扩展功能
文章信息
- 李霖, 江睿南
- LI Lin, JIANG Rui-nan
- 基于等距测定的弯沉对沥青路面裂缝影响范围的研究
- Study on Influence Range of Deflection on Asphalt Pavement Cracks Based on Isometric Determination
- 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(7): 17-21
- Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Denelopment, 2021, 38(7): 17-21
- 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.07.003
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2021-04-28
沥青路面在其服役过程中,会由于设计、建设、荷载耦合、温度等方面的因素,产生不同类型和程度的病害,如纵向裂缝、横向裂缝、车辙、拥包等[1]。这就需要对路面整体状况(路面损坏状况和强度状况)进行评估。对于表面层的病害,往往采用传统外观观测进行确定,其方法包括多功能道路检测车、人工现场观测等。而对于沥青路面内部的强度衰减情况,公路行业一般通过落锤式弯沉仪(FWD)获得路面施加动荷载下实测弯沉盆,结合路面各结构层的材料性能、厚度、模量范围等数值进行各结构层的模量反演,以实现对路面各结构层强度及路面整体承载能力的评估[2-3]。比如有些研究人员利用ANSYS,构建了动态弯沉值图谱,通过对各种影响因素的敏感性权重进行分析,明确了FWD动荷载下路面力学性能变化情况,提出了弯沉值与结构层强度的回归方程[4];有些则利用静力学模型,回归分析结构层模量与各个层位的应力应变关系,总体而言,目前只利用了FWD检测信息中的一小部分,有更多的数值分析有待于进一步发展[7-9]。
综上可知,目前有关FWD测定弯沉盆的研究主要集中在反演路面结构模量,从而评价路面结构性能,但对于在病害路段的测定位置并没有达成一致看法,并且我国现行养护规范中,也未对病害路段弯沉检测位置进行明确约定,仅要求间隔一定距离进行弯沉检测,常常出现路面裂缝病害严重,但弯沉评定指标优良的情况,因此无法准确评价路面结构病害实际情况。关于裂缝周围测定距离的研究鲜有报道,其评价体系也尚不明确,需进一步深入探讨研究。
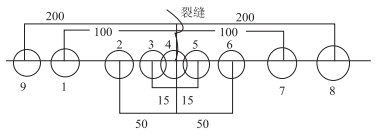
1 表面裂缝弯沉变化利用FWD弯沉检测方法在表面裂缝处及距裂缝不同位置处进行弯沉测试,以便掌握不同类型裂缝对弯沉指标的影响。测试位置如图 1所示,分别在裂缝顶面、距裂缝两侧各15,50,100,150 cm处和200 cm处进行无损弯沉检测。
|
| 图 1 裂缝弯沉检测位置(单位: cm) Fig. 1 Detection positions of crack deflection(unit: cm) |
| |
|
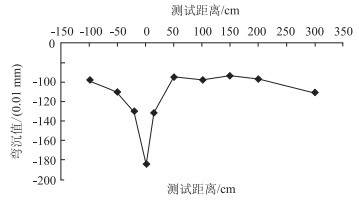
| 图 2 单独横向裂缝处弯沉响应 Fig. 2 Deflection response at separate transverse cracks |
| |
|
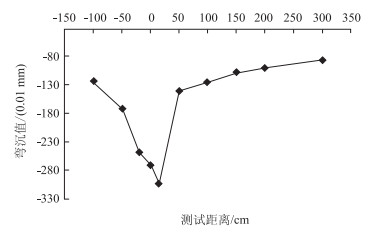
| 图 3 带支缝裂缝处弯沉响应 Fig. 3 Deflection response at cracks with branches |
| |
|
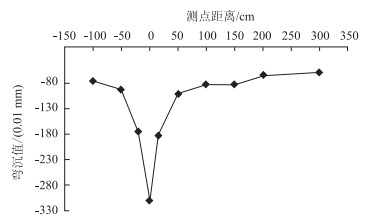
| 图 4 横向裂缝处弯沉响应 Fig. 4 Deflection response at transverse cracks |
| |
|
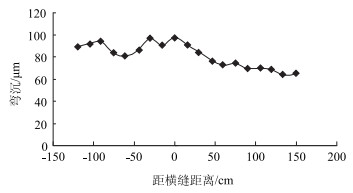
| 图 5 病害较轻横向裂缝弯沉检测 Fig. 5 Detecting deflections of lateral cracks with lighter disease |
| |
|
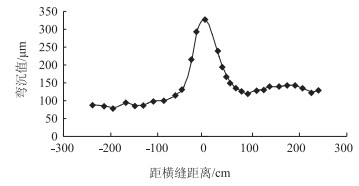
| 图 6 病害较重横向裂缝弯沉检测 Fig. 6 Detecting deflections of lateral cracks with heavier disease |
| |
|
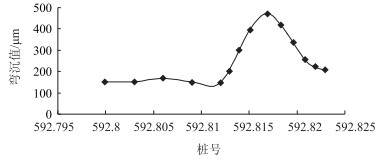
| 图 7 横向裂缝并发生唧浆弯沉检测 Fig. 7 Detecting deflections of lateral cracks with slurry |
| |
(1) 单独裂缝处弯沉响应
裂缝主要在路面横缝处,从路面铣刨情况看,造成横缝的主要原因是半刚性基层开裂导致的反射裂缝。从图中可以看出,在裂缝点4#的弯沉最大,横缝对弯沉的影响范围为距离缝中心±50 cm范围。
(2) 带支缝裂缝和横向裂缝弯沉响应
带支缝裂缝处,由于横缝处产生了网裂,此裂缝影响范围在±75 cm内。
对于横向裂缝,测得的完成基本情况与单独裂缝情况类似,但在测点4#处的弯沉比单独裂缝相同测点的弯沉值大,因此认定此时的半刚性基层开裂更为严重,同时明确对于横向裂缝而言,其影响范围在±50 cm内。
(3) 带不同病害程度下弯沉响应分析
裂缝的损伤程度不能仅靠观察,需要通过仪器检测,不同裂缝损伤程度不同。首先是病害较轻的情况,如图 5横向裂缝,在裂缝位置处的弯沉,与未发生开裂位置弯沉基本相同。
损伤程度较大的裂缝,在裂缝处的弯沉与周边区域的弯沉差别较大,弯沉差别达到甚至达到3倍以上,如图 6及图 7所示。病害较重的横向裂缝弯沉的影响区域大约为1 m左右。如图 6所示,裂缝中心弯沉最大,裂缝左右对称50 cm之外弯沉下降趋于稳定,故对裂缝进行彻底处理,需要至少1 m宽左右的处理区域。发生了唧浆的裂缝,弯沉明显大于未发生唧浆的裂缝,如图 7所示。由此可知,水进入路面结构内部对路面结构承载力的影响是非常明显的,因此应该避免水渗入裂缝中,并尽快排出进入裂缝内的水分。
2 结构层当量回弹模量路面结构层的当量回弹模量是旧路加铺设计最重要的参数之一,表征路面结构的整体承载能力。裂缝等病害处是路面结构的薄弱环节,如果不进行病害处理就进行加铺补强,应该考虑病害处的实际当量模量,保证设计期内加铺的结构或材料不在病害处发生早期损坏。表 1为路表裂缝处当量回弹模量与周边区域未发生裂缝处的当量回弹模量比较。
| 序号 | 位置描述 | 荷载/kPa | 弯沉值/(0.001 mm) | 当量回弹模量/MPa |
| 横缝1 | 缝前20 cm处 | 708 | 134.7 | 669.5 |
| 裂缝处 | 708 | 183.7 | 490.8 | |
| 横缝2 | 缝前20 cm处 | 706.5 | 248.5 | 362.9 |
| 裂缝处 | 706 | 269.2 | 334.9 | |
| 横缝3 | 缝前20 cm处 | 706 | 174.4 | 518 |
| 裂缝处 | 709.5 | 310 | 290 |
从表中可知,由于损伤程度的不同,裂缝处的当量回弹模量有的下降比较小,有的则衰减程度很大,因此进行加铺设计不能简单采用当量模量平均值,应该考虑最薄弱环节的处理方法。
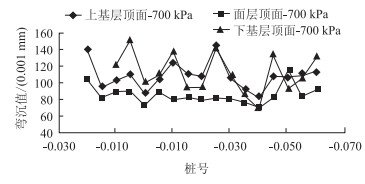
分别测定路面铣刨前后的不同层位弯沉值,如表 2、图 8所示,FWD测点分别位于面层、上基层顶面、下基层顶面等不同层位。
| 测定代号 | 层位 | 弯沉/(0.001mm) | 当量模量/MPa |
| 1 | 土基顶面 | 116.8 | 772.1 |
| 下基层顶面 | 100.2 | 900 | |
| 上基层顶面 | 84 | 1 073.5 | |
| 路表面 | 69.7 | 1 293.8 | |
| 2 | 土基顶面 | 169 | 533.6 |
| 下基层顶面 | 148 | 609.3 | |
| 上基层顶面 | 105.8 | 852.3 | |
| 路表面 | 85 | 1 060.9 | |
| 3 | 土基顶面 | 150 | 601.2 |
| 下基层顶面 | 117.5 | 767.5 | |
| 上基层顶面 | 100 | 901.8 | |
| 路表面 | 87 | 1 036.5 |
|
| 图 8 不同层位当量模量变化 Fig. 8 Variations of equivalent moduli at different depths |
| |
从图 8中可看出,面层部分路面弯沉不仅数值较小,且变化幅度也小;随着结构层深度增大,弯沉值也增大,并且出现较大的波动。因此在进行道路不同铣刨深度的加铺设计时,应该进行不同层位当量模量的检测。另外,从基层和底基层的当量模量水平看,铣刨面层或上基层后,除了裂缝位置外,半刚性基层沥青路面的当量模量处于较高的水平,适合进行合理的加铺补强设计,避免大的路面结构深层铣刨量和较高代价的结构重建。
3 结论针对弯沉测定技术的特点,以FWD作为检测手段,在裂缝处开展基于等距的弯沉值测量对比分析,并绘制弯沉曲线,根据弯沉曲线线形及最大弯沉值综合确定裂缝损伤状态,通过等距方法解决了沥青路面裂缝影响范围外观观测判定不准的问题,主要结论有:
(1) 利用不同荷载FWD对表层裂缝及两端的弯沉进行测试发现,裂缝处的弯沉值随荷载增大增加。加载值较大,裂缝较浅时更易在裂缝位置处产生奇角峰值。
(2) 外观观测无法确定裂缝的损伤程度,而通过等距弯沉测试发现横向裂缝弯沉的影响区域大约为距离1 m左右;裂缝中心处弯沉值最大,并呈现中心向边缘发散下降的趋势,即裂缝左右对称50 cm之外弯沉下降趋于稳定,故养护过程中需要在宽度1 m覆盖范围内对裂缝进行彻底处理。
(3) 存在唧浆的裂缝,其弯沉值明显大于未发生唧浆的,表明水损害对路面路面结构承载力的影响巨大,因此应该避免水渗入裂缝中,并尽快排出进入裂缝内的水分。
(4) 通过对上下基层的深层裂缝弯沉测试发现,纵向裂缝处的弯沉值比横向裂缝处的弯沉值大,横向裂缝处的弯沉均大于非裂缝处的弯沉。
| [1] |
黄仰贤. 路面分析与设计[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 1998. HUANG Yang-xian. Pavement Analysis and Design[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 1998. |
| [2] |
赵为天. 基于三维探地雷达和落锤式弯沉仪的路面结构状况无损评估[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020. ZHAO Wei-tian. Nondestructive Evaluation of Pavement Structure Condition Based on 3D Ground Penetrating Radar and Falling Weight Deflectometer[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020. |
| [3] |
林翔, 李强. 高速公路沥青路面半刚性基层结构剩余寿命评价方法研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(4): 1-8. LIN Xiang, LI Qiang. Study on Residual Life Evaluation Method of Semi-rigid Base Structure of Expressway Asphalt Pavement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2021, 38(4): 1-8. |
| [4] |
赵璐璐. 探地雷达在道路质量检测中的应用研究[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学, 2009. ZHAO Lu-lu. Application Study of Ground Penetrating Radar to Quality Inspection of Road[D]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences, 2009. |
| [5] |
谢兆星, 丛林, 郭忠印. 基于FWD弯沉盆参数的沥青路面土基模量评价方法研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2009, 26(12): 28-31. XIE Zhao-xing, CONG Lin, GUO Zhong-yin. Evaluation of Subsoil Modulus for Asphalt Pavement Based on FWD Deflection Basin Parameter[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2009, 26(12): 28-31. |
| [6] |
LEE Y C. Condition Assessment of Flexible Pavement Using FWD Deflections[D]. Raleigh: North Carolina State University, 1997.
|
| [7] |
巩建, 常成利, 程珊珊, 等. 基于弯沉的沥青路面使用性能评价模型[J]. 公路交通科技, 2016, 33(7): 414-429. GONG Jian, CHANG Cheng-li, CHENG Shan-shan, et al. An Asphalt Pavement Performance Evaluation Model Based on Deflection[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2016, 33(7): 414-429. |
| [8] |
杨国良. 基于落锤式弯沉仪评价路基路面结构层状态的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学大学, 2007. YANG Guo-liang. Study on Evaluation of Subgrade and Pavement Structure Layer State Based on Falling Weight Deflectometer[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2007. |
| [9] |
王旭东, 郭大进. 落锤式弯沉仪模量反算的可靠性研究[J]. 中国公路学报, 1999(7): 35-39. WANG Xu-dong, GUO Da-jin. The Reliability Research on the Backcalculation Modulus[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 1999(7): 35-39. |
| [10] |
王复明, 刘文廷. 路面无破损检测与评价技术的研究与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997: 36-41. WANG Fu-ming, LIU Wen-ting. Research and Application of Nondestructive Detection and Evaluation Technology for Pavement[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1997: 36-41. |
| [11] |
TURESSON A. Water Content and Porosity Estimated from Ground-Penetrating Radar and Resistivity[J]. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2006, 58(2): 99-111. |
| [12] |
王帅. 高速公路探测中探地雷达三维成像技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. WANG Shuai. Research on 3D Imaging Technology of Ground Penetrating Radar in Expressway Detection[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018. |
| [13] |
熊春龙. 基于无损检测技术的沥青路面结构性健康状况评估方法研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2017. XIONG Chun-long. Research on Asphalt Pavement Structural Health Evaluation Method Based on Non-destructive Testing Technology[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2017. |
| [14] |
DANIELS D J. Ground Penetrating Radar[M]. London: Institution of Electrical Engineers, 2004.
|
| [15] |
LAGARKOV A N, SARYCHEV A K. Electromagnetic Properties of Composites Containing Elongated Conducting Inclusions[J]. Physical Review B: Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 1996, 53(9): 6318-6336. |
| [16] |
ZHDANOV M. Generalized Effective-medium Theory of Induced Polarization[J]. Geophysics, 2008, 73(5): 197-211. |
| [17] |
王建章, 李红. 沥青路面半刚性基层结构承载能力评价方法研究[J]. 公路工程, 2018(10): 209-212. WANG Jian-zhang, LI Hong. The Method to Evaluate Structure-load-carrying Capacity of Semi-rigid Base[J]. Highway Engineering, 2018(10): 209-212. |
| [18] |
刘伟. 柔性基层沥青路面性能观测预估研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2015. LIU Wei. Study on Observation and Forecast of Flexible Base Asphalt Pavement Performance[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2015. |
 2021, Vol. 38
2021, Vol. 38
