生产与配送计划是供应链中两个核心优化问题。其中,生产计划通常决定在一定计划周期内,常规/加班生产时间、转包量、生产力水平等,配送计划通常决定配送量、配送方式和配送路径[1]。在传统供应链中,尽管制造商、批发商和零售商都清楚要追求共同的利益,但是由于其追求利益最大化的动机,使得制造商、批发商和零售商还是作为独立实体来进行生产、配送[2]。目前已经证明,在供应链背景下的生产配送计划是相互联系且需要在整体上同时优化的两个环节,也出现了不少关于生产配送协调调度的综述性文章[1, 3-5]。鉴于快速消费品单位价值低、品种种类多、更新速度快等特点,为了寻求更快的补给和更短的生产周期,就需要紧密协调生产与配送环节,避免库存过剩带来成本、资源浪费[6-7]。
启发式算法可以帮助求解大规模的生产配送协调调度问题,可以弥补传统优化方法的不足,快速找到接近最优解的有效解。目前用于求解生产配送协调调度问题常用算法有模拟退火[8]、粒子群算法[9]、禁忌搜索[10]、文化基因算法[11]和遗传算法[12]等。和声搜索算法[13-15]是一种新的启发式搜索算法。该算法的新和声生成方式及微调方式非常适合离散优化问题,但是目前较少用于生产配送协调调度问题。本文尝试采用遗传和声搜索算法对快速消费品生产配送协调调度方案进行优化,并通过算例验证该算法的可行性。
1 问题描述及模型建立为建模方便,假设在某种快速消费品生产配送网络中存在多个工厂、多个配送中心和多个客户。工厂和配送中心均有库存。每个工厂只能生产一种产品,且能够满足所有客户的需求,在切换产品品种时需要考虑生产准备成本。工厂和配送中心库存有限制。工厂和配送中心的配送能力无限。
参数与决策变量如下。
n为工厂编号,n=1, 2, …, N;
i为产品编号,i=1, 2, …, I;
j为配送中心编号,j=1, 2, …, J;
m为客户编号,m=1, 2, …, M;
t为周期编号,t=1, 2, …, T;
anit为周期t工厂n产品i的单位常规生产成本;
bnit为周期t工厂n产品i的单位加班生产成本;
hnit为周期t工厂n产品i的单位库存成本;
dnit为周期t工厂n产品i的生产准备成本;
enit为周期t工厂n产品i的单位产能;
fnit为周期t工厂n产品i的单位劳动力水平;
gnijt为周期t工厂n到配送中心j产品i的单位配送成本;
gjimt为周期t配送中心j到客户m产品i的单位配送成本;
hijt为周期t配送中心j产品i的单位库存成本;
Vjit为周期t配送中心j产品i的库存量;
Vnit为周期t工厂n产品i的库存量;
Dimt为周期t客户m对产品i的需求;
Mntmax为周期t工厂n的最大产能;
Fntmax为周期t工厂n的最大可用劳动力水平;
vi为产品i的体积;
Wntmax为周期t工厂n的最大库存空间;
Wjtmax为周期t配送中心j的最大库存空间;
M为一个大正数;
Pnit为周期t工厂n产品i的常规生产量;
Onit为周期t工厂n产品i的加班生产量;
Rnijt为周期t工厂n到配送中心j产品i的配送量;
Rjimt为周期t配送中心j到客户m产品i的配送量;
Ynit为周期t工厂n产品i的生产决策变量。
目标函数:
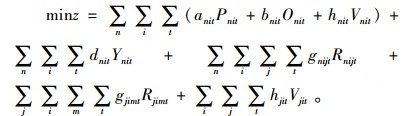
|
(1) |
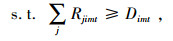
|
(2) |
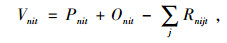
|
(3) |
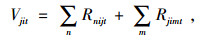
|
(4) |

|
(5) |
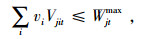
|
(6) |
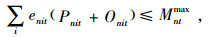
|
(7) |
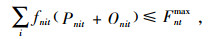
|
(8) |

|
(9) |
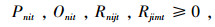
|
(10) |
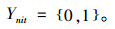
|
(11) |
其中,式(1)表示总成本目标函数,包括生产成本、加班成本、库存成本、配送成本;式(2)表示从配送中心到客户的配送量应大于客户需求量;式(3)和式(4)分别表示工厂和配送中心的库存平衡约束;式(5)和式(6)表示工厂和配送中心的库存空间限制;式(7)和式(8)分别表示工厂的产能限制和劳动力水平限制;式(9)表示生产决策变量与常规生产量和加班生产量的相关关系;式(10)为非负约束;式(11)为生产决策变量。
2 本文提出的遗传和声搜索算法和声搜索算法是由Geem等[13]提出的模仿音乐演奏过程的一种新的智能优化算法,具有时间复杂度小,适用范围广等优点。但是和声搜索算法非常依赖于和声记忆库和新解产生方式。为了克服这一缺点,本文提出通过遗传算法来产生初始解,并且调整新解的产生方式,使和声算法具有更好的收敛性和最优性。具体步骤如下。
步骤1 初始化遗传和声搜索算法参数。包括和声搜索算法参数和声记忆库大小HMS、和声记忆库考虑概率HMCR、和声微调概率PAR、迭代次数NI。
由仿真实验和文献[16],本文中和声记忆库选择概率HMCR在[0.63, 0.99]范围内取0.95,和声微调概率PAR在[0.01, 0.73]范围内取0.1,距离带宽BW在[0.01, 0.50]范围内取0.5,迭代次数NI在[50, 150]范围内取100。
遗传算法参数有种群规模GS、变异概率PM、交叉概率PC、迭代次数NI。本文中种群规模GS在[10, 200]范围内取200,交叉概率PC在[0.1, 0.9]范围内取0.7,变异概率PM在[0.05, 0.35]范围内取0.2,迭代次数NG在[50, 150]范围内取100。
步骤2 初始化和声记忆库。利用遗传算法产生初始种群,从种群中选择最好的HMS个体作为初始和声记忆库的解。其过程如下。
a) 初始化种群。参数优化后会以自然数进行编码。
b) 选择操作。采用锦标赛方法,随机选择2个适应度高的个体x1和x2,如果x1优于x2,则保留x1。同样,选择两个目标函数值高的个体x3和x4,如果x3优于x4,则保留x3。
c) 交叉操作。b1=ux3+(1-u)x1,b2=ux1+(1-u)x3,其中,u代表交叉因子。
d) 变异操作。b1和b2通常用来取代相应的个体。
e) 计算新个体的目标函数值f(x),不断循环选择、交叉和变异操作,直到达到迭代次数。
f) 新种群中的HMS个体将作为初始和声记忆库的解向量被保存起来。
步骤3 产生新和声。通过HMCR与PAR产生一个新解Xnew。根据Xnew=Xnew+2w·rand-w。其中, w代表微调幅度;rand代表 0-1之间的随机数。
步骤4 更新和声记忆库。若上述产生的新解优于和声记忆库中的最差解,那么就用新解替换最差解;否则,保持不变。
步骤5 判断是否达到迭代次数。若没有,则重新进行步骤3。
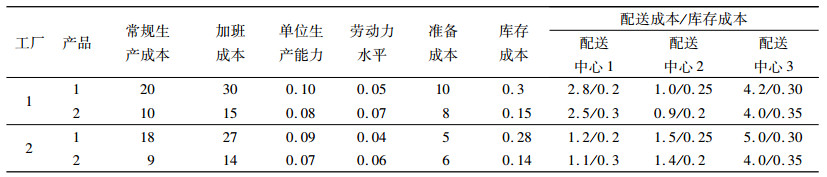
3 数值算例2种按单生产产品分别由2个工厂生产,产成品经过3个配送中心,最后配送至4个客户。已知工厂1中产品1、2的初始库存为400和200单位;工厂2中产品1、2的初始库存为300和200单位。产品1、2的库存空间分别是2和3单位,2个工厂的最大库存容量是20 000和15 000,3个配送中心的最大库存空容量分别是20 000、18 000、20 000单位。工厂1、2的最大生产能力分别为17 100和20 500。工厂1、2的最大可用劳动力水平分别为10 400和9 200。表 1~3分别为其他相关数据。
| 表 1 各产品的相关成本 Tab. 1 The related cost of each product |
| 表 2 各配送中心到客户的配送成本和客户需求 Tab. 2 The distribution cost from each DC to each customer and the demand of customer |
使用Matlab R2014a编制程序求解,目标值为1 418 046。最优值如图 1所示。
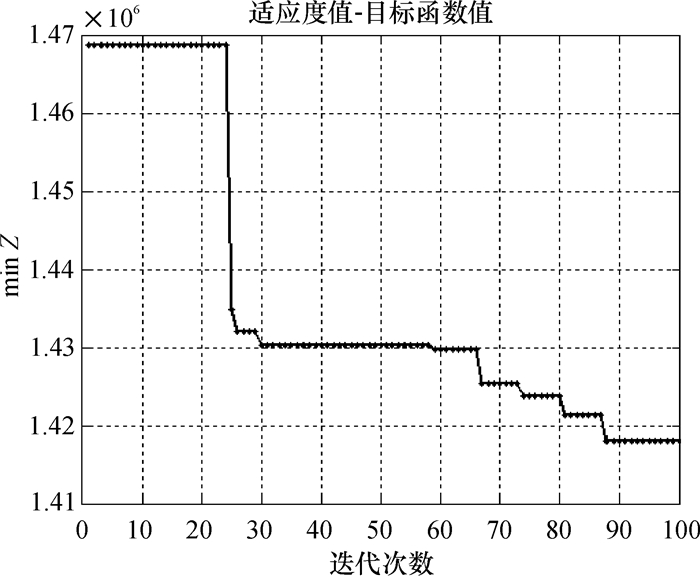
|
图 1 最优值图 Fig. 1 The optimal value |
上述遗传和声搜索算法对求解具有生产准备环节的且库存、产能、劳动力水平均有限制的快速消费品生产配送协调调度问题具有良好的求解效率,随着迭代次数增加,目标值趋于最优。但是现实生产配送过程中还可能存在不确定性参数,因此,在此基础上在模型中添加不确定参数,进一步模仿现实环境,才能得到更加有效合理的模型和解法。
| [1] |
BEHNAM Fahimnia, REZA Zanjirani Farahani, ROMEO Marian, et al. A review and critique on integrated production-distribution planning models and techniques[J].
Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2013, 32(1): 1-19.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2012.07.005. |
| [2] |
GULAY Barbarosoglu, DEMET Ozgur. Hierarchical design of an integrated production and 2-echelon distribution system[J].
European Journal of Operational Research, 1999, 118(3): 464-484.
DOI: 10.1016/S0377-2217(98)00317-8. |
| [3] |
CHEN Zhilong. Integrated production and outbound distribution scheduling: review and extensions[J].
Operations Research, 2010, 58(1): 130-148.
DOI: 10.1287/opre.1080.0688. |
| [4] |
GOETSCHALCKX M, VIDAL C J, DOGAN K. Modeling and design of global logistics systems: A review of integrated strategic and tactical models and design algorithms[J].
European Journal of Operational Research, 2002, 143(1): 1-18.
DOI: 10.1016/S0377-2217(02)00142-X. |
| [5] |
BILGEN B, OZKARAHAN I. Strategic tactical and operational production-distribution models: a review[J].
International Journal of Technology Management, 2004, 28(2): 151-171.
DOI: 10.1504/IJTM.2004.005059. |
| [6] |
BILGEN Bilge, GUNTHER Hans-Otto. Integrated production and distribution planning in the fast moving consumer goods industry: a block planning application[J].
OR Spectrum, 2010, 32(4): 927-955.
DOI: 10.1007/s00291-009-0177-4. |
| [7] |
SEL C, BILGEN B. Hybrid simulation and MIP based heuristic algorithm for the production and distribution planning in the soft drink industry[J].
Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2014, 33(3): 385-399.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2014.01.002. |
| [8] |
SARRAFHA K, RAHMATI S H A, NIAKI S T A, et al. A bi-objective integrated procurement, production, and distribution problem of a multi-echelon supply chain network design: a new tuned MOEA[J].
Computer & Operations Research, 2015, 54: 35-51.
|
| [9] |
VARTHANAN P A, MURUGAN N, KUMAR G M. A simulation based heuristic discrete particle swarm algorithm for generating integrated prodution-distribution plan[J].
Applied Soft Computing, 2012, 12(9): 3034-3050.
DOI: 10.1016/j.asoc.2012.05.001. |
| [10] |
ARMENTANO V A, SHIGUEMOTO A L, LOKKETANGEN A. Tabu search with path relinking for an integrated production-distribution problem[J].
Computers & Operations Research, 2011, 38(8): 1199-1209.
|
| [11] |
BOUDIA M, PRINS C. A memetic algorithm with dynamic population management for an integrated production-distribution problem[J].
European Journal of Operational Research, 2009, 195(3): 703-715.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ejor.2007.07.034. |
| [12] |
ALIEV R A, FAZLOLLAHI B, GUIRIMOV B G, et al. Fuzzy-genetic approach to aggregate production-distribution planning in supply chain management[J].
Information Sciences, 2007, 177(20): 4241-4255.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ins.2007.04.012. |
| [13] |
GEEM Z W, KIM J H, LOGANATHAN G V. A new heuristic optimization algorithm: harmony search[J].
Simulation, 2001, 76(2): 60-68.
DOI: 10.1177/003754970107600201. |
| [14] |
DAS S, MUKHOPADHYAY A, ROY A, et al. Exploratory power of the harmony search algorithm: analysis and improvements for global numerical optimization[J].
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B: Cybernetics, 2011, 41(1): 89-106.
DOI: 10.1109/TSMCB.2010.2046035. |
| [15] |
MANJARRES D, LANDA-TORRES I, GIL-LOPEZ S, et al. A survey on application of the harmony search algorithm[J].
Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2013, 26(8): 1818-1831.
DOI: 10.1016/j.engappai.2013.05.008. |
| [16] |
赖志柱. 和声搜索算法优化多时间窗多式联运运输方案[J].
计算机应用, 2013, 33(9): 2640-2642, 2693.
LAI Zhizhu. Harmony search algorithm for solving selection of multimodal transportation scheme with several time windows[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2013, 33(9): 2640-2642, 2693. |
 2016, Vol. 19
2016, Vol. 19