文章信息
- 苏健, 陶然, 周金意, 杨婕, 覃玉, 胡一河, 陆艳, 金建荣, 卞铮, 郭彧, 陈铮鸣, 李立明, 武鸣.
- Su Jian, Tao Ran, Zhou Jinyi, Yang Jie, Qin Yu, Hu Yihe, Lu Yan, Jin Jianrong, Bian Zheng, Guo Yu, Chen Zhengming, Li Liming, Wu Ming.
- 成年人睡眠状况与糖尿病患病关系的研究
- Relationship between sleep status and the risk of diabetes in adults
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(5): 597-601
- Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2017, 38(5): 597-601
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.05.008
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2016-10-12
2. 850000 拉萨市疾病预防控制中心;
3. 215004 苏州市疾病预防控制中心;
4. 215100 苏州市吴中区疾病预防控制中心;
5. 102308 北京, 中国医学科学院;
6. 英国牛津大学临床与流行病学研究中心;
7. 100191 北京大学公共卫生学院
2. Lhasa Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Lhasa 850000, China;
3. Suzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Suzhou 215004, China;
4. Wuzhong District Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Suzhou 215100, China;
5. Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 102308, China;
6. Clinical Trial Service Unit and Epidemiological Studies Unit, University of Oxford, UK;
7. School of Public Health, Peking University, Beijing 100191, China
糖尿病不仅与遗传因素有关,还与体力活动减少、膳食不合理、超重/肥胖、吸烟和精神压力等行为心理因素密切相关[1-2]。现今越来越多国外研究表明,睡眠时间不足或睡眠质量不佳也会增加罹患糖尿病的风险[3-4],但国内相关研究较少,且样本量较小,研究因素较少,结果也不一致[5-6]。为此本研究利用中国慢性病前瞻性研究(CKB)项目苏州市吴中区基线调查数据,探讨睡眠状况与糖尿病患病的关系。
对象与方法1.调查对象:CKB项目是在我国10个地区开展的针对慢性病长期追踪随访项目,苏州市吴中区为项目点之一。CKB项目调查对象的入选标准和排除标准以及项目相关情况见文献[7-9]。本研究资料源于该项目点的基线调查数据,调查时间为2004年11月至2008年1月。
2.调查方法:包括问卷调查、体格检查、血样样本采集和现场随机血糖检测等。问卷调查采用牛津大学项目组开发的专用电子问卷,包括一般人口社会学信息(性别、年龄、学历、职业和家庭收入等)、健康相关行为(吸烟、饮酒、饮食、睡眠状况和体力活动等)、疾病史(糖尿病家族史和个人患病史等)。体格检查包括身高、体重、腰围和血压等。现场采集调查对象任意时点静脉血样,并记录采血时间距上次就餐时间间隔,取微量静脉血样现场检测血糖(采用Sure Step Plus强生稳步倍加型血糖仪)。随机血糖值在7.8~11.0 mmol/L者于次日现场复查FPG。调查均由经过系统培训并考核合格的人员完成。
3.指标定义及分组:① 入睡困难:每周至少有3 d需>30 min方可入睡;② 容易早醒:每周至少3 d很早醒来,并难以重新入睡;③ 药物助眠:每周至少1 d需服用安眠药帮助睡眠;④ 睡觉打鼾:询问睡觉时打呼噜习惯(是,经常有/是,有时有/没有);⑤ 睡眠时间:每天平均睡眠时间,即由晚入睡到早醒来整个熟睡时间加上午休时间的总和。睡眠相关信息均通过调查员询问,由调查对象自主回答而获得。BMI(kg/m2)参照《中国成人超重和肥胖症预防控制指南》分为4组[10]:<18.5为低体重,18.5~23.9为正常,24.0~27.9为超重,≥28.0为肥胖;体力活动水平根据调查对象通常参加体力活动的类型(包括工作、交通和休闲相关活动)和相应时间长度换算为1 d的代谢当量值(MET-h/d)[11]。现场调查时自报曾经被乡或区级及以上医院诊断为糖尿病,或随机血糖(调查现场采血时间距上次就餐时间<8 h时测得的血糖值)≥11.1 mmol/L,或FPG(调查次日复查的血糖值或调查现场采血时间距上次就餐时间≥8 h时所测得的随机血糖值)≥7.0 mmol/L定义为糖尿病[12]。
4.统计学分析:使用SPSS 21.0软件进行数据分析。计量资料采用x±s表示,组间差异比较采用t检验;计数资料采用频数(百分比)表示,组间差异比较采用χ2检验。分别采用单因素和多因素非条件logistic回归模型分析睡眠状况各相关变量与糖尿病的关系,调整可能的混杂因素,其中模型1调整的因素包括年龄、文化程度、婚姻状况、家庭年收入和糖尿病家族史,模型2在模型1的基础上调整吸烟、饮酒、体力活动水平和BMI。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
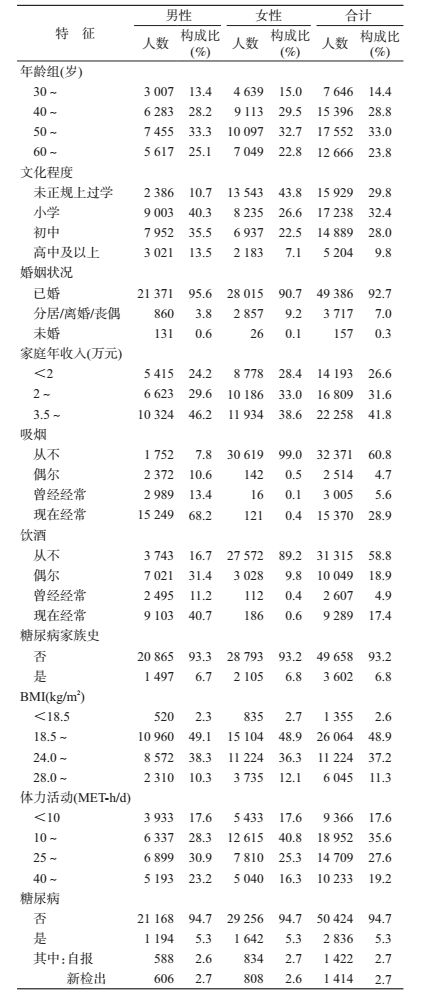
结果1.基本情况:共53 260人完成基线调查,平均年龄(51.60±10.35)岁。其中男性22 362人,平均年龄(52.01±10.33)岁;女性30 898人,平均年龄(51.31±10.35)岁。文化程度主要集中在初中及以下(90.2%),且43.8%的女性未正规上过学。73.4%的调查对象家庭年收入≥2万元。68.2%的男性现在经常吸烟,比例显著高于女性(0.4%)。现在经常饮酒的男性占40.7%,女性占0.6%。超重和肥胖的比例分别为37.2%和11.3%;总人群平均BMI(kg/m2)为24.03±3.21,其中男性为23.98±3.08,女性为24.06±3.30。体力活动(MET-h/d)平均水平为25.52±15.17,其中男性为27.40±16.11,女性为24.18±14.30。6.8%的调查对象有糖尿病家族史。糖尿病患病率(包括自报和新检出者)为5.3%,其中自报和新检出糖尿病患者各占一半,且无性别差异(表 1)。
2.睡眠状况:平均睡眠时间男性为(7.35±1.24)h,女性为(7.38±1.25)h,差异有统计学意义(t=-3.17,P=0.002)。以睡眠时间8 h为主(37.4%),其次为7 h(26.9%),≤6 h和≥9 h的比例分别为22.6%和13.1%。女性入睡困难、容易早醒和药物助眠的比例分别为8.8%、12.0和1.8%,显著高于男性(5.1%、7.3%和0.8%),差异均有统计学意义(入睡困难:χ2=255.81,容易早醒:χ2=314.08,药物助眠:χ2=85.68,均P<0.001)。37.3%的男性在睡觉时经常打鼾,显著高于女性(23.8%)χ2=1 400.24,P<0.001(表 2)。
3.睡眠状况与糖尿病患病关系:单因素分析结果显示,入睡困难(男:OR=1.60,95%CI:1.28~1.99;女:OR=1.64,95%CI:1.41~1.90)、容易早醒(男:OR=1.43,95%CI:1.17~1.74;女:OR=1.46,95%CI:1.27~1.67)和经常打鼾者(男:OR=1.58,95%CI:1.38~1.81;女:OR=2.10,95%CI:1.87~2.35)与糖尿病患病风险存在统计学关联,通过模型1和模型2调整相关混杂因素后,OR值略降低,但仍有统计学意义。在模型2中,女性药物助眠者患糖尿病OR值有统计学意义(OR=1.42,95%CI:1.06~1.92),男性OR值无统计学意义(OR=0.95,95%CI:0.52~1.74)。见表 3。
睡眠时间为8 h调查对象糖尿病患病率最低,以此为参照,睡眠时间增加或减少均呈现糖尿病患病风险增加,呈U形分布,并且睡眠时间不足者患病风险更高。通过模型1和模型2调整相关混杂因素后,睡眠时间与糖尿病患病风险的U形分布特征减弱,男性睡眠时间≤6 h的OR值为1.37(95%CI:1.17~1.60),女性为1.24(95%CI:1.08~1.41),而睡眠时间≥9 h的OR值变为无统计学意义(表 3)。
讨论我国居民睡眠质量问题的发生率较高,男女性分别为26%和29%[13],睡眠时间也呈下降趋势,2002年和2007年分别为8.3 h和8.1 h[14],2010年江苏省居民的睡眠时间降至7.4 h[15]。本研究结果表明,入睡困难、容易早醒和经常打鼾均与男女性人群糖尿病患病密切相关,而药物助眠仅与女性罹患糖尿病存在关联。睡眠时间与糖尿病患病率关系呈U形分布,调整相关混杂因素后,睡眠时间不足(≤6 h)仍与糖尿病患病有统计学关联,但未发现睡眠时间过长(≥9 h)与糖尿病患病有统计学关联。
Nilsson等[16]研究发现入睡困难或药物助眠者罹患糖尿病的风险增加52%,同时存在上述两种睡眠问题者罹患糖尿病的风险增加78%。Kowall等[17]通过5年随访研究发现,容易早醒可致糖尿病发病风险显著上升(RR=1.56,95%CI:1.10~2.22)。本研究结果显示,入睡困难和容易早醒人群呈现糖尿病患病风险增高,与既往研究结果一致[3-4]。存在睡眠问题者虽然服用药物助眠,但糖尿病的发生风险仍然较高,说明药物助眠未降低糖尿病的患病风险。药物助眠与糖尿病的关系仅在女性人群中显示有统计学意义,与Rod等[18]研究结果不一致,可能与本次调查人群中男性服用助眠药物比例较低有关。此外,本研究还发现经常打鼾与糖尿病存在统计学关联,男女性OR值分别为1.16和1.39,与Pamidi和Tasali[19]研究结果一致。
国内外相关研究发现,睡眠时间与糖尿病的患病风险存在相关性,睡眠时间不足或者过长都可能增加人群罹患糖尿病的风险[5, 20]。本研究结果提示随着人群睡眠时间增加,糖尿病患病率呈现U形分布特征,调整相关混杂因素后,睡眠时间不足(≤6 h)与糖尿病在不同性别人群中均有关联,而睡眠时间过长(≥9 h)的OR值则变为无统计学意义,与既往的一些研究结果一致[21-22]。本研究在调整混杂因素后睡眠时间过长的影响消失,提示年龄、社会经济状况和生活行为习惯等因素可能对睡眠过长与糖尿病的相关性具有一定的稀释作用,也可能由于睡眠时间过长人群数量相对较少,统计效能降低。此外,有研究显示睡眠时间不足与糖尿病之间的相关性仅在男性中存在,而在女性中未见统计学意义[23],但也有研究发现这种相关性仅见于女性[24],因此睡眠时间与糖尿病的相关性是否存在性别差异尚需要更多的大样本量前瞻性研究证据。
本研究存在局限性。首先,本文糖尿病患病率(5.3%)远低于同期全国14个省的研究结果(9.7%)[25],其主要原因为本研究人群是通过自愿方式在社区招募获得,其构成为非代表全人群,而且仅根据FPG值诊断糖尿病,未进行口服糖耐量试验,糖尿病患病率存在一定程度低估;其次,调查中睡眠相关问题均为自报,带有一定的主观性,从而可能造成错分偏倚;此外本研究中某些特征分类数量较少,如男性服用药物助眠、睡眠时间≥9 h等,可能会降低统计效能。
志谢: 感谢中国慢性病前瞻性研究项目管理委员会、国家项目办公室、牛津协助中心和江苏省项目办公室的专家和工作人员的大力支持和帮助利益冲突: 无
| [1] |
刘景超, 郭志荣, 胡晓抒, 等.
江苏省社区人群生活方式与超重肥胖对糖尿病发病的影响[J]. 中华预防医学杂志, 2012, 46(4): 311–315.
Liu JC, Guo ZR, Hu XS, et al. Impact of lifestyle and obesity on the occurrence of type 2 diabetes:a prospective study in Jiangsu province[J]. Chin J Prev Med, 2012, 46(4): 311–315. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0253-9624.2012.04.006 |
| [2] |
陈培培, 娄培安, 余加席, 等.
徐州市居民糖尿病危险因素的调查与分析[J]. 中华健康管理学杂志, 2010, 4(2): 78–80.
Chen PP, Lou PA, Yu JX, et al. Risk factors of diabetes mellitus of residents living in Xuzhou city[J]. Chin J Health Manage, 2010, 4(2): 78–80. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1674-0815.2010.02.006 |
| [3] | Cappuccio FP, D'Elia L, Strazzullo P, et al. Quantity and quality of sleep and incidence of type 2 diabetes:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Diabetes Care, 2010, 33(2): 414–420. DOI:10.2337/dc09-1124 |
| [4] | Anothaisintawee T, Reutrakul S, van Cauter E, et al. Sleep disturbances compared to traditional risk factors for diabetes development:systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Sleep Med Rev, 2015, 30: 11–24. DOI:10.1016/j.smrv.2015.10.002 |
| [5] |
李志强, 奚悦, 吴东妮, 等.
不同午睡状况下夜间睡眠时长与2型糖尿病的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志, 2014, 34(22): 6339–6340.
Li ZQ, Xi Y, Wu DN, et al. Relationship between sleep duration at night and type 2 diabetes with different napping conditions[J]. Chin J Gerontol, 2014, 34(22): 6339–6340. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2014.22.045 |
| [6] |
张雷, 张盼, 娄培安, 等.
睡眠质量及时间与2型糖尿病的关系研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志, 2012, 16(2): 117–120.
Zhang L, Zhang P, Lou PA, et al. Association study of sleep quality and duration with type 2 diabetes[J]. Chin J Dis Contr Prev, 2012, 16(2): 117–120. |
| [7] |
李立明, 吕筠, 郭彧, 等.
中国慢性病前瞻性研究:研究方法和调查对象的基线特征[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2012, 33(3): 249–255.
Li LM, Lv J, Guo Y, et al. The China KadoorieBiobank:related methodology and baseline characteristics of the participants[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2012, 33(3): 249–255. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2012.03.001 |
| [8] | Li L, Guo Y, Chen Z, et al. Epidemiology and the control of disease in China, with emphasis on the Chinese Biobank Study[J]. Public Health, 2012, 126(3): 210–213. DOI:10.1016/j.puhe.2011.11.012 |
| [9] | Chen ZM, Lee LM, Chen JS, et al. Cohort profile:the Kadooriestudy of Chronic Disease in China (KSCDC)[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2005, 34(6): 1243–1249. DOI:10.1093/ije/dyi174 |
| [10] |
中华人民共和国卫生部疾病控制司.中国成人超重和肥胖症预防控制指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2006: 1–5.
Division of Disease Control, Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China.Prevention and control guidelines of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults[M]. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2006: 1–5. |
| [11] | Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Herrmann SD, et al. 2011 Compendium of physical activities:a second update of codes and MET values[J]. Med Sci Sports Exerc, 2011, 43(8): 1575–1581. DOI:10.1249/MSS.0b013e31821ece12 |
| [12] |
中华医学会糖尿病学分会.中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2010年版)[M]. 北京: 北京大学医学出版社, 2011: 5.
The Chinese Medical Association Diabetes Branch.Chinese guidelines on prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (2010)[M]. Beijing: Pecking University Medical Press, 2011: 5. |
| [13] | Sun WJ, Yu YQ, Yuan JQ, et al. Sleep duration and quality among different occupations-China national study[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(3): e0117700. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0117700 |
| [14] |
殷鹏, 张梅, 李镒冲, 等.
中国15~69岁居民睡眠状况分析[J]. 中国慢性病预防与控制, 2011, 19(2): 152–153.
Yin P, Zhang M, Li YC, et al. Analysis on characteristics of sleeping in Chinese population aged 15-69 years[J]. Chin J Prev Contr Chronic Dis, 2011, 19(2): 152–153. |
| [15] |
江苏省疾病预防控制中心.江苏省慢性病及其危险因素监测报告(2010)[M]. 南京: 南京师范大学出版社, 2013: 68–69.
Jiangsu Provincial Center for Disease Control and Prevention.Report on chronic disease risk factor surveillance in Jiangsu province (2010)[M]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University Press, 2013: 68–69. |
| [16] | Nilsson PM, ööst M, Engström G, et al. Incidence of diabetes in middle-aged men is related to sleep disturbances[J]. Diabetes Care, 2004, 27(10): 2464–2469. DOI:10.2337/diacare.27.10.2464 |
| [17] | Kowall B, Lehnich AT, Strucksberq KH, et al. Associations among sleep disturbances, nocturnal sleep duration, daytime napping, and incident prediabetes and type 2 diabetes:the Heinz Nixdorf Recall Study[J]. Sleep Med, 2016, 21: 35–41. DOI:10.1016/j.sleep.2015.12.017 |
| [18] | Rod NH, Vahtera J, Westerlund H, et al. Sleep disturbances and cause-specific mortality:results from the GAZEL cohort study[J]. Am J Epidemiol, 2011, 173(3): 300–309. DOI:10.1093/aje/kwq371 |
| [19] | Pamidi S, Tasali E. Obstructive sleep apnea and type 2 diabetes:is there a link?[J]. Front Neurol, 2012, 3: 126. DOI:10.3389/fneur.2012.00126 |
| [20] | Yaggi HK, Araujo AB, McKinlay JB. Sleep duration as a risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes[J]. Diabetes Care, 2006, 29(3): 657–661. DOI:10.2337/diacare.29.03.06.dc05-0879 |
| [21] | Rafalson L, Donahue RP, Stranges S, et al. Short sleep duration is associated with the development of impaired fasting glucose:The Western New York Health Study[J]. Ann Epidemiol, 2010, 20(12): 883–889. DOI:10.1016/j.annepidem.2010.05.002 |
| [22] | Lou P, Chen PP, Zhang L, et al. Relation of sleep quality and sleep duration to type 2 diabetes:a population-based cross-sectional survey[J]. BMJ Open, 2012, 2(4): e000956. DOI:10.1136/bmjopen-2012-000956 |
| [23] | Mallon L, Broman JE, Hetta J. High incidence of diabetes in men with sleep complaints or short sleep duration:a 12-year follow-up study of a middle-aged population[J]. Diabetes Care, 2005, 28(11): 2762–2767. DOI:10.2337/diacare.28.11.2762 |
| [24] | Tuomilehto H, Peltonen M, Partinen M, et al. Sleep duration is associated with an increased risk for the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in middle-aged women-The FIN-D2D Survey[J]. Sleep Med, 2008, 9(3): 221–227. DOI:10.1016/j.sleep.2007.04.015 |
| [25] | Yang WY, Lu JM, Weng JP, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 362(12): 1090–1101. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa0908292 |
 2017, Vol. 38
2017, Vol. 38