扩展功能
文章信息
- 李丽峰, 常锋强
- LI Li-feng, CHANG Feng-qiang
- 深埋长大隧道风流温湿度的预测及应用
- Prediction and Application of Temperature and Humidity of Airflow in Deep and Long Tunnel
- 公路交通科技, 2021, 38(2): 110-116
- Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Denelopment, 2021, 38(2): 110-116
- 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2021.02.014
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2020-07-31
随着我国高速公路建设的快速发展,山区隧道开挖越来越多,而近些年深埋长大隧道所占的比例也越来越高,随之而引起的高温高湿已成为深埋长大隧道开挖的主要问题之一[1-3],不仅影响施工的进度,而且使得作业环境恶化,危害施工人员的健康与安全。对隧道内热环境进行控制的前提是对隧道中风流的温湿度进行预测[4-6],目前,国内外的专家学者对隧道施工中围岩散热、水分蒸发与凝结、风流温湿度的预测计算进行了一定的研究[7-11],并建立了相关的温度预测模型[12-17]。然而对整个施工隧道内通风风流湿度的预测仍缺少进一步的分析与验证。
本研究基于三维围岩温度场的理论数学模型构建隧道内风流温湿度的预测模型,并编制实用的解算程序,进一步根据隧道内不同的影响条件预测风流温湿度的变化情况,最后与隧道温湿度的实测值进行对比验证。
1 隧道施工数学模型的建立 1.1 模型建立的基础条件考虑隧道内部导热的实际情况,对隧道内围岩壁面导热进行设定:隧道围岩内部导热均匀,不考虑隧道围岩的热辐射;隧道围岩壁面的换热条件相同。
1.2 数学模型的构建隧道施工中风流的温度将会受到很多因素的影响,但是热量的产生主要有以下两个方面:一是隧道围岩壁面和流动空气的热湿交换,二是会受到隧道推进方向角度的影响,风流在流动过程中会受到膨胀或压缩进而产生热量交换。
隧道中的施工围岩壁面和流动中的风流之间会进行热量的交换,其换热量q[18]如式(1)所示:
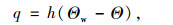
|
(1) |
式中,h为对流换热系数;Θw为隧道围岩壁面温度;Θ为隧道内的风流温度。
风流在流动过程中受到压缩而产生的热量qco [18]如式(2)所示:
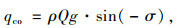
|
(2) |
式中,ρ为隧道内空气的密度;Q为隧道内的通风风量;g为重力加速度;σ为隧道推进方向的角度。
下面计算隧道潮湿围岩壁面蒸发的水分。
通常情况下,隧道围岩壁都是处于潮湿状态,因此隧道围岩壁面所传递出的总热量qto[18]与隧道内风流温度升高需要的显热qse与潮湿围岩壁面水分蒸发需要的潜热qla之和相等,如式(3)所示:
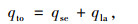
|
(3) |
式中,qto为隧道围岩壁传递出的总热量;qse为隧道围岩壁散发到风流中的显热;qla为隧道围岩壁散发到风流中的潜热。
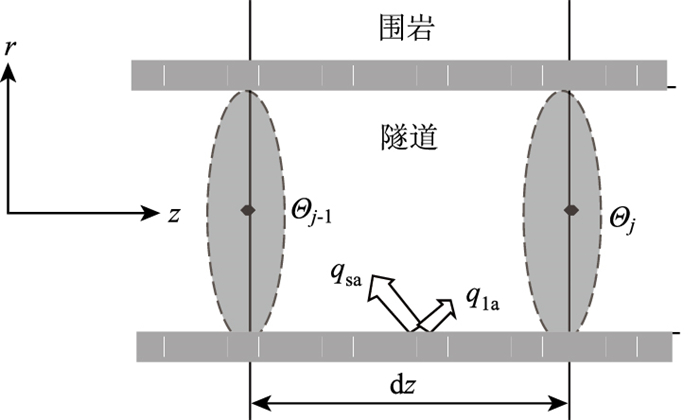
|
| 图 1 隧道内围岩散热示意图 Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of surrounding rock heat dissipation in tunnel |
| |
隧道潮湿围岩壁面蒸发水分的速率如式(4)所示:
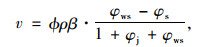
|
(4) |
式中,ϕ为隧道围岩壁面的潮湿率;β为物质交换律系数[19];φws为隧道内处于围岩壁温度时的饱和绝对湿度;φs为隧道内风流饱和温度时的绝对湿度;φj为隧道内处于风流温度时的绝对湿度。
2 隧道内风流温度湿度的解算 2.1 隧道内部风流温湿度解算模型的建立基于风流热湿交换的理论,结合隧道内模型建立的基础条件,构建出隧道潮湿围岩壁面水分蒸发情况下风流温湿度的解算模型。
隧道围岩内部模型如式(5)所示:
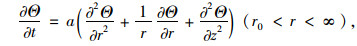
|
(5) |
式中,t为隧道通风时间;a为热扩散率;r为隧道围岩距隧道轴心的距离。
根据泰勒展开式,对式(5)中的各项进行差分变换可得:
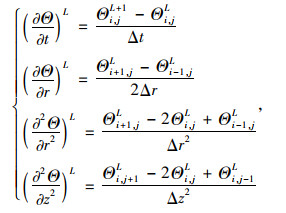
|
(6) |
式中,Δt为分割时间;Δr为隧道内部径向分割距离;Δz为隧道内轴向分割距离;L为隧道中某一时刻。
由式(5)~(6)化简可知:
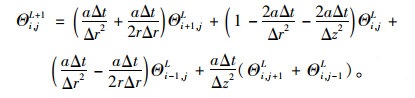
|
(7) |
如果L时的温度为ΘiL, j,则在L+1时的温度可由式(7)算出。
隧道围岩壁表面模型如式(8)所示:
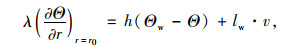
|
(8) |
式中,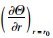
下面计算隧道内风流温湿度。隧道围岩中向隧道内部散发出的热量有显热量及潜热量,沿着隧道风流z方向中的风流温湿度上升梯度的计算模型如式(9)所示:
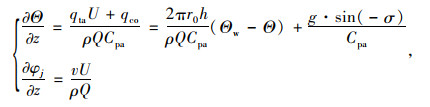
|
(9) |
式中,U为周长;r0为隧道半径;Cpa为空气的定压比热。
根据差分法可分别计算得出隧道内风流温湿度的计算模型,如式(10)所示:
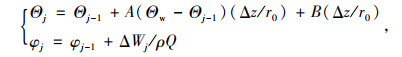
|
(10) |
式中,A为隧道中导热引起的风流温度的增高的系数,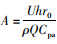
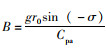
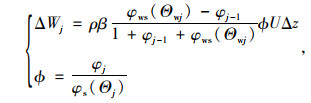
|
(11) |
式中Θwj为隧道j点的围岩壁面温度。
根据式(11)可计算求得隧道中不同时间不同隧道长度的风流温湿度。
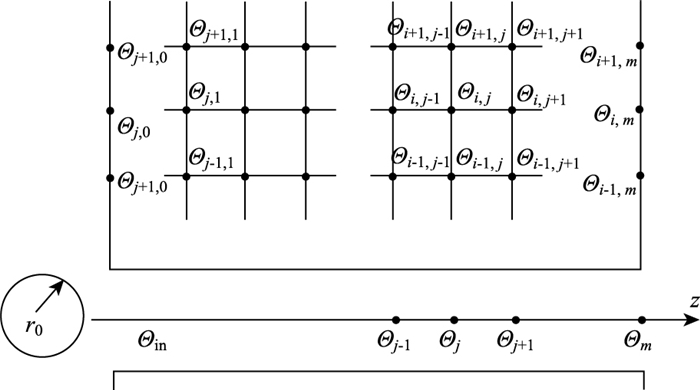
如图 2所示,沿隧道的径向[0,R]进行了n等分,分点用i表示(ri=0, 1, …, n), 则Δr=R/n,沿隧道z轴方向[0,z]进行了m等分,分点用j表示(zj=0, 1, …, m), 则Δz=z/m,Δr和Δz称之为步长, 分别沿着径向R和轴向z作出平行线,其交点即为节点,即Θij, 因此Θ在任一时间节点Θij的值为风流温度值。
|
| 图 2 隧道风流温度解析示意图 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of analysing airflow temperature in tunnel |
| |
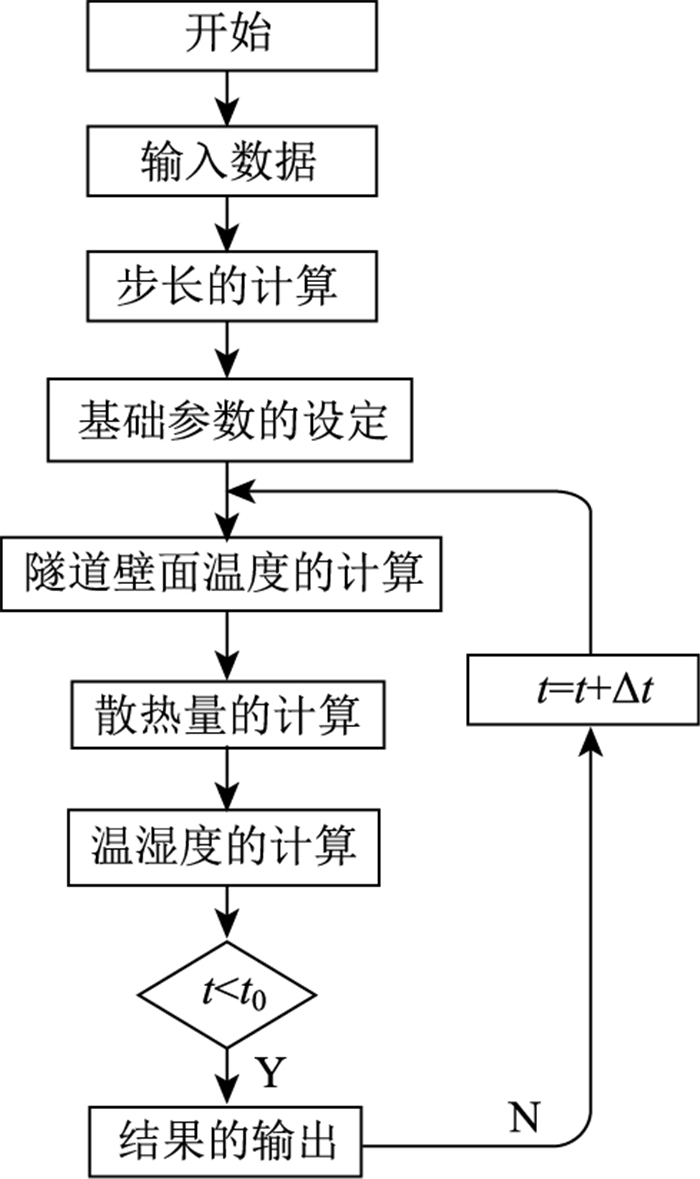
2.2 隧道内部风流温湿度解算程序
基于隧道内风流温度湿度的计算模型编制出程序解算软件,其主要步骤为:
(1) 将隧道起点通风输入的风流温湿度看作计算的初始数值。
(2) 利用输入的初始赋值计算出隧道围岩壁面温度值。
(3) 根据式(3)和式(4)可计算出每个不同长度隧道区段的围岩壁传递出的热量。
(4) 根据式(8)和式(9)可依次求得隧道中不同时间不同隧道长度的风流温湿度。
(5) 如果时间t < t0(实际通风时间),满足要求,输出结果,否则会返回到(2)重复上述步骤计算。
|
| 图 3 风流温湿度解算流程 Fig. 3 Flowchart of calculating temperature and humidity of airflow |
| |
3 施工隧道内部风流温湿度解算模拟
为了进一步探讨隧道内部风流温湿度的变化规律,在此模拟在各种状态下隧道中风流温度和湿度的变化情况,并分析出现不同结果的原因,以便为隧道实际施工中对温湿度的控制奠定基础。模拟所用的基础参数见表 1。
| 基础参数 | 数值 |
| 隧道内部原始岩温/℃ | 40 |
| 隧道岩石热导率/[W·(m·℃)-1] | 3.72 |
| 热扩散系数/(m2·s-1) | 1.64×10-6 |
| 对流换热系数/(W·m-2·℃-1) | 14 |
| 隧道半径/m | 3.5 |
3.1 隧道入风口不同温度对隧道内部风流温度的影响
在隧道掘进的水平方向,进风口风流相对湿度为0.5,隧道进风口温度分别为10,20,30 ℃,隧道围岩壁面的潮湿率分别为0.1和0.5时,在隧道通风为1月、1 a和2 a的时间内风流温度的变化规律见图 4。

|
| 图 4 隧道进风口温度对内部风流温度的影响 Fig. 4 Influence of tunnel air inlet temperature on internal airflow temperature |
| |
根据图 4隧道内风流温度的变化规律可知,当隧道通风时间为1月时,隧道内的温度会随着推进长度的加大而上升,进风口温度越低风流温度增加的幅度越大,主要是由于在隧道通风时间较短的情况下,围岩内部的温度比较高,通过热传导及热交换到隧道内部的风流热量多而引起。如果在隧道通风时间增加到2 a的情况下, 就会使得围岩内部的温度逐渐降低,传递到隧道内部的热量减少,所以计算预测的温度增加幅度降低。
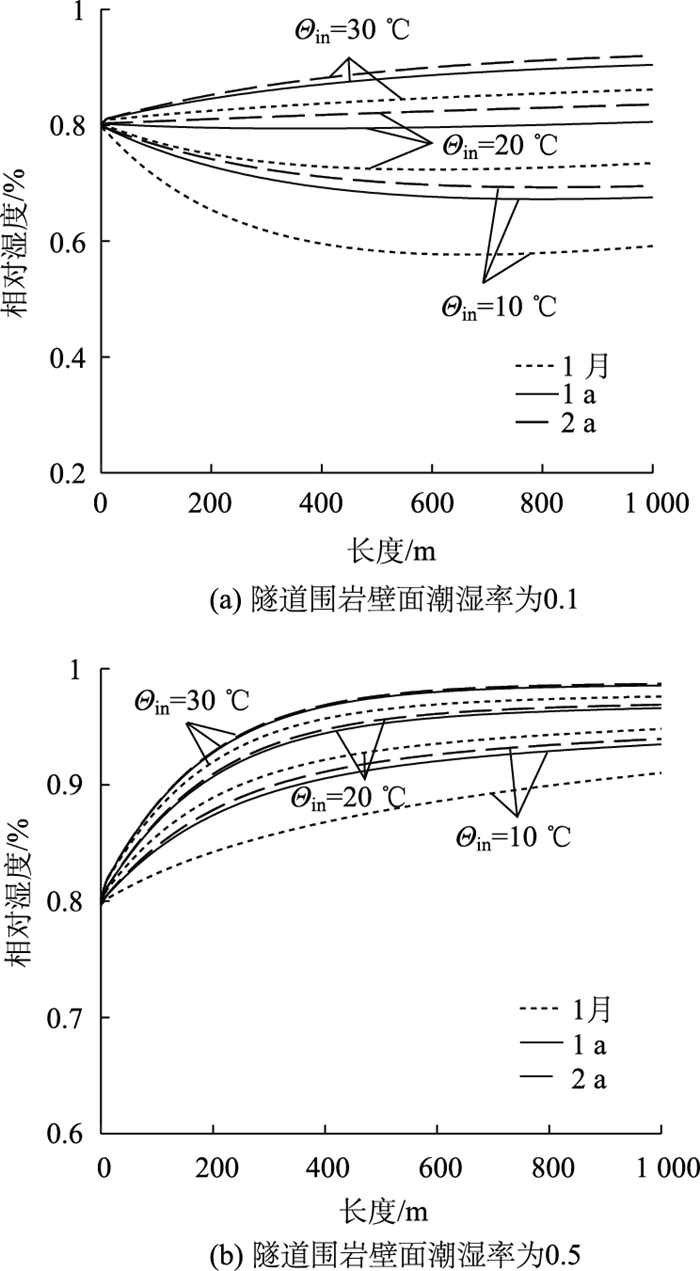
3.2 隧道入风口不同温度对隧道内部风流湿度的影响在隧道掘进的水平方向,进风口风流相对湿度为0.8,隧道进风口温度分别为10,20,30 ℃,隧道围岩壁面的潮湿率分别为0.1和0.5时,在隧道通风为1月、1 a和2 a的时间内风流湿度的变化规律见图 5。
|
| 图 5 隧道进风口温度对内部风流湿度的影响 Fig. 5 Influence of tunnel air inlet temperature on internal airflow humidity |
| |
根据图 5隧道内风流湿度的变化规律可知,进风口温度越高隧道内风流的相对湿度会越大,相反,风流的相对湿度会先降低(图 5(a)),这主要是由于进风流温度低、温度上升幅度大而引起的。而当围岩壁面的潮湿率加大后(图 5(b)), 进风口温度越高隧道内风流的相对湿度上升幅度越快,在隧道通风时间增长的情况下,风流的相对湿度将接近于饱和情况,因此其增长的幅度减小。
4 工程实践某山岭重丘公路特长隧道A为分离式特长隧道,隧道左线全长为3 672 m。某隧道B为双洞单线深埋式隧道,隧道左线全长6 336 m。
测试地点为上述两隧道的左洞,采用红外激光测温仪及机械通风干湿表分别对隧道内部壁面温度和隧道风流温度进行测量,两测点间的距离为50 m,并向前递增到100 m,仪器设备如图 6所示。
|
| 图 6 仪器设备 Fig. 6 Instruments |
| |
最后将实地勘测的风流温湿度与计算模拟的隧道温湿度进行对比验证。
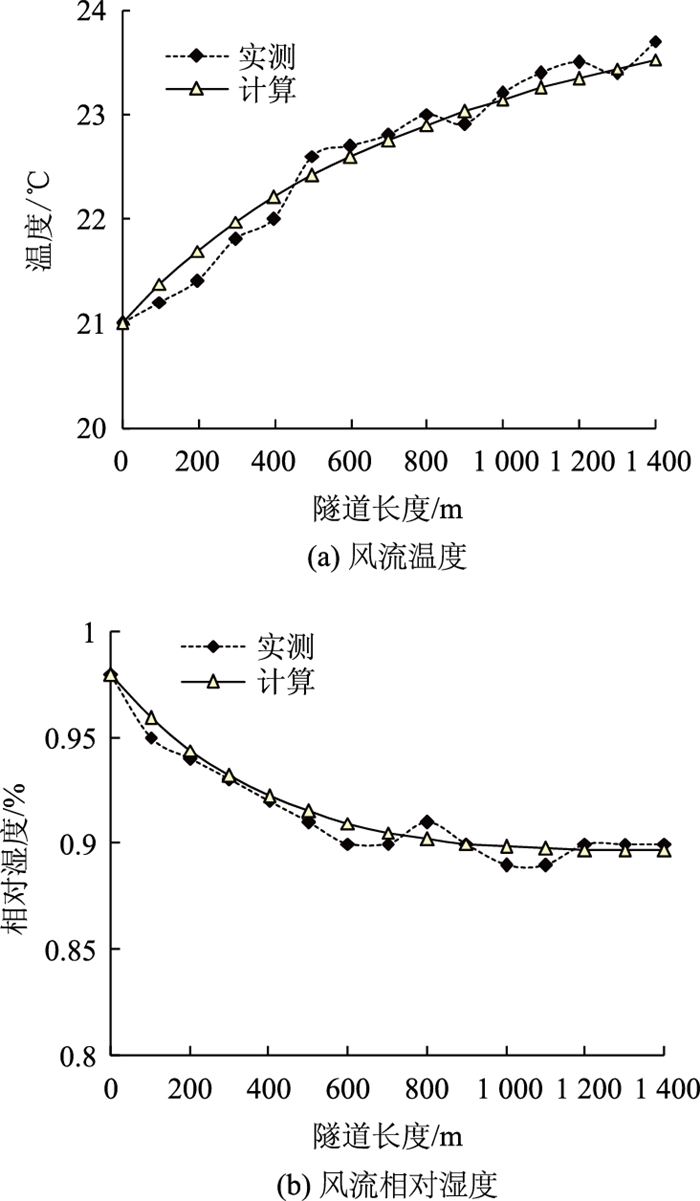
4.1 隧道A内风流温湿度实测与模拟计算变化规律分析图 7是隧道A内风流温湿度测量与计算的分布规律。由图 7(a)可以看出,随着隧道长度的加长,在热湿交换的影响下风流温度逐渐上升,隧道内实地勘测的数值与计算的风流温度值基本一致,由于隧道实际围岩壁面属于局部潮湿,因此测试出的风流温度值会呈现出上下波动的状况,模拟是基于围岩壁面为均匀潮湿而计算出的,所以分布图为一条平滑的上升曲线。由图 7(b)可知,隧道内实地勘测的风流湿度与计算的风流湿度值基本相同,但是相对湿度随着隧道长度的加长呈现降低趋势,这主要是由于温度上升导致的,同样测试出的风流湿度值出现上下波动是由于围岩壁面潮湿非均匀分布引起的。
|
| 图 7 隧道A内风流温湿度分布曲线 Fig. 7 Distribution curves of temperature and humidity of airflow in tunnel A |
| |
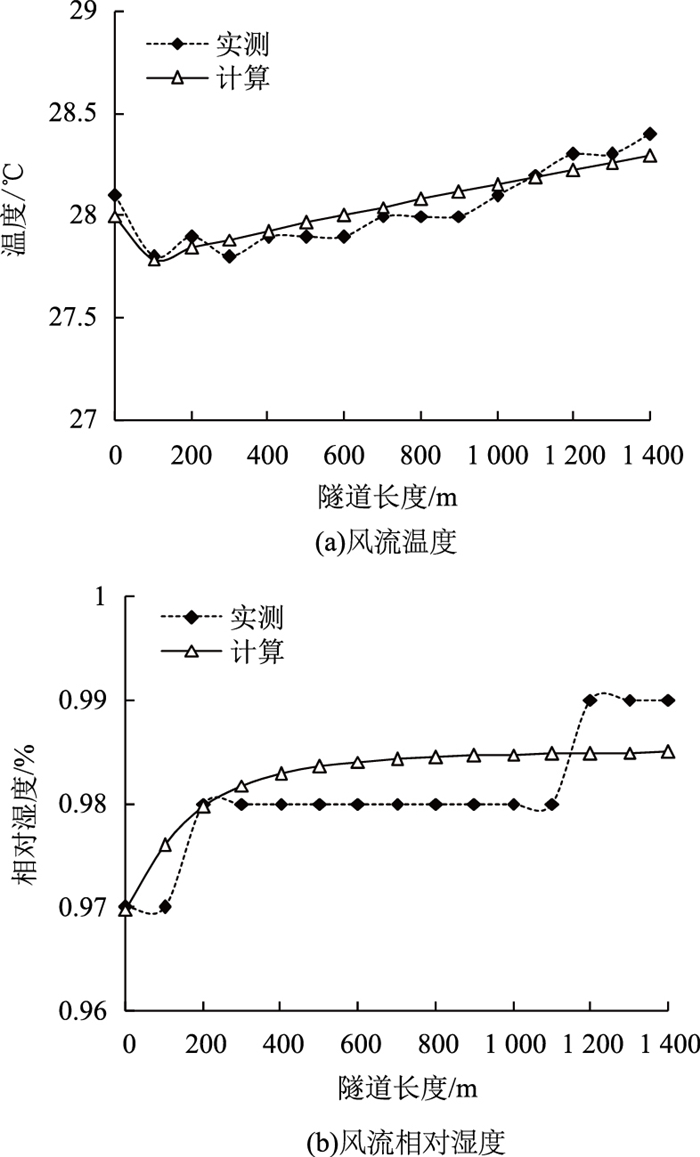
4.2 隧道B内风流温湿度实测与模拟计算变化规律分析
图 8是隧道B内风流温湿度的测量与计算分布曲线。由图 8(a)可以看出,隧道入口进风流温度较高,风流温度呈现出先降低后升高的变化趋势,其主要原因是受到围岩壁面潮湿率的影响,壁面的水分在蒸发过程中会吸收热量,因此在通风初期温度有降低的情况。由图 8(b)可知,实地勘测的隧道内相对湿度表现出阶梯式增高趋势,其主要原因是由隧道围岩壁潮湿程度非均匀所致,并且随着长度的增加,风流湿度慢慢趋近于饱和状态,模拟计算显示连续变化情况且与测量结果相近。
|
| 图 8 隧道B内风流温湿度分布曲线 Fig. 8 Distribution curves of temperature and humidity of airflow in tunnel B |
| |
由于隧道内很多因素都将影响风流温湿度的变化,比如围岩壁面非均匀潮湿及风流的非稳定性,因此通过计算模拟和现场实际勘查得出的风流温湿度数值有一定的误差在所难免,但总体上的变化趋势是相同的。
5 结论(1) 根据隧道围岩壁面潮湿率对风流温度的影响可知,随着潮湿率的增大,隧道内的风流温度上升幅度逐渐降低。
(2) 基于隧道围岩壁面均匀潮湿的情况,可以模拟计算出非均匀潮湿风流温湿度的变化趋势,该趋势接近于隧道的实际勘测值。
(3) 隧道内部风流温湿度预测计算时可将隧道入风口温度作为预测计算的输入初值。
(4) 由所编制的计算模型软件在深埋长大隧道中的应用效果可知,实测结果与预测结果的变化趋势基本吻合,证明了构建的数学模型可以预测隧道内风流的温湿度,为在隧道施工过程中对热环境的控制提供可靠的理论依据。
| [1] |
陈文化. 高温高湿环境下高铁隧道洞口段热湿病害分析[J]. 铁道工程学报, 2016, 33(11): 102-105, 119. CHEN Wen-hua. Analysis of Railway Tunnel Portal Section Thermal-humidity Failure in High Temperature and High Humidity[J]. Journal of Railway Engineering Society, 2016, 33(11): 102-105, 119. |
| [2] |
孙璐, 周正兵, 金姣萍. 基于模糊熵和AHP的山区公路交通气象安全评价[J]. 公路交通科技, 2011, 28(12): 138-144. SUN Lu, ZHOU Zheng-bing, JIN Jiao-ping. Assessment of Weather Condition for Traffic Safety of Mountain Highway Based on Fuzzy Entropy and Analytic Hierarchy Process[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2011, 28(12): 138-144. |
| [3] |
杨德源, 杨天鸿. 矿井热环境及其控制[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2009. YANG De-yuan, YANG Tian-hong. Thermal Environment in Mine and Its Control[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2009. |
| [4] |
宋国森, 胡斌. 特长公路隧道平导通风方案研究及优化[J]. 公路交通科技, 2011, 28(4): 84-90, 95. SONG Guo-sen, HU Bin. Research and Optimization of Parallel Heading Ventilation Scheme for Super-long Highway Tunnel[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2011, 28(4): 84-90, 95. |
| [5] |
王亚琼, 谢永利, 张素磊, 等. 氮氧化物对隧道需风量影响研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(10): 89-94. WANG Ya-qiong, XIE Yong-li, ZHANG Su-lei, et al. Study on Effect of Nitrogen Oxides on Tunnel Required Ventilation[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2010, 27(10): 89-94. |
| [6] |
石零, 余新明, 杨伟忠, 等. 高温巷(隧)道热环境控制实验研究[J]. 工业安全与环保, 2014, 40(7): 26-27, 46. SHI LING, YU Xin-ming, YANG Wei-zhong, et al. Experimental Study of Thermal Environment Control for High Temperature Tunnel[J]. Industrial Safety and Environmental Protection, 2014, 40(7): 26-27, 46. |
| [7] |
高建良, 张学博. 潮湿巷道风流温度与湿度变化规律分析[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2007, 17(4): 136-139. GAO Jian-liang, ZHANG Xue-bo. Analysis on the Changing Rule of Airflow's Temperature and Humidity in Wet Airway[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2007, 17(4): 136-139. |
| [8] |
易赛莉. 公路隧道火灾烟气特性数值模拟分析[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(1): 89-94. YI Sai-li. Analysis on Characteristics of Fire Smoke in Highway Tunnel by CFD Simulation[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2010, 27(1): 89-94. |
| [9] |
林强, 刘明华, 茹锋, 等. 隧道通风系统模糊控制算法研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(9): 85-88. LIN Qiang, LIU Ming-hua, RU Feng, et al. Research on Fuzzy Control Algorithm of Tunnel Ventilation System[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2010, 27(9): 85-88. |
| [10] |
严健, 何川, 曾艳华, 等. 高海拔特长隧道低温大风环境及对围岩-结构温度场的影响[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(11): 192-201. YAN Jian, HE Chuan, ZENG Yan-hua, et al. Strong Cold Wind Environment Outside Extra-long Tunnel in High-altitude Region and Its Influence on Temperature Field of Surrounding Rock Structure[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(11): 192-201. |
| [11] |
李现者, 贾晓云, 朱永全. 高纬度寒区隧道施工热环境数值计算研究[J]. 制冷与空调(四川), 2016, 30(2): 205-207. LI Xian-zhe, JIA Xiao-yun, ZHU Yong-quan. Numerical Simulation of Tunnel Construction Thermal Environment in High Altitude Cold Regions[J]. Refrigeration & Air Conditioning, 2016, 30(2): 205-207. |
| [12] |
张小康. 矿井通风系统环境温度实时计算与应用[J]. 煤炭学报, 2012, 37(5): 863-867. ZHANG Xiao-kang. Real-time Calculation and Application of Mine Ventilation System Environmental Temperature[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(5): 863-867. |
| [13] |
王华牢, 刘学增, 马小君. 长大公路隧道火灾安全疏散研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(11): 83-87. WANG Hua-lao, LIU Xue-zeng, MA Xiao-jun. Research on Safe Evacuation in Long Road Tunnel during Fire[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2010, 27(11): 83-87. |
| [14] |
张晓明, 李丽峰, 王志光. 煤矿井下热害分析与风流温度预测[J]. 辽宁工程技术大学学报: 自然科学版, 2012, 31(6): 826-829. ZHANG Xiao-ming, LI Li-feng, WANG Zhi-guang. Heat Harm Analysis and Prediction of Airflow Temperature in Coal Mine[J]. Journal of Liaoning Technical University: Natural Science Edition, 2012, 31(6): 826-829. |
| [15] |
巩航军, 魏显威. 高速公路隧道运营安全综合评价研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(8): 127-130, 135. GONG Hang-jun, WEI Xian-wei. Study on Comprehensive Evaluation of Operation Safety of Expressway Tunnel[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2010, 27(8): 127-130, 135. |
| [16] |
高建良, 魏平儒. 掘进巷道风流热环境的数值模拟[J]. 煤炭学报, 2006, 31(2): 201-205. GAO Jian-liang, WEI Ping-ru. Numerical Simulation of the Thermal Environment at Working Face of Diving Airway[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2006, 31(2): 201-205. |
| [17] |
孙庆翔, 秦刚, 丁国锋. 高速公路隧道灾害事件检测新方法及应用研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2010, 27(11): 94-99. SUN Qing-xiang, QIN Gang, DING Guo-feng. A New Detection Method and Application for Expressway Tunnel Accidents and Disasters[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2010, 27(11): 94-99. |
| [18] |
杨世铭, 陶文铨. 传热学[M]. 4版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. YANG Shi-ming, TAO Wen-quan. Heat Transfer[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006. |
| [19] |
胡汉华. 深热矿井环境控制[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2009. HU Han-hua. Deep Heat Mine Environmental Control[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2009. |
 2021, Vol. 38
2021, Vol. 38
