文章信息
- 黄硕, 刘才兄, 邓源, 张翠红, 范思萌, 郑建东, 王丽萍.
- Huang Shuo, Liu Caixiong, Deng Yuan, Zhang Cuihong, Fan Simeng, Zheng Jiandong, Wang Liping
- 世界主要国家和地区传染病监测预警实践进展
- Progress in the practice of surveillance and early warning of infectious diseases in major countries and regions
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2022, 43(4): 591-597
- Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2022, 43(4): 591-597
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20211105-00856
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2021-11-05
全球新型冠状病毒肺炎(新冠肺炎)大流行再次警示我们,传染病对人类的威胁从未远去。我国把增强早期监测预警能力作为健全公共卫生体系当务之急,推动建立智慧化预警多点触发机制,健全多渠道监测预警机制,提高实时分析、集中研判的能力[1]。传染病监测预警是指通过长期、连续、系统地收集、整理、分析和解释传染病在人群中的动态分布及其影响因素的资料,将有关信息及时反馈给相关人员或机构,在传染病暴发或流行发生前以及发生早期发出警示信号,以提醒暴发或流行可能发生或其发生的范围可能扩大的风险[2-3]。自WHO在第21届世界卫生大会上明确监测在公共卫生领域的内涵和意义以来,越来越多的国家和地区建立了监测预警系统,并在数据来源、技术方法、信息发布等方面形成了多元化格局,对我国建立健全智慧化多点触发、多渠道监测预警机制具有很好的借鉴意义。本文通过对世界主要国家和地区的传染病监测预警实践进行综述,探讨了传染病监测预警领域的发展方向,以期为加强我国传染病监测预警体系建设和能力提升提供参考。
一、传染病监测传染病监测是预警的基础。传染病监测历史悠久,美国CDC在20世纪中叶首次系统阐明了疾病监测原理并应用于疾病预防控制实践,在WHO的推动下,监测是传染病防控的基石这一理念被广泛接受[4]。随着微生物学和检验检测技术的发展,病原体实验室监测登上历史舞台,并逐步成为各国和地区传染病监测的重要组成部分;20世纪90年代中后期,能够早期探测异常的症状监测得到了更多重视,传染病监测及其系统发展呈现出多元化趋势[5-12]。
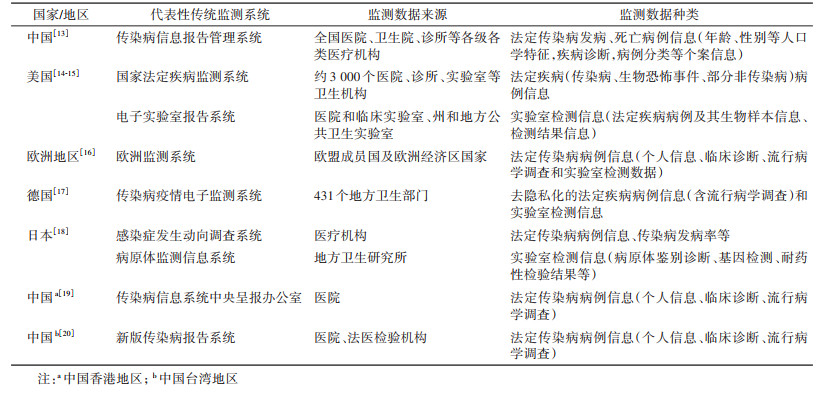
1. 传统监测:基于病例临床或实验室确诊信息的监测手段,其应用较早、覆盖广泛、技术成熟,多依赖医疗卫生机构被动报告,主要包括法定传染病报告和病原体实验室监测(表 1)。我国的传染病信息报告管理系统(National Notifiable Diseases Reporting System,NNDRS)实现了基于医疗卫生机构的法定传染病病例实时、在线、直接报告,对病例个案、诊断及流行病学信息等进行监测,可获得人群传染病发病及死亡数据。美国通过国家法定疾病监测系统(National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System,NNDSS),对覆盖范围内约3 000个卫生机构开展法定疾病病例信息监测,使用电子实验室报告(electronic laboratory reporting,ELR)系统监测病例生物样本的检测和结果信息等。
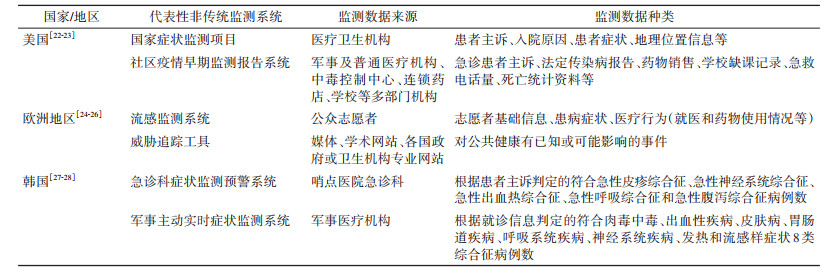
2. 非传统监测:不依赖特定的诊断,而是基于非特异临床症状和传染病相关现象的监测手段,相对于传统监测,更加注重早期多源数据的使用,多属于主动监测范畴,主要包括症状监测、事件舆情监测以及药物销售、学校缺课等多源数据监测。其中,症状监测应用最多:通过持续、系统地收集、分析临床明确诊断前能够指示疾病暴发的相关资料并作出合理解释,以及时发现疾病在时间和空间分布上的异常聚集[21]。如我国已在北京奥运会、上海世博会等大型人群聚集性活动中,对发热、腹泻、皮疹等重点症状进行监测并起到了积极作用[9-10]。欧洲地区针对流感样病例和急性呼吸道感染病例开发了Influenzanet系统,事先收集志愿者的基础信息,再以调查问卷的形式每周采集志愿者是否出现发热、流涕、肌肉酸痛等症状以及出现症状后的医疗行为,实现在公众中开展症状监测。此外,传染病相关多源数据的监测也逐渐丰富,如美国社区疫情早期监测报告系统(Early Notification of Community-Based Epidemics,ESSENCE),对急诊患者主诉、药物销售、学校缺课记录、卫生热线记录等医疗相关数据进行监测。欧洲地区开发了威胁追踪工具(threat tracking tool,TTT),对媒体、学术网站、各国政府或卫生机构传染病公告等途径发布的威胁事件开展持续监测追踪等(表 2)。
传染病预警的基本原理是通过一定的预警技术,从传染病监测数据中发现和识别超出期望常态水平的异常情况[8],即预警是监测系统的重要产出之一,其发展与监测历史基本契合。最初的预警系统多基于法定报告传染病监测建立,如美国在军事医疗机构中基于病例监测进行早期预警的ESSENCE系统、我国对法定传染病监测数据进行分析探测的国家传染病自动预警系统(China Infectious Diseases Automated-Alert and Response System,CIDARS)等[8, 29]。随着症状监测以及更广泛的非传统监测不断涌现,预警数据源极大丰富,推动了预警系统的多元化发展,如WHO建立的全球公共卫生情报网络(Global Public Health Intelligence Network,GPHIN),使用非政府渠道的媒体监测数据进行预警,一定程度上避免了政府对信息干预的影响,提高了预警及时性[30]。美国2004年实施的Biosense系统,根据军事医疗机构中监测的发热、胃肠道症状、出血性疾病等11种综合征数据进行早期预警[31],后又加入了对药品销售量、学校缺课记录、急救车派遣量等数据的探测分析。就传染病预警而言,预警数据源是基础,预警模型分析技术是核心,预警信息发布是影响预警效果的重要环节。
1. 预警数据源:
(1)临床和实验室诊断数据:即传统监测数据,具有预警准确性高的优势,是当前预警数据源中最重要的组成部分。如我国基于此类数据运行的CIDARS可以在病例异常增加、出现人群聚集或发生单例的敏感病例(如鼠疫、新冠肺炎、人感染禽流感等)时实现自动预警[29, 32]。值得注意的是,李中杰等[33]、张洪龙等[34]的评价研究发现,虽然CIDARS信号响应率和响应及时性较好,但疑似信号比例较低,这种现象在国际层面也普遍存在,可能原因是追求高灵敏度导致的系统过于敏感,特异度无法保证。此外,由于这些数据产生于病例诊断后且需要被动上报,导致CIDARS的预警及时性不足,特别是对新发传染病(如新冠肺炎)暴发无法发挥预警作用。总之,基于临床和实验室诊断数据的预警高度依赖报告单位质量,易受诊断能力、队伍建设、地方干预等因素影响导致信息滞后[35-38],对新突发传染病往往难以实现早期预警,需要其他多点触发机制加以补充。
(2)症状监测数据:症状监测数据不需要等待临床和实验室确诊,能与基于临床和实验室数据的预警形成较好补充。如美国佛罗里达州在2016-2017年利用国家症状监测项目开展的症状监测,发现了17例未报告的寨卡病毒感染病例,帮助州卫生部门及时采取了防控措施[39]。Canas等[40]在英国开展的使用自我报告症状监测探测新冠肺炎感染风险的研究,初步取得了较好效果,在遏制疫情发展和分配医疗卫生资源方面,具有应用前景。但使用症状监测数据预警,存在特异性低的问题,容易产生假阳性信号,导致早期监测预警效果不理想,且症状监测预警系统建设成本更高、分析技术更困难,影响了大规模的推广应用[41-42]。
(3)其他多源数据:随着大数据的发展和应用,传染病预警数据源进一步扩展到了其他与传染病相关的行为和社会活动领域,这些多源数据往往发生更早、传播更快,有利于更早期捕捉异常信号、推动预警工作的“关口前移”。如美国ESSENCE,将临床数据和非临床数据同时纳入监测分析,在保证准确性的同时,增强了预警感知能力,近些年在水源性疾病、结核病、落基山斑疹热等传染病的预警追踪中发挥了重要作用[23]。WHO建立的GPHIN,通过每天自动检索分析全球范围9种语言的互联网新闻报道(超30 000个数据源),探测传染病暴发的早期信号,在传染性非典型肺炎、中东呼吸综合征、埃博拉出血热等疫情预警中发挥了重要作用[43]。但多源数据的信息可靠性得不到保证,用于预警时,“信号-噪声比”低会耗费大量公共卫生资源,给预警分析处理技术提出了更高的要求。如曾被寄予厚望的谷歌流感趋势,几次修改算法也没能很好地校正数据,并在2009年和2013年分别出现了明显低估和高估真实流感流行的情况,目前也不再更新[44-46]。
2. 预警技术方法:
(1)时间预警模型:其基本原理是根据特定区域内同期历史指标(如发病率)资料设置阈值,若当前监测数据超过该阈值或者在某时间段内发生聚集,就根据既定规则发出预警信号。不同预警系统使用的时间预警模型有所差异,如美国在ESSENCE中,使用指数加权移动平均模型(early aberration reporting system),将当前监测数据与过去监测数据的时间加权平均值(时间越近权重越大)进行比较分析,对短期波动具有较高敏感性,并引入自适应多元回归模型校正节假日效应,以避免因节假日就诊人数减少导致的预警不敏感、节假日后第一天就诊量突增导致的假阳性预警发生[23]。德国SurvNet采用自动暴发探测算法(automatic outbreak detection algorithm),以周为单位对法定传染病数据进行分析,当探测高于阈值(暴发信号)发病数时生成信号[47]。我国CIDARS采用移动百分位数法和累积和控制图法模型,对不同类型传染病进行探测预警,其中最主要的是移动百分位数法,若当前7 d病例数的发病水平超过过去5年历史同期基线数据的第n百分位数(Pn)水平时(各病种阈值不尽相同),系统发出1条预警信号。
(2)空间预警模型:其理论依据是当传染病暴发或新发传染病发生时,病例会在短时间内异常增加,且往往聚集在特定的地区内,与其他地区的发病水平存在明显的差异[48]。Kulldorff[49]提出并开发的空间扫描统计量(spatial scan statistic)与SaTScan软件,是影响最大的方法与工具,其中空间扫描统计量是将地理空间划分成许多小区域作为扫描窗口,通过利用蒙特卡罗假设检验,探测监测指标与常规水平有统计学差异的区域,以识别空间聚集性发挥预警作用。如Mostashari等[50]在美国纽约市开展的基于空间扫描统计量的死鸟监测系统,预警西尼罗病毒活动研究收到了积极效果,指导有关部门早期采取了防控措施。但Kulldorff提出的空间扫描统计量属于“圆形扫描窗口”,对非圆形聚集性区域的检验效能有所欠缺,故又衍生出了可探测“不规则形状”聚集区域的Flexible空间扫描统计量,我国学者周剑南等[51]的评价研究显示,Flexible空间扫描统计量在实际应用中具有更好的暴发区域探测能力。
(3)时空预警模型:同时从时间和空间两个维度开展监测预警,可以获得更充分的信息,具有更高的及时性和准确性,近年来受到了很大关注,具有较好的前景。Desjardins等[52]利用前瞻性时空扫描统计量,在美国开展新冠肺炎聚集性预警,帮助公共卫生部门和决策者采取防控措施和优化医疗资源分配。我国CIDARS使用移动百分位数法,与基于空间扫描统计量的空间监测模型组合,进行传染病时空预警,评价结果显示,可以降低错误预警率、提高预警及时性,总体效果好于时间模型预警[53]。此外,一种基于规则的异常模式探测方法(What's strange about recent events,WSARE)时空模型,在流行性腮腺炎、猩红热、手足口病等疫情暴发早期预警研究中也显示了良好的时效性和精确性,有一定的应用前景[54-55]。
(4)多源数据预警技术:上述三类预警模型多基于单一数据源,随着近些年多学科融合发展,多源数据技术日趋成熟,与传染病相关的非结构化数据分析在疫情预警、响应和追踪方面发挥着愈发重要的作用,相应的技术方法也得到了广泛的探索与应用。如Santillana等[56]提出了一种基于机器学习算法的流感预警模型,将谷歌搜索、社交媒体数据、医院就诊记录、流感样病例监测等多源数据优化组合,效果优于单一数据源预警。Kogan等[57]在美国使用贝叶斯模型,对社交媒体上新冠肺炎疫情相关信息、互联网搜索信息以及发热监测数据综合分析,可提前2~3周捕捉到新冠肺炎确诊病例数的指数上升。这些探索性研究,为未来传染病预警系统发展提供了重要的经验,证明了多源数据融合探测可以弥补单一数据用于预警的局限性,能够更好地作为传统监测预警的补充。
3. 预警信息发布:
预警信息能否有效发布给应该知道的人,是监测预警全过程的关键,将直接影响预警效果。传染病预警信息发布可以分为纵向至下级监测机构,横向给有关的医疗卫生机构、科研单位和社会公众。根据信息推送方式的不同,目前的预警信息发布可以分为:
(1)专业系统发布:将预警信息发布至卫生专业人员,指导采取防控措施、遏制疾病发展,是最为基础和重要的信息发布方式。如我国CIDARS将预警信号通过手机短信平台发送至各级CDC的指定人员,以快速开展信号核实,必要时进行现场调查处置。美国专设了卫生警报网络,用于CDC与公共信息官员、各级公共卫生专业人员、临床医师和公共卫生实验室共享发布警报信息。欧洲CDC运行着仅供内部访问和发布信息的早期预警和响应系统,允许欧盟及其成员国,通过该网络发布可能会造成严重健康威胁的事件警报和有关数据[26, 29, 58]。
(2)其他途径发布:传染病防控需要全社会参与,及时向各界发布相关信息有助于防控措施有效实施,亦可以避免不必要的恐慌。目前,通过期刊、互联网、监测及风险评估报告等载体发布预警信息最为常见。
① 期刊报告:代表性期刊有美国Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report(MMWR)和欧盟Eurosurveillance,主要刊登监测和暴发调查报告、流行病学情报、卫生研究文章、政策解读和评论等,在特殊情况(如传染病流行时)下,还会以速报的形式向外界发布预警信息[59-60]。中国CDC于2019年创办的China CDC Weekly,作为我国公共卫生信息和建议的平台,在新冠肺炎疫情流行期间,向外界发布了很多重要的预警信息和卫生建议,在国际上形成了一定影响力[61]。此外,官方传染病周(月、年)报等也是各国或地区发布传染病信息和预警的重要途径。
② 互联网:网络已成为公众获取和交流信息的重要载体,网站建设在预警信息发布过程中越发占据重要的地位,如欧洲CDC官方网站(https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en)开设了“流行病学信息发布”“暴发数据和地图”等特设模块,为查看监测数据、流行病学信息、健康建议提供了便捷的入口,并实现了数据可视化,便于普通公众理解。WHO针对新冠肺炎疫情,开设了“WHO Coronavirus(COVID-19)Dashboard”模块,将各国新冠肺炎统计数据(包括发病/患病数、死亡病例数、疫苗接种数等)和采取的防控措施强度以可视化、交互式的方式呈现,使全球疫情概况一目了然[62]。中国CDC每逢法定节假日,会在官方网站和微信公众号提前发布健康提示,内容包括假期期间风险疾病的特征及预防措施,指导公众在享受假期的同时有效防范疾病[63]。日本、韩国、中国香港地区的官方卫生网站建设也较为清楚,诸如“健康建议”“旅行禁令”等警示模块位置醒目,可方便获取相关信息。值得一提的是,中国台湾地区专设了一个公布法定传染病确诊病例和相关症状数据的公开网站(https://nidss.cdc.gov.tw),将监测数据可视化并提供了预警值和流行阈值作为参考,使普通公众也能理解传染病信息,起到预警作用。
三、展望传染病监测预警依然是各个国家和地区疾病预防控制工作不断完善提高的重点,相关系统和体制建设得到不断加强,监测预警体系朝着多渠道、多点触发的方向发展。对我国而言,虽然近年来取得了长足进步,中国疾病预防控制信息系统实现了“横向到边、纵向到底”的实时网络直报,CIDARS也具有良好的灵敏度和特异度,但仍存在着监测数据单一、预警关口滞后、预警技术相对落后等问题[34, 64]。总结其他国家和地区监测预警现状,提示我国可以从以下几个方面入手,进一步提升我国传染病监测预警能力。
1. 丰富监测预警数据来源,建立智慧化多点触发机制:症状监测、媒体舆情、期刊文献乃至传染病流行相关影响因素覆盖了传染病发生、发展的多个节点,且受人为因素干扰小,已被证实有助于早期探测疾病异常信号。此类数据在我国监测预警工作中尚未真正应用并发挥更重要的价值,应当继续加强监测预警指标研究,探索适合国情的监测方法,积极推动传统与非传统监测数据的整合,最终实现自动化和智慧化监测预警模式。
2. 加强预警技术方法研究,提升整合分析多源数据与预警能力:随着数据来源和使用场景的不断丰富,现有的技术方法已不能很好满足预警需求,应加大跨学科协作与发展,借助统计学、数学建模以及机器学习理论等加强相关模型算法的开发研究。结合地理信息系统、计算机技术以及现代化人工智能大数据分析技术,加强时空聚集性探测预警方法研究,推动时空预警模型算法在预警系统中的运用和优化,探索多模型综合预警技术方法。
3. 统筹常态化防控机制,加强医防信息协同:打通不同部门、机构之间的壁垒,建立起常态化联防联控机制,需特别重视医疗机构首诊医师报告的重要性,健全相关法律法规、建立医师报告奖惩机制,继续加强医师传染病防控技术培训,提高医护人员对传染病的警惕性。探索流行病学监测与医疗机构自身工作需要相结合的模式,如允许医疗机构利用严重急性呼吸道感染监测数据分析指导抗生素使用、允许报告医师通过监测系统查询服务范围内疾病流行情况和风险等级,指导采取应对措施等,体现疾病监测对医院诊疗所发挥的价值,提高医疗机构积极性,推动医防协同落到实处。
4. 改善专业网站信息发布,提高公众接收预警信息效能:我国相关官方网站建设尚不完备,公众主动查询传染病预警信息的便捷性不足,建议利用好信息时代官方网站的优势,在醒目位置开设传染病信息快讯类模块,并做好数据可视化呈现,帮助公众理解有关信息、建议和防控措施。可以参考借鉴气象预警领域的信息发布方式,多途径发布传染病防控建议,提升公众传染病防控意识,使传染病监测预警更加贴近民众生活。
利益冲突 所有作者声明无利益冲突
| [1] |
刘金妹, 高倩倩, 焦敏, 等. 新发(重大)传染病"全哨点""多症候"监测体系构建[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2021, 37(10): 1468-1472. Liu JM, Gao QQ, Jiao M, et al. Establishment of a full-coverage sentinel and multi-symptom surveillance system for new (major) infectious diseases-a literature study[J]. Chin J Public Health, 2021, 37(10): 1468-1472. DOI:10.11847/zgggws1134197 |
| [2] |
王丽萍, 曹务春. 实施传染病监测是预防控制传染病的有效途径[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(4): 417-418. Wang LP, Cao WC. Surveillance as an effective approach to infectious diseases control and prevention[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2017, 38(4): 417-418. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.04.001 |
| [3] |
杨维中. 传染病预警理论与实践[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2012. Yang WZ. Early warning of infectious disease theory and practice[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2012. |
| [4] |
熊玮仪, 冯子健. 中国传染病监测的发展历程、现状与问题[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2011, 32(10): 957-960. Xiong WY, Feng ZJ. Overview on communicable disease surveillance in China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2011, 32(10): 957-960. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2011.10.001 |
| [5] |
李苑, 刘昊. 症状监测预警技术研究进展[J]. 江苏预防医学, 2017, 28(3): 291-293. Li Y, Liu H. Advances in symptom early warning technology[J]. Jiangsu J Prev Med, 2017, 28(3): 291-293. DOI:10.13668/j.issn.1006-9070.2017.03.15 |
| [6] |
Loonsk JW. BioSense—a national initiative for early detection and quantification of public health emergencies[J]. MMWR Suppl, 2004, 53: 53-55. |
| [7] |
关静, 张震, 周红玲, 等. 北京市西城区中学传染病症状监测预警系统研究[J]. 中国热带医学, 2009, 9(10): 2049-2050. Guan J, Zhang Z, Zhou HL, et al. Discussion on the infections disease symptom monitoring and prediction system in middle school in Xicheng District of Beijing[J]. China Trop Med, 2009, 9(10): 2049-2050. |
| [8] |
杨维中, 兰亚佳, 李中杰. 传染病预警研究回顾与展望[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2014, 48(4): 244-247. Yang WZ, Lan YJ, Li ZJ. Review and prospect on early warning of infectious diseases[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2014, 48(4): 244-247. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2014.04.002 |
| [9] |
黎新宇, 高婷, 杨鹏, 等. 北京奥运会期间疾病监测与分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2010, 44(1): 82-83. Li XY, Gao T, Yang P, et al. Disease surveillance and analysis during Beijing Olympic Games[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2010, 44(1): 82-83. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2010.01.020 |
| [10] |
何永超, 林庆能, 何懿, 等. 大型活动就诊异常情况监测预警系统的建立及在上海世博保障中的实践[J]. 环境与职业医学, 2011, 28(1): 1-5. He YC, Lin QN, He Y, et al. A syndromic surveillance system for public health security in expo 2010 Shanghai China[J]. J Environ Occup Med, 2011, 28(1): 1-5. DOI:10.13213/j.cnki.jeom.2011.01.007 |
| [11] |
祝丙华, 王立贵, 孙岩松, 等. 基于大数据传染病监测预警研究进展[J]. 中国公共卫生, 2016, 32(9): 1276-1279. Zhu BH, Wang LG, Sun YS, et al. Progress in researches on surveillance and early warning of infectious diseases based on big data[J]. Chin J Public Health, 2016, 32(9): 1276-1279. DOI:10.11847/zgggws2016-32-09-38 |
| [12] |
张颖, 徐文体, 董晓春, 等. 药物销售监测在社区流感监测中的应用[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2012, 46(6): 571-572. Zhang Y, Xu WT, Dong XC, et al. Application of pharmaceutical sales surveillance in community influenza surveillance[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2012, 46(6): 571-572. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2012.06.020 |
| [13] |
赵自雄, 赵嘉, 马家奇. 我国传染病监测信息系统发展与整合建设构想[J]. 疾病监测, 2018, 33(5): 423-427. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-www.jbjc.org9961.2018.05.016. Zhao ZX, Zhao J, Ma JQ. Conception of an integrated information system for notifiable disease communicable surveillance in China[J]. Dis Surveill, 2018, 33(5): 423-427. DOI: 10.3784/j.issn.1003-www.jbjc.org9961.2018.05.016. |
| [14] |
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. What is case surveillance[EB/OL]. (2021-06-11)[2021-06-26]. https://www.cdc.gov/nndss/about/index.html.
|
| [15] |
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. How does ELR work[EB/OL]. (2021-04-06)[2021-06-26]. https://www.cdc.gov/elr/how-does-elr-work.html.
|
| [16] |
张晨曦, 金春林, 王晓雯, 等. 欧洲传染病预防与控制中心监测系统分析与启示[J]. 中国卫生质量管理, 2020, 27(4): 123-126. Zhang CX, Jin CL, Wang XW, et al. Operational analysis and implications of the surveillance system of the European Centre for Diseases Prevention and Control[J]. Chin Health Qual Manag, 2020, 27(4): 123-126. DOI:10.13912/j.cnki.chqm.2020.27.4.33 |
| [17] |
Krause G, Altmann D, Faensen D, et al. SurvNet electronic surveillance system for infectious disease outbreaks, Germany[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2007, 13(10): 1548-1555. DOI:10.3201/eid1310.070253 |
| [18] |
国立感染症研究所. 日本の感染症サーベイランス[EB/OL]. (2018-02-22)[2021-07-20]. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/images/epi/nesid/nesid_ja.pdf. The National Institute of Infectious Diseases. Surveillance of infectious diseases in Japan[EB/OL]. (2018-02-22)[2021-07-20]. https://www.niid.go.jp/niid/images/epi/nesid/nesid_ja.pdf. |
| [19] |
中国香港卫生防护中心. 中央呈报办公室网络呈报常见问题解答[EB/OL]. (2017-03-06)[2021-07-18]. https://cdis.chp.gov.hk/CDIS_DINS_ONLINE/document/previewPDF?id=1979265. Hong Kong Centre for Health Protection. Central Notification Office On-line FAQ[EB/OL]. (2017-03-06) [2021-07-18]. https://cdis.chp.gov.hk/CDIS_DINS_ONLINE/document/previewPDF?id=1979265. |
| [20] |
中国台湾卫生福利部疾病管制署. 新版传染病通报系统[EB/OL]. (2021-04-30)[2021-07-16]. https://www.cdc.gov.tw/Category/MPage/g2B1VbUeuu_gEgdYmNiiKw. Taiwan Centers for Disease Control of China. New Infectious Disease Reporting System. [EB/OL]. (2021-04-30)[2021-07-16]. https://www.cdc.gov.tw/Category/MPage/g2B1VbUeuu_gEgdYmNiiKw. |
| [21] |
林玫, 王鑫, 梁大斌. 症状监测在新发传染病和暴发疫情预警中应用的进展[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2015, 49(7): 659-664. Lin M, Wang X, Liang DB. Advance in application of syndromic surveillance for detection of emerging infectious diseases and outbreak alerts[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2015, 49(7): 659-664. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2015.07.017 |
| [22] |
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The national syndromic surveillance program[EB/OL]. (2021-04-13)[2021-07-11]. https://www.cdc.gov/nssp/images/nsspinfo/Final_NSSP-Infographic.pdf.
|
| [23] |
Burkom H, Loschen W, Wojcik R, et al. Electronic surveillance system for the early notification of community-based epidemics (ESSENCE): Overview, components, and public health applications[J]. JMIR Public Health Surveill, 2021, 7(6): e26303. DOI:10.2196/26303 |
| [24] |
Guerrisi C, Turbelin C, Blanchon T, et al. Participatory syndromic surveillance of influenza in Europe[J]. J Infect Dis, 2016, 214 Suppl 4: S386-392. DOI:10.1093/infdis/jiw280 |
| [25] |
European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control. Epidemic intelligence tools and information resources[EB/OL]. (2021-06-22)[2021-07-16]. https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/threats-and-outbreaks/epidemic-intelligence.
|
| [26] |
Nichols GL, Andersson Y, Lindgren E, et al. European monitoring systems and data for assessing environmental and climate impacts on human infectious diseases[J]. Int J Environ Res Public Health, 2014, 11(4): 3894-3936. DOI:10.3390/ijerph110403894 |
| [27] |
Ahn S, Lee JH, Kim W, et al. Analysis of the Korean emergency department syndromic surveillance system: Mass type acute diarrheal syndrome[J]. Healthc Inform Res, 2010, 16(3): 177-184. DOI:10.4258/hir.2010.16.3.177 |
| [28] |
Rhee C, Burkom H, Yoon CG, et al. Syndromic surveillance system for Korea-US joint biosurveillance portal: Design and lessons learned[J]. Health Secur, 2016, 14(3): 152-160. DOI:10.1089/hs.2015.0067 |
| [29] |
杨维中, 兰亚佳, 李中杰, 等. 国家传染病自动预警系统的设计与应用[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2010, 31(11): 1240-1244. Yang WZ, Lan YJ, Li ZJ, et al. The application of national outbreak automatic detection and response system, China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2010, 31(11): 1240-1244. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2010.11.009 |
| [30] |
陈强, 郭岩, 万明, 等. 全球公共卫生情报网及对我国的启示[J]. 医学信息学杂志, 2011, 32(8): 2-5, 19. Chen Q, Guo Y, Wan M, et al. Global Public Health Intelligence Network (GPHIN) and its enlightenment to China[J]. J Med Inform, 2011, 32(8): 2-5, 19. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1673-6036.2011.08.002 |
| [31] |
Bradley CA, Rolka H, Walker D, et al. BioSense: implementation of a National Early Event Detection and Situational Awareness System[J]. MMWR Suppl, 2005, 54: 11-19. |
| [32] |
Yang WZ, Li ZJ, Lan YJ, et al. A nationwide web-based automated system for outbreak early detection and rapid response in China[J]. Western Pac Surveill Response J, 2011, 2(1): 10-15. DOI:10.5365/WPSAR.2010.1.1.009 |
| [33] |
李中杰, 马家奇, 赖圣杰, 等. 2011-2013年国家传染病自动预警系统运行结果分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2014, 48(4): 252-258. Li ZJ, Ma JQ, Lai SJ, et al. The implement performance of China Infections Diseases Automated-alert and Response System in 2011-2013[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2014, 48(4): 252-258. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2014.04.004 |
| [34] |
张洪龙, 曾令佳, 赖圣杰, 等. 2016年国家传染病自动预警信息系统运行情况分析[J]. 疾病监测, 2018, 33(2): 159-167. Zhang HL, Zeng LJ, Lai SJ, et al. Performance of China infectious disease automated-alert and response system in 2016[J]. Dis Surveill, 2018, 33(2): 159-167. DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2018.02.011 |
| [35] |
Lake IR, Colón-González FJ, Takkinen J, et al. Exploring Campylobacter seasonality across Europe using The European Surveillance System (TESSy), 2008 to 2016[J]. Euro Surveill, 2019, 24(13): 1800028. DOI:10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2019.24.13.180028 |
| [36] |
Bagherian H, Farahbakhsh M, Rabiei R, et al. National Communicable Disease Surveillance System: A review on Information and Organizational Structures in Developed Countries[J]. Acta Inform Med, 2017, 25(4): 271-276. DOI:10.5455/aim.2017.25.271-276 |
| [37] |
Schumacher J, Diercke M, Salmon M, et al. Timeliness in the German surveillance system for infectious diseases: Amendment of the infection protection act in 2013 decreased local reporting time to 1 day[J]. PLoS One, 2017, 12(10): e0187037. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0187037 |
| [38] |
Yoo HS, Park O, Park HK, et al. Timeliness of national notifiable diseases surveillance system in Korea: a cross-sectional study[J]. BMC Public Health, 2009, 9: 93. DOI:10.1186/1471-2458-9-93 |
| [39] |
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Florida department of health syndromic surveillance identifies unreported cases of Zika virus disease, 2016-2017[EB/OL]. (2021-04-30)[2021-09-28]. https://www.cdc.gov/nssp/success-stories/FL-Zika.html.
|
| [40] |
Canas LS, Sudre CH, Pujol JC, et al. Early detection of COVID-19 in the UK using self-reported symptoms: a large-scale, prospective, epidemiological surveillance study[J]. Lancet Digit Health, 2021, 3(9): e587-598. DOI:10.1016/S2589-7500(21)00131-X |
| [41] |
赖圣杰, 冯录召, 冷志伟, 等. 传染病暴发早期预警模型和预警系统概述与展望[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2021, 42(8): 1330-1335. Lai SJ, Feng LZ, Leng ZW, et al. Summary and prospect of early warning models and systems for infectious disease outbreaks[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2021, 42(8): 1330-1335. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20210512-00391 |
| [42] |
严薇荣, 魏晟, 张惠娟, 等. 试论开展突发公共卫生事件症状监测的必要性和困难[J]. 疾病控制杂志, 2007, 11(1): 79-81. Yan WR, Wei S, Zhang HJ, et al. Necessity and difficulties of implementation of syndromic surveillance in China[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2007, 11(1): 79-81. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3679.2007.01.022 |
| [43] |
Dion M, AbdelMalik P, Mawudeku A. Big Data and the Global Public Health Intelligence Network (GPHIN)[J]. Can Commun Dis Rep, 2015, 41(9): 209-214. DOI:10.14745/ccdr.v41i09a02 |
| [44] |
Olson DR, Konty KJ, Paladini M, et al. Reassessing Google Flu Trends data for detection of seasonal and pandemic influenza: a comparative epidemiological study at three geographic scales[J]. PLoS Comput Biol, 2013, 9(10): e1003256. DOI:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003256 |
| [45] |
Butler D. When Google got flu wrong[J]. Nature, 2013, 494(7436): 155-156. DOI:10.1038/494155a |
| [46] |
秦磊, 谢邦昌. 谷歌流感趋势的成功与失误[J]. 统计研究, 2016, 33(2): 107-110. Qin L, Xie BC. Success and failure of Google flu trends[J]. Statist Res, 2016, 33(2): 107-110. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1002-4565.2016.02.015 |
| [47] |
Straetemans M, Altmann D, Eckmanns T, et al. Automatic outbreak detection algorithm versus electronic reporting system[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2008, 14(10): 1610-1612. DOI:10.3201/eid1410.071354 |
| [48] |
李晓松, 冯子健, 殷菲, 等. 传染病时空聚集性探测与预测预警方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2014. Li XS, Feng ZJ, Yin F, et al. Spatio-temporal cluster detection, forecasting and early warning for infectious disease[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2014. |
| [49] |
Kulldorff M. A spatial scan statistic[J]. Commun Stat-Theor Math, 1997, 26(6): 1481-1496. DOI:10.1080/03610929708831995 |
| [50] |
Mostashari F, Kulldorff M, Hartman JJ, et al. Dead bird clusters as an early warning system for West Nile virus activity[J]. Emerg Infect Dis, 2003, 9(6): 641-646. DOI:10.3201/eid0906.020794 |
| [51] |
周剑南, 冯子健, 谭柯, 等. Flexible空间扫描统计量在传染病聚集性探测的应用研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2010, 14(6): 475-478. Zhou JN, Feng ZJ, Tan K, et al. Study on the application of flexible spatial scan statistic to spatial aggregation of infection disease[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev, 2010, 14(6): 475-478. |
| [52] |
Desjardins MR, Hohl A, Delmelle EM. Rapid surveillance of COVID-19 in the United States using a prospective space-time scan statistic: Detecting and evaluating emerging clusters[J]. Appl Geogr, 2020, 118: 102202. DOI:10.1016/j.apgeog.2020.102202 |
| [53] |
赖圣杰, 廖一兰, 张洪龙, 等. 2011-2013年国家传染病自动预警系统中时间模型和时空模型应用效果比较[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2014, 48(4): 259-264. Lai SJ, Liao YL, Zhang HL, et al. Comparing the performance of temporal model and temporal-spatial model for outbreak detection in China Infectious Diseases Automated-alert and Response System, 2011-2013, China[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2014, 48(4): 259-264. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2014.04.005 |
| [54] |
郑庆鸣, 李媛, 王铁强, 等. WSARE 3.0算法在深圳市流行性腮腺炎暴发早期预警中的应用[J]. 疾病监测, 2014, 29(5): 399-402. Zheng QM, Li Y, Wang TQ, et al. Applicability of WSARE 3.0 algorithms in early warning of mumps outbreak in Shenzhen[J]. Dis Surveill, 2014, 29(5): 399-402. DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2014.05.016 |
| [55] |
张代涛, 张奕, 杨鹏, 等. WSARE计算方法在猩红热暴发预警中的应用[J]. 中国预防医学杂志, 2012, 13(1): 26-29. Zhang DT, Zhang Y, Yang P, et al. The application of WSARE algorithm in early detection of the scarlet fever outbreak[J]. China Prev Med, 2012, 13(1): 26-29. DOI:10.16506/j.1009-6639.2012.01.004 |
| [56] |
Santillana M, Nguyen AT, Dredze M, et al. Combining search, social media, and traditional data sources to improve influenza surveillance[J]. PLoS Comput Biol, 2015, 11(10): e1004513. DOI:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004513 |
| [57] |
Kogan NE, Clemente L, Liautaud P, et al. An early warning approach to monitor COVID-19 activity with multiple digital traces in near real time[J]. Sci Adv, 2021, 7(10): eabd6989. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.abd6989 |
| [58] |
Sharma D, Panigrahi A. Health alert network[J]. Arch Community Med Public Health, 2020, 6(1): 26-27. DOI:10.17352/2455-5479.000066 |
| [59] |
隋明爽, 黄亚明. 《发病率和死亡率周报》[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2016, 50(10): 926. Sui MS, Huang YM. Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2016, 50(10): 926. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253.9624.2016.10.102 |
| [60] |
Eurosurveillance. About us[EB/OL]. (2021-08-16)[2021-08-16]. https://www.eurosurveillance.org/about.
|
| [61] |
Tan F, Feng ZJ, Gao GF. China CDC Weekly: A trusted resource on public health[J]. China CDC Wkly, 2020, 2(49): 933-934. DOI:10.46234/ccdcw2020.255 |
| [62] |
WHO. WHO coronavirus (COVID-19) dashboard[EB/OL]. (2021-11-03)[2021-11-04]. https://covid19.who.int.
|
| [63] |
中国疾病预防控制中心. 2021年中秋国庆假期健康提示[EB/OL]. (2021-09-07)[2021-11-04]. http://www.chinacdc.cn/yyrdgz/202109/t20210918_248169.html. Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Health tips for 2021 mid-autumn and national day[EB/OL]. (2021-09-07)[2021-11-04]. http://www.chinacdc.cn/yyrdgz/202109/t20210918_248169.html. |
| [64] |
杨维中, 兰亚佳, 吕炜, 等. 建立我国传染病智慧化预警多点触发机制和多渠道监测预警机制[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2020, 41(11): 1753-1757. Yang WZ, Lan YJ, Lv W, et al. Establishment of multi-point trigger and multi-channel surveillance mechanism for intelligent early warning of infectious diseases in China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2020, 41(11): 1753-1757. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20200722-00972 |
 2022, Vol. 43
2022, Vol. 43