文章信息
- 王醴湘, 樊萌语, 余灿清, 郭彧, 卞铮, 谭云龙, 裴培, 陈君石, 吕筠, 李立明 .
- Wang Lixiang, Fan Mengyu, Yu Canqing, Guo Yu, Bian Zheng, Tan Yunlong, Pei Pei, Chen Junshi, Lyu Jun, Li Liming .
- 中国成年人体质指数与主要慢性病死亡风险的前瞻性研究
- Association between body mass index and both total and cause-specific mortality in China: findings from data through the China Kadoorie Biobank
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2017, 38(2): 205-211
- CHINESE JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY, 2017, 38(2): 205-211
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2017.02.014
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2016-07-26
2. 100730 北京, 中国医学科学院 北京协和医学院;
3. 100022 北京, 国家食品安全风险评估中心
2. Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences, Beijing 100730, China;
3. China National Center for Food Safety Risk Assessment, Beijing 100022, China
BMI与很多健康结局有关联。诸多前瞻性队列研究显示,BMI与死亡风险呈“U型”或“J型”关联,即低体重和超重都会使死亡风险增加。相关研究规模较小[1],数据整合后的协作性研究受不同研究收集信息的限制,只能控制有限的混杂变量,不同研究实施上的差异可能带来一定的影响。本研究利用中国慢性病前瞻性研究(CKB)50余万成年人的随访数据,分析BMI与全死因死亡及主要慢性病死亡风险之间的前瞻性关联。
对象与方法1. 研究对象:CKB项目点包括5个城市和5个农村地区,项目介绍见文献[2-4]。项目中有完整基线调查数据的调查对象共512 891人。本研究分析中剔除基线时自报患有心脏病(n=15 472)、脑卒中(n=8 884)、恶性肿瘤(n=2 577)、COPD(n=37 063)与糖尿病(n=30 299);剔除基线调查完成后即失访(n=3)、基线BMI信息缺失(n=2)。最终纳入分析428 593人。
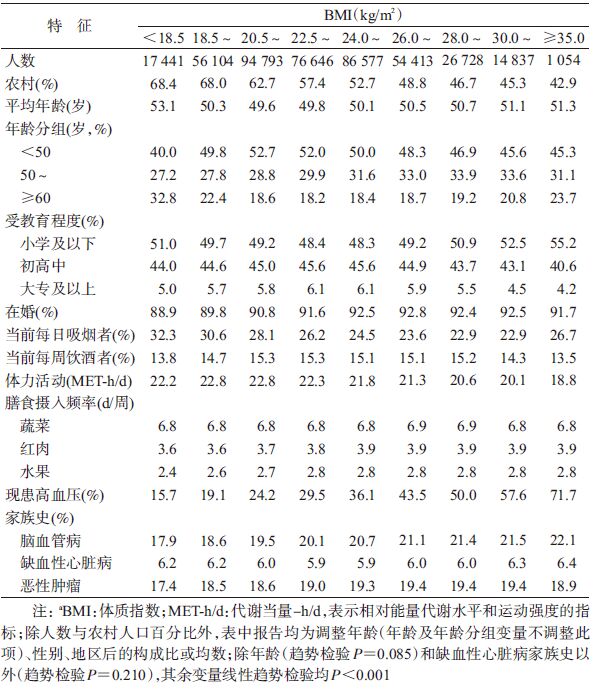
2. 研究内容:身高(身高仪)和体重(TANITA TBF-300GS体质构成分析仪)由统一培训的调查员测量获得。BMI为体重(kg)与身高(m)平方的比值(kg/m2)。参考2006年《中国成人超重和肥胖症预防控制指南》[5]中设定的BMI值,并在此基础上将BMI(kg/m2)分为9组:<18.5、18.5~20.4、20.5~22.4、22.5~23.9、24.0~25.9、26.0~27.9、28.0~29.9、30.0~34.9、≥35.0。本研究分析中涉及的其他一般人口社会学信息、生活方式特征、个人及家庭健康状况等通过调查员面对面询问获得。
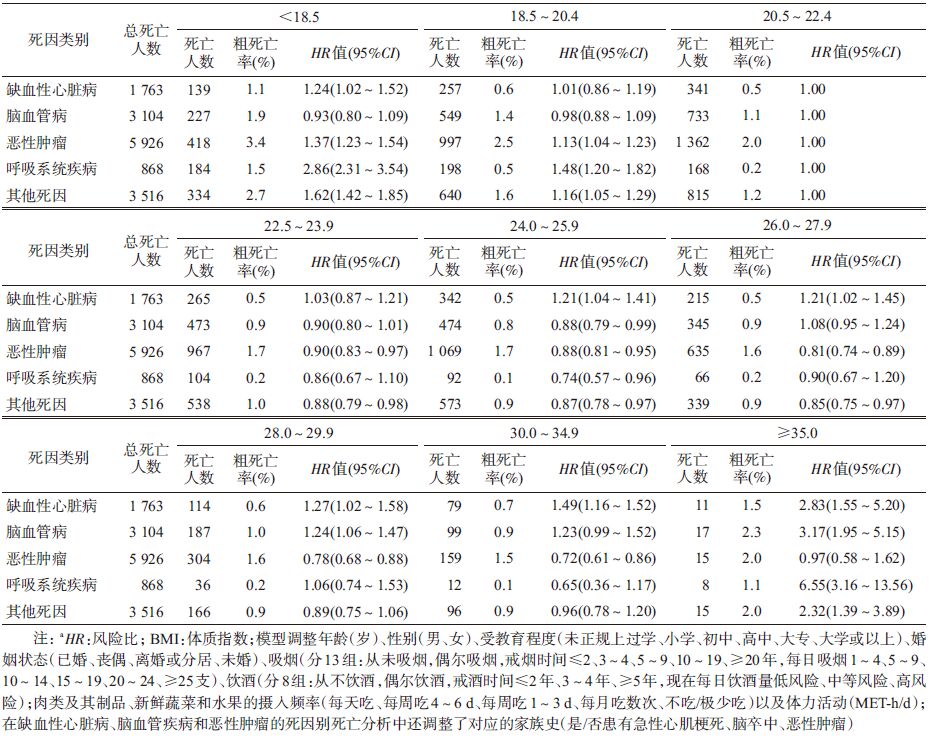
死亡信息主要通过中国疾病监测点系统(Disease Surveillance Points,DSP)和户籍系统获取,同时辅以主动的定向监测。死因信息主要通过居民死亡医学证明书获得,必要时根据既往医院病案记录或入户调查进行死因推断(verbal autopsy)。死因分类采用国际疾病分类(ICD)第10版,即ICD-10。本研究的主要终点包括全死因死亡和5类死因别死亡,即缺血性心脏病(I20~I25)、脑血管疾病(I60~I69)、恶性肿瘤(C00~C97)、呼吸系统疾病(J00~J99)及其他。
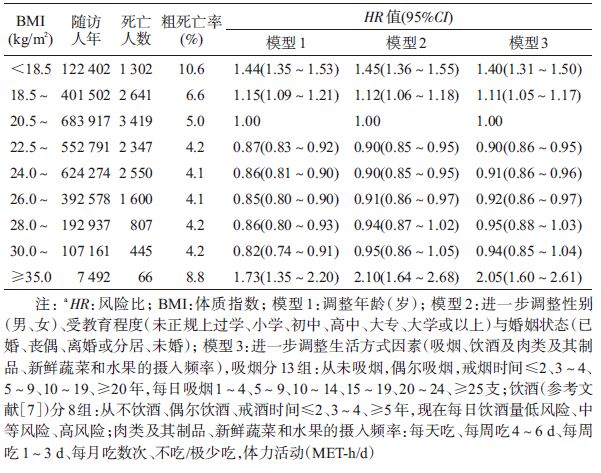
3. 统计学分析:比较不同BMI分组的研究对象的基线特征。连续型变量采用General linear model模型,分类变量根据变量类型分别采用二元或多元logistic回归模型,调整年龄、性别及地区后的均数或构成比,并以BMI的连续变量形式进行线性趋势检验。随访人年的计算从基线调查开始,到死亡、失访或2013年12月31日为止。分析分别在全人群、男女性人群及基线调查时从未吸烟人群中进行,使用Cox比例风险回归模型分析BMI与死亡之间的关联,以年龄作为时间尺度,并按年龄(5岁一组)和项目地区(10个地区)分层,计算风险比(HR)及其95%CI。多变量模型对已知或可能影响死亡风险的因素进行逐步调整:模型1:仅调整年龄;模型2:在此基础上增加调整人口学特征(性别、受教育程度和婚姻状态);模型3:增加调整生活方式特征(吸烟、饮酒、膳食和体力活动)和疾病史(在死因别分析中调整)。其中,对于吸烟、饮酒、体力活动变量进行了重新编码,具体方法参考文献[6-8]。最后,用似然比检验性别对BMI与死亡结局是否存在效应修饰作用。两部分数据分别采用SAS 9.3和Stata 13.0软件进行,所有检测均为双侧检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
结 果1. 研究对象:年龄(50.2±10.2)岁,男性占40.3%,农村地区人群占57.2%,BMI为(23.6±0.6)kg/m2。全人群不同BMI水平研究对象的基线特征见表 1。与低BMI的个体相比,BMI越高组:农村人群比例越低、当前吸烟者比例越低、体力活动水平越低、每周进食红肉和水果的频率越高、高血压现患率越高。
2. BMI与全人群全死因死亡风险关联:共随访(7.2±1.3)年,累计随访3 085 054人年。随访期间共观察到死亡15 177人,其中男性7 862人,女性6 315人。全人群不同BMI分组全死因死亡和死因别风险关联分析结果见表 2、3。全人群Cox回归分析在调整了多种死亡危险因素后(模型3),与BMI为20.5~22.4 kg/m2的人群相比,BMI<18.5、18.5~20.4和≥35.0 kg/m2的人群死亡风险升高,HR值(95%CI)分别为1.40(1.31~1.50)、1.11(1.05~1.17)和2.05(1.60~2.61)。与死亡风险最低组相比,超额风险在15%以内的BMI范围值为20.5~34.9。上述关联在男性和女性之间比较,差异无统计学意义(交互作用P>0.05)。
3. BMI与各死因别死亡风险关联:为了更直观地判断风险增加程度,在原结果基础上计算各BMI组与死亡风险最低组相比的超额风险。与死亡风险最低组相比,超额风险<15%者的BMI范围:缺血性心脏病为18.5~23.9,脑血管病为<26.0,恶性肿瘤为26.0~34.9,呼吸系统疾病为24.0~25.9。BMI与上述死因别死亡风险间的关联,男性和女性比较,差异无统计学意义(交互作用P>0.05)。
4. 从未吸烟人群BMI与死亡风险关联:从未吸烟人群(269 219人)与全人群BMI与死亡风险关联的对比情况见图 1,从未吸烟人群中BMI与全死因死亡风险的关联无明显改变。对于各死因别死亡风险,脑血管病、恶性肿瘤和呼吸系统疾病死亡风险相对较低的BMI范围值略有变化:脑血管病为<28.0,恶性肿瘤为22.5~34.9,呼吸系统疾病为22.5~25.9。
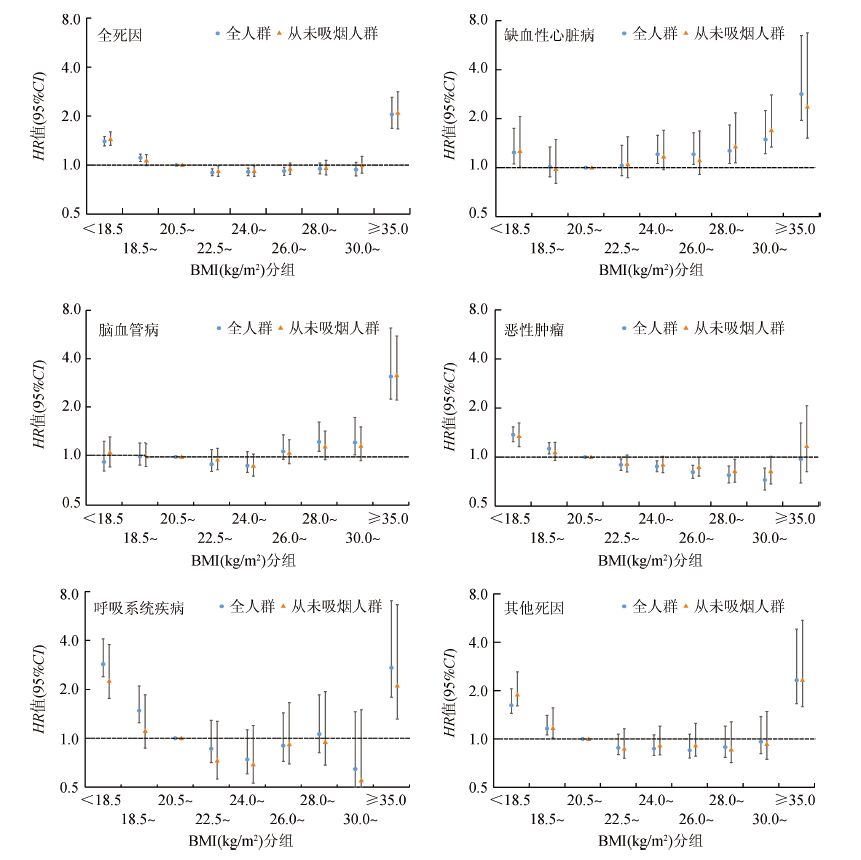
|
| 注: HR值:风险比; CI:置信区间; 纵坐标采用对数坐标轴;部分死因别(呼吸系统疾病)结果95%CI超出坐标轴范围,以无端线直线表示 图 1 中国10个地区428 593名研究对象全人群及从未吸烟人群BMI与死亡风险关联 |
为检验上述分析方法的稳定性,分析中剔除了随访时间不满2年的死亡者(n=2 891),或剔除基线前一年内体重减轻≥2.5 kg者(n=42 589),结果均未见明显变化。
讨 论本研究利用大规模的中国人群前瞻性队列数据检验了基线BMI水平与总死亡和主要慢性病死亡风险之间的前瞻性关联。结果显示,在10年随访期内,BMI与全死因死亡风险间呈“U型”关联,BMI<20.4和≥35.0 kg/m2时的死亡风险显著增加。不同死因别死亡风险相对较低的BMI范围不尽相同,但总体表现为低体重和肥胖者的死亡风险明显增加。BMI与死亡风险之间的关联在男女性别之间的表现相似。
本研究结果与欧美地区大队列(如美国的AARP膳食健康研究队列[9]、CPS-Ⅱ队列[10]和欧洲地区的EPIC队列[11])、亚洲地区其他国家大型队列(如日本国家心血管调查队列[12]、韩国国民健康保险队列[13])以及我国部分队列[14-16]的研究结果基本相似。肥胖是心血管疾病死亡的重要危险因素之一,对于全死因死亡和其他死因别死亡,严重肥胖也是重要危险因素之一。该人群的体内脂肪含量过多,游离脂肪酸水平高,同时生成一系列促炎性因子,伴随脂联素水平的降低;这些化学物质的改变导致机体产生功能结构上的变化[17],产生一系列代谢症状,使其发生重大疾病和死亡的风险增加[18-19]。
本研究及国内外研究均显示,对于全死因死亡和部分死因别死亡(呼吸系统疾病、恶性肿瘤和其他死因别),超重及轻度肥胖人群的死亡风险比正常体重人群并未增加,甚至还有降低;即体重正常或低体重个体的死亡风险反而更高。有研究者将这一现象称为“肥胖悖论(obesity paradox)”[17, 20],认为主要是由“因果倒置”和吸烟混杂因素导致的。换言之,患有重大疾病的个体可能因疾病导致体重下降,或因疾病而采取减重措施;而这些个体死亡风险的增加也是因疾病引起[21]。因此,部分低体重或正常体重范围的个体表现出的死亡风险增加可能是因果倒置的结果,而不是低体重对死亡风险的真实影响[22]。针对这一情况,本研究在分析时参照其他研究的措施[1, 11-12, 23-27],剔除了基线时患有重大疾病的个体,甚至剔除了近一年体重有明显降低的个体以控制基线时未被发现的潜在疾病的可能影响。这些措施在一定程度上避免了“因果倒置”对结果的影响。
吸烟的混杂也可导致“肥胖悖论”。吸烟通常导致体重减轻[21];同时也是多种疾病的重要危险因素之一,可增加死亡风险[28]。本研究在分析时,结合吸烟状态、当前吸烟者的每日吸烟量与戒烟者的戒烟年限构建了吸烟变量,在多因素分析中进行了控制,很大程度上控制了吸烟可能带来的混杂因素。本研究在从未吸烟人群中进行重复分析,BMI与死亡风险的大体趋势无明显改变。本研究结果与部分研究结果相同[1, 14, 29-31];也有一些研究发现,在从未吸烟人群中全死因死亡风险在低BMI人群未升高,在高BMI人群中则明显增高[10, 20, 28, 32-34]。
全球BMI死亡协作组最新发表的1篇整合了全球239项前瞻性研究的BMI与全死因死亡风险的Meta分析结果显示,当采取偏倚控制措施剔除基线患有重大疾病者及调整吸烟状况时,与BMI为18.5~24.9组相比,25.0~29.9组的死亡风险低于参照组或与参照组差异无统计学意义。但是,当研究进一步剔除随访开始5年的随访信息时,超重人群的死亡风险高于参照组[35]。本研究队列成员平均随访7年,通过剔除前2年的随访死亡病例并不能完全避免因果倒置的影响,但是进一步剔除更长年限的随访信息会降低研究的统计学效力。随访时间仍然相对较短是本研究的局限。
本研究的优势在于前瞻性设计,样本量大,可对BMI指标进行更小范围的分组,更好地观察暴露与结局间的剂量反应关系;全部研究人群采用统一的研究方案和评价方法。除因果倒置的控制措施和吸烟混杂作用的控制,分析时还控制了其他已知的和可能的混杂因素。此外,研究人群的身高和体重非自报,而是由经培训的专业人员按统一的操作流程测量得到,更好地控制了BMI相关的信息偏倚。根据研究对象自报信息进行基线疾病剔除,纳入分析的研究对象中仍可能存在少数患病且不知的情况,导致残余混杂因素。且利用基线时一次性测量的BMI水平对个体进行暴露分组,无法考虑个体BMI在随访期间可能发生的变化,也无法调整可能的回归稀释偏倚。
综上所述,本研究显示低体重人群和肥胖人群的死亡风险均增加。由于队列随访年限相对较短,仍有可能受因果倒置的影响。在以死亡作为结局指标时,可能受疾病严重程度和个体生存能力的影响,不能完全反映BMI与疾病发生风险的关联。人群队列更长期的随访以及更多关于BMI与主要慢性病发病风险的分析将有助于更加全面地理解BMI对人群健康的影响。
利益冲突: 无
| [1] | Zheng W, McLerran DF, Rolland B, et al. Association between body-mass index and risk of death in more than 1 million Asians[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011, 364(8): 719–729. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1010679 |
| [2] | Chen ZM, Chen JS, Collins R, et al. China Kadoorie Biobank of 0.5 million people:survey methods,baseline characteristics and long-term follow-up[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2011, 40(6): 1652–1666. DOI:10.1093/ije/dyr120 |
| [3] | Chen ZM, Lee L, Chen JS, et al. Cohort profile:the Kadoorie study of chronic disease in China (KSCDC)[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2005, 34(6): 1243–1249. DOI:10.1093/ije/dyi174 |
| [4] |
李立明, 吕筠, 郭彧, 等.
中国慢性病前瞻性研究:研究方法和调查对象的基线特征[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2012, 33(3): 249–255.
Li LM, Lyu J, Guo Y, et al. The China Kadoorie Biobank:related methodology and baseline characteristics of the participants[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2012, 33(3): 249–255. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2012.03.001 |
| [5] |
中华人民共和国卫生部疾病控制司.中国成人超重和肥胖症预防控制指南[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2006.
Bureau of Disease Prevention and Control,Ministry of Health of China.The Guideline for prevention and control of overweight and obesity in Chinese adults[M].Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2006. |
| [6] |
王昕, 吕筠, 郭彧, 等.
中国慢性病前瞻性研究:10个项目地区成年人群吸烟行为特征差异分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2015, 36(11): 1200–1204.
Wang X, Lyu J, Guo Y, et al. Regional differences in adults' smoking pattern:findings from China Kadoorie Biobank study in 10 areas in China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2015, 36(11): 1200–1204. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2015.11.004 |
| [7] |
吕筠, 郭彧, 卞铮, 等.
中国慢性病前瞻性研究:10个项目地区人群饮酒行为特征差异的分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2014, 35(8): 875–881.
Lyu J, Guo Y, Bian Z, et al. Regional differences in patterns of alcohol consumption:findings from the China Kadoorie Biobank study on half a million people from 10 regions[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2014, 35(8): 875–881. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2014.08.001 |
| [8] |
樊萌语, 吕筠, 郭彧, 等.
中国慢性病前瞻性研究:10个项目地区成人体力活动和休闲静坐时间特征差异的分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志, 2015, 36(8): 779–785.
Fan MY, Lyu J, Guo Y, et al. Regional differences on patterns of physical activity and leisure sedentary time:findings from the China Kadoorie Biobank study,including a million people from 10 regions[J]. Chin J Epidemiol, 2015, 36(8): 779–785. DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2015.08.002 |
| [9] | Adams KF, Schatzkin A, Harris TB, et al. Overweight,obesity,and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old[J]. N Engl J Med, 2006, 355(8): 763–778. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa055643 |
| [10] | Patel AV, Hildebrand JS, Gapstur SM. Body mass index and all-cause mortality in a large prospective cohort of white and black U.S. Adults[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(10): e109153. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0109153 |
| [11] | Pischon T, Boeing H, Hoffmann K, et al. General and abdominal adiposity and risk of death in Europe[J]. N Engl J Med, 2008, 359(20): 2105–2120. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa0801891 |
| [12] | Hozawa A, Okamura T, Oki I, et al. Relationship between BMI and all-cause mortality in Japan:NIPPON DATA80[J]. Obesity, 2008, 16(7): 1714–1717. DOI:10.1038/oby.2008.237 |
| [13] | Jee SH, Sull JW, Park J, et al. Body-mass index and mortality in Korean men and women[J]. N Engl J Med, 2006, 355(8): 779–787. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa054017 |
| [14] | Wu CY, Chou YC, Huang N, et al. Association of body mass index with all-cause and cardiovascular disease mortality in the elderly[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(7): e102589. DOI:10.1371/journal.pone.0102589 |
| [15] | Chen ZM, Yang GH, Offer A, et al. Body mass index and mortality in China:a 15-year prospective study of 220000 men[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2012, 41(2): 472–481. DOI:10.1093/ije/dyr208 |
| [16] |
王悠清. 成人体质指数与死亡风险的前瞻性研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2015.
Wang YQ. Association between body mass index and mortality in adults:a prospective study in China[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2015. |
| [17] | Goyal A, Nimmakayala KR, Zonszein J. Is there a paradox in obesity?[J]. Cardiol Rev, 2014, 22(4): 163–170. DOI:10.1097/CRD.zhlxbxzz-38-2-20500004 |
| [18] | Bastien M, Poirier P, Lemieux I, et al. Overview of epidemiology and contribution of obesity to cardiovascular disease[J]. Prog Cardiovasc Dis, 2014, 56(4): 369–381. DOI:10.1016/j.pcad.2013.10.016 |
| [19] | Sharma S, Batsis JA, Coutinho T, et al. Normal-weight central obesity and mortality risk in older adults with coronary artery disease[J]. Mayo Clin Proc, 2016, 91(3): 343–351. DOI:10.1016/j.mayocp.2015.12.007 |
| [20] | Tobias DK, Hu FB. Does being overweight really reduce mortality?[J]. Obesity, 2013, 21(9): 1746–1749. DOI:10.1002/oby.20602 |
| [21] | Lee JY, Kim HC, Kim C, et al. Underweight and mortality[J]. Public Health Nutr, 2016, 19(10): 1751–1756. DOI:10.1017/S136898001500302X |
| [22] | Jackson CL, Yeh HC, Szklo M, et al. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality in US adults with and without diabetes[J]. J Gen Intern Med, 2014, 29(1): 25–33. DOI:10.1007/s11606-013-2553-7 |
| [23] | Prospective Studies Collaboration. Body-mass index and cause-specific mortality in 900000 adults:collaborative analyses of 57 prospective studies[J]. Lancet, 2009, 373(9669): 1083–1096. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60318-4 |
| [24] | Wienpahl J, Ragland DR, Sidney S. Body mass index and 15-year mortality in a cohort of black men and women[J]. J Clin Epidemiol, 1990, 43(9): 949–960. DOI:10.1016/0895-4356(90)90078-4 |
| [25] | Yi SW, Ohrr H, Shin SA, et al. Sex-age-specific association of body mass index with all-cause mortality among 12.8 million Korean adults:a prospective cohort study[J]. Int J Epidemiol, 2015, 44(5): 1696–1705. DOI:10.1093/ije/dyv138 |
| [26] | Berrington de Gonzalez A, Hartge P, Cerhan JR, et al. Body-mass index and mortality among 1.46 million white adults[J]. N Engl J Med, 2010, 363(23): 2211–2219. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1000367 |
| [27] | Yamauchi Y, Hasegawa W, Yasunaga H, et al. Paradoxical association between body mass index and in-hospital mortality in elderly patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Japan[J]. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis, 2014, 9: 1337–1346. DOI:10.2147/COPD.S75175 |
| [28] | Tobias DK, Pan A, Jackson CL, et al. Body-mass index and mortality among adults with incident type 2 diabetes[J]. N Engl J Med, 2014, 370(3): 233–244. DOI:10.1056/NEJMoa1304501 |
| [29] | Tamakoshi A, Yatsuya H, Lin YS, et al. BMI and all-cause mortality among Japanese older adults:findings from the Japan collaborative cohort study[J]. Obesity, 2010, 18(2): 362–369. DOI:10.1038/oby.2009.190 |
| [30] | Bhaskaran K, Douglas I, Forbes H, et al. Body-mass index and risk of 22 specific cancers:a population-based cohort study of 5.24 million UK adults[J]. Lancet, 2014, 384(9945): 755–765. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(14)60892-8 |
| [31] | Teucher B, Rohrmann S, Kaaks R. Obesity:focus on all-cause mortality and cancer[J]. Maturitas, 2010, 65(2): 112–116. DOI:10.1016/j.maturitas.2009.11.018 |
| [32] | Sjöström LV. Mortality of severely obese subjects[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 1992, 55(2 Suppl): S516–523. |
| [33] | Winter JE, MacInnis RJ, Wattanapenpaiboon N, et al. BMI and all-cause mortality in older adults:a meta-analysis[J]. Am J Clin Nutr, 2014, 99(4): 875–890. DOI:10.3945/ajcn.113.068122 |
| [34] | Zamboni M, Mazzali G, Zoico E, et al. Health consequences of obesity in the elderly:a review of four unresolved questions[J]. Int J Obes, 2005, 29(9): 1011–1029. DOI:10.1038/sj.ijo.0803005 |
| [35] | The Global BMI Mortality Collaboration. Body-mass index and all-cause mortality:individual-participant-data meta-analysis of 239 prospective studies in four continents[J]. Lancet, 2016, 388(10046): 776–786. DOI:10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30175-1 |
 2017, Vol. 38
2017, Vol. 38