The article information
- Guang-Hua Fu, Xue-Mei Liu, Yan-Fu Chen, Jin Yuan
- Fast-growing forest pruning robot structure design and climbing control
- Advances in Manufacturing, 2015, 3(2): 166-172
- http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40436-015-0114-5
-
Article history
- Received: 2014-12-29
- Accepted: 2015-05-08
- Published online: 2015-06-18
2 Shandong Provincial Key Laboratory of Horticultural Machinery and Equipment, Taian 271018, Shandong, P.R. China
Fast-growing forest is plantation with short rotation cycle, and is widely used in paper-making industry. Because it has many good qualities,such as fast-growing advantage, good material,high afforestation survival rate,etc. So fastgrowing forest has good economic value. Reasonable pruning can promote the growth of trees,improve the trees on the straight,improve the growth environment of trees, and increase the income of forest management [1]. Reasonable pruning can also increase the upper photosynthesis. The robot mainly prunes all the collateral branches of the net consumption to form a reasonable branch structure and crown height percentage. At present,the pruning tools, such as hand saw,machete,are relatively backward and primitive. So it is of very important significance to study the automatic pruning device of the fast-growing forest.
Pruning machines produced abroad are very advanced [2]. Climbing pruning machines manufactured by Japanese company have a high degree of automation,they use wireless control technology to climb tree trunks,their pruning saw is the chain saw blade and they use low-pressure tires to climb trees [3, 4]. Pruning machines manufactured in Japan have high production cost,high cost of repair andmaintenance,and they require technicians with certain professional skills. So they can not meet the need of Chinese forestry. Pruning machines produced in the United States,Sweden are manual type without power. The main principle is to improve ordinary pruning saws,and add a scalable "arm" in the original mechanical machine. They are simple,convenient,practical, of low cost,and they do not require technicians with certain professional skills [5]. But they may have defects such as easily broken saws in practice,big labor intensity,and low efficiency.
In China,research level of the pruning machinery is backward. At present,fast-growing forestry pruning machines include hand-held,vehicular,and other forms. Hand pruning machines are divided into no power system and power system. Hand-held pruning tools without power are handsaw,machete,etc. These machines can quickly and easily prune small branches,but the pruning height is only 4 m-6 m,which can not meet the requirements [6]. Hand-held pruning tools with power rely on small gasoline engine to provide power. Saw chain or circular saw blade works through soft shaft. These machines with simple structure and high efficiency have many disadvantages, such as heavy joystick,large cutting vibration amplitude, large gasoline noise,etc.,which can not meet the requirements of working comfort [7]. Vehicular pruning machine is a kind of pruning machine with small labor intensity and high efficiency. The machines are mainly used to prune the city street trees,but not suitable for forest and forestry [8].
This paper introduces the robot structures and the cosimulation ofADAMSand Matlab,then develops the control system,and carries on the prototype experiment of forest. 2 Pruning robot 2.1 Pruning robot structure
The mass of the robot is 40 kg,the speed of climbing trees is 20 mm/s,and the robot can climb the tree trunk with diameter of 150 mm-350 mm. The maximum cutting diameter is 30 mm. The power of the robot is provided by 24 V DC battery,so robot can easily work in the field. The pruning robot structure includes: climbing mechanism, turntable mechanism,pruning mechanism.
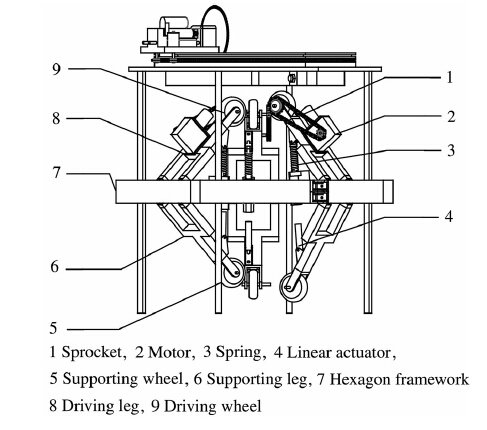
Climbing mechanism includes climbing device and clamping device,as shown in Fig. 1. Climbing device includes driving legs,drive motors,driving wheels and drive chain; clamping device includes supporting legs,supporting wheels,linear actuators and pressing springs. Robot climbs tree trunks depending on the climbing mechanism. Climbing device and clamping device have three same mechanism groups (see Fig. 2). Mechanism is average distribution,and the interval is 120°.
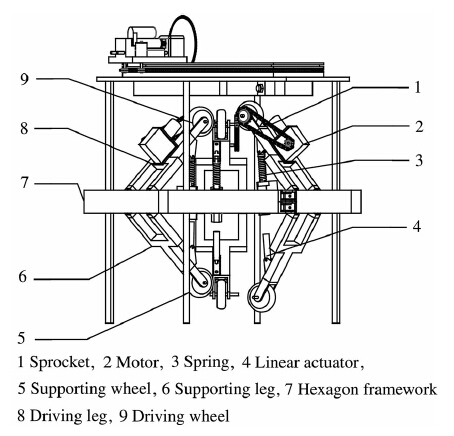 |
| Fig. 1 Pruning robot |
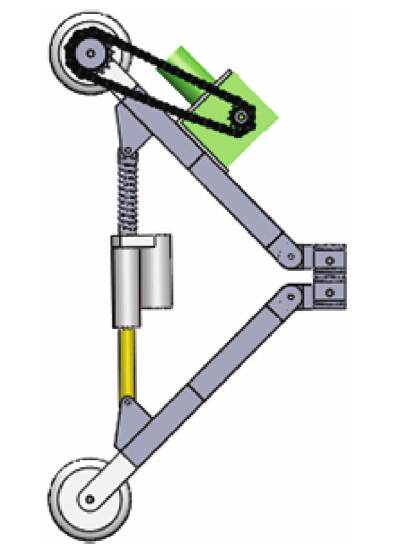 |
| Fig. 2 Mechanism of the climbing device and clamping device |
Turntable mechanism includes circular orbit,slide-way and turntable chain (see Fig. 3). The slide-way includes supporting slide,chain slide and wheel slide.
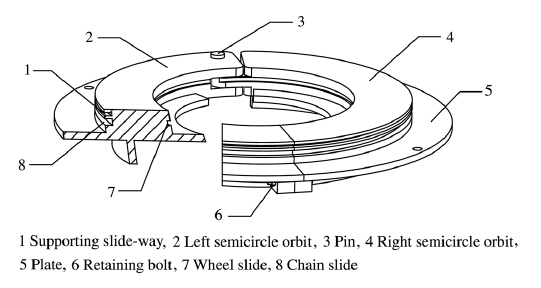 |
| Fig. 3 Turntable mechanism |
Pruning mechanism includes flat base,turntable motor, turntable gear,turntable wheel,optical axis,radial feed linear actuator,pruning saw motor and circular saw (see Fig. 4). Pruning mechanism can rotate around the turntable mechanism to prune branches.
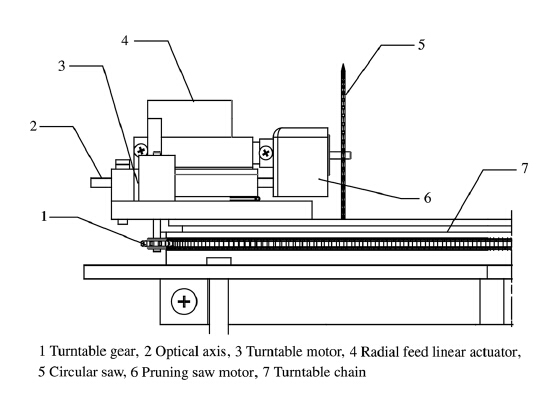 |
| Fig. 4 Pruning mechanism |
Starting the robot,clamping device can fix the robot on the trunk,and climbing device drives the robot to climb tree trunks. When the robot climbs to a certain height,pruning mechanism spins around the turntable mechanism to carry out pruning operations. The robot mainly prunes all the collateral branches of the net consumption to form a reasonable branch structure and crown height percentage. 3 Dynamic model of the pruning robot 3.1 Force analysis of pruning robot
This paper sets up the robot’s force model,and selects a group of driving legs and driving wheels to analyze force condition [9, 10, 11, 12]. The force model diagram is shown in Fig. 5.
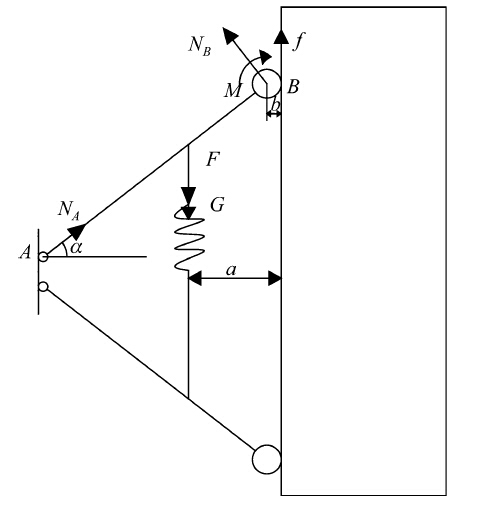 |
| Fig. 5 Force model diagram |
According to the force balance (see Fig. 5),we can get


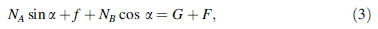
We can get Eq. (4) from Eqs. (1)-(3):

We set up the torque equation in point B:

As shown in Eq. (5),M is associated with f and f. So, selecting the appropriate spring and motor can ensure that pruning robot climbs in the tree trunk.
As shown in Fig. 6,when pruning robot climbs the tree burl,the elongation L1 of the spring that climbs the tree burl will be greater than the other two springs,and the spring tension F1 will also be greater than the other two springs tensions.

As Eq. (4) shows, f increases with F.

Pruning robot will tilt,because of the height of the climbing leg that climbs the tree burl is less than the other legs. When spring elongation is greater than critical value, pruning robot will fall from the tree trunk.
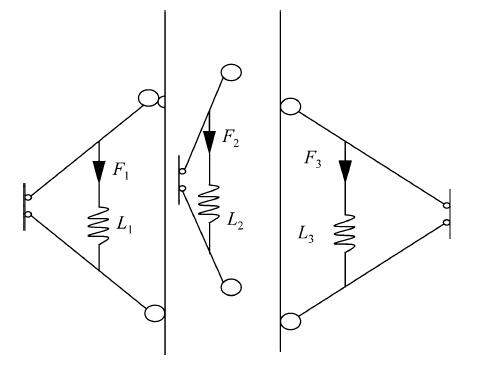 |
| Fig. 6 Schematic diagram of robot climbing the tree burl |
According to the force analysis of the pruning robot,we use ADAMS software to establish the simulated kinematic model of the robot. Firstly,we use Solidworks software to build the pruning robot’s 3D model,and use a dedicated interface module to import it into ADAMS software. Secondly, we build the simulated kinematic model referring to the physical characteristics,unit,gravity,restriction relations. Finally,by looking for the mechanical design manual,we add friction in ADAMS,as shown in Fig. 7.
 |
| Fig. 7 Pruning robot simulation diagram |
This paper confirms that the simulated kinematic model is correct through the ADAMS/view simulation analysis [13, 14, 15]. 3.3 Analysis of pruning robot simulation results
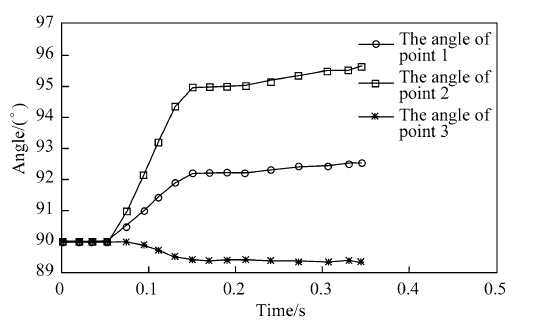
We can get the robot’s posture curve through simulation,as shown in Fig. 8. This paper establishes the points in the connection parts of hexagon framework and driving legs, supporting legs (point 1,point 2,point 3),and point 3 climbs the tree burl.
 |
| Fig. 8 Simulation of the angles at three points |
As shown in Fig. 8,the curves reflect the angles of robot in vertical direction,the three initial angles are 90°, which shows that the robot is level. Then,after climbing a period of time,when the three angles’s deviations from 90° increase,tilt phenomenon can appear. As the tilt angle is bigger,pruning robot will fall off from the tree trunk.
Because point 3 climbed the tree burl,so the time that angle of point 3 began to change is longer than the rest two points,and the range of the tilt is less than the rest two points. The results of simulation are consistent with the force analysis in Sect. 2.1. 4 Determination of the input and output of ADAMS
We use ADAMS/control module and Matlab/Simulink module to build the control plan. ADAMS simulation software provides three-dimensional model of the robot prototype, Matlab software provides control algorithm to control the robot’s motor speed at different locations. Through the data interface between them (ADAMS/controls module), Matlab software sends prototype motor speed control command to the ADAMS,the ADAMS sends feedback of the prototype tilt angle to Matlab,they form a complete closedloop control system and co-simulation [16, 17, 18].
We take the torques of three driving wheels as inputs, and the three-point orientation measurements as outputs,as shown in Fig. 9.
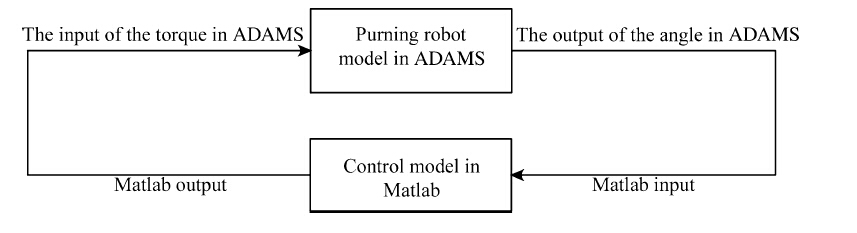 |
| Fig. 9 ADAMS/Matlab input and output |
Through the analysis of the ADAMS simulation curve,we can find that the angle shows the tilt of the frame. We use the PID controller to control motor speed of adjacent driving legs to adjust the tilt of the frame,and then pruning robot can successfully climb the tree trunk and tree burl [19, 20, 21].
PID controller is a linear controller,and it constitutes a control deviation (e(t) = r(t) - y(t)) according to the given value r(t) and the actual output value y(t). PID control rule is
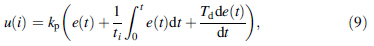
The control scheme is shown in Fig. 10. In the process of co-simulation,mechanical dynamics solution is carried out by implanting ADAMS module,control solution is carried out by controlling the software solver. The connection of the interface varies by the state space. When the simulation runs,the results of the simulation curves can be observed and imported in Matlab\Simulink. And after the simulation,the ADAMS simulation animation can be watched after treatment (post process) module.
 |
| Fig. 10 Control block diagram |
Through Fig. 11,we can get that three angles are kept at 90°,and their deviations from 90° are little. The simulation curves show that the control plan can ensure that pruning robot can climb steadily and cross the tree burl.
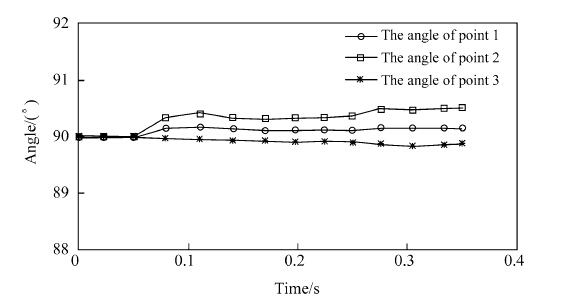 |
| Fig. 11 The angle of co-simulation |
According to the result of co-simulation,this paper designs the controller (see Fig. 12).
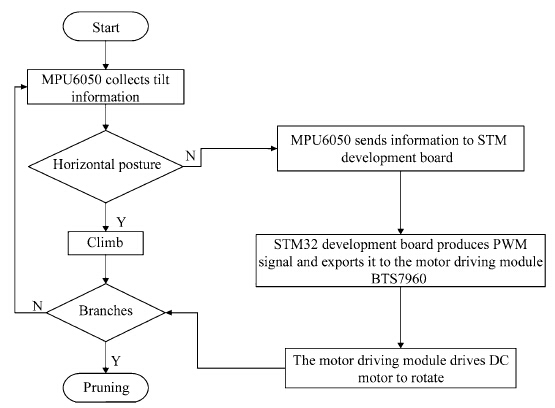 |
| Fig. 12 System control block diagram |
When the tilt problems appear in the climbing process, the motor speeds at different positions can be controlled to adjust pruning robot posture and keep the level state. When the robot starts to climb tree,MPU6050 module collects tilt information,if the robot is horizontal,robot continues to climb tree until meeting the branch trunk; if the robot is not horizontal,MPU6050 module collects tilt information of the robot and sends it to the STM32 development board. Then,STM32 development board produces PWM signal and imports it to the motor driving module BTS7960. Finally,the motor driving module drives DC motor to rotate. 6.2 Experiment purpose
After the completion of the prototype,this paper conducts the prototype experiments on campus. The main purpose of the experiment has two aspects: the ability determination of climbing system and raised climbing trunk; the effect determination of pruning system and residual amounts of branches. 6.3 Experiment content
The experiment was conducted in Shandong Agricultural University,as shown in Fig. 13. The diameter of the tree is 250 mm,and the trunk surface has 630 mm raised parts. The experiment is divided into four stages: pruning robot climbs 1 m on the trunk without raised trunk; pruning robot climbs 1 m on the trunk with raised trunk; static clings in the trunk for 20 min; pruning saw cuts branches.
 |
| Fig. 13 The prototype experiment |
This paper conducts many experiments and observes the effect,as shown in Fig. 13,and then measures the angle between the frame and the trunk at different heights. The experiment results are shown in Table 1.
In this paper,we design a pruning robot model,establish the simulated kinematic model,research the pruning tilt problem through the co-simulation between ADAMS and Matlab,and put forward a method to control the motor speed of different driving legs. Through the prototype experiment,pruning robot can climb the tree,and cross the tree burl. Pruning robot can cut off branches,and the residual amount of branches is small.
Acknowledgments This work was supported by the Science and Technology Development Program of Shandong Province (Grant No. 2013GNC11203),the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51475278 & 3110146) and the National Key Technology R&D Program (Grant No. 2014BAD08B01-2).| 1. | Huang Y, Yuan YF, Kong HW (2002) The effect of pruning on growth and wood mechanical properties of Pinus koraiensis. J Northeast For Univ 01:76-77 | |
| 2. | Kim S, Spenko M, Trujillo S (2008) Smooth vertical surface climbing with directional adhesion. IEEE Trans Rob 24:65-74 | |
| 3. | Kawasaki H, Murakami S, Hirai K et al (2008) Novel climbing method of pruning robot. In: Proceedings of SICE Annual Conference2008, Japan, pp 160-163 | |
| 4. | Ueki S, Kawasaki H, Ishigure Y et al (2011) Development and testal study of a novel pruning robot.Artif Life Robot 16:86-89 | |
| 5. | Fauroux J, Morillon J (2010) Design of a climbing robot for cylindro-conic poles based on rolling self-locking. Ind Robot37(3):287-292 | |
| 6. | Li SW, Wang SY, Wang H et al (2008) Tree pruning cut machinery present situation and development trend. For Mach Woodwork Equip 01:15-16 | |
| 7. | Xu J (2011) Study on the fuzzy-controlled driving system of plantation pruning robot. Dissertation, Northeast Forestry University, Harbin, China | |
| 8. | Wang C, Zhang H, Yu J (2013) Analysis on working principle and existing problem of the pruning machinery of garden and fruit industry. Guangdong Agric Sci 03:176-178 | |
| 9. | Liu GZ (2006) The mechanism design and kinematics analysis of climbing tree robot. Dissertation, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin, China | |
| 10. | Sun W, Huang HS, Wang JL et al (2013) A new type of tree climbing device and its theoretical analysis. For Mach Woodwork Equip 41:20-22 | |
| 11. | Liu JZ, Liu W, Mao HP et al (2014) Design and coordinated motion simulation of transplanting robot for column cultivation. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 45(7):48-53 | |
| 12. | Xiong JT, Ye M, Zou XJ et al (2013) System design and performance analysis on multi-type fruit harvesting robot. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 44(Supp1):230-235 | |
| 13. | Du YF, Zhu ZX, Mao ER et al (2011) Simulation on small-scale corn harvester for hilly area based on ADAMS. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 42(Z1):1-5 | |
| 14. | Du YF, Mao ER, Song ZH et al (2011) Simulation on corn plants in harvesting process based on ADAMS. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 43(Z1):106-111 | |
| 15. | Li YH, Nie LX (2010) ADAMS virtual prototype-based multibody system dynamics simulation. Eng J Wuhan Univ43:757-761 | |
| 16. | Chen K, Yang XJ, Yan H et al (2013) Design and parameter optimization of seedling pick-up mechanism based on Matlab. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 44(Supp1):24-26 | |
| 17. | Alan W (2008) Study of fuzzy control for controllable suspension based on ADAMS and Matlab co-simulation. In: Proceedings of2008 International Conference on Modelling, Identification and Control, Innsbruck, Austria, February 2008 | |
| 18. | Xu JZ, Diao Y, Luo H et al (2012) Matlab/Simulink and ADAMS based co-simulation for self-balance robot. Mod Electron Tech35:90-92 | |
| 19. | Song KP, Hu PH, Li BS (2007) A control system for parallel manipulator based on Matlab and MCU. Trans Chin Soc Agric Mach 38(5):147-149 | |
| 20. | Ying ZE, Ping XL, Chen LG (2012) Co-Simulation of doubleloop PID control inverted pendulum based on ADAMS and Matlab. J Mech Transm 36:64-67 | |
| 21. | Huang KY, Chen Q (2012) Robot motion control based on digital PID algorithm. Autom Appl 12:73-75 | |
 2015, Vol. 3
2015, Vol. 3