文章信息
- 姚仕堂, 叶润华, 杨跃诚, 项丽芬, 王继宝, 杜本丽, 韩文香, 聂永英, 杨忠桔, 李唯美, 何纳, 段松. 2014.
- Yao Shitang, Ye Runhua, Yang Yuecheng, Xiang Lifen, Wang Jibao, Du Benli, Han Wenxiang, Nie Yongying, Yang Zhongju, Li Weimei, He Na, Duan Song. 2014.
- 云南省德宏州HIV感染者拒绝抗病毒治疗的比例及其影响因素
- Proportion and related influencing factors of HIV-infected individuals that rejecting the antiretroviral therapy among all the HIV infections, Dehong prefecture,Yunnan province
- 中华流行病学杂志, 2014, 35(12): 1324-1328
- Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 2014, 35(12): 1324-1328
- http://dx.doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0254-6450.2014.12.003
-
文章历史
- 投稿日期:2014-06-19
2 芒市疾病预防控制中心;
3 陇川县疾病预防控制中心;
4 盈江县疾病预防控制中心;
5 瑞丽市疾病预防控制中心;
6 梁河县疾病预防控制中心;
7 复旦大学公共卫生学院流行病学教研室 公共卫生安全教育部重点实验室
2 Mangshi City Center for Disease Control and Prevention;
3 Longchuan County Center for Disease Control and Prevention;
4 Yingjiang County Center for Disease Control and Prevention;
5 Ruili City Center for Disease Control and Prevention;
6 Lianghe County Center for Disease Control and Prevention;
7 Department of Epidemiology and Key Laboratory of Public Health Safety of Ministry of Education, School of Public Health, Fudan University
云南省德宏州自2004年7月起实施开展了大规模的免费高效抗反转录病毒治疗(HAART)工作以来,显著改善了艾滋病患者的生存状况[1, 2, 3]。截止2013年12月德宏州本地存活感染者的抗病毒治疗比例达79%,符合抗病毒治疗条件患者(CD4+T淋巴细胞计数≤350 cell/mm3或报告为AIDS)的抗病毒治疗覆盖率达到89%,为了解应治但未治的患者能否入组抗病毒治疗,于2014年1月对未参加抗病毒治疗的患者进行调查,本研究对拒绝参加抗病毒治疗的患者进行分析。 材料与方法
1. 研究对象:截止2013年12月31日现住址为德宏州的HIV感染者有8 502例,年龄≥16岁且存活的感染者有8 136例,对其中从未参加过抗病毒治疗的1 700例(20.9%)进行调查,除了外出(643例,37.8%)、羁押和正在吸毒(339例,19.9%)以及其他原因(113例,6.6%)外,605例患者拒绝抗病毒治疗,本研究对其进行分析。
2. 调查方法:利用2014年1月1日下载的中国疾病预防控制中心信息管理系统艾滋病抗病毒治疗数据库及疫情库进行对接,找出德宏本地从未参加过抗病毒治疗的存活患者进行未治疗原因调查,调查的具体原因为:怕暴露、自觉健康状况良好(回答自身感觉良好和不承认自己有病)、对治疗认识有误区(回答怕药物毒副反应和不相信治疗效果)、其他。
3. 统计学分析:利用SPSS 11.5软件进行描述和统计学分析,运用logistic回归模型对拒绝治疗的影响因素进行单因素和多因素分析。P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。 结 果
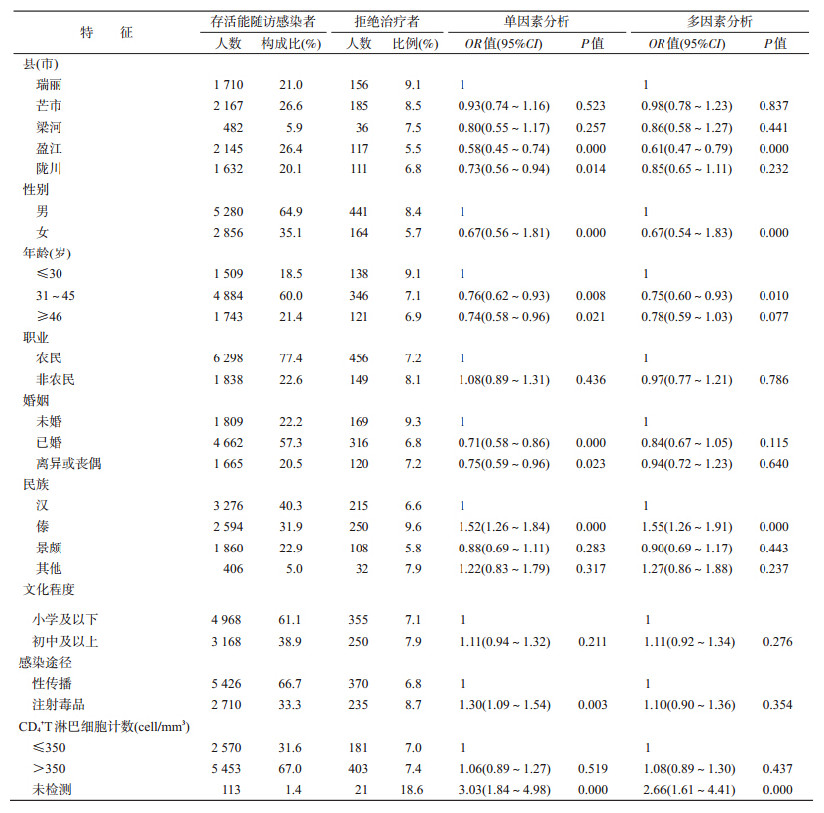
1. 一般情况:605例拒绝抗病毒治疗的HIV感染者以男性、年龄31~45岁、农民、已婚、傣族、小学及以下文化程度、性传播、CD4+T淋巴细胞计数>350 cell/mm3为主,构成比分别为72.9%、57.2%、75.4%、52.2%、41.3%、58.7%、61.2%、66.6%。
2. 拒绝抗病毒治疗HIV感染者比例及其影响因素:德宏州本地存活的HIV感染者中拒绝抗病毒治疗的比例为7.4%(605/8 136),不同特征的存活HIV感染者中拒绝抗病毒治疗的比例,见表 1。单因素logistic回归分析显示,HIV感染者拒绝抗病毒治疗与其所在县(市)、性别、年龄、婚姻、民族、感染途径、CD4+T淋巴细胞计数等特征均有显著关联。进一步的多因素logistic回归分析显示,在调整控制了潜在混杂因素影响后,感染者所在县(市)、性别、年龄、民族、CD4+T淋巴细胞计数等特征与其拒绝抗病毒治疗有显著关联,盈江县、女性、年龄31~45岁的HIV感染者拒绝抗病毒治疗的比例低于瑞丽市、男性、年龄≤30岁感染者;傣族、无CD4+T淋巴细胞计数的HIV感染者拒绝抗病毒治疗比例高于汉族、CD4+T淋巴细胞计数≤350 cell/mm3感染者,见表 1。
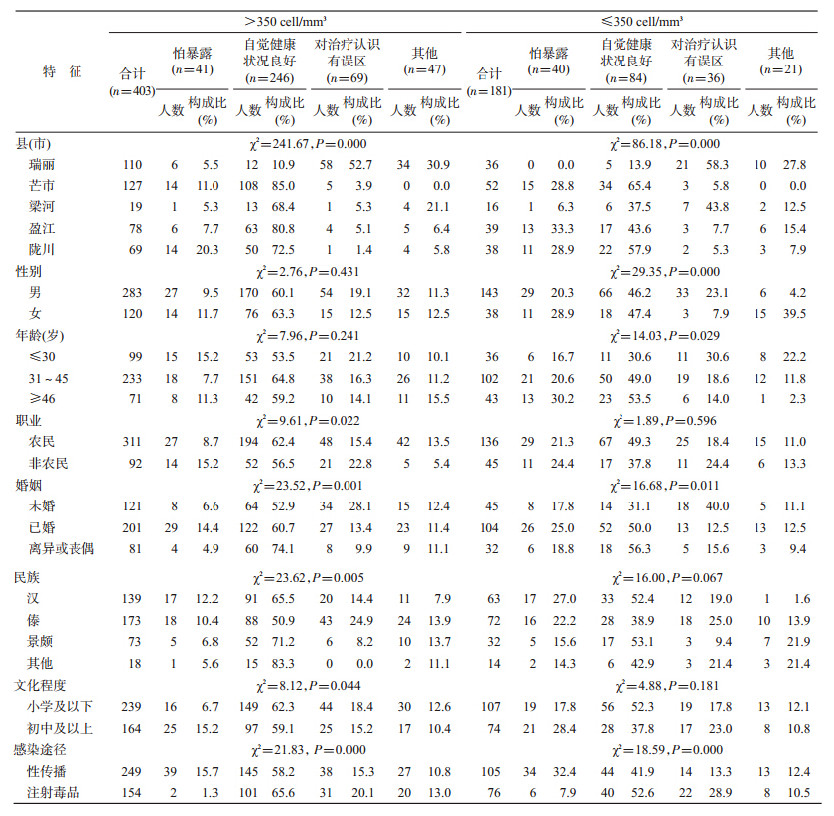
3. HIV感染者拒绝抗病毒治疗的原因:调查显示,605例HIV感染者拒绝抗病毒治疗的原因情况为:怕暴露84例(13.9%)、对治疗认识有误区111例(18.3%)、自觉健康状况良好340例(56.2%)、其他70例(11.6%)。其中CD4+T淋巴细胞计数>350 cell/mm3的403例拒绝治疗的患者中,怕暴露41例(10.2%)、对治疗认识有误区69例(17.1%)、自觉健康状况良好246例(61.0%)、其他47例(11.7%);不同县(市)、不同职业、不同婚姻状态、不同民族、不同文化程度、不同感染途径者其拒绝抗病毒治疗的原因不同(表 2)。CD4+T淋巴细胞计数≤350 cell/mm3的181例拒绝治疗的患者中,怕暴露40例(22.1%)、对治疗认识有误区36例(19.9%)、自觉健康状况良好84例(46.4%)、其他21例(11.6%);不同县(市)、不同性别、不同年龄、不同婚姻状态、不同感染途径者其拒绝抗病毒治疗的原因不同(表 2)。
本研究显示,德宏州本地存活的HIV感染者中拒绝抗病毒治疗的比例为7.4%。多因素logistic回归分析显示,女性拒绝治疗的比例显著低于男性,原因可能是女性患者对抗病毒治疗的依从性较男性患者好[4, 5, 6]。年龄>30岁的患者拒绝抗病毒治疗比例低于年龄≤30岁的患者,主要原因可能是德宏地 区≤30岁的患者外出打工比例较高,以至于无法保证抗病毒治疗的依从性。已婚患者拒绝抗病毒治疗的比例低于未婚患者,与已婚患者抗病毒治疗可获得家庭支持有关,这是保证抗病毒治疗依从性的重要因素。傣族患者拒绝抗病毒治疗的比例高于汉族患者,其原因可能是由于傣族患者惧怕抽血,而参加抗病毒治疗需要定期进行随访监测,导致傣族患者拒绝参加抗病毒治疗。性途径感染的患者拒绝治疗比例显著低于静脉吸毒感染患者,既往研究证实吸毒患者抗病毒治疗依从性低[4, 5, 6, 7, 8]。未接受过CD4+T淋巴细胞计数检测的患者拒绝治疗的比例较高,主要因为患者依从性不好,既然不参加CD4+T淋巴细胞计数检测,也就不会参加抗病毒治疗。瑞丽市患者拒绝参加抗病毒治疗的比例显著高于盈江县,存在的原因需进一步深入调查分析。
HIV感染者自觉健康状况良好是其拒绝治疗的主要原因之一,与李培龙等[9]研究结果相似,但自觉健康状况并不反映HIV感染者实际免疫缺陷状况和病情。事实上在本研究中,自觉健康状况良好是CD4+T淋巴细胞计数≤350 cell/mm3患者拒绝参加抗病毒治疗的主要原因,而CD4+T淋巴细胞计数≤350 cell/mm3属于严重免疫缺陷,患者只有参加抗病毒治疗才能提高其生存质量、延长生命[1],因此,有必要对HIV感染者加强艾滋病自然史和病情进展知 识宣传,促进其对艾滋病疾病进程有正确的知晓和态度,及时接受抗病毒治疗。
本研究还发现,外出打工是德宏本地存活HIV感染者不参加抗病毒治疗的重要原因,这与黑发欣等[10]在四川省凉山州的调查结果一致,为此,针对外出打工的艾滋病患者,建议国家对进一步完善抗病毒治疗的异地转诊机制,以便外出打工的艾滋病患者能够在其打工目的地就地方便地获得治疗,从而提高其生存质量,减少其传染性。
| [1] Yao ST, Duan S, Xiang LF,et al. Survival analysis of 3 103 HIV/AIDS patients receiving antiretroviral treatment in Dehong prefecture,Yunnan province[J]. Chin J Epidemiol,2010,31(11):1215-1218. (in Chinese)姚仕堂,段松,项丽芬,等. 云南省德宏州3 103 例艾滋病患者抗病毒治疗后生存分析[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2010,31(11):1215-1218. |
| [2] Yao ST, Xiang LF, Li YL, et al. Effectiveness assessment of highly active antiretroviral therapy for 1 039 adult HIV/AIDS patients in Dehong prefecture[J]. Chin J Infect Dis,2010,28(9):43-47. (in Chinese)姚仕堂,项丽芬,李艳玲,等. 德宏州1 039名在治成人HIV/AIDS患者抗病毒治疗效果评价[J]. 中华传染病杂志,2010,28(9):43-47. |
| [3] Yao ST,Yang J,Zhou L,et al. Plasma HIV viral load and drug resistanceamong AIDS patients receiving antiretroviral treatment in Dehong prefecture,Yunnan province[J]. Chin J Epidemiol,2014,35(4):411-416. (in Chinese)姚仕堂,杨锦,周琳,等. 云南省德宏州抗病毒治疗艾滋病患者血浆HIV病毒载量及耐药研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2014,35(4):411-416. |
| [4] Lou JC, Li HQ, Lao YF, et al. Effectiveness analysis on antiretroviral therapy among HIV infected adults in Yunnan[J].Chin J AIDS STD,2013,19(8):557-559. (in Chinese)楼金成,李惠琴,劳云飞,等. 云南省成人AIDS病人抗病毒治疗的疗效分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病杂志,2013,19(8):557-559. |
| [5] Yao ST,Ma YL,Xu YW,et al. Incidence and risk factors of HIV resistance among AIDS patients receiving antiretroviral treatment in Dehong prefecture Yunnan province[J]. Chin J Control Prev,2012,16(12):1019-1023. (in Chinese)姚仕堂,马艳玲,许元武,等. 云南省德宏州艾滋病患者抗病毒治疗后HIV耐药突变率及其影响因素研究[J]. 中华疾病控制杂志,2012,16(12):1019-1023. |
| [6] Li H,Wang Z,Cui WG,et al. Study on adherence and interrelated factors of acquired immunedeficiency syndrome patients receiving antiretroviral treatment[J]. Chin J Epidemiol,2005,26(7):507- 510. (in Chinese)李宏,王哲,崔为国,等. 艾滋病感染者抗病毒治疗的服药依从性及其相关因素研究[J]. 中华流行病学杂志,2005,26(7):507-510. |
| [7] Cai ZH,Chen YY,Gao J,et al. Correlates and responding policies of adherence among AIDS patients using drugs[J]. Today Nurse,2011,5:108-110. (in Chinese)蔡仲华,陈毅英,高静,等. 吸毒行为艾滋病患者依从性影响因素及对策[J]. 当代护士,2011,5:108-110. |
| [8] Wang HH,Zhou J,Huang L,et al. Adherence to highly active antiretroviral therapy and quality of life in patients with acquired immunedeficienc syndrome[J]. Chin J Nnrs,2008,43(9):776-779. (in Chinese)王红红,周俊,黄玲,等. 艾滋病患者高效抗逆转录病毒治疗依从性及生活质量分析[J]. 中华护理杂志,2008,43(9):776-779. |
| [9] Li PL,Qing QQ,Wang LY,et al. Why 395 HIV/AIDS patiants failed to receive HAAT[J]. Chin J AIDS STD,2013,19(5):334-343. (in Chinese)李培龙,秦倩倩,王丽艳,等. 395例HIV/AIDS病人未进行抗病毒治疗的原因分析[J]. 中国艾滋病性病,2013,19(5):334-343. |
| [10] Hei FX,Wang QX,Gong YH,et al. Epidemiological sureey to identify the causes for non-treatment of HIV/AIDS cases with CD4 cell count less than 350 cell/μl in Liangshan Prefecture of Sichuan[J]. Chin J AIDS STD,2012,18(12):824-827. (in Chinese)黑发欣,王启兴,龚煜汉,等. 凉山州CD4细胞<350 cell/μl的HIV/AIDS病例未治疗原因调查[J]. 中国艾滋病性病,2012,18(12):824-827.. |
 2014, Vol. 35
2014, Vol. 35