2 中国科学院地球科学研究院, 北京 100029)
黄河改道进入淮北平原(以下称“黄河入淮”)是影响淮北平原地区最重要的地质过程之一,深刻改变了淮北平原地区的自然环境状况,这一系列环境变化对当地社会生产和国民经济带来巨大影响[1~5],甚至影响了中国历史发展的进程,是政府部门和科学家们共同关注的重大问题。
历史上,黄河以“善淤、善决、善徙”而闻名[6~12]。其河道的决溢泛滥和改道迁徙,集中于其下游平原地区。4000年以来,黄河发生过1000多次的泛滥、改道等事件(图 1)[13~14]。迄今所见由于人为原因导致黄河南泛、侵占淮河水系的最早记载,始于公元前361年,“楚师决河水,水出长垣之外”(《竹书纪年》)[8, 14~15]。主流观点一般认为,大规模的黄河入淮发生在南宋、金朝时期,南宋建炎二年(1128年),东京(今河南开封)留守杜充企图阻止金兵南下,以水代兵,“是年冬,杜充决黄河,以阻金兵”《宋史·高宗本纪》,此为黄河历史上长期南泛入淮的开始[16~20]。金末,黄河在淮北、苏北地区长期泛滥,经由泗水、汴水、濉水、涡河、颍河等5条泛道南下夺淮,形成黄河全流入淮之势。直到明朝万历二十五年(1546年),黄河入淮才由上述5股泛淮改变为由泗水一股泛淮。黄河不再北流入渤海,而是全部南流经淮河水道汇入黄海。直到清朝咸丰五年(1855年),黄河在河南兰阳(今兰考)铜瓦厢决口,水道北上,重新回到由渤海湾入海的局面,黄河大规模夺淮的历史宣告结束[21~23]。最后一次黄河入淮是1938年的花园口决口,主要是人为因素造成[24~26]。
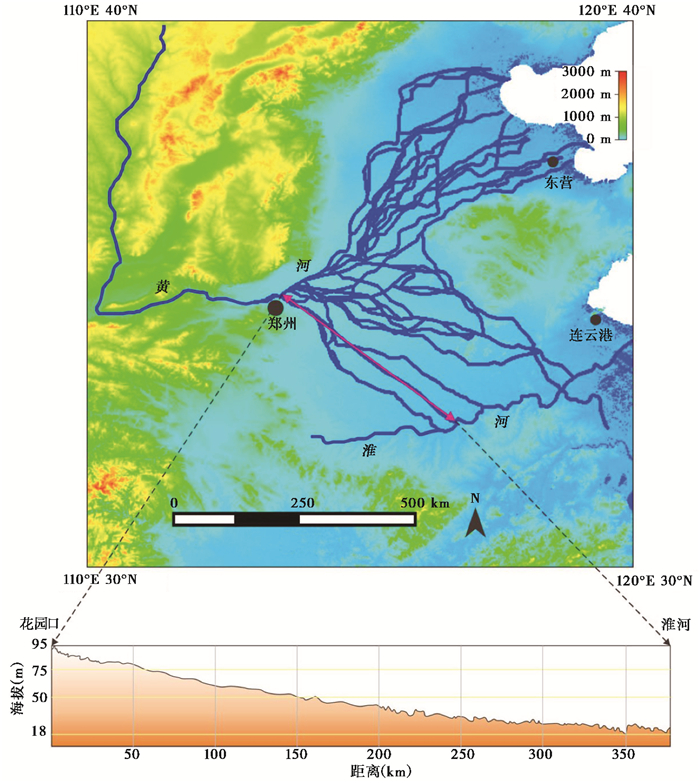
|
图 1 历史上的黄河改道路径(根据Zhang等[15]修改) Fig. 1 Migrate channels of the lower reach of the Yellow River in history, modified from reference[15] |
黄河入淮对中国东部水系(包括黄河、淮河、长江及大运河)的塑造具有十分深刻的影响,尤其是对淮北平原的水系格局产生了重要影响。首先,黄河入淮促成了淮河“入江水道”的形成。淮河与长江本不交汇,“入江水道”本来也不存在。明万历年间,由于黄河涨水,明朝政府实施分黄导淮策略,开通了淮河至长江的通道,出现“入江水道”,江淮两水的相互影响由此开始[18, 27~28]。其次,黄河入淮将统一的淮河水系分成两个独立水系。1855年黄河改道北上以后,在淮北平原留下一条废河道,废河道因其高出周围地面4~8 m,成为“悬河”,并将沂沭泗水系和淮河水系隔断,成为两大水系的分水岭。废黄河以北的苏北地区称为沂沭泗水系,以南地区称为淮河水系[29~31]。最后,除了使淮河水系分布发生变迁外,黄河入淮对于中国东部大湖泊的形成和消亡也起到了关键作用[6]。洪泽湖在唐代以前的地理著作中并没有记载,洪泽湖是黄河入淮导致洪泽湖水面不断扩大,加之高家堰的修建,使其形成今日之规模[32~35]。另外,也是由于黄河入淮,导致河水无法排泄,微山湖、昭阳湖、独山湖和南阳湖积水面积越来越大,最后连成一片形成南四湖[36~37](图 2)。骆马湖与南四湖的形成原因基本相似,都是黄河入淮导致[33, 38~39]。
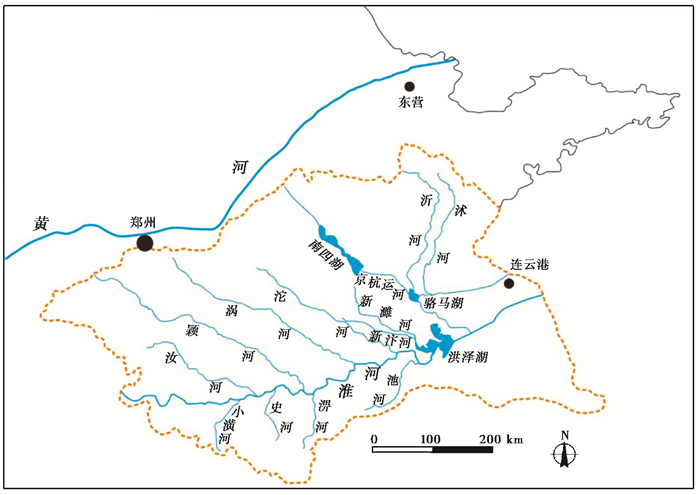
|
图 2 黄淮地区现代水系示意图 Fig. 2 Contemporary drainage of Huang Huai area |
淮河入江水道的初步形成、沂河和沭河与淮河水系的分离、废黄河以及三大湖泊(洪泽湖、南四湖、骆马湖)的形成等(图 2),都是黄河入淮对水环境的直接影响。这些变迁打乱了淮河原有的水系,破坏了淮北平原既有的水环境及生态格局。
1.2 黄河入淮改变淮北平原地表过程黄河入淮之后深刻地改变了淮北平原的地形、地貌以及地表过程。黄河入淮前淮北平原大大小小的湖泊广泛分布,黄河入淮后直接导致了淮北地区河道淤平,古湖泊群的消亡[18]。全新世时期黄河入淮携带大量泥沙入海,使得淮北平原沿海地区(主要是江苏沿海)全线向海推进,海岸线持续东扩[22, 40~45]。历史时期黄河夺淮对中国东部海岸(包括渤海、南黄海乃至浙江沿海)的塑造具有十分深刻的影响,是中国东部现代海陆环境分异的重要影响因素,它奠定了现在陆海界面的框架[42, 46~48]。黄河在淮北平原留下的废河道,成为沂沭泗水系和淮河水系的分水岭,改变了区域地形、地貌[18]。淮河流域原来土地肥沃,由于黄河泛滥造成这一流域的土壤沙漠化和盐碱化非常严重,沙漠化的地方主要分布在开封、兰考和中牟一带,盐碱化集中在苏北一带[5, 49]。
1.3 黄河入淮影响淮北盆地“源-汇”沉积过程在黄河入淮之前,淮北盆地是一个独立的盆地,接收的沉积物的物源主要是盆地内的物质[50]。黄河入淮后给淮北盆地带来大量盆地外的物质——黄土高原物质[15]。石长青和董玉良[51]通过对黄河冲积平原中、上部的地质-地理背景研究认为,中更新世晚期黄河贯通,形成了古黄河三角洲,顶点在郑州附近,其范围已经抵达安徽蒙城一带,进入了淮北平原。黄河冲积扇在晚更新世规模最大,南翼前缘已经到达安徽淮南、蚌埠等地[52~54]。全新世期间,黄河多次入淮,并由淮入海,黄河入淮给淮北平原带来大量泥沙物质[30, 55],进入平原后,地形较缓,水流减速,大量泥沙物质因此卸载,在入淮水道两侧堆积大量泥沙,在淮北平原形成大面积黄泛层。黄河入淮为淮北平原全新世沉积输入了大量物质。黄河入淮,使得黄土高原与淮北平原连在了一起,改变了淮北平原“源-汇”过程[15]。
黄河入淮除了给淮北盆地带来盆地外物质外,还加速淮北盆地成为中国东部海洋的直接物源区[15, 56]。淮北盆地最初并不与海相通,黄河入淮加速了淮北盆地的填满过程,使得淮北盆地快速填满,形成淮北平原,河流从内流转向外流入海,并向海洋输送物质[57]。黄河入淮加速了淮北平原的形成,加速了淮北平原“源-汇”变化过程。
1.4 黄河入淮改变海洋物源黄河形成之后在淮北平原起了巨大作用,它除了广泛塑造堆积地貌之外,还影响或控制了淮河及海河陆续在晚更新世晚期及全新世中晚期的发生和发展[52],进而影响了渤海、黄海的物源变化[19, 58~64]。前人通过对渤海、黄海海域地貌做得大量调查研究工作,清楚的显示在这两海域海底有多条古河道存在,表明黄河第四纪时期在河北平原和淮北平原多次交叉改道,入海口在渤海与黄海之间多次变化[65~66]。
杨守业等[67]通过对东营石化2井钻孔沉积物的地球化学研究认为,早更新世时黄河流经华北平原的现代黄河三角洲地区入渤海。深海氧同位素(Marine Isotope Stages, 简称MIS)MIS 6期中期与MIS 5期中晚期北黄海物源主要受到黄河、鸭绿江及大洋河共同作用,MIS 5期早期与MIS 4期晚期,其物源主要来源于黄河物质[68]。蓝先洪[69]认为MIS 6中期黄河主要经华北平原入渤海,MIS 6晚期黄河主要经苏北平原入黄海,MIS 5和MIS 4时期主要经华北平原入渤海。王青[46]通过对钻孔样品的沉积环境分析,认为在晚更新世的间冰期的距今45000~25000年前之间,黄河不是从渤海入海的,而是取道淮北平原从南黄河入海;并且认为在距今4600年前后的龙山文化早期,黄河下游河道发生了改道,走今淮北平原的废黄河故道一带入海。黄河在1494 A.D.于苏北入黄海对南黄海的沉积环境产生了较大影响[40, 70]。1855年黄河北上注入渤海[71],使得渤海中部沉积物来源、沉积动力环境发生明显的改变,物源由复杂变得单一,沉积环境从氧化环境转为还原环境[61]。
1.5 黄河入淮约束黄河贯通的上限时间最早的黄河入淮事件能够直接约束黄河贯通的上限时间。德日进和杨钟健[72]认为黄河形成时代不晚于上新世保德期;杨守业等[67]认为早更新世时黄河贯通;朱照宇[73]认为黄河形成于1.67~1.43 Ma;滕志宏[74]认为黄河形成于早更新世,约1.6~1.5 Ma;Kong等[75]认为黄河在1.3~1.5 Ma切穿三门峡,贯通入海;李吉均和方小敏[76]认为黄河在1.2 Ma切穿三门峡东流入海;岳乐平等[77]认为在1.2 Ma前后,黄河贯通;潘宝田和李吉均[78]认为1.1 Ma黄河打通三门峡;薛铎[79]认为三门峡以东的黄河形成于0.7~1.0 Ma左右;刘书丹等[80]认为黄河形成于约0.73 Ma左右;吴锡浩、王苏民等[81~82]认为黄河贯通,大致发生在0.15 Ma,此时外流黄河形成;蒋复初等[83]也认为黄河大约于0.15 Ma前后贯通三门峡东流入海;王书兵等[84]认为现今统一的黄河形成于0.1 Ma前后;袁宝印和王振海[85]认为晚更新世现今黄河面貌基本形成;夏东兴和吴桑云[7]则认为全新世早期黄河贯通,冲出三门峡,黄河形成。
通过以上可以发现对于黄河何时贯通三门峡东流入海,存在很大的争议,这是因为不同学者的研究角度和研究材料不同造成的[86]。而且大多从黄河中上游的河流阶地或古湖发育、消亡等角度研究,很少有从黄河下游响应的角度来研究。如果从黄河下游淮北平原沉积物中识别出最早的黄河入淮事件,对于黄河贯通的最晚时间能提供直接证据,黄河贯通的时间不会晚于最早的黄河入淮时间。黄河应该在最早的黄河入淮事件之前就已经贯通,因为如果黄河没有贯通是不会有黄河入淮事件的。因此深入研究黄河入淮,寻找最早的黄河入淮事件,可以确定黄河贯通的上限时间,黄河入淮的环境意义将被拓宽。
综上可以看出,前人对黄河入淮事件的环境效应研究主要集中在黄河入淮对地表环境的影响,而黄河入淮对于地质时期的沉积过程的影响、作用和意义等研究还不够充分。这对于全面理解黄河入淮的环境意义是一个不足。
2 黄河入淮事件的确定方法与原因机制 2.1 黄河入淮事件的确定方法黄河入淮是黄河极端水文(洪水)事件的表现之一。对于黄河流域极端洪水事件(黄河入淮事件)的识别多采用的是历史文献考证对比方法和沉积学等方法来确定。
(1) 历史文献考证方法
祁正卫等[16]和薛春汀等[50]概括性地梳理了黄河夺淮的历史演变过程,在西汉末年(公元前132年)黄河开始了较大规模的侵淮,1851年淮河干流改道经长江入海。荀德麟[17]通过历史文献记载,发现北宋以前淮河没有发生过大的特殊变化,很少有泛滥决溢现象。而北宋160多年中,黄河决溢入泗、入淮就多达10次,从1128年到1193年的65年间,黄河决溢入泗、入淮8次。彭安玉[18]对黄河夺淮后历史的总结发现:1194年,河决阳武,灌封丘而东,由泗入淮。1547年,“全河尽出徐、邳,夺泗入淮”。1677年,黄河大决于宿迁杨家庄,“故道涸竭”。1696年,安东(今涟水县)童家营溃堤,黄河洪水挟带泥沙直灌山阳、盐城一带。1821年,沭阳县后沭河自大坊集北决,直入青伊湖,其东出入涟河之道遂废。
从前人的研究可以发现,历史文献考证研究方法得到的黄河入淮记录不但材料详尽且定年准确,但所能触及的时间尺度有限,若要研究发生年代更为久远的黄河入淮事件,则还需要另外选取长时间尺度的沉积记录进行研究。
(2) 沉积学方法
有一些学者采用地质的岩相观察、寻找沉积相标志、对沉积层进行粒度分析等方法,确定洪水滞留层,从而确定出事件性洪水沉积(黄河入淮沉积),在黄河流域有很多应用[87~94]。前人对古洪水的研究,认为洪水沉积有水平波状层理,下部含有较多细沙,上部含有粘土质盖层,明显表达出沉积过程当中的分选特征。多个古洪水事件形成的洪水滞留沉积层之间有明显间断等[95~98]。古洪水沉积在沉积层理、颜色、粒度、分选性、矿物组合以及特殊含有物(陶片、埋藏古树、砾石等)等方面有可识别的标志,有助于确定事件性洪水沉积[99~104]。
通过沉积相、岩性观察等方法确定事件性洪水沉积虽然具有快捷、方便等优点,但由于其无法量化,可能存在一定的多解性或不确定性。粒度指标能够实现一定的量化判断,能够帮助识别古洪水沉积,但无法区分某次洪水沉积是黄河洪水形成的,还是其他河流洪水形成的。对黄河入淮事件的研究,必须要明确出是黄河洪水沉积,因此可以通过加强对洪水沉积物的物源进行分析,用地球化学物源示踪的方法限定洪水沉积物的物源,进而确定出淮北平原事件性洪水沉积是黄河入淮沉积,从而能更准确、深入理解黄河入淮。
2.2 黄河入淮事件的年代学(1) 更新世黄河入淮
根据资料显示更新世已经发生过黄河入淮事件[46]。更新世黄河入淮事件由于研究程度不够,资料较少,其发生时间大多是定性的,如中更新世、MIS 6晚期等[51, 69]。目前能够有确定测年结果的更新世黄河入淮事件发生在13.2 ka B.P.的末次冰消期,主要是通过14 C测年方法确定[15](表 1)。
| 表 1 第四纪黄河入淮事件年代学统计表(据文献[14~15,46,51,105~106]编制) Table 1 Statistics invasion of the Yellow River into the Huaibei Plain events during Quaternary(edited from references[14~15, 46, 51, 105~106]) |
(2) 全新世黄河入淮
秦汉之前,有一些零星的记录,可能与黄河入淮有关,但尚未证实[46]。秦汉之后由于历史文献记录,黄河入淮的准确时间能够记录下来。历史记录最早的黄河入淮可能发生在公元前361年,这次主要是人为原因[14]。历史文献记录最早的自然原因导致的黄河入淮可能是《史记·河渠书·封禅记》中记载的公元前168年,“河决酸枣,东溃金堤……河溢通泗”,黄河河溢通泗、入淮[105]。
根据历史文献记录[14~15, 46, 51, 105~106],秦汉时期黄河入淮事件发生在公元前361、公元前168、公元前132年、公元1~5年、公元58年;隋唐时期,这一时期黄河泛淮记载缺略,大规模夺淮事件鲜有发生,公元607年发生过一次,规模不大。北宋时期,黄河有5次较大的泛淮活动,分别发生于公元983年、996年、1020年、1077年、1082年;南宋在公元1128~1234年间共发生过6次大的黄河泛淮事件,其中1128年的人工改道,拉开了黄河长期泛淮的序幕。元朝在公元1278~1358年间的历史记录有19次黄河入淮事件。明朝和清朝历史记录最全面也最详尽,分别记录有70次和62次黄河入淮事件,公元1855年黄河在铜瓦厢决口,黄河从此由渤海入海(图 3)。民国时期的1926年、1933年、1935年、1938年发生过4次黄河入淮,其中1938年花园口决口是最后一次[14, 106](表 1)。
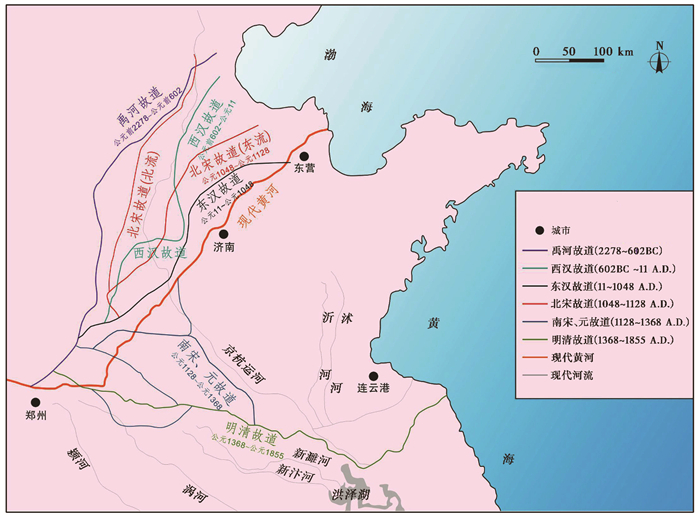
|
图 3 历史时期黄河主河道(根据陈蕴真[14]修改) Fig. 3 The main river course of the Yellow River in history(modified from reference[14]) |
黄河入淮的年代学目前主要依据的是历史文献记录,其年代精确,但时间跨度较窄,越到早期,记录越少,另外无法与实际的沉积记录相对应。14 C、光释光测年等方法在黄河入淮沉积记录中应用较少。因此,需要将历史文献记录与沉积记录结合,另外需要多种测年方法来确定黄河入淮沉积记录的时间。
2.3 黄河入淮事件的自然原因及机制黄河入淮的地貌实质是黄河径流越过黄淮二水系的分水岭进入淮河流域,因此黄河夺淮的自然原因主要有两种可能:一是原黄河中游河道淤高及侧蚀导致河床接近分水岭高度;二是淮河(北部支流)上游发生溯源侵蚀导致淮河袭夺黄河。但是从实际情况来看,历史时期淮河支流溯源侵蚀导致黄河入淮的现象很少存在,其原因是淮北平原坡降非常小,只有1/8000[15, 57],溯源侵蚀比较弱。至于更早的地质时期是否存在淮河支流溯源侵蚀贯通了黄河与淮河,目前没有研究,尚不得而知。而目前已知的黄河入淮的主要自然原因是黄河的古洪水事件,古洪水事件是最强烈的侧蚀作用表现之一。突然的古洪水事件可能直接导致黄河侧蚀加强,黄河决堤,冲破分水岭,进入淮北平原地区。由于古洪水事件对理解河流极端水文事件对全球气候变化的响应能提供重要信息[100, 104, 107],因此,了解黄河入淮事件发生的自然背景对于理解黄河下游河道变迁与东亚季风的响应关系能提供重要信息。
黄河入淮是黄河下游极端洪水事件的直接反映。对于黄河流域极端洪水事件发生的自然原因前人有不同看法。一种观点认为该极端洪水事件多发生在气候暖湿期。例如:李胜利和赵景波[108]认为气候湿润期,降水量多,径流量大,对应洪水事件会较多,反之,如果气候干冷,对应洪水事件就较少;Zhang等[109]也发现在全新世大暖期黄河中游发生过3次大洪水事件(7600~7400 a B.P.、5800~5000 a B.P.和4200~4000 a B.P.); Yang等[102]对黄河小浪底地区古洪水的研究发现,全新世黄河最大的一次洪水事件发生在7362 a B.P.,那时气候较为湿润,降雨量较多,处于全新世大暖期。另一观点认为黄河流域古洪水事件多发生在气候转型期[110]。例如:黄春长等[89, 103, 111~113]通过对古洪水滞留沉积物的研究发现,全新世大暖期的开始阶段(气候由冷干向暖湿转变)与全新世大暖期的结束阶段(气候由暖湿向冷干转变),黄河、渭河流域都有明显的特大洪水发生,也就是在气候转型阶段,明显多发特大洪水事件。这是由于气候的异常变化导致降水量年内和年际分配不均匀,造成极端性暴雨洪水及大洪灾频繁发生的主要原因,导致大洪水在气候转型期、突变期出现频率高,气候平稳期出现频率较低[110]。Zhang等[15]通过对淮北平原沉积物的研究发现,在末次冰消期(13.2 ka B.P.)发生过黄河入淮事件,该次黄河入淮事件发生在气候由干冷的末次冰期向暖湿的全新世过渡的气候转型阶段(末次冰消期)。
由此可见,对于黄河入淮这一极端水文事件发生的主要气候背景存在不同认识。这需要对黄河入淮事件的频次序列进行系统研究,尤其是需要建立全新世以前黄河入淮事件序列,掌握长时间尺度的黄河入淮事件序列才能有助于明晰黄河入淮这一极端水文事件发生的特点和原因机制。进而对于理解黄河下游河道变迁与东亚季风的响应关系能提供重要信息。
3 存在问题与展望综上所述,前人将黄河入淮对淮北平原地区的水系格局、湖泊形成与消亡、海岸线变迁、源-汇过程以及中国东部海洋物源等自然环境的影响进行了深入研究,使用了多种方法确定黄河入淮事件,并探讨了黄河入淮事件的自然原因及机制,目前还有以下几方面值得进一步研究:
(1) 环境影响方面
黄河入淮事件对自然环境的影响和意义的研究,集中在对地表过程的影响和意义,对地质时期的沉积过程的影响和意义研究较少,黄河入淮的地质意义有待进一步拓宽。寻找最早的黄河入淮事件对于理解淮河盆地的源-汇过程的转变、以及对黄河贯通上限时间的约束均具有重要意义,能进一步拓宽黄河入淮的环境意义。
(2) 时间尺度方面
黄河入淮事件研究的时间尺度集中于历史时期,不超过全新世,时间尺度短,黄河入淮事件的完整序列,有待完善。今后应加强长时间尺度(第四纪以来)研究,系统研究第四纪时期黄河入淮事件,建立长尺度黄河入淮事件频次序列。
(3) 方法综合方面
用粒度分析、岩相观察等方法识别黄泛沉积(确定黄河入淮事件)的研究方法具有一定的多解性或不确定性,今后应引入多学科不同的研究方法(如:地球化学物源示踪方法等),解决单一指标的多解性、不确定性问题,并结合14 C、光释光等地质测年方法综合来确定黄河入淮事件,这样得出的结论可靠性更高。
(4) 气候响应方面
黄河入淮事件发生的气候背景、原因机制存在不同认识,使得黄河入淮事件对气候的响应规律难以揭示。因此对于地质时期黄河入淮发生的气候背景以及原因机制需要进一步深入研究探讨。这不仅对于理解极端古洪水事件对古气候变化的响应规律具有重要的理论意义,对于深入理解淮北平原的形成、演化等具有重要的科学意义,而且对于黄淮流域现代水利工程建设、洪旱灾防御等能够提供亟需的水文数据,具有重要的现实意义。
致谢: 感谢同行评审专家和编辑部杨美芳老师提出的宝贵修改意见!
| [1] |
房晓军. 黄河夺淮及其对淮阴的影响. 淮阴师专学报, 1996, 18(3): 49-52. Fang Xiaojun. The Yellow River invasion into Huaihe basin and its impact on Huaiyin area. Journal of Huaiyin Teachers College, 1996, 18(3): 49-52. |
| [2] |
凌申. 黄河夺淮与江苏两淮盐业的兴衰. 中国社会经济史研究, 2011(1): 11-17. Ling Shen. The Yellow River invasion into Huaihe basin and the rise and fall of salt industry in two Huai in Jiangsu. The Journal of Chinese Social and Economic History, 2011(1): 11-17. |
| [3] |
孙寿成. 黄河夺淮与江苏沿海潮灾. 灾害学, 1991, 6(4): 88-90. Sun Shoucheng. Huai River seized by the Yellow River and tide disaster of Jiangsu coast. Journal of Catastrophology, 1991, 6(4): 88-90. |
| [4] |
孟凡超. 黄河河道变迁与徐州社会兴衰. 淮南师范学院学报, 2012, 14(5): 45-48. Meng Fanchao. The Yellow River changes with the social prosperity and decline of Xuzhou. Journal of Huainan Normal University, 2012, 14(5): 45-48. |
| [5] |
葛兆帅, 吉婷婷, 赵清. 黄河南徙在徐州地区的环境效应研究. 江汉论坛, 2011(1): 102-107. Ge Zhaoshuai, Ji Tingting, Zhao Qing. Study on environmental effects of the Yellow River migration in Xuzhou region. Jianghan Luntan, 2011(1): 102-107. |
| [6] |
范成泰. 黄河夺淮改变湖泊分布[N]. 中国水利报, 2009-05-07. Fan Chengtai. The Yellow River seizes the Huaihe River to change the lake distribution[N]. China Water Resources News, 2009-05-07. |
| [7] |
夏东兴, 吴桑云. 末次冰期以来黄河变迁. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1993, 13(2): 83-88. Xia Dongxing, Wu Sangyun. Changes of the Yellow River since the Last Glacial age. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1993, 13(2): 83-88. |
| [8] |
Chen Y Z, Syvitski J P M, Gao S et al. Socio-economic impacts on flooding:A 4000-year history of the Yellow River, China. Ambio, 2012, 41(7): 682-698. DOI:10.1007/s13280-012-0290-5 |
| [9] |
Cui B L, Chang X L, Shi W Y. Abrupt changes of runoff and sediment load in the lower reaches of the Yellow River, China. Water Resources, 2014, 41(3): 252-260. DOI:10.1134/S009780781403004X |
| [10] |
Fan L J, Huang C C, Pang J L et al. Sedimentary records of palaeofloods in the Wubu reach along the Jin-Shaan gorges of the middle Yellow River, China. Quaternary International, 2015(380-381): 368-376. |
| [11] |
He H M, Tian Y Q, Mu X M et al. Confluent flow impacts of flood extremes in the middle Yellow River. Quaternary International, 2015(380-381): 382-390. |
| [12] |
Liu Y, Huang H, Liu Y et al. Linking land subsidence over the Yellow River delta, China, to hydrocarbon exploitation using multi-temporal InSAR. Natural Hazards, 2016, 84(1): 271-291. DOI:10.1007/s11069-016-2427-5 |
| [13] |
黄河水利委员会黄河志总编辑室. 黄河大事记. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 2001: 1-755. Editorial Office of the Yellow River Annals of the Yellow River Water Conservancy Commission. Memorabilia of the Yellow River. Zhengzhou: The Yellow River Water Conservancy Press, 2001: 1-755. |
| [14] |
陈蕴真. 黄河泛滥史: 从历史文献分析到计算机模拟[D]. 南京: 南京大学博士学位论文, 2013: 1-171. Chen Yunzhen. Investigating the Flood History of the Yellow River:From Analyzing Historical Records to Computer Modeling[D]. Nanjing:The Doctoral Dissertation of Nanjing University, 2013:1-171. |
| [15] |
Zhang L, Qin X G, Liu J Q et al. Geochemistry of sediments from the Huaibei Plain(East China):Implications for provenance, weathering, and invasion of the Yellow River into the Huaihe River. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016(121): 72-83. |
| [16] |
祁正卫, 张嘉涛, 刘志中. 黄河夺淮的历史演变. 江苏水利, 1998(7): 47-48. Qi Zhengwei, Zhang Jiatao, Liu Zhizhong. The historical evolution of the Yellow River invasion into the Huai River. Jiangsu Water Resources, 1998(7): 47-48. |
| [17] |
荀德麟. 黄河夺淮述略. 江苏水利, 1999(6): 47-48. Xun Delin. A brief review of the Yellow River invasion into the Huai River. Jiangsu Water Resources, 1999(6): 47-48. |
| [18] |
彭安玉. 黄河夺淮后江苏淮北地区自然环境的变迁. 南京林业大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2013(4): 56-63. Peng Anyu. Natural environment changes in Huaibei region in Jiangsu Province after discharge of the Yellow River into the sea through the Huai River estuary. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 2013(4): 56-63. |
| [19] |
Liu S H, Li P Y, Feng A P et al. Seismic and core investigation on the modern Yellow River delta reveals the development of the uppermost fluvial deposits and the subsequent transgression system since the postglacial period. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016(128): 158-180. |
| [20] |
Lu J, Qiao F L, Wang X H et al. A numerical study of transport dynamics and seasonal variability of the Yellow River sediment in the Bohai and Yellow seas. Estuarine Coastal & Shelf Science, 2011, 95(1): 39-51. |
| [21] |
李春霞. 花园口决堤事件与南京国民政府黄泛区方略再认识. 郑州大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2016, 49(1): 126-130. Li Chunxia. Reknow the excavation events of Huayuankou and the Yellow River flooded area strategy of Nanjing National Government. Journal of Zhengzhou University(Philosophy and Social Sciences Edition), 2016, 49(1): 126-130. |
| [22] |
Zhang X D, Zhang Y X, Ji Y et al. Shoreline change of the northern Yellow River(Huanghe)delta after the latest deltaic course shift in 1976 and its influence factors. Journal of Coastal Research, 2016, S1(74): 48-58. |
| [23] |
Su M, Yao P, Wang Z B et al. Exploratory morphodynamic hindcast of the evolution of the abandoned Yellow River delta, 1578-1855 CE. Marine Geology, 2017(383): 99-119. |
| [24] |
渠长根, 陈树涵. 近代黄泛之源:1938年花园口决堤原因探索. 华北水利水电大学学报(社会科学版), 2003, 19(1): 58-62. Qu Changgen, Chen Shuhan. The source of the Yellow River flood in modern times:The reasons for the burst of the Huayuankou in 1938. Journal of North China Institute of Water Conservancy and Hydroelectric Power(Social Sciences Edition), 2003, 19(1): 58-62. |
| [25] |
Edgerton-Tarpley K. Between war and water:Farmer, city, and state in China's Yellow River flood of 1938-1947. Agricultural History, 2016, 90(1): 94-116. DOI:10.3098/ah.2016.090.1.94 |
| [26] |
Li H C, Wang B B, Yan J, et al. Environmental impact of Huayuankou dike breach in 1938[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 4th International Conference on Sustainable Energy and Environmental Engineering, 2016:1105-1108
|
| [27] |
周君亮. 淮河下游水安全及其对策. 水利水电科技进展, 2011, 31(4): 13-19. Zhou Junliang. Water safety and countermeasures for lower reaches of the Huaihe River. Advances in Science and Technology of Water Resource, 2011, 31(4): 13-19. DOI:10.3880/j.issn.1006-7647.2011.04.003 |
| [28] |
赵筱侠. 黄河夺淮对苏北水环境的影响. 南京林业大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2013(3): 92-101. Zhao Xiaoxia. Influences of discharge of the Yellow River into the sea through the Huai River estuary on water environment in northern Jiangsu region. Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(Humanities and Social Sciences Edition), 2013(3): 92-101. |
| [29] |
邹逸麟. 黄河下游河道变迁及其影响概述. 复旦学报(社会科学版), 1980(S1): 12-24. Zou Yilin. An overview of river course changes in the lower reaches of the Yellow River and their impacts. Fudan Journal(Social Sciences Edition), 1980(S1): 12-24. |
| [30] |
Ren M E. Sediment discharge of the Yellow River, China:Past, present and future-A synthesis. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2015, 34(2): 1-8. DOI:10.1007/s13131-015-0619-6 |
| [31] |
Dou M, Zuo Q T, Ma J X et al. Simulation and control of the linked systems of water quantity-water quality-socio-economics in the Huaihe River basin. Hydrological Sciences Journal-Journal Des Sciences Hydrologiques, 2016, 61(4): 763-774. DOI:10.1080/02626667.2014.959953 |
| [32] |
杨达源, 王云飞. 近2000年淮河流域地理环境的变化与洪灾——淮河中游的洪灾与洪泽湖的变化. 湖泊科学, 1995, 7(1): 1-7. Yang Dayuan, Wang Yunfei. On changes of geographic environment and flood damage along the Huaihe River basin during the last 2000 years. Journal of Lake Sciences, 1995, 7(1): 1-7. DOI:10.18307/1995.0101 |
| [33] |
Yin Y X, Chen Y, Yu S T et al. Maximum water level of Hongze Lake and its relationship with natural changes and human activities from 1736 to 2005. Quaternary International, 2013(304): 85-94. |
| [34] |
张瑞虎. 洪泽湖的成因及其水灾治理. 农业灾害研究, 2012, 2(3): 72-75. Zhang Ruihu. Research on the causes of formation and flood control in the Hongze Lake. Journal of Agricultural Catastrophology, 2012, 2(3): 72-75. |
| [35] |
王庆, 陈吉余. 洪泽湖和淮河入洪泽湖河口的形成与演化. 湖泊科学, 1999, 11(3): 237-244. Wang Qing, Chen Jiyu. Formation and evolution of Hongze Lake and the Huaihe River mouth along the Lake. Journal of Lake Sciences, 1999, 11(3): 237-244. DOI:10.18307/1999.0308 |
| [36] |
林仲秋. 南四湖的形成时代和原因探讨. 徐州师范学院学报(自然科学版), 1988(2): 80-84. Lin Zhongqiu. The discussion on forming age and root cause of the Nansihu Lake. Journal of Xuzhou Teachers College(Nature Sciences Edition), 1988(2): 80-84. |
| [37] |
Zhang Z L, Shen J, Liu E F et al. Formation and water environmental evolution of the Nansihu Lake. Journal of Geographical Science, 2003, 13(2): 241-249. DOI:10.1007/BF02837464 |
| [38] |
张义丰. 淮河流域两大湖群的兴衰与黄河夺淮的关系. 河南大学学报(自然科学版), 1985(1): 45-50. Zhang Yifeng. The relationship between the rise and fall of the two lakes groups in the Huaihe basin and the Yellow River capture the Huai River. Journal of Henan University(Natural Science Edition), 1985(1): 45-50. |
| [39] |
吴必虎. 黄河夺淮后里下河平原河湖地貌的变迁. 扬州师院学报(自然科学版), 1988, 8(1-2): 132-138. Wu Bihu. Geomorphological changes of Lixiahe basin in north Jiangsu Province. Journal of Yangzhou Teachers College(Natural Science Edition), 1988, 8(1-2): 132-138. |
| [40] |
王庆, 李道季, 孟庆海等. 黄河夺淮期间淮河入海河口动力、地貌与演变机制. 海洋与湖沼, 1999, 30(6): 751-757. Wang Qing, Li Daoji, Meng Qinghai et al. Dynamic processes, geomorphology of the Huaihe River estuary and its evolution mechanism associated with capture by the Huanghe River. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1999, 30(6): 751-757. |
| [41] |
胡进. 废黄河三角洲海岸演变过程与悬浮泥沙研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学硕士学位论文, 2014: 1-84. Hu Jin. Coastal Evolution Process and Nearshore Suspended Sediment Research of the Abandoned Yellow River Delta[D]. Shanghai:The Master's Dissertation of East China Normal University, 2014:1-84. |
| [42] |
张晓祥, 王伟玮, 严长清等. 南宋以来江苏海岸带历史海岸线时空演变研究. 地理科学, 2014, 34(3): 344-351. Zhang Xiaoxiang, Wang Weiwei, Yan Changqing et al. Historical coastline spatio-temporal evolution analysis in Jiangsu coastal area during the past 1000 years. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2014, 34(3): 344-351. |
| [43] |
Peng J, Chen S L, Dong P. Temporal variation of sediment load in the Yellow River basin, China, and its impacts on the lower reaches and the river delta. Catena, 2010, 83(2-3): 135-147. DOI:10.1016/j.catena.2010.08.006 |
| [44] |
Chen X Y, Liu D H, Lu J. The sedimentary environment of current estuary and abandoned estuary at the modern Yellow River delta. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 356-360: 914-919. DOI:10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.356-360 |
| [45] |
Zhang L, Chen S L, Yi L. The sediment source and transport trends around the abandoned Yellow River delta, China. Marine Georesources & Geotechnology, 2016, 34(5): 440-449. |
| [46] |
王青. 试论史前黄河下游的改道与古文化的发展. 中原文物, 1993(4): 65-74. Wang Qing. Try to discuss the rechannel in lower reaches of the Yellow River in prehistoric and the development of ancient culture. Cultural Relics of Central China, 1993(4): 65-74. |
| [47] |
凌申. 全新世以来江苏中部地区海岸的淤进. 台湾海峡, 2006, 25(3): 445-451. Ling Shen. Deposition and forward movement of the coastline in the middle part of Jiangsu since Holocene. Journal of Oceanography in Taiwan Strait, 2006, 25(3): 445-451. |
| [48] |
刘艳霞, 黄海军, 董慧君等. 渤海西南岸全新世最大海侵界线及其地貌特征. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2): 340-353. Liu Yanxia, Huang Haijun, Dong Huijun et al. Geomorphic characteristics and location of the maximum Holocene transgression boundary in the southwestern coast of the Bohai Sea. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(2): 340-353. DOI:10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.09 |
| [49] |
崔宇. 明清淮河水灾对生态环境的影响研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学硕士学位论文, 2010: 1-44. Cui Yu. Study on Huai River Floods and Ecosystem during Ming and Qing Dynasties[D]. Yangling:The Master's Dissertation of Northwest A & F University, 2010:1-44. |
| [50] |
薛春汀, 刘健, 孔祥淮. 全新世淮河三角洲初步研究. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30(5): 892-901. Xue Chunting, Liu Jian, Kong Xianghuai. Preliminary study of Holocene Huaihe River delta on west coastal plain of Yellow Sea, China. Quaternary Sciences, 2010, 30(5): 892-901. |
| [51] |
石长青, 董玉良. 论黄河冲积平原中、上部的地质-地理背景和区域性土壤改良水文地质条件. 中国地质科学院水文地质工程地质研究所所刊, 1986(2): 151-176. Shi Changqing, Dong Yuliang. Geologic-geographical background and hydrogeological conditions for regional melioration in the middle and upper parts of Huanghe alluvial plain. Bulletin Institute of Hydrageology and Engineering Geology, CAGS, 1986(2): 151-176. |
| [52] |
邵时雄, 郭盛乔, 韩书华. 黄淮海平原地貌结构特征及其演化. 地理学报, 1989, 44(3): 314-322. Shao Shixiong, Guo Shengqiao, Han Shuhua. Geomorphic structures and evolution of Huang-Huaihai plain in China. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1989, 44(3): 314-322. |
| [53] |
孙国华, 彭国田. 淮北平原晚更新世以来岩相古地理及其水文地质意义的初步研究. 水文地质工程地质, 1987(1): 41-43. Sun Guohua, Peng Guotian. A preliminary study on the lithofacies palaeogeography of the Huaibei Plain since Late Pleistocene and its hydrogeological significance. Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, 1987(1): 41-43. |
| [54] |
王长荣, 顾也萍. 安徽淮北平原晚更新世以来地质环境与土壤发育. 安徽师大学报(自然科学版), 1995, 18(2): 59-65. Wang Changrong, Gu Yeping. Geologic environment after Late Pleistocene and soil development in Huaibei Plain of Anhui. Journal of Anhui Normal University(Natural Science), 1995, 18(2): 59-65. |
| [55] |
高文华, 高抒, 王丹丹等. 废黄河沉积记录中来自不同河流物质的信息——基于重矿物与地球化学元素分析. 地理科学, 2015, 35(12): 1631-1639. Gao Wenhua, Gao Shu, Wang Dandan et al. Sediment source information of different catchments in the sedimentary records of the abandoned Yellow River:Heavy mineral and geochemical analyses. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2015, 35(12): 1631-1639. |
| [56] |
Li X S, Zhao Y X, Feng Z B et al. Quaternary seismic facies of the South Yellow Sea shelf:Depositional processes influenced by sea-level change and tectonic controls. Geological Journal, 2016, 51: 77-95. |
| [57] |
金权. 安徽淮北平原第四系. 北京: 地质出版社, 1990: 1-170. Jin Quan. Quaternary of Huaibei Plain in Anhui Province. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1990: 1-170. |
| [58] |
Xia F, Zhang Y Z, Wang Q et al. Evolution of sedimentary environments of the middle Jiangsu coast, South Yellow Sea since late MIS 3. Journal of Geographical Sciences, 2013, 23(5): 883-914. DOI:10.1007/s11442-013-1051-5 |
| [59] |
Wang L S, Hu S Y, Yu G et al. Paleoenvironmental reconstruction of the radial sand ridge field in the South Yellow Sea(East China)since 45 ka using the sediment magnetic properties and granulometry. Journal of Applied Geophysics, 2015(122): 1-10. |
| [60] |
范勇勇, 毕乃双, 李云海等. 百年来黄河三角洲东北部毗邻海域沉积记录演化及其影响因素. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2016, 36(4): 29-39. Fan Yongyong, Bi Naishuang, Li Yunhai et al. High-resolution depositional records in the northeastern adjacent area of the Huanghe(Yellow River)delta for the past hundred years and their influence factors. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2016, 36(4): 29-39. |
| [61] |
廖永杰, 范德江, 刘明等. 1855年黄河改道事件在渤海的沉积记录. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 45(2): 88-100. Liao Yongjie, Fan Dejiang, Liu Ming et al. Sedimentary records correspond to relocation of the Huanghe River in Bohai Sea. Periodical of Ocean University of China(Natural Science), 2015, 45(2): 88-100. |
| [62] |
胡邦琦. 中国东部陆架海泥质沉积区的物源识别及其环境记录[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学博士学位论文, 2010: 1-163. Hu Bangqi. Sediment Provenance Discrimination and Paleoenvironment Records in the Mud Area of East China Seas since the Holocene[D]. Qingdao:The Doctoral Dissertation of Ocean University of China, 2010:1-163. |
| [63] |
刘世昊, 丰爱平, 李培英等. 现代黄河三角洲地区晚更新世以来高分辨率沉积粒度特征及动力沉积环境演化. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2): 291-306. Liu Shihao, Feng Aiping, Li Peiying et al. High-resolution grain size distribution and evolution of the sediment-dynamic environment in the modern Yellow River delta since the Latest Pleistocene. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(2): 291-306. DOI:10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.05 |
| [64] |
陈晓辉, 李日辉, 孙荣涛等. 末次冰消期以来辽东半岛东南近岸泥质区的古环境演化. 第四纪研究, 2016, 36(6): 1489-1501. Chen Xiaohui, Li Rihui, Sun Rongtao et al. Paleo-environmental evolution in the southeast coastal mud area of Liaodong Peninsula since the Last Deglaciation. Quaternary Sciences, 2016, 36(6): 1489-1501. |
| [65] |
耿秀山. 黄渤海地貌特征及形成因素探讨. 地理学报, 1981, 36(4): 423-434. Geng Xiushan. The geomorphological features and forming factors of submarine relief in the Bohai Sea and the Yellow Sea. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1981, 36(4): 423-434. |
| [66] |
胥勤勉, 胡云壮, 袁桂邦等. 渤海湾西南岸古黄河三角洲全新世地层层序和演化过程. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(2): 326-339. Xu Qinmian, Hu Yunzhuang, Yuan Guibang et al. Holocene sequence stratigraphy and evolution of the ancient Yellow River delta in the southwestern coast of the Bohai Bay. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(2): 326-339. DOI:10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2015.02.08 |
| [67] |
杨守业, 蔡进功, 李从先等. 黄河贯通时间的新探索. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2001, 21(2): 15-20. Yang Shouye, Cai Jingong, Li Congxian et al. New discussion about the run-through time of the Yellow River. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2001, 21(2): 15-20. |
| [68] |
陈晓辉. 北黄海陆架晚第四纪地层结构与物源环境演变研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所)博士学位论文, 2014: 1-139. Chen Xiaohui. Sedimentary Stratigraphic Structure and Provenance Environmental Evolution in the North Yellow Sea during the Late Quaternary[D]. Qingdao:The Doctoral Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Institute of Oceanology), 2014:1-139. |
| [69] |
蓝先洪. 南黄海NT2孔沉积物物源研究. 沉积学报, 2010, 28(6): 1182-1189. Lan Xianhong. Provenance study of sediments in core NT2 of the south Yellow Sea. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 2010, 28(6): 1182-1189. |
| [70] |
卢健. 南黄海西部晚更新世末期以来沉积特征及其物源环境意义[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院研究生院(海洋研究所)博士学位论文, 2013: 1-135. Lu Jian. Sedimentary Characteristics and Significance of Provenance and Sedimentary Environment since the Late Pleistocene in the Western South Yellow Sea[D]. Qingdao:The Doctoral Dissertation of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences(Institute of Oceanology), 2013:1-135. |
| [71] |
王庆, 王小鲁, 李雪艳等. 黄河三角洲南部废弃三角洲潮间滩涂表层沉积粒度特征及其粗化现象. 第四纪研究, 2017, 37(2): 353-367. Wang Qing, Wang Xiaolu, Li Xueyan et al. Grain size characteristics and coarsening phenomenon of inter-tidal flat surficial sediment along the abandoned southern Yellow River sub-delta. Quaternary Sciences, 2017, 37(2): 353-367. |
| [72] |
德日进, 杨钟健. 山西西部、陕西北部蓬蒂纪后黄土期之地层观察. 地质专报, 1930, 甲种第八号: 1-19. Teihard de Chardin Pierre, Young Chung Chien. The strata observation in western Shanxi, northern Shaanxi after Pengdiji in loess period. Geological Special Report, 1930, 甲种第八号(8): 1-19. |
| [73] |
朱照宇. 中国黄土高原第四纪古气候与新构造演化. 北京: 地质出版社, 1994: 1-226. Zhu Zhaoyu. The Climatic and Tectonic Evolution in the Loess Plateau of China during the Quaternary. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1994: 1-226. |
| [74] |
腾志宏. 郑州-洛阳黄河南岸黄土地层及更新世环境分析. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 1998, 28(2): 153-156. Teng Zhihong. Loess stratum and an analysis on the environment of Pleistocene in south bank of the Yellow River between Zhengzhou and Luoyang. Journal of Northwest University(Natural Science Edtion), 1998, 28(2): 153-156. |
| [75] |
Kong P, Jia J, Zheng Y. Time constraints for the Yellow River traversing the Sanmen Gorge. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 2014, 15(2): 395-407. DOI:10.1002/ggge.v15.2 |
| [76] |
李吉均, 方小敏. 晚新生代黄河上游地貌演化与青藏高原隆起. 中国科学(D辑), 1996, 26(4): 316-322. Li Jijun, Fang Xiaomin. Geomorphic evolution of the upper the Yellow River and the uplift of the Tibetan Plateau in Late Cenozoic. Science in China(Series D), 1996, 26(4): 316-322. |
| [77] |
岳乐平, 雷祥义, 屈红军. 黄河中游水系的阶地发育时代. 地质论评, 1997, 43(2): 186-192. Yue Leping, Lei Xiangyi, Qu Hongjun. The age of terrace development in the middle reaches of the Yellow River. Geology Review, 1997, 43(2): 186-192. |
| [78] |
潘保田, 李吉均. 黄河中游的地貌与地文期问题. 兰州大学学报(自科版), 1994, 30(1): 115-123. Pan Baotian, Li Jijun. The landform in the middle reaches of the Yellow River and problem of physiographic stage. Journal of Lanzhou University(Natural Science), 1994, 30(1): 115-123. |
| [79] |
薛铎. 黄河东段形成时代管见. 河南地质, 1996, 14(2): 110-112. Xue Duo. A humble option of the formed age for the eastern section of the Yellow River. Henan Geology, 1996, 14(2): 110-112. |
| [80] |
刘书丹, 李广坤, 李玉信等. 从河南东部平原第四纪沉积物特征探讨黄河的形成与演变. 河南地质, 1988, 6(2): 22-26. Liu Shudan, Li Guangkun, Li Yuxin et al. Discuss formation and evolution of the Yellow River constraint by Quaternary sediments in eastern Henan plain. Henan Geology, 1988, 6(2): 22-26. |
| [81] |
吴锡浩, 王苏民. 关于黄河贯通三门峡东流入海问题. 第四纪研究, 1998, 18(2): 188-188. Wu Xihao, Wang Sumin. Discuss about the Yellow River gets through Sanmenxia Gorge and eastward flow to the sea. Quaternary Sciences, 1998, 18(2): 188-188. |
| [82] |
王苏民, 吴锡浩, 张振克等. 三门古湖沉积记录的环境变迁与黄河贯通东流研究. 中国科学(D辑), 2001, 31(9): 760-776. Wang Sumin, Wu Xihao, Zhang Zhenke et al. Study of the environmental change recorded in Sanmen paleolake sedimentary and the Yellow River perforation and flow eastward to the sea. Science in China(Series D), 2001, 31(9): 760-776. |
| [83] |
蒋复初, 傅建利, 王书兵等. 关于黄河贯通三门峡的时代. 地质力学学报, 2005, 11(4): 293-301. Jiang Fuchu, Fu Jianli, Wang Shubing et al. The age of the Yellow River passing through the Sanmen Gorge. Journal of Geomechanics, 2005, 11(4): 293-301. |
| [84] |
王书兵, 蒋复初, 傅建利等. 关于黄河形成时代的一些认识. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33(4): 705-714. Wang Shubing, Jiang Fuchu, Fu Jianli et al. Some knowledge of the formation of the Yellow River. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33(4): 705-714. |
| [85] |
袁宝印, 王振海. 青藏高原隆起与黄河地文期. 第四纪研究, 1995(4): 353-359. Yuan Baoyin, Wang Zhenhai. Uplift of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and the Yellow River physiographic period. Quaternary Sciences, 1995(4): 353-359. |
| [86] |
季军良, 郑洪波, 李盛华等. 山西平陆黄河阶地与古三门湖消亡-黄河贯通三门峡时代问题的探讨. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26(4): 665-672. Ji Junliang, Zheng Hongbo, Li Shenghua et al. The terraces of the Huanghe River in Pinglu County, Shanxi Province and their relationship with the disappearance of the Sanmen palaeolake and the formation of the Huanghe River. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26(4): 665-672. |
| [87] |
谢悦波, 王文辉, 王平. 古洪水平流沉积粒度特征. 水文, 2000, 20(4): 18-20. Xie Yuebo, Wang Wenhui, Wang Ping. Characteristics of grain size for paleoflood slackwater deposits. Hydrology, 2000, 20(4): 18-20. |
| [88] |
胡贵明, 黄春长, 周亚利等. 伊河龙门峡段全新世古洪水和历史洪水水文学重建. 地理学报, 2015, 70(7): 1165-1176. Hu Guiming, Huang Chunchang, Zhou Yali et al. Hydrological reconstruction of Holocene palaeofloods and historical floods in the Longmen Gorge of the Yihe River. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2015, 70(7): 1165-1176. |
| [89] |
黄春长, 李晓刚, 庞奖励等. 黄河永和关段全新世古洪水研究. 地理学报, 2012, 67(11): 1493-1504. Huang Chunchang, Li Xiaogang, Pang Jiangli et al. Palaeoflood sedimentological and hydrological studies on the Yongheguan reach in the middle Yellow River. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2012, 67(11): 1493-1504. DOI:10.11821/xb201211006 |
| [90] |
Kochel R C, Baker V R. Paleoflood hydrology. Science, 1982, 215(4531): 353-361. DOI:10.1126/science.215.4531.353 |
| [91] |
Johnson B A, Carpenter P J. Geophysical response of slackwater and sandy terrace deposits near Savanna, northwestern Illinois. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2013, 68(4): 955-964. DOI:10.1007/s12665-012-1798-5 |
| [92] |
Guo Y Q, Huang C C, Pang J L et al. Grain size characteristics of modern flood slackwater deposits along the upper Hanjiang River. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2014, 34(11): 1369-1376. |
| [93] |
Li X G, Huang C C. Characteristics of the flood slackwater deposits occurred in 2012 in the Jin-Shaan Gorges of the Yellow River. Journal of Arid Land Resources and Environment, 2015, 29(10): 165-171. |
| [94] |
Liu T, Huang C C, Pang J L et al. Late Pleistocene and Holocene palaeoflood events recorded by slackwater deposits in the upper Hanjiang River valley, China. Journal of Hydrology, 2015(529): 499-510. |
| [95] |
Jones A P, Shimazu H, Oguchi T et al. Late Holocene slackwater deposits on the Nakagawa River, Tochigi Prefecture, Japan. Geomorphology, 2001, 39(1-2): 39-51. DOI:10.1016/S0169-555X(01)00050-2 |
| [96] |
Zhou L, Huang C C, Zhou Y L et al. Late Pleistocene and Holocene extreme hydrological event records from slackwater flood deposits of the Ankang east reach in the upper Hanjiang River valley, China. Boreas, 2016, 45(4): 673-687. DOI:10.1111/bor.2016.45.issue-4 |
| [97] |
Zhao X R, Huang C C, Pang J L et al. Holocene climatic events recorded in palaeoflood slackwater deposits along the middle Yiluohe River valley, middle Yellow River basin, China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016(123): 85-94. |
| [98] |
吴帅虎, 庞奖励, 程和琴等. 汉江上游谷地辽瓦店剖面风化成壤特征以及成壤环境演变. 第四纪研究, 2015, 35(4): 1030-1040. Wu Shuaihu, Pang Jiangli, Cheng Heqin et al. Pedogenensis characteristics and pedogenic environmental change of Liaowadian profile in the upper Hanjiang River valley, China. Quaternary Sciences, 2015, 35(4): 1030-1040. |
| [99] |
袁胜元, 赵新军, 李长安. 古洪水事件的判别标志. 地质科技情报, 2006, 25(4): 55-58. Yuan Shengyuan, Zhao Xinjun, Li Chang'an. Identification marks of paleoflood. Geological Science and Technology Information, 2006, 25(4): 55-58. |
| [100] |
Baker V R. Paleoflood hydrology:Origin, progress, prospects. Geomorphology, 2008, 101(1-2): 1-13. DOI:10.1016/j.geomorph.2008.05.016 |
| [101] |
Munoz S E, Gruley K E, Massie A et al. Cahokia's emergence and decline coincided with shifts of flood frequency on the Mississippi River. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015, 112(20): 6319-6324. DOI:10.1073/pnas.1501904112 |
| [102] |
Yang D, Yu G, Xie Y et al. Sedimentary records of large Holocene floods from the middle reaches of the Yellow River, China. Geomorphology, 2000, 33(1): 73-88. |
| [103] |
Huang C C, Pang J L, Zha X C et al. Extraordinary floods of 4100-4000 a BP recorded at the late Neolithic ruins in the Jinghe River Gorges, middle reach of the Yellow River, China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2010, 289(1-4): 1-9. DOI:10.1016/j.palaeo.2010.02.003 |
| [104] |
Guo Y, Huang C C, Zhou Y L et al. Extraordinary flood events and the response to monsoonal climatic change during the last 3000 years along the middle Yangtze River valley, China. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2016(462): 70-84. |
| [105] |
李高金. 黄河南徙对徐淮地区生态和社会经济环境影响研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学博士学位论文, 2010: 1-126. Li Gaojin. Effects of Southward Diversion of the Yellow River on Eco-environment and Social Economy of Xu-Huai River Basin. Xuzhou:The Doctoral Dissertation of China University of Mining and Technology, 2010:1-126. |
| [106] |
水利部淮河水利委员会, 《淮河志》编纂委员会. 淮河志第二卷:淮河综述志. 北京: 科学出版社, 2000: 1-422. The Huaihe River Commission of the Ministry of Water Resources, the Compilation Committee of the Huaihe Chronicles. Second Vols of Huaihe Chronicles:Huaihe Overview. Beijing: Science Press, 2000: 1-422. |
| [107] |
Knox J C. Sensitivity of modern and Holocene floods to climate change. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2000, 19(1-5): 439-457. DOI:10.1016/S0277-3791(99)00074-8 |
| [108] |
李胜利, 赵景波. 渭河西安高陵耿镇历史时期古洪水研究. 中国沙漠, 2007, 27(3): 379-384. Li Shengli, Zhao Jingbo. Historical flood changes of Weihe River at Genzhen Town section in Gaoling County of Xi'an. Journal of Desert Research, 2007, 27(3): 379-384. |
| [109] |
Zhang Y Z, Huang C C, Pang J L et al. Holocene palaeoflood events recorded by slackwater deposits along the middle Beiluohe River valley, middle Yellow River basin, China. Boreas, 2015, 44(1): 127-138. DOI:10.1111/bor.12095 |
| [110] |
殷淑燕, 黄春长, 查小春. 论极端性洪水灾害与全球气候变化——以汉江和渭河洪水灾害为例. 自然灾害学报, 2012, 21(5): 41-48. Yin Shuyan, Huang Chunchang, Zha Xiaochun. On extreme flood disasters and global climate change:A case study of flooding of Hanjiang River and Weihe River. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2012, 21(5): 41-48. |
| [111] |
黄春长, 庞奖励, 黄萍等. 关中盆地西部黄土台塬全新世气候事件研究. 干旱区地理, 2002, 25(1): 10-15. Huang Chunchang, Pang Jiangli, Huang Ping et al. Holocene climatic events on the loess tableland in the western Guanzhong basin, China. Arid Land Geography, 2002, 25(1): 10-15. |
| [112] |
Huang C C, Jia Y F, Pang J L et al. Holocene colluviation and its implications for tracing human-induced soil erosion and redeposition on the piedmont loess lands of the Qinling Mountains, Northern China. Geoderma, 2006, 136(3-4): 838-851. DOI:10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.06.006 |
| [113] |
Huang C C, Pang J L, Zha X C et al. Impact of monsoonal climatic change on Holocene overbank flooding along Sushui River, middle reach of the Yellow River, China. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2007, 26(17-18): 2247-2264. DOI:10.1016/j.quascirev.2007.06.006 |
2 Institutions of Earth Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029)
Abstract
The Yellow River's flooding into the Huaibei Plain has profoundly changed the natural environment of the latter, made great influence on local social production and national economy, and even affected the process of Chinese history. It has become an important issue of concern to government and scientists. The Yellow River has flooded numerous times into the Huai River throughout the Quaternary. The flooding of the Yellow River into the Huai River drainage basin has occurred during the last deglaciation(13.2 ka B.P.)in the late Pleistocene. The Yellow River has also frequently shifted course in its lower reaches in the Holocene as a result of natural floods and human activity. More than 1000 floods have occurred in the past 4000 years. According to The Chronicle of Bamboo Book(《竹书纪年》), the first time that the Yellow River flooded into the Huai River drainage basin was in 361 BC as a result of human activity(canal digging), but the first historical record of a natural flooding was in 168 BC. The last time the Yellow River flooded into the Huai River drainage area was in 1938 A.D. as a result of military sabotage of a dam. Research on the flooding of the Yellow River into the Huai River is of great importance for the understanding of the formation and evolution of the Huaibei Plain. It is of great theoretical significance to understand the paleoclimate response to the extreme paleo-floods in the lower Yellow River, and provides basic hydrological data for modern water conservancy construction, as well as flood and drought mitigation in the Huanghuai area. This paper summarizes the environmental impacts of the Yellow River flooding into the Huai River, as well as the determination method and mechanism of the flooding of Yellow River into the Huaibei Plain. Environmental impacts include impacts on the Huai River system, the surface process of Huaibei Plain, the source-sink process in Huaihe basin, ocean(in the Eastern China)provenance and the significance of the formation of the Yellow River. Previous research on the impact and significance of the constraint age of the events of the flooding of the Yellow River into the Huaibei Plain focuses on the process of the surface, but little has done on the influence and significance of the sedimentation process during the geological period. In addition, a comprehensive summary is made on determination methods, dating, climatic background and mechanism of the flooding of Yellow River into the Huaibei Plain. There exist some ambiguities or uncertainties in the methods such as grain size analysis and lithofacies observation for recognizing the Yellow River floods sediment. The time scale of the Yellow River flooding into Huai River is concentrated on the historical period, which is short and does not exceed the Holocene. There are different views on the natural causes(climatic background and mechanism)of the Yellow River flooding into the Huaibei Plain. One point of view is that the events occur mostly in the period of warm and wet climate, while the other holds that the events often occur during the climate transition period. Finally, we point out the problems in the research of the Yellow River flooding into the Huaibei Plain and put forward the solution to these problems. The geological significance of the Yellow River flooding into the Huaibei Plain needs to be further explored. The complete sequence in Quaternary of the Yellow River flooding into Huai River needs to be reconstructed. Multiple methods(provenance analysis etc.)should be used to solve the ambiguities and uncertainties. 2018, Vol.38
2018, Vol.38

