枳壳为中医临床常用理气药, 目前枳壳来源于酸橙Citrus aurantium L.及其栽培变种干燥未成熟的果实[1]。枳壳药用历史悠久, 但其药材正品来源在宋代以前来源于芸香科枳属植物枸橘Poncirus trifoliata(L.)Raf.的果实, 宋代来源于酸橙的枳壳逐渐取代以枸橘果实为来源的枳壳并逐渐成为其正品来源, 且一直沿用至今。枳壳药用正品来源为何从枳属枸橘的果实向柑橘属酸橙的果实演变?是中医临床病症的变化还是酸橙枳壳后来药效证明优于枸橘枳壳?文献报道酸橙枳壳和枸橘枳壳均含有黄酮、香豆素、生物碱、挥发油等化学成分[2-10], 药效试验证明药材中的黄酮苷类成分柚皮苷和新橙皮苷配伍对正常小鼠小肠推进具有促进作用[11]。枳属苷具有抗炎[12]、抗幽门螺旋杆菌[13]和保护胃黏膜[14]等生物活性。本研究建立了酸橙枳壳和枸橘枳壳中异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷HPLC含量测定方法, 可为酸橙枳壳和枸橘枳壳活性成分的含量比较研究及其药材与饮片的质量评价提供简便、准确和可靠的方法, 结果也可为揭示枳壳基源变迁的原因提供参考。
1 仪器与试药 1.1 仪器安捷伦公司Agilent 1260高效液相色谱仪(包括四元泵、在线脱气机、自动进样器、DAD检测器和色谱工作站)。迪马科技有限公司Dikma C18(2)色谱柱(150 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm;填料:十八烷基硅烷键合硅胶)。昆山市超声仪器有限公司KQ-200VDE型超声波清洗器(200 W, 45 kHz);Sartoris公司BT224S万分之一天平。
1.2 试药枳壳药材自采或购于当地农户, 经江西中医药大学药学院药用植物学科组赖学文副教授鉴定为酸橙Citrus aurantium L.干燥未成熟的果实和枸橘(Poncirus trifoliate(L.)Raf.)的干燥未成熟果实;异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷的对照品, 自制(枳壳药材用乙醇提取, 不同极性溶剂分段萃取, 过硅胶柱, 进行重结晶, 即得), 以1H-NMR和13C-NMR、ESI-MS鉴定结构, 含量采用HPLC峰面积归一化法计算均不低于98%)。乙腈、甲醇为HPLC级, 水为双蒸水, 其他试剂均为分析纯。
2 方法与结果 2.1 溶液的制备 2.1.1 混合对照品储备液分别取减压干燥至恒重的异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷的对照品适量, 精密称定, 置同一100 mL量瓶中, 加甲醇溶解并定容至刻度, 摇匀, 即得含异柚皮苷1.081 μg·mL-1, 柚皮苷523.7 μg·mL-1, 橙皮苷22.81 μg·mL-1, 新橙皮苷528.3 μg·mL-1, 枳属苷255.5 μg·mL-1的混合溶液, 即得。
2.1.2 供试品溶液[15]取枳壳粗粉(过2号筛)约1 g, 精密称定, 置100 mL平底烧瓶中, 精密加入甲醇50 mL, 密塞, 称量, 水浴加热回流1.5 h, 放冷, 再称量, 用甲醇补足减失的量, 摇匀, 过0.45 mm滤膜, 取续滤液, 即得。
2.2 色谱条件[15]采用Dikma C18(2)色谱柱(150 mm×4.6 mm, 5 μm), 以乙腈(A)-0.1%磷酸水(B)为流动相, 梯度洗脱(0~10 min, 20%A;10~11min, 20%A→30%A;11~25min, 30%A), 流速1 mL·min-1, 检测波长283 nm, 柱温25 ℃, 进样量10 μL。色谱图见图 1。
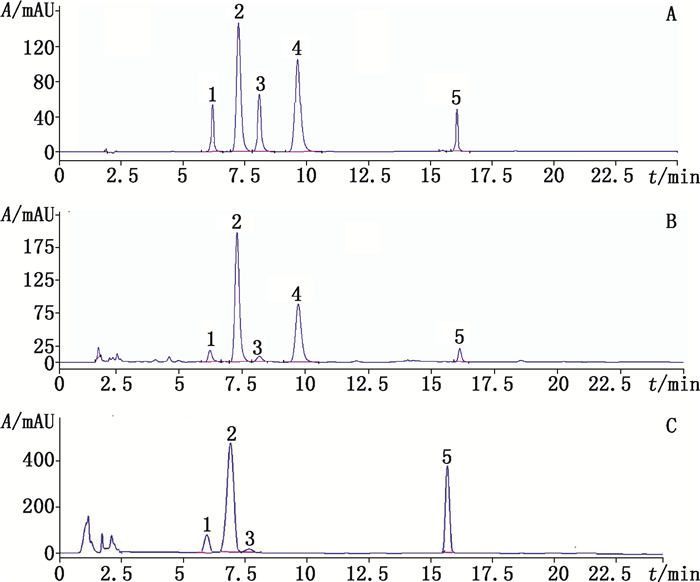
|
1.异柚皮苷(narirutin)2.柚皮苷(naringin)3.橙皮苷(hesperidin)4.新橙皮苷(neohesperidin)5.枳属苷(poncirin)A.对照品(reference substances)B. 16号酸橙枳壳样品(sample No. 16 of Fructus Aurantii)C. 24号枸橘枳壳样品(sample No. 24 of Fructus Ponciri Trifoliatae) 图 1 酸橙枳壳和枸橘枳壳中5个黄酮苷成分的HPLC图 Figure 1 HPLC chromatograms of 5 flavonoids in Fructus Aurantii and Fructus Ponciri Trifoliatae |
因样品中5个黄酮苷类成分含量较低, 对其定量限和检测限进行考察, 取混合对照品溶液适量, 以甲醇逐级稀释, 按上述色谱条件进行测定。当S/N=10时, 异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷的定量限分别为1.38、1.35、1.49、1.15、1.28 ng;当S/N=3时, 检测限分别为0.14、0.10、0.12、0.11、0.09 ng。
2.4 线性关系考察精密吸取“2.1.1”项下混合对照品储备液10 mL, 置25 mL量瓶中, 加甲醇定容至刻度, 摇匀, 即得含异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷分别为0.432 0、209.5、9.124、211.3、102.2 μg·mL-1的混合对照品溶液。分别进样2、4、6、8、10、12、14、16 μL, 按上述色谱条件进行测定, 以对照品的量X(μg)为横坐标, 峰面积(Y)为纵坐标, 绘制标准曲线, 得回归方程。线性范围、回归方程和相关系数结果见表 1。
|
|
表 1 各黄酮苷成分的线性范围、回归方程及相关系数(n=6) Table 1 The linear ranges, regression equations and correlation coefficients of the flavonoid components |
精密吸取混合对照品溶液10 μL, 在上述色谱条件下连续进样6次, 测定峰面积。异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷峰面积的RSD分别为1.3%、1.9%、1.7%、1.6%、0.21%, 结果表明精密度良好。
2.6 重复性试验取酸橙枳壳样品(16号)粗粉6份, 每份约1 g, 精密称定, 按“2.1.2”项下方法制备供试品溶液, 按上述色谱条件进行测定, 计算含量。结果异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷的平均含量分别为0.01%、10.9%、0.23%、5.14%和1.32%, RSD分别为1.5%、0.44%、1.8%、0.43%和1.7%;表明重复性良好。
2.7 稳定性试验取酸橙枳壳样品(16号)粗粉约1 g共6份, 精密称定, 按“2.1.2”项下方法制备供试品溶液, 精密吸取供试品溶液10 μL, 分别在制备后0、2、4、6、8、10、12 h按照上述色谱条件注入液相色谱仪, 测定峰面积, 异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷峰面积的RSD分别为1.7%、2.0%、1.3%、2.0%、1.4%, 结果表明供试品溶液在室温下12 h内稳定。
2.8 加样回收率试验取已测知含量(异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷的含量分别为0.01%、10.9%、0.23%、5.14%、1.32%)的酸橙枳壳样品(16号)粗粉约0.5 g共6份, 分别精密加入一定量的混合对照品溶液(异柚皮苷1.251 μg·mL-1, 柚皮苷1 362 μg·mL-1, 橙皮苷28.75 μg·mL-1, 新橙皮苷642.5 μg·mL-1, 枳属苷165.1 μg·mL-1)40 mL, 按“2.1.2”项下方法制备供试溶液并进样测定, 结果异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷的平均回收率(n=6)分别为102.5%、99.60%、101.4%、100.1%、99.61%, 其RSD分别为1.5%、2.1%、1.9%、0.34%、0.23%。
2.9 样品含量测定分别取26批不同产地枳壳粗粉(过2号筛)约1 g, 精密称定, 按“2.1.2”项下方法制备供试品溶液, 进样测定, 以外标法计算含量, 结果见表 2。
|
|
表 2 不同产地酸橙枳壳和枸橘枳壳中5个黄酮苷成分的含量(n=3) Table 2 Content of five flavonoids in Fructus Ponciri Trifoliatae and Fructus Aurantii from different habitats |
本文含量测定结果表明, 酸橙枳壳中柚皮苷和新橙皮苷含量与枸橘枳壳的相比均较高, 达到中国药典2015年版一部枳壳项下的含量测定标准;异柚皮苷、橙皮苷和枳属苷含量与枸橘枳壳的相比均较低。文献报道[11]酸橙枳壳水煎液对正常小鼠小肠推进具有明显作用, 其所含主要黄酮苷柚皮苷、新橙皮苷单独给药对正常小鼠小肠推进无明显作用, 两者配伍给药对正常小鼠小肠推进具有明显作用, 证明了柚皮苷和新橙皮苷是枳壳的药效物质, 枸橘枳壳中新橙皮苷的含量低于定量限, 柚皮苷和枳属苷含量相对较高, 枸橘枳壳的药效物质基础有待进一步阐明。
本试验采用HPLC法测定酸橙枳壳和枸橘枳壳中异柚皮苷、柚皮苷、橙皮苷、新橙皮苷和枳属苷的含量, 方法操作简便, 准确、可靠, 重复性好, 可用于测定上述5个黄酮苷成分的含量。
| [1] |
中国药典2015年版. 一部[S]. 2015: 246 ChP 2015.Vol Ⅰ[S].2015:246 |
| [2] |
宋玉鹏, 胡源祥, 陈海芳, 等. 对枳实和枳壳药用品种变迁的思考[J]. 江西中医药大学学报, 2016, 28(4): 120. SONG YP, HU YX, CHEN HF, et al. Thinking about Aurantii Fructus Immaturus and Aurantii Fructus species change[J]. Jiangxi J Tradit Chin Med, 2016, 28(4): 120. |
| [3] |
付小梅, 吴志魏, 褚小兰, 等. 枳壳中黄酮类成分的研究[J]. 中药材, 2006, 29(11): 1187. FU XM, WU ZW, ZHE XL, et al. Study on the flavonoids in Fructus Aurantii[J]. J Chin Med Mater, 2006, 29(11): 1187. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1001-4454.2006.11.026 |
| [4] |
丁邑强, 熊英, 周斌, 等. 枳壳中黄酮类成分的分离与鉴定[J]. 中国中药杂志, 2015, 40(12): 2352. DING YQ, XIONG Y, ZHOU B, et al. Isolation and identification of flavonoids in Fructus Aurantii[J]. China J Chin Mater Med, 2015, 40(12): 2352. |
| [5] |
张金莲, 何敏, 谢一辉, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定枳壳饮片中柚皮苷、橙皮苷和新橙皮苷的含量[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志, 2010, 16(6): 68. ZHANG JL, HE M, XIE YH, et al. Determination of content of narigin and hesperidin and neohesperidin in Fructus Auranti pieces by HPLC[J]. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Form, 2010, 16(6): 68. |
| [6] |
郑莹, 王帅, 孟宪生, 等. 中药枳壳挥发油成分气相色谱-质谱联用分析和促进胃肠动力药效研究[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2015, 26(3): 516. ZHENG Y, WANG S, MENG XS, et al. The analysis and research to promote gastrointestinal motility drug combined with Chinese medicine Fructus Aurantii oil components by gas chromatography mass spectrometry[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2015, 26(3): 516. |
| [7] |
邢娜, 舒尊鹏, 徐炳清, 等. 不同产地枳壳挥发油成分的气相色谱-质谱分析及抗肿瘤活性研究[J]. 中医药信息, 2015, 32(5): 1. XING N, SHU ZP, XU BQ, et al. GC-MS analysis of volatile oil components in Fructus Aurantii from different regions and study of its antitumor activity[J]. Inf Tradit Chin Med, 2015, 32(5): 1. |
| [8] |
陈海芳, 魏玲, 袁金斌, 等. RP-HPLC法测定枳壳中五个脂溶性成分的含量[J]. 药物分析杂志, 2010, 30(9): 1610. CHEN HF, WEI L, YUAN JB, et al. Determination of five fat soluble components in Fructus Aurantii by RP-HPLC[J]. Chin J Pharm Anal, 2010, 30(9): 1610. |
| [9] |
陈海芳, 徐欢, 王发英, 等. HPLC法测定枳壳中葡萄内酯的含量[J]. 中药材, 2010(33): 7. CHEN HF, XU H, WANG FY, et al. Determination of auraptene in Fructus Aurantii by HPLC[J]. J Chin Med Mater, 2010(33): 7. |
| [10] |
蒋以号, 曹旻旻, 龚千锋. HPLC法测定枳壳饮片中辛弗林的含量[J]. 中华中医药杂志, 2011, 26(10): 2363. JIANG YH, CAO MM, GONG QF. Determination of synephrine in Fructus Auranti pieces by HPLC[J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2011, 26(10): 2363. |
| [11] |
易徐航, 夏放高, 陈海芳, 等. 枳壳中黄酮苷类成分对正常小鼠小肠推进的影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2015, 26(2): 278. YI XH, XIA FG, CHEN HF, et al. Effect of flavonoid glycosides in Fructus Aurantii on mice small intestine propulsion[J]. Lishizhen Med Mater Med Res, 2015, 26(2): 278. |
| [12] |
KIM JB, HAN AR, PARK EY, et al. Inhibition of induced IONS, COX-2 and cytokines expression by poncirin through the NF-ΚB inactivation in RAW 264.7 macrophage cells[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 2007, 30(12): 2345. DOI:10.1248/bpb.30.2345 |
| [13] |
KIM DH, BAE EA, HAN MJ. Anti-Helicobacter pylori activity of the metabolites of poncirin from Poncirus trifoliate by human intestinal bacteria[J]. Biol Pharm Bull, 1999, 22(4): 422. DOI:10.1248/bpb.22.422 |
| [14] |
LEE JH, LEE SH, KIM YS, et al. Protective effects of neohesperidin and poncirin isolated from the fruits of Poncirus trifoliate on potential gastric diserse[J]. Phytother Res, 2009, 23(12): 1748. DOI:10.1002/ptr.v23:12 |
| [15] |
李正红, 陈海芳, 骆利平, 等. 江枳壳不同采收期活性成分HPLC含量测定[J]. 中药材, 2013, 36(1): 28. LI ZH, CHEN HF, LUO LP, et al. Determination of the active constituents in Aurantii Fructus from Jiangxi Province at different harvest time by HPLC[J]. J Chin Med Mater, 2013, 36(1): 28. |
 2017, Vol. 37
2017, Vol. 37 
