文章信息
- 牛建梅, 孔繁智, 张研婷, 尚玉秀.
- Niu Jianmei, Kong Fanzhi, Zhang Yanting, Shang Yuxiu.
- 老年居民抑郁与情绪调节策略的相关性研究
- Study on the correlation between depression and emotion regulation strategies in the elderly residents
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(12): 1611-1615
- Chinese journal of Epidemiology, 2017, 38(12): 1611-1615
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.12.005
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2017-05-09
2. 030012 太原, 山西省疾病预防控制中心
2. Shanxi Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Taiyuan 030012, China
我国老年人抑郁发生率达22.8%[1]。抑郁作为一类情绪功能紊乱的心境障碍,主要表现为积极情绪的缺乏和过度的消极情绪,即在抑郁、焦虑、愤怒、沮丧等情绪存在时,通过情绪调节的调控机制来控制认知改变,实现情绪应答或情绪状态变化使机体产生适应性心理生理状态的过程[2]。情绪调节策略中能降低情绪反应的是认知重评和表达抑制的正性情绪调节策略。认知重评是通过改变思维来改变不良认识,缓解、消除不良情绪[3];表达抑制是抑制将要发生或正在发生的情绪表达行为。而可能会延长、加剧消极情感和抑郁症状的是反刍思维这种负性情绪调节策略[4],它是指个体在遇到不良情绪时,只关注自我产生情绪的原因和各种不良后果。研究表明,35%老年抑郁症患者具有情绪调节障碍问题[5]。本研究旨在了解银川市老年居民抑郁与情绪调节策略的现况及两者的关系,为促进老年人心理健康提供依据。
对象与方法1.研究对象:选择2016年3-5月银川市社区和养老机构的老年居民1 043名。社区老年人采用方便抽样的方法,分别是银川市兴庆区和金凤区5个社区(长城花园、景墨家园、军干所、燕兴花园和林华苑),共538人。养老机构老年人采用整群抽样的方法,分别是银川市兴庆区和金凤区5所养老机构(兴庆区中心敬老院、兴庆区社会福利院、唐徕老年托护中心、阅海养老中心和金凤区社会福利院),共505人。纳入标准:①年龄≥60岁,性别不限;②自愿参与调查。排除标准:①非银川市常住人口;②有意识障碍、无法交流者;③精神疾病(非抑郁症)及严重的躯体疾病,不能配合调查者。
2.研究方法:采用问卷调查方法,由调查员复述题目,老年人判断后,再由调查员填写。
(1) 基本情况:包括年龄、性别、婚姻状况、既往职业、经济收入等。
(2) 老年人抑郁调查:采用老年抑郁量表(GDS),量表 30个条目中的10条用反序计分,20条用正序计分。0~10分为正常范围,即无抑郁症;11~20分为轻度抑郁;21~30分为中重度抑郁,GDS得分≥11者,认为有抑郁。GDS中文版在中国社区老年人群中的内部一致性Cronbach α系数为0.846,2周重测信度为0.812[6],本研究显示该量表在调查人群内部一致性系数为0.839。
(3) 养老机构老年人情绪调节调查:采用王力等[7]翻译的Cross情绪调节问卷(ERQ)及韩秀和杨宏飞[8]翻译的反刍思维量表(RRS)。ERQ问卷共有10个项目,项目1、3、5、7、8、10测量个体的认知重评情况、项目2、4、6、9测量表达抑制情况。本研究使用该量表在调查人群中两个维度的内部一致性系数为0.874和0.872。RRS由22个项目组成,包括症状反刍、强迫思考、反省深思3个因子,按1~4评分(1=从不;2=有时;3=经常;4=总是),得分越高表明反刍思维倾向越严重,本研究使用该量表在调查人群的内部一致性系数为0.947。
3.统计学分析:采用SPSS 18.0软件进行分析,计量资料采用x±s表示,组间比较采用t检验及方差分析;计数资料用χ2检验;两变量的相关性采用Pearson相关分析。
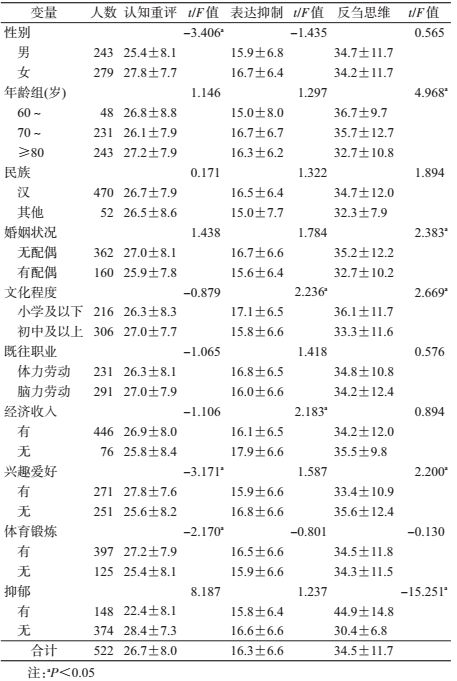
结果1.社区和养老机构老年人抑郁发生率及得分:1 043名老年居民抑郁发生率为32.0%,其中轻度抑郁266例(25.5%);中、重度抑郁68例(6.5%)。社区老年人抑郁发生率为35.5%,养老机构老年人抑郁发生率为28.3%,差异有统计学意义(χ2=6.187,P<0.05)。经倾向评分法匹配后,社区老年人抑郁发生率为38.3%,养老机构老年人抑郁发生率为39.8%,差异无统计学意义(χ2=0.066,P=0.798)。养老机构老年人抑郁得分为(8.55±6.54)分,不同年龄、兴趣爱好和体育锻炼抑郁得分差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05)。社区老年人抑郁得分为(9.62±4.42)分,不同年龄、婚姻状况、文化程度、经济收入、兴趣爱好和体育锻炼抑郁得分差异均有统计学意义(均P<0.05),见表 1。
2.老年居民情绪调节策略得分:养老机构522名老年人认知重评得分6~42(26.7±8.0)分;表达抑制得分4~28(16.3±6.6)分;反刍思维得分22~79(34.5±11.7)分。认知重评得分在性别、兴趣爱好、体育锻炼和抑郁状况上差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05),表达抑制得分在文化程度、固定经济收入上差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05),反刍思维得分在年龄、配偶、文化程度、兴趣爱好和抑郁状况上差异有统计学意义(均P<0.05),见表 2。
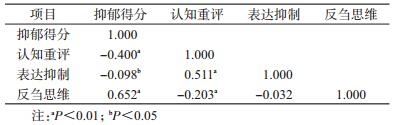
3.老年居民抑郁与情绪调节策略的相关性分析:522名养老机构老年人抑郁得分与认知重评得分呈负相关(r=-0.400,P<0.01),即老年人越少采用认知重评,越容易发生抑郁。抑郁得分与表达抑制呈负相关(r=-0.098,P<0.05),经计算其决定系数很小,提示在抑郁得分中表达抑制的贡献度较小而未发生明显的作用。抑郁得分与反刍思维呈正相关(r=0.652,P<0.01),即老年人越多采用反刍思维,越容易发生抑郁,见表 3。
本调查结果显示,银川市老年居民抑郁发生率为32.0%,与刘启玲等[9]对宁夏地区老年人抑郁发生率32.86%(标化率30.4%)接近;但高于范珊红[10]报道的西安城区老年人抑郁发生率(24.9%)。原因一方面可能与本地区的经济收入、受教育水平、家庭开支、民族文化背景及退休前职业等衡量社会经济地位的指标有关,另一方面可能与调查者使用的调查抑郁量表等工具不同造成的差异有关。
本研究结果显示,随着年龄增加,社区老年人抑郁得分逐渐增加,而养老机构老年人抑郁得分逐渐降低,可能的原因是本研究中社区≥80岁的老年人丧偶者(60.0%)、不参加体育锻炼者(56.0%)居多,丧偶的老年人生活孤独、幸福感低,加之年龄大行动迟缓造成活动量减少、生活自理能力差等容易产生抑郁情绪。与社区老年人相比,本研究中养老机构≥80岁老年人参加体育锻炼(74.2%)、有兴趣爱好(53.1%)者居多,另外,养老机构服务功能完善,老年人生活丰富、交流和锻炼的同伴多[11],以此可以缓解心理压力,减少抑郁的发生。Meta分析结果显示,<85岁的老年人抑郁发生率随年龄增加而升高,但是在85岁以上者没有这种现象[12],故年龄对老年人抑郁影响尚存在争议。有兴趣爱好和体育锻炼的老年人抑郁得分较低,使用认知重评策略要多于无兴趣爱好和不锻炼者,而在使用反刍思维上无兴趣爱好老年人会更多使用这一策略,贾丽娜等[13]发现有兴趣爱好及体育锻炼的老年人可通过丰富日常生活来转移注意力,提高抵御不良情绪的能力,提示积极的生活态度有益于改善情绪调节方式。文化程度低、经济收入低和独身的老年人抑郁得分较高,小学及以下文化程度的老年人更多使用表达抑制和反刍思维策略,可能是日常生活中,这些弱势群体因社会地位和经济状况较差[14],遇到困难不善于表达自己情绪,而反复思考不良事件的原因,习惯性的压抑情绪而陷入沉思。配偶支持在很大程度上影响老年人的情绪调节方式,老年人丧偶后缺乏交流与支持更增强了对孤独、无助和衰老感等潜在忧虑的感知。这与宁自衡等[15]的结论一致,提示这类老年人缺少社会及家庭支持而容易产生自卑的负性情绪,故需要来自家庭成员的关心照顾、支持和安慰来减轻其孤独寂寞感。
抑郁作为一种情绪障碍,被普遍认为是情绪调节困难的后果[16-17]。本研究结果显示,认知重评与抑郁呈负相关,提示越多使用认知重评情绪调节策略,越少患抑郁症。当个体更多采用认知重评这一正性情绪调节策略时能对事件做出重新解释、使其合理化,反刍思维与抑郁呈正相关,这与Garnefski等[18]的报道结果一致,可能是当负性事件发生时,有情绪调节障碍的老年人表现为情绪低落、愉快感丧失,即不能有效地抑制负性情绪,而对周围事物易激惹或产生淡漠状态,这样的思维方式使消极情绪倾向长时间存在导致无法脱离负性心境,并且会妨碍老年人使用有效的情绪调节策略及积极解决问题的行为,积极的态度对待,从而改变情绪评价和相关情绪反应来降低抑郁的发生[19]。本研究结果显示长此以往形成的沉思习惯是发生和维持抑郁症状的重要因素之一[20]。因此,老年人越少使用认知重评策略、越多使用反刍思维策略,越可能出现抑郁。本研究结果显示,老年人抑郁与表达抑制无关,表达抑制在东西方文化背景下研究结果不太一致,中国文化强调对情绪的控制和忍耐,而西方文化强调对情绪的自由表达[21]。因此,在东方文化背景下,老年人是否用表达抑制来降低负性情绪体验,有待进一步深入研究。
利益冲突: 无
| [1] |
聂晓璐, 王红英, 孙凤, 等.
2000-2012年中国社区人群老年期抑郁情绪检出率-系统综述和更新的Meta分析[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2013, 27(11): 805–814.
Nie XL, Wang HY, Sun F, et al. Detection rate of depression among community-dwelling older adults in China:A systematic review and updated Meta-analysis of studies in 2000-2012[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 2013, 27(11): 805–814. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6729.2013.11.002 |
| [2] | Lewis MD, Stieben J. Emotion regulation in the Brain:conceptual issues and directions for developmental research[J]. Child Devel, 2004, 75(2): 371–376. DOI:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2004.00680.x |
| [3] |
王敬欣, 王春梅, 谢芳, 等.
负性情绪调节中认知重评和分心策略的作用:ERPs研究[J]. 心理科学, 2015, 38(5): 1039–1044.
Wang JX, Wang CM, Xie F, et al. The effect of cognitive reappraisal and distraction in regulating negative emotion:ERPs study[J]. Psychol Sci, 2015, 38(5): 1039–1044. DOI:10.16719/j.cnki.1671-6981.2015.05.004 |
| [4] |
戴必兵, 彭义升, 李娟.
老年人抑郁症状与情绪调节策略的横断面研究[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2014, 28(3): 192–196.
Dai BB, Peng YS, Li J. A cross-sectional study of depressive symptom and emotion regulation in older adults[J]. Chin Ment Health J, 2014, 28(3): 192–196. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6729.2014.03.006 |
| [5] |
马静怡. 老年抑郁、焦虑与认知功能的现状、影响因素及其关系研究[D]. 临汾: 山西师范大学, 2014.
Ma JY. Depression, Anxiety and Cognitive Abilities of the Elderly:Current situation and Risk Factors[D]. Linfen:Shanxi Normal University, 2014. |
| [6] |
刘杰, 王瑛, 王晓慧, 等.
中文版老年抑郁量表在城市社区老年人群中应用的信效度研究[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2013, 21(1): 39–41.
Li J, Wang Y, Wang XH, et al. Reliability and validity of the Chinese version of geriatric depression scale among Chinese urban community-dwelling elderly population[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2013, 21(1): 39–41. DOI:10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2013.01.041 |
| [7] |
王力, 柳恒超, 李中权, 等.
情绪调节问卷中文版的信效度研究[J]. 中国健康心理学杂志, 2007, 15(6): 503–505.
Wang L, Liu HC, Li ZQ, et al. Reliability and validity of emotion regulation questionnaire Chinese revised version[J]. Chin J Health Psychol, 2007, 15(6): 503–505. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-1252.2007.06.034 |
| [8] |
韩秀, 杨宏飞.
Nolen-Hoeksema反刍思维量表在中国的试用[J]. 中国临床心理学杂志, 2009, 17(5): 550–551.
Han X, Yang HF. Chinese version of nolen-hoeksema ruminative responses scale (RRS)Used in 912 college students:reliability and validity[J]. Chin J Clin Psychol, 2009, 17(5): 550–551. DOI:10.16128/j.cnki.1005-3611.2009.05.028 |
| [9] |
刘启玲, 王志忠, 张颖, 等.
宁夏地区社区回族和汉族老年人抑郁现况及其影响因素调查分析[J]. 吉林大学学报:医学版, 2013, 39(5): 1014–1019.
Liu QL, Wang ZZ, Zhang Y, et al. Analysis on depressive status and influence factors of Hui nationality and Han nationality elderly in community of Ningxia area[J]. J Jilin Univ:Med Sci, 2013, 39(5): 1014–1019. DOI:10.7694/jldxyxb20130532 |
| [10] |
范珊红. 西安市城市社区老年抑郁症状发生率现况调查及危险因素的病例对照研究[D]. 西安: 第四军医大学, 2007.
Fan SH. A case-control study on risk factors and investigation on incidence of geriatric depression in Xi'an urban communities[D]. Xi'an:Fourth Military Medical University, 2007. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Thesis/D036576 |
| [11] |
任飞林, 徐海军, 仝振东, 等.
老年人情绪行为能力的影响因素研究[J]. 浙江预防医学, 2015, 27(2): 109–112, 116.
Ren FL, Xu HJ, Tong ZD, et al. A study on influence factors of ability of emotional and behavior management among the elderly[J]. Zhejiang Prev Med, 2015, 27(2): 109–112, 116. DOI:10.19485/j.cnki.issn1007-0931.2015.02.001 |
| [12] | Zhao KX, Huang CQ, Xiao Q, et al. Age and risk for depression among the elderly:a Meta-analysis of the published literature[J]. CNS Spectr, 2012, 17(3): 142–154. DOI:10.1017/S1092852912000533 |
| [13] |
贾丽娜, 庄海林, 陈越, 等.
城市社区老年高血压患者抑郁状况及影响因素分析[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2015, 34(11): 1257–1261.
Jia LN, Zhuang HL, Chen Y, et al. Analysis of depressive status and influencing factors of elderly hypertensive patients in urban community[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2015, 34(11): 1257–1261. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-9026.2015.11.029 |
| [14] | Li D, Zhang DJ, Shao JJ, et al. A Meta-analysis of the prevalence of depressive symptoms in Chinese older adults[J]. Arch Gerontol Geriat, 2014, 58(1): 1–9. DOI:10.1016/j.archger.2013.07.016 |
| [15] |
宁自衡, EstevesJ, 林中宝, 等.
澳门老年人抑郁症状及其影响因素调查分析[J]. 中国心理卫生杂志, 2001, 15(5): 331–333.
Ning ZH, Esteves J, Lin ZB, et al. Depression and related factors in elderly of Macao[J]. Chin J Psych, 2001, 15(5): 331–333. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.2001.05.022 |
| [16] | Campbell-Sills L, Barlow DH. Incorporating emotion regulation into conceptualizations and treatments of anxiety and mood disorders[M]//Gross JJ, ed. Handbook of Emotion Regulation. New York:Guilford Press, 2007:542-559. |
| [17] | Mennin DS, Farach FJ. Emotion and evolving treatments for adult psychopathology[J]. Clin Psychol Sci Pract, 2007, 14(4): 329–352. DOI:10.1111/j.1468-2850.2007.00094.x |
| [18] | Garnefski N, Teerds J, Kraaij V, et al. Cognitive emotion regulation strategies and depressive symptoms:Differences between males and females[J]. Personal Individ Diff, 2004, 36(2): 267–276. DOI:10.1016/S0191-8869(03)00083-7 |
| [19] | Ochsner KN. Characterizing the functional architecture of affect regulation:emerging answers and outstanding questions[M]//Cacioppo JT, Visser PS, Pickett CL, eds. Social Neuroscience:People Thinking About People. Cambridge, MA:MIT Press, 2005:245-268. |
| [20] | Rood L, Roelofs J, Bögels SM, et al. The influence of emotion-focused rumination and distraction on depressive symptoms in nonclinical youth:a Meta-analytic review[J]. Clin Psychol Rev, 2009, 29(7): 607–616. DOI:10.1016/j.cpr.2009.07.001 |
| [21] | Butler EA, Lee TL, Gross JJ. Does expressing your emotions raise or lower your blood pressure? The answer depends on cultural context[J]. J Cross Cult Psychol, 2009, 40(3): 510–517. DOI:10.1177/0022022109332845 |
 2017, Vol. 38
2017, Vol. 38