b Ethnic Pharmaceutical Institute, Southwest University for Nationalities, Chengdu 610041, China
Dioscorea panthaica (Huang-shan-yao in Chinese),belonging to the Dioscoreaceae family,is an endemic plant of China,growing as a shrub near the edges of forests at altitudes of 1000-3500 meters in southwest and central south of China [1]. Its rhizomes have been used in traditional Chinese medicine for the treatment of gastropathy,anthrax,rheumatic heart disease and rheumatoid arthritis [2]. The modern Chinese medicine of ‘Di’Ao Xin Xue Kang’, which is famous for treating coronary heart disease in China markets,is produced from the extract of D. panthaica rhizomes. Steroidal saponins are the major effective constituents of this plant,and about twenty such compounds have been isolated to date [3, 4].
During our systematic search for the structural novel and biologically active components from endemic plants in China,two 27-norergostanol steroids,panthogenins A (1) and B (2),possessing an unusual seven-membered E ring which features a ketal moiety at C-25,were isolated from the rhizomes of D. panthaica. Both compounds exhibited potent insulin sensitizing activity. It is worth noting that D. opposite,which is also used to produce the medicine ‘Di’Ao Xin Xue Kang’,has been reported to possess the same activity [5]. Herein we report the isolation,structure elucidation,and biological assessment of the two novel steroids. 2. Experimental
Optical rotations were measured on a Perkin-Elmer model 341 polarimeter using a Na lamp at 25 8C. IR spectra were recorded on a Perkin-Elmer Spectrum-One FT-IR spectrometer. 1H NMR and 13C NMR,HSQC,HMBC and COSY spectra were measured with a Bruker AM-600P spectrometer using TMS as an internal standard. ESI-MS data were obtained on a Finnigan LCQDECA mass spectrometer, and HR-ESI-MS data were obtained on a Bruker Bio TOF Q mass spectrometer. Column chromatographies were carried out with silica gel (160-200 and 200-300 mesh,Qingdao Marine Chemical Co.,Ltd.,China) and ODS (Nacalai,Japan). Thin-layer chromatography plates were based on silica gel GF254 (Qingdao Marine Chemical Co.,Ltd.,China).
The rhizomes of D. panthaica were bought from Medical Material market in Chengdu,Sichuan Province of China. They were identified and authenticated in the Herbarium of the Chengdu Institute of Biology,Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The air-dried rhizomes of D. panthaica (37.5 kg) were powdered and extracted with 95% ethanol (80 L × 3) at room temperature for seven days. The extractions were combined and concentrated into a small volume (70 L),which was kept still overnight. After removal of the precipitates by filtration,the filtrates were concentrated in vacuo to give a crude extract of water-soluble steroidal saponins (2700 g). The extract was then suspended in hot water (15 L) and exhaustively partitioned with ethyl acetate and nbutanol (15 L × 3) sequentially. The n-butanol extract (2000 g) was subjected to silica gel column chromatography eluted with a gradient of chloroform-methanol (from 30:1 to 0:1) to give six fractions (A-F). Fraction A (20 g) was purified by column chromatography over silica gel eluted with petroleum-acetone (from 20:1 to 0:1) to afford compounds 1 (149 mg) and 2 (42 mg). Insulin sensitizing activity was assessed by the effect of panthogenin A and B on the glucose uptake of dexamethasone induced insulin resistant 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Firstly,insulin resistance of 3T3-L1 adipocytes was induced as described previously [6]. Secondly,the influence of panthogenins A and B on glucose uptake of the insulin resistant 3T3-L1 adipocytes was measured as reported [7]. The influence of each compound was reflected by the relatively increased sensitivity rate. With rosiglitazone as reference,the relative increased sensitivity rate was calculated by the ratio of increased sensitivity of each compound to that of rosiglitazone. 3. Results and discussion
Panthogenin A (1) was obtained as a colorless crystal. Its molecular formula,C27H40O7,was established on the basis of HRESIMS at m/z 477.2852 [M+H]+ (calcd. 477.2852),requiring eight degrees of unsaturation. The IR spectrum showed characteristic absorptions for carbonyl group at 1710. The 13C NMR spectrum showed 27 carbon signals,which were sorted by DEPT experiments into five methyls,six methylenes,ten methines,one carbonyl,and five saturated quaternary carbons (Table 1). The 1H NMR signals at δH 1.43 (s),1.21 (s),1.18 (s),1.16 (s),and 1.08 (d, 6.6) were consistent with the five methyls.
| Table 1 1H (600MHz) and 13C NMR (150 MHz) data of 1 and 2 in pyridine-d5. |
As the major components presented in this plant are C-27 steroids,compound 1 presumably belongs to the same group from the biogenetic point of view. Its overall NMRdata was familiar with one known steroid,6α,7α-epoxy-3β,5α,17α-trihydroxy-1-oxowitha- 24-enolide,which was isolated from the leaves of Withania somnifera [8]. A comparison of their 13C NMR data suggested that they possessed the same rings A,B,C,and D,which could be evidenced by a thorough analysis of 13C NMR,1H-1H COSY,and HMBC. The HMBC correlations between angular methyl protons H- 19/C-1,C-5 and H-3/C-1,C-5 suggested that the carbonyl carbon was at C-1. Two vicinal methines with fairly low chemical shifts (around δ 57) were assigned to C-6 and C-7 which attached to the same oxygen to form an epoxy ring [9].
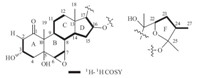
Apart from six degrees of unsaturation present in rings A-D, there remained two degrees of unsaturation,indicating the existence of two extra rings. Considering 1H NMR signals of the five methyl groups were not in agreement with cholestane or spirostane type steroids (in 1H NMR,the former consisted of two singlets and three doublets,and the latter consisted of two singlets and two doublets),compound 1 was probably a distorted C27 steroid. 1H-1H COSY revealed the carbon chain of C22-C23-C24- C27,and the HMBC correlations of H-22,H-23,H-27/C-25 allowed a five-membered ring (ring F) as shown in Fig. 1.
|
Download:
|
| Fig. 1.Partial structures of rings A-D,and F of 1. | |
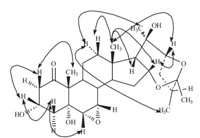
All twenty-seven carbons were assigned to two partial structures shown in Fig. 1,and there remains one degree of unsaturation,suggesting that the two moieties linked to each other to form the ring E. The HMBC correlation of H-21/C-22,C-17,and H-22/C-17,C-20 revealed the carbon chain of C17-C20-C22, indicating that C-22 was attached to C-17 of ring D via C-20. In addition,the chemical shift of C-25 (δ 107.3) was characteristic of the acetal carbon,suggesting that C-25 was linked to C16 via an oxygen atom to form a seven-membered ring E. Therefore, compound 1 was elucidated as a 27-norergostane possessing an unusual seven-membered ring E as shown in Fig. 2.
|
Download:
|
| Fig. 2.Structure of 1 with the key correlations of HMBC. | |
In the NOESY experiment,the correlations of H-2β/19-CH3,H-3, H-4b/H-3,and H-6 indicated that these hydrogen atoms were oriented in the same direction. As 18-CH3 and 19-CH3 always adopted b configuration in steroids,H-3 and H-6 here were suggested to be b-oriented,and as thus 3-OH was a-oriented. The other NOESY correlations of 18-CH3/H-17,H-16,H-22,and H-12b indicated that H-17,H-16,and H-22 were in b-orientation. The correlations of H-12a/21-CH3,27-CH3,H-9,and H-9/H-8 indicated that 21-CH3,27-CH3,H-8,and H-9 were in a-orientation and 20- OH was in b-orientation. The NOESY correlations of Panthogenin A are shown in Fig. 3. Finally,the chemical structure of compound 1 was unambiguously confirmed by X-ray crystallography as illustrated in Fig. 4,and named panthogenin A. Its MS spectrum, 1D and 2D NMR spectra were provided as supplementary data.
|
Download:
|
| Fig. 3.Selected NOESY correlations of 1. | |

|
Download:
|
| Fig. 4.X-ray crystal structure of 1. | |
Panthogenin B (2) was obtained as a colorless crystal. Its molecular formula,C27H38O6,was established on the basis of HRESIMS atm/z 459.2738 [M+H]+ (calcd. 459.2747),requiring nine degrees of unsaturation. IR spectrum showed characteristic absorptions for a conjugated carbonyl group at 1685 [10]. Its 13C NMR spectrum showed 27 carbon signals,which were sorted by DEPT experiments into five methyls,five methylenes,eleven methines,one carbonyl and five saturated quaternary carbons (Table 1). The 1H NMR signals at δH 1.46 (s),1.25 (s),1.23 (s),1.20 (s),and 1.16 (d,7.0) were consistent with the five methyls.
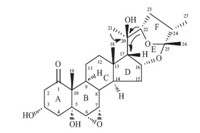
According to the biogenesis hypothesis,panthogenin B (2) was also a 27-norergostanol steroid. Its NMR spectra were similar to panthogenin A,except for those of ring A. It is clear that there was a double bond between C-2 and C-3 (δC 130.1,141.5,δH 6.03 dd,6.56 m),which formed a conjugated ketone with C-1 carbonyl,while in panthogenin A,there was one hydroxyl group attached to b position of the carbonyl.
The arrangement of the seven rings,together with the stereochemistry,was confirmed by comprehensive analysis of 2D NMR similar to that of panthogenin A. Therefore,compound 2 was elucidated as a novel steroid possessing the same unusual E and F rings with compound 1 as drawn in Fig. 5 and named panthogenin B. Its MS spectra,1D and 2D NMR spectra were provided as supplementary data.

|
Download:
|
| Fig. 5.Chemical structure of 2 and key correlations of 1H-1H COSY and HMBC. | |
In the bioactive assays,compounds 1 and 2 were evaluated in vitro for their effects upon dexamethasone induced insulin resistance in adipocytes. Using rosiglitazone as reference whose sensitization rate is 100% at 10 μg/mL,the result showed that both of them possessed potent insulin sensitizing activity,i.e. the relative sensitization rate is 84.8% for compound 1 at 10 mg/mL, and 89.4% for compound 2 at 10 μg/mL. 4. Conclusion
Previous phytochemical investigation revealed that the main components in D. panthaica were furostanol steroids. Our present work isolated and identified two 27-norergostanol steroids from this plant (and the genus Dioscorea) for the first time. Particularly, both steroids contain an unusual seven-membered E ring featuring a ketal moiety at C-25. In addition,these two compounds were found to possess potent insulin sensitizing activity,indicating the potential of this herb in anti-obesity drug development. Acknowledgment
Financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21072184,30973634 and 81173536) is gratefully acknowledged. Appendix A. Supplementary data
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found,in the online version,at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cclet.2014.04.004.
| [1] | Chengdu Institute of Biology, Chinese Academy of Sciences; Chengdu Di'Ao Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. Research and Industrial Development of Chinese Medicinal Plant Resources of Dioscorea. Science Press, Beijing. 2006. |
| [2] | H.W. Liu, S.L. Wang, B. Cai, et al., New furostanol glycosides from the rhizomes of Dioscorea futschaumenis R. Kunth, J. Asian Nat. Prod. Res. 5 (2003) 241-247. |
| [3] | S.R. Tang, R.T. Yang, F.S. Pan, A.M. Zhao, Z.J. Pang, Steroidal saponin and steroidal sapogenin in Chinese Dioscorea L, J. Plant Resour. Environ. 16 (2007) 64-72. |
| [4] | M. Sautour, A.C. Mitaine-Offer, M.A. Lacaille-Dubois, The Dioscorea genus: a review of bioactive steroid saponins, J. Nat. Med. 61 (2007) 91-101. |
| [5] | X.P. Gao, B.G. Li, H.W. Jiang, et al., Dioscorea opposita reverses dexamethasone induced insulin resistance, Fitoterapia 78 (2007) 12-15. |
| [6] | W.T. Garvey, T.P. Huecksteadt, R. Monzon, S. Marshall, Dexamethasone regulates the glucose-transport system in primary cultured adipocytes-different mechanisms of insulin resistance after acute and chronic exposure, Endocrinology 124 (1989) 2063-2073. |
| [7] | B. Urso, D.L. Cope, H.E. Kalloo-Hosein, et al., Differences in signaling properties of the cytoplasmic domains of the insulin receptor and insulin-like growth factor receptor in 3T3-L1 adipocytes, J. Biol. Chem. 274 (1999) 30864-30873. |
| [8] | L. Misra, P. Lal, R.S. Sangwan, et al., Unusually sulfated and oxygenated steroids from Withania somnifera, Phytochemistry 66 (2005) 2702-2707. |
| [9] | B.Y. Yang, Q.H. Wang, Y.G. Xia, W.S. Feng, H.X. Kuang, Withanolide compounds from the flower of Datura metel L., Helvetica Chim. Acta 90 (2007) 1522-1528. |
| [10] | Atta-ur-Rahman, A. Dur-e-Shahwar, A.M. Naz, Choudhary, Withanolides from Withania coagulans, Phytochemistry 63 (2003) 387-390. |