文章信息
- 赵艳芳, 王卓群, 杨静, 刘韫宁, 刘世炜, 曾新颖, 李镒冲, 殷鹏, 周脉耕.
- Zhao Yanfang, Wang Zhuoqun, Yang Jing, Liu Yunning, Liu Shiwei, Zeng Xinying, Li Yichong, Yin Peng, Zhou Maigeng.
- 2013年中国25岁及以上人群高血糖归因死亡对期望寿命的影响
- Number of deaths that attributable to high fasting plasma glucose among population aged 25 and above and its impact on life expectancy in China, 2013
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(8): 1028-1032
- Chinese journal of Epidemiology, 2017, 38(8): 1028-1032
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.08.006
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2017-03-03
2. 100050 北京, 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心生命登记与死因监测室;
3. 100050 北京, 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心合防控与评价室;
4. 100191 北京大学临床研究所;
5. 100050 北京, 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心
2. Division of Vital Registry and Mortality Surveillance, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 100050, China;
3. Division of Integrated Prevention and Evaluation, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 100050, China;
4. Peking University Clinical Research Institute, Beijing 100191, China;
5. National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Beijing 100050, China
长期高血糖是血管病变的重要危险因素之一,可显著增加缺血性心脏病、脑血管疾病和慢性肾病等疾病的发生风险[1-3]。中国≥18岁居民糖尿病患病率由2002年2.6%[4]上升至2013年10.4%[5];在糖尿病上的医疗费用已从1993年22.16亿元上升至2007年2 000亿元,卫生费用占比也从1993年1.96%上升至2007年18.2%[6]。糖尿病及其他高血糖相关疾病给社会带来了沉重的经济负担。此外,高血糖造成的早死和伤残对我国居民期望寿命的影响也不容忽视。本研究用2013年中国居民死因监测以及慢性病及其危险因素监测等数据,开展高血糖归因死亡对期望寿命的影响研究,为确定慢性病防控中的重点疾病和危险因素提供依据。
资料与方法1.数据来源:血糖的流行水平数据来源于2013年中国慢性病及其危险因素监测,是以605个全国疾病监测系统死因监测工作点为基础,随机抽取302个监测点开展调查。本次调查具有城乡和东中西部地区代表性,有效样本为176 534人[5]。死亡数据来自于2013年全国疾病监测系统死因监测;人口数据来源于国家统计局2013年常住人口;高血糖与相关疾病的RR值以及血糖理论最小暴露均值和标准差指标值来源于2013年全球疾病负担研究(GBD2013)[7]。
2.相关定义及标准:
(1)高血糖:FPG水平高于最低期望暴露均值水平。本研究血糖的最低期望暴露均值水平取5.1 mmol/L,标准差取0.3 mmol/L。
(2)与高血糖具有病因学联系的疾病:结核病、缺血性心脏病、脑血管疾病、糖尿病和慢性肾病[8-9]。
(3)血糖的暴露分布:暴露数据主要来源于2013年中国慢性病及其危险因素监测数据。利用监测数据,分别计算全国、分城乡、东中西部地区、分性别、分年龄组的血糖的均值和标准差。年龄分组为25~、30~、35~、40~、45~、50~、55~、60~、65~、70~、75~、80~、≥85岁。
(4)理论最小暴露分布:高血糖的最小理论暴露分布均值为4.8~5.4 mmol/L,标准差为0.3 mmol/L,即认为血糖在该分布时导致人群发生疾病或死亡的风险最低[8]。
(5)人群归因分值(population attributable fraction,PAF)计算:按照GBD2013的比较风险评估理论计算归因于高血糖的PAF。GBD2013将高血糖作为连续型变量计算PAF,高血糖PAF计算无需回归稀释,具体计算方法和公式见文献[9-11]。
(6)计算去除高血糖危险因素后相关疾病的死亡率。
(7)计算该危险因素对期望寿命的影响。
3.分析方法:采用PAF估计高血糖危险因素造成的死亡和对期望寿命的影响。PAF是对实际人群中危险因素暴露的分布与理论最小分布比较,如人群中危险因素暴露降低到理论最小分布,估计疾病或死亡降低的比例。高血糖对人群归因死亡和期望寿命的影响估计分为7个步骤:① 确定高血糖的定义及具有病因学联系的疾病[9];② 估计血糖的暴露分布;③ 估计高血糖与RR值;④ 确定血糖理论最小暴露分布;⑤ 计算PAF;⑥ 利用PAF计算去除高血糖暴露后的相关疾病的死亡率;⑦ 计算高血糖对期望寿命的影响。
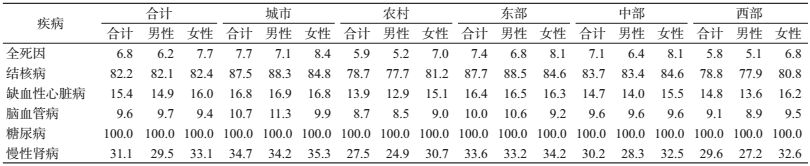
结果1.血糖暴露水平:2013年我国≥25岁居民平均血糖水平为5.7 mmol/L。城市居民平均血糖水平为5.7 mmol/L,农村居民为5.6 mmol/L。东部和中部地区人群平均血糖水平均为5.7 mmol/L,西部地区人群平均为5.5 mmol/L。不同性别和地区城乡居民血糖均值水平和标准差分布情况见表 1。
2. PAF:高血糖造成结核病、缺血性心脏病、脑血管病、糖尿病和慢性肾病的PAF依次为82.2%、15.4%、9.6%、100.0%和31.1%(表 2)。
3.高血糖造成相关疾病的死亡:
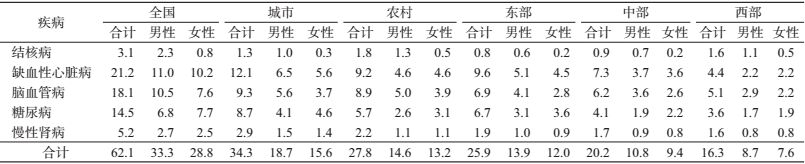
(1)归因死亡人数:2013年归因于高血糖的总死亡人数为62.1万,其中男性33.3万,女性28.8万。城市归因于高血糖的死亡人数(34.3万)多于农村(27.8万);归因高血糖的死亡人数以东部地区最多(25.9万),中部次之(20.2万),西部最少(16.3万)。高血糖造成的相关疾病死亡人数以缺血性心脏病为最多(21.2万),其次为脑血管病(18.1万),其他依次为糖尿病(14.5万)、慢性肾病(5.2万)和结核病(3.1万)。见表 3。
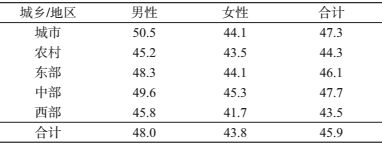
(2)高血糖归因死亡率:2013年中国全人群高血糖归因死亡率为45.9/10万,其中男性为48.0/10万,女性43.8/10万。城市为47.3/10万,农村44.3/10万。东部、中部和西部分别为46.1/10万、47.7/10万和43.5/10万。2013年高血糖归因死亡率呈现男性高于女性、城市高于农村、东、中部高于西部的特点。见表 4。
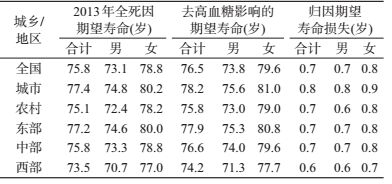
4.高血糖暴露对期望寿命的影响:去除高血糖暴露对期望寿命的影响后,2013年我国居民期望寿命为76.5岁,其中男性73.8岁,女性79.6岁。与2013年全死因期望寿命相比,人群期望寿命可提高0.7岁。高血糖造成的期望寿命损失呈现女性高于男性、城市高于农村、东中部高于西部的特点。见表 5。
本研究利用2013年中国慢性病及其危险因素监测血糖暴露数据和死因监测等数据,采用PAF估算了高血糖暴露造成的死亡以及对期望寿命的影响。结果显示,2013年中国≥25岁居民高血糖导致的死亡人数为62.1万。归因于高血糖的死亡人数呈现男性高于女性、城市高于农村,东中西部地区依次递减的特点。研究显示,2013年高血糖造成的疾病负担同样呈现男性高于女性,经济发达省份高于欠发达省份的特点[3]。2010年与1990年相比,糖尿病标化死亡率从1990年8.8/10万上升至2010年12.8/10万,增长了45.0%,男性标化死亡率的年均增长速度远高于女性[12]。糖尿病死亡负担和失能负担均呈现城市高于农村,东中西部地区依次递减的现象[13]。考虑可能与经济发展水平、工业化和城市化进程以及人口老龄化等因素有关[13-14]。本研究显示,归因于高血糖相关疾病的死亡人数总体上以缺血性心脏病最多,结核病最少,这与中国人群结核病和缺血性心脏病的发病、患病和死亡水平密切相关。2013年中国肺结核报告发病率为66.8/10万[15]。据中国死因监测数据显示[16],2013年中国居民结核病死亡率为2.54/10万,而缺血性心脏病的死亡率(99.35/10万)远高于结核病的死亡水平。不同地区高血糖相关疾病归因死亡顺位又有所差异,如中、东部地区高血糖相关疾病的归因死亡人数以缺血性心脏病为首,而西部地区以脑血管病为首,缺血性心脏病次之。这与不同地区死因别死亡情况一致[16]。
高血糖的暴露水平对我国居民的期望寿命具有重要影响,如去除高血糖暴露,我国居民期望寿命可达到76.5岁,较全死因期望寿命将平均增高0.7岁。高血糖造成的期望寿命损失呈现女性高于男性、城市高于农村、东中部高于西部的特点,与高血糖相关疾病的患病和死亡水平的分布特点密切相关[13-16]。国内外研究均已证实[1, 17-18],控制血糖能够有效地预防糖尿病微血管以及大血管病变的发生或延缓其发展,从而降低糖尿病患者的死亡以及并发症的发生。然而,我国≥18岁成年人糖尿病患者知晓、治疗和控制率依然处于较低水平,分别为30.1%、25.8%,治疗中的血糖控制率为39.7%[19]。糖尿病防控需要从控制血糖、血压、血脂等多个方面综合防治,才能达到最佳效果。而我国糖尿病患者中血糖、血压、血脂同时达标的比例仅为5.6%[20],也就是说,绝大部分中国2型糖尿病患者处于并发症高风险状态。然而,高血糖除了造成糖尿病之外,还与结核病、脑血管疾病、缺血性心脏病和慢性肾病的发病和死亡密切相关。如不能有效控制高血糖,将会严重影响我国居民期望寿命的提升水平。
本研究存在局限性。如采用高血糖与相关疾病的RR值来源于GBD2013[8],该研究通过系统综述全球不同国家的多项大型队列研究数据确定了不同危险因素与疾病结局的RR值。鉴于不同研究的年龄不同,仅确定了≥25岁人群高血糖与相关疾病的RR值数据,且只考虑性别的影响,未考虑不同国家、地区和人种等因素的影响,因此可能会造成一定程度的低估。
利益冲突: 无
| [1] | The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus[J]. N Engl J Med, 1993, 329(14): 977–986. DOI:10.1056/NEJM199309303291401 |
| [2] | Zarowitz BJ. Management of diabetes mellitus in older persons[J]. Geriatr Nurs, 2006, 27(2): 77–82. DOI:10.1016/j.gerinurse.2006.02.001 |
| [3] |
赵艳芳, 王卓群, 杨静, 等.
1990与2013年中国归因于高血糖的疾病负担分析[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2016, 50(9): 769–775.
Zhao YF, Wang ZQ, Yang J, et al. Burden of disease attributable to high fasting plasma glucose in 1990 and 2013 in China[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2016, 50(9): 769–775. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2016.09.005 |
| [4] |
王陇德.中国居民营养与健康状况调查报告之一:2002综合报告[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2005.
Wang LD.Comprehensive report on national nutrition and health survey (2002)[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House People's, 2005. |
| [5] |
中国疾病预防控制中心, 中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心.中国慢性病及其危险因素监测报告(2013)[M]. 北京: 军事医学科学出版社, 2013.
Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.Report on China chronic disease and risk factor survey (2013)[M]. Beijing: Military Medical Science Press, 2013. |
| [6] |
郑亚明, 纪立农, 吴晶.
中国糖尿病经济负担研究系统综述[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2012, 28(10): 821–825.
Zheng YM, Ji LN, Wu J. Cost-of-illness studies of diabetes mellitus in China:a systematic review[J]. Chin J Endocrinol Metab, 2012, 28(10): 821–825. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1000-6699.2012.10.009 |
| [7] | GBD 2013 Mortality and Causes of Death Collaborators. Global, regional, and national age-sex specific all-cause and cause-specific mortality for 240 causes of death, 1990-2013:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2013[J]. Lancet, 2015, 385(9963): 117–171. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61682-2 |
| [8] | GBD 2013 Risk Factors Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 79 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks in 188 countries, 1990-2013:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2013[J]. Lancet, 2015, 386(10010): 2287–2323. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00128-2 |
| [9] | Lim SS, Vos T, Flaxman AD, et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990-2010:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2010[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380(9859): 2224–2260. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61766-8 |
| [10] | Murray CJL, Vos T, Lozano R, et al. Disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 291 diseases and injuries in 21 regions, 1990-2010:a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease study 2010[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380(9859): 2197–2223. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61689-4 |
| [11] |
李镒冲, 刘世炜, 王丽敏, 等.
1990年与2010年中国慢性病主要行为危险因素的归因疾病负担研究[J]. 中华预防医学, 2015, 49(4): 303–308.
Li YC, Liu SW, Wang LM, et al. Burden of disease attributable to main behavioral risk factor of chronic disease inactivity in China, 1990 and 2010[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2015, 49(4): 303–308. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2015.04.005 |
| [12] |
曾新颖, 周脉耕, 李镒冲, 等.
1990年和2010年中国糖尿病的疾病负担研究[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2015, 23(12): 904–907.
Zeng XY, Zhou MG, Li YC, et al. Disease burden of diabetes in China during 1990 and 2010[J]. Chin J Prev Contr Chron Dis, 2015, 23(12): 904–907. DOI:10.16386/j.cjpccd.issn.1004-6194.2015.12.007 |
| [13] |
李镒冲, 刘晓婷, 胡楠, 等.
中国2010年糖尿病疾病负担[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2013, 34(1): 33–36.
Li YC, Liu XT, Hu N, et al. Disease burden on diabetes in China, 2010[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2013, 34(1): 33–36. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2013.01.008 |
| [14] | Li YC, Zhang M, Jiang Y, et al. Co-variations and clustering of chronic disease behavioral risk factors in China:China chronic disease and risk factor surveillance, 2007[J]. PLoS One, 2012, 7(3): e33881. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0033881 |
| [15] |
王丽萍, 曾令佳, 任翔, 等.
中国2013年报告法定传染病发病及死亡特征分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2015, 36(3): 194–198.
Wang LP, Zeng LJ, Ren X, et al. Analysis of morbidity and mortality characteristics of the notifiable diseases reported in 2013 in China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2015, 36(3): 194–198. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2015.03.002 |
| [16] |
中国疾病预防控制中心慢性非传染性疾病预防控制中心, 国家卫生和计划生育委员会统计信息中心.中国死因监测数据集2013[M]. 北京: 科学普及出版社, 2015.
National Center for Chronic and Non-communicable Disease Control and Prevention, Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Health Statistical Information Center of National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China.National death cause monitoring data set (2013)[M]. Beijing: Popular Science Press, 2015. |
| [17] | UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33)[J]. Lancet, 1998, 352(9131): 837–853. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(98)07019-6 |
| [18] |
陈燕燕, 王金平, 安雅莉, 等.
生活方式干预对糖尿病前期人群心脑血管事件和死亡的影响——大庆糖尿病预防长期随访研究[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2015, 54(1): 13–17.
Chen YY, Wang JP, An YL, et al. Effect of lifestyle interventions on reduction of cardiovascular disease events and its mortality in pre-diabetic patients:long-term follow-up of Da Qing diabetes prevention study[J]. Chin J Intern Med, 2015, 54(1): 13–17. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1426.2015.01.005 |
| [19] | Xu Y, Wang LM, He J, et al. Prevalence and control of diabetes in Chinese adults[J]. JAMA, 2013, 310(9): 948–959. DOI:10.1001/jama.2013.168118 |
| [20] | Ji LN, Hu DY, Pan CY, et al. Primacy of the 3B approach to control risk factors for cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes patients[J]. Am J Med, 2013, 126(10): 925. DOI:10.1016/j.amjmed.2013.02.035 |
 2017, Vol. 38
2017, Vol. 38