铀(U)是自然界中最重的天然元素。U的价态随氧化-还原条件的变化而变化: 在还原环境下多形成难溶于水的+4价铀离子沉淀[1],而在氧化环境中多形成易溶于水的+6价铀酰离子[UO2]2+随溶液迁移[2],并易与碳酸根离子(CO32-)、 磷酸根离子(PO43-)和氟离子(F-)形成络合离子[1]。岩溶地下水由于具有较高的CO2分压(pCO2)和pH值,铀酰离子主要以碳酸根离子络合态的形式存在[2, 3]。在表生环境下,土壤氧化还原状态(Eh)与土壤水分含量密切相关,水分含量降低有利于氧化环境形成和土壤Eh上升,因而有利于U的迁移。氧化还原状态也会影响U的同位素组成(234 U/238 U)[4]。一些研究发现石笋234 U/238 U和生长速率之间存在明显关系[5, 6, 7],而石笋的沉积和生长速率又与气候环境尤其是降水量变化密切相关[8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13]。此外,来源也是影响岩溶洞穴沉积234 U/238 U变化的重要因素[6, 14]。因此,石笋的U含量(或U/Ca比)和234 U/238 U是研究过去气候环境变化的重要指标[4, 5, 6, 7, 14, 15, 16]。
国内对石笋234 U/238 U变化进行的研究非常少见[15, 16],仅见报道了况润元等[15]对华东葫芦洞两支石笋234 U/238 U变化的分析及杨琰等[16]对西南地区9支石笋的研究。况润元等[15]在国内首次进行了这方面的研究。他们发现虽然两支石笋234 U/238 U存在差异,但234 U/238 U的相对变化与气候环境的对应关系是一致的: 在相对温暖湿润时期葫芦洞石笋234 U/238 U较高,而在相对寒冷干旱时期则相反。况润元等[15]认为葫芦洞石笋234 U/238 U长期变化趋势与234 U的选择性淋洗(相对于 238 U)有关: 相对温暖湿润的气候环境导致更多的234 U被选择性淋洗到地下水中,并最终导致岩溶洞穴沉积中234 U/238 U的升高。由于我国季风区植被发育与季风气候的关系,况润元等[15]的解释与将石笋234 U/238 U作为古降水指标的解释[4, 5, 6, 7]基本一致; 另外,还没有对U来源对234 U/238 U的影响进行的研究。
本文报道了采自川东北的石笋SJ1的234 U/238 U变化初步研究结果。SJ1采自诺水河溶洞群的宋家洞(107°10′45″E,32°24′46″N),总长244mm。该地区属于典型的季风气候,年平均温度大约15℃,年降水量1000~1200mm,降水主要集中在夏半年。宋家洞发育在晚二叠纪石灰岩中; 灰岩之上覆盖的土层很薄,通常厚度<30cm,地表土壤绝大部分来源于粉尘沉积物; 区域植被以乔木为主,包括松、 柏和一些阔叶落叶树种[17]。该石笋氧同位素(δ 18 O)记录已另文发表[18]。 234 U/238 U同位素组成的年龄依据文献[18]中建立的年龄模式,根据该模式,这些234 U/238 U同位素组成的年龄范围在43~17ka,对应深度(或离SJ1顶部距离)240~9mm。
图1显示了SJ1的234 U/238 U长期变化趋势。一方面,可以看到,在相对冷干的阶段(如26~27ka以来的末次冰盛期)234 U/238 U较低。这与之前国内外的多数研究结果相似[4, 5, 6, 7, 14, 15]。似乎反映了与古降水有关的土壤氧化还原条件是影响SJ1的234 U/238 U长期变化的主要因素; 另一方面,SJ1的234 U/238 U长期变化趋势显示了与黄土高原粉尘记录长期变化趋势[19]很好的一致性。由于研究地点靠近粉尘沉积中心,地表土壤就基本来自粉尘沉积物[20]。因此,SJ1的234 U/238 U长期变化也可能受到U来源的影响。
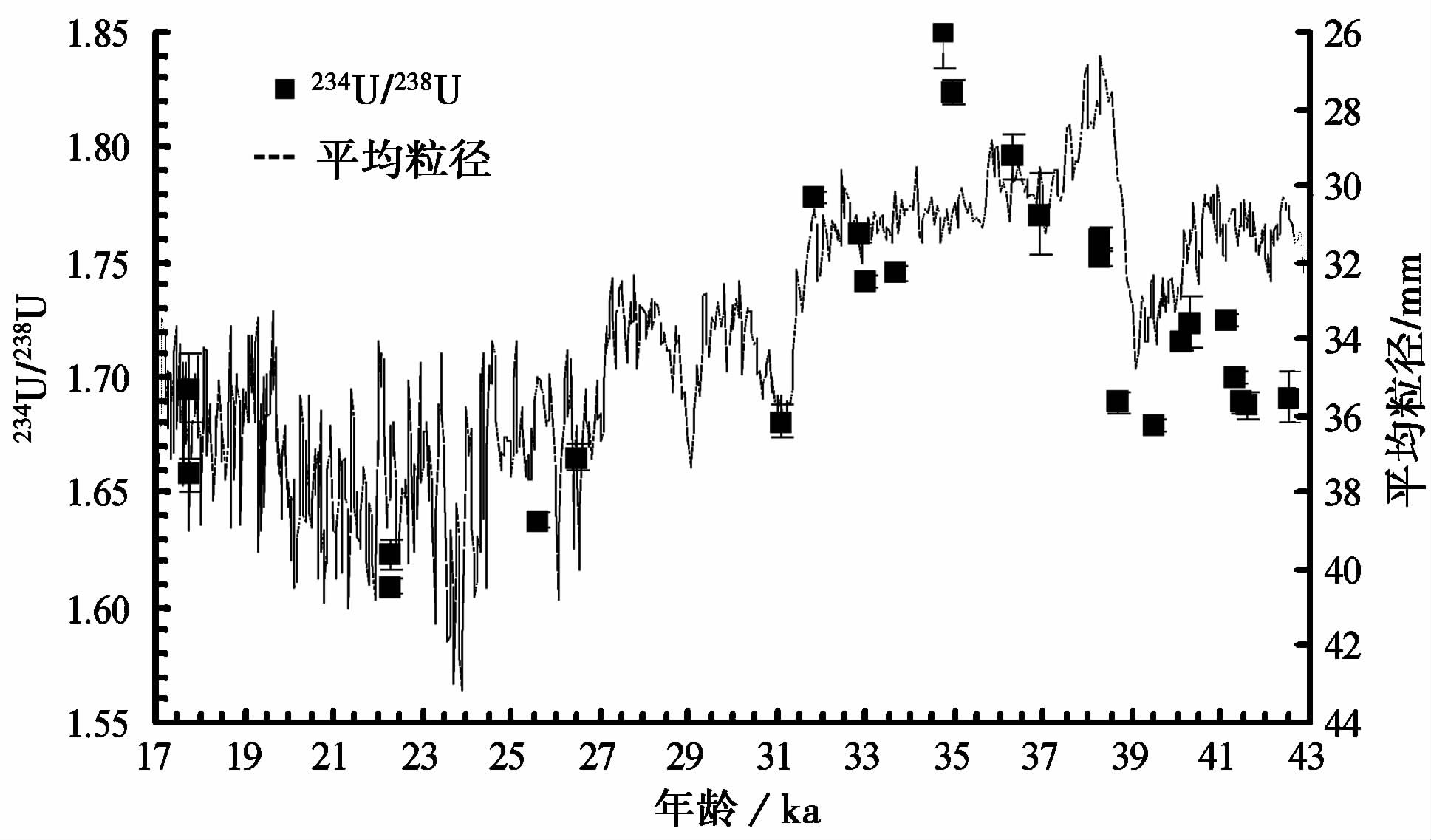
|
图1 石笋SJ1的234 U/238 U变化(黑色短柱状符号,误差棒代表2σ误差)及与黄土高原泾塬黄土平均粒径[19]的比较 |
如果SJ1的234 U/238 U长期变化主要受到土壤的氧化还原条件和湿度的影响,也就是可以作为古地下水水文和降水变化的指标,则在目前对石笋的 δ 18 O记录的气候环境意义解读存在重大争议的条件下,石笋的234 U/238 U记录可能从另一侧面为我们提供过去夏季风气候变化的重要信息; 如果SJ1的234 U/238 U长期变化主要受到U的来源的影响,则该地区石笋的234 U/238 U变化可以成为指示粉尘活动的又一重要指标。无论如何,图1显示了该地区石笋的234 U/238 U变化在研究过去气候环境变化方面的潜在重要价值。不过,由于目前没有对该地区粉尘沉积和现代岩溶地下水的234 U/238 U进行分析,因而还不能对这两方面的影响机制(“土壤氧化还原条件”和“U的来源”)进行区分和评估,还有待于在今后的工作中进行更深入的研究。
| 1 | Gascoyne M. Geochemistry of the actinides and their daughters. In:Harmon R S ed. Uranium-Series Disequilibrium:Applications to Earth, Marine, and Environmental Sciences. Oxford:Clarendon Press, 1992. 910 |
| 2 | Langmuir D. Uranium solution-mineral equilibria at low temperatures with applications to sedimentary ore deposits. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1978, 42 (6):547~569 |
| 3 | Bonotto D M, Andrews J N. The mechanism of 234 U/238 U activity ratio enhancement in karstic limestone groundwater. Chemical Geology, 1993, 103 (1):193~206 |
| 4 | Zhou J, Lundstrom C C, Fouke B et al. Geochemistry of speleothem records from southern Illinois:Development of 234 U/238 U as a proxy for paleoprecipitation. Chemical Geology, 2005, 221 (1):1~20 |
| 5 | Kaufman A, Wasserburg G J, Porcell D et al. U-Th isotope systematics from the Soreq Cave, Israel and climatic correlations. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 1998, 156 (3):141~155 |
| 6 | Hellstrom J C, McCulloch M T. Multi-proxy constraints on the climatic significance of trace element records from a New Zealand speleothem. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, 179 (2):287~298 |
| 7 | Zhao J, Xia Q, Collerson K D. Timing and duration of the Last Interglacial inferred from high resolution U-series chronology of stalagmite growth in Southern Hemisphere. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2001, 184 (3):635~644 |
| 8 | Genty D, Quinif Y. Annually laminated sequences in the internal structure of some Belgian stalagmites——Importance for paleoclimatology. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 1996, 66 (1):275~288 |
| 9 | Wang X, Auler A S, Edwards R L et al. Wet periods in Northeastern Brazil over the past 210 kyr linked to distant climate anomalies. Nature, 2004, 432 (7018):740~743 |
| 10 | 董进国. 湖北三宝洞石笋生长速率及其古气候意义. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33 (1):146~154 Dong Jinguo. The growth and the paleoclimatic significance of stalagmites in Sanbao Cave, Hubei. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33 (1):146~154 |
| 11 | 桑文翠, 张德忠, 王晓锋等. 甘肃武都万象洞方解石现代沉积控制因素分析. 第四纪研究, 2013, 33 (5):936~944 Sang Wencui, Zhang Dezhong, Wang Xiaofeng et al. Analysis of modern calcite deposition controlling factors in Wanxiang Cave from Wudu, Gansu. Quaternary Sciences, 2013, 33 (5):945~953 |
| 12 | 张振球, 刘殿兵, 汪永进等. 中全新世东亚季风年至10年际气候变率: 湖北青天洞5.56~4.84ka B.P. 石笋年层厚度与地球化学证据. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34 (6):1246~1255 Zhang Zhenqiu, Liu Dianbing, Wang Yongjin et al. Annual-to decadal-scale variability of Asian monsoon climates during Mid-Holocene:Evidence from proxies of annual bands and geochemical behaviors of a speleothem from 5.56ka B.P. to 4.84ka B.P. in Qingtian Cave, Central China. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34 (6):1246~1255 |
| 13 | 谭亮成, 蔡演军, 安芷生等. 石笋氧同位素和微量元素记录的陕南地区4200~2000a B.P. 高分辨率季风降雨变化. 第四纪研究, 2014, 34 (6):1238~1245 Tan Liangcheng, Cai Yanjun, An Zhisheng et al. High-resolution monsoon precipitation variations in southern Shaanxi, Central China during 4200~2000a B.P. as revealed by speleothem δ18O and Sr/Ca records. Quaternary Sciences, 2014, 34 (6):1238~1245 |
| 14 | Frumkin A, Stein M. The Sahara-East Mediterranean dust and climate connection revealed by strontium and uranium isotopes in a Jerusalem speleothem. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2004, 217 (3):451~464 |
| 15 | 况润元, 汪永进, 张向华等. 石笋铀同位素组成对土壤环境变化的指示. 科学通报, 2002, 47 (13):1022~1026 Kuang Runyuan, Wang Yongjin, Zhang Xianghua et al. Implications for soil environment from uranium isotopes of stalagmites. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2002, 47 (13):1022~1026 |
| 16 | 杨 琰, 袁道先, 程 海等. 洞穴石笋初始234 U/238 U值变化的古气候记录意义. 地质学报, 2008, 82 (5):692~701 Yang Yan, Yuan Daoxian, Cheng Hai et al. Initial234 U/238 U variation of stalagmites:Implications for paleoclimate reconstruction. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2008, 85 (5):692~701 |
| 17 | Zhou H, Feng Y, Zhao J et al. Deglacial variations of Sr and 87 Sr/86 Sr ratio recorded by a stalagmite from Central China and their association with past climate and environment. Chemical Geology, 2009, 268 (3):233~247 |
| 18 | Zhou H, Zhao J, Feng Y et al. Heinrich event 4 and Dansgaard/Oeschger events 5~10 recorded by high-resolution speleothem oxygen isotope data from Central China. Quaternary Research, 2014, 82 (2):394~404 |
| 19 | Sun Y, Wang X, Liu Q et al. Impacts of post-depositional processes on rapid monsoon signals recorded by the last glacial loess deposits of Northern China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2010, 289 (1):171~179 |
| 20 | Zhou H, Greig A, Tang J et al. Rare earth element patterns in a Chinese stalagmite controlled by sources and scavenging from karst groundwater. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2012, 83 :1~18 |
 2015, Vol.35
2015, Vol.35

