文章信息
- 赵庆革, 龚煜汉, 廖强, 余刚, 王科, 王菊, 尹碧波, 杨淑娟, 张建新, 梁鹏艳, 王启兴 .
- Zhao Qingge, Gong Yuhan, Liao Qiang, Yu Gang, Wang Ke, Wang Ju, Yin Bibo, Yang Shujuan, Zhang Jianxin, Liang Pengyan, Wang Qixing .
- 凉山彝族自治州2011-2013年基于BED捕获酶联免疫法估算HIV-1新发感染率
- Estimation on the HIV-1 incidence in Liangshan Yi Autonomous Prefecture, under BED-capture enzyme immunoassay, from 2011 to 2013
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2016, 37(8): 1105-1107
- CHINESE JOURNAL OF EPIDEMIOLOGY, 2016, 37(8): 1105-1107
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2016.08.010
-
文章历史
收稿日期: 2016-01-07
2. 615000 西昌, 凉山州疾病预防控制中心
2. Liangshan Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Xichang 615000, China
四川省凉山彝族自治州(凉山州)是我国艾滋病疫情最为严重的地区之一[1]。2008年以前,主要采取自愿咨询检测(VCT)、哨点监测、行为监测等监测方法。但无法直接获得准确的新发感染数据,更不能敏感地反映艾滋病疫情的变化趋势和干预措施的效果。因此,有必要对凉山州进行HIV新发感染检测及监测,以获得当地HIV新发感染率及其变化趋势。为全面了解凉山州地区的艾滋病疫情,为估算确证的HIV感染者中新发感染者的比例[2],本研究采用BED捕获酶联免疫法(BED-CEIA)对凉山州2011-2013年艾滋病疫情进行监测,估算出HIV 新发感染情况。
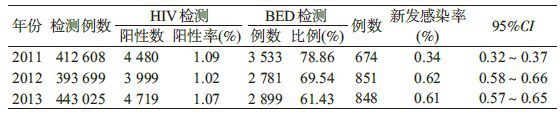
资料与方法1. 研究对象:通过凉山州各县医疗和卫生部门,收集2011-2013年当年报告的所有HIV感染者样本,然后根据每年的病例报告汇总所有医疗机构的总监测人数。其中2011年412 608人,2012年393 699人,2013年443 025人。采用酶联免疫和蛋白印迹方法检测出HIV抗体阳性样本,获得HIV-1抗体阳性样本数量分别为2011年4 480份;2012年3 999份;2013年4 719份。所有发现的免疫印迹法检测为阳性的样本均保存于-70 ℃超低温冰箱。为排除HIV-1既往感染阳性样本,严格按照《HIV-1新发感染血清学方法检测方案(试行)(2011年版)》控制阳性样本的入选和排除,针对4种情况对样本进行排除:① 6个月前已经向监测系统报告过的感染者的样品;② 如果同一人在1年之内出现≥2份确认阳性样品,将第1份样品纳入新发感染检测,其余样品从总样品中删除;③ 临床诊断为艾滋病患者或CD4+T淋巴细胞计数(CD4)<200个/μl的艾滋病患者样品(尽可能收集CD4检测结果);④ 所有接受抗病毒治疗的HIV感染者样品。
2. BED-CEIA检测:检测仪器为酶标仪、洗斑机、恒温箱等。BED检测试剂为SEDIATM BEDHIV-1新发感染率检测EIA试剂盒(SEDIA BIOSCIENCES Portland,OR USA,批号:LN-6016.02)。BED-CEIA 检测分为初筛和确认两步,检测过程相同,结果判断标准有区别。具体操作流程见文献[3]。
3. 新发感染率计算方法:
HIV感染率=监测人群中所有HIV阳性例数/总监测人数×100%,新发感染率(I)
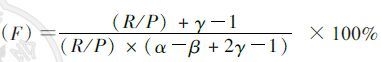
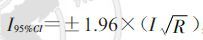
4. 统计学分析:本研究统计分析使用Excel和SPSS 17.0 软件,进行新发感染率计算。
结 果1. HIV感染率及新发感染率: 2011-2013年凉山州所有医疗机构的总监测人群HIV感染率分别为1.09%、1.02%、1.07%;而HIV新发感染率分别为0.34%、0.62%和0.61%,呈上升趋势(表 1)
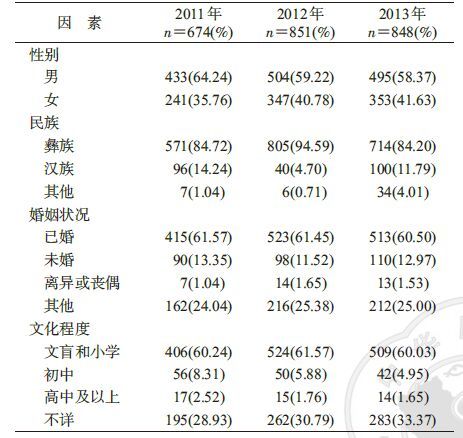
2. 新发感染者的人口学特征:2011-2013年新发感染人群中,男性感染者2011年为64.24%、2012年为59.22%、2013年为58.37%;每年的新发感染者中均以彝族为主(2011-2013年分别为84.72%、94.59%和84.20%);按照婚姻状况划分,已婚新发感染者占60%以上(2011-2013年分别为61.57%、61.45%和60.50%);新发感染者中文盲和小学教育程度超过了60%(表 2)
本研究发现2011-2013年凉山州医疗机构总监测人群的HIV-1的阳性感染率各年均维持在1%左右,但是HIV新发感染率从2011年的0.34%上升到2013年的0.61%。说明利用HIV感染率和HIV新发感染率反映艾滋病流行趋势存在差异。由于HIV感染属于慢性过程,随着抗病毒治疗水平的发展,艾滋病感染者和患者的生命质量大幅度提高,存活时间延长[4]。所以,与感染率相比,新发感染率更能说明HIV的流行趋势,是评价艾滋病预防控制效果的直接和客观的指标。本研究结果提示凉山州的HIV-1新发感染形势依旧严峻。
凉山州为我国最大的彝族人口聚集地,当地人群文化水平普遍较低。本文HIV新发感染人群以彝族为主,与2010年凉山州艾滋病流行情况及防治现状调查的结果相似[5];各年度新发感染人群中文化程度为文盲和小学占大多数,这和当地总人群人口学特征吻合,表明由于当地人群受教育程度低,缺乏对艾滋病防治知识的了解,自我保护意识淡薄。
2011-2013年HIV新发感染人群中的已婚人群所占比例均超过60%,与曾刚等[6]调查结果相似,提示婚内性传播值得警惕。由于彝族社会传统性观念和性习俗,配偶间发生性行为时安全套使用率较低[7],可能是导致艾滋病婚内传播的原因。
应用BED-CEIA在个体水平上会产生一定的假阳性和假阴性[8]。因此本研究采用BED-CEIA方法将特定的感染者归为新发感染或既往感染时可能会出现偏差,导致估算HIV-1新发感染率有可能出现归类错误从而产生一定偏倚,但是本研究纳入的感染者多,其中新发感染者也较多,假阳性和假阴性存在相互抵消的可能,所以本研究的结果仍然具有应用价值。
| [1] | 龚煜汉, 王启兴, 余刚, 等. 四川省凉山州1995-2012年HIV/AIDS病人死亡情况分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病 , 2014, 20 (11) : 849–852 Gong YH, Wang QX, Yu G, et al. An analysis on death and related factors among HIV/AIDS patients in Liangshan Prefecture of Sichuan during 1995-2012[J]. Chin J AIDS STD , 2014, 20 (11) : 849–852 |
| [2] | 梁姝, 魏东兵, 胡莹, 等. 2009年第1季度四川省报告HIV感染者中新近感染状况[J]. 预防医学情报杂志 , 2011, 27 (3) : 175–176 Liang S, Wei DB, Hu Y, et al. Newly infection among reported HIV infection cases in Sichuan,January to March,2009[J]. J Prev Med Inf , 2011, 27 (3) : 175–176 |
| [3] | 唐翼龙, 易志强, 廖清华, 等. BED-CEIA技术在江西省艾滋病监测重点人群HIV-1新发感染率估算中的应用[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志 , 2014, 24 (23) : 3358–3360 Tang YL, Yi ZQ, Liao QH, et al. The application of BED-CEIA in the estimate of HIV-1 new infections rates among key AIDS surveillance population in Jiangxi province[J]. Chin J Health Lab Technol , 2014, 24 (23) : 3358–3360 |
| [4] | 杨莉, 马艳玲, 罗红兵, 等. 云南省2000-2007年静脉吸毒者、性病就诊者和孕产妇HIV-1新近感染率及流行趋势变化[J]. 中华流行病学杂志 , 2008, 29 (12) : 1204–1207 Yang L, Ma YL, Luo HB, et al. A dynamic analysis on incidence and trend of HIV-1 epidemics among Intravenous Drug Users,attendants at the STD clinics and pregnant women in Yunnan province,China[J]. Chin J Epidemiol , 2008, 29 (12) : 1204–1207 |
| [5] | 周文瑞, 孙雪. 2010年凉山州艾滋病流行情况及防治现状调查[J]. 亚太传统医药 , 2011, 7 (8) : 190–193 Zhou WR, Sun X. Liangshan prefecture in 2010 and control status of the AIDS epidemic[J]. Asia-Pacific Trad Med , 2011, 7 (8) : 190–193 |
| [6] | 曾刚, 陈虹, 李崇行, 等. 四川省凉山州艾滋病病毒感染者配偶感染状况调查[J]. 疾病监测 , 2010, 25 (6) : 461–463 DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2010.06.012 Zeng G, Chen H, Li CX, et al. Survey on HIV-infection of spouses of HIV infected persons in Liangshan Autonomous Prefecture,Sichuan province[J]. Dis Surveill , 2010, 25 (6) : 461–463 DOI:10.3784/j.issn.1003-9961.2010.06.012 |
| [7] | 梁照升, 张林, 程卫民, 等. 艾滋病病毒感染者配偶艾滋病知识、态度、行为调查及HIV感染状况分析[J]. 疾病控制杂志 , 2005, 9 (4) : 309–311 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3679.2005.04.007 Liang ZS, Zhang L, Cheng WM, et al. The survey on the knowledge,attitude and behavior of AIDS among HIV-infected patients'spouses and analysis of HIV-infected status[J]. Chin J Dis Control Prev , 2005, 9 (4) : 309–311 DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-3679.2005.04.007 |
| [8] | 秦义组, 金琳, 刘爱文, 等. 安徽省2011-2012年报告HIV-1新发感染者流行病学特征分析[J]. 中国人兽共患病学报 , 2014, 30 (6) : 605–606 DOI:10.3969/cjz.j.issn.1002-2694.2014.06.012 Qin YZ, Jin L, Liu AW, et al. Epidemiological characteristics of recent HIV-1 infection reported in Anhui Province,China,2011-2012[J]. Chin J Zoonoses , 2014, 30 (6) : 605–606 DOI:10.3969/cjz.j.issn.1002-2694.2014.06.012 |
 2016, Vol. 37
2016, Vol. 37