扩展功能
文章信息
- 叶妤文, 麦健, 张学峰
- YE Yu-wen, MAI Jian, ZHANG Xue-feng
- 公路桥梁桩基础受竖向荷载桩侧土接触面损伤机理模型试验研究
- Experimental Study on Damage Mechanism Model of Pile-soil Contact Surface of Highway Bridge Pile Foundation Subjected to Vertical Load
- 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(6): 104-111
- Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Denelopment, 2021, 38(6): 104-111
- 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.06.014
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2021-01-20
2. 宁夏道路运输事务中心, 宁夏 银川 750002;
3. 交通运输部公路科学研究院, 北京 100088
2. Ningxia Road Transport Affairs Center, Yinchuan Ningxia 750002, China;
3. Research Institute of Highway, Ministry of Transport, Beijing 100088, China
改革开放以来,我国经济实现跨越式发展,基础设施发展迅速,截止2020年底,我国公路桥梁数量91.28万座,由于钻孔灌注桩基础具有施工工艺成熟、质量可靠、承载能力大等优越性,在桥梁工程中被广泛采用[1-2]。桥梁基础是否安全关系到整个桥梁结构能否安全工作,桩基础与土体相互作用对桥梁极限状态具有重要影响,在设计中需要考虑[3-6]。对于摩擦桩其桩侧摩阻力是桩基传递荷载的主要途径,桩体的失效模式往往表现为位移失效[7-8]。本研究旨在研究钻孔灌注桩基础受竖向荷载桩侧与土体接触面损伤机理。
调研分析表明国内外关于桩土接触面损伤方面研究成果不多[9-11]。张嘎等通过室内模型试验对桩-粗粒砂土基接触面损伤分析模型进行研究,并提出了桩-粗粒砂土接触面损伤指数,并经过模型试验数据验证了模型的可靠性[12]。此项成果中损伤指数适用范围比较狭窄,且损伤指数采用土体剪切应变作为损伤指标,该指标在实际工程应用中量测困难,不便于工程应用。本研究目的是通过桩土作用理论分析推导出桩土传递函数,掌握钻孔灌注桩基础桩土损伤机理,在此基础上建立钻孔灌注桩基础桩土损伤指数和损伤传递函数。
1 理论分析桩基在竖向荷载作用下桩基受到轴向荷载发生压缩变形,桩土接触面发生相对剪切变形导致相应土体变形受力对桩体产生向上的阻力,即桩基摩阻力。研究桩土接触面损伤机理要分析清楚竖向荷载作用下桩土间荷载的传递路径及相互关系[13-15]。
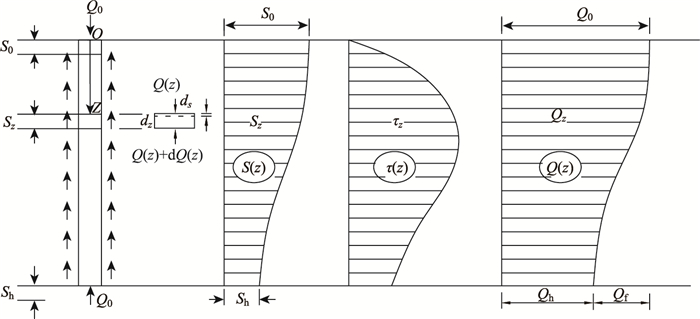
为研究钻孔灌注桩基础桩土荷载传递关系,在桩身任意深度处取一微分桩段见(图 1),由平衡条件可得[7]:
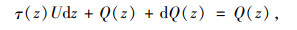
|
(1) |
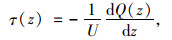
|
(2) |
|
| 图 1 桩土作用示图 Fig. 1 Pile-soil interaction diagram |
| |
式中,τ(z)为桩侧土体深度z处提供的侧摩阻力Q(z) 为桩体深度z处截面轴向力;U为桩基周长。
若加于桩顶的荷载为Q0,则深度Z处桩身轴力Q(z)为:
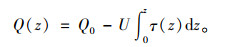
|
(3) |
桩微分段产生的弹性变形dS(z)为:
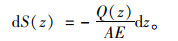
|
(4) |
将式(4)变形后,可得:
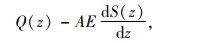
|
(5) |
式中,A为桩基横截面面积;E为桩基混凝土弹性模量。
由式(5)和式(2)得到:
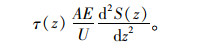
|
(6) |
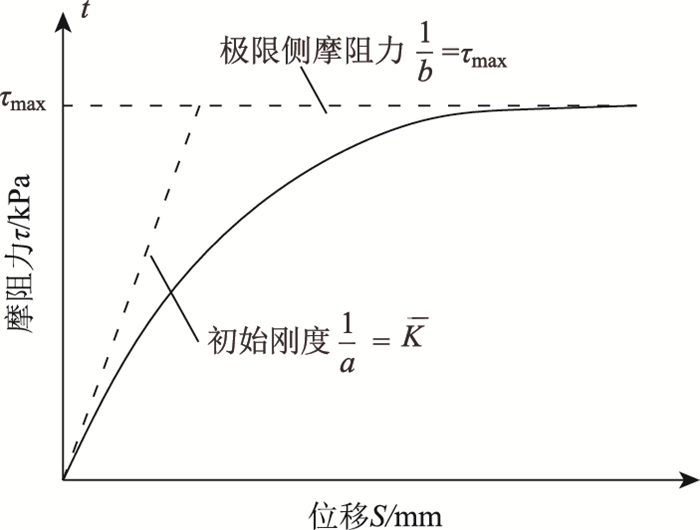
式(6)为钻孔灌注桩基础桩土作用微分方程,该微分方程是反映桩土接触面侧摩阻力与剪切变形量之间的函数关系,该方程只有确立τ-S的关系曲线才能进行求解[16-17]。通过本研究进行的室内模型试验和大量桩基工程试桩试验及相关研究成果表明钻孔灌注桩基础桩土接触面τ-S关系呈现双曲线关系[18],τ-S关系曲线见图 2。
|
| 图 2 τ-S关系曲线 Fig. 2 τ-S relationship curve |
| |
τ-S关系曲线关系式为:
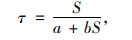
|
(7) |
式中,τ为钻孔灌注桩桩土间侧摩阻力;S为桩土接触面相对变形量; a、b为双曲线模型常数。
取桩土接触面相对变形S趋于无限大时,桩土接触面达到极限侧摩阻力τm。
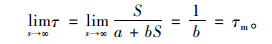
|
(8) |
取桩土接触面相对变形S趋于0时:
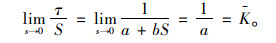
|
(9) |
假定τ-S关系曲线中原点处的斜率为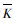
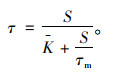
|
(10) |
钻孔灌注桩在上部结构传递竖向荷载下,桩身发生压缩变形,由于钻孔灌注桩基础桩侧土体与桩身紧密接触,桩侧土体也受到向下的摩擦力,产生剪切变形,对桩基产生向上的摩阻力,当竖向荷载逐渐加大时,桩侧摩阻力也逐渐增大;当竖向荷载达到一定值时,部分土层土体摩阻力达到极限,不再增加;当竖向荷载继续增加,桩顶位移快速增加,此时对于竖向荷载即为桩基极限承载力[19]。
由以上分析可知,桩侧土体提供的桩侧摩阻力大小跟桩土相对位移量有关,桩土相对位移量增大,则土体提供的桩侧摩阻力就增大,当桩土相对位移量增大到一定值之后,桩侧摩阻力不再增加。因此桩土接触面损伤与桩土相对位移量相关,可将桩土相对位移量作为桩土接触面损伤指标,建立损伤指数如下:
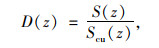
|
(11) |
式中,S(z)为桩土接触面相对滑移量;Scu(z)为桩侧土体极限滑移量,0≤D(z)≤1, D(z)=0表示接触面没有损伤,D(z)=1表示接触面破坏。由式(10)和(11)得桩侧土损伤传递函数模型为:
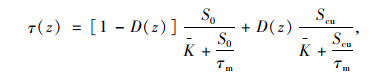
|
(12) |
式中S0为桩顶位移。
3 模型试验 3.1 试验方案为掌握钻孔灌注桩基础桩土接触面损伤机理,本研究开展了25组桩-土接触剪切模型试验,试验采用5种有代表性土样进行桩土接触面损伤试验,采用竖向应力等效模拟不同深度土体,每种土体分别模拟10,20,30,40,50 m深度工况,试验加载照片见图 2。桩土接触面试验剪切盒有两个盒体容器组成,分别是桩体盒和土体盒,容器净截面为20 cm×20 cm,容器采用厚度为4 cm的钢板制作而成,两盒体接触面用为3 mm的高强四氟板,容器如图 3所示。
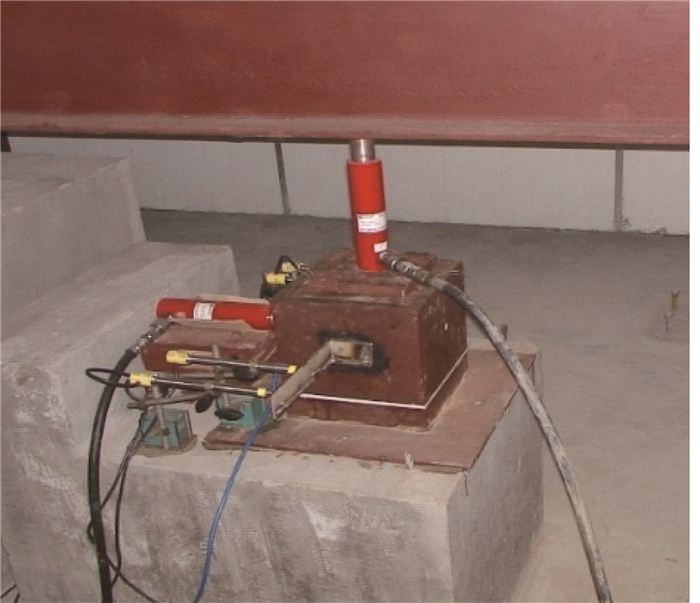

|
| 图 3 桩-土摩擦损伤机理试验总体布置 Fig. 3 Pile-soil friction damage mechanism test overall arrangement |
| |
3.2 试验结果分析
(1) 桩-土接触面τ-S测试结果
各种土体桩-土接触面损伤模型试验各工况测试τ-S曲线见图 5。从图中可以看出:①各土体极限摩阻力随土体深度增加而增大;②土体摩阻力发挥随桩土相对位移增加而加大,当相对位移达到一定量时,相对位移增加桩土摩阻力不再增大,此时对应的摩阻力即为桩土极限摩阻力;③桩-土接触面曲线呈双曲线形态。
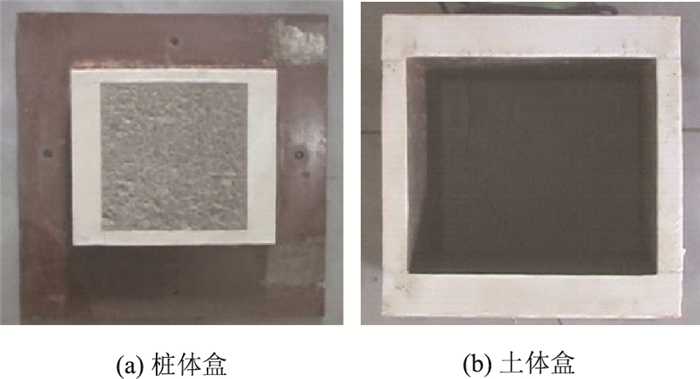
|
| 图 4 桩土接触面试验剪切盒 Fig. 4 Shear box for pile-soil interface test |
| |
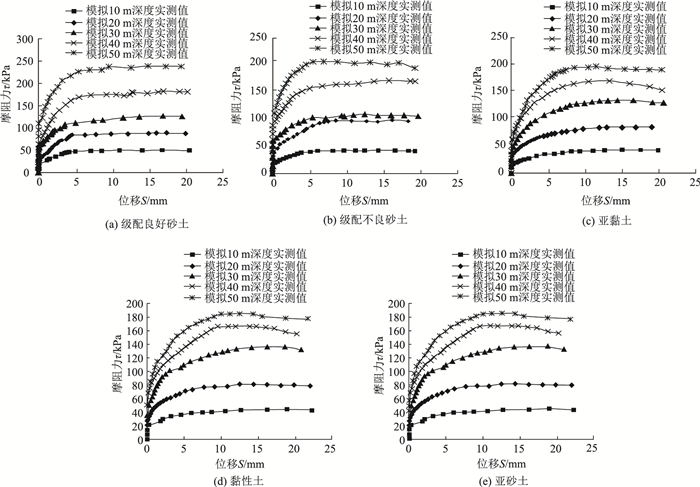
|
| 图 5 各工况测试τ-S曲线 Fig. 5 τ-S curves in test under different conditions |
| |
(2) 桩土接触面损伤指数结果分析
根据各种土体桩-土接触面损伤模型试验各工况测试数据和式(12)得出各土体桩土接触面D-S曲线见图 6,从图中可以看出:①各土体不同深度工况接触面D-S曲线形状相似;②土体损伤指数随桩土相对位移量S增加而变大,当S达到一定量值时D=1,表示接触面破坏;③在桩土相对位移量相等时,损伤指数随深度增加减小。
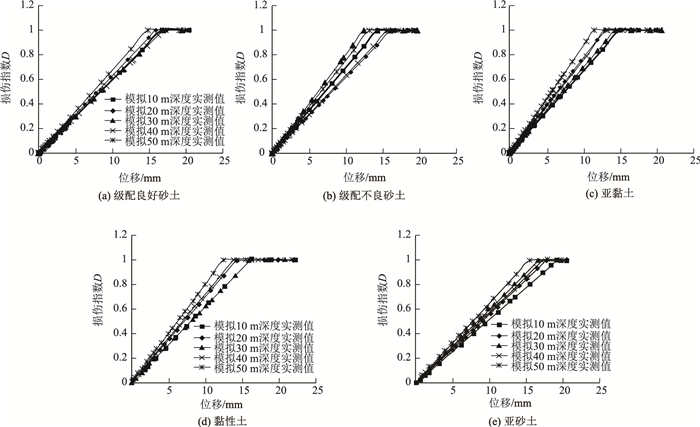
|
| 图 6 各工况D-S测试曲线 Fig. 6 D-S curves in test under different conditions |
| |
(3) 桩土接触面传递函数模型试验验证
根据桩侧土接触面传递函数模型计算出各种土体(级配良好砂土、级配不良砂土、亚黏土、黏性土、亚砂土)各深度工况桩-土接触面τ-S关系曲线,各模型试验实测值与模型计算值结果如图 7~图 11所示。
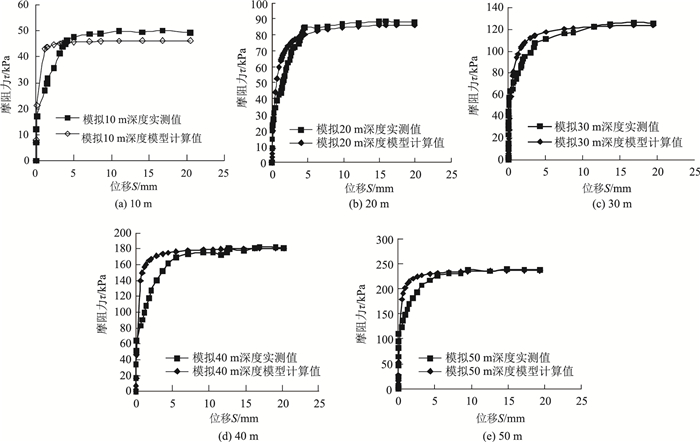
|
| 图 7 级配良好砂土实测数据与模型计算结果比较 Fig. 7 Comparison of measured data of well-graded sand and calculation result of model |
| |
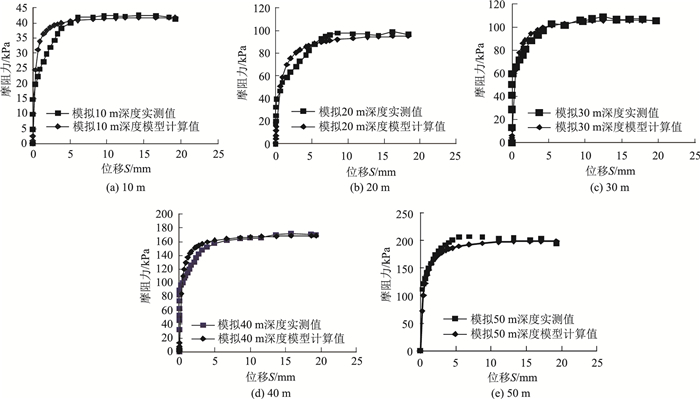
|
| 图 8 级配不良砂土实测数据与模型计算结果比较 Fig. 8 Comparison of measured data of poor-graded sand and calculation result of model |
| |
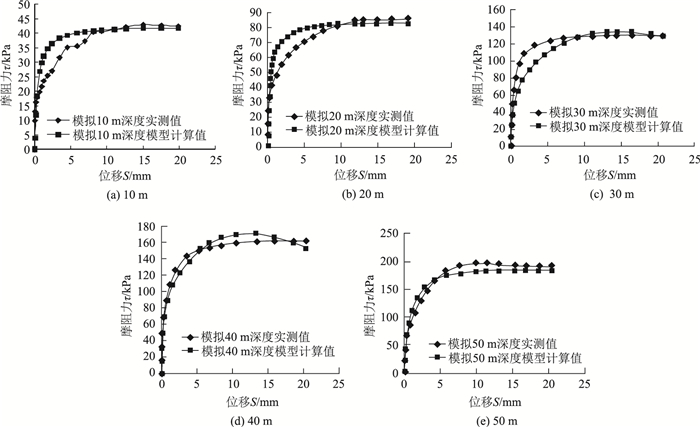
|
| 图 9 亚黏土实测数据与模型计算结果比较 Fig. 9 Comparison of measured data of loam and calculation result of model |
| |
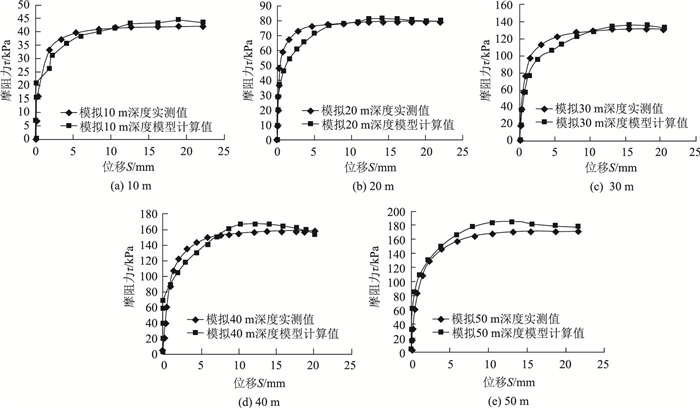
|
| 图 10 黏性土实测数据与模型计算结果比较 Fig. 10 Comparison of measured data of cohesive soil and calculation result of model |
| |
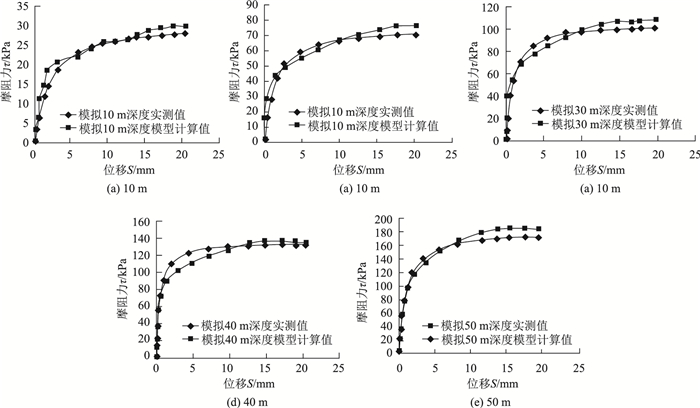
|
| 图 11 亚砂土实测数据与模型计算结果比较 Fig. 11 Comparison of measured data of sub-sand soil and calculation result of model |
| |
从以上各种土样各工况实测数据与桩侧土接触面模型计算结果对比图中可以看出桩侧土接触面传递函数模型计算值与实测值基本相符,验证了本研究提出模型是适用和可靠的。
4 结论由理论分析及桩侧土接触面损伤机理模型试验结果分析,得出结论如下:
(1) 模型试验表明土体所处深度对桩土接触面侧摩阻力影响较大,从测试结果来看,桩土接触面侧摩阻力与土体深度成正比。
(2) 大量模型试验测试结果表明桩土接触损伤与桩土相对滑移量正相关,当相对滑移量达到一定值时,接触面破坏。
(3) 本研究提出的损伤指数模型能够很好地反映桩土接触面的损伤程度,与模型试验结果吻合。
(4) 从模型试验结果来看,不同桩侧土体的损伤变形过程是不一样的,且同一土体不同深度其损伤变形也是不同的,因此工程计算分析中应考虑不同土层协调变形和桩侧土体深度效应。
| [1] |
吴鹏. 超大群桩基础竖向承载性能及设计理论研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2006. WU Peng. Vertical Bearing Characters and Design Theory about Great Pile Group Foundation[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2006. |
| [2] |
袁灯平. 大直径超长桥梁桩基与群桩基础竖向承载特性及沉降控制研究[D]. 上海: 同济大学, 2007. YUAN Deng-ping. Research on Vertical Bearing Characteristics and Settlement Control of Pile Foundation and Pile Group Foundation for Large Diameter and Super Long Bridge[D]. Shanghai: Tongji University, 2007. |
| [3] |
KUYUMCU Z, ATES S. Soil-structure-foundation Effects on Stochastic Response Analysis of Cable-stayed Bridges[J]. Structural Engineering & Mechanics, 2012, 43(5): 637-655. |
| [4] |
DORAN B, SECKIN A. Soil-pile Interaction Effects in Wharf Structures under Lateral Loads[J]. Structural Engineering & Mechanics, 2014, 51(2): 267-276. |
| [5] |
DIAS D, GRIPPON J. Numerical Modelling of a Pile-supported Embankment Using Variable Inertia Piles[J]. Structural Engineering & Mechanics, 2016, 61(2): 245-253. |
| [6] |
JIN C, LIU X L. Reliability Analysis of Steel Cable-stayed Bridges Including Soil-pile Interaction[J]. Steel & Composite Structures, 2012, 13(2): 109-122. |
| [7] |
DENISE-PENELOPE K, AHMED F. 3D FEM Analysis of a Pile-supported Riverine Platform under Environmental Loads Incorporating Soil-pile Interaction[J]. Computation, 2018, 6(1): 8. |
| [8] |
LI Z, FENG D, FENG M Q, et al. System Identification of the Suspension Tower of Runyang Bridge Based on Ambient Vibration Tests[J]. Smart Structures and Systems, 2017, 19(5): 523-538. |
| [9] |
YI J H, KIM S B, YO ON, G L, et al. Natural Frequency of Bottom-fixed Offshore Wind Turbines Considering Pile-soil-interaction with Material Uncertainties and Scouring Depth[J]. Wind & Structures, 2015, 21(6): 625-639. |
| [10] |
LEMNITZER A, N ÑEZ E, MASSONE L M. Model Verification and Assessment of Shear-flexure Interaction in Pile Foundations[J]. Earthquakes & Structures, 2016, 11(1): 141-163. |
| [11] |
QIN H, WEI D G. Nonlinear Response of Laterally Loaded Rigid Piles in Sand[J]. Geomechanics and Engineering, 2014, 7(6): 679-703. |
| [12] |
张嘎, 张建民. 土与结构接触面弹塑性损伤模型用于单桩与地基相互作用分析[J]. 工程力学, 2006, 23(2): 72-77. ZHANG Ga, ZHANG Jian-min. Elastoplastic Damage Model of Soil-structure Interface in Single Pile-soil Interaction Analysis[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2006, 23(2): 72-78. |
| [13] |
MCGANN C R, ARDUINO P, MACKENZIE-HELNWEIN P. Applicability of Conventional p-y Relations to the Analysis of Piles in Laterally Spreading Soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical & Geoenvironmental Engineering, 2011, 133(6): 557-567. |
| [14] |
KHARI M, KASSIM K A, ADNAN A. Development of p-y Curves of Laterally Loaded Piles in Cohesionless Soil[J]. Scientific World Journal, 2014(1): 1-8. |
| [15] |
戴国亮, 龚维明. 基于单桩荷载试验的群桩荷载与位移关系模拟[J]. 公路交通科技, 2011, 28(5): 1-5, 140. DAI Guo-liang, GONG Wei-ming. Simulation of Relationship between Load and Displacement of Group Pile Based on Single Pile Loading Test[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2011, 28(5): 1-5, 140. |
| [16] |
张学峰. 跨海大桥主墩基础损伤分析及检测评价技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2017. ZHANG Xue-feng. Research on Damage Analysis and Detection Evaluation Technology of Main Pier Foundation of Cross-sea Bridge[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology, 2017. |
| [17] |
苏静波, 邵国建, 刘宁. 基于P-Y曲线法的水平受荷桩非线性有限元分析[J]. 岩土力学, 2006, 27(10): 1781-1785. SU Jing-bo, SHAO Guo-jian, LIU Ning. Nonlinear Finite Element Analysis of Piles under Lateral Load Based on P-Y Curves[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2006, 27(10): 1782-1785. |
| [18] |
姚文娟, 吴怀睿, 程泽坤, 等. 基于p-y曲线法的超长桩非线性数值分析[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2011, 33(11): 1683-1690. YAO Wen-juan, WU Huai-rui, CHENG Ze-kun, et al. Nonlinear Numerical Analysis of Super-long Piles Based on p-y Curves[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2011, 33(11): 1683-1690. |
| [19] |
CUI X Z, WANG Y L, LIU K W, et al. A Simplified Model for Evaluating the Hardening Behaviour of Sensor-enabled Geobelts During Pullout Tests[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes, 2019, 47(3): 377-388. |
 2021, Vol. 38
2021, Vol. 38
