扩展功能
文章信息
- 刘莲娟, 张勐
- LIU Lian-juan, ZHANG Meng
- 冬季极端气候下城市快速路钢桥面铺装力学响应
- Mechanical Response of Steel Bridge Deck Pavement on Urban Expressway in Extreme Weather in Winter
- 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(8): 44-49
- Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Denelopment, 2021, 38(8): 44-49
- 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.08.007
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2021-04-25
2. 交通运输部公路科学研究院, 北京 100088;
3. 道路结构与材料交通运输行业重点实验室, 北京 100088
2. Research Institute of Highway, Ministry of Transport, Beijing 100088, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Road Structure and Material of MOT, Beijing 100088, China
冬季极端气候的环境温度通常最低能达到-45 ℃,极端的气候条件要求钢桥面铺装的材料和结构具有较高的低温力学性能。在行车荷载作用下,钢桥面环氧沥青混凝土铺装易发生铺装疲劳开裂、车辙及黏结层失效等病害,损害桥梁结构的稳定性与耐久性。
现有研究主要集中于钢桥面铺装体系的静荷载响应、动力响应及温度效应分析,多采用单轮荷载进行加载,铺装层模量多采用常温(30 ℃)时的模量。侯贵等[1]通过系列低温试验研究了不同沥青混合料劲度模量、劈裂强度、弯曲蠕变柔量随温度变化的规律,结果表明浇注式沥青混凝土具备良好的低温性能。张德佳等[2]对钢桥面铺装数值分析模型的尺寸大小、约束、边界条件进行了优化研究,并通过实测钢桥面铺装的力学响应验证了优化模型的有效性;钱振东等[3]利用有限元软件,把正交异性钢桥面板与铺装层视作受力整体,对铺装层进行了受力分析,并根据正交异性铺装层体系中局部区域容易产生破坏的特性,总结了桥面铺装的力学控制指标以及铺装层参数对于铺装层力学响应的影响规律;成峰[4]建立了车辆移动荷载下钢桥面铺装体系模型,研究了在不同车辆移动荷载作用下铺装体系的受力特点;逯彦秋等[5]研究了钢桥面层温度场的分布特征,并对钢桥面层的温度分布规律进行了分析。在润扬大桥沥青铺装层摊铺过程中,刘其伟等[6]对断面测点的温度开展动态测量,采集了钢-混凝土组合箱梁内部的温度分布并分析了其变化规律。对冬季极端气候钢桥面铺装在不同铺装厚度、不同铺装材料工况下力学响应的研究较少。
因此,以钢桥面铺装的最大拉应力、最大拉应变、最大竖向位移及层间最大剪应力为力学控制指标[7-9],采用数值模拟的方法建立钢桥面铺装体系模型,计算不同服役温度和不同铺装层厚度组合等条件下,“双层EA”结构和“下层EA+上层SMA”结构的铺装层上表面最大拉应力、最大拉应变、最大竖向位移及层间最大剪应力,研究冬季极端气候下快速路钢桥面铺装的力学响应及适合的铺装方案。
1 城市快速路钢箱梁桥桥面铺装模型的建立 1.1 钢桥面三维铺装体系模型通过ABAQUS软件建立钢桥面三维铺装体系模型,如图 1所示,采用局部正交异性板结构模型,在钢桥的纵桥向设置3跨(4块横隔板),横桥向设置7个U型加劲肋。根据实际桥梁设计参数,钢桥面铺装体系模型详细参数如表 1所示。
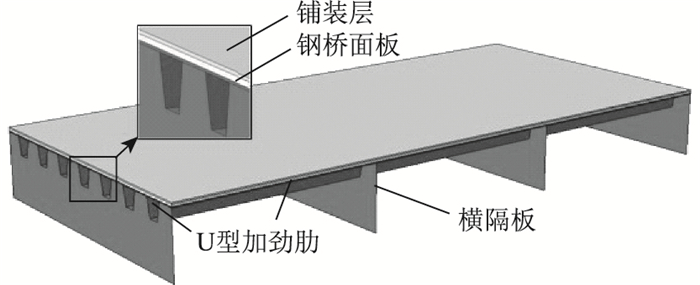
|
| 图 1 钢桥面铺装体系模型 Fig. 1 Steel bridge deck pavement system model |
| |
| 构建参数名称 | U肋宽度 | U肋高度 | U肋厚度 | U肋间距 | 横隔板厚度 | 横隔板间距 | 铺装层厚度 | 钢板厚度 |
| 几何尺寸 | 280 | 280 | 8 | 600 | 14 | 3 000 | 60 | 16 |
1.2 荷载作用位置
依据对桥梁工程的实际调研情况,横向拉应力导致的桥面铺装层纵向裂缝是桥面铺装的主要病害[10-12],因此对桥面铺装力学分析的主要控制指标为位于纵向加劲肋顶部铺装层上表面的最大横向拉应力;而位于横肋顶部铺装层上表面的最大纵向拉应力是引起桥面铺装层横向裂缝的主要因素,将其作为次要控制指标。采用双轮荷载,荷载大小为标准轴载下的轮胎接地压强0.7 MPa。双轮荷载对称布置于铺装层上表面,同时位于横肋顶部、纵向加劲肋肋边顶部,如图 2(a)所示。双轮荷载的作用范围为200 mm×180 mm×2,如图 2(b)所示。

|
| 图 2 荷载的设置 Fig. 2 Load setting |
| |
1.3 力学控制指标输出
钢桥面铺装常见病害有疲劳开裂、车辙及黏结层失效等,钢桥面铺装的疲劳开裂是由于铺装层表面受到拉应力和拉应变的作用导致,且钢桥面铺装产生最大拉应力、最大拉应变处更易发生开裂;车辙病害是由于桥面铺装层的抗永久变形能力过低引起;黏结层失效是铺装层与钢板之间结合界面的抗水平剪切力不足导致[13-14]。选取最大拉应力、最大拉应变、最大竖向位移及层间最大剪应力等力学控制指标,评价钢桥面铺装的力学性能,并通过各力学控制指标,提出能够适应冬季极端气候的快速路钢箱梁桥桥面铺装方案。
2 铺装层厚度对钢桥面铺装力学控制指标的影响选取10 ℃时环氧沥青混凝土、SMA和钢板的模量和泊松比,如表 2所示。钢桥面沥青混凝土铺装层总厚度一般为50~80 mm[15-17],本节讨论铺装层厚度对钢桥面铺装力学控制指标的影响。选取“下层3 cm+上层3.5 cm”(厚度方案Ⅰ)、“下层2.5 cm+上层3.5 cm”(厚度方案Ⅱ)和“下层3 cm+上层4 cm”(厚度方案Ⅲ)3种铺装厚度组合,计算3种铺装厚度组合下“双层EA”与“下层EA+上层SMA”两种铺装方案的各力学控制指标,并根据计算结果,初步比较冬季极端气候下快速路钢箱梁桥的铺装厚度方案。计算结果如图 3所示。
| 钢板参数 | 环氧沥青混凝土参数 | SMA参数 | |||||
| 弹性模量/MPa | 泊松比 | 模量/MPa | 泊松比 | 模量/MPa | 泊松比 | ||
| 2.1×105 | 0.25 | 3 800 | 0.25 | 1 600 | 0.25 | ||

|
| 图 3 铺装层厚度对钢桥面铺装力学控制指标的影响 Fig. 3 Influence of pavement thickness on mechanical control indicators of steel deck pavement |
| |
由图 3可以看出,对3种桥面铺装层厚度方案的上表面最大拉应力、最大拉应变、最大竖向位移及层间最大剪应力进行比较,均符合“下层2.5 cm+上层3.5 cm”结构>“下层3 cm+上层3.5 cm”结构>“下层3 cm+上层4 cm”结构的规律,说明“下层3 cm+上层4 cm”结构可抗疲劳开裂、永久变形、层间脱黏性能最优,故快速路钢箱梁桥推荐使用“下层3 cm+上层4 cm”的铺装厚度组合。本节主要计算了10 ℃时“双层EA”与“下层EA+上层SMA”铺装方案的各力学控制指标,由于不同温度下沥青混合料的材料属性差异较大,提出能够适应冬季极端气候的快速路钢箱梁桥铺装材料方案需进一步考虑温度因素的影响。
3 温度对钢桥面铺装力学控制指标的影响沥青混合料温度依赖性较高,温度对沥青混合料模量的影响较大[18-21]。冬季极端气候的环境温度通常最低能达到-45 ℃,同时考虑钢箱梁的特性,在夏季易产生箱体不通风、散热速度慢等问题,相比于传统的桁架梁桥钢箱梁桥面钢板温度会高10 ℃以上[16]。研究冬季极端气候下快速路钢箱梁桥桥面铺装设计的工作温度范围为-45~50 ℃,计算不同温度下“双层EA”与“下层EA+上层SMA”两种铺装方案的各力学控制指标,并根据计算结果,提出能够适应冬季极端气候的快速路钢箱梁桥铺装材料方案。不同温度下沥青混合料的模量如表 3所示,计算结果如图 4所示。
| 混合料 | 温度/℃ | ||||||||||
| -45 | -40 | -30 | -20 | -10 | 0 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | |
| EA | 9 500 | 9 400 | 9 300 | 9 000 | 8 000 | 5 000 | 3 800 | 3 000 | 1 200 | 700 | 460 |
| SMA | 3 800 | 3 500 | 3 300 | 3 200 | 3 000 | 2 000 | 1 600 | 1 200 | 560 | 240 | 180 |
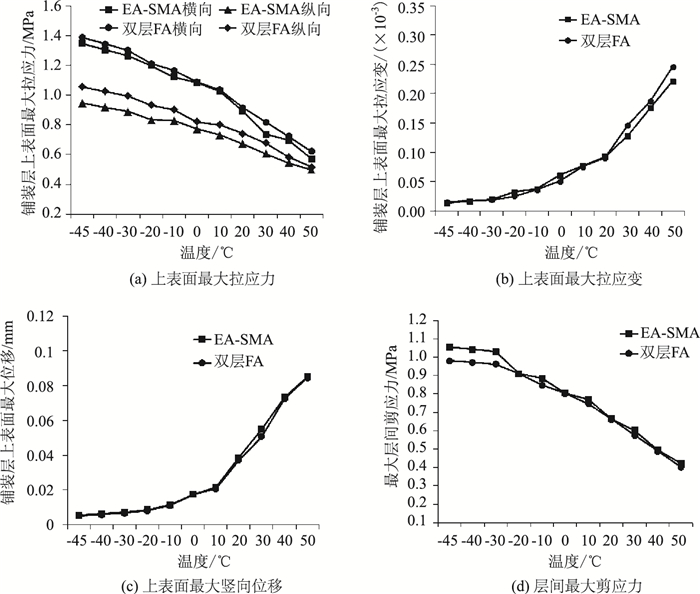
|
| 图 4 温度对钢桥面铺装力学控制指标的影响 Fig. 4 Influence of temperature on mechanical control indicators of steel deck pavement |
| |
由图 4可以看出,两种铺装结构铺装层上表面的最大纵向、横向拉应力及层间最大剪应力均随温度降低而变大,而最大拉应变与最大竖向位移均随温度降低而变小;相同温度下,“下层EA+上层SMA”结构上表面的最大纵向、横向拉应力均小于“双层EA”结构,说明“下层EA+上层SMA”结构的抗疲劳开裂性能优于“双层EA”结构;两种铺装结构铺装层上表面最大拉应变、最大竖向位移及层间最大剪应力相差不大。结合3.1节快速路钢箱梁桥的铺装厚度推荐组合,“下层3 cmEA+上层4 cm SMA”铺装方案能够适应冬季极端气候的工况。
4 结论(1) 对3种铺装层厚度方案的铺装层上表面最大拉应力、最大拉应变、最大竖向位移及层间最大剪应力进行比较,均符合“下层2.5 cm+上层3.5 cm”结构>“下层3 cm+上层3.5 cm”结构>“下层3 cm+上层4 cm”结构的规律。
(2)“双层EA”铺装结构与“下层EA+上层SMA”铺装结构的上表面最大纵向、横向拉应力及层间最大剪应力均随温度降低而变大,最大拉应变与最大竖向位移均随温度降低而变小;相同温度下,“下层EA+上层SMA”铺装结构的上表面最大纵向、横向拉应力均小于“双层EA”结构,两种铺装结构铺装层上表面最大拉应变、最大竖向位移及层间最大剪应力相差不大。
(3)“下层3 cmEA+上层4 cmSMA”铺装方案能够适应冬季极端气候的工况。
主要研究了钢桥面铺装静荷载响应,由于实际钢桥面铺装使用过程中,荷载作用的主要形式为车辆移动荷载的重复作用,对于移动荷载和重复荷载作用下钢桥面铺装的力学响应仍需进一步研究。
| [1] |
侯贵, 王选仓, 孙耀宁, 等. 严寒地区钢桥面浇注式沥青混凝土低温性能试验研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2018, 35(3): 58-63. HOU Gui, WANG Xuan-cang, SUN Yao-ning, et al. Experimental Study on Low Temperature Performance of Steel Deck Gussasphalt in Cold Region[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2018, 35(3): 58-63. |
| [2] |
张德佳, 叶奋, 袁金凤, 等. 基于实桥加载的钢桥面铺装数值模型优化[J]. 公路交通科技, 2013, 30(7): 103-106. ZHANG De-jia, YE Fen, YUAN Jin-feng, et al. Optimization of Numerical Model of Steel Deck Pavement Based on Practical Bridge Loading[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2013, 30(7): 103-106. |
| [3] |
钱振东, 黄卫, 茅荃, 等. 南京长江第二大桥钢桥面铺装层受力分析研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2001, 18(6): 43-46. QIAN Zhen-dong, HUANG Wei, MAO Quan, et al. Mechanical Analysis of Nanjing Second Yangtze River Bridge Deck Pavement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2001, 18(6): 43-46. |
| [4] |
成峰. 大跨径钢桥面铺装力学分析深入研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2004. CHENG Feng. Deep Research on Mechanical Analysis of Long Span Steel Deck Pavement[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2004. |
| [5] |
逯彦秋, 陈宜言, 孙占琦, 等. 钢桥桥面铺装层的温度场分布特征[J]. 华南理工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2009, 37(8): 116-121. LU Yan-qiu, CHEN Yi-yan, SUN Zhan-qi, et al. Characteristics of Temperature Field Distribution of Steel Bridge Deck Pavement[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology: Natural Science Edition, 2009, 37(8): 116-121. |
| [6] |
刘其伟, 丁峰, 朱俊, 等. 钢混凝土组合箱梁沥青摊铺温度场试验[J]. 东南大学学报: 自然科学版, 2006, 36(4): 572-575. LIU Qi-wei, DING Feng, ZHU Jun, et al. Temperature Field Caused by Bituminous Deck Pavement of Steel-concrete Composed Box Girder Bridge[J]. Journal of Southeast University: Natural Science Edition, 2006, 36(4): 572-575. |
| [7] |
黄卫. 大跨径桥梁钢桥面铺装设计理论与方法[M]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2006. HUANG Wei. Design Theory and Method of Steel Deck Pavement for Long-span Bridges[M]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2006. |
| [8] |
刘振清, 黄卫, 曹东伟, 等. 大跨径斜拉桥设纵隔板对钢桥面铺装力学特性的影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2006, 23(3): 44-48. LIU Zhen-qing, HUANG Wei, CAO Dong-wei, et al. Mechanical Characteristic Analysis of Long-span Stable Bridge Steel-deck Surfacing with Longitudinal Clapboard[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2006, 23(3): 44-48. |
| [9] |
资建民, 路庆昌, 黄贤顺, 等. 正交异性钢桥沥青混凝土桥面铺装的力学分析[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2008, 30(2): 90-93. ZI Jian-min, LU Qing-chang, HUANG Xian-shun, et al. Mechanical Analysis of the Asphalt Pavement on Orthotropic Steel Bridge Deck[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2008, 30(2): 90-93. |
| [10] |
刘振清. 大跨径钢桥桥面铺装体系设计理论关键技术研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2006. LIU Zhen-qing. Research on Key Technology of Design Theory of Long-span Steel Bridge Deck Pavement System[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2006. |
| [11] |
钱振东, 罗剑, 敬淼淼. 沥青混凝土钢桥面铺装方案受力分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2005, 18(2): 68-72. QIAN Zhen-dong, LUO Jian, JING Miao-miao. Mechanical Analysis of Asphalt Concrete Paving Projects on Steel Bridge Deck[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2005, 18(2): 68-72. |
| [12] |
钱振东, 黄卫. 钢桥面沥青铺装养护维修及评价[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2014. QIAN Zhen-dong, HUANG Wei. Maintenance and Evaluation of Asphalt Pavement on Steel Bridge Decks[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2014. |
| [13] |
刘振清, 黄卫, 林广平. 大跨径钢桥桥面铺装设计方法[J]. 公路, 2005(2): 32-36. LIU Zhen-qing, HUANG Wei, LIN Guang-ping. Design Method for Deck Pavement of Long-span Steel Bridge[J]. Highway, 2005(2): 32-36. |
| [14] |
陈先华. 基于复合梁的桥面铺装疲劳特性研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2005. CHEN Xian-hua. Research on Fatigue Characteristics of Bridge Deck Pavement Based on Composite Beams[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2005. |
| [15] |
王兴昌, 李灏, 方星, 等. SMA沥青混凝土断裂与疲劳性能试验研究[J]. 公路, 2011(9): 196-200. WANG Xing-chang, LI Hao, FANG Xing, et al. Experimental Study on Fracture and Fatigue Performance of SMA Asphalt Concrete[J]. Highway, 2011(9): 196-200. |
| [16] |
LIU Y, QIAN Z, HU J, et al. Temperature Behavior and Stability Analysis of Orthotropic Steel Bridge Deck during Gussasphalt Pavement Paving[J]. Journal of Bridge Engineering, 2017, 23(1): 04017117. |
| [17] |
黄卫. 大跨径桥梁钢桥面铺装设计[J]. 土木工程学报, 2007, 40(9): 65-77. HUANG Wei. Design of Deck Pavement For long-span Steel Bridges[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2007, 40(9): 65-77. |
| [18] |
邓强民, 倪富健, 顾兴宇, 等. 非均布轮载下钢桥面铺装力学响应分析[J]. 公路交通科技, 2008, 25(2): 63-67. DENG Qiang-min, NI Fu-jian, GU Xing-yu, et al. Mechanical Response of Orthotropic Steel Deck Pavement under Non-uniform Distributed Tire Pressure[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2008, 25(2): 63-67. |
| [19] |
黄卫, 林广平, 钱振东, 等. 正交异性钢桥面铺装层疲劳寿命的断裂力学分析[J]. 土木工程学报, 2006, 39(9): 112-116. HUANG Wei, LIN Guang-ping, QIAN Zhen-dong, et al. Fracture-mechanics Analysis of the Fatigue Life of the Pavement on Orthotropic Steel Bridge Decks[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2006, 39(9): 112-116. |
| [20] |
邓强民, 倪富健, 顾兴宇, 等. 荷载形状对钢桥面铺装力学响应的影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2007, 24(8): 7-11. DENG Qiang-min, NI Fu-jian, GU Xing-yu, et al. Effects of Load Shape on Mechanical Response of Orthotropic Steel Deck Pavement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2007, 24(8): 7-11. |
| [21] |
吴海涛, 钱振东, 陈磊磊. 钢桥面环氧沥青混凝土铺装层病害冬季修复技术研究[J]. 施工技术, 2014, 43(23): 73-75. WU Hai-tao, QIAN Zhen-dong, CHEN Lei-lei. Study on Winter Maintenance Technique of Epoxy Asphalt Concrete Pavement on Steel Bridge Deck[J]. Construction Technology, 2014, 43(23): 73-75. |
 2021, Vol. 38
2021, Vol. 38
