扩展功能
文章信息
- 涂慕溪, 严二虎, 陈礼彪, 曾俊铖, 肖光书
- TU Mu-xi, YAN Er-hu, CHEN Li-biao, ZENG Jun-cheng, XIAO Guang-shu
- 基于性能的级配碎石混合料设计指标
- Performance-based Design Indicators for Graded Macadam Mixture
- 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(9): 31-36
- Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Denelopment, 2019, 36(9): 31-36
- 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0268.2019.09.005
-
文章历史
- 收稿日期: 2019-07-12
2. 交通运输部公路科学研究院, 北京 100088;
3. 福建路桥建设有限公司, 福建 福州 350002
2. Research Institute of Highway, Ministry of Transport, Beijing 100088, China;
3. Fujian Road and Bridge Construction Co., Ltd., Fuzhou Fujian 350002, China
沥青路面结构对沥青路面早期损坏和耐久性影响非常大,各地需要结合具体的交通、气候和荷载条件选择合适的结构[1]。福建省高温潮湿,山区多,传统半刚性沥青路面适应性差,为此自2006年开始在高速公路上推广应用组合式基层沥青路面结构,该结构主要特点之一是在沥青面层和半刚性材料之间设置了15~18 cm级配碎石[2]。设置级配碎石主要是发挥其提高结构排水和改善半刚性材料反射裂缝的功能。
大量成功经验表明,严格材料技术要求、选择合理的级配是提高级配碎石强度和稳定性的关键[3]。目前,国内级配碎石配合比设计指标主要是CBR和固体体积率两项指标[4-5]。福建省在大量工程实践基础上制定了地方标准指南,指南中对级配碎石的粗、细集料提出了要求,同时规定了级配碎石混合料CBR和固体体积率指标。相关技术要求见表 1~表 3。
无论是CBR还是固体体积率,都只能间接地反应级配碎石现场性能,即这些参数均是性能相关的。为了提高级配碎石混合料性能,国内外在级配碎石成型方法等方面开展了大量研究[6-9], 同时一直努力开发基于性能的级配碎石设计指标[10-16]。福建省作为国内级配碎石应用最为典型的地区,也一直努力基于大量理论分析和试验研究,提出了在基于性能的级配碎石设计指标,指导全省高速公路建设。
1 分析用典型结构、参数及基本模型表 4是福建省典型结构,相关结构参数按照《公路沥青路面设计规范》(JTG D50—2017)取值。
| 层位 | 混合料类型 | 厚度/cm | 动稳定度/(次·mm-1) | 模量/MPa | 泊松比 |
| 1 | 改性AC-13 | 4 | 3 500 | 4 500 | 0.35 |
| 2 | AC-20 | 6 | 3 500 | 4 200 | 0.35 |
| 3 | ATB-25 | 16 | 2 500 | 3 500 | 0.35 |
| 4 | 级配碎石基层PGG-25 | 16 | — | 300 | 0.35 |
| 5 | 水稳底基层 | 30 | — | 5 000 | 0.25 |
| 6 | 路基土 | — | 34 | 0.45 |
沥青面层的永久变形量模型采用《公路沥青路面设计规范》(JTG D50—2017)中模型。为了计算级配碎石的永久变形量,引进了AASHTO 2002的级配碎石永久变形模型[18]:

|
(1) |
式中, δα为永久变形;N为作用次数;ε0,β,ρ,β1为材料参数;εr为回弹应变;εv为平均竖向回弹应变; h为材料厚度。
其中材料参数可以通过第2节中动态三轴压缩试验确定。
为了计算累积永久变形,假定100 kN标准荷载的累计标准轴次为2 000万次。
2 研究用级配碎石混合料为了研究级配碎石混合料的性能指标,从福建省在建的5条高速公路上取12种混合料,按照工程配合比设计确定的级配进行试验。
| 级配碎石编号 | 通过下列筛孔(mm)的质量百分率/% | 原材 | ||||||||||||
| 31.5 | 26.5 | 19 | 16 | 13.2 | 9.5 | 4.75 | 2.36 | 1.18 | 0.6 | 0.3 | 0.15 | 0.075 | ||
| 1 | 100 | 99.9 | 83.6 | 74.0 | 63.9 | 53.5 | 35.1 | 24.1 | 18.5 | 13.6 | 8.7 | 6.3 | 3.8 | 石灰岩 |
| 2 | 100 | 99.0 | 85.5 | 71.7 | 61.2 | 55.2 | 39.2 | 28.9 | 23.2 | 18.5 | 13.1 | 9.4 | 4.6 | 石灰岩 |
| 3 | 100 | 99.8 | 85.7 | 75.0 | 67.0 | 60.2 | 40.6 | 29.9 | 22.3 | 16.8 | 11.0 | 7.8 | 4.9 | 石灰岩 |
| 4 | 100 | 96.9 | 85.7 | 74.2 | 65.4 | 60.6 | 40.9 | 25.5 | 17.4 | 11.7 | 6.9 | 4.4 | 2.6 | 砂岩 |
| 5 | 100 | 98.6 | 79.8 | 70.5 | 63.4 | 56.0 | 41.9 | 26.3 | 18.0 | 12.1 | 7.5 | 5.4 | 3.7 | 砂岩 |
| 6 | 100 | 100.0 | 84.2 | 74.6 | 66.3 | 56.0 | 39.8 | 22.9 | 15.7 | 10.8 | 7.4 | 5.7 | 4.0 | 凝灰岩 |
| 7 | 100 | 99.9 | 89.4 | 81.4 | 74.4 | 64.3 | 42.8 | 27.1 | 20.0 | 14.5 | 10.0 | 7.7 | 5.0 | 石灰岩 |
| 8 | 100 | 97.4 | 84.2 | 73.9 | 66.6 | 58.0 | 40.5 | 31.7 | 22.5 | 14.2 | 8.9 | 6.9 | 4.7 | 石灰岩 |
| 9 | 100 | 96.8 | 80.6 | 69.7 | 62.1 | 53.2 | 34.9 | 27.0 | 19.2 | 12.2 | 7.7 | 6.0 | 4.1 | 石灰岩 |
| 10 | 100 | 96.1 | 80 | 68.9 | 59.8 | 47.5 | 34.8 | 24.3 | 18.4 | 13.0 | 9.1 | 6.2 | 4.3 | 砂岩 |
| 11 | 99.9 | 98.1 | 84.8 | 77.9 | 70.0 | 59.5 | 35.1 | 22.3 | 16.0 | 11.3 | 7.7 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 花岗岩 |
| 12 | 100 | 98.6 | 86.1 | 76.9 | 70.6 | 53.8 | 36.7 | 26.5 | 20.7 | 14.7 | 10.2 | 7.8 | 5.0 | 花岗岩 |
3 级配碎石混合料性能试验方法 3.1 动态三轴压缩试验
动态三轴压缩试验基本按照《公路沥青路面设计规范》(JTG D50—2017)附录D粒料类材料回弹模量试验方法[17]进行,其中调整之处如下:
(1) 按照最大干密度的98%压实度和最佳含水率成型试件;
(2) 应力条件,垂直偏应力460 kPa,围压196 kPa;
(3) 重复加载50 000次。
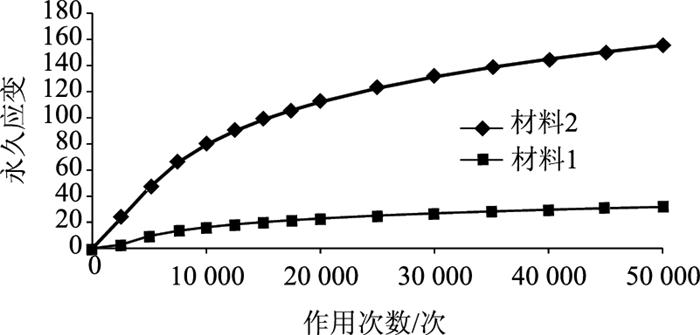
动态三轴压缩试验结束后,计算加载20 000次的回弹模量作为混合料模量结果;计算20 000~50 000次永久变形率之差作为抗永久变形试验结果。
通过数据分析可以得到式(2)的模型中材料参数,不过对于应力水平一定条件下室内模型可以进一步简化为:
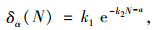
|
(2) |
式中,k1,k2,a为材料参数。
|
| 图 1 级配碎石动三轴永久变形-作用次数曲线 Fig. 1 Curves of permanent deformation vs. load cycles of graded macadam obtained by dynamic triaxial test |
| |
3.2 静三轴试验
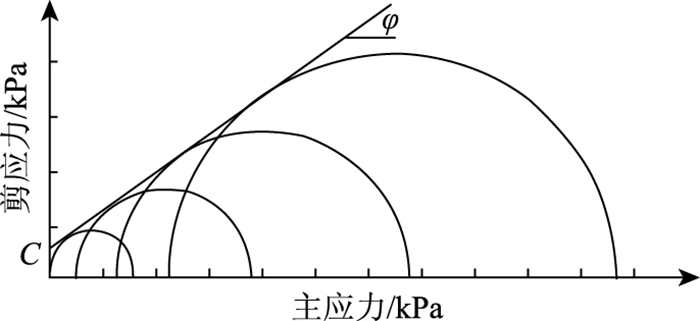
试件成型要求同动态三轴压缩试验,采用60,90 kPa和120 kPa围压条件进行剪切试验,通过图 2计算可以得到摩擦角和凝聚力,进而计算级配碎石的抗剪切强度。
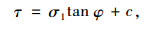
|
(3) |
|
| 图 2 莫尔包络线示意图 Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of Mohr envelope |
| |
式中,τ为抗剪强度;σ1为轴向主应力,取400 kPa;φ为内摩擦角;c为黏聚力。
4 级配碎石混合料试验结果表 6是动态三轴试验测定的各级配碎石试验结果。在福建省高速公路中级配碎石模量一般取值300 MPa。除6号级配碎石达不到外,其他级配碎石回弹模量,均能够达到此要求。目前福建省高速公路结构设计时级配碎石回弹模量均取值为300 MPa。因此可以将回弹模量300 MPa作为级配碎石混合料一个性能指标。按此指标,12个级配碎石合格率为92%。
| 级配碎石编号 | k1/(×10-8) | k2 | a | 变形率/(×10-8) | 回弹模量/MPa |
| 1 | 8.54 | 18.64 | 0.30 | 0.84 | 323 |
| 2 | 7.88 | 11.49 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 376 |
| 3 | 1.04 | 14.15 | 0.29 | 0.96 | 401 |
| 4 | 1.63 | 10.37 | 0.27 | 1.35 | 319 |
| 5 | 1.50 | 8.00 | 0.27 | 1.10 | 335 |
| 6 | 3.01 | 7.21 | 0.23 | 2.16 | 281 |
| 7 | 4.09 | 6.44 | 0.31 | 0.23 | 354 |
| 8 | 6.00 | 10.57 | 0.30 | 0.48 | 359 |
| 9 | 9.81 | 23.82 | 0.29 | 0.95 | 375 |
| 10 | 1.66 | 3.75 | 0.27 | 0.76 | 337 |
| 11 | 1.17 | 32.90 | 0.28 | 0.94 | 361 |
| 12 | 7.27 | 14.22 | 0.30 | 0.67 | 384 |
表 7是各级配碎石静态三轴试验结果。理论上,级配碎石属于无结合料材料,黏聚力c为零;而实际上,由于细集料中含有一部分黏性物质,因此级配碎石的c值并不为零,其中石灰岩混合料的黏聚力较大。根据剪切强度公式,剪切强度取决于内摩擦角、黏聚力和主应力水平,为便于分析,根据福建典型结构中级配碎石平均应力水平400 kPa计算剪切强度。表 7中各可见各级配碎石混合料剪切强度差异较大,这主要是内摩擦角影响较大,这说明由于级配碎石具有应力依赖性,提高内摩擦角是级配碎石抗剪强度重要保障。
| 级配碎石编号 | 内摩擦角/(°) | 黏聚力/kPa | 剪切强度(主应力为400 kPa)/kPa |
| 1 | 47.2 | 46.5 | 478 |
| 2 | 48.6 | 54.6 | 508 |
| 3 | 49.3 | 37.2 | 502 |
| 4 | 45.3 | 2.3 | 407 |
| 5 | 41.3 | 1.4 | 353 |
| 6 | 40.5 | 0.3 | 342 |
| 7 | 47.3 | 53.5 | 487 |
| 8 | 49.1 | 47.9 | 510 |
| 9 | 47.9 | 46.1 | 489 |
| 10 | 46.4 | 4.6 | 425 |
| 11 | 48.9 | 1.2 | 460 |
| 12 | 50.8 | 0.9 | 491 |
5 典型结构中级配碎石层性能计算
采用BISAR程序,进行BZ100标准荷载下级配碎石性能计算分析,计算级配碎石层最大剪应力为332.8 kPa,最大主应力为396 kPa,标准荷载2 000万次作用下级配碎石永久变形量占结构总变形率结果见表 8。
| 级配碎石编号 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 级配碎石变形量占总变形量比率/% | 10.8 | 8.7 | 11.2 | 22.7 | 16.8 | 35.1 | 5.6 | 7.6 | 12.4 | 10.1 | 11.3 | 9.5 |
由于级配碎石属于无结合料、粒料材料,模量较低,当沥青路面结构中承受较大的应力水平时,级配碎石PGG-25存在剪切破坏或产生较大的永久变形的风险,这就要求级配碎石具有较高的抗剪切强度和抗永久变形能力。
根据BISAR程序计算结果,级配碎石层最大剪应力为332.8 kPa,考虑一定的可靠度,取395 kPa(332.8 kPa的1.2倍)作为级配碎石混合料的剪切强度标准,根据表 7,目前83%混合料是满足该技术要求的。
根据《公路沥青路面设计规范》(JTG D50—2017),高速公路总车辙深度为15 mm,对于柔性高速公路要求沥青面层车辙深度不大于10 mm,这就意味着级配碎石车辙深度不大于5 mm,即级配碎石车辙深度占总车辙深度约33%。对于福建省柔性结构,一旦级配碎石产生较大的车辙深度,由于产生的层位较深,其危害较大。为此,福建省规定级配碎石车辙深度不大于2 mm,即级配碎石车辙深度占总车辙深度约13%。将表 8级配碎石变形量占总变形量比率和表 6级配碎石动态三轴的变形率数据表示在图 3中,可以看出,随着混合料变形率增加,沥青路面结构中级配碎石变形量占比也迅速增加,按照级配碎石变形量占比13%推算,混合料变形率应不大于10-8。
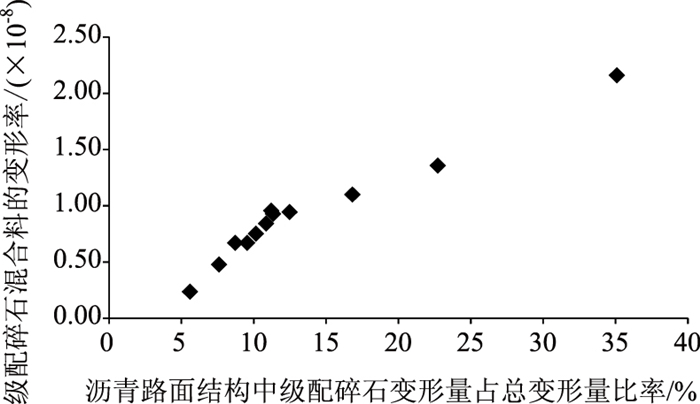
|
| 图 3 沥青路面结构中级配碎石变形量占总变形量比率-混合料变形率曲线 Fig. 3 Curve of ratio of deformation of graded macadam to total deformation of asphalt pavement structure vs. deformation rate of mixture |
| |
6 结论
(1) 目前福建省级配碎石混合料设计主要是控制原材质量,以及混合料的CBR和固体体积率,这些指标与其路面性能间接相关,有必要制定基于性能的级配碎石混合料设计指标。
(2) 可以采用动态三轴回弹模量和变形率作为级配碎石抗永久变形能力的性能指标,其中回弹模量建议不小于300 MPa,变形率不大于10-8;
(3) 可以采用静态三轴剪切强度作为级配碎石抗剪切破坏的性能指标,其中400 kPa应力条件下剪切强度建议不小于395 kPa。
(4) 以上提出的回弹模量,变形率和剪切强度指标还是初步的指标,尚需工程进一步验证。
| [1] |
沈金安, 李福普, 陈景. 高速公路沥青路面早期损坏分析与防治对策[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2004. SHEN Jin-an, LI Fu-pu, CHEN Jing. Analysis and Preventive Techniques of Premature Damage of Asphalt Pavement in Expressway[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2004. |
| [2] |
曾俊铖. 高温条件下沥青路面结构剪应变分析[J]. 公路交通科技, 2018, 35(6): 30-36. ZENG Jun-cheng. Analysis on Shear Strain in Asphalt Pavement Structural at High Temperature[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2018, 35(6): 30-36. |
| [3] |
严二虎, 沈金安, 李福普. 沥青路面级配碎石基层的设计与施工工艺[J]. 公路交通科技, 2004, 21(3): 9-13. YAN Er-hu, SHEN Jin-an, LI Fu-pu. Material Composition Design and Construction Process of Unbound Graded Aggregate Base of Asphalt Pavement[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2004, 21(3): 9-13. |
| [4] |
李福普, 严二虎. 沥青稳定碎石与级配碎石结构设计与施工技术应用指南[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2008. LI Fu-pu, YAN Er-hu. Guidelines for Design and Construction of Asphalt Stabilized Crushed Stone and Graded Crushed Stone Structures[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2008. |
| [5] |
福建省高速公路建设总指挥部. 福建省高速公路施工标准化管理指南(路基路面)[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2010. Fujian Provincial Expressway Construction Headquarters. Guidelines for Standardized Management of Expressway Construction in Fujian Province (Roadbed and Pavement)[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2010. |
| [6] |
张永升, 黄晓明, 孟书涛, 等. 不同成型方法对级配碎石的影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2015, 32(9): 32-35. ZHANG Yong-sheng, HUANG Xiao-ming, MENG Shu-tao, et al. Influence of Different Forming Methods on Graded Gravel[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2015, 32(9): 32-35. |
| [7] |
王龙, 解晓光, 栾海. 成型方法对级配碎石混合料抗剪性能的影响[J]. 公路交通科技, 2008, 25(5): 40-50. WANG Long, XIE Xiao-guang, LUAN Hai. Influence of Compacting Methods on Grade Macadam Shear Characteristics[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2008, 25(5): 40-50. |
| [8] |
蒋应军, 任皎龙, 徐寅善, 等. 级配碎石力学性能的颗粒流数值模拟方法[J]. 同济大学学报:自然科学版, 2011, 39(5): 699-706. JIANG Ying-jun, REN Jiao-long, XU Yin-shan, et al. Simulation Method of Mechanical Properties of Graded Broken Stone Based on Particle Flow Code[J]. Journal of Tongji University:Natural Science Edition, 2011, 39(5): 699-706. |
| [9] |
高世君, 韩微微, 韩森. 不同成型方法对级配碎石物理性能影响研究[J]. 路基工程, 2009(4): 42-44. GAO Shi-jun, HAN Wei-wei, HAN Sen. Research on Influence of Different Forming Methods on Physical Properties of Gradation Macadam[J]. Subgrade Engineering, 2009(4): 42-44. |
| [10] |
李頔.基于振动法的级配碎石设计标准与设计方法研究[D].西安: 长安大学, 2010. LI Di. Research on Graded Broken Stone Design Standard and Design Method Based on Vibrating Compaction[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2010. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-2010221580.htm |
| [11] |
EVANS G, VUONG B T. Development of Performance-based Specifications for Unbound Granular Materials-Part A:Issues and Recommendations[M]. Sydney: Austroads, 2003.
|
| [12] |
HORNYCH P. COST 337: Unbound Granular Materials for Road Pavements[R]. Nantes: Central Laboratory of Bridges and Pavements, 1998.
|
| [13] |
王龙, 孟书涛, 徐全亮. 级配碎石基层的设计参数研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2006, 23(8): 22-27. WANG Long, MENG Shu-tao, XU Quan-liang. Study on the Design Parameter of Graded Macadam Base[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development, 2006, 23(8): 22-27. |
| [14] |
刘星.级配碎石的级配与模量研究[D].西安: 长安大学, 2007. LIU Xing. Research on Gradation and Modulus of Graded Gravel[D.Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2007. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-2009257110.htm |
| [15] |
刘士全.级配碎石配合比设计及施工质量控制[D].西安: 长安大学, 2010. LIU Shi-quan. Graded Gravel Mix Design and Construction Quality Control[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2010. http://xueshu.baidu.com/s?wd=paperuri%3A%285bfa3142a2061ab4694b182a3a2c8912%29&filter=sc_long_sign&tn=SE_xueshusource_2kduw22v&sc_vurl=http%3A%2F%2Fcdmd.cnki.com.cn%2FArticle%2FCDMD-11941-2010220615.htm&ie=utf-8&sc_us=2716703119738733112&sc_as_para=sc_lib%3A |
| [16] |
鲁华征.级配碎石设计方法研究[D].西安: 长安大学, 2006. LU Hua-zheng. LU Hua-zheng. Research on Design Method of Graded Broken Stone[D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2006. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11941-2006163340.htm |
| [17] |
JTG D50-2017, 公路沥青路面设计规范[S] JTG D50-2017, Specifications for Design of Highway Asphalt Pavement[S]. |
| [18] |
AASHTO. Guide for the Mechanistic-empirical Design of New and Rehabilitated Pavement Structures[M]. Wanshington, D.C.: American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials, 2002.
|
 2019, Vol. 36
2019, Vol. 36
