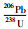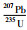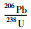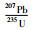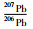2. 成都理工大学地球科学学院, 成都 610059
2. College of Earth Sciences, Chengdu University of Technology, Chengdu 610059, China
花岗岩作为大陆地壳的重要组成部分,是地球岩石圈区别于其它行星岩石圈、大陆地壳有别于大洋地壳最主要的物质标志(Lundstrom and Glazner, 2016; 陈国能等, 2017),详细记录了陆壳形成演化、壳-幔相互作用过程的丰富信息(Hawkesworth and Kemp, 2006; 吴福元等, 2007a; 翟明国, 2017; Zhang et al., 2021)。因此,长期以来花岗岩的成因、形成的构造环境与地球动力学背景,以及花岗质岩浆和矿化之间的关系等问题都是重要的前沿研究课题,也是大陆形成演化研究的核心内容(Chappell and White, 1974; Pearce et al., 1984; Monecke et al., 2002; Clemens, 2003; Zurevinski et al., 2017; 王孝磊, 2017; 翟明国, 2017; Zhang et al., 2021)。俯冲造山和碰撞造山是大陆地壳生长和花岗岩形成的重要动力学机制,造山带花岗岩是探索大陆地壳形成和演化的重要对象(Zhang et al., 2021),岩浆作用发生的时间和位置以及熔融产物的类型和组成研究,可以再造造山带的构造演化历史(高永丰等, 2003)。
拉萨地块位于青藏高原南部,其作为东冈瓦纳大陆的重要组成部分,从古生代到新生代经历了复杂的演化历史(Zhu et al., 2011a, 2013, 2016)。尤其是中生代以来,拉萨地块经历了班公湖-怒江特提斯洋俯冲消减、拉萨-羌塘地块碰撞、新特提斯洋俯冲以及印度-欧亚大陆碰撞等一系列地质过程,导致中-新生代岩浆大爆发,形成的岩浆岩完好地记录了拉萨地块构造演化与深部作用过程,为研究和探索拉萨地块中-新生代演化及岩石圈构造提供了重要依据(Yin and Harrison, 2000; Kapp et al., 2005, 2007; Mo et al., 2008; Zhu et al., 2008, 2009a, b, 2011a; 朱弟成等, 2008a; Zhao et al., 2009; 闫晶晶等, 2017; 崔浩杰等, 2019)。前人对于南拉萨地块的中-新生代岩浆作用已有较好的研究,而对于中拉萨地块和北拉萨地块,同样保存了三叠纪-白垩纪的岩浆作用记录,但目前还缺乏深入系统的研究。近年来在中拉萨地块和北拉萨地块相继发现了一系列中生代的岩浆活动(Wang et al., 2014; Zheng et al., 2015; Cao et al., 2019),涉及到洋壳岩石圈俯冲和羌塘地块-拉萨地块碰撞等重要地质过程。目前对于中拉萨地块中-西段的晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆作用已取得了部分认识,这些广泛发育的岩浆岩被认为与班公湖-怒江洋的南向俯冲、板片回转以及随后的板片断离作用密切相关(Zhu et al., 2009a, 2011a; Cao et al., 2016; Cao et al., 2019)。相比之下,对于中拉萨地块东段该时期发育的岩浆作用的系统研究还相对薄弱,除了有些年代学及部分锆石Hf同位素研究成果的报道之外,尚缺乏高质量的岩石地球化学数据来约束中拉萨地块岩浆作用的性质与成因及其深部动力学机制。
基于此,本文以西藏中拉萨地块东段南缘那茶淌地区花岗岩类为研究对象,在详细的野外地质调研和室内岩相学观察基础上,对该地区黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩开展了系统的岩石学、元素地球化学、锆石U-Pb年代学和Hf同位素研究,结合区域上已发表的相关文献数据,以期揭示中拉萨地块东段晚侏罗世-早白垩世时期的岩浆作用过程、源区性质及岩石成因,并为揭示该时期岩浆作用的深部动力学机制提供更加全面的岩石学和地球化学新证据。
1 地质背景与样品特征青藏高原是由一系列起源于冈瓦纳大陆的地块从早古生代开始不断增生到亚洲大陆形成的(Dewey et al., 1988; Yin and Harrison, 2000; Pan et al., 2012; 张泽明等, 2019)。其组成单元从北到南依次可分为昆仑地块、松潘-甘孜地块、南羌塘、北羌塘、拉萨地块和喜马拉雅地块(图 1a; Allégre et al., 1984; Yin and Harrison, 2000; Yin, 2006; Gehrels et al., 2011; Zhang and Santosh, 2012; Zhang et al., 2017),这些地体依次被昆仑(KSZ)、金沙江(JSSZ)、龙木错-双湖(LSSZ)、班公湖-怒江(BNSZ)和雅鲁藏布江缝合带(IYZSZ)分隔(Yin and Harrison, 2000; Pan et al., 2012)。作为青藏高原的重要组成部分,拉萨地块是夹持于班公湖-怒江缝合带以南和雅鲁藏布缝合带以北的巨型构造-岩浆岩带,东西向长约2500km,南北向宽150~300km,面积达45万平方千米(朱弟成等, 2006; 闫晶晶等, 2017),主要由前寒武纪的结晶基底、古生代-中生代的沉积岩和古生代-新生代的岩浆岩组成(潘桂棠等, 2006; Zhu et al., 2011a; Zhang et al., 2012; Lin et al., 2013; Xu et al., 2013; Hu et al., 2018; 张泽明等, 2019)。根据沉积盖层和基底性质的差异,拉萨地块可以进一步划分为北拉萨地块(NL)、中拉萨地块(CL)和南拉萨地块(SL),其间分别以狮泉河-纳木错蛇绿混杂岩带(SNMZ)和洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带(LMZ)为界(图 1, Zhu et al., 2011a, 2013)。已有研究表明,南拉萨地块和北拉萨地块以新生地壳为其主要特征(Mo et al., 2007, 2008; Zhu et al., 2011b),目前尚未发现寒武纪结晶基底(Dong et al., 2011; Zhu et al., 2012),而中拉萨地块是具有古老结晶基底的微陆块(Zhu et al., 2009a, 2011a)。

|
图 1 西藏高原构造单元(a)及拉萨地块主要岩浆岩分布图(b)(据Zhu et al., 2011a; Cao, et al., 2019修改) 年龄数据引自Chu et al., 2006; Zhu et al., 2009b, c, 2011a; Chen et al., 2014, 2015, 2017a, b; Meng et al., 2014; Hou et al., 2015; Fei et al., 2015; Zhang et al., 2015; Sun et al., 2015a, 2015b; Yang et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2016; Cao et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2015, 2016, 2017; 曲晓明等, 2006; 康志强等, 2008; 周长勇等, 2008; 高一鸣等, 2009; 刘伟等, 2010, 2012; 孟繁一等, 2010; 李奋其等, 2010; 姜昕等, 2010; 费光春等, 2010a, b; 杜德道等, 2011; 余红霞等, 2011; 于玉帅等, 2011; 崔晓亮等, 2011; 李应栩等, 2011, 张亮亮等, 2011; 张晓倩等, 2010, 2012; 姚晓峰等, 2012; 黄克贤等, 2012; 王保弟等, 2012, 2013; 李湘玉等, 2013; 张予杰等, 2014; 王力圆等, 2014, 2016; 张志等, 2015; 范淑芳等, 2015; 周华等, 2016; 王立强等, 2016; 高家昊等, 2016; 李跃等, 2017 Fig. 1 Tectonic subdivision of the Tibetan Plateau (a) and distribution of main magmatic rocks in Lhasa Block (b) (modified after Zhu et al., 2011a; Cao, et al., 2019) |
本文研究的花岗岩体位于中拉萨地块东段南缘,地理位置处于拉萨市墨竹工卡县北东约30km的扎雪乡那茶淌地区(30°10'57″~30°12'01″N、91°55'15″~91°56'57″E)。岩性包括黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩,其中黑云母二长花岗岩呈近东西向侵位于上石炭统-下二叠统来姑组(C2-P1l)砂岩、板岩中(图 2),热接触变质作用较弱,在局部地段发生轻微角岩化;花岗闪长岩以岩脉形式侵入于黑云母二长花岗岩体中,在钻孔中二者接触界线清晰可见(图 3a),研究样品采集自不同钻孔的不同深度。

|
图 2 那茶淌地区地质图 1-来姑组第三岩性段第一亚层砂岩、板岩;2-来姑组第三岩性段第二亚层灰岩、大理岩;3-矽卡岩;4-黑云母二长花岗岩;5-钻孔及编号 Fig. 2 Geological map of the Nachatang area |
|
图 3 那茶淌地区花岗岩野外及岩相学照片 (a)黑云母二长花岗岩与花岗闪长岩接触带;(b)黑云母二长花岗岩野外露头;(c、d)黑云母二长花岗岩镜下照片,见斜长石聚片双晶和卡氏双晶;(e)花岗闪长岩岩心照片;(f、g)花岗闪长岩镜下照片,石英晶体见溶蚀结构,斜长石见聚片双晶. Qtz-石英;Pl-斜长石;Bt-黑云母 Fig. 3 Photos of handspeciem and microphotographs of the granites in the Nachatang area |
黑云母二长花岗岩,呈灰白色,中-粗粒半自形粒状结构,块状构造,主要矿物组成为:石英(25%~30%)、斜长石(35%~40%)、钾长石(30%~35%)、黑云母(5%~8 %)、角闪石(2%~3 %),副矿物(磁铁矿、磷灰石、褐帘石、锆石等)小于1%。石英为他形粒状,粒度不均,粒径2~5mm,镜下见溶蚀和次生加大边,波状消光,偶见裂纹;长石多为柱状、板状等自形结构,可见聚片双晶、简单双晶和环带结构;黑云母多为片状结构,具有明显多色性(图 3c, d)。
花岗闪长岩,呈灰绿色-灰白色,中-粗粒半自形粒状结构和似斑状结构,块状构造,主要矿物组成为:石英(20%~25%)、斜长石(40%~45%)、钾长石(15%~20%)、角闪石(8%~10%)、黑云母(3%~5%),副矿物(磁铁矿、榍石、磷灰石、锆石等)小于1%;石英颗粒见贝壳断口,油脂光泽,镜下波状消光,溶蚀孔明显,偶见次生加大边;斜长石多为半自形长板状,镜下有明显的聚片双晶和环带结构;角闪石主要为黑色,长柱状,两组解理明显;黑云母主要呈片状,镜下有棕绿色-棕黄色多色性(图 3f, g)。
2 分析方法 2.1 岩石地球化学分析本次研究采集8件花岗岩样品用于全岩主、微量元素分析,相关测试在西南冶金地质测试所完成。采集新鲜岩石样品利用蒸馏水进行清洗,经过破碎、缩分、称重产生的粉末用于元素地球化学测试。主量元素测试方法为XRF法,仪器为Axios X荧光仪(PANalytical Company, Netherlands)。微量元素检测方法为等离子体质谱法,仪器为NexLON 300x ICP-MS。主、微量元素分析精度优于5%。
2.2 锆石U-Pb测年本次研究采集2件测年样品,黑云母二长花岗岩(NCTYT-1)和花岗闪长岩(NCTYT-2)。岩石碎样、锆石挑选、样品制靶和阴极发光(CL)显微照相由中国科学院广州地球化学研究所实验室完成。锆石U-Pb同位素定年在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心实验室分析完成,所采用的测试设备为激光烧蚀多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICP-MS)系统,其中多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱仪为Thermo Fisher公司制造的Neptune,激光器为美国ESI公司生产的UP193-FX ArF准分子激光器,激光波长193nm,脉冲宽度5ns。详细的仪器操作条件和实验流程方法见李怀坤等(2009)。采用208Pb校正法对普通铅进行校正。元素含量及U-Th-Pb同位素比值和年龄计算均采用软件ICPMSDataCal 9.0进行处理。锆石U-Pb年龄谐和图的绘制和MSWD的计算则采用Isoplot /Ex_ver3。
2.3 锆石Hf同位素分析锆石原位Hf同位素的分析测试在中国地质调查局天津地质调查中心同位素实验室利用Neptune公司LA-MC-ICP MS完成,分析测试点位于锆石U-Pb同位素测试点附近,激光剥蚀束斑直径约35μm,具体实验条件和流程详见耿建珍等(2011)。使用GJ-1作为标准锆石检测实验数据,本次分析过程中GJ-1的Hf同位素含量为0.282020±0.000016 (2σ,N=11),与文献报道值在误差范围内一致。εHf(t)值根据测点的锆石U-Pb年龄计算,采用176Lu衰变常数为1.876×10-11y-1(Söderlund et al., 2004),球粒陨石176Hf/177Hf比值为0.282785,176Lu/177Hf比值为0.0336 (Bouvier et al., 2008)。亏损地幔模式年龄(tDM)的计算参考现今亏损地幔176Lu/177Hf比值0.28325,176Lu/177Hf比值为0.0384 (Griffin et al., 2000)。假设每颗锆石的母岩浆来自平均大陆地壳,采用176Lu/177Hf比值为0.015 (Griffin et al., 2002)计算锆石Hf同位素的地壳模式年龄(tDMC)。选择不同衰变常数不会影响实验结果。
3 分析结果 3.1 岩石地球化学 3.1.1 主量元素黑云母二长花岗岩的SiO2含量为71.02%~71.81%,平均71.47%;Al2O3含量为13.45%~13.57%,平均13.51%;Na2O含量为2.26%~2.59%,平均2.45%;K2O含量为4.53%~4.89%,平均4.77%;MgO含量为0.32%~0.38%,平均0.35%;全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量为6.79%~7.47%,K2O/Na2O值为1.89~2.00(表 1)。
|
|
表 1 那茶淌地区花岗岩主量元素(wt%)和微量元素(×10-6)地球化学数据 Table 1 Whole-rock major (wt%) and trace (×10-6) elements of the granites in the Nachatang area |
花岗闪长岩的SiO2含量为65.17%~66.73%,平均66.21%;Al2O3含量为14.43%~15.20%,平均14.63%;Na2O含量为2.85~3.09%,平均3.01%;K2O含量为3.70% ~4.28%,平均4%;MgO含量为1.11%~1.20%,平均1.15%;全碱(Na2O+K2O)含量为6.55%~7.37%,K2O/Na2O值为1.29~1.38(表 1)。
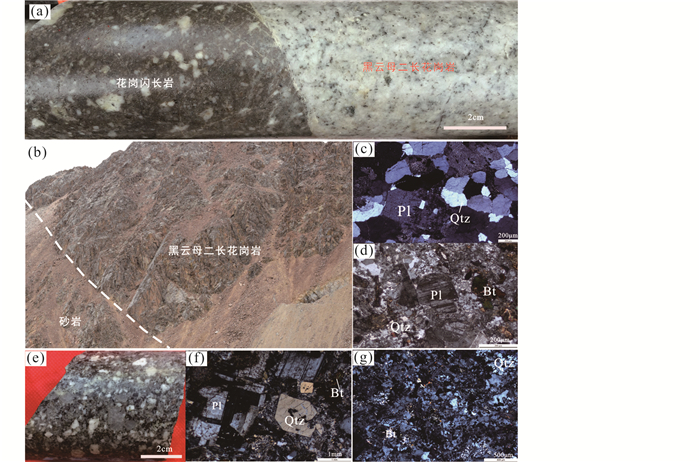
在A/NK-A/CNK图(图 4a)上,两种岩石投点主要落在准铝质-弱过铝质区域,其中,黑云母二长花岗岩A/CNK值为1.03~1.14(>1)、平均1.01,A/NK值为1.41~1.57(>1),Al2O3>CaO+Na2O+K2O,属于弱过铝质岩石特征;花岗闪长岩A/CNK值为0.98~1.02,平均值为0.99(<1),A/NK值为1.50~1.66(>1),显示准铝质-弱过铝质的特征。在SiO2-K2O图解上,黑云母二长花岗岩样品成分的投点落在花岗岩区,花岗闪长岩成分投点落入花岗闪长岩区域,二者同属于高钾钙碱性系列岩石(图 4b)。
|
图 4 那茶淌地区花岗岩地球化学图解(a, 据Rickwood, 1989; b, 据Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) Fig. 4 Geochemical plots of granitiods in the Nachatang area (a, after Rickwood, 1989; b, after Peccerillo and Taylor, 1976) |
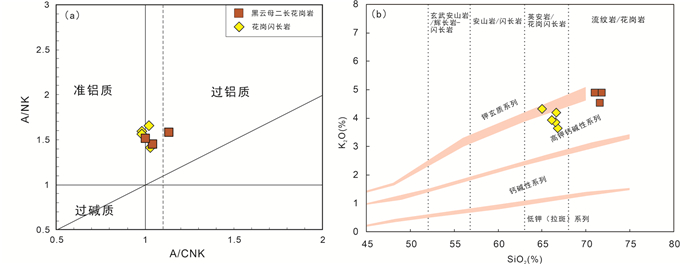
那茶淌地区两类花岗岩具有相似的微量元素地球化学特征。黑云母二长花岗岩的大离子亲石元素(LILE)Rb、Ba、K含量分别为:212.6×10-6~216.5×10-6、727.0×10-6~2001×10-6和37585×10-6~40552×10-6;花岗闪长岩的大离子亲石元素(LILE)Rb、Ba、K含量分别为:147.4×10-6~185.0×10-6、646.9×10-6~1283×10-6和30718×10-6~35537×10-6;黑云母二长花岗岩的高场强元素(HFSE)Nb、P、Ta、Ti含量分别为:10.50×10-6~15.77×10-6、201.6×10-6~231.8×10-6、0.74×10-6~1.56×10-6和869.9×10-6~1233×10-6,花岗闪长岩的高场强元素(HFSE)Nb、P、Ta、Ti含量分别为:17.13×10-6~20.11×10-6、640.7×10-6~767.3×10-6、1.24×10-6~1.71×10-6和3692×10-6~4117×10-6(表 1)。由原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(图 5a)可以看出,该地区黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩均表现出大离子亲石元素(LILE)Rb、Ba、K富集,高场强元素(HFSE)Nb、P、Ta、Ti亏损,Nd、La等元素富集的特征,说明花岗岩成岩过程中经历了斜长石、磷灰石和钛铁矿等矿物的分离结晶作用。
|
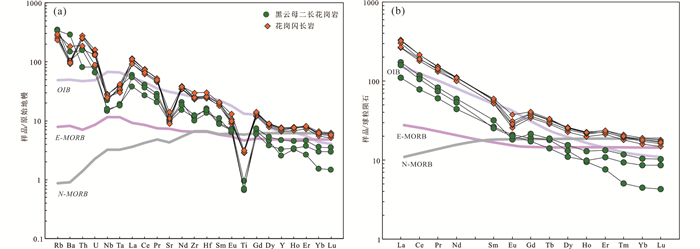
图 5 那茶淌地区花岗岩原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(a, 标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(b, 标准化值据Boynton, 1984) Fig. 5 Primitive-mantle normalized trace element spider diagrams (a, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) and chondrite-normalized rare earth element patterns (b, normalization values after Boynton, 1984) for the granites in the Nachatang area |
稀土元素组成方面,花岗闪长岩稀土元素总量(ΣREE=263.9×10-6~313.8×10-6,平均289.8×10-6)高于黑云母二长花岗岩的(ΣREE=116.3×10-6~168.8×10-6,平均145.2×10-6),(表 1)。总体上黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩具有相似的稀土元素配分型式(图 5b),黑云母二长花岗岩LREE/HREE的比值范围为9.84~12.49,花岗闪长岩LREE/HREE的比值范围为10.1~11.6,均表现为轻稀土元素相对富集,重稀土元素亏损的特征。黑云母二长花岗岩δEu值范围为0.69~0.94,花岗闪长岩δEu值范围为0.59~0.76,呈现铕亏损的特征;黑云母二长花岗岩δCe值范围为0.91~0.92,花岗闪长岩δCe值范围为0.88~0.93,呈现轻微亏损的特征。黑云母二长花岗岩(La/Yb)N比值范围为16.5~25.0,花岗闪长岩(La/Yb)N比值范围为14.8~18.0,说明该地区花岗岩类在成岩过程中轻重稀土元素发生了强烈的分馏作用。
3.2 锆石U-Pb定年那茶淌地区花岗岩的锆石CL图像(图 6)显示,锆石的主要特征为灰白色-灰黑色,半自形-自形结构,外形主要为长柱状或菱柱形,长约30~300μm,宽约20~110μm,长宽比值为1.5~2.7,发育明显的振荡环带结构,Th/U值为0.68~2.16,具有典型的岩浆锆石特征(吴元保, 2004)。黑云母二长花岗岩(样品NCTYT-1)21个锆石测点的U含量为140×10-6~860×10-6,Th含量为490×10-6~1826×10-6,Th/U比值为1.38~2.16(表 2)。花岗闪长岩(样品NCTYT-2)20个锆石测点的U含量为140×10-6~750×10-6,Th含量为234×10-6~1120×10-6,Th/U比值为0.68~2.08(表 2)。207Pb/235U-206Pb/238U协和图(图 7),所有测试点均落在谐和线上或者附近,说明锆石没有发生明显的Pb流失,得到的年龄真实可靠,对测点获得年龄进行加权平均计算,得到黑云母二长花岗岩结晶年龄为147±1.4Ma (MSWD=1.50, n=21),花岗闪长岩结晶年龄为140.6±1.3Ma (MSWD=0.89, n=20),显示那茶淌地区花岗岩的成岩时代为晚侏罗世-早白垩世。

|
图 6 那茶淌地区黑云母二长花岗岩(NCTYT-1)和花岗闪长岩(NCTYT-2)的锆石阴极发光CL图像 Fig. 6 Cathodoluminescence images of selected zircon grains from the biotite granite(NCTYT-1) and granodiorite(NCTYT-2) |
|
|
表 2 那茶淌地区花岗岩LA-MC-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年结果 Table 2 Zircon LA-MC-ICPMS U-Pb analysis data of the granites in the Nachatang area |

|
图 7 那茶淌地区黑云母二长花岗岩(NCTYT-1)和花岗闪长岩(NCTYT-2)锆石U-Pb定年谐和图及加权平均年龄图 Fig. 7 Zircon U-Pb dating concordances and weighted mean ages of the biotite monzogranite (NCTYT-1) and granodiorite (NCTYT-2) in the Nachatang area |
本次研究在锆石U-Pb年代学测试基础上,对黑云母二长花岗岩(NCTYT-1)和花岗闪长岩(NCTYT-2)样品的年代学测点开展了Lu-Hf同位素测试,数据见表 3。黑云母二长花岗岩锆石原位21个测点进行Hf同位素测试,176Hf/177Hf值为0.282073~0.282467,平均为0.282397;176Lu/177Hf值为0. 000721~0.001822,平均为0.001389;两种花岗岩锆石176Lu/177Hf值均小于0.002,说明锆石在形成过程中具有很低的放射性成因Hf的积累,可以判定锆石的176Hf/177Hf比值和锆石形成时的比值一致(Amelin et al., 1999)。黑云母二长花岗岩锆石εHf(0)值为-24.73~-13.25,εHf(t)值为-21.64~-7.66,Hf同位素地壳模式年龄(tDMC)介于1.69~2.56Ga之间,平均为1.84Ga。花岗闪长岩锆石原位20个测点进行Hf同位素进行分析测试,176Hf/177Hf值为0.282349~0.282456,平均为0.282404;176Lu/177Hf值为0.000699~0.001762,平均为0.001126;εHf(0)值-14.96~-11.18,平均为-13.02;εHf(t)值为-11.95~-8.15,平均为-10.04;Hf同位素地壳模式年龄(tDMC)介于1.71~1.95Ga之间,平均为1.83Ga。
|
|
表 3 那茶淌地区花岗岩的锆石Hf同位素组成 Table 3 Hf isotopic composition of zircons of the granites in the Nachatang area |
区域上,中拉萨地块晚侏罗世岩浆岩主要分布于措勤、雄巴、盐湖、许如错、亚热、门巴等地区(黄俊平等, 2006; 姜昕等, 2010; Zhu et al., 2011a; 闫晶晶等, 2017)。许如错岩体,岩性主要为黑云母二长花岗岩和闪长岩,成岩时代为155~161Ma(黄俊平等, 2006; 闫晶晶等, 2017);夏定勒岩体,岩性为二长花岗岩,成岩时代为153Ma(闫晶晶等, 2017);雄巴岩体,岩性主要为花岗闪长岩,成岩时代为149Ma(姜昕等, 2010);则弄群火山岩,成岩时代为129~131Ma(朱弟成等,2008b);措勤花岗岩体,成岩时代为152Ma(Zhu et al., 2011a);盐湖地区的流纹岩,成岩时代为146Ma(Zhu et al., 2011a)。1/25万区域地质调查报告在文部、科波熊、夏定勒地区也报道了该时期的岩浆活动(闫晶晶等, 2017),在文部复式岩体中获得了154±8.4Ma的锆石U-Pb年龄(闫晶晶等, 2017),在央雄勒复式岩体中分别获得了142Ma的白云母K-Ar年龄(卢书炜等, 2006)。此外,Zhu et al.(2011a)在门巴(154Ma)、梅朵(153Ma)和亚热(146Ma,160Ma)地区也发现了晚侏罗世中酸性岩浆作用的记录。本文锆石U-Pb年代学研究显示,那茶淌地区黑云母二长花岗岩侵位时代为147±1.4Ma,为晚侏罗世中酸性岩浆活动的产物,与上述年龄值较为一致。
中拉萨地块的早白垩世岩浆岩整体上呈东西向带状展布,主要分布于措勤、申扎、门巴、波密、八宿、察隅等地区。措勤地区的早白垩世花岗质岩石主要分布于江让-尼雄一带,岩体主要侵位于石炭系-二叠系、侏罗系和白垩系地层中,岩石类型丰富,主要包括花岗闪长(斑)岩、黑云母二长花岗岩、石英闪长岩和正长花岗岩等,富含大量同期闪长质包体(张晓倩等, 2012),这些岩体成岩时代为107~122Ma,大多数据集中于110Ma左右(周长勇等, 2008; Zhu et al., 2009a; 张晓倩等, 2012)。申扎地区的早白垩世花岗岩类分布于娘热藏布、甲岗山、阳定、扁前浦南一带,包括闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、二云母花岗岩、黑云母花岗岩和花岗斑岩等,同期闪长岩多以包体形态产出,侵位于石炭系-二叠系沉积地层中,侵位时代为113~134Ma(Zhu et al., 2009a; 张亮亮等, 2011; 孟繁一, 2014)。门巴地区的早白垩世花岗质岩石主要分布于巴嘎-色日荣一带,岩石类型主要为黑云母二长花岗岩、斑状花岗闪长岩和二长花岗岩等,侵入于石炭系-二叠系来姑组地层中,成岩时代为117~128Ma(孟繁一, 2014)。此外,前人对中拉萨地块念青唐古拉成矿带部分矿区的早白垩世岩浆作用也进行了报道,如亚贵拉铅锌矿区石英斑岩(126.7~130.6Ma,高一鸣等, 2009),洞中拉铅锌矿区花岗斑岩(124±1.9Ma,费光春等, 2010a)和辉绿玢岩(117±1Ma,费光春等,2010b)。波密-八宿-察隅地区的早白垩世花岗岩类岩性主要为闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、和二长花岗岩,成岩时代为110~133Ma(Booth et al., 2004; Chiu et al., 2009; Zhu et al., 2009b),有学者将其解释为后碰撞背景下增厚地壳重熔形成的S型花岗岩,并受到了新特提斯洋壳岩石圈北向俯冲的影响(Chiu et al., 2009)。Zhu et al.(2009b)发现了同期的察隅Ⅰ型花岗岩,认为该岩体很可能是在班公湖-怒江海洋岩石圈南向俯冲作用下,由俯冲带之上的幔源岩浆既提供热量诱发古老地壳物质重熔,又与该壳源熔体发生混合而形成。本文获得的那茶淌地区花岗闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为140.6±1.3Ma,为早白垩世中酸性岩浆活动的产物,这一年龄结果与前人研究相比有些偏老。
4.2 岩石成因及岩浆源区每种源岩和岩石形成作用都与特定的构造环境密切相关(Pitcher, 1983),因此准确鉴别花岗岩的成因类型是解译岩石成因和构造背景的基础。根据实际矿物含量、全岩地球化学成分和微量元素丰度的不同,可以将花岗岩类分为Ⅰ型、S型、A型和M型4类(Chappell and White, 1974; 马鸿文, 1992; Chappell, 1999)。Chappell and White(1974)根据源岩的性质提出Ⅰ型和S型花岗岩的分类标准;Collins et al.(1982)提出A型花岗岩的概念,具有相对不含水(Anhydrous)、富碱(Alkali)和非造山环境(Anorogenic)的特征;随后Pitcher(1983)识别出M型花岗岩,认为这种类型花岗岩主要是产于大洋盆地之中,常与蛇绿岩套共生产出,岩浆源区来自于地幔(Mantle)。不同成因类型的花岗岩代表了不同构造活动带、不同源岩和岩石形成作用过程的最终产物,每一种成因类型都具有代表其物质来源和形成条件的特殊标志。
不同成因类型的花岗岩在矿物组成和元素地球化学成分上通常存在较大差异(马鸿文, 1992)。岩石矿物成分在确定了岩石的铝饱和指数(A/CNK)基础上,根据源岩是否经历地表化学沉积作用,划分出了Ⅰ型和S型花岗岩。如,堇青石、角闪石和碱性暗色矿物是识别Ⅰ型、S型和A型花岗岩最重要的标志性矿物。堇青石、白云母、石榴子石等富铝矿物的出现则可以说明岩石达到铝饱和状态,同时这些矿物也是鉴别S型花岗岩的特征矿物,尤其是岩石中若出现堇青石则可以确定为S型花岗岩;而角闪石则是Ⅰ型花岗岩的特征判别矿物(谢富伟, 2019)。
本文研究的那茶淌地区黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩都含有角闪石,未见堇青石和碱性暗色矿物,从矿物学特征上表明该区花岗岩具有Ⅰ型花岗岩的特征。在元素地球化学成分上,黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩具有高度相似的稀土配分型式和微量元素蛛网曲线,表明二者具有强烈的亲缘关系,且经历了相似的演化过程。
在(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO图解中(Whalen et al., 1987),本文的研究样品均落入未分异的花岗岩区域(图 8b),而未经强烈分异的花岗岩可用A/CNK=1.1作为划分Ⅰ和S型花岗岩的分界,前已述及本文花岗岩样品多数为A/CNK < 1.1(图 3),符合Ⅰ型花岗岩的地球化学特征。
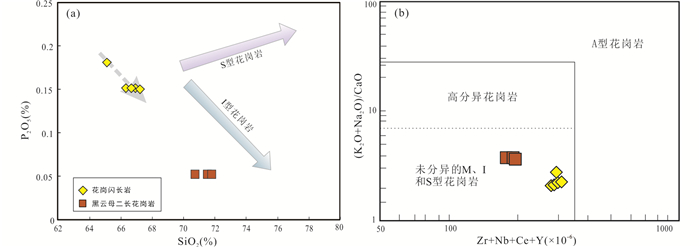
|
图 8 那茶淌地区花岗岩体岩石成因判别图解 (a)SiO2-P2O5图解;(b)(Zr+Nb+Ce+Y)-(Na2O+K2O)/CaO图解 Fig. 8 Discrimination diagrams of petrogenetic types for granitoids in the Nachatang area |
实验岩石学研究表明,磷灰石在准铝质-弱过铝质岩浆中的溶解度较低(P2O5含量约为0.1%),并会随着岩浆温度的降低和SiO2的增加而降低,所以准铝质-弱过铝质的花岗岩中磷灰石总是会优先结晶,残余岩浆的P2O5含量也会逐渐降低(Watson, 1979; Watson and Capobianco, 1981)。然而,磷灰石在过铝质花岗岩中(A/CNK=1.1~1.3)的溶解度表现出不同的变化趋势,会随着A/CNK的增加而增加(A/CNK=1.3时,P2O5含量可达到0.63%),过铝质岩浆中由于磷灰石的溶解度较高,不会优先结晶,所以过铝质花岗岩中随着SiO2的增加,P2O5含量会增高或保持不变(Watson, 1979; Watson and Capobianco, 1981; 谢富伟, 2019)。因此,磷灰石的这种地球化学行为被用于区分Ⅰ型和S型花岗岩(Chappell,1999; Wu et al., 2003; 闫晶晶等,2017; 谢富伟, 2019)。在SiO2-P2O5图解中(图 8a),本文花岗岩类岩石样品SiO2与P2O5呈现出一定负相关关系,与中拉萨地块同期岩浆岩样品的P2O5含量主体显示出随SiO2含量的增加而降低的趋势(闫晶晶等,2017),与Ⅰ型花岗岩的演化趋势较一致。综上所述,那茶淌地区的晚侏罗世-早白垩世花岗质岩石为准铝质-弱过铝质钙碱性Ⅰ型花岗岩。
在判别岩浆源区方面,锆石原位Lu-Hf同位素是可以详细记录岩浆混合和分异过程中同位素的组成变化,以及有效识别地幔岩浆端元的一种重要同位素示踪方法(Li et al., 2007; 吴福元等, 2007b)。一般而言,具有较高的εHf(t)值和相应较年轻的模式年龄,表明花岗岩可能来源于大陆地壳中地幔物质的混入或新生地壳的再循环;而具有较低的εHf(t)值和相应老的模式年龄,则表明花岗岩可能来源于古老地壳的深融或重融(Ben-Bassat et al., 1980; Mo et al., 2007)。Ⅰ型花岗岩可由地壳重熔过程中幔源物质的加入而形成(Kemp et al., 2007; Collins and Richards, 2008; Zhu et al., 2009b, c)或是壳内中基性火成岩或变质岩部分熔融形成(Chappell and Stephens, 1988)。本文黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩均以较负的、变化范围较大的锆石εHf(t)值为特征(表 3、图 9)。其中,黑云母二长花岗岩锆石εHf(t)值为-21.64~-7.66,Hf同位素地壳模式年龄(tDMC)为1.68~2.56Ga;花岗闪长岩锆石εHf(t)值为-11.95~-8.15,Hf同位素地壳模式年龄(tDMC)为1.71~1.95Ga。这种变化范围大的锆石Hf同位素组成可能是由于长英质岩浆和镁铁质岩浆发生岩浆混合的产物或是表明岩石的源区物质组成的不均一性。大量的中拉萨地块样品显示出非常负的εHf(t)值特征(图 9),结合中拉萨地块具有古老地壳基底的特征,认为那茶淌地区准铝质-弱过铝质Ⅰ型花岗岩可能来源于中拉萨地块古老下地壳物质的重熔。
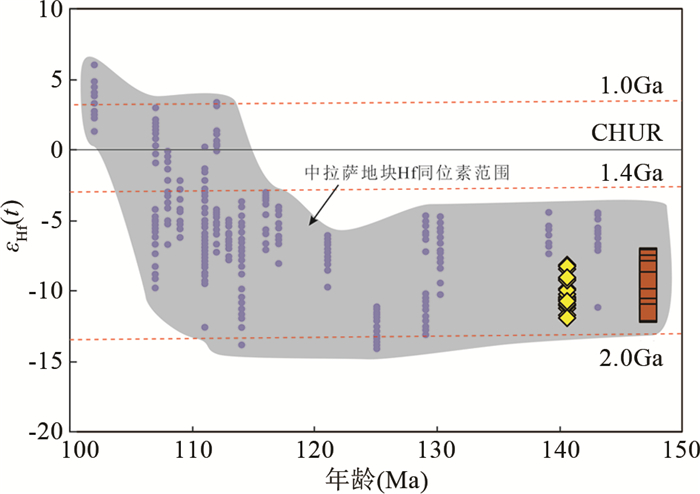
|
图 9 中拉萨地块晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆活动的锆石εHf(t)与U-Pb年龄图解 中拉萨地块其它岩浆岩锆石Hf同位素数据引自Zhu et al., 2009b, 2011a Fig. 9 Plot of zircon εHf(t) vs. ages of the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous igneous rocks in the Central Lhasa Terrane |
花岗岩类的形成和大地构造环境具有密切的关系(Barbarin, 1999),岩石的地球化学特征在判别构造环境和地球动力学演化方面提供有用的信息。那茶淌地区黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩的主量元素地球化学特征分析显示Al2O3含量较高,分别为13.45%~13.57%(平均13.51%)和14.43%~15.20%(平均14.63%),TiO2含量较低,分别为0.15%~0.21%(平均0.17%)和(0.62%~0.69%,平均0.64%),与弧背景下的岩浆岩地球化学特征相似(Crawford et al., 1987)。微量元素以富集K、Rb、Ba、Th等大离子亲石元素,亏损Ta、Nb、P、Ti等高场强元素为特征;稀土元素均表现为轻稀土元素富集,重稀土元素相对亏损,具弱的负Eu异常,同样显示出弧岩浆岩的地球化学特征(Pearce, 1983)。在构造环境判别Yb-Ta图(图 10a)和(Yb+Ta)-Rb图(图 10b)中,两种岩石样品均落入火山弧花岗岩区域内;在Y-Sr/Y图解(图 10c)和YbN-(La/Yb)N图解(图 10d)中,样品均落入经典岛弧岩石区域,显示出那茶淌地区花岗岩具有弧型岩浆岩的地球化学特征(Sun and McDonough, 1989; Taylor et al., 1985; Kang et al., 2014),表明那茶淌地区花岗岩类形成于与板片俯冲有关的火山弧环境中。
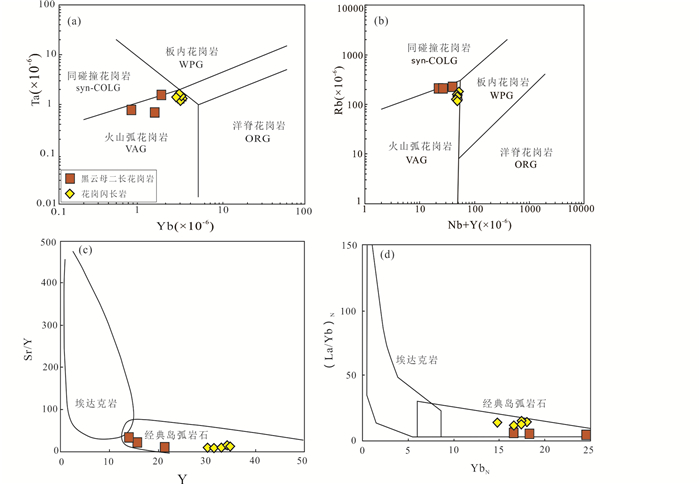
|
图 10 那茶淌地区花岗岩Yb-Ta(a)、(Nb+Y)-Rb(b)、Y-Sr/Y(c)和YbN-(La/Yb)N(d)图解(a, b, 底图据Pearce et al., 1984;c, d, 底图据Defant and Drummond, 1990) Fig. 10 Diagrams of Yb vs. Ta (a), (Nb+Y) vs. Rb (b), Y vs. Sr/Y (c) and YbN vs. (La/Yb)N (d) for the granites in the Nachatang area (a, b, after Pearce et al., 1984; c, d, after Defant and Drummond, 1990) |
目前对于中拉萨地块中生代岩浆岩的成因和地球动力学背景还存在较大争论,主要集中在新特提斯洋壳北向的低角度或平板俯冲(Coulon et al., 1986; Kapp et al., 2007)和班公湖-怒江洋壳南向俯冲及断离(潘桂棠等, 2006; 朱弟成等, 2006, 2008a, b; Zhu et al., 2009a, b)两大观点的争论。研究表明,洋壳板片俯冲作用形成的弧型岩浆作用,将产生从缝合带到内部的逐渐年轻的趋势(Gutscher et al., 2000; Cao et al., 2019),然而这种趋势从南拉萨地块到中拉萨地块的岩浆活动尚未得到证实(Chen et al., 2017a;Cao et al., 2019)。通过对中部和北部拉萨地块已发表年代学和地球化学数据的综合归纳,结合本文数据,表明在中侏罗世-早白垩世期间,中部和北部拉萨地块有连续的岩浆作用记录,岩石类型从偏铝质到过铝质均有出现,主要为Ⅰ型花岗岩(大部分A/CNK<1.1)(Cao et al., 2016; 闫晶晶等, 2017)。此外,有学者研究了中拉萨地块早白垩世花岗岩的K2O含量与班公湖-怒江缝合带的距离呈正相关关系,认为是班公湖-怒江大洋板块南向俯冲导致了这些岩浆岩的形成(Wu et al., 2016; Cao et al., 2019)。因此,根据本文研究结果,结合拉萨地块同时代岩浆作用成果(Zhu et al., 2011a; 闫晶晶等, 2017; Cao et al., 2019),本文认为中拉萨地块东段晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆活动,是在班公湖-怒江洋壳南向俯冲的地球动力学背景之下(图 11),由俯冲带之上的幔源岩浆提供热量诱发中拉萨地块古老地壳物质重熔所形成的。
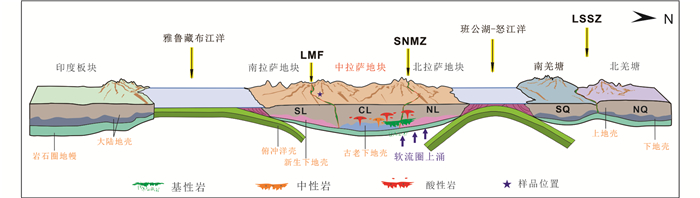
|
图 11 拉萨地块晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆活动的动力学模型(据Cao et al., 2019修改) Fig. 11 Schematic illustration of the tectono-magmatic evolution of the Lhasa subterrane during Late Jurassic- Early Cretaceous time (modified after Cao et al., 2019) |
(1) 锆石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果显示中拉萨地块东段南缘那茶淌地区黑云母二长花岗岩成岩年龄为147.1±1.4Ma,花岗闪长岩成岩年龄为140.6±1.3Ma,表明该区花岗岩类为晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆活动的产物。
(2) 那茶淌地区黑云母二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩具有相似的地球化学特征,表现为:富SiO2、Al2O3和(Na2O+K2O),低TiO2;微量元素富集大离子亲石元素K、Rb、Ba和轻稀土元素,亏损高场强元素Ta、Nb、P、Ti和重稀土元素,有弱的负Eu异常;显示Ⅰ型准铝-弱过铝质的高钾钙碱性系列特征。
(3) 那茶淌地区花岗岩类锆石εHf(t)为较大的负值和古老的地壳模式年龄,指示岩浆可能来源于古老下地壳物质的重熔,其形成的构造背景与班公湖-怒江洋南向俯冲有关。
致谢 西藏鑫茂矿业有限公司为本研究的野外工作提供了大量帮助;四川省核工业地质调查院李盛俊、史子豪、李文祥参与了野外地质调查;审稿专家提出了大量富有建设性的修改意见和建议;在此一并致以诚挚的谢意!
Allégre CJ, Courtillot V, Tapponnier P, Hirn A, Mattauer M, Coulon C, Jaeger JJ, Achache J, Schärer U, Marcoux J, Burg JP, Girardeau J, Armijo R, Gariépy C, Göpel C, Li TD, Xiao XC, Chang CF, Li GQ, Lin BY, Teng JW, Wang NW, Chen GM, Han TL, Wang XB, Den WM, Sheng HB, Cao YG, Zhou J, Qiu HR, Bao PS, Wang SC, Wang BX, Zhou YX and Xu RH. 1984. Structure and evolution of the Himalaya-Tibet orogenic belt. Nature, 307(5946): 17-22 DOI:10.1038/307017a0
|
Amelin Ⅱ. 1999. On the instability of the p-electron subsystem of anions in the CuO2, planes in high-Tc superconductors. Journal of Experimental and Theoretical Physics Letters, 70(1): 23-28 DOI:10.1134/1.568124
|
Barbarin B. 1999. A review of the relationships between granitoid types, their origins and their geodynamic environments. Lithos, 46(3): 605-626 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00085-1
|
Ben-Bassat M, Carlson RW, Puri VK, Davenport MD, Schriver JA, Latif M, Smith R, Portigal LD, Lipnick EH and Weil MH. 1980. Pattern-based interactive diagnosis of multiple disorders: The MEDAS system. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, PAMI-2(2): 148-160
|
Booth AL, Zeitler PK, Kidd WSF, Wooden J, Liu YP, Idleman B, Hren M and Chamberlain CP. 2004. U-Pb zircon constraints on the tectonic evolution of southeastern Tibet, Namche Barwa area. American Journal of Science, 304(10): 889-929 DOI:10.2475/ajs.304.10.889
|
Bouvier A, Vervort JD and Patchett PJ. 2008. The Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd isotopic composition of CHUR: Constraints from unequilibrated chondrites and implications for the bulk composition of terrestrial planets. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 273(1-2): 48-57 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2008.06.010
|
Cao HW, Zhang YH, Santosh M, Li GM, Hollis SP, Zhang LK, Pei QM, Tang L and Duan ZM. 2019. Petrogenesis and metallogenic implications of Cretaceous magmatism in Central Lhasa, Tibetan Plateau: A case study from the Lunggar Fe skarn deposit and perspective review. Geological Journal, 54(4): 2323-2346 DOI:10.1002/gj.3299
|
Cao MJ, Qin KZ, Li GM, Li JX, Zhao JX, Evans NJ and Hollings P. 2016. Tectono-magmatic evolution of Late Jurassic to Early Cretaceous granitoids in the west central Lhasa subterrane, Tibet. Gondwana Research, 39: 386-400 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.01.006
|
Chappell BW and White AJR. 1974. Two contrasting granite types. Pacific Geology, 8: 173-174
|
Chappell BW and Stephens WE. 1988. Origin of infracrustal (Ⅰ-type) granite magmas. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, 79(2-3): 71-86 DOI:10.1017/S0263593300014139
|
Chappell BW. 1999. Aluminium saturation in Ⅰ- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites. Lithos, 46(3): 535-551 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
|
Chen GN, Wang Y, Chen Z and Peng ZL. 2017. Advance and consideration on the mechanism of formation and emplacement of granitic magma. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(5): 1489-1497 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen JL, Xu JF, Yu HX, Wang BD, Wu JB and Feng YX. 2015. Late Cretaceous high-Mg# granitoids in southern Tibet: Implications for the early crustal thickening and tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau?. Lithos, 232: 12-22 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.020
|
Chen SS, Fan WM, Shi RD, Gong XH and Wu K. 2017a. Removal of deep lithosphere in ancient continental collisional orogens: A case study from central Tibet, China. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 18(3): 1225-1243 DOI:10.1002/2016GC006678
|
Chen SS, Shi RD, Gong XH, Liu DL, Huang QS, Yi GD, Wu K and Zou HB. 2017b. A syn-collisional model for Early Cretaceous magmatism in the northern and central Lhasa subterranes. Gondwana Research, 41: 93-109 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.04.008
|
Chen Y, Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Meng FY, Wang Q, Santosh M, Wang LQ, Dong GC and Mo XX. 2014. Slab breakoff triggered ca. 113Ma magmatism around Xainza area of the Lhasa Terrane, Tibet. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 449-463 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.06.005
|
Chiu HY, Chung SL, Wu FY, Liu DY, Liang YH, Lin IJ, Iizuka Y, Xie LW, Wang YB and Chu MF. 2009. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic constraints from eastern Transhimalayan batholiths on the precollisional magmatic and tectonic evolution in southern Tibet. Tectonophysics, 477(1-2): 3-19 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2009.02.034
|
Chu MF, Chung SL, Song B, Liu DY, O'Reilly SY, Pearson NJ, Ji JQ and Wen DJ. 2006. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on the Mesozoic tectonics and crustal evolution of southern Tibet. Geology, 34(9): 745-748 DOI:10.1130/G22725.1
|
Clemens JD. 2003. S-type granitic magmas-petrogenetic issues, models and evidence. Earth-Science Reviews, 61(1-2): 1-18 DOI:10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00107-1
|
Collins WJ, Beams SD, White AJR and Chappell BW. 1982. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 80(2): 189-200 DOI:10.1007/BF00374895
|
Collins WJ and Richards SW. 2008. Geodynamic significance of S-type granites in circum-Pacific orogens. Geology, 36(7): 559-562 DOI:10.1130/G24658A.1
|
Coulon C, Maluski H, Bollinger C and Wang S. 1986. Mesozoic and Cenozoic volcanic rocks from central and southern Tibet: 40Ar-39Ar dating, petrological characteristics and geodynamical significance. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 79(3-4): 281-302 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(86)90186-X
|
Crawford AJ, Falloon TJ and Eggins S. 1987. The origin of island arc high-alumina basalts. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 97(3): 417-430 DOI:10.1007/BF00372004
|
Cui HJ, Gou ZB, Liu H, Li J and Yang Y. 2019. The petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the late Early Cretaceous granodiorites in the Nyixung area, western Lhasa block, Xizang. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 39(1): 1-13 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Cui XL, Tang JX, Dorji, Zhong KH, Gao YM, Liu HF, Zhang JS, Wang CH and Liu TT. 2011. Zircon U-Pb age of the quartz porphyry from Dongzhongla Pb-Zn deposit in Tibet, China. Journal of Chengdu University of Technology (Science & Technology Edition), 38(5): 557-562 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662-665 DOI:10.1038/347662a0
|
Dewey JF, Shackleton RM, Chang CF and Sun YY. 1988. The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences, 327(1594): 379-413
|
Dong X, Zhang ZM, Liu F, Wang W, Yu F and Shen K. 2011. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Nyainqêntanglha Group from the Lhasa terrane: New constraints on the Triassic orogeny of the south Tibet. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 42(4): 732-739
|
Du DD, Qu XM, Wang GH, Xin HB and Liu ZB. 2011. Bidirectional subduction of the Middle Tethys oceanic basin in the west segment of Bangonghu-Nujiang suture, Tibet: Evidence from zircon U-Pb LAICPMS dating and petrogeochemistry of arc granites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7): 1993-2002 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Fan SF, Qu XM, Song Y and Xin HB. 2015. Petrogenesis of the ore-forming granodiorite in the Nixiong iron deposit and its implications for the metallogenic tectonic background. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 39(2): 286-299 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Fei GC, Wen CQ, Wang CS, Zhou X, Wu PY, Wen Q and Zhou Y. 2010a. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age of porphyry granite in the Dongzhongla lead-zinc deposit, Maizhokunggar County, Tibet. Geology in China, 37(2): 470-476 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Fei GC, Wen CQ, Wang CS, Wu PY, Wen Q and Zhou X. 2010b. Zircon SHRIMP U-Pb age and its geological significance in Dongzhongla allgovite, Mozhugongka area, eastern segment of Gangdise, Tibet, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(8): 1138-1142 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Gao JH, Zeng LS, Gao LE, Hou KJ and Guo CL. 2016. Two episodes of Early Cretaceous magmatism in Geji area of the Lhasa Block, Tibet. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(1): 55-70 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Gao YF, Hou ZQ and and Wei RH. 2003. Neogene porphyries from Gangdese: petrological, geochemical characteristics and geodynamic significances. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 19(3): 418-428 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Gao YM, Chen YC, Tang JX, Du X, Li XF, Gao M and Cai ZC. 2009. SHRIMP U-Pb dating of zircon from quartz porphyry in the Yaguila Pb-Zn-Mo deposit, Gongbujiangda County, Tibet and its geological implication. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(10): 1436-1444 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Gehrels G, Kapp P, DeCelles P, Pullen A, Blakey R, Weislogel A, Ding L, Guynn J, Martin A, McQuarrie N and Yin A. 2011. Detrital zircon geochronology of pre-Tertiary strata in the Tibetan-Himalayan orogen. Tectonics, 30(5): TC5016
|
Geng JZ, Li HK, Zhang J, Zhou HY and Li HM. 2011. Zircon Hf isotope analysis by means of LA-MC-ICP-MS. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(10): 1508-1513 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, Belousova E, Jackson SE, van Achterbergh E, O'Reilly SY and Shee SR. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133-147 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
|
Griffin WL, Wang X, Jackson SE, Pearson NJ, O'Reilly SY, Xu XS and Zhou XM. 2002. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China: In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos, 61(3-4): 237-269 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8
|
Gutscher MA, Spakman W, Bijwaard H and Engdahl ER. 2000. Geodynamics of flat subduction: Seismicity and tomographic constraints from the Andean margin. Tectonics, 19(5): 814-833 DOI:10.1029/1999TC001152
|
Hawkesworth CJ and Kemp AIS. 2006. Evolution of the continental crust. Nature, 443(7113): 811-817 DOI:10.1038/nature05191
|
Hou ZQ, Duan LF, Lu YJ, Zheng YC, Zhu DC, Yang ZM, Yang ZS, Wang BD, Pei YR, Zhao ZD and McCuaig TC. 2015. Lithospheric architecture of the Lhasa Terrane and its control on ore deposits in the Himalayan-Tibetan Orogen. Economic Geology, 110(6): 1541-1575 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.110.6.1541
|
Hu PY, Zhai QG, Wang J, Tang Y, Wang HT and Hou KJ. 2018. Precambrian origin of the North Lhasa Terrane, Tibetan Plateau: Constraint from Early Cryogenian back-arc magmatism. Precambrian Research, 313: 51-67 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2018.05.014
|
Huang JP, Cao SH, Chen ZH and Liao LG. 2006. Geological characteristics and tectonic significance for Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous granite in Middle Gangdise, Tibet. Resources Survey & Environment, 27(4): 277-285 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Huang KX, Zheng YC, Zhang S, Li W, Sun QZ, Li QY, Liang W, Fu Q and Hou ZQ. 2012. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb dating of two types of porphyry in the Yaguila mining area, Tibet. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 31(3): 348-360 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Ji WQ, Wu FY, Liu CZ and Chung SL. 2009. Geochronology and petrogenesis of granitic rocks in Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet. Science in China (Series D), 52(9): 1240-1261 DOI:10.1007/s11430-009-0131-y
|
Jiang X, Zhao ZD, Zhu DC, Zhang FQ, Dong GC, Mo XX and Guo TY. 2010. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic geochemistry of Jiangba, Bangba, and Xiongba granitoids in western Gangdese, Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2155-2164 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Kang ZQ, Xu JF, Dong YH and Wang BD. 2008. Cretaceous volcanic rocks of Zenong Group in north-middle Lhasa block: Products of southward subducting of the Slainajap Ocean?. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(2): 303-314 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Kang ZQ, Xu JF, Wilde SA, Feng ZH, Chen JL, Wang BD, Fu WC and Pan HB. 2014. Geochronology and geochemistry of the Sangri Group volcanic rocks, southern Lhasa Terrane: Implications for the early subduction history of the Neo-Tethys and Gangdese Magmatic Arc. Lithos, 200-201: 157-168 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.04.019
|
Kapp P, Yin A, Harrison TM and Ding L. 2005. Cretaceous-Tertiary shortening, basin development, and volcanism in central Tibet. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 117(7-8): 865-878
|
Kapp P, DeCelles PG, Gehrels GE, Heizler M and Ding L. 2007. Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 119(7-8): 917-933 DOI:10.1130/B26033.1
|
Kemp AIS, Hawkesworth CJ, Foster GL, Paterson BA, Woodhead JD, Hergt JM, Gray CM and Whitehouse MJ. 2007. Magmatic and crustal differentiation history of granitic rocks from Hf-O isotopes in zircon. Science, 315(5814): 980-983 DOI:10.1126/science.1136154
|
Li FQ, Gao M, Tang WQ and Liang T. 2010. U-Pb zircon LA-ICP-MS age of the Yaguila molybdenum-bearing intrusion in Tibet and its geological significance. Geology in China, 37(6): 1566-1574 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li HK, Geng JZ, Hao S, Zhang YQ and Li HM. 2009. Zircon U-Pb isotopic ages determined by Laser-ablated multi-receiver Plasma mass Spectrometry (LA-MC-ICPMS). Acta Mineralogica Sinica, (Suppl.)): 600-601 (in Chinese)
|
Li XH, Li ZX, Li WX, Liu Y, Yuan C, Wei GJ and Qi CS. 2007. U-Pb zircon, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic constraints on age and origin of Jurassic Ⅰ- and A-type granites from central Guangdong, SE China: A major igneous event in response to foundering of a subducted flat-slab?. Lithos, 96(1-2): 186-204 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.09.018
|
Li XY, Ma RZ, Yi LW, He XC, Zhang J and Yue XY. 2013. The determination and petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous post-collision granitoids in Coqen Tibet. Xinjiang Geology, 31(1): 57-64 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li Y, Ding F, Lin JC, Liu SH, Xu ZB, Wei ML, Li Q, Gao JG, Fan YH and Qiu X. 2017. LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb ages and geochemical characteristics of Tajilixialong granodiorite in Nuocang area, Coqen, Xizang (Tibet). Geological Review, 63(2): 484-498 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li YX, Xie YL, Chen W, Tang YW, Li GM, Zhang L, Liu YF and Liu XM. 2011. U-Pb age and geochemical characteristics of zircon in monzogranite porphyry from Qiagong deposit, Tibet, and geological implication. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7): 2023-2033 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Lin YH, Zhang ZM, Dong X, Shen K and Lu X. 2013. Precambrian evolution of the Lhasa Terrane, Tibet: Constraint from the zircon U-Pb geochronology of the gneisses. Precambrian Research, 237: 64-77 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.09.006
|
Liu W, Li FQ, Yuan SH, Zhang WP, Zhou JW, Wang BD and Tang WQ. 2010. Volcanic rock provenance of Zenong Group in Coqen area of Tibet: Geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopic constraint. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 29(4): 367-376 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu W, Li FQ, Yang XY and Yuan SH. 2012. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous rhyolite in Luozha area of Namling County, Tibet. Geology in China, 39(5): 1151-1161 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Lu SW, Ren JD, Bai GD, Yang JF and Lv JG. 2006. Discovery of the Mid-Late Jurassic Songmuguo strongly peraluminous granite belt in the southern part of Nyima County, Tibet, and its significance. Geology in China, 34(2): 332-339 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Lundstrom CC and Glazner AF. 2016. Silicic magmatism and the volcanic-plutonic connection. Elements, 12(2): 91-96 DOI:10.2113/gselements.12.2.91
|
Ma HW. 1992. Discrimination of genetic types of granitoid rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 8(4): 341-350 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Meng FY, Zhao ZD, Zhu DC, Zhang LL, Guan Q, Liu M, Yu F and Mo XX. 2010. Petrogenesis of Late Cretaceous adakite-like rocks in Mamba from the Eastern Gangdese, Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(7): 2180-2192 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Meng FY. 2014. Mesozoic magmatic rocks in Mamba Area, Central Lhasa subterrane: Geochronology, geochemistry, and geodynamic implications. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-163 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Meng FY, Zhao ZD, Zhu DC, Mo XX, Guan Q, Huang Y, Dong GC, Zhou S, Depaolo DJ, Harrison TM, Zhang ZC, Liu JL, Liu YS, Hu ZC and Yuan HL. 2014. Late Cretaceous magmatism in Mamba Area, Central Lhasa subterrane: Products of back-arc extension of Neo-Tethyan Ocean?. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 505-520 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.017
|
Mo XX, Dong GC, Zhao ZD, Zhou S, Wang LL, Qiu RZ and Zhang FQ. 2005. Spatial and temporal distribution and characteristics of granitoids in the Gangdese, Tibet and implication for crustal growth and evolution. Geological Journal of China Universities, 11(3): 281-290 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Mo XX, Hou ZQ, Niu YL, Dong GC, Qu XM, Zhao ZD and Yang ZM. 2007. Mantle contributions to crustal thickening during continental collision: Evidence from Cenozoic igneous rocks in southern Tibet. Lithos, 96(1-2): 225-242 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.10.005
|
Mo XX, Niu YL, Dong GC, Zhao ZD, Hou ZQ, Zhou S and Ke S. 2008. Contribution of syncollisional felsic magmatism to continental crust growth: A case study of the Paleogene Linzizong volcanic succession in southern Tibet. Chemical Geology, 250(1-4): 49-67 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.02.003
|
Monecke T, Kempe U, Monecke J, Sala M and Wolf D. 2002. Tetrad effect in rare earth element distribution patterns: A method of quantification with application to rock and mineral samples from granite-related rare metal deposits. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66(7): 1185-1196 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00849-3
|
Pan GT, Mo XX, Hou ZQ, Zhu DC, Wang LQ, Li GM, Zhao ZD, Geng QR and Liao ZL. 2006. Spatial-temporal framework of the Gangdese Orogenic Belt and its evolution. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 521-533 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Pan GT, Wang LQ, Li RS, Yuan SH, Ji WH, Yin FG, Zhang WP and Wang BD. 2012. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 53: 3-14 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.018
|
Pearce JA. 1983. Role of the sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at active continental margins. In: Hawkesworth CJ and Norry MJ (eds.). Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths. Nantwich: Shiva Publishing, 230-249
|
Pearce JA, Harris NBW and Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983 DOI:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
|
Pitcher WS. 1982. Granite type and tectonic environment. In: Hsü KJ (ed.). Mountain Building Processes. London: Academic Press, 19-40
|
Qu XM, Xin HB, Xu WY, Yang ZS and Li ZQ. 2006. Discovery and significance of copper-bearing bimodal rock series in Coqin area of Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 707-716 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Söderlund U, Patchett PJ, Vervoort JD and Isachsen CE. 2004. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4): 311-324 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3
|
Sun GY, Hu XM, Zhu DC, Hong WT, Wang JG and Wang Q. 2015a. Thickened juvenile lower crust-derived ~90Ma adakitic rocks in the central Lhasa terrane, Tibet. Lithos, 224-225: 225-239 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.03.010
|
Sun GY, Hu XM, Sinclair HD, BouDagher-Fadel MK and Wang JG. 2015b. Late Cretaceous evolution of the Coqen Basin (Lhasa terrane) and implications for early topographic growth on the Tibetan Plateau. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 127: 1001-1020
|
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345
|
Taylor R, Bennett P, Uili R, Joffres M, Germain R, Levy S and Zimmet P. 1985. Diabetes in Wallis Polynesians: A comparison of residents of Wallis Island and first generation migrants to Noumea, New Caledonia. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, 1(3): 169-178 DOI:10.1016/S0168-8227(85)80007-3
|
Wang BD, Guo L, Wang LQ, Li B, Huang HX, Chen FQ, Duan ZM and Zeng QG. 2012. Geochronology and petrogenesis of the ore-bearing pluton in Chagele deposit in middle of the Gangdese Metallogenic Belt. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1647-1662 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang BD, Xu JF, Liu BM, Chen JL, Wang LQ, Guo L, Wang DB and Zhang WP. 2013. Geochronology and ore-forming geological background of ~90Ma porphyry copper deposit in the Lhasa Terrane, Tibet Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(1): 71-80 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang LQ, Tang JX, Deng J, Kang HR, Lin X, Cheng WB, Li Z and Zhang Z. 2015. The Longmala and Mengya'a skarn Pb-Zn deposits, Gangdese Region, Tibet: Evidence from U-Pb and Re-Os geochronology for formation during early India-Asia collision. International Geology Review, 57(14): 1825-1842 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2015.1029540
|
Wang LQ, Xie FW and Wang Y. 2016. U-Pb geochronology and trace element compositions of zircon in biotite granite from the Bagaladong Pb-Zn deposit, Tibet and their geological significance. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 35(6): 650-657 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang LQ, Tang JX, Bagas L, Wang Y, Lin X, Li Z and Li YB. 2017. Early Eocene Longmala skarn Pb-Zn-Cu deposit in Tibet, China: Geochemistry, fluid inclusions, and H-O-S-Pb isotopic compositions. Ore Geology Reviews, 88: 99-115 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.04.026
|
Wang LY, Zheng YY, Gao SB, Li WL and Xue ZL. 2014. The Upper Cretaceous magmatism from Gangzai pluton in Middle-Gangdese, Jiwa, Tibet and its tectonic significance. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 45(8): 2740-2751 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang LY, Zheng YY, Yang B, Gao SB, Xue ZL, Li WL and Huang LL. 2016. Petrogenesis and tectonic setting of Early Cretaceous magmatism in the Jiwa area, Central Lhasa Terrane, Tibet. International Geology Review, 58(11): 1311-1323 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2015.1137083
|
Wang LY, Zheng YY, Gao SB, Li WL, Mao RW and Huang LL. 2016. The discovery of the Early Cretaceous Zenong Group volcanic rocks and geological significance in Jiwa area in south of the Central Lhasa subterrane. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(5): 1543-1555 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang Q, Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Liu SA, Chung SL, Li SM, Liu D, Dai JG, Wang LQ and Mo XX. 2014. Origin of the ca. 90Ma magnesia-rich volcanic rocks in SE Nyima, central Tibet: Products of lithospheric delamination beneath the Lhasa-Qiangtang collision zone. Lithos, 198-199: 24-37 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.019
|
Wang XL. 2017. Some new research progresses and main scientific problems of granitic rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(5): 1445-1458 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Watson EB. 1979. Apatite saturation in basic to intermediate magmas. Geophysical Research Letters, 6(12): 937-940 DOI:10.1029/GL006i012p00937
|
Watson EB and Capobianco CJ. 1981. Phosphorus and the rare earth elements in felsic magmas: An assessment of the role of apatite. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45(12): 2349-2358 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(81)90088-0
|
Whalen JB, Currie KL and Chappell BW. 1987. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419 DOI:10.1007/BF00402202
|
Wu FY, Jahn BM, Wilder SA, Lo CH, Yui TF, Lin Q, Ge WC and Sun DY. 2003. Highly fractionated Ⅰ-type granites in NE China (Ⅰ): Geochronology and petrogenesis. Lithos, 66(3-4): 241-273 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00222-0
|
Wu FY, Li XH, Yang JH and Zheng YF. 2007a. Discussions on the petrogenesis of granites. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(6): 1217-1238 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007b. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wu ZH, Zhao Z, Barosh PJ and Ye PS. 2016. Early Cretaceous tectonics and evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(3): 847-857 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.12728
|
Xie FW. 2019. The Jurassic magmatism and its mineralization potentiality in the southern Lhasa subterrane. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 1-234 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Xu WC, Zhang HF, Harris N, Guo L, Pan FB and Wang S. 2013. Geochronology and geochemistry of Mesoproterozoic granitoids in the Lhasa terrane, South Tibet: Implications for the early evolution of Lhasa terrane. Precambrian Research, 236: 46-58 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2013.07.016
|
Yan JJ, Zhao ZD, Liu D, Wang ZZ and Tang Y. 2017. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Late Jurassic Xuru Tso batholith in central Lhasa Terrane, Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(8): 2437-2453 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yao XF, Tang JX, Li ZJ, Deng SL, Ding S, Hu ZH and Zhang Z. 2012. Magma origin of two plutons from Gaerqiong Copper-gold deposit and it's geological significance, Western Bangonghu-Nujiang Metallogenic Belt, Tibet: Implication from Hf isotope characteristics. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 42(Suppl.2): 188-197 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yin A and Harrison TM. 2000. Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 28(1): 211-280 DOI:10.1146/annurev.earth.28.1.211
|
Yin A. 2006. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the Himalayan orogen as constrained by along-strike variation of structural geometry, exhumation history, and foreland sedimentation. Earth-Science Reviews, 76(1-2): 1-131 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2005.05.004
|
Yu HX, Chen JL, Xu JF, Wang BD, Wu JB and Liang HY. 2011. Geochemistry and origin of Late Cretaceous (~90Ma) ore-bearing porphyry of Balazha in mid-northern Lhasa terrane, Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7): 2011-2022
|
Yu YS, Gao Y, Yang ZS, Tian SH, Liu YC, Cao SH, Hu WZ and Qie HM. 2011. Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating and geochemistry of intrusive rocks from Gunjiu iron deposit in the Nixiong ore field, Coqen, Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7): 1949-1960 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhai MG. 2017. Granites: Leading study issue for continental evolution. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(5): 1369-1380
|
Zhang LL, Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Liao ZL, Wang LQ and Mo XX. 2011. Early Cretaceous granitoids in Xainza, Tibet: Evidence of slab break-off. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(7): 1938-1948 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang XQ, Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Wang LQ, Huang JC and Mo XX. 2010. Petrogenesis of the Nixiong pluton in Coqen, Tibet and its potential significance for the Nixiong Fe-rich mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1793-1804 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang XQ, Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Sui QL, Wang Q, Yuan SH, Hu ZC and Mo XX. 2012. Geochemistry, zircon U-Pb geochronology and in-situ Hf isotope of the Maiga batholith in Coqen, Tibet: Constraints on the petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous granitoids in the Central Lhasa Terrane. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(5): 1615-1634 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang YJ, Liu W, Zhu TX, An XY and Liao ZL. 2014. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemistry of Early Cretaceous intrusive rocks in Maiba area of Xainza County, Tibet. Geology in China, 41(1): 50-60 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang YZ, Wang XL, Li JY, He ZY, Zhang FF, Chen X, Wang S, Du DH, Huang Y and Jiang CH. 2021. Oligocene leucogranites of the Gangdese batholith, southern Tibet: Fractional crystallization of felsic melts from juvenile lower crust. Journal of Petrology, 62(11): 1-29
|
Zhang Z, Yao XF, Tang JX, Li ZJ, Wang LQ, Yang Y, Duan JL, Song JL and Lin X. 2015. Lithogeochemical, Re-Os and U-Pb geochronological, Hf-Lu and S-Pb isotope data of the Ga'erqiong-Galale Cu-Au ore-concentrated area: Evidence for the Late Cretaceous magmatism and metallogenic event in the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone, Northwestern Tibet, China. Resource Geology, 65(2): 76-102 DOI:10.1111/rge.12064
|
Zhang Z, Chen YC, Tang JX, Li Z, Song JL, Yang Y, Hu ZH, Yang HH, Yang C and Kang HR. 2015. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemical characteristics of volcanic rocks in Gaerqiong-Galale Cu-Au ore district, Tibet. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 40(1): 77-97 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.3799/dqkx.2015.006
|
Zhang ZM and Santosh M. 2012. Tectonic evolution of Tibet and surrounding regions. Gondwana Research, 21(1): 1-3 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.08.007
|
Zhang ZM, Ding L, Zhao ZD and Santosh M. 2017. Tectonic evolution and dynamics of the Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Research, 41: 1-8 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.09.001
|
Zhang ZM, Ding HX, Dong X and Tian ZL. 2019. Formation and evolution of the Gangdese magmatic arc, southern Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(2): 275-294 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.02.01
|
Zhao JX, Qin KZ, Li GM, Cao MJ, Evans NJ, McInnes BIA, Li JX, Xiao B and Chen L. 2015. The exhumation history of collision-related mineralizing systems in Tibet: Insights from thermal studies of the Sharang and Yaguila deposits, Central Lhasa. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 1043-1061 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.09.026
|
Zhao JX, Li GM, Evans NJ, Qin KZ, Li JX and Zhang XN. 2016. Petrogenesis of Paleocene-Eocene porphyry deposit-related granitic rocks in the Yaguila-Sharang Ore District, Central Lhasa Terrane, Tibet. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 129: 38-53 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.08.004
|
Zhao ZD, Mo XX, Dilek Y, Niu YL, Depaolo DJ, Robinson P, Zhu DC, Sun CG, Dong GC and Zhou S. 2009. Geochemical and Sr-Nd-Pb-O isotopic compositions of the post-collisional ultrapotassic magmatism in SW Tibet: Petrogenesis and implications for India intra-continental subduction beneath southern Tibet. Lithos, 113(1-2): 190-212 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.02.004
|
Zheng YY, Sun X, Gao SB, Wu S, Xu J, Jiang JS, Chen X, Zhao ZY and Liu Y. 2015. Metallogenesis and the minerogenetic series in the Gangdese polymetallic copper belt. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 103: 23-39 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.11.036
|
Zhou CY, Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Xu JF, Wang LQ, Chen HH, Xie LW, Dong GC and Zhou S. 2008. Petrogenesis of Daxiong pluton in Western Gangdese, Tibet: Zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(2): 348-358 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhou H, Qiu JS, Yu SB and Wang RQ. 2016. Geochronology and geochemistry of volcanic rocks from Coqen district of Tibet and their implications for petrogenesis. Acta Geologica Sinica, 90(11): 3173-3191 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhu DC, Pan GT, Mo XX, Wang LQ, Liao ZL, Zhao ZD, Dong GC and Zhou CY. 2006. Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous geodynamic setting in middle-northern Gangdese: New insights from volcanic rocks. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(3): 534-546 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhu DC, Pan GT, Chung SL, Liao ZL, Wang LQ and Li GM. 2008. SHRIMP Zircon age and geochemical constraints on the origin of Lower Jurassic volcanic rocks from the Yeba Formation, southern Gangdese, South Tibet. International Geology Review, 50(5): 442-471 DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.50.5.442
|
Zhu DC, Pan GT, Wang LQ, Mo XX, Zhao ZD, Zhou CY, Liao ZL, Dong GC and Yuan SH. 2008a. Tempo-spatial variations of Mesozoic magmatic rocks in the Gangdise belt, Tibet, China, with a discussion of geodynamic setting-related issues. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(9): 1535-1550 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhu DC, Mo XX, Zhao ZD, Xu JF, Zhou CY, Sun CG, Wang LQ, Chen HH, Dong GC and Zhou S. 2008b. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of Zenong Group volcanic rocks in Coqen area of the Gangdese, Tibet and tectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(3): 401-412 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Pan GT, Lee HY, Kang ZQ, Liao ZL, Wang LQ, Li GM, Dong GC and Liu B. 2009a. Early Cretaceous subduction-related adakite-like rocks of the Gangdese belt, southern Tibet: Products of slab melting and subsequent melt-peridotite interaction?. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 34(3): 298-309 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2008.05.003
|
Zhu DC, Mo XX, Niu YL, Zhao ZD, Wang LQ, Liu YS and Wu FY. 2009b. Geochemical investigation of Early Cretaceous igneous rocks along an east-west traverse throughout the central Lhasa Terrane, Tibet. Chemical Geology, 268(3-4): 298-312 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.09.008
|
Zhu DC, Mo XX, Wang LQ, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Zhou CY and Yang YH. 2009c. Petrogenesis of highly fractionated Ⅰ-type granites in the Zayu area of eastern Gangdese, Tibet: Constraints from zircon U-Pb geochronology, geochemistry and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes. Science in China (Series D), 52(9): 1223-1239 DOI:10.1007/s11430-009-0132-x
|
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Mo XX, Chung SL, Hou ZQ, Wang LQ and Wu FY. 2011a. The Lhasa Terrane: Record of a microcontinent and its histories of drift and growth. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 301(1-2): 241-255 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2010.11.005
|
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Dilek Y and Mo XX. 2011b. Lhasa Terrane in southern Tibet came from Australia. Geology, 39(8): 727-730 DOI:10.1130/G31895.1
|
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Dilek Y, Wang Q, Ji WH, Dong GC, Sui QL, Liu YS, Yuan HL and Mo XX. 2012. Cambrian bimodal volcanism in the Lhasa Terrane, southern Tibet: Record of an Early Paleozoic Andean-type magmatic arc in the Australian proto-Tethyan margin. Chemical Geology, 328: 290-308 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.12.024
|
Zhu DC, Li SM, Cawood PA, Wang Q, Zhao ZD, Liu SA and Wang LQ. 2016. Assembly of the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in central Tibet by divergent double subduction. Lithos, 245: 7-17 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.06.023
|
Zurevinski S, Hollings P, Zhou TF and Wang SW. 2017. Exploring the links between granitic magmas and mineralization: Key concepts and critical features. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(5): 1541-1553 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zurevinski S, Hollings P, 周涛发, 王世伟. 2017. 花岗质岩浆和矿化之间的关系: 重要概念和关键特征. 岩石学报, 33(5): 1541-1553. |
陈国能, 王勇, 陈震, 彭卓伦. 2017. 花岗岩浆形成定位机制的思考与研究进展. 岩石学报, 33(5): 1489-1497. |
崔浩杰, 苟正彬, 刘函, 李俊, 杨洋. 2019. 拉萨地块西段尼雄地区早白垩世晚期花岗闪长岩的成因及构造意义. 沉积与特提斯地质, 39(1): 1-13. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1009-3850.2019.01.001 |
崔晓亮, 唐菊兴, 多吉, 钟康惠, 高一鸣, 刘鸿飞, 张金树, 王成辉, 刘婷婷. 2011. 西藏洞中拉铅锌矿床石英斑岩锆石U-Pb年代学研究. 成都理工大学学报(自然科学版), 38(5): 557-562. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-9727.2011.05.012 |
杜德道, 曲晓明, 王根厚, 辛洪波, 刘治博. 2011. 西藏班公湖-怒江缝合带西段中特提斯洋盆的双向俯冲: 来自岛弧型花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和元素地球化学的证据. 岩石学报, 27(7): 1993-2002. |
范淑芳, 曲晓明, 宋扬, 辛洪波. 2015. 西藏尼雄铁矿成矿花岗岩成因及其对成矿构造背景的启示. 大地构造与成矿学, 39(2): 286-299. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2015.02.009 |
费光春, 温春齐, 王成松, 周雄, 吴鹏宇, 温泉, 周玉. 2010a. 西藏墨竹工卡县洞中拉铅锌矿床花岗斑岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年. 中国地质, 37(2): 470-476. |
费光春, 温春齐, 王成松, 吴鹏宇, 温泉, 周雄. 2010b. 西藏冈底斯东段墨竹工卡地区洞中拉辉绿玢岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb定年及意义. 地质通报, 29(8): 1138-1142. |
高家昊, 曾令森, 高利娥, 侯可军, 郭春丽. 2016. 西藏拉萨地体西北部革吉地区两期早白垩世岩浆作用——锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素和地球化学特征. 地质通报, 35(1): 55-70. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.01.006 |
高永丰, 侯增谦, 魏瑞华. 2003. 冈底斯晚第三纪斑岩的岩石学、地球化学及其地球动力学意义. 岩石学报, 19(3): 418-428. |
高一鸣, 陈毓川, 唐菊兴, 杜欣, 李新法, 高明, 蔡志超. 2009. 西藏工布江达县亚贵拉铅锌钼多金属矿床石英斑岩锆石SHRIMP定年及其地质意义. 地质学报, 83(10): 1436-1444. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.10.008 |
耿建珍, 李怀坤, 张健, 周红英, 李惠民. 2011. 锆石Hf同位素组成的LA-MC-ICP-MS测定. 地质通报, 30(10): 1508-1513. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.10.004 |
黄俊平, 曹圣华, 陈振华, 廖六根. 2006. 西藏冈底斯中段晚侏罗-早白垩世花岗岩特征. 资源调查与环境, 27(4): 277-285. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-4814.2006.04.005 |
黄克贤, 郑远川, 张松, 李为, 孙清钟, 李秋耘, 梁维, 付强, 侯增谦. 2012. 西藏亚贵拉矿区两期岩体LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 31(3): 348-360. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2012.03.005 |
姜昕, 赵志丹, 朱弟成, 张凤琴, 董国臣, 莫宣学, 郭铁鹰. 2010. 西藏冈底斯西部江巴、邦巴和雄巴岩体的锆石U-Pb年代学与Hf同位素地球化学. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2155-2164. |
康志强, 许继峰, 董彦辉, 王保弟. 2008. 拉萨地块中北部白垩纪则弄群火山岩: Slainajap洋南向俯冲的产物?. 岩石学报, 24(2): 303-314. |
李怀坤, 耿建珍, 郝爽, 张永清, 李惠民. 2009. 用激光烧蚀多接收器等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定锆石U-Pb同位素年龄的研究. 矿物学报, (增): 600-601. |
李奋其, 高明, 唐文清, 梁婷. 2010. 西藏亚贵拉含钼岩体锆石LA-ICP-MS年龄和地质意义. 中国地质, 37(6): 1566-1574. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.06.003 |
李湘玉, 马润则, 易立文, 何显川, 张巨, 岳相元. 2013. 西藏措勤早白垩世后碰撞花岗岩厘定及岩石成因. 新疆地质, 31(1): 57-64. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-8845.2013.01.014 |
李跃, 丁枫, 蔺吉春, 刘寿航, 徐忠彪, 魏美丽, 李青, 高建国, 范宇航, 邱雄. 2017. 西藏措勤县诺仓地区塔吉里霞隆花岗闪长岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学特征. 地质论评, 63(2): 484-498. |
李应栩, 谢玉玲, 陈伟, 唐燕文, 李光明, 张丽, 刘云飞, 柳小明. 2011. 西藏恰功铁矿二长花岗斑岩锆石的U-Pb年代学与地球化学特征及意义. 岩石学报, 27(7): 2023-2033. |
刘伟, 李奋其, 袁四化, 张万平, 卓皆文, 王保弟, 唐文清. 2010. 西藏措勤地区则弄群火山岩源区——地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素制约. 岩石矿物学杂志, 29(4): 367-376. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2010.04.003 |
刘伟, 李奋其, 杨晓勇, 袁四化. 2012. 西藏南木林县罗扎地区早白垩世流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学特征. 中国地质, 39(5): 1151-1161. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.05.004 |
卢书炜, 任建德, 白国典, 杨俊峰, 吕际根. 2006. 西藏尼玛县南部中晚侏罗世松木果强过铝质花岗岩带的发现及其意义. 中国地质, 34(2): 332-339. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2006.02.012 |
马鸿文. 1992. 花岗岩成因类型的判别分析. 岩石学报, 8(4): 341-350. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1992.04.005 |
孟繁一, 赵志丹, 朱弟成, 张亮亮, 管琪, 刘敏, 于枫, 莫宣学. 2010. 西藏冈底斯东部门巴地区晚白垩世埃达克质岩的岩石成因. 岩石学报, 26(7): 2180-2192. |
孟繁一. 2014. 西藏中部拉萨地块门巴地区中生代岩浆岩年代学、地球化学及动力学意义. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学, 1-163
|
潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 侯增谦, 朱弟成, 王立全, 李光明, 赵志丹, 耿全如, 廖忠礼. 2006. 冈底斯造山带的时空结构及演化. 岩石学报, 22(3): 521-533. |
曲晓明, 辛洪波, 徐文艺, 杨竹森, 李振清. 2006. 藏西措勤含铜双峰岩系的发现及其意义. 岩石学报, 22(3): 707-716. |
王保弟, 郭琳, 王立全, 李冰, 黄瀚霄, 陈富琦, 段志明, 曾庆高. 2012. 中冈底斯成矿带查个勒矿床含矿岩体的年代学及成因. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1647-1662. |
王保弟, 许继峰, 刘保民, 陈建林, 王立全, 郭琳, 王冬兵, 张万平. 2013. 拉萨地块北部~90Ma斑岩型矿床年代学及成矿地质背景. 地质学报, 87(1): 71-80. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2013.01.007 |
王立强, 谢富伟, 王勇. 2016. 西藏巴嘎拉东铅锌矿床黑云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄、微量元素组成及地质意义. 岩矿测试, 35(6): 650-657. |
王力圆, 郑有业, 高顺宝, 李伟良, 薛兆龙. 2014. 西藏吉瓦地区中冈底斯带岗在岩体晚白垩世的岩浆作用及构造意义. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 45(8): 2740-2751. |
王力圆, 郑有业, 高顺宝, 李伟良, 毛荣威, 黄亮亮. 2016. 中部拉萨地体南侧吉瓦地区早白垩世则弄群火山岩的发现及意义. 岩石学报, 32(5): 1543-1555. |
王孝磊. 2017. 花岗岩研究的若干新进展与主要科学问题. 岩石学报, 33(5): 1445-1458. |
吴福元, 李献华, 杨进辉, 郑永飞. 2007a. 花岗岩成因研究的若干问题. 岩石学报, 23(6): 1217-1238. |
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007b. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. |
谢富伟. 2019. 拉萨地块南缘侏罗纪岩浆作用及其含矿性研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质科学院, 1-234
|
闫晶晶, 赵志丹, 刘栋, 王珍珍, 唐演. 2017. 西藏中拉萨地块晚侏罗世许如错花岗岩地球化学与岩石成因. 岩石学报, 33(8): 2437-2453. |
姚晓峰, 唐菊兴, 李志军, 邓世林, 丁帅, 胡正华, 张志. 2012. 班怒带西段尕尔穷铜金矿两套侵入岩源区及其地质意义——来自Hf同位素特征的指示. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 42(增2): 188-197. |
余红霞, 陈建林, 许继峰, 王保弟, 邬建斌, 梁华英. 2011. 拉萨地块中北部晚白垩世(约90Ma)拔拉扎含矿斑岩地球化学特征及其成因. 岩石学报, 27(7): 2011-2022. |
于玉帅, 高原, 杨竹森, 田世洪, 刘英超, 曹圣华, 胡为正, 郄海满. 2011. 西藏措勤尼雄矿田滚纠铁矿侵入岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄与地球化学特征. 岩石学报, 27(7): 1949-1960. |
翟明国. 2017. 花岗岩: 大陆地质研究的突破口以及若干关键科学问题——"岩石学报"花岗岩专辑代序. 岩石学报, 33(5): 1369-1380. |
张亮亮, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 廖忠礼, 王立全, 莫宣学. 2011. 西藏申扎早白垩世花岗岩类: 板片断离的证据. 岩石学报, 27(7): 1938-1948. |
张晓倩, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 王立全, 黄建村, 莫宣学. 2010. 西藏措勤尼雄岩体的岩石成因及其对富Fe成矿作用的潜在意义. 岩石学报, 26(6): 1793-1804. |
张晓倩, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 隋清霖, 王青, 袁四化, 胡兆初, 莫宣学. 2012. 西藏措勤麦嘎岩基的锆石U-Pb年代学、地球化学和锆石Hf同位素: 对中部拉萨地块早白垩世花岗岩类岩石成因的约束. 岩石学报, 28(5): 1615-1634. |
张予杰, 刘伟, 朱同兴, 安显银, 廖忠礼. 2014. 西藏申扎县买巴地区早白垩世侵入岩锆石U-Pb年龄及地球化学. 中国地质, 41(1): 50-60. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2014.01.004 |
张志, 陈毓川, 唐菊兴, 李壮, 宋俊龙, 杨毅, 胡正华, 杨欢欢, 杨超, 康浩然. 2015. 西藏尕尔穷-嘎拉勒铜金矿集区火山岩年代学及地球化学. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 40(1): 77-97. |
张泽明, 丁慧霞, 董昕, 田作林. 2019. 冈底斯岩浆弧的形成与演化. 岩石学报, 35(2): 275-294. |
周长勇, 朱弟成, 赵志丹, 许继峰, 王立全, 陈海红, 谢烈文, 董国臣, 周肃. 2008. 西藏冈底斯带西部达雄岩体的岩石成因: 锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素约束. 岩石学报, 24(2): 348-358. |
周华, 邱检生, 喻思斌, 王睿强. 2016. 西藏措勤地区火山岩的年代学与地球化学及其对岩石成因的制约. 地质学报, 90(11): 3173-3191. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.11.013 |
朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 莫宣学, 王立全, 廖忠礼, 赵志丹, 董国臣, 周长勇. 2006. 冈底斯中北部晚侏罗世-早白垩世地球动力学环境: 火山岩约束. 岩石学报, 23(3): 534-546. |
朱弟成, 潘桂棠, 王立全, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 周长勇, 廖忠礼, 董国臣, 袁四化. 2008a. 西藏冈底斯带中生代岩浆岩的时空分布和相关问题的讨论. 地质通报, 27(9): 1535-1550. |
朱弟成, 莫宣学, 赵志丹, 许继峰, 周长勇, 孙晨光, 王立全, 陈海红, 董国臣, 周肃. 2008b. 西藏冈底斯带措勤地区则弄群火山岩锆石U-Pb年代学格架及构造意义. 岩石学报, 24(3): 401-412. |
 2022, Vol. 38
2022, Vol. 38