-LFD敏感性。
1.2.6 LAMP-LFD方法临床样品检测 以提取的88份临床病料DNA作为模板,进行LAMP-LFD临床样品检测试验,并与国标方法相比较,计算LAMP-LFD符合率。
2 结果 2.1 普通PCR通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳可见,PCR成功扩增出预期的条带,目的条带在427 bp,符合预期的结果,由图 1可知,普通PCR最低可以检测到103 ng·μL-1DNA。
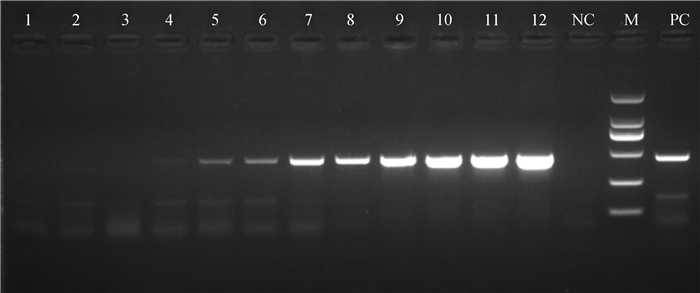
|
1~12分别为100~1011ng·μL-1 Mhp DNA;M. DL2000 DNA相对分子质量标准;NC.以水为模板的阴性对照;PC.以Mhp DNA为模板的阳性对照 1-12. 1×100-1011ng·μL-1 of Mhp, respectively; NC. Negative control with water as template; PC. Positive control with Mhp DNA as template; M. DL2000 DNA marker 图 1 琼脂糖凝胶电泳PCR敏感性结果 Fig. 1 Sensitivity of the PCR reaction by agarose gel electrophoresis |
2.2.1 LAMP反应条件的优化 经优化探索LAMP条件筛选,确立第3套可行的引物,确定出最佳反应时间与温度。由图 2A可知,在65 ℃时,经凝胶电泳出现阶梯状条带,由图 2B可知,反应体系在15 min后开始出现阶梯状条带。
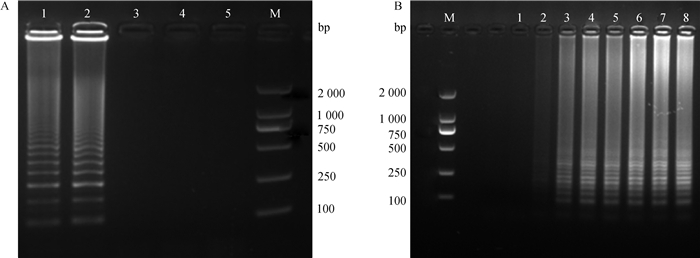
|
A.1~5.70、65、60、55、50 ℃;B.1~8. 5、10、15、20、25、30、35、40 min;M. DL2000 DNA相对分子质量标准 A. The effect of temperature (lane 1-5 indicate 70, 65, 60, 55 and 50 ℃, respectively); B. The effect of LAMP reaction time (lane 1-8 indicate 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35 and 40 min, respectively); M. DL2000 DNA marker 图 2 LAMP反应条件优化 Fig. 2 Optimization of the LAMP reaction conditions for Mhp |
2.2.2 特异性 分别以PCV(1、2、3型)、TTV、PRV、PRRSV基因组DNA或cDNA和Mhr、APP、S.aureus、E.coli的DNA为模板验证LAMP反应的特异性,琼脂糖凝胶电泳结果显示仅Mhp DNA出现特征性阶梯状扩增条带,而其他病原均未出现梯形条带(图 3)。
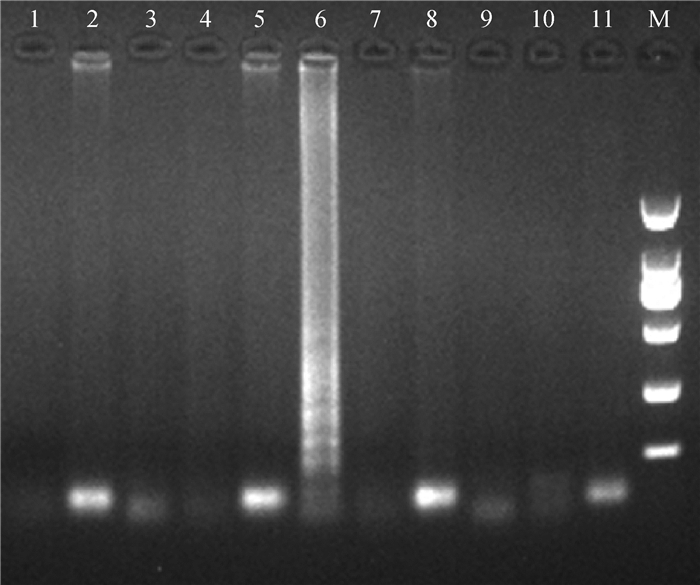
|
1.PCV1;2. PCV2;3. PCV3;4. TTV;5. PRV;6. Mhp;7. PRRSV;8. Mhr;9. App;10. S. aureus;11. E. coli;M. DL2000 DNA相对分子质量标准 1. PCV1; 2. PCV2; 3. PCV3; 4. TTV; 5. PRV; 6. Mhp; 7. PRRSV; 8. Mhr; 9. App; 10. S. aureus; 11. E. coli; M. DL2000 DNA marker 图 3 LAMP反应的特异性 Fig. 3 The specificity result of LAMP |
2.2.3 敏感性 LAMP的敏感性试验可以检测到100 ng·μL-1DNA(图 4)。
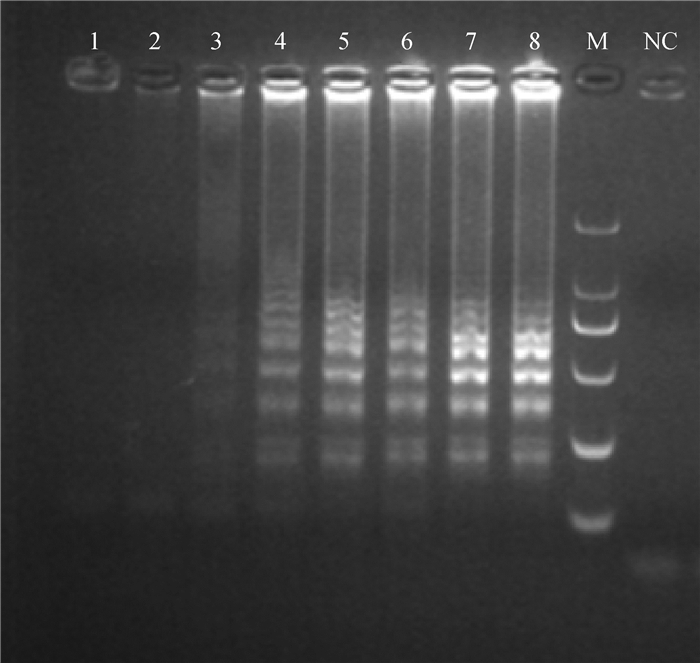
|
1~8.1×10-3、1×10-2、1×10-1、1×100、1×101、1×102、1×103、1×104ng·μL-1 DNA;M. DL2000 DNA相对分子质量标准;NC.以水为模板的阴性对照 1-8. 1×10-3, 1×10-2, 1×10-1, 1×100, 1×101, 1×102, 1×103, 1×104ng·μL-1 of Mhp DNA, respectively; M. DL2000 DNA marker; NC. Negative control with water as template 图 4 LAMP反应的敏感性 Fig. 4 The sensitivity of the LAMP reaction by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis |
2.3.1 LFD试纸条检测结果 以Mhp基因组DNA为模板进行LAMP反应,反应产物分别用琼脂糖凝胶电泳、SYBR Green Ⅰ、LFD进行检测,验证该方法的可行性。结果显示,通过琼脂糖凝胶电泳,阳性出现明显的阶梯状条带,而阴性对照无条带(图 5A);SYBR Green Ⅰ通过肉眼可见阳性显现黄绿色,而阴性为橘黄色,在紫外分析仪下,阳性发出强烈的黄绿色荧光,而阴性呈现橘色(图 5B);LFD显示,阳性在检测线和控制线区域内出现2条红线,而阴性仅在控制线出现1条红线(图 5C)。因此,LAMP-LFD检测方法可行。
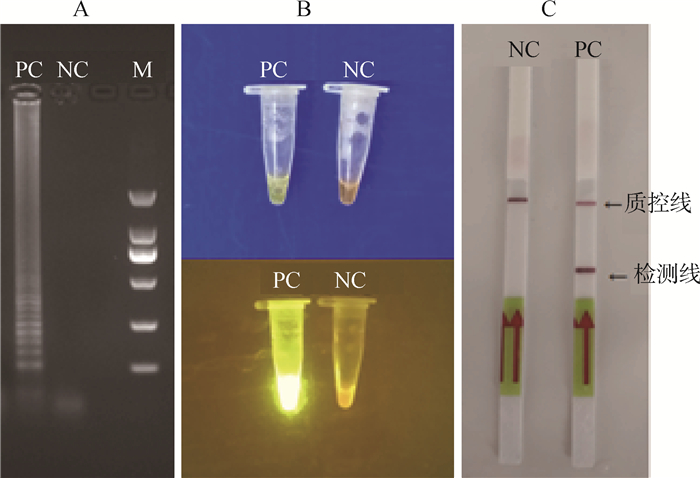
|
A.琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测结果;B. SYBR GreenⅠ检测结果;C. LFD检测结果;PC.以Mhp DNA为模板的阳性对照;NC.以水为模板的阴性对照;M. DL2000 DNA相对分子质量标准 A. 2% agarose gel electrophoresis; B. SYBR Green Ⅰ; C. LFD; PC. Positive control with Mhp DNA as template; NC. Negative control with water as template; M. DL2000 DNA marker 图 5 LAMP产物不同方法的检测结果 Fig. 5 Detection results of lamp products by different methods |
2.3.2 LAMP-LFD方法特异性分析 结果显示,仅Mhp出现两条红线,阴性对照和以PCV(1、2、3型)、TTV、PRV、PRRSV、Mhr、App、S.aureus、E.coli为模板的反应均只在质控线出现一条红线。结果证明LAMP-LFD的特异性良好(图 6)。
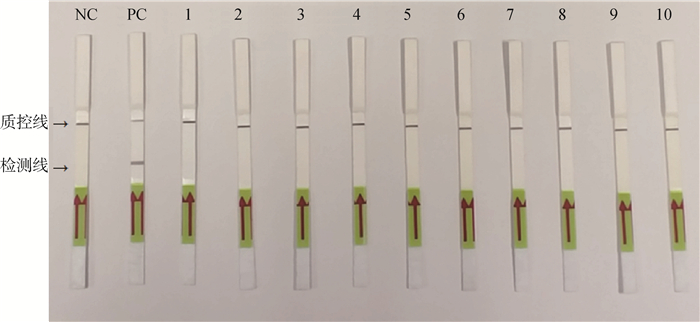
|
NC.以水为模板的阴性对照;PC.以Mhp DNA为模板的阳性对照;1. PCV1;2. PCV2;3. PCV3;4. TTV;5. PRV;6. PRRSV;7. Mhr;8. App;9. S. aureus;10. E. coli NC. Negative control with water as template; PC. Positive control with Mhp DNA as template; 1. PCV1; 2. PCV2; 3. PCV3; 4. TTV; 5. PRV; 6. PRRSV; 7. Mhr; 8. App; 9. S. aureus; 10. E. coli 图 6 LAMP-LFD特异性检测结果 Fig. 6 Specific test results of LAMP-LFD |
2.3.3 LAMP-LFD敏感性分析 反应结果经试纸条分析(图 7),最低可检测的Mhp DNA浓度是100 ng·μL-1,比普通PCR敏感度高1 000倍。
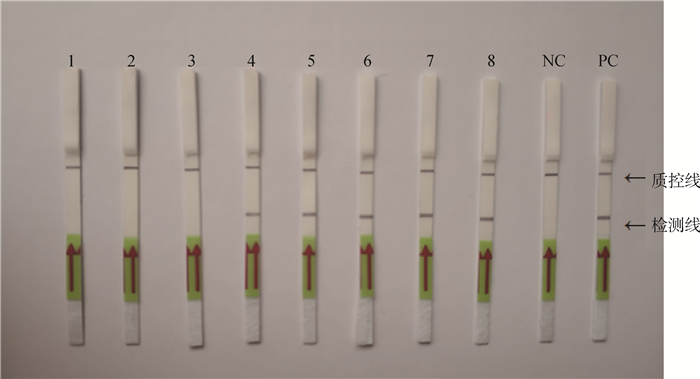
|
1~8分别为1×10-3、1×10-2、1×10-1、1×100、1×101、1×102、1×103、1×104ng·μL-1Mhp DNA;NC.以水为模板的阴性对照;PC.以Mhp DNA为模板的阳性对照 1-8. 1×10-3, 1×10-2, 1×10-1, 1×100, 1×101, 1×102, 1×103, 1×104ng·μL-1 of Mhp DNA, respectively; NC. Negative control with water as template; PC. Positive control with Mhp DNA as template 图 7 Mhp LAMP-LFD检测方法灵敏度 Fig. 7 Sensitivity of the LAMP reaction by LFD |
分别检测了88份疑似Mhp感染的病料,与邵国青等[19]建立检测Mhp国标方法(GB/T 35909—2018)相比,国标可检测到56份阳性,LAMP-LFD可检测到64份阳性, LAMP-LFD比国标可多检测出8份病料,此8份病料参考文献[12]应用荧光定量PCR方法检测,结果均为阳性,则LAMP-LFD符合率可达到90.9%,LAMP-LFD的临床检测方法更灵敏一些。
3 讨论猪支原体肺炎感染在生猪养殖过程中存在较普遍,几乎所有养猪的国家和地区均存在。近年来,诸多学者致力于Mhp的致病机制研究,但如何有效的防控也迫在眉睫[20-21],因此, 建立起一套快速、敏感、特异、准确的检测方法对生猪养殖业以及该病的诊断具有重大的研究意义[22]。
国内外对于Mhp的检测方法多样,其中经典方法是病原分离培养,但该方法费时费力,Mhp较难分离培养[23],而且在分离培养过程中与Mhr存在较严重的交叉污染,其次,培养周期长,一般需要1周以上的时间,还需要特定的培养基,再者,活菌极易形成气溶胶污染,很难排除污染[13]。ELISA、血清学、分子生物学、PCR、荧光定量PCR检测[3]敏感性较高,但PCR和荧光检测需要借助专业昂贵的试验仪器和试剂,费用相对较高,而且需要相对专业的技术人员操作[22]。目前,针对猪肺炎支原体的国标检测方法是PCR[19],整个过程需要2 h。师丽刚等[24]建立的普通PCR方法最低检出量为2.6×10-3 μg·μL-1,宋建领等[25]建立的Mps荧光定量PCR检测方法可检测到101 ng·μL-1,Kimaru等[26]建立的荧光定量PCR方法可以在1 h左右完成Mhp的检测。LAMP仅需要简单的水浴锅或者可以加温的仪器,操作简单,方便快捷,安全高效,经济费用较低,无需专业的操作与昂贵仪器设备,更适用于养殖场的基层检测[25]。Li(李家和)等[27]建立的LAMP可以在30 min内完成肺炎支原体的扩增。武昱孜等[28]建立的环介导恒温扩增检测Mps,可达标准质粒的10拷贝·μL-1。在本研究中, 建立了1个LAMP-LFD可视化方法,DNA可以在65 ℃反应15 min,与探针杂交5 min[17],整个过程只需要40 min(包括15 min的DNA快速制备),省时,灵敏度高,可达到100ng·μL-1。
|
|
表 2 国标PCR和LAMP-LFD临床样品检测结果 Table 2 The results of clinical samples by standard PCR and LAMP-LFD |
武昱孜等[28]建立的环介导恒温扩增检测猪支原体肺炎在63 ℃反应45 min,通过肉眼观察、SYBR Green Ⅰ染色及电泳来判定扩增结果。迄今为止,对LAMP扩增产物的检测方法应用最广的是琼脂糖凝胶电泳和SYBR GreenⅠ。琼脂糖凝胶电泳易形成气溶胶,造成假阳性,SYBR Green Ⅰ需要借助紫外分析仪[29],这两种方法适于实验室检测。本研究建立的LAMP-LFD方法,应用LFD试纸条进行检测猪肺炎支原体LAMP扩增产物,可通过肉眼观测检测线有无判定结果[15, 30],简便,快捷,仅需5 min,最低检测限为100ng·μL-1DNA,这也是对猪支原体肺炎LAMP-LFD的首次报道与应用。在现场应用时,应提供高灵敏度、高特异性的最佳诊断技术,同时,低成本、快速、易操作也是必须考虑的因素[31-32]。LFD不依赖于高端设备,整个诊断过程仅需5 min[33],对Mhp的有效诊断有一定的参考价值,该方法简单有效更适用于临床基础检测或难以达到实验室诊断条件的偏远地区[34-35]。本研究首次建立了基于LAMP-LFD的检测Mhp诊断方法,缩短检测时间。该方法的建立对于开发Mhp感染的新型诊断工具,具有良好应用前景,为更高效便捷的临床检测另辟蹊径。
4 结论本研究首次建立了以Mhp DNA为靶标的LAMP-LFD可视化快速检测方法,能够快速、准确的检测Mhp,敏感性高,最低可检测到100 ng·μL-1 DNA;耗时短,从基因组DNA提取到结果判读仅需40 min,较常规PCR可缩短2 h;特异性强,操作简单,成本低,无需特殊仪器和特定的实验室条件,更适用于现场检测及基层普及应用,为Mhp的诊断防治提供了新颖的发展方向,以期成为快速的常规简易检测手段。
| [1] | SIBILA M, NOFRARIAS M, LÓPEZ-SORIA S, et al. Chronological study of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection, seroconversion and associated lung lesions in vaccinated and non-vaccinated pigs[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2007, 122(1-2): 97–107. |
| [2] |
武昱孜, 邢宪平, 韦艳娜, 等. 不同猪支原体肺炎活疫苗菌株P46和P97基因序列差异性分析[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2017, 48(12): 2365–2373.
WU Y Z, XING X P, WEI Y N, et al. Comparison of nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of P46 and P97 for the different live vaccine strains of Mycoplasmal pneumonia of swine[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2017, 48(12): 2365–2373. (in Chinese) |
| [3] | MAES D, SIBILA M, KUHNERT P, et al. Update on Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infections in pigs:knowledge gaps for improved disease control[J]. Transbound Emerg Dis, 2018, 65(S1): 110–124. |
| [4] | MAES D, SEGALES J, MEYNS T, et al. Control of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infections in pigs[J]. Vet Microbiol, 2008, 126(4): 297–309. |
| [5] | MARE C J, SWITZER W P. New species: Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae: a causative agent of virus pig pneumonia[J]. Vet Med Small Anim Clin, 1965, 60: 841–846. |
| [6] | NIELSEN G B, HAUGEGAARD J, JOLIE R. Field evaluation of a ready-to-use combined Porcine circovirus type 2 and Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae vaccine in Denmark- a historical comparison of productivity parameters in 20 nursery and 23 finishing herds[J]. Porcine Health Manag, 2018, 4: 29. |
| [7] |
刘建民. 猪支原体肺炎诊断及防治[J]. 畜牧兽医科学:电子版, 2019(11): 104–105.
LIU J M. The diagnosis and prevention of Mycoplasmal pneumonia of swine[J]. Graziery Veterinary Sciences:Electronic Version, 2019(11): 104–105. (in Chinese) |
| [8] |
许立阳. 一起猪支原体肺炎的诊断与防治[J]. 当代畜禽养殖业, 2019(7): 47–48.
XU L Y. A diagnosis and prevention of Mycoplasmal pneumonia of swine[J]. Modern Animal Husbandry, 2019(7): 47–48. (in Chinese) |
| [9] |
王贵平, 李君佩, 罗广, 等. 猪肺炎支原体对猪肺泡巨噬细胞外源性抗原递呈加工功能相关因子mRNA表达量的影响[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2017, 37(11): 2101–2107.
WANG G P, LI J P, LUO G, et al. Effect of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae on mRNA expression of the some factors' related to presentation and processing of exogenous antigen in porcine alveolar macrophage[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2017, 37(11): 2101–2107. (in Chinese) |
| [10] | TSAI S M, LIU H J, SHIEN J H, et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of infectious bursal disease virus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick[J]. J Virol Methods, 2012, 181(1): 117–124. |
| [11] |
杨若松, 冯志新, 华利忠, 等. 猪支原体肺炎发病模型的建立[J]. 河北农业大学学报, 2015, 38(6): 79–82, 87.
YANG R S, FENG Z X, HUA L Z, et al. The establishment of a swine model with high virulence organization of Mycoplasma pneumonia[J]. Journal of Agricultural University of Hebei, 2015, 38(6): 79–82, 87. (in Chinese) |
| [12] |
武昱孜, 熊祺琰, 刘蓓蓓, 等. 猪肺炎支原体和猪鼻支原体双重荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立[J]. 畜牧兽医学报, 2017, 48(8): 1491–1498.
WU Y Z, XIONG Q Y, LIU B B, et al. Duplex real-time PCR method for detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae and Mycoplasma hyorhinis[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica, 2017, 48(8): 1491–1498. (in Chinese) |
| [13] | NOTOMI T, OKAYAMA H, MASUBUCHI H, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification of DNA[J/OL]. Nucleic Acids Res, 2000, 28(12): e63. [2020-01-01]https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.12.e63. |
| [14] |
李秀梅, 石瑜, 朱雅宁, 等. 环介导等温扩增技术与横向流动试纸条法快速检测鸡贫血病毒的研究[J]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2018, 26(1): 25–31.
LI X M, SHI Y, ZHU Y N, et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of chicken anemia virus by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with lateral-flow dipstick[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Parasitology, 2018, 26(1): 25–31. (in Chinese) |
| [15] |
李秀梅, 梁智选, 李颖, 等. 环介导等温扩增技术与横向流动试纸条法快速检测布鲁氏杆菌[J]. 食品与生物技术学报, 2017, 36(12): 1276–1282.
LI X M, LIANG Z X, LI Y, et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of Brucella spp. by loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral-flow dipstick[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2017, 36(12): 1276–1282. (in Chinese) |
| [16] |
乔艳, 周前进, 李孝军, 等. 环介导等温扩增联合横向流动试纸条检测简单异尖线虫/派氏异尖线虫方法的建立[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2019, 50(2): 324–335.
QIAO Y, ZHOU Q J, LI X J, et al. A loop-mediated isothermal amplification technique combined with a lateral flow dipstick for the detection of Anisakis simplex sensu stricto/Anisakis pegreffii in commercial fish[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2019, 50(2): 324–335. (in Chinese) |
| [17] | ZHANG B, NAN T G, XIN J, et al. Development of a colloidal gold-based lateral flow dipstick immunoassay for rapid detection of chlorogenic acid and luteoloside in Flos Lonicerae Japonicae[J]. J Pharm Biomed Anal, 2019, 170: 83–88. |
| [18] |
柴方超, 周前进, 陈炯. 环介导等温扩增联合横向流动试纸条可视化检测迟缓爱德华菌[J]. 中国兽医学报, 2017, 37(6): 1103–1110.
CHAI F C, ZHOU Q J, CHEN J. Visual detection of Edwardsiella tarda based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science, 2017, 37(6): 1103–1110. (in Chinese) |
| [19] |
中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会.猪肺炎支原体PCR检测方法: GB/T 35909—2018[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018.
General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the P.R.C. Detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae using PCR method: GB/T 35909-2018[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2018(in Chinese) |
| [20] |
徐引弟, 张青娴, 王治方, 等. 快速直接PCR检测猪肺炎支原体方法的建立及其应用[J]. 养猪, 2019(6): 100–102.
XU Y D, ZHANG Q X, WANG Z F, et al. Establishment and application of rapid direct PCR for the detection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae[J]. Swine Production, 2019(6): 100–102. (in Chinese) |
| [21] |
赵国胜. 猪支原体肺炎临床诊断及综合防治[J]. 畜牧兽医科学:电子版, 2019(16): 110–111.
ZHAO G S. Clinical diagnosis and comprehensive prevention and treatment of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae[J]. Graziery Veterinary Sciences:Electronic Version, 2019(16): 110–111. (in Chinese) |
| [22] |
李石, 李劼, 周霞. 猪肺炎支原体生长培养基的筛选[J]. 黑龙江畜牧兽医, 2014(18): 61–63.
LI S, LI J, ZHOU X. The screen of growth medium by Mycoplasma pneumonia[J]. Heilongjiang Animal Science and Veterinary Medicine, 2014(18): 61–63. (in Chinese) |
| [23] |
刘金媛. 猪支原体肺炎诊断与防治措施[J]. 畜牧兽医科学:电子版, 2019(7): 100–101.
LIU J Y. Diagnosis and prevention of Mycoplasma pneumonia in pigs[J]. Graziery Veterinary Sciences:Electronic Version, 2019(7): 100–101. (in Chinese) |
| [24] |
师丽刚, 周飞. 猪肺炎支原体PCR检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 现代畜牧兽医, 2016(9): 11–15.
SHI L G, ZHOU F. Establishment and application of PCR detection method of mycoplasma pneumonia in pigs[J]. Modern Journal of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, 2016(9): 11–15. (in Chinese) |
| [25] |
宋建领, 高华峰, 信爱国, 等. 猪肺炎支原体实时荧光定量PCR检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 畜牧与兽医, 2013, 45(5): 71–74.
SONG J L, GAO H F, XIN A G, et al. Establishment and application of real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR for Mycoplasma pneumoniae[J]. Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine, 2013, 45(5): 71–74. (in Chinese) |
| [26] | KIMARU W K, BAI F F, WU Y Z, et al. Comparative analysis for the detection and monitoring of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae infection by nested PCR (n-PCR) and real time PCR (q-PCR) from field swine herds[J]. Agric Sci Technol, 2014, 15(6): 918–921. |
| [27] | LI J H, MINION C F, PETERSEN A C, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification for rapid and convenient detection of Mycoplasma hyopneumoniae[J]. World J Microbiol Biotechnol, 2013, 29(4): 607–616. |
| [28] |
武昱孜, 刘茂军, 杜改梅, 等.快速敏感的环介导恒温扩增技术检测猪肺炎支原体P36基因[C]//中国畜牧兽医学会动物传染病学分会第十六次学术研讨会论文集.济南: 中国畜牧兽医学会动物传染病学分会, 解放军军事医学科学院军事兽医研究所, 2015: 169.
WU Y Z, LIU M J, DU G M, et al. The detection for the P36 gene of mycoplasma pneumonia by rapid sensitive loop-mediated thermostatic amplification[C]//Proceedings of the 16th Symposium of Zoology Branch of Chinese Society of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine. Ji'nan: Animal Infectious Diseases Branch of Chinese Society of Animal Husbandry and Veterinary Medicine, Institute of Military Veterinary Medicine, PLA Academy of Military Medical Sciences, 2015: 169. (in Chinese) |
| [29] |
张莉, 王利丽, 魏财文, 等. 环介导等温扩增技术结合横向流动试纸条检测猪链球菌2型的应用研究[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报, 2016, 32(12): 1077–1082, 1090.
ZHANG L, WANG L L, WEI C W, et al. Rapid detection of Streptococcus suis serotype 2 with loop mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick[J]. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 2016, 32(12): 1077–1082, 1090. (in Chinese) |
| [30] | LALLE M, POSSENTI A, DUBEY J P, et al. Loop-mediated isothermal amplification-lateral-flow dipstick (LAMP-LFD) to detect Toxoplasma gondii oocyst in ready-to-eat salad[J]. Food Microbiol, 2018, 70: 137–142. |
| [31] | WU Y Y, TIAN K Y, ZHANG Y H, et al. Rapid and visual detection of Lawsonia intracellularis with an improved recombinase polymerase amplification assay combined with a lateral flow dipstick[J]. BMC Vet Res, 2019, 15(1): 97. |
| [32] |
张洁, 曹军军, 祝明松, 等. 绵羊肺炎支原体环介导等温扩增联合横向流动试纸条可视化检测方法的建立[J]. 动物医学进展, 2019, 40(3): 1–8.
ZHANG J, CAO J J, ZHU M S, et al. Establishment of loop-mediated isothermal amplification-lateral-flow dipstick for detecting Mycoplasma ovipneumoniae[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2019, 40(3): 1–8. (in Chinese) |
| [33] | DENG J R, PEI J J, GOU H C, et al. Rapid and simple detection of Japanese encephalitis virus by reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick[J]. J Virol Methods, 2015, 213: 98–105. |
| [34] |
朱俊灵, 叶佐东, 邓洁汝, 等. 猪瘟病毒RT-LAMP-LFD检测方法的建立与应用[J]. 华南农业大学学报, 2016, 37(1): 1–7.
ZHU J L, YE Z D, DENG J R, et al. Rapid detection of classical swine fever virus by loop-mediatedisothermal amplification combined with lateral flow dipstick method[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University, 2016, 37(1): 1–7. (in Chinese) |
| [35] |
程蝶, 柴方超, 蔡怡, 等. 环介导等温扩增联合横向流动试纸条可视化检测哈维氏弧菌的研究[J]. 生物技术通报, 2016, 32(6): 60–68.
CHENG D, CHAI F C, CAI Y, et al. Visual detection of Vibrio harveyi based on loop-mediated isothermal amplification combined with a lateral flow dipstick[J]. Biotechnology Bulletin, 2016, 32(6): 60–68. (in Chinese) |



