全新世海平面变化[1]和不同的河流相作用,形成不同的三角洲类型[2, 3]。如: 长江三角洲具有下切河谷充填模式[4, 5],以及自西向东形成多个三角洲叶瓣[6, 7, 8],形成不同的地层结构[9],记录了古环境信息[10]; 珠江三角洲在末次盛冰期之后海平面上升时期,海水顺珠江海侵[11],至6.8ka B.P. 开始发育三角洲[12, 13]; 红河三角洲、 湄公河三角洲主要是在8ka B.P. 海平面快速上升时期开始形成的[14, 15, 16],伴随着海平面变化和三角洲进积,海岸线[17]、 河流类型[18]和地貌类型[19]均发生相应的变化。所以,对不同区域的三角洲进行系统的研究,可以了解三角洲的形成、 演化历史以及气候环境[20, 21, 22, 23]。依据贝壳堤[24, 25, 26]、 历史文献[27, 28],以及少量钻孔资料,黄河全新世在渤海湾西、 南岸形成了多期三角洲[24]。
依据历史文献、 遥感和地貌特征,不同的学者均提出渤海湾西南岸的河北黄骅和海兴之间分布西汉古黄河三角洲[27, 28, 29]。随后,又从沉积和物源等方面论述了古黄河三角洲的特征[30, 31]。但其详细的沉积特征、 地层层序较少研究,更无从论及其发育过程,以及对海平面变化、 气候变化和人类活动等方面的响应过程。
本文主要利用“河北省1 ︰ 5万官庄、 黄骅、 南排河幅区调”和“河北1 ︰ 25万黄骅县幅区调”在渤海湾西南岸实施的6个钻孔,在详细分析其沉积特征和微体古生物的基础上,依据层序地层学原理划分地层层序,组成钻孔联合剖面,分析古黄河三角洲的演化过程,探讨其对海平面变化、 气候变化和人类活动的响应过程。
1 地质概况渤海湾西南岸在构造上横跨黄骅坳陷和埕宁隆起,以羊二庄断裂为分界断裂。古近纪主要为断陷时期,坳陷和隆起区沉降差异较大; 新近纪和第四纪主要为坳陷时期,整体沉降[32, 33, 34, 35]。渤海湾西南第四纪厚度在黄骅坳陷和埕宁隆起上也有差异,黄骅坳陷内的HB1孔厚400余米[36]; 埕宁隆起上的7-17-1孔则仅有320余米[37],且包含5期火山活动[38],晚更新世晚期喷发形成小山[39]。晚第四纪渤海湾西南岸形成3次海侵,并与深海氧同位素(MIS)第5、 3和1阶段相对应[40, 41, 42, 43]。全新世渤海湾西南岸存在多期古黄河三角洲[44, 45]( 图1)。
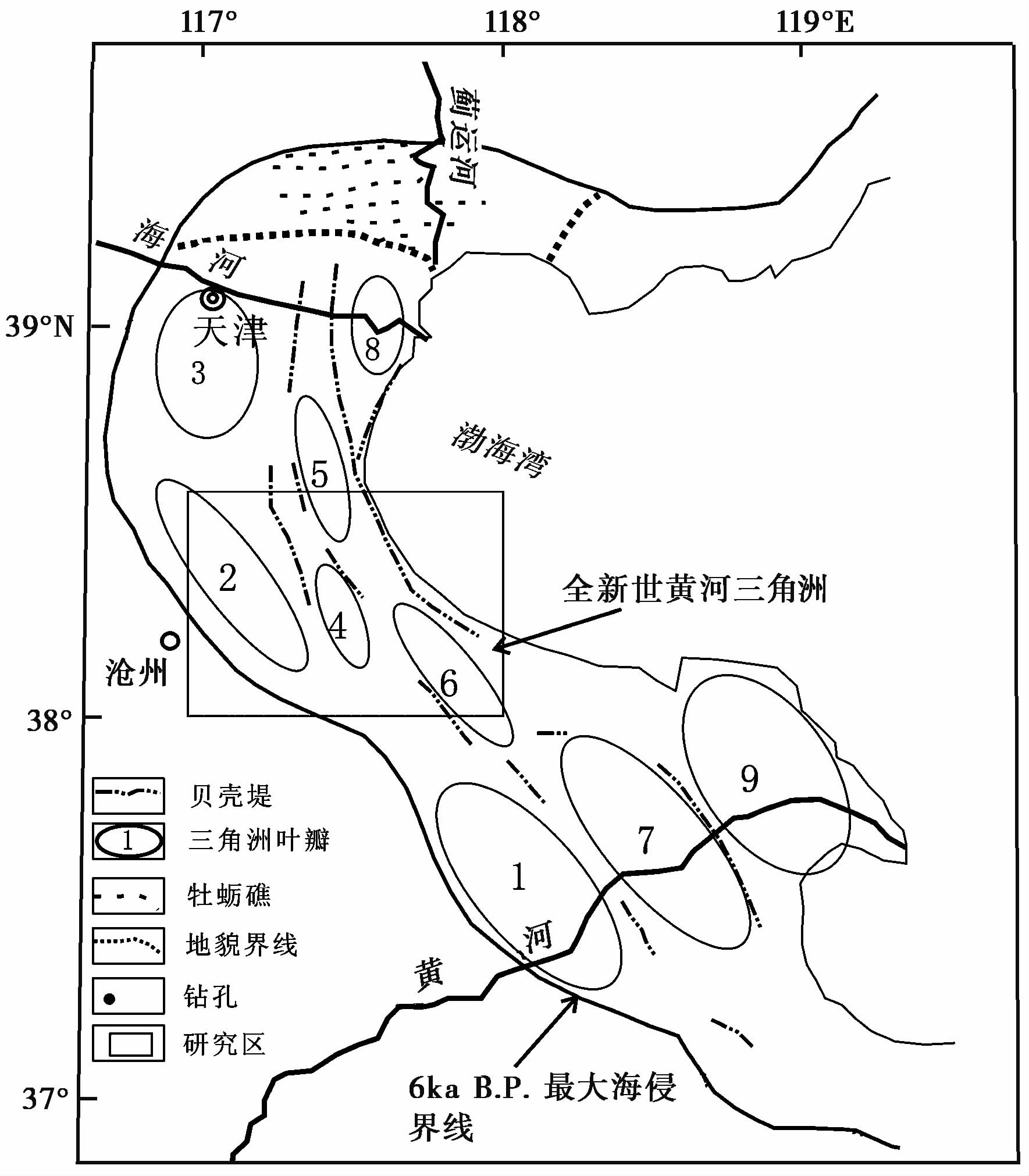
|
图1 渤海西、 南岸古黄河三角洲[24, 25] 1——6000~5000a B.P.; 2——5000~4500a B.P.; 3——4500~3400a B.P.; 4——3400~3000a B.P.; 5——3000a B.P.~602 BC; 6——602BC~ 11A .D .; 7——11~1048A.D.; 8——1048~1128A.D.; 9——1855A.D.至今 Fig.1 The deltas on the western and southern coasts of the Bohai Bay |
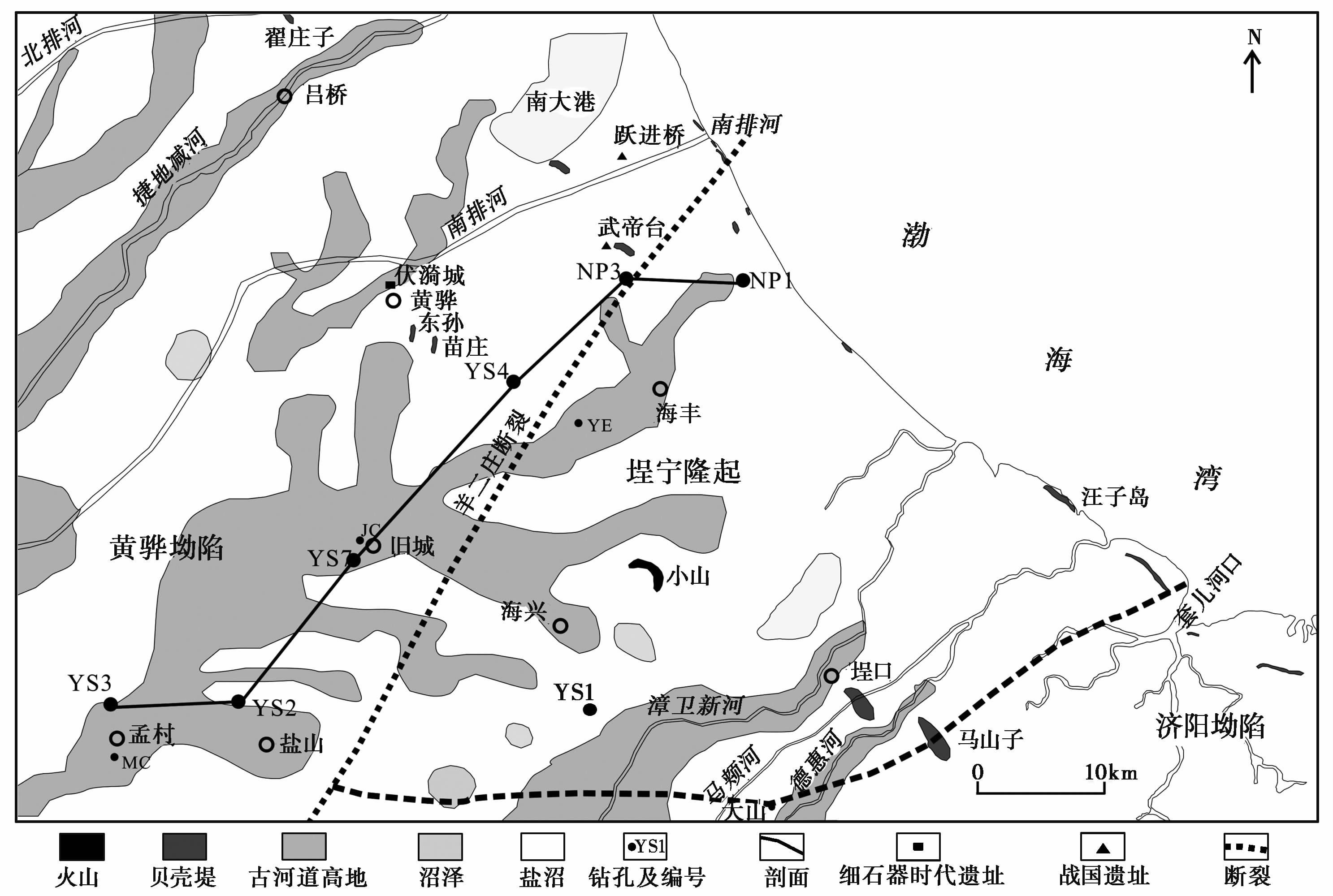
|
图2 渤海湾西南岸地貌和钻孔分布图 Fig.2 The geomorphological map of southwestern coast of the Bohai Bay and the location of boreholes |
渤海湾西南岸地势整体呈现为西高东低,中部高两端低,最高的孟村县附近海拔约9m。地貌则包括古河道、 沼泽、 盐沼、 贝壳堤和火山等多种地貌类型( 图2)。古河道高地主要有西汉古黄河、 捷地减河和漳卫新河等。古河道高地之间分布有多个沼泽,海边则为盐沼,如南大港。贝壳堤主要有东孙、 翟庄子、 苗庄、 武帝台和现代海岸等地,其时代和成因也各不相同[46],东孙庄贝壳堤年龄为7.0~6.1ka B.P. [47, 48],翟庄子贝壳堤年龄为6.0~4.9ka B.P. [48, 49],苗庄贝壳堤年龄为5.6~4.6ka B.P. [48, 50],武帝台贝壳堤年龄为4.1~3.2ka B.P. [47, 48],现代海岸为近千年来的贝壳堤[51~53]。黄骅的水漪城分布有细石器时代、 战国和西汉时期的遗址[54, 55],武帝台、 跃进桥分布有西汉时期的遗址[54]。本区分布大山和小山两座火山,海兴小山为火山堆积物构成的隆丘,时代为1~3万或4万年[56]; 无棣大山为锥形复合火山堆,其时代为0.55~0.83Ma或0.33Ma[57, 58]。
2 研究方法本次研究中的6个钻孔分两次实施,NP1和NP3孔于2003~2005年实施,孔深20~30m; YS2、 YS3、 YS4和YS7孔于2006~2008年实施,孔深68~75m( 表1)。均采用旋转机械钻,岩芯管直径108mm,岩芯采取率达90 % 。末次盛冰期硬粘土又称古土壤[59]和“desiccated crust”[60],其成因与气候变化、 海平面变化相关[61, 62],可以作为区域的标志层。本次研究地层下延至末次盛冰期硬粘土,但以全新世地层为主。末次盛冰期地层埋深为15~20m,下切河谷埋深可达29m,因此,本次工作仅利用这些钻孔上部的岩芯。
| 表1 渤海湾西南岸古黄河三角洲分布钻孔信息表 Table 1 Informations of boreholes of the old deltas in southwestern coast of the Bohai Bay |
粒度样品在南京大学地理与海洋科学学院测试。对含较多贝壳碎屑、有机质和钙质结核的样品用H2O2和HCl进行前处理;测试仪器为英国产Mastersizer 2000粒度仪,测量范围为0.2~2000μm,重复测量的相对误差<3%。YS4和YS7孔进行系统的粒度测量,本文涉及到的共160个。
微体样品重20g,经双氧水浸泡,用0.063mm的孔筛进行冲洗,烘干,然后在显微镜下挑选鉴定。YS2、YS3、NP1和NP3孔进行了系统的微体鉴定,本文涉及到的样品共计94件。
采集钻孔中泥炭和腐殖泥22件,在国土资源部青岛海洋地质研究所做常规14C测年(表 2)。上部三角洲发育形成的泥炭和腐殖泥亦受到上游冲积下来的较老的沉积物的污染[63],而下部海侵时形成的又亦受到冲刷和年轻沉积物的污染[64],因此尽量选择原生的。样品14C测试的半衰期为5730年,再换算为半衰期5568年,其余采用INTCAL04校准(1kaB.P.=1000cal.aB.P.),测年结果见表 2。
| 表2 渤海湾西南岸古黄河三角洲钻孔14C年代 Table 2 List of 14C ages from boreholes of the old deltas in southwestern coast of the Bohai Bay |
利用沉积物的颜色、岩性和沉积结构、构造等特征,结合粒度和微体古生物判别沉积物的沉积相。沉积物颜色依据Munsell土壤色彩系统命名,岩性根据粒度分析结果采用福克沉积物分类体系,依据矩法计算粒度的平均粒径、分选系数、偏差和峰态等参数[65]。
层序地层依托于全球海平面变化模型[66],在旋回面和可容纳空间等概念的明确下[67, 68],形成了基准面变化的模型[69]。本次工作主要研究末次盛冰期硬粘土以来的地层层序,依据海平面变化模型划分为低海面层序、海侵层序、高海面层序和加积层序。
YS4和YS7孔位于研究区中部,位于最大海侵附近; YS7孔下部为低海面和海侵层序,上部为加积层序中的河流相( 图3); YS4孔下部为高海面时期的河流相,上部为高海面三角洲相和加积层序( 图4)。 两孔有不同类型的河流相,且能组合成完成的地层层序,因此,本文选择YS4和YS7孔分析其典型的沉积环境。
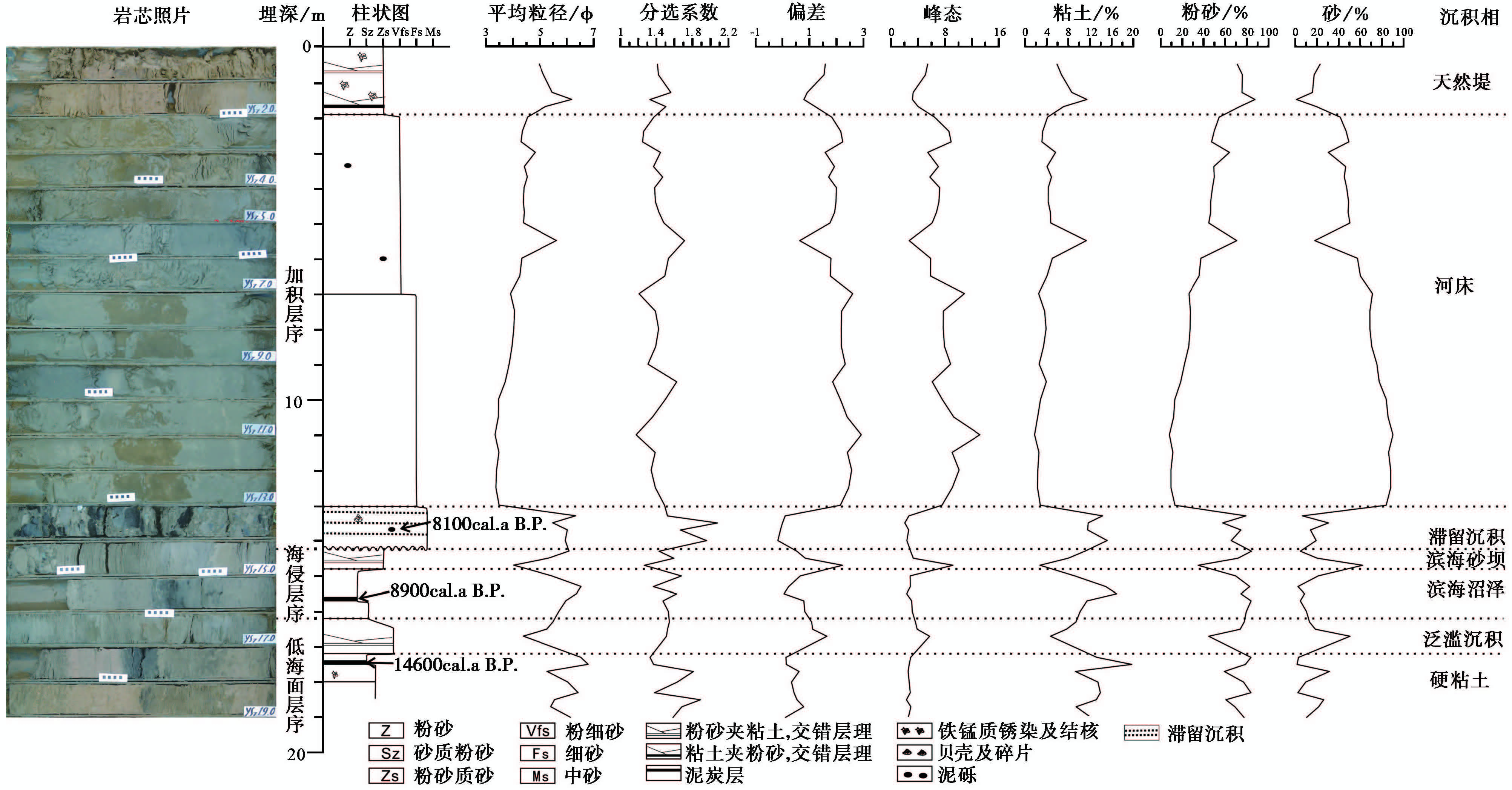
|
图3 YS7孔综合柱状图 Fig.3 Summary profile of YS7 Core |

|
图4 YS4孔综合柱状图 Fig.4 Summary profile of YS4 Core |
低海面层序主要包括硬粘土和泛滥沉积( 图5a和5b),分布高程为-10.0~-20m,厚度2~4m,岩性以砂质粉砂和粉砂质砂为主,岩性自下而上增粗,同时颜色由黄色(10YR7/6)至黄棕色(10YR6/6)变为棕灰色(2.5Y6/2),基本没有有孔虫和介形类化石。

|
图5 渤海湾西南岸全新世古黄河三角洲沉积特征 Fig.5 Sedimentary characteristics in borehole of the old deltas in southwestern coast of the Bohai Bay |
硬粘土岩性主要为黄色砂质粉砂夹少量粉砂质砂,含有弱钙质淀积,以及少量铁锰质淀积,质地较硬( 图5a); 平均粒径5~7,少数4左右,分选系数为1.5~2.0,偏差多数在1.0以下,少量负偏态,峰态2.0~3.0( 图3)。硬粘土在世界上三角洲地区几乎都有发育,长江三角洲地区硬粘土形成于11440~15050a B.P. [70, 71],YS7孔中该层的年龄为14.6ka B.P.,对应晚更新世末期低海面时期。因此,本区的硬粘土也形成于晚更新世末期低海面时期。
泛滥沉积岩性主要为黄棕、 棕灰色粉砂质砂,含有少量冲积的钙质结核,直径1~2cm,质地较软( 图5b); 平均粒径为3~5,分选系数为1.6~2.0,偏差为1.0~2.0,峰态为3.0~6.0( 图3)。
该层时代应为末次盛冰期至全新世底界。
3.1.2 海侵层序海侵层序主要为滨海湖沼相、 滨海砂坝和河流相( 图5c、 5d和5e)。
滨海湖沼分布高程为-8.0~-16.5m,厚度为2~5m,岩性主要为亮灰色(5Y7/2)粉砂、 砂质粉砂,夹少量粉砂质砂,有少量波状层理,粉砂层中含少量碳质斑点( 图5c); 含少量有孔虫和介形类,以毕克卷 转虫(Ammonia beccarii)、五玦虫(Quinqueloculina sp.) 和凹陷中华美花介(Sinocytheridea impressa (Brady))等广盐类物种为主,且多土星介(Ilyocypris sp.)、 玻璃介(Candona sp.)等淡水介形类; 平均粒度为5.5~6.5,分选系数为1.4~1.7,偏差为0.1~0.7,峰态为2.3~2.9( 图3)。YS2孔中该层中部年龄为9.5ka B.P. 。西部滨海湖沼上覆地层为海相沉积,东部则为滨海砂坝。
滨海砂坝主要分布在YS2和YS7,分布高程为-8.0~-10.5m,厚度为0.6m,岩性主要为亮灰色(5Y7/2)粉砂质砂和粉细砂,具水平层理,结构疏松( 图5d); 含少量介形类,以中华美花介为主,多淡水介形类; 平均粒度为4.0~5.5,向上减小,分选系数为1.3~1.6,偏差为0.5~2.2,峰态为2.9~9.2( 图3)。YS2孔中该层上覆地层的年龄为8.5ka B.P.。
河床相主要分布在YS3和NP1孔,上覆地层为滨海湖沼相,该层河流下切至-23.7m。 该层岩性主要为棕灰色(2.5Y6/2)粉细砂、 细砂,向上变细,底部含有少量海相贝壳碎片,和下伏地层具有冲刷面( 图5e),上部具有交错层理和水平层理。YS3孔中该层上覆地层年龄为8.5ka B.P.,NP1孔该层上覆地层顶部年龄为8.3ka B.P.,推断YS3孔和NP1孔为同期河流。
该层沉积时代为8.5ka B.P. 至全新世底界。
3.1.3 高海面层序该层在本区内东西部由于受到海洋作用程度的不同,沉积相也有差异,西部主要为滨海湖沼和积水洼地等滨海相,以及沼泽、 河间洼地等泛滥平原相( 图5f、 5g和5h),东部则主要以潮成沙脊、 前三角洲、 潮下带、 潮间带和河口砂坝等多种海相沉积( 图5i、 5j、 5k、 5l和5m); 该层分布高程为在-10~2m,厚度为6~12m。另外,该层还包括一些水下河道和河口相( 图5n和5o)。
西部为滨海相和泛滥平原相( 图5f、 5g和5h),岩性分为两段,下段为灰黄色(5Y7/1)粉砂质泥和粉砂,多夹泥炭和碳质碎屑,上段为灰棕色(2.5Y7/3)砂质粉砂和粉砂质砂,多铁锰质淀积和还原条斑; 自下而上颜色渐黄,岩性渐粗; 平均粒径为5~7,分选系数为1.2~1.8,偏差为0~1.2,峰态为2.5~4.0。本层含有少量广盐类微体古生物,多非海相介形类。YS3孔中本层上部地层校正年龄为3.6ka B.P.,该层底部校正年龄为8.5ka B.P. 。
东部为潮成沙脊、 潮间带、 前三角洲和潮下带( 图5i、 5j、 5k和5l),岩性主要为暗灰绿色(5GY4/2)粉砂质砂、 砂质粉砂和粉砂,多具有波状、 透镜状和交错层理等,含有贝壳碎片和生物潜穴; 河口砂坝的岩性灰棕色(2.5Y7/3)粉砂质砂和粉细砂,具有交错层理和水平层理( 图5m); 粒度向上递减,后增加,反映了海进和三角洲进积的层序。平均粒径为4~7,分选系数为1.3~2.1,偏差为0~1.9,峰态为2.3~6.5,粒度呈交错状向上减少( 图4)。前三角洲和潮下带中主要有毕克卷转虫(Ammonia beccarii)、 九字虫(Cribrononion sp.)、 五玦虫(Quinqueloculina sp.) 和凹陷中华美花介(Sinocytheridea impressa (Brady))等微体古生物,河口砂坝中则少微体古生物[72]。NP3孔中本层底部校正年代为8.6ka B.P.,YS4孔中本层顶部校正年龄为3.0ka B.P. 。
河床相主要为YS4孔中水下河道和河口相( 图5n和5o)。水下河道主要黄灰色(2.5Y5/2)粉细砂夹粉砂泥块,泥块夹粉细砂薄层,具交错、 水平层理,粉细砂平均粒径为3~4,泥块的平均粒径约为5.5,分选系数为1.0~2.1,偏差为-0.1~3.4,峰态为2.1~17。河口相为(2.5Y5/2)粉细砂和粉砂互层,薄层状,水平层理,平均粒径为4.6~6.1,分选系数为1.4~2.1,偏差为0.2~1.2,峰态为2.2~4.4( 图4)。
该层的时代为3.0~8.5ka B.P. 。
3.1.4 加积层序本层主要包括决口扇、 河间洼地和天然堤等沉积相( 图3q、 3r和3s),分布的高程为-7~-2m,厚度2~5m。岩性主要为棕黄色(10YR6/6)粉砂质砂夹少量浅灰色(5Y7/1)砂质粉砂,多铁锰质淀积和碳质斑点,本层较少微体古生物; 平均粒径为5.2~7.0,分选系数为1.2~1.5,偏差为0.1~1.5,峰态为2.8~4.8。本层主要是3.0ka B.P. 以来的沉积物。
河床相主要为YS7孔中河床相,为灰黄色(5Y7/1)、 灰棕色(2.5Y7/3)粉细沙、 细砂,向上颜色渐黄,含少量泥砾和碳屑,底部为泥砾、 蚌类碎片和泥炭碎块组成的滞留沉积( 图5p); 平均粒径为3~4,分选系数为1.2~1.6,偏差为1.9~2.6,峰态为6~13( 图3),微体古生物较少。 该孔位于西汉古黄河的河道上,其年龄为1.9~2.6ka B.P. 。水下河道分布在NP1孔,碳屑的年龄为2.4~2.8ka B.P.,与YS7孔为同期河流。
3.2 钻孔联合剖面YS3、 YS2、 YS7、 YS4、 NP3和NP1等6个钻孔组成剖面( 图6),分析全新世黄河三角洲的沉积发育过程。
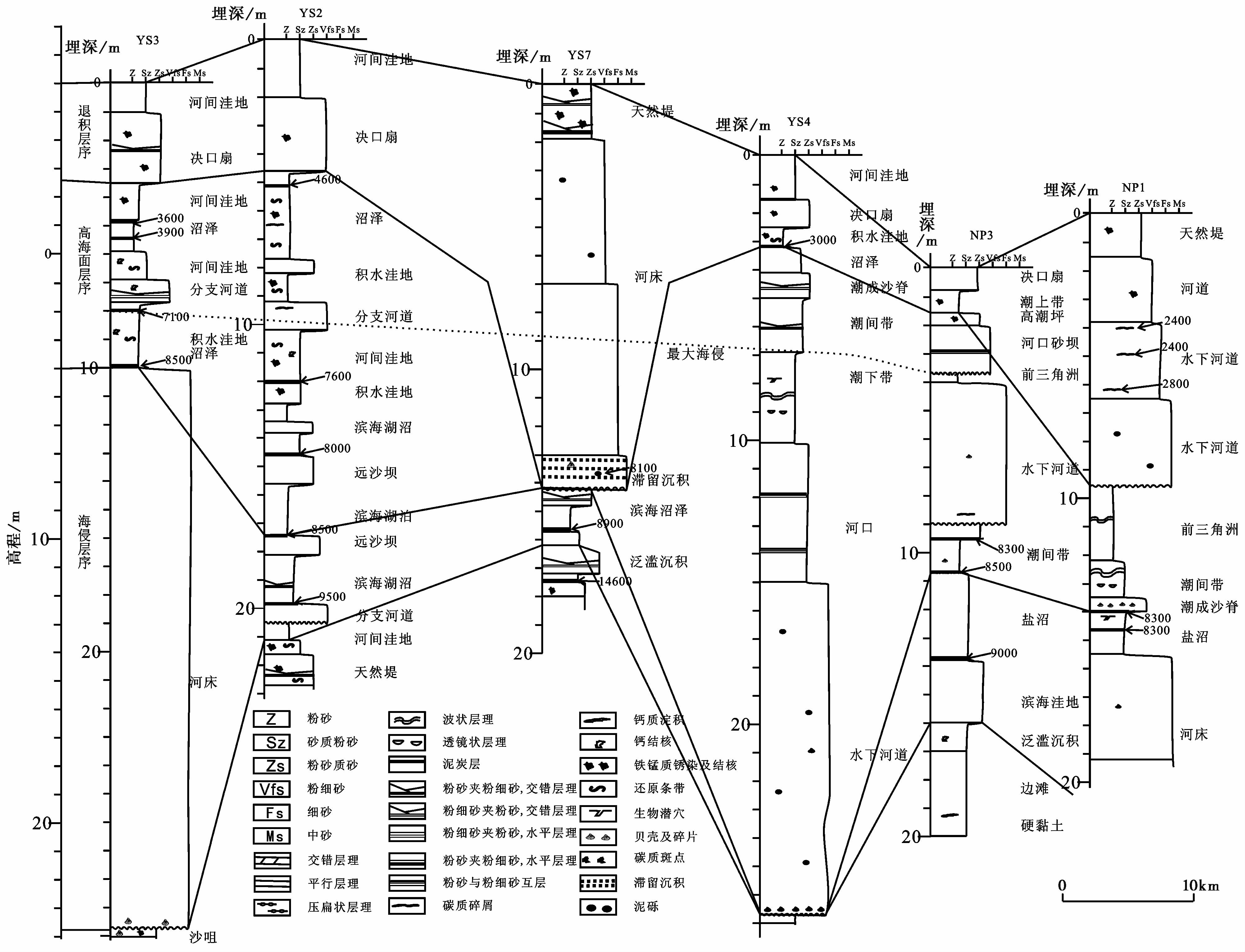
|
图6 渤海湾西南岸钻孔联合剖面沉积、 地层特征(数值代表校正年代) Fig.6 Sedimentary facies and stratigraphic characteristics of boreholes joint profile in southwestern coast of the Bohai Bay(numbers for calibration years) |
低海面层序在该剖面包括硬粘土、 边滩、 河间洼地和泛滥沉积等。海侵层序包含滨海湖沼、 滨海砂坝和下切河床,东部NP3和NP1孔为滨海湖沼,上覆海相地层; YS3和NP1孔发育下切河床; 西部YS2和YS7孔为滨海湖沼和滨海砂坝。高海面层序相变较多,西部下段为滨海湖沼和积水洼地等滨海相,上段则为河间洼地、 沼泽和分支河道等泛滥平原相; 东部下段为潮成沙脊、 潮间带、 前三角洲和潮下带等海进的沉积相,上段则为河口砂坝、 潮间带和潮成沙脊等海退的沉积相,部分钻孔为水下河道,侵蚀下伏部分地层。加积层序主要为河间洼地和决口扇相以及河床和水下河道; 东部为决口扇和潮上带等冲积平原相,西部主要为决口扇和河间洼地等泛滥平原相; YS7和NP1孔发育下切河床。
4 讨论 4.1 河流发育时代依据上述分析,YS7和NP1孔中上部河流为西汉古黄河,年龄为1.9~2.6ka B.P.,形成西汉古黄河三角洲。
YS4和NP3孔下部河流相为水下河道,没有测定年龄,只能依据上下地层和沉积特征推断。NP3孔中水下河道下伏潮间带底部的年龄为8.3ka B.P.,上覆前三角洲相; YS4孔为水下河道和河口,上覆为潮下带; NP3和YS4孔中河流相上覆地层为本区最大海侵。YS2孔中7.6~9.5ka B.P. 为滨海相,7.1~4.6ka B.P. 为泛滥平原相,7.1~7.6ka B.P. 为最大海侵时期。依据NP3和YS4孔中的河流相上覆地层的时代,推测河流结束的年龄为7.6ka B.P.; 依据下伏地层的时代,推测河流开始的年龄为8.3ka B.P.; NP3孔中水下河道下切深度小,可能为后期河道摆动中形成,推测NP3和YS4孔中的河流应略早,可能为古黄河自YS3孔处废弃之后摆动形成,其时代为7.6~8.5ka B.P.。
YS3孔中河床相上覆地层年龄为8.5ka B.P.,其开始的年龄则需要依据沉积特征推断。YS7孔西汉古黄河发育时海平面基本和现代相当,其侵蚀基准约为2m,其河床底部高程为-8m, 共下切了10m。将西汉古黄河论YS3孔中的古黄河,YS3孔中古黄河河床底部高程为-23.7m,假设下切10m,推测当时作为侵蚀基准的海平面高程为-13.7m。依据巽他陆架的海平面变化曲线[73],推断年龄为8.7~9.2ka B.P.;
依据东黄海海平面变化曲线[74],推断年龄为9.0ka B.P. ( 图7)。9.0ka B.P. 时,海岸线位于现代黄河三角洲的北侧,海平面高程为-23.7m[26],与YS3孔河床的下切深度相当,可能为河流的侵蚀基准。因此,YS3孔和NP1孔河流的时代为8.5~9.0ka B.P. 。
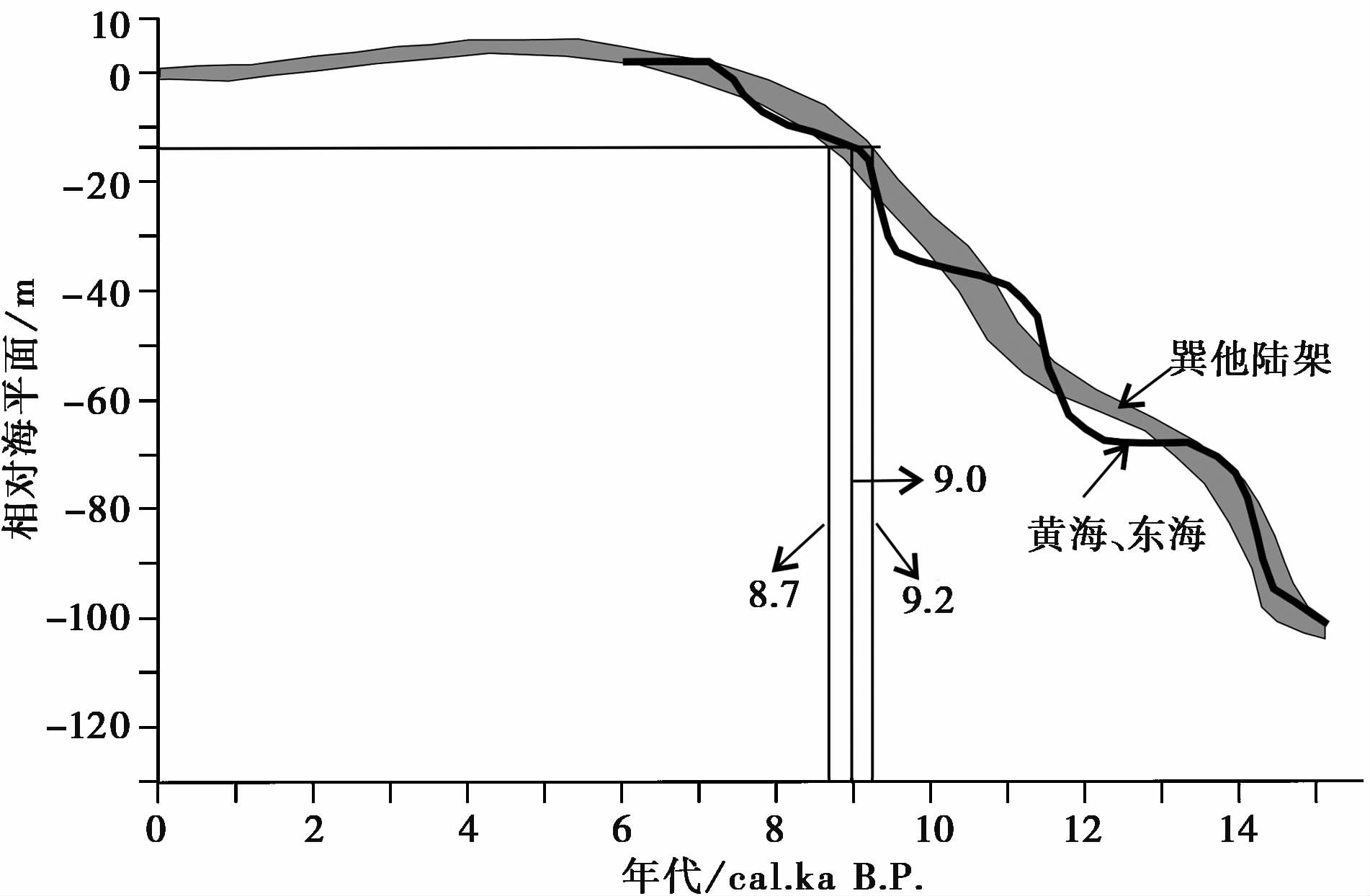
|
图7 利用太平洋西部海平面变化反演YS3孔河流发育时代 Fig.7 The times of river in YS3 borehole based on sea level changes in the western Pacific analyzing |
NP3孔中前三角洲上覆地层为河口砂坝,说明在最大海侵之后NP3孔处为当时古黄河三角洲的侧翼,并与YS4孔中潮间带和潮成沙脊大体相当,为古黄河三角洲废弃之后,潮汐对下伏沉积物重新改造形成,岸边则形成苗庄贝壳堤。依据NP3孔河口砂坝下伏前三角洲,推断该期古黄河三角洲开始的年龄晚于为7.1ka B.P.; 依据YS4孔中潮成沙脊和苗庄贝壳堤,推断其结束的年龄为5.6ka B.P.; 因此,该期古黄河三角洲的时代为5.6~7.1ka B.P. 。
4.2 海岸线变迁11.4~11.6ka B.P.,海岸线位于山东半岛北部[75],高程为-40~-60m[74]。10.2ka B.P. 时,位于渤海中部,高程为-25.8m[76]; 9.0ka B.P. 时,位于现代黄河三角洲北部的水下三角洲处,高程为-23.7[26]; 8.7ka B.P. 时,海岸线到达NP3孔,高程约为-11.1m; 7.1~7.6ka B.P. 为最大海侵时期,海岸线可能越过YS7孔,并未越过YS2孔; 5.6ka B.P. 时,海岸线位于苗庄贝壳堤一带; 3.0ka B.P. 时,位于YS4孔和NP3孔之间; 2.0ka B.P. 时,基本达到现代岸线。
4.3 演化过程末次盛冰期,区域内广泛发育硬粘土,并与14.6ka B.P. 时期结束,上覆泛滥沉积,这说明末次盛冰期至14.6ka B.P. 之间,海平面上升并未影响到研究区。泛滥沉积物粒度粗、 分选差、 质地软,且含钙质冲积结核,为上游河流冲积至此泛滥形成,其过程可能对应融冰水事件(MWP-1B)。此时,海岸线已达到山东半岛北部[75],海水可以通过渤海海峡进入渤海,使得河床比降减小,河流泛滥。
9.0~10.2ka B.P. 海平面缓慢上升,速率为1.7mm/a[26, 76]。研究区东部为盐沼,西部为滨海湖沼,均为滨海相为主。8.7ka B.P. 时,海岸线到达NP3孔,海平面高程约为-11.1m; 8.5~9.0ka B.P. 快速上升,速率为42.3mm/a。同时,早全新世气候暖湿[77, 78],降水丰沛; 黄河摆动至此深切,经YS3和NP1孔入海( 图8),河谷两侧为滨海湖沼相; 伴随海平面的不断上升,河口向陆迁移,并在两侧泛滥形成滨海砂坝。黄河于8.5ka B.P. 后摆动到YS4孔和NP3孔,并形成下切河流。随海平面的不断上升,YS4孔也被淹没于海水之下,形成河口,之后达到最大海侵形成潮下带( 图6)。 结合YS1孔烂泥湾的时代为7.7~8.8ka[42],判断此时黄河走向整体为南北向(图8)。 7.1~7.6ka B.P. 为最大海侵时期,黄河摆动离开研究区,研究区西部为积水洼地和河间洼地等滨海相,东部为潮下带和前三角洲相。最大海侵之后,3.6~7.1ka B.P.时研究区西部主要为河间洼地、 分支河道和沼泽等泛滥平原相; 5.6~7.1ka B.P.时古黄河三角洲在研究区外侧发育,研究区内形成潮间带和河口砂坝; 三角洲废弃之后,YS4孔中形成潮成沙脊,岸边形成苗庄贝壳堤( 图6)。3.0~5.6ka B.P.时黄河走其他区域入海,海岸线位于NP3孔附近,向东移动约20km( 图8),区域广泛成陆。这可能是因为晚全新世气候变干[79],黄土高原植被植被退化,侵蚀强烈[80, 81, 82, 83],华北平原沉积速率增加[84],海岸带沉积通量增大,海岸线外移。西汉古黄河自战国至西汉末期(2.6~1.9ka B.P. ),在研究区走孟村,经旧城,在NP1孔附近入海; 此时武帝台以西区域均已成陆,但地势较低,贝壳堤上多有西汉遗址[54]。公元前340年(2.3ka B.P. )赵魏堤和齐堤修建[27],使得下游沉积通量增大,因此西汉古黄河在研究区形成较多的分支河道,范围也较大( 图1)。1.9ka B.P. 以来,黄河经历多次摆动在天津、 东营和苏北入海[85]。
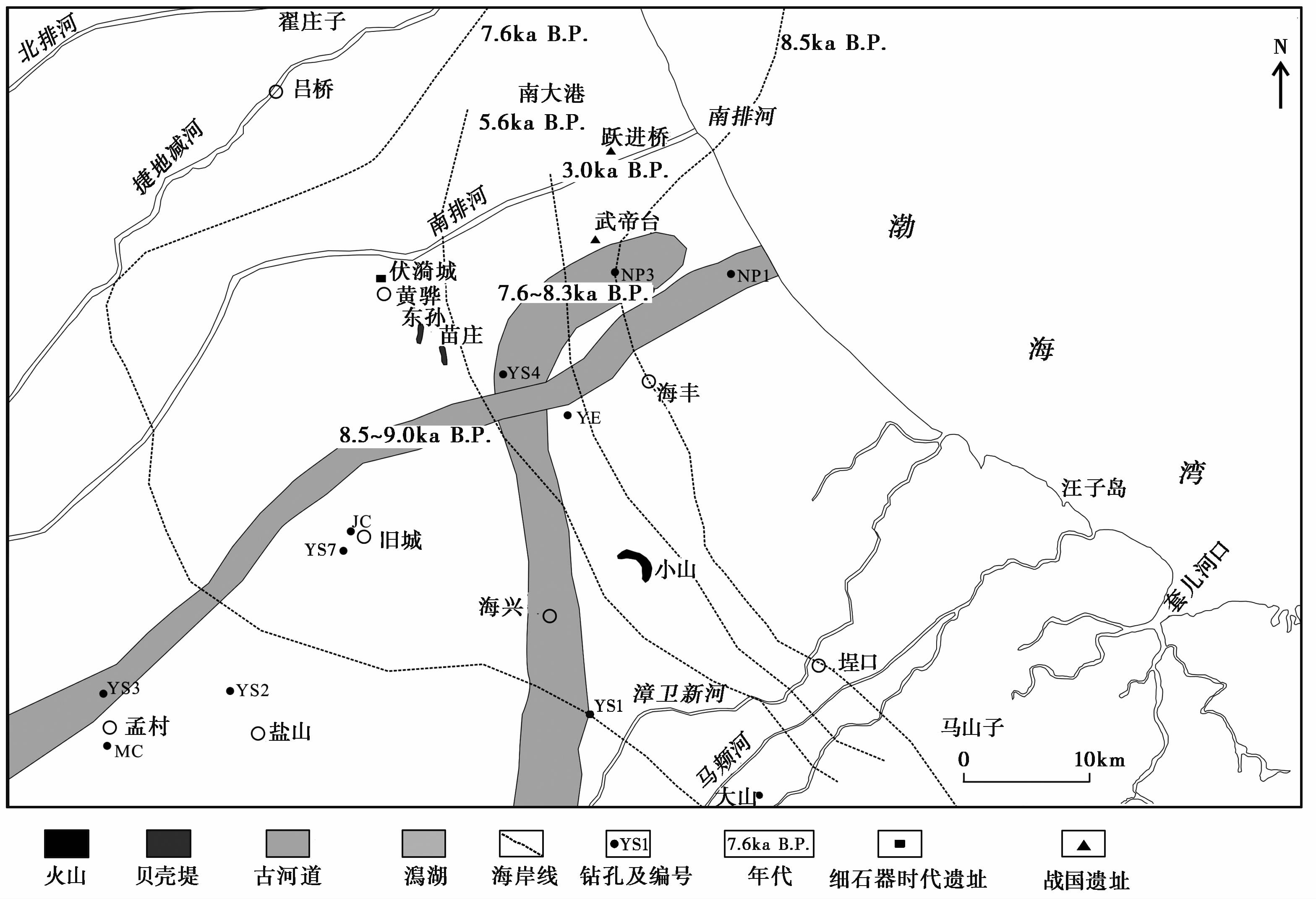
|
图8 渤海湾西南岸全新世岩相古地理 Fig.8 The paleogeography near the southwest Bohai Bay since Holocene |
渤海湾西南岸全新世黄河三角洲地层层序主要包括海侵层序、 高海面层序和加积层序。海侵层序形成于8.5~10.2ka B.P.,包括滨海沼泽和滨海砂坝,具有上粗下细结构,反映了海平面上升过程中,区域积水成泽,发育滨海沼泽; 随后下切河流的河口位置上溯,并在两侧形成滨海砂坝。高海面层序形成于3.0~8.5ka B.P.,其中7.1~7.6ka B.P. 为最大海侵时期。7.6~8.5ka B.P.时,西部为滨海洼地和积水洼地等,以滨海相为主,粒度小,分选较好,含少量广盐类微体古生物; 中部为水下河道和河口相,粒度较大,并向上减小,反映了下切河流在海平面不断上升中逐渐充填转变为河口的过程,含少量广盐类微体古生物; 东部主要为潮间带和潮成沙脊等浅海相,多海相贝壳碎片和微体古生物。7.1~7.6ka B.P.时为最大海侵时,西部为积水洼地,海岸线越过YS4,可能到达YS7孔,但未到达YS2孔; 东部为潮下带和三角洲相。3.0~7.1ka B.P.时西部部为河间洼地、 分支河道和沼泽等泛滥平原相; 东部为潮间带和河口砂坝相。加积层序形成于3.0ka B.P. 以来,主要为河流、 分支河道、 决口扇和河间洼地等泛滥平原相。
9.0~10.2ka B.P.时海岸线由渤海中部到达现代黄河三角洲,研究区东部为盐沼,西部为滨海湖沼,均为滨海相为主。8.5~9.0ka B.P.时黄河经YS3和NP1孔入海,形成下切河谷,河谷两侧为滨海湖沼相和滨海砂坝的二元结构。7.6~8.5ka B.P.时,黄河于YS4孔和NP3孔,形成水下河道和河口相沉积。7.1~7.6ka B.P.时为最大海侵时期,海岸线位于YS7孔和YS2孔之间,黄河离开研究区; 研究区西部为积水洼地和河间洼地等滨海相,东部为潮下带和前三角洲相。5.6~7.1ka B.P.时研究区为古黄河三角洲的侧翼,发育潮间带和河口砂坝相; 废弃之后,YS4孔中发育潮成沙脊,并和苗庄贝壳堤相对应。3.0~5.6ka B.P.时黄河走其他区域入海,晚全新世干冷气候使得黄土高原侵蚀加剧,黄河泥沙含量加大,海岸带沉积通量增大,区域广泛成陆。西汉古黄河于战国至西汉末期(2.6~1.9ka B.P. ),经YS7孔和NP1孔入海,形成下切河谷; 由于赵魏堤和齐堤的修建,下游沉积通量增大,形成较多的分支河道,范围也较大并形成广泛的河流地貌。1.9ka B.P. 以来,黄河经历多次摆动在天津、 东营和苏北入海。
致谢 感谢南京大学地理与海洋学院杨达源教授对本文的修改,天津地质矿产研究所王强研究员鉴定微体古生物,南京大学地理与海洋学院杨海飞测试粒度。
| 1 | 谢志仁, 袁林旺. 略论全新世海面变化的波动性及其环境意义. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32 (6):1065~1077 Xie Zhiren, Yuan Linwang. Fluctuation characteristics of Holocene sea-level change and its environmental implications. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32 (6):1065~1077 |
| 2 | 王 颖, 邹欣庆, 殷 勇等. 河海交互作用与黄东海域古扬子大三角洲体系研究. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32 (6):1055~1064 Wang Ying, Zou Xinqing, Yin Yong et al. Study on river-sea interaction and formation of paleo-Yangtze grand delta system in the area of South Yellow Sea and East China Sea. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32 (6):1055~1064 |
| 3 | 王 颖, 傅光翮, 张永战. 河海交互作用沉积与平原地貌发育. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27 (5):674~689 Wang Ying, Fu Guanghe, Zhang Yongzhan. River-sea interactive sedimentation and plain morphological evolution. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27 (5):674~689 |
| 4 | Li C X, Wang P, Sun H P et al. Late Quaternary incised-valley fill of the Yangtze Delta(China):Its stratigraphic framework and evolution. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 152 (1~2):133~158 |
| 5 | Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H et al. Sedimentary facies of the tide-dominated paleo-Changjiang(Yangtze)estuary during the last transgression. Marine Geology, 2001, 177 (3~4):331~351 |
| 6 | Chen Z Y, Song B P, Wang Z H et al. Late Quaternary evolution of the subaqueous Yangtze Delta:Stratigraphy, sedimentation, palynology and deformation. Marine Geology, 2000, 162 (2~4):423~441 |
| 7 | Hori K, Saito Y, Zhao Q H et al. Architecture and evolution of the tide-dominated Changjiang(Yangtze)River delta, China. Sedimentary Geology, 2002, 146 (3~4):249~264 |
| 8 | Song Bin, Li Zhen, Saito Yoshiki et al. Initiation of the Changjiang(Yangtze)delta and its response to the Mid-Holocene sea level change. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 2013, 388:81~97 |
| 9 | 缪卫东, 李世杰, 王润华. 长江三角洲北翼J9孔岩芯沉积特征及地层初步划分. 第四纪研究, 2009, 29 (1):126~134 Miao Weidong, Li Shijie, Wang Runhua. Preliminary study on sedimentary characteristics and stratum division of J9 Core in the north wing of the Yangtze River delta. Quaternary Sciences, 2009, 29 (1):126~134 |
| 10 | 黎 兵, 魏子新, 李 晓. 长江三角洲第四纪沉积记录与古环境响应. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31 (2):316~328 Li Bing, Wei Zixin, Li Xiao. Records from Quaternary sediment and palaeo-environment in the Yangtze River delta. Quaternary Sciences, 2011, 31 (2):316~328 |
| 11 | Zong Yongqiang, Huang Kangyou, Yu Fengling et al. The role of sea-level, monsoonal discharge and the paleo-landscape in the Early Holocene evolution of the Pearl River delta, Southern China. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2012, 54:77~88 |
| 12 | Zong Y, Huang G, Switzer A D et al. An evolutionary model for the Holocene formation of the Pearl River delta, China. The Holocene, 2009, 19 (1):129~142 |
| 13 | 韦 惺, 吴超羽. 全新世以来珠江三角洲的地层层序和演变过程. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2011, 41 (8):1134~1149 Wei Xing, Wu Chaoyu. Holocene delta evolution and sequence stratigraphy of the Pearl River delta in South China. Science China:Earth Sciences, 2011, 41 (8):1134~1149 |
| 14 | Tanabe Susumu, Hori Kazuaki, Saito Yoshiki et al. Sedimentary facies and radiocarbon dates of the Nam Dinh-1 core from the Song Hong(Red River)delta, Vietnam. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2003, 21 (5):503~513 |
| 15 | Hori Kazuaki, Tanabe Susumu, Saito Yoshiki et al. Delta initiation and Holocene sea-level change:Example from the Song Hong(Red River)delta, Vietnam. Sedimentary Geology, 2004, 164 (3~4):237~249 |
| 16 | Tamura Toru, Saito Yoshiki, Sieng Sotham et al. Depositional facies and radiocarbon ages of a drill core from the Mekong River lowland near Phnom Penh, Cambodia:Evidence for tidal sedimentation at the time of Holocene maximum flooding. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 29 (5~6):585~592 |
| 17 | Funabiki Ayako, Haruyama Shigeko, Quy Nguyen Van et al. Holocene delta plain development in the Song Hong(Red River)delta, Vietnam. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2007, 30 (3~4):518~529 |
| 18 | Tanabe Susumu, Saito Yoshiki, Vu Quang Lan et al. Holocene evolution of the Song Hong(Red River)delta system, Northern Vietnam. Sedimentary Geology, 2006, 187 (1~2):29~61 |
| 19 | Tanabe Susumu, Hori Kazuaki, Saito Yoshiki et al. Song Hong(Red River)delta evolution related to millennium-scale Holocene sea-level changes. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22 (21~22):2345~2361 |
| 20 | 薛春汀, 刘 健, 孔祥淮. 全新世淮河三角洲初步研究. 第四纪研究, 2010, 30 (5):892~901 Xue Chunting, Liu Jian, Kong Xianghuai. Preliminary study of Holocene Huaihe River delta on coastal plain of Yellow Sea, China. Quaternary Sciences, 2010, 30 (5):892~901 |
| 21 | 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 秦雅飞等. 滦河三角洲南部MT04孔磁性地层研究及其构造与气候耦合关系的探讨. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34 (3):540~552 Xu Qinmian, Yuan Guibang, Qin Yafei et al. Magnetostratigraphy and discussion of coupling relationship between tectonic movement and climate change of MT04 borehole in southern Luanhe River delta. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34 (3):540~552 |
| 22 | 董艺辛, 刘春莲, 陈木宏等. 珠江三角洲中部大鳌平原晚第四纪古生物记录及环境演化. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32 (6):1183~1198 Dong Yinxin, Liu Chunlian, Chen Muhong et al. Late Quaternary paleontology and environmental changes in Da'ao Plain, middle Pearl River delta, Southern China. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32 (6):1183~1198 |
| 23 | 张梦莹, 范代读, 吴国瑄等. 瓯江三角洲南翼晚第四纪孢粉、藻类记录及其古气候意义. 第四纪研究, 2012, 32 (6):1234~1247 Zhang Mengying, Fan Daidu, Wu Guoxuan et al. Palynological characters of Late Quaternary in the south flank of the Oujiang River delta and their paleoclimate implications. Quaternary Sciences, 2012, 32 (6):1234~1247 |
| 24 | Xue Chunting. Historical changes in the Yellow River delta, China. Marine Geology, 1993, 113 (3~4):321~329 |
| 25 | Saito Y, Wei Helong, Zhou Yongqing et al. Delta progradation and chenier formation in the Huanghe(Yellow River)delta, China. Journal of Asian Earth Science, 2000, 18 (4):469~497 |
| 26 | Liu J, Saito Y, Wang H et al. Stratigraphic development during the Late Pleistocene and Holocene offshore of the Yellow River delta, Bohai Sea. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2009, 36 (4~5):318~331 |
| 27 | 谭其骧. 西汉以前的黄河下游河道. 历史地理, 1981,(1):48~64 Tan Qixiang. The channel of the Yellow River in its lower reaches before the Western Han. Historical Geography, 1981,(1):48~64 |
| 28 | 薛春汀, 周永青, 王桂玲. 古黄河三角洲若干问题的思考. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2003, 23 (3):23~29 Xue Chunting, Zhou Yongqing, Wang Guiling. Reviews of the Yellow River delta superlobes since 700 BC. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2003, 23 (3):23~29 |
| 29 | 李元芳. 西汉古黄河三角洲初探. 地理学报, 1994, 49 (6):544~550 Li Yuanfang. The preliminary study on the ancient Yellow River delta of Xihan Dynasty. Acta Geographica Sinica, 1994, 49 (6):544~550 |
| 30 | 吴 忱, 陈 萱, 许清海等. 黄河古三角洲的发现及其与水系变迁的关系. 见: 吴 忱主编. 华北平原古河道研究论文集. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1991. 237~253 Wu Chen, Chen Xuan, Xu Qinghai et al. The discovery of ancient Huanghe River delta and its relationship of changes of river system. In:Wu Chen ed. Collected Papers of Paleochanle in Huabei Plain. Beijing:China Science and Technology Press, 1991. 237~253 |
| 31 | 周永青, 任于灿. 黄骅全新世古黄河三角洲特点及演化研究. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1995, 15 (1):73~80 Zhou Yongqing, Ren Yucan. Feature and evolution of Holocene old Huanghe River delta in Huanghua. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1995, 15 (1):73~80 |
| 32 | 漆家福, 张一伟, 陆克政等. 渤海湾盆地新生代构造演化. 石油大学学报(自然科学版), 1995, 19 (增刊):1~5 Qi Jiafu, Zhang Yiwei, Lu Kezheng et al. Cenozoic tectonic evolution in Bohai Bay basin province, China. Journal of the University of Petroleum, 1995, 19 (Suppl.):1~5 |
| 33 | 郭兴伟, 施小斌, 丘学林等. 渤海湾盆地新生代沉降特征及其动力学机制探讨. 大地构造与成矿学, 2007, 31 (3):273~280 Guo Xingwei, Shi Xiaobin, Qiu Xuelin et al. Cenozoic subsidence in Bohai Bay basin:Characteristics and dynamic mechanism. Geotectonica et Matallogenia, 2007, 31 (3):273~280 |
| 34 | 汤良杰, 万桂梅, 周心怀等. 渤海盆地新生代构造演化特征. 高校地质学报, 2008, 14 (2):191~198 Tang Liangjie, Wang Guimei, Zhou Xinhuai et al. Cenozoic geotectionic evolution of the Bohai basin. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2008, 14 (2):191~198 |
| 35 | Qi Jiafu, Yang Qiao. Cenozoic structural deformation and dynamic processes of the Bohai Bay basin province, China. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2010, 27 (4):757~771 |
| 36 | 范淑贤, 刘海坤, 赵 华等. 3.2Ma, BP以来河北黄骅地区孢粉地层学与古气候变迁. 微体古生物学报, 2009, 26 (2):173~180 Fan Shuxian, Liu Haikun, Zhao Hua et al. Palynology stratigraphy and palaeoclimate evolution in Huanghua district of Hebei Province since 3.2Ma BP. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 2009, 26 (2):173~180 |
| 37 | 杨子赓, 李幼军, 丁秋玲等. 试论河北平原东部第四纪地质几个基本问题. 地质学报, 1979, 53 (4):263~279 Yang Zigeng, Li Youjun, Ding Qiuling et al. Some fundamental problems of Quaternary geology of eastern Hebei Plain. Acta Geologica Sinica, 1979, 53 (4):263~279 |
| 38 | 邵时雄, 张玉芳, 韩书华. 河北平原第四纪火山堆积及火山活动分期的特征. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1983, 3 (2):87~94 Shao Shixiong, Zhang Yufang, Han Shuhua. Quaternary volcanic deposits in Hebei Plain and the periods of their activities. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1983, 3 (2):87~94 |
| 39 | 尹功明, 赵 波, 许建东等. 河北沧州小山火山的ESR年代学研究. 岩石学报, 2013, 29 (12):4415~4420 Yin Gongming, Zhao Bo, Xu Jiandong et al. Electron spin resonance data of the Xiaoshan volcano in Cangzhou, Hebei Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29 (12):4415~4420 |
| 40 | 刘泽纯. 我国东部更新世以来海侵与深海岩芯对比. 科学通报, 1983, 28 (17):1062~1067 Liu Zechun. Comparisons of transgressions and deep-ocean core since Pleistocene in Eastern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1983, 28 (17):1062~1067 |
| 41 | 杨怀仁, 王 建. 黄河三角洲地区第四纪海进与岸线变迁. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 1990, 10 (3):1~14 Yang Huairen, Wang Jian. Quaternary transgressions and coastline changes in Huanghe River(Yellow River)delta. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 1990, 10 (3):1~14 |
| 42 | 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦, 张金起等. 渤海湾沿岸晚第四纪地层划分及地质意义. 地质学报, 2011, 85 (8):1352~1367 Xu Qinmian, Yuan Guibang, Zhang Jinqi et al. The stratigraphic division and geology significance of the Late Quaternary strata along coast of Bohai Bay. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2011, 85 (8):1352~1367 |
| 43 | 阎玉忠, 王 宏, 李凤林等. 渤海湾西岸晚更新世沉积的差异性特征. 第四纪研究, 2006, 26 (3):321~326 Yan Yuzhong, Wang Hong, Li Fenglin et al. Different depositional processes of boreholes BQ1 and BQ2 in the Late Pleistocene on the west coast of Bohai Bay. Quaternary Sciences, 2006, 26 (3):321~326 |
| 44 | Xue C T, Zhu X G, Lin H M. Holocene sedimentary sequence, foraminifera and ostracoda in west coastal lowland of Bohai sea, China. Quaternary Science Reviews, 1995, 14 (5):521~530 |
| 45 | 薛春汀, 成国栋. 渤海西岸贝壳堤及全新世黄河三角洲体系. 见: 杨子庚, 林和茂主编. 中国近海及沿海地区第四纪进程与事件. 北京: 海洋出版社, 1989. 117~125 Xue Chunting, Cheng Guodong. Shelly ridges in west coast of Bohai Sea and Holocene Yellow River Delta system. In:Yang Zigeng, Lin Hemao eds. Quaternary Processes and Events in China Offshore and Onshore Areas. Beijing:China Ocean Press, 1989. 117~125 |
| 46 | 王 强, 袁桂邦, 张 熟等. 渤海湾西岸贝壳堤堆积与海陆相互作用. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27 (5):775~786 Wang Qiang, Yuan Guibang, Zhang Shu et al. Shelly ridge accumulation and sea-land interaction on the west coast of the Bohai Bay. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27 (5):775~786 |
| 47 | 徐家声. 渤海湾黄骅沿海贝壳堤与海平面变化. 海洋学报, 1994, 16 (1):68~77 Xu Jiasheng. Chenier and sea-level change on the coast of Huanghua, Bohai Gulf. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 1994, 16 (1):68~77 |
| 48 | 王 宏, 范昌福. 渤海湾海岸带 14C 数据集(Ⅱ). 第四纪研究, 2005, 25 (3):141~156 Wang Hong, Fan Changfu. The 14C database (Ⅱ) on the circum-Bohai Sea-coast. Quaternary Sciences, 2005, 25 (3):141~156 |
| 49 | 赵希涛, 张景文. 渤海湾西岸第四道贝壳堤存在和年代的新证据. 地质科学, 1981, 16 (1):29Zhao Xitao, Zhang Jingwen. A new evidence on the existence of the forth chenier ridge along the west coast of the Bohai Bay and its 14C dating. Chinese Journal of Geology, 1981, 16 (1):29 |
| 50 | 赵希涛, 张景文, 焦文强等. 渤海湾西岸贝壳堤. 科学通报, 1980, 25 (6):279~281 Zhao Xitao, Zhang Jingwen, Jiao Wenqiang et al. The chenier on western coast of Bohai Bay. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1980, 25 (6):279~281 |
| 51 | 王 宏, 张金起, 张玉发等. 渤海湾西岸的第一道贝壳堤的年代学研究及1千年来的岸线变化. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 2000, 20 (2):7~14 Wang Hong, Zhang Jinqi, Zhang Yufa et al. Chronology of the chenier Ⅰ and shoreline changes since the last 1ka on western coast of Bohai Bay. Marine Geology & Quaternary Geology, 2000, 20 (2):7~14 |
| 52 | 王 宏, 张玉发, 张金起等. 渤海湾西岸第二道贝壳堤的细分及其年龄序列. 地球学报, 2000, 21 (3):320~327 Wang Hong, Zhang Yufa, Zhang Jinqi et al. The chenier Ⅱ on the western coast of Bohai Bay:Its suddivison and amended time-frame work. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 2000, 21 (3):320~327 |
| 53 | 王 宏, 李建芬, 张玉发等. 渤海湾西岸年轻贝壳堤: 形态、结构和多成因过程. 地质论评, 2000, 46 (3):276~287 Wang Hong, Li Jianfen, Zhang Yufa et al. The younger cheniers(shell banks)on the the western coast of Bohai Bay:Morphology, structure and polygenetic processes. Geological Review, 2000, 46 (3):276~287 |
| 54 | 韩嘉谷. 渤海湾西岸古文化遗址调查. 考古, 1965, 15 (2):62~69 Han Jiagu. Survey of ancient cultural sites in western coast of Bohai Bay. Archaeology, 1965, 15 (2):62~69 |
| 55 | 安志敏. 河北黄骅发现的细石器. 考古, 1989, 34 (6):481~488 An Zhimin. A new discovery of microlith in Huanghua, Hebei Province. Archaeology, 1989, 34 (6):481~488 |
| 56 | 胡云壮, 胥勤勉, 袁桂邦等. 河北海兴小山CK3孔磁性地层与第四纪火山活动记录. 古地理学报, 2014, 16 (3):411~426 Hu Yunzhuang, Xu Qinmian, Yuan Guibang et al. Magnetostratigraphy of borehole CK3 and record of the Quaternary volcanic activities in Xiaoshan of Haixing, Hebei Province. Journal of Palaeogeography, 2014, 16 (3):411~426 |
| 57 | 陈道公, 彭子成. 山东新生代火山岩K-Ar年龄和Pb-Sr同位素特征. 地球化学, 1985, 14 (4):293~303 Chen Daogong, Peng Zicheng. K-Ar ages and Pb, Sr isotopic characteristics of Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Shandong, China. Geochimica, 1985, 14 (4):293~303 |
| 58 | 王慧芬, 杨学昌, 朱炳泉等. 中国东部新生代火山岩K-Ar年代学及其演化. 地球化学, 1988, 17 (1):1~12 Wang Huifen, Yang Xuechang, Zhu Bingquan et al. K-Ar geochronology and evolution of Cenozoic volcanic rocks in Eastern China. Geochimica, 1988, 17 (1):1~12 |
| 59 | Li C X, Chen Q, Zhang J et al. Stratigraphy and paleoenvironmental changes in the Yangtze delta during Late Quaternary. Journal Asian Earth Sciences, 2000, 18 (4):63~79 |
| 60 | Yim W-S, Inanovich M, Yu K-F. Young age bias of radiocarbon dates in pre-Holocene marine deposits of Hong Kong and implications for Pleistocene stratigraphy Geo-Marine Letters, 1990, 10 (3):165~172 |
| 61 | 邓 兵, 李从先, 张 经等. 长江三角洲古土壤发育与晚更新世末海平面变化的耦合关系. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24 (2):222~230 Deng Bing, Li Congxian, Zhang Jing et al. Correlation of paleosoil development in the Changjiang delta with sea level fluctuations in the Late Pleistocene. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24 (2):222~230 |
| 62 | 覃军干, 吴国碹, 郑洪波等. 从孢粉、藻类化石组合看长江三角洲第一硬质粘土层的成因及其古环境意义. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24 (5):546~554 Tan Jungan, Wu Guoxuan, Zhen Hongbo et al. Palynomorph assemlages, origin and palaeoenvironmental significance of the upper most hard clay in the deltaic area of the Changjiang River. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24 (5):546~554 |
| 63 | Stanley G J, Hait A K. Deltas, radiocarbon dating, and measurements of sediment storage and subsidence. Geology, 2000, 28 (4):295~298 |
| 64 | Yim W-S. Radiocarbon dating and the reconstruction of Late Quaternary sea-level changes in Hong Kong. Quaternary International, 1999, 55 (1):77~91 |
| 65 | McManus J. Grain size determination and interpretation. In:Tucker M ed. Techniques in Sedimentology. Oxford:Backwell, 1988. 63~85 |
| 66 | Vail P R, Mitchum Jr R M, Todd R G et al. Seismic stratigraphy and global changes of sea-level. In:Payton C E ed. Seismic Stratigraphy——Applications to Hydrocarbon Exploration. American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir, 1977, 26:49~212 |
| 67 | Muto T, Steel R J. The accommodation concept in sequence stratigraphy:Some dimensional problems and possible redefinition. Sedimentary Geology, 2000, 130 (1~2):1~10 |
| 68 | Catuneanu O, Willis A J, Miall A D. Temporal significance of sequence boundaries. Sedimentary Geology, 1998, 121 (3~4):157~178 |
| 69 | Catuneanu O, Abreu V, Bhattacharya J P et al. Towards the standardization of sequence stratigraphy. Earth-Science Reviews, 2009, 92 (1~2):1~33 |
| 70 | 李从先, 闵秋宝, 孙和平. 长江三角洲南翼全新世地层和海侵. 科学通报, 1986, 46 (21):1650~1653 Li Congxian, Min Qiubao, Sun Heping. Holocene strata and transgression on the south side of Changjiang delta. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1986, 46 (21):1650~1653 |
| 71 | 陈中原, 许世远. 尼罗河与长江三角洲晚更新世末期硬土层特征及其成因对比研究. 第四纪研究, 1996,(2):168~175 Chen Zhongyuan, Xu Shiyuan. Comparative study of the Late Pleistocene Nile and Yangtze stiff muds:Sediment and origin. Quaternary Sciences, 1996,(2):168~175 |
| 72 | 王 强, 张玉发, 袁桂邦等. MIS 3阶段以来河北黄骅北部地区海侵与气候期对比. 第四纪研究, 2008, 28 (1):79~95 Wang Qiang, Zhang Yufa, Yuan Guibang et al. Since MIS 3 stage the correlation between transgerssion and climatic changes in the north Huanghua area, Hebei. Quaternary Sciences, 2008, 28 (1):79~95 |
| 73 | Hanebuth T J J, Voris H K, Yokoyama Y et al. Formation and fate of sedimentary depocentres on Southeast Asias Sunda Shelf over the past sea-level cycle and biogeographic implications. Earth-Science Reviews, 2011, 104 (1~3):92~110 |
| 74 | Liu Jingpu, Milliman J D, Gao Shu et al. Holocene development of the Yellow River's subaqueous delta, North Yellow Sea. Marine Geology, 2004, 209 (1~4):45~67 |
| 75 | Liu Jian, Saito Y, Wang Hong et al. Sedimentary evolution of the Holocene subaqueous clinoform off the Shandong Peninsula in the Yellow Sea. Marine Geology, 2007, 236 (3~4):165~187 |
| 76 | Liu Jianguo, Li Anchun, Chen Muhong et al. Sedimentary changes during the Holocene in the Bohai Sea and its paleoenvironmental implication. Continental Shelf Research, 2008, 28 (10~11):1333~1339 |
| 77 | 李文漪, 梁玉莲. 河北东部全新世温暖期植被与环境. 植物学报, 1985, 27 (6):640~651 Li Wenyi, Liang Yulian. Vegetation and environment of the hypsithermal interval of Holocene in estern Hebei Plain. Acta Botanica Sinica, 1985, 27 (6):640~651 |
| 78 | Yi Sangheon, Saito Yoshiki, Oshim Hideaki et al. Holocene environmental history inferred from pollen assemblages in the Huanghe(Yellow River)delta, China:Climatic change and human impact. Quaternary Science Reviews, 2003, 22 (5~7):609~628 |
| 79 | Sun Dongyan, Tan Wenbing, Pei Yandong et al. Late Quaternary environmental change of Yellow River basin:An organic geochemical record in Bohai Sea(Northern China). Organic Geochemistry, 2011, 42 (6):575~585 |
| 80 | 唐克丽, 贺秀斌. 黄土高原全新世黄土-古土壤演替及气候演变的再研讨. 第四纪研究, 2004, 24 (2):129~139 Tang Keli, He Xiubin. Re-discussion on loess-paleosol evolution and climatic change on the Loess Plateau during the Holocene. Quaternary Sciences, 2004, 24 (2):129~139 |
| 81 | 程玉芬, 姜文英. 末次冰盛期以来陕北黄土高原的植被和气候变化. 第四纪研究, 2011, 31 (6):982~989 Cheng Yufen, Jiang Wenying. Vegetation and climate changes since the Last Glacial Maximum in the northern Loess Plateau. Quaternary Sciences, 2011, 31 (6):982~989 |
| 82 | 张 晓, 贾 鑫, 饶志国等. 陇西黄土高原东南部地区末次冰期以来C3/C4植物相对丰度变化及其区域性剖面的对比研究. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33 (1):187~196 Zhang Xiao, Jia Xin, Rao Zhiguo et al. C3/C4 variation since the Last Glacial in the southeastern Longxi Loess Plateau and its comparison with other results. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33 (1):187~196 |
| 83 | 赵得爱, 吴海斌, 吴建育等. 过去典型增温期黄土高原东西部C3/C4植物组成变化特征. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33 (5):848~855 Zhao De'ai, Wu Haibin, Wu Jianyu et al. C3/C4 plants characteristics of the eastern and western parts of the Chinese Loess Plateau during Mid-Holocene and last interglacial. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33 (5):848~855 |
| 84 | 徐炯心. 基于大样本 14C 测年资料的华北平原沉积速率研究. 第四纪研究, 2007, 27 (3):437~443 Xu Jiongxin. A study of depositional rate in the North China plain during the past 40000 years, based on 14C dating data form a large wealth of samples. Quaternary Sciences, 2007, 27 (3):437~443 |
| 85 | 邹逸麟, 谭其骧, 史念海. 历史时期的水系变迁, 黄河. 见: 中国科学院《中国自然地理》编辑委员会主编. 中国自然地理, 历史自然地理. 北京: 科学出版社, 1982. 38~86 Zhou Yilin, Tan Qixiang, Shi Nianhai. Changes of river system in Chinese history, Yellow River. In:Editorial Committee of Chinese Physical Geography of the Chinese Academy of Sciences ed. The Physical Geography of China, Historical Physical Geography. Beijing:Science Press, 1982. 38~86 |
Abstract
To study Holocene evolution of the ancient Yellow River delta in southwestern coast of the Bohai Bay, 6 boreholes penetrated Holocene strata have been detailed sedimentological and chronological studied. 160 samples for grain size and 94 samples for micropaleontological analysis are used to establish sedimentary facies, 22 conventional 14C ages are used to establish exact age frame. Holocene sequence stratigraphy has been devided by the theory of sequence stratigraphy, and evolution of the ancient Yellow River delta has been recovered.
Holocene sequence stratigraphy of the ancient Yellow River delta include of transgressive sequence, sea-level highstand sequence and retrograding sequence. transgressive sequence has main three sedimentary facies, such as coastal marsh, coastal sand bank and incised valley, and its age is form the begin of Holocene to 8.5ka B.P. (1ka B.P. =1000cal.a B.P.). The lower sea-level highstand sequence contains mainly littoral facies in the west, such as coastal marsh and soak lowland, and mainly marine facies in the east, such as tidal sand ridge, prodelta and subtidal zone and so on, and its age is form 8.5ka B.P. to 7.6ka B.P. The upper sea-level highstand sequence contains mainly flood plain facies in west, such as interfluvial lowland, wetland and branch channel, mainly marine facies in the east, such as intertidal flat, river mouth bar, and tidal sand ridge, and its age is form 7.1ka B.P. to 3.0ka B.P. Retrograding sequence has branch channel, interfluvial lowland and crevasse splay, and its age is form 3.0ka B.P. to now.
9.0~10.2ka B.P., the shoreline reached to the northern modern Yellow River delta from the middle of the Bohai Bay, littoral facies had formed in study area. 8.5~9.0ka B.P., the Yellow River had formed incised valley from YS3 to NP1, and formed the dual-texture included coastal marsh and coastal sand bank on both sides of the valley. 7.6~8.5ka B.P., the Yellow River passed YS4 into the sea, and formed under-water channel and estuary. 7.1~7.6ka B.P. was the maximum transgressive period, while the Yellow River did not into the study area, the shoreline located between YS7 and YS2. The western and eastern had formed littoral facies and marine facies respectively. 5.6~7.1ka B.P., the study area was the flank of the ancient Yellow River delta, and formed intertidal flat and river mouth bar. After delta abandoned, tidal sand ridge and shell ridge had formed in YS4 and Miaozhuang respectively. 3.0~5.6ka B.P., the ancient Yellow River passed by the other area into the sea, but the study area had been accumulated to land because that the erosion of loess plateau became intensified in Middle and Late Holocene, the sediment charge of Yellow River increased, so the sedimentation flux of coastal zone increased. 2.6~1.9ka B.P. was the period of Warring States to Western Han Dynasty last stage, the ancient Yellow River passed by YS7 and NP1 into the sea, and formed incised valley. While the river levee of Qi State, Zhao State and Wei State, the sediment charge of Yellow River increased, many branch channels had formed in study area. The Yellow River have passed by Tianjin, Dongyang and the northern Jiangsuan into the sea since 1.9ka B.P.
 2015, Vol.35
2015, Vol.35
