扩展功能
文章信息
- 旷新辉, 江海, 殷源, 吴超, 何雄君
- KUANG Xin-hui, JIANG Hai, YIN Yuan, WU Chao, HE Xiong-jun
- 拉索线形参数的解析解研究
- Study on Analytical Solution of Cable Shape Parameters
- 公路交通科技, 2020, 37(10): 92-97
- Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Denelopment, 2020, 37(10): 92-97
- 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2020.10.010
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2019-09-26
2. 湖北省联合发展投资集团有限公司, 湖北 武汉 430000;
3. 武汉理工大学 交通学院, 湖北 武汉 430063;
4. 湖北省公路工程研究中心, 湖北 武汉 430063
2. Hubei Provincial United Development and Investment Group Co., Ltd., Wuhan Hubei 430000, China;
3. School of Transportation, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan Hubei 430063, China;
4. Hubei Provincial Highway Engineering Research Center, Wuhan Hubei 430063, China
斜拉桥因跨越能力强、经济指标好以及结构形式新颖、美观等特点,已成为现代桥梁工程中最热门的桥型之一[1]。斜拉索作为斜拉桥结构中的主要承重构件,为梁体提供弹性支撑,将桥跨结构的自重以及桥面活载传递至索塔;同时斜拉索的存在使得梁跨截面的最大弯矩得以降低,提高了桥梁的跨越能力[2]。斜拉索是一种柔性结构,其在拉索自重和张力的作用下线形呈悬链线[3],实际斜拉索线形受端部张力、索长、弹性变形、几何非线性等因素的影响,拉索的线形问题一直以来都是桥梁工作者研究的热点[4]。
Bernoullis,Leibnitz,Routh,Feld先后计算得到了斜拉索的悬链线解,为斜拉索的静力分析奠定了基础,但其计算方法相当繁琐。Ernst在1965年提出了修正弹性模量的表达式——Ernst公式,考虑将曲线斜拉索用两节点直线杆来代替,通过修正斜拉索的弹性模量来考虑其刚度,但由于斜拉索位移和索力增量之间的非线性关系,这种算法会导致斜拉索索力和拉伸量之间关系的不闭合。张震陆等[5]提出了“悬链段”分析方法,对于一个特定的问题,只要求出各悬链段对应水平悬链的跨度及其他参数,即可得到待求量。该方法由于利用了水平悬链线的精确解,精度高于其他近似方法。彭力军等[6]提出了利用斜拉索索长来计算水平张拉力,以及通过斜拉索端部张拉力反求斜拉索索长的迭代方法。李强兴[7]推导了斜拉索的计算公式,假定水平张力为已知量来计算索长、倾角等,但从实际应用的角度考虑,其假定的索长和水平张拉力均是待求的未知参数,误差大。魏建东[8]推导了含待定参数的斜拉索线形的静力方程,可以应用于工程设计及强度验算,但该方法需要编程并进行迭代求解,在实际工程应用中不太方便。麦深林[9]利用斜拉索自重作用下斜拉索微段的静力平衡方程,推导出考虑弹性变形和不考虑弹性变形两种情况下斜拉索悬链线线形所对应的物理量,并提出了基于移动坐标原点的斜拉索简化计算方法。目前许多工程技术人员在计算中利用抛物线方程近似替代悬链线方程来求解斜拉索参数,该方法虽然能够满足一些工程应用的要求,但当处理有关斜拉索的非线性问题而又考虑弹性变形的影响时,就会遇到数学上的困难[10]。
因此有必要研究一种没有限制的精确计算方法,笔者在本研究中利用自重作用下任意微段的静力平衡方程,推导出斜拉索的线形理论公式,并从斜拉索的基本线形方程出发,推导出有工程应用价值的斜拉索参数。
1 拉索线形的解析解推导如图 1所示,以梁端锚点处为原点建立直角坐标系,塔端锚点坐标(X1, Y1),拉索上任一点坐标(x, y)。拉索在拉力N,重力场G的作用下,发生拉伸和下挠,任意微元体之间的拉力N、N~和重力ΔG满足力的平衡条件,以任意微元体的平衡条件构造拉索线形的微分方程并求解。
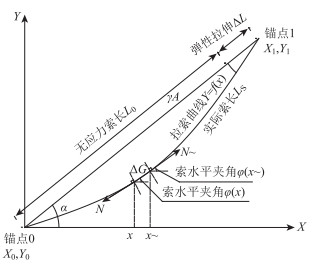
|
| 图 1 斜拉索悬挂参数 Fig. 1 Suspension parameters of stay cable |
| |
根据斜拉索的微段平衡条件,计算图如图 2所示。
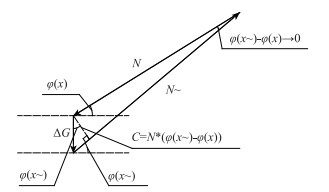
|
| 图 2 斜拉索任意微段的平衡 Fig. 2 Equilibrium of any micro segment of stay cable |
| |
设拉索曲线方程为:
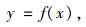
|
(1) |
则拉索任一点的水平夹角:
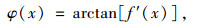
|
(2) |
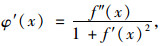
|
(3) |
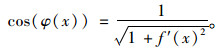
|
(4) |
任意微元体的重力:
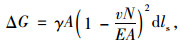
|
(5) |
式中,A为拉索正截面面积;N为拉索任意一点索力;E为拉索弹性模量。
微元体长:
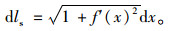
|
(6) |
索长:
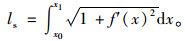
|
(7) |
由任意微元体的静力平衡可得:
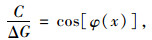
|
(8) |
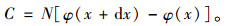
|
(9) |
当dx→0时,C为正无穷小量。
将式(9)Taylor展开[11],取前2项,略去dx高次项,公式化简为:
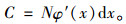
|
(10) |
将方程(3)~(6),(10)代入式(8),化简整理得:
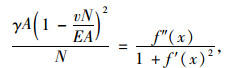
|
(11) |
令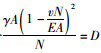
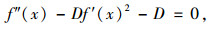
|
(12) |
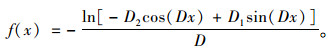
|
(13) |
参数D1,D2为解微分方程后的待定系数。将坐标系建立在梁端锚点,式中梁端锚点坐标为(0, 0),塔端锚点坐标(X1, Y1),求出待定参数D1,D2。
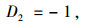
|
(14) |
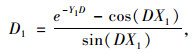
|
(15) |
拉索的线形方程解即解析解为:
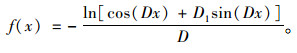
|
(16) |
根据推导的拉索线形方程,可以求解出:曲线索长ls、无应力索长l0、等效弹性模量Eeq、梁端锚点水平夹角φ(0)、塔端水平夹角φ(x)、拉索的垂度fm。
2.1 曲线索长求解D可改写成为:
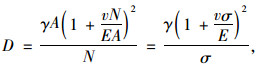
|
(17) |
展开式(17),得:
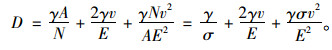
|
(18) |
考查式(18),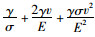
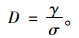
|
(19) |
将D,X,Y值代入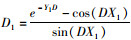
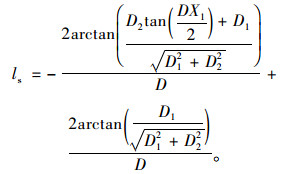
|
(20) |
拉索在拉应力σ作用下发生体积变化,其体积变化满足体积柔量公式[12]:
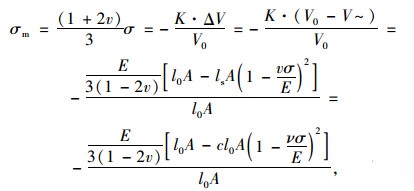
|
(21) |
式中,V为泊松比;ΔV为体积变化量;C为待求参量;体积柔量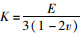
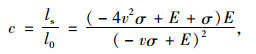
|
(22) |
故:
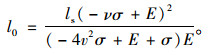
|
(23) |
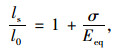
|
(24) |
将式(22)代入式(24)左侧,可求得任意应力σ作用下的Eeq。
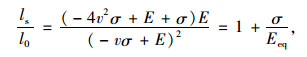
|
(25) |
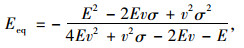
|
(26) |
展开式(26),后两项占Eeq的比值小于0.2%,做近似计算时,等效弹模公式[13-14]可简化为:
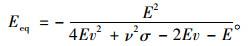
|
(27) |
任意点拉索的角度为:
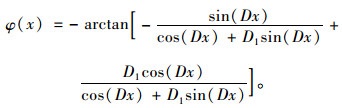
|
(28) |
拉索梁端锚固角度:
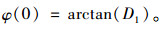
|
(29) |
拉索塔端锚固角度:
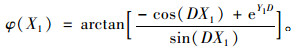
|
(30) |
坐标原点建立在梁端锚点,fm(x)=f(x)-x·tan(α);最大取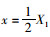
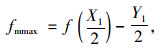
|
(31) |
将f(x)表达式代入化简为:
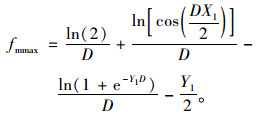
|
(32) |
拉索锚具变形、主塔与主梁弹性压缩、混凝土的收缩徐变对索力的影响本质上均由拉索锚点的几何变形导致。
考查式(24),拉索的锚点几何变形量可改写为:
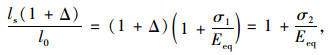
|
(33) |
求出:
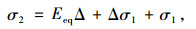
|
(34) |
应力变化值:
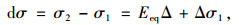
|
(35) |
式中Δ为锚点间距变化增量[15](无量纲数):
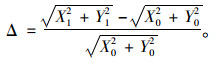
|
(36) |
以文献[15]中提供的计算实例进行计算。取某长江公路大桥编号为J10,J18的斜拉索进行计算,计算方法分别采用Ernst公式[16-18]和本研究介绍方法。计算参数及计算结果如表 1所示。
| 输入参数 | J10 | J18 | |||
| 梁端XA/m | 379 | 475 | |||
| 塔端XB/m | 254.023 | 254.096 | |||
| 梁端YA/m | 51.218 | 51.482 | |||
| 塔端YB/m | 148.871 | 163.885 | |||
| 梁端ZA/m | 17.361 | 17.361 | |||
| 塔端ZB/m | 7.250 | 7.250 | |||
| 弹性模量/(t·m-2) | 19 500 000 | 19 500 000 | |||
| 截面面积/m2 | 5.811e-03 | 8.581e-03 | |||
| 泊松比 | 0.300 | 0.300 | |||
| 梁端索力垂直分力 | 148.002 | 176.559 | |||
| 输出结果 | J10 | J18 | |||
| 本研究计算 结果 |
Ernst公式 | 本研究计算 结果 |
Ernst公式 | ||
| 梁端斜率 | 0.760 | 0.779 | 0.484 | 0.508 | |
| 塔端斜率 | 0.798 | 0.779 | 0.533 | 0.508 | |
| 索长/m | 158.930 | 158.926 | 248.078 | 248.063 | |
| 伸长量/m | 0.410 | 0.344 | 0.701 | 0.595 | |
| 无应力索长/m | 158.520 | 158.582 | 247.377 | 247.468 | |
3.2 算例2
以笔者承担施工的某在建长江公路大桥为例,分别取M10,M20,M30,这3根索,按Ernst公式方法和本研究介绍方法进行计算斜拉索索长及无应力索长等参数,计算参数表及计算结果如表 2所示。
| 输入参数 | M10 | M20 | M30 | |||||
| 塔端XA/m | 2.250 | 2.000 | 1.700 | |||||
| 塔端YA/m | 215.934 | 245.280 | 273.769 | |||||
| 塔端ZA/m | 9.802 | 6.863 | 3.977 | |||||
| 梁端XB/m | 143.772 | 293.027 | 442.248 | |||||
| 梁端YA/m | 61.082 | 62.281 | 62.823 | |||||
| 梁端ZA/m | 20.789 | 20.792 | 20.784 | |||||
| 自重集度/(t·m-1) | 0.060 | 0.085 | 0.108 | |||||
| 弹性模量/(t·m-2) | 19 500 000 | 19 500 000 | 19 500 000 | |||||
| 截面面积/m2 | 7.197e-03 | 1.020e-03 | 1.297e-02 | |||||
| 设计索力 | 3 767 000 | 5 379 000 | 6 241 000 | |||||
| 输出结果 | M10 | M20 | M30 | |||||
| 本研究计算结果 | Ernst 公式 |
本研究计算结果 | Ernst 公式 |
本研究计算结果 | Ernst 公式 |
|||
| 梁端斜率 | 1.068 | 1.091 | 0.599 | 0.628 | 0.436 | 0.479 | ||
| 塔端斜率 | 1.114 | 1.091 | 0.658 | 0.628 | 0.522 | 0.479 | ||
| 索长/m | 210.071 | 210.071 | 344.089 | 344.089 | 488.837 | 488.837 | ||
| 伸长量/m | 0.698 | 0.564 | 1.152 | 0.931 | 1.493 | 1.206 | ||
| 无应力索 长/m |
209.374 | 209.508 | 342.937 | 343.158 | 487.344 | 487.631 | ||
实际施工M10,M20,M30,这3根索的无应力索长分别为209.379,342.940,487.351 m。这说明按Ernst公式计算的无应力索长偏长,而利用本研究计算方法的无应力索长等计算相对准确。
4 结论本研究的拉索线形公式推导抛开了Ernst公式的假定条件,等效弹性模量推导直接利用广义胡克定律中的体积柔量公式,以上参数和结果均为理论推导值,避免了近似计算带来的误差,在超大跨度斜拉索的计算上有着更好的适应性,并在实际应用过程中得到验证。
| [1] |
刘平, 许慧, 璆玮. 大跨度斜拉索自重下的垂度分析[J]. 公路交通科技, 2016, 33(3): 60-63. LIU Ping, XU Hui, QIU Wei. Analysis of Deadweight Induced Sag of Long-span Stay Cable[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2016, 33(3): 60-63. |
| [2] |
龚平, 苏潇阳, 蔡向阳, 等. 拉索对斜拉桥竖向频率的影响研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2018, 31(6): 957-965. GONG Ping, SU Xiao-yang, CAI Xiang-yang, et al. The Influence of Cables on Vertical Frequency of Cable-stayed Bridge[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2018, 31(6): 957-965. |
| [3] |
杨雄伟, 李明水, 李暾. 悬链线型斜拉索风雨激振模型及特性分析[J]. 中国公路学报, 2019, 32(10): 237-246. YANG Xiong-wei, LI Ming-shui, LI Tun. Wind-rain-induced Vibration Model and Characteristic Analysis of Catenary Type Stay Cable[J]. Journal of China Highway and Transport, 2019, 32(10): 237-246. |
| [4] |
程纬, 易伟建, 刘光栋. 斜拉桥柔性索线型分析及快速迭代计算方法[J]. 公路, 1998(6): 8-11. CHENG Wei, YI Wei-jian, LIU Guang-dong. Analysis on Flexible Cable Shape of Cable-stayed Bridge and Fast Iterative Calculation Method[J]. Highway, 1998(6): 8-11. |
| [5] |
张震陆, 陈本贤. 柔索分析的"悬链段"方法研究[J]. 工程力学, 1990, 7(4): 41-50. ZHANG Zhen-lu, CHEN Ben-xian. A Study on the Catenary-segment Method for the Analysis of Flexible Suspending Cables[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 1990, 7(4): 41-50. |
| [6] |
彭力军, 陈明宪, 颜东煌.斜拉桥柔性索索形方程分析及拉索套管修正角计算[C]//1994年桥梁学术讨论会论文集.铜陵: 中国公路学会桥梁和结构工程学会, 1994. PENG Li-jun, CHEN Ming-xian, YAN Dong-huang. Analysis of Flexible Cable-shape Equations of Cable-stayed Bridges and Calculation of Cable Casing Correction Angle[C]//Proceedings of 1994 Symposium of Bridges. Tongling: Bridges and Structural Engineering Society of China Highway and Transportation Society, 1994. |
| [7] |
李强兴. 斜拉索静力解[J]. 桥梁建设, 1996, 26(3): 21-24. LI Qiang-xing. Static Force Solution to Stayed Cables[J]. Bridge Construction, 1996, 26(3): 21-24. |
| [8] |
魏建东, 车惠民. 斜拉索静力解及其应用[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 1998, 33(5): 539-543. WEI Jian-dong, CHE Hui-min. Static Solutions to Stay Cables and Their Applications[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 1998, 33(5): 539-543. |
| [9] |
麦深林, 郑万山. 公路桥梁斜拉索线形参数实用计算方法[J]. 公路交通技术, 2015, 29(2): 86-88, 93. MAI Shen-lin, ZHENG Wan-shan. Practical Computing Method for Linear Parameters of Stayed-cables of Highway Bridges[J]. Technology of Highway and Transport, 2015, 29(2): 86-88, 93. |
| [10] |
单圣涤, 李飞龙, 陈洁余, 等. 悬索曲线理论及其应用[M]. 长沙: 湖南科技出版社, 1983: 70-110. SHAN Sheng-di, LI Fei-long, CHEN Jie-yu, et al. Cable Curve Theory and Its Application[M]. Changsha: Hunan Science and Technology Press, 1983: 70-110. |
| [11] |
王寿梅, 赵国兴. 用泰勒级数求解非线性代数和微分方程组[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 1996, 41(3): 86-91. WANG Shou-mei, ZHAO Guo-xing. Solution of Nonlinear Algebraic and Differential Equation Sets via Taylor Expansion[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1996, 41(3): 86-91. |
| [12] |
张栋洋, 李登峰, 王兵. 粘弹性材料动态体积模量测试方法研究进展[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2019, 34(1): 106-112. ZHANG Dong-yang, LI Deng-feng, WANG Bing. Review of Research on the Dynamic Bulk Modulus Measurement of Viscoelastic Materials[J]. Development and Application of Materials, 2019, 34(1): 106-112. |
| [13] |
王立彬, 王达, 吴勇. 损伤拉索的等效弹性模量及其参数分析[J]. 计算力学学报, 2015, 32(3): 339-345. WANG Li-bin, WANG Da, WU Yong. The Equivalent Elastic Modulus of Damaged Cables and Parameter Analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics, 2015, 32(3): 339-345. |
| [14] |
彭树勇. 拉索弹性模量时效改变对斜拉桥抗震性能的影响[J]. 西部交通科技, 2009, 4(4): 40-44. PENG Shu-yong. Effects of Time-varying with Elasticity Equivalent Modulus of Cable on Seismic Behavior of Cable-stayed Bridge[J]. Western China Communications Science & Technology, 2009, 4(4): 40-44. |
| [15] |
刘明虎.几种方法进行斜拉索静力计算比较[C]//中国土木工程学会桥梁及结构工程学会第十四届年会论文集.上海: 中国土木工程学会, 2000: 661-666. LIU Ming-hu. Comparison of Calculation of Static Forces of Stay Cable by Several Methods[C]//Proceedings of the 14th Annual Conference of Bridge and Structural Engineering Society of Chinese Society of Civil Engineering Society. Shanghai: Chinese Civil Engineering Society, 2000: 661-666. |
| [16] |
方志, 李学有. 斜拉索无应力长度求解及成品索长合理确定[J]. 桥梁建设, 2009, 39(4): 54-58. FANG Zhi, LI Xue-you. Calculation of Unstressed Length and Reasonable Determination of Finished Length of Stay Cable[J]. Bridge Construction, 2009, 39(4): 54-58. |
| [17] |
杨佑发, 白文轩, 魏建东. 采用Ernst公式计算斜拉桥拉索振动特性的精度分析[J]. 世界地震工程, 2008, 24(2): 50-53. YANG You-fa, BAI Wen-xuan, WEI Jian-dong. Precision Analysis of Dynamic Characteristics of Cable Using Ernst's Modified Formula in Cable-stayed Bridge[J]. World Earthquake Engineering, 2008, 24(2): 50-53. |
| [18] |
张志恒, 李明. 基于拉索等效弹模修正的大跨度斜拉桥动力特性及参数分析[J]. 山西交通科技, 2013, 41(2): 40-42. ZHANG Zhi-heng, LI Ming. The Analysis of Dynamic Characteristics and Parameters for Long-span Cable-stayed Bridge Based on Cable Equivalent Modulus Correction[J]. Shanxi Science & Technology of Communications, 2013, 41(2): 40-42. |
 2020, Vol. 37
2020, Vol. 37
