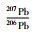2. 中国地质大学地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室,北京 100083;
3. 盛屯矿业集团股份有限公司,厦门 361012
2. State Key Laboratory of Geological Processes and Mineral Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China;
3. Shengtun Mining Group Co. Ltd, Xiamen 361012, China
峨眉山大火成岩省产出一大批成岩成矿一体的镁铁-超镁铁质岩体及黑色和稀有金属矿床(胡瑞忠等, 2005; Zhou et al., 2008),如攀西(攀枝花-西昌)地区的钒钛磁铁矿床和铜镍硫化物及铂族元素矿床,前者钒、钛储量占到世界的一半左右(宋谢炎等, 2018)。此外,区带上产出众多同时代不成矿的镁铁-超镁铁质岩体,范围遍布扬子克拉通西缘的攀西到松潘-甘孜地区(王登红等, 2007),其中在攀西地区研究相对较多(赵正等, 2012; 刘军平等, 2020),在松潘-甘孜地区报道较少。上述不成矿岩体同为峨眉山玄武质岩浆结晶分异作用的产物(张招崇等, 2001; 徐义刚和钟孙霖, 2001; Xu et al., 2003, 2008)。显然,具有相似岩浆演化过程和紧密时空联系的(超)基性岩体成矿差异性是有关该区域黑色和稀有金属矿床找矿勘查的重要科学问题。
氧逸度通过控制岩浆熔体中的变价元素,尤其是铁的氧化还原态来改变矿物结晶顺序和成分(Lee and Tang, 2020)。高岩浆氧逸度可以促使Fe-Ti氧化物较早结晶,可能在攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿形成过程中发挥关键作用(Ganino et al., 2008; Bai et al., 2019)。罗雕等(2020)报道了攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿岩体苦橄岩和浅色辉长岩的锆石微量数据,认为其估算的较高氧逸度源自扬子克拉通西缘不均一的高氧化态地幔源区。此外,分离结晶作用对钒钛磁铁矿成矿有重要影响(宋谢炎等, 2005; 汤庆艳等, 2013)。Fe-Ti氧化物通常与橄榄石和辉石同时结晶(Howarth and Prevec, 2013; Bai et al., 2019),因此高结晶分异程度往往伴随更彻底的Fe-Ti氧化物沉淀。综上所述,分离结晶作用和高氧逸度是钒钛磁铁矿形成的重要条件,但根据鲍文演化序列二者为相互促进关系(Charlier et al., 2015),哪种因素起主导作用尚不明确。
扬子西缘丹巴地区散布暂无经济价值的(超)基性岩体,其中基性岩墙群时代多为新元古代(Lin et al., 2007)。本文选取尚无精确年龄限定的水子乡辉石岩为研究对象,其锆石U-Pb定年结果为~260Ma。该岩体与攀枝花地区~260Ma钒钛磁铁矿岩体同为扬子克拉通西缘峨眉山大火成岩省的产物,均发育粗晶辉石岩-粗晶辉长岩-细粒辉长岩相变(胡世华等, 2000①; Zhang et al., 2009; Bai et al., 2012),可分别作为不成矿和成矿岩体代表。本文运用锆石微量元素估算二者岩浆氧逸度,并探讨二者结晶分异程度与成矿关系。
① 胡世华, 李云泉, 曾宜君, 杨学俊, 刘开榜, 刘建清, 李开元. 2000. 1/5万丹巴幅区域地质调查报告. 四川省地质矿产勘查开发局
1 地质背景 1.1 峨眉山大火成岩省峨眉山大火成岩省位于扬子克拉通西缘(图 1a),主要由大规模的大陆溢流玄武岩和少量(超)基性岩侵入体以及同源的正长岩、花岗岩组成(Shellnutt and Zhou, 2007; Zhong et al., 2007)。溢流玄武岩是峨眉山大火成岩省喷出岩的主体,可分为高钛和低钛系列(张招崇等, 2001; 徐义刚等, 2007)。(超)基性岩侵入体主要分布在大火成岩省南部攀西地区(图 1a),除超大型攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿岩体群外,也零星分布中、小型成矿岩体(叶小春等, 2019),其余多为不成矿岩体(刘军平等, 2020)。(超)基性岩侵入体在大火成岩省北端松潘-甘孜地区分布较少(图 1a),除形成大型杨柳坪铜镍硫化物及铂族元素矿床的岩体外,丹巴水子乡辉石岩体为规模较大的不成矿岩体(胡世华等, 2000)。正长岩和花岗岩主要分布在攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿岩体群范围内(钟宏等, 2008)。
|
图 1 丹巴水子乡辉石岩地质背景及区域地质图 (a)峨眉山大火成岩省地质图(据Xu et al., 2007, 除本文外的成岩成矿年龄据Zhang et al., 2009及其中文献);ANHF-安宁河断裂;MPSF-磨盘山断裂;PZHF-攀枝花断裂;XSHF-鲜水河断裂;(b)丹巴水子乡辉石岩地质图(据胡世华等, 2000) Fig. 1 Geological background and regional geological map of the Shuizi pyroxenite at Danba (a) geological map of the Emeishan Large Igneous Province (modified after Xu et al., 2007). The ages from Zhang et al. (2009) and references therein. ANHF-Anninghe Fault; MPSF-Mopanshan Fault; PZHF-Panzhihua Fault; XSHF-Xianshuihe Fault. (b) geological map of the Danba area containing the Shuizi pyroxenite |
扬子克拉通西缘出现新元古代岛弧特征的侵入岩-变质岩组合,被认为与860~750Ma期间大洋岩石圈俯冲到扬子板块之下有关(Zhou et al., 2002; Zhao and Zhou, 2008)。这套弧岩浆组合及其变质形成的花岗质片麻岩、混合岩以及残留的元古代沉积变质岩构成了扬子西缘基底的主体(图 1a)。基底之上为不整合覆盖的古生代地层(Roger et al., 2010),其中二叠系地层岩石主要为碳酸盐岩和峨眉山玄武岩。古生代地层之上不整合覆盖以三叠系复理石建造为主的中、新生代地层(Yan et al., 2003)。
扬子克拉通西缘沿龙门山-锦屏山逆冲推覆带发育>1000km的晚古生代-中生代穹窿带(He et al., 2003; Zhao et al., 2019)。南部攀西地区的南北向岩石圈规模断裂控制(超)基性岩体产出,如攀枝花岩体群的产出范围限定在安宁河断裂、磨盘山断裂和攀枝花断裂之间(图 1a);北端松潘-甘孜地区(超)基性岩体产出于鲜水河断裂的次级断裂带(图 1a)。
攀枝花岩体群为成矿的镁铁质-超镁铁质层状岩体(邓军等, 2014; Bai et al., 2019),如攀枝花、红格、新街、白马和太和等岩体赋存钒钛磁铁矿矿床;力马河等岩体赋存铜镍硫化物及铂族元素矿床(图 1a)。不管赋存何种类型矿床,这些岩体的成岩成矿年龄均集中在~260Ma(Zhang et al., 2009)。其中攀枝花、白马和太和岩体为辉长岩相控矿,红格和新街岩体为辉石岩相控矿(Bai et al., 2012; Hou et al., 2013)。
1.2 攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿岩体攀枝花层状岩体侵位于新元古代灯影组白云质灰岩/大理岩中,赋存的钒钛磁铁矿床矿石储量为1.333Mt,平均品位为TFe=33%、TiO2=12%、V2O5=0.3%(马玉孝等, 2003)。攀枝花岩体自下而上分为:含辉石橄榄石边缘相带、含大量钒钛磁铁矿矿层的辉长岩相带、含少量钒钛磁铁矿矿层的辉长岩相带、浅色辉长岩相带(Zhang et al., 2009)。苦橄岩产出于边缘相带,其全岩Ti含量为0.7×10-6~1.4×10-6,锆石U-Pb年龄为261.4±4.6Ma(Hou et al., 2013)。浅色辉长岩含大量粗粒斜长石,锆石U-Pb年龄为259.8±0.8Ma(Hou et al., 2012)。岩体上部出露晚期分异形成的斜长岩(Hou et al., 2012)。此外,攀枝花地区二滩和龙帚山玄武岩全岩Ti含量分别为~2.8×10-6和~3.5×10-6(Bai et al., 2014)。
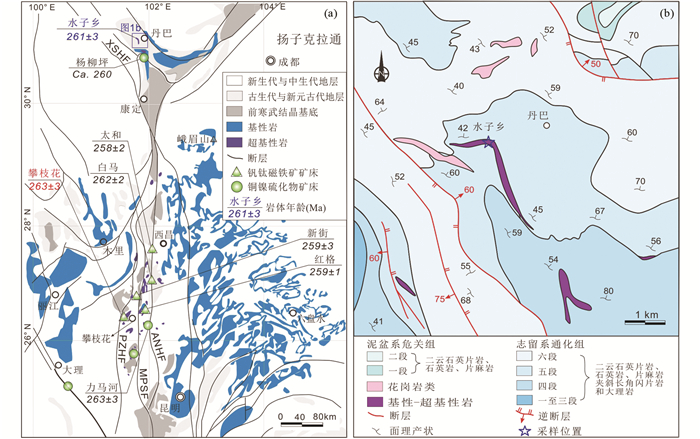
2 水子乡辉石岩岩体水子乡辉石岩岩体位于丹巴县城南西(图 1b),侵位于志留系通化组角闪岩相变质地层,围岩为二云石英片岩和石英岩等(图 2a)。岩体有弱的相变分带,由巨晶辉石岩-粗晶辉石辉长岩-中粒辉长岩组成,其主体为粗晶辉石岩(胡世华等, 2000)。粗晶辉石岩为深灰色到墨绿色(图 2b),略具堆晶特征(图 2c),主要矿物为单斜辉石(普通辉石),受风化蚀变影响,其部分晶体边缘或全部转变为角闪石和黑云母(图 2d)。水子乡辉石岩体南南西约15km为杨柳坪超基性岩体,产出铜镍硫化物铂族元素矿床(王登红等, 2007);岩体以东区域上的二叠系大石包(变)玄武岩全岩Ti含量为1.4×10-6~3.2×10-6(平均2.2×10-6;胡世华等, 2000)。
|
图 2 丹巴水子乡辉石岩野外及镜下照片 (a)辉石岩侵入志留系变质岩;(b)辉石岩手标本照片;(c)略具堆晶特征的粗粒辉石岩;(d)辉石多蚀变为角闪石及黑云母 Fig. 2 Field, hand specimen and microscopic photos of the Shuizi pyroxenite in the Danba area (a) the pyroxenite emplaced into the high-grade metamorphic Silurian rocks; (b) hand specimen photograph of the pyroxenite; (c) the coarse-grained pyroxenite with mild cumulate structures; (d) clinopyroxene (Cpx) replaced by amphibole (Amp) and biotite (Bt) |
本次研究使用的单颗粒锆石样品挑选自丹巴水子乡粗晶单斜辉石岩(图 2b),其与对比对象攀枝花岩体苦橄岩和浅色辉长岩的特征见表 1。锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及微量元素分析在北京中国地质科学院地质研究所完成,使用的仪器为Agilent 7900 ICP-MS及配套的NWR 193UC激光剥蚀系统,束斑直径为25μm,剥蚀速率为5Hz,激光能量为2J/cm2。锆石91500和NIST610作为标样,锆石GJ-1和Plešovice用于数据质量评估。数据处理使用Iolite软件(Paton et al., 2010),206Pb/238U加权平均年龄计算使用Isoplot 3.0(Ludwig, 2003)。
|
|
表 1 丹巴水子乡辉石岩与攀枝花岩体(超)基性岩特征对比表 Table 1 Characteristics of the Shuizi pyroxenite in the Danba area and mafic-ultramafic rocks from the Panzhihua intrusion |
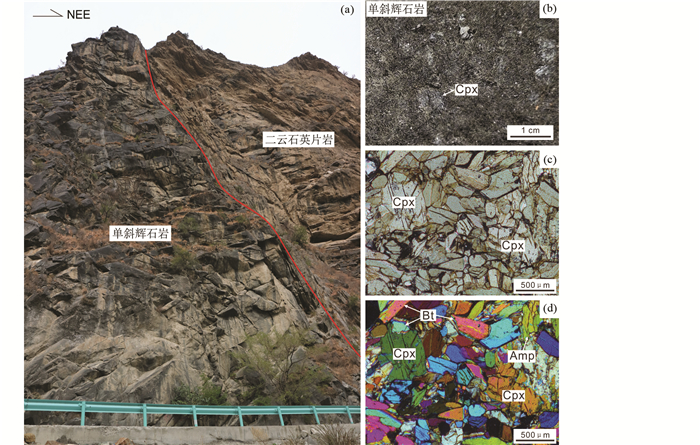
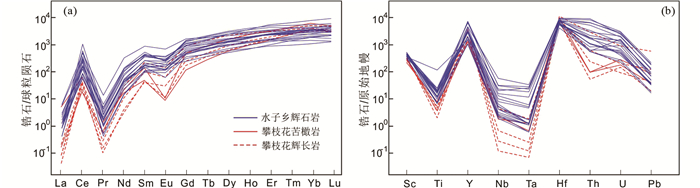
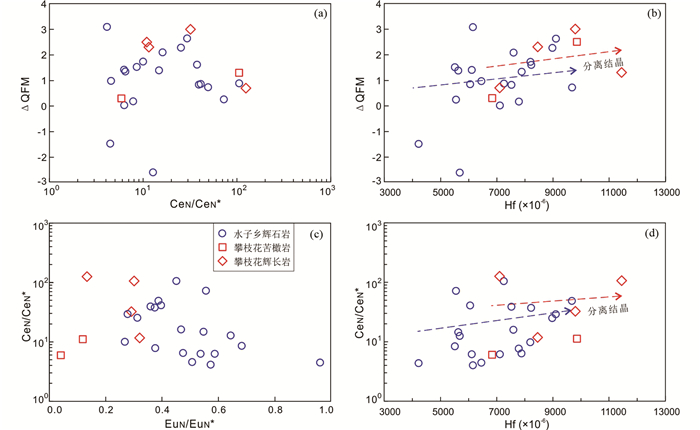
水子乡辉石岩锆石U-Pb定年结果见表 2。206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为260.7±3.3Ma(MSWD=0.16,N=20;图 3a)。水子乡辉石岩锆石微量元素测试结果见表 3,其稀土元素含量在1000×10-6~4000×10-6之间,稀土元素配分形式与攀枝花苦橄岩和浅色辉长岩锆石大体一致(图 4a)。相比之下,水子乡辉石岩锆石轻稀土含量稍高,重稀土部分更为平坦,Eu负异常更不明显(图 4a);攀枝花苦橄岩和浅色辉长岩锆石Ti、Nb和Ta含量明显偏低(图 4b)。水子乡辉石岩锆石Hf含量为4200×10-6~9700×10-6,比攀枝花苦橄岩和浅色辉长岩锆石6800×10-6~11500×10-6低(图 5、图 6)。水子乡辉石岩锆石微量元素估算的代表岩浆氧逸度的ΔQFM值(logfO2(sample)-logfO2(FMQ),样品氧逸度相对于铁橄榄石-磁铁矿-石英缓冲剂的值;Loucks et al., 2020)主要在0~3.1范围内(平均~1.0;图 5a, b),Ce异常(CeN/CeN*=CeN·SmN/NdN2;Loader et al., 2017)为4~125(平均30;图 5c, d)。
|
|
表 2 丹巴水子乡辉石岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb数据 Table 2 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb data of the Shuizi pyroxenite in the Danba area |
|
图 3 丹巴水子乡辉石岩锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb协和图(a)及阴极发光照片(b) Fig. 3 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb concordia diagram (a) and cathodoluminesence (CL) images (b) of the Shuizi pyroxenite in the Danba area |
|
|
表 3 丹巴水子乡辉石岩锆石微量元素含量(×10-6)、Th/U比值及氧逸度估算值 Table 3 Trace elements (×10-6), Th/U ratios, and estimated oxygen fugacity values of zircon from the Shuizi pyroxenite in the Danba area |
|
图 4 丹巴水子乡辉石岩及攀枝花岩体锆石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分形式(a, 标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989)和原始地幔值标准化微量元素蛛网图(b, 标准化值据McDonough and Sun, 1995) Fig. 4 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) and primitive mantle-normalized trace element diagram (b, normalization values after McDonough and Sun, 1995) for zircons from the Shuizi pyroxenite in the Danba area and those from the Panzhihua intrusion |
|
图 5 丹巴水子乡辉石岩及攀枝花岩体锆石微量元素估算岩浆氧逸度及其与锆石Hf含量关系图 Fig. 5 Estimation of the oxygen fugacity of the Shuizi pyroxenite in the Danba area and those from the Panzhihua intrusion based on zircon trace element contents and their evolution trends relative to Hf contents |
|
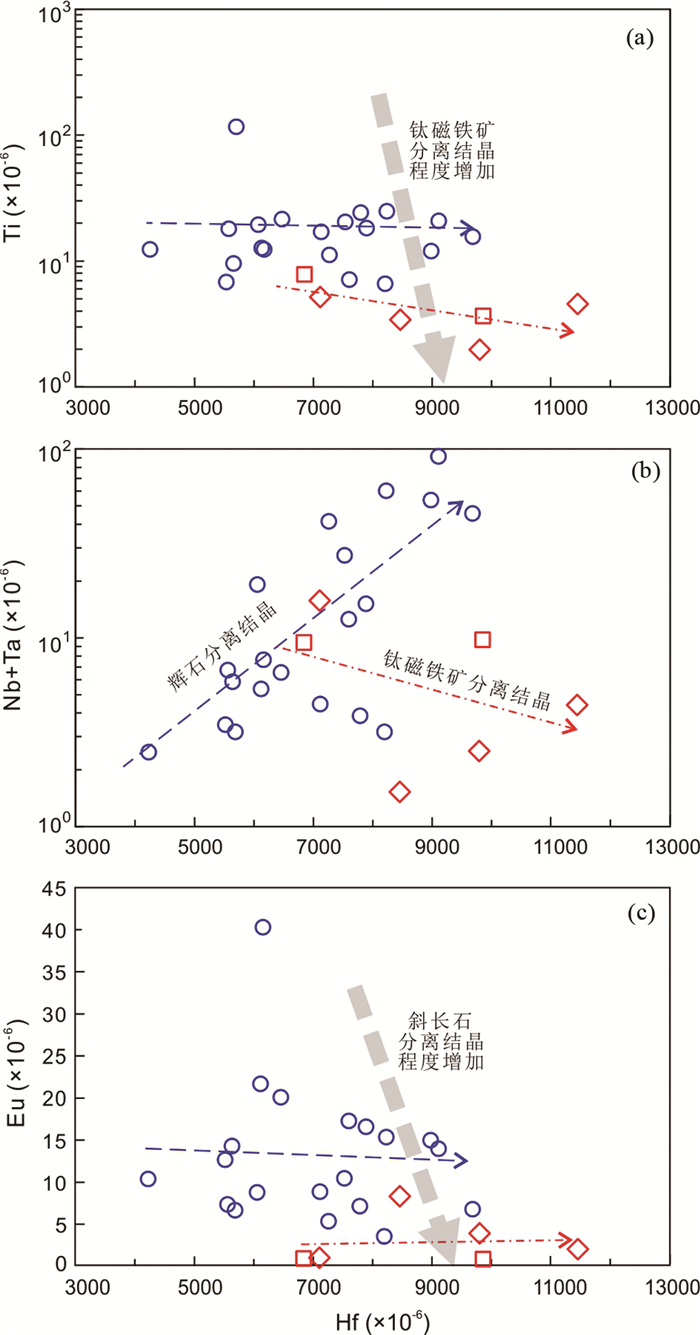
图 6 丹巴水子乡辉石岩及攀枝花岩体分离结晶程度差异 Fig. 6 Difference of fractional crystallization degrees for the Shuizi pyroxenite in the Danba area and those for the Panzhihua intrusion |
尽管丹巴水子乡辉石岩体早已发现,但尚无年龄报道(胡世华等, 2000)。本次锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb测年结果为260.7±3.3Ma(图 3a)。锆石应用于超基性岩研究相对较少,主要原因是(超)基性岩大多数情况下硅、锆不饱和,因而锆石较为稀少(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004)。此外,超基性岩中挑选出的锆石是否为原生岩浆锆石存疑(宫江华等, 2020)。这类岩石事实上很难挑选出锆石用于测年,其锆石在形成过程、野外采样和挑选单矿物过程中容易混入其它来源锆石,造成混乱的年龄结果(宫江华等, 2020)。然而镁铁质岩浆经历一定程度演化,结晶出来的岩相仍是(超)基性岩(如本文略具堆晶特征的单斜辉石岩;图 2c),但是硅、锆可以饱和并生成锆石(Xue et al., 2016, 2019; Wang et al., 2018, 2020b, 2021)。攀西地区近年也有较高精度镁铁-超镁铁质岩锆石U-Pb年龄报道(叶小春等, 2019; 刘军平等, 2020;代堰锫等,2021)。
丹巴辉石岩锆石Th/U比为0.4~4.5(表 2),不发育环带或环带很宽(图 3b),为典型的(超)基性岩浆锆石,反映微量元素在高温条件下的快速扩散(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004)。部分锆石边缘发育少量浅色的变质增生边(图 3b)。然而所有锆石核部测得年龄非常均一,在误差范围内一致(图 3a),测得的微量元素也相对均一(图 4),]表明所测锆石核部U-Pb同位素体系和微量元素未明显受到后期变质影响(Liu et al., 2010)。总的来说,丹巴辉石岩锆石为原生岩浆锆石,261±3Ma的年龄表明其为~260Ma峨眉山大火成岩省北端松潘-甘孜岩区镁铁-超镁铁质岩的组成部分(王登红等, 2007)。
5.2 水子乡辉石岩高氧逸度本文采用锆石ΔQFM、CeN/CeN*和EuN/EuN*三种方法估算水子乡辉石岩和攀枝花岩体岩浆氧逸度。为验证方法可靠性,引用攀枝花岩体锆石前人数据并采用相同方法计算所得ΔQFM在0~3,平均~1.5,与前人结果一致(表 3; 罗雕等, 2020)。该结果与同样针对攀枝花岩体但采用橄榄石-尖晶石矿物对估算方法所得ΔQFM范围也一致(Bai et al., 2019)。以上表明锆石ΔQFM值为反映岩浆氧逸度的可靠指标(Loucks et al., 2020; 邹心宇等, 2021)。运用锆石ΔQFM估算得出水子乡辉石岩氧逸度为0~3.1,平均~1.0,与攀枝花岩体值相当(图 5a, b)。采用锆石CeN/CeN*估算所得水子乡辉石岩与攀枝花岩体氧逸度也基本一致(图 5a, c),表明锆石CeN/CeN*也是反映此两处岩体岩浆氧逸度的可靠指标(Loader et al., 2017)。相比之下,运用锆石EuN/EuN*估算的攀枝花岩体氧逸度比水子乡辉石岩明显偏低(图 5c),可能是因为前者斜长石分离结晶导致残余岩浆显著Eu负异常(Snyder et al., 1993)。因此运用锆石Eu异常反映攀枝花岩体岩浆氧逸度并不可靠。
锆石ΔQFM和CeN/CeN*估算表明水子乡单斜辉石岩与攀枝花苦橄岩和浅色辉长岩具有相近的较高氧逸度(图 5)。较高氧逸度的特征是源于岩浆演化还是母岩浆本身仍有一定争议(罗雕等, 2020)。本文岩浆氧逸度与反映岩浆分离结晶程度的锆石Hf含量呈一定正相关关系(图 5b, d),暗示随岩浆结晶分异进行,氧逸度有略微升高,可能是温度降低和/或成分变化等造成(Liu et al., 2010)。橄榄石和辉石分离结晶会消耗岩浆体系中的Fe2+,导致残余熔体氧逸度小幅升高(Ghiorso, 1997),但在此二者分离结晶对氧逸度的影响非常有限(图 5b, d)。攀枝花岩体侵位过程中,其围岩大理岩被同化导致CO2的加入可能引起氧逸度升高(Zhou et al., 2005; Pang et al., 2008)。然而Re-Os、Sr-Nd和O同位素等分析表明攀枝花岩体未受到明显地壳混染(Hou et al., 2013; Yu et al., 2015)。水子乡辉石岩体围岩并非碳酸盐岩(图 2a),也显示出较高氧逸度,从侧面印证围岩混染对氧逸度的影响微弱。因此,水子乡辉石岩和攀枝花岩体较高氧逸度的特征应源于母岩浆本身,且均可能继承自峨眉山大火成岩省的较高氧逸度、不均一地幔源区(Hou et al., 2011; Bai et al., 2019)。扬子克拉通西缘的岩石圈地幔在新元古代受到洋壳板片俯冲交代(Zhou et al., 2002; Hou et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2020a)。此类俯冲作用在峨眉山大火成岩省和中国东部板内玄武岩均有地球化学记录(Deng et al., 2017; Ren et al., 2017; Xu et al., 2018)。俯冲板片释放H2O-CO2流体使得交代岩石圈地幔氧逸度升高(Foley, 2011; Gerrits et al., 2019),可到ΔQFM~2(Malaspina and Tumiati, 2012)。
5.3 高氧逸度与钒钛磁铁矿成矿前人研究表明镁铁-超镁铁质岩浆在高氧逸度环境下,Fe-Ti氧化物(磁铁矿-钛铁尖晶石、钛铁矿-赤铁矿固溶体)较早饱和沉淀(Toplis and Carroll, 1995; Jugo, 2009; Jugo et al., 2010)。较高氧逸度使得水子乡辉石岩具备成矿条件之一,暗示含钛磁铁矿可能在其深部岩浆房已经饱和卸载。然而水子乡辉石岩锆石高Ti含量(图 6a)及其对应的全岩Ti含量,明显高于区域上玄武岩全岩Ti含量(1.4×10-6~3.2×10-6;胡世华等, 2000),暗示水子乡辉石岩岩浆演化过程中并未明显抽提过Ti,即大量Fe-Ti氧化物的分离结晶,在此氧逸度可能是次要影响因素。由于镁铁-超镁铁质岩浆演化过程中Fe-Ti氧化物基本与硅酸盐矿物同时结晶(Howarth and Prevec, 2013; Bai et al., 2019),而水子乡辉石岩只发育弱的岩相分带(胡世华等, 2000),其较低的结晶分异程度不利于含钛磁铁矿沉淀,在此可能是主要影响因素。前人研究认为岩浆高度演化/高结晶分异造就共结硅酸盐矿物被移出而Fe-Ti氧化物遗留岩浆房对攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿矿床形成至关重要(Bai et al., 2019)。
攀枝花苦橄岩和浅色辉长岩锆石Ti不饱和,并随岩浆结晶分异程度增加进一步亏损(图 6a),其低Ti含量对应全岩低Ti含量(0.75×10-6~1.39×10-6;Hou et al., 2012),后者远低于区域上玄武岩全岩Ti含量(2.8×10-6~3.5×10-6;Bai et al., 2014),表明攀枝花岩体经历过Ti的抽提,即Fe-Ti氧化物的分离结晶(Hou et al., 2011),与大规模钒钛磁铁矿成矿现象一致。Nb、Ta对于暗色矿物辉石是不相容元素,且一般进入金红石等Ti-Fe氧化物(Stepanova et al., 2014),因此Nb、Ta在水子乡岩体辉石分离结晶过程中富集到残留熔体,但在攀枝花岩体钛磁铁矿分离结晶过程中亏损(图 6b)。上文已述及,随斜长石分离结晶进行,残余岩浆Eu负异常加剧(图 6c),这与攀枝花浅色辉长岩含大量粗粒斜长石、岩体上部有晚期结晶分异产物斜长岩以及矿区有同源正长岩和花岗岩的地质现象一致(Shellnutt and Zhou, 2007; 钟宏等, 2008)。总的来说,攀枝花岩体经历了比水子乡辉石岩体更高程度的Fe-Ti氧化物和斜长石的分离结晶作用(图 5、图 6),这是除高氧逸度外钒钛磁铁矿矿床形成的关键条件之一(宋谢炎等, 2005; 汤庆艳等, 2013)。
6 结论(1) 扬子西缘丹巴地区水子乡~260Ma辉石岩为峨眉山大火成岩省北端松潘-甘孜岩区镁铁-超镁铁质岩的组成部分。
(2) 水子乡单斜辉石岩具有与攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿岩体苦橄岩和浅色辉长岩近似的高岩浆氧逸度,较高氧逸度是钒钛磁铁矿成矿的重要条件。
(3) 水子乡辉石岩岩体经历了相对低程度的结晶分异,不利于钛磁铁矿饱和结晶;攀枝花岩体经历了更高程度的钛磁铁矿和斜长石分离结晶,对应大规模钒钛磁铁矿成矿。
致谢 两位审稿专家对论文提出了许多宝贵的建设性意见和建议,在此致以衷心感谢。感谢中国地质大学(北京)张静老师和《岩石学报》编辑部俞良军老师等对论文提出的修改意见和建议。
Bai ZJ, Zhong H, Naldrett AJ, Zhu WG and Xu GW. 2012. Whole-Rock and mineral composition constraints on the genesis of the giant Hongge Fe-Ti-V oxide deposit in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, Southwest China. Economic Geology, 107(3): 507-524 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.107.3.507
|
Bai ZJ, Zhong H, Li CS, Zhu WG, He DF and Qi L. 2014. Contrasting parental magma compositions for the Hongge and Panzhihua magmatic Fe-Ti-V oxide deposits, Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China. Economic Geology, 109(6): 1763-1785 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.109.6.1763
|
Bai ZJ, Zhong H, Hu RZ, Zhu WG and Hu WJ. 2019. Composition of the chilled marginal rocks of the Panzhihua layered intrusion, Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China: Implications for parental magma compositions, sulfide saturation history and Fe-Ti oxide mineralization. Journal of Petrology, 60(3): 619-648 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egz008
|
Charlier B, Namur O, Bolle O, Latypov R and Duchesne JC. 2015. Fe-Ti-V-P ore deposits associated with Proterozoic massif-type anorthosites and related rocks. Earth-science Reviews, 141: 56-81 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.11.005
|
Dai YP, Li TZ and Zhang HH. 2021. Petrogenesis of the ultramafic pluton in the Jianglang dome, western margin of the Yangtze block: Zircon U-Pb dating, geochemistry and Sr-Nd isotopes. Sedimentary Geology and Tethyan Geology, 41(4): 573-584 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Deng J, Wang CM, Li WC, Yang LQ and Wang QF. 2014. The situation and enlightenment of the research of the tectonic evolution and metallogenesis in the Sanjiang Tethys. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(1): 52-64 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Dilek Y and Liang YY. 2017. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking: Lithospheric extension in the North China craton, eastern Asia. GSA Bulletin, 129(11-12): 1379-1407 DOI:10.1130/B31609.1
|
Foley SF. 2011. A reappraisal of redox melting in the Earth's mantle as a function of tectonic setting and time. Journal of Petrology, 52(7-8): 1363-1391 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egq061
|
Ganino C, Arndt NT, Zhou MF, Gaillard F and Chauvel C. 2008. Interaction of magma with sedimentary wall rock and magnetite ore genesis in the Panzhihua mafic intrusion, SW China. Mineralium Deposita, 43(6): 677-694 DOI:10.1007/s00126-008-0191-5
|
Gerrits AR, Inglis EC, Dragovic B, Starr PC, Baxter EF and Burton BW. 2019. Release of oxidizing fluids in subduction zones recorded by iron isotope zonation in garnet. Nature Geoscience, 12(12): 1029-1033 DOI:10.1038/s41561-019-0471-y
|
Ghiorso MS. 1997. Thermodynamic models of igneous processes. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 25: 221-241 DOI:10.1146/annurev.earth.25.1.221
|
Gong JH, Wang ZQ, Wang DS and Qin XF. 2020. A discussion on genesis, provenance and U-Pb ages of the zircons from ultrabasic-basic rocks: A case study in western Jiangnan orogenic belt. Geological Review, 66(6): 1536-1554 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
He B, Xu YG, Chung SL, Xiao L and Wang YM. 2003. Sedimentary evidence for a rapid, kilometer-scale crustal doming prior to the eruption of the Emeishan flood basalts. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 213(3-4): 391-405 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(03)00323-6
|
Hou T, Zhang ZC, Ye XR, Encarnacion J and Reichow MK. 2011. Noble gas isotopic systematics of Fe-Ti-V oxide ore-related mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions in the Panxi area, China: The role of recycled oceanic crust in their petrogenesis. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(22): 6727-6741 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2011.09.003
|
Hou T, Zhang ZC and Pirajno F. 2012. A new metallogenic model of the Panzhihua giant V-Ti-iron oxide deposit (Emeishan Large Igneous Province) based on high-Mg olivine-bearing wehrlite and new field evidence. International Geology Review, 54(15): 1721-1745 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2012.665211
|
Hou T, Zhang ZC, Encarnacion J, Santosh M and Sun YL. 2013. The role of recycled oceanic crust in magmatism and metallogeny: Os-Sr-Nd isotopes, U-Pb geochronology and geochemistry of picritic dykes in the Panzhihua giant Fe-Ti oxide deposit, central Emeishan large igneous province, SW China. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 165(4): 805-822 DOI:10.1007/s00410-012-0836-3
|
Howarth GH and Prevec SA. 2013. Trace element, PGE, and Sr-Nd isotope geochemistry of the Panzhihua mafic layered intrusion, SW China: Constraints on ore-forming processes and evolution of parent magma at depth in a plumbing-system. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 120: 459-478 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2013.06.019
|
Hu RZ, Tao Y, Zhong H, Huang ZL and Zhang ZW. 2005. Mineralization systems of a mantle plume: A case study from the Emeishan Igneous Province, Southwest China. Earth Science Frontiers, 12(1): 42-54 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Jugo PJ. 2009. Sulfur content at sulfide saturation in oxidized magmas. Geology, 37(5): 415-418 DOI:10.1130/G25527A.1
|
Jugo PJ, Wilke M and Botcharnikov RE. 2010. Sulfur K-edge XANES analysis of natural and synthetic basaltic glasses: Implications for S speciation and S content as function of oxygen fugacity. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 74(20): 5926-5938 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2010.07.022
|
Lee CTA and Tang M. 2020. How to make porphyry copper deposits. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 529: 115868 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2019.115868
|
Lin GC, Li XH and Li WX. 2007. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon age, geochemistry and Nd-Hf isotope of Neoproterozoic mafic dyke swarms in western Sichuan: Petrogenesis and tectonic significance. Science in China (Series D), 50(1): 1-16
|
Liu JP, Wang XF, Wang XH, Yang AP, Song DH, Tian SM, Xia CX, Zhang K and Yang SP. 2020. Characteristics of the late Middle Permian mafic-ultramafic rocks in Dianzhong area, central Yunnan, and their relationship with the Emei Mantle Plume: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age and petrogeochemistry. Geological Review, 66(5): 1284-1298 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egp082
|
Loader MA, Wilkinson JJ and Armstrong RN. 2017. The effect of titanite crystallisation on Eu and Ce anomalies in zircon and its implications for the assessment of porphyry Cu deposit fertility. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 472: 107-119 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2017.05.010
|
Loucks RR, Fiorentini ML and Henríquez GJ. 2020. New magmatic oxybarometer using trace elements in zircon. Journal of Petrology, 61(3): egaa034 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egaa034
|
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 70
|
Luo D, Hou T and Pan RH. 2020. Constraints of oxygen fugacity on the formation of the Panzhihua layered intrusion and its mineralization: Evidence from trace element in zircon. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(7): 2116-2126 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.07.13
|
Ma YX, Ji XT, Li JC and Huang M. 2003. Mineral Resources of Panzhihua, Sichuan Province, SW China. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology Press, 1-275 (in Chinese)
|
Malaspina N and Tumiati S. 2012. The role of C-O-H and oxygen fugacity in subduction-zone garnet peridotites. European Journal of Mineralogy, 24(4): 607-618 DOI:10.1127/0935-1221/2012/0024-2213
|
McDonough WF and Sun SS. 1995. The composition of the earth. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 223-253 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(94)00140-4
|
Pang KN, Li CS, Zhou MF and Ripley EM. 2008. Abundant Fe-Ti oxide inclusions in olivine from the Panzhihua and Hongge layered intrusions, SW China: Evidence for early saturation of Fe-Ti oxides in ferrobasaltic magma. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 156(3): 307-321 DOI:10.1007/s00410-008-0287-z
|
Paton C, Woodhead JD, Hellstrom JC, Hergt JM, Greig A and Maas R. 2010. Improved laser ablation U-Pb zircon geochronology through robust downhole fractionation correction. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 11(5): Q0AA06
|
Ren ZY, Wu YD, Zhang L, Nichols ARL, Hong LB, Zhang YH, Zhang Y, Liu JQ and Xu YG. 2017. Primary magmas and mantle sources of Emeishan basalts constrained from major element, trace element and Pb isotope compositions of olivine-hosted melt inclusions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 208: 63-85 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2017.01.054
|
Roger F, Jolivet M and Malavieille J. 2010. The tectonic evolution of the Songpan-Garzê (North Tibet) and adjacent areas from Proterozoic to present: A synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 39(4): 254-269 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2010.03.008
|
Shellnutt JG and Zhou MF. 2007. Permian peralkaline, peraluminous and metaluminous A-type granites in the Panxi district, SW China: Their relationship to the Emeishan mantle plume. Chemical Geology, 243(3-4): 286-316 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.05.022
|
Snyder GA, Taylor LA and Crozaz G. 1993. Rare earth element selenochemistry of immiscible liquids and zircon at Apollo 14: An ion probe study of evolved rocks on the Moon. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 57(5): 1143-1149 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(93)90046-Y
|
Song XY, Zhang CJ, Hu RZ, Zhong H, Zhou MF, Ma RZ and Li YG. 2005. Genetic links of magmatic deposits in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province with dynamics of mantle plume. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 25(4): 35-44 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Song XY, Chen LM, Yu SY, Tao Y, She YW, Luan Y, Zhang XQ and He HL. 2018. Geological features and genesis of the V-Ti magenetite deposits in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 37(6): 1003-1018 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Stepanova AV, Samsonov AV, Salnikova EB, Puchtel IS, Larionova YO, Larionov AN, Stepanov VS, Shapovalov YB and Egorova SV. 2014. Palaeoproterozoic continental MORB-type tholeiites in the Karelian Craton: petrology, geochronology, and tectonic setting. Journal of Petrology, 55(9): 1719-1751 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egu039
|
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds. ). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Tang QY, Zhang MJ, Yu M, Wang QL and Shang H. 2013. The magmatic ore-forming system of Late-Permian Emeishan mantle plume. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 32(5): 680-692 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Toplis MJ and Carroll MR. 1995. An experimental study of the influence of oxygen fugacity on Fe-Ti oxide stability, phase relations, and mineral-melt equilibria in ferro-basaltic systems. Journal of Petrology, 36(5): 1137-1170 DOI:10.1093/petrology/36.5.1137
|
Wang DH, Li JK, Wang CH, Qu WJ, Fu XF and Fu DM. 2007. New advances in geochronologic study related to Emei mantle plume and their significance. Mineral Deposits, 26(5): 550-556 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang QF, Deng J, Li GJ, Liu JY, Li CS and Ripley EM. 2018. Geochronological, petrological, and geochemical studies of the Daxueshan magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide deposit in the Tethyan Orogenic Belt, Southwest China. Economic Geology, 113(6): 1307-1332 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.2018.4593
|
Wang QF, Zhao HS, Groves DI, Deng J, Zhang QW and Xue SC. 2020a. The Jurassic Danba hypozonal orogenic gold deposit, western China: Indirect derivation from fertile mantle lithosphere metasomatized during Neoproterozoic subduction. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 309-324 DOI:10.1007/s00126-019-00928-x
|
Wang YN, Xue SC, Deng J, Wang QF, Li CS and Ripley EM. 2020b. Triassic arc mafic magmatism in North Qiangtang: Implications for tectonic reconstruction and mineral exploration. Gondwana Research, 82: 337-353 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2020.01.013
|
Wang YN, Wang QF, Deng J, Xue SC, Li CS and Ripley EM. 2021. Late Permian-Early Triassic mafic dikes in the southwestern margin of the South China block: Evidence for Paleo-Pacific subduction. Lithos, 384-385: 105994 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2021.105994
|
Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(15): 1554-1569 DOI:10.1007/BF03184122
|
Xu JF, Suzuki K, Xu YG, Mei HJ and Li J. 2007. Os, Pb, and Nd isotope geochemistry of the Permian Emeishan continental flood basalts: Insights into the source of a large igneous province. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(8): 2104-2119 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2007.01.027
|
Xu YG and Zhong SL. 2001. The Emeishan large igneous province: Evidence for mantle plume activity and melting conditions. Geochimica, 30(1): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Xu YG, Mei HJ, Xu JF, Huang XL, Wang YJ and Chung SL. 2003. Origin of two differentiation trends in the Emeishan flood basalts. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(4): 390-394
|
Xu YG, He B, Huang XL, Luo ZY, Zhu D, Ma JL and Shao H. 2007. The debate over mantle plumes and how to test the plume hypothesis. Earth Science Frontiers, 14(2): 1-9 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1016/S1872-5791(07)60011-6
|
Xu YG, Luo ZY, Huang XL, He B, Xiao L, Xie LW and Shi YR. 2008. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotope constraints on crustal melting associated with the Emeishan mantle plum. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 72(13): 3084-3104 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2008.04.019
|
Xu YG, Li HY, Hong LB, Ma L, Ma Q and Sun MD. 2018. Generation of Cenozoic intraplate basalts in the big mantle wedge under eastern Asia. Science China (Earth Sciences), 61(7): 869-886 DOI:10.1007/s11430-017-9192-y
|
Xue SC, Li CS, Qin KZ and Tang DM. 2016. A non-plume model for the Permian protracted (266~286Ma) basaltic magmatism in the Beishan-Tianshan region, Xinjiang, western China. Lithos, 256-257: 243-249 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2016.04.018
|
Xue SC, Li CS, Wang QF, Ripley EM and Yao ZS. 2019. Geochronology, petrology and Sr-Nd-Hf-S isotope geochemistry of the newly-discovered Qixin magmatic Ni-Cu sulfide prospect, southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 111: 103002 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103002
|
Yan DP, Zhou MF, Song HL, Wang XW and Malpas J. 2003. Origin and tectonic significance of a Mesozoic multi-layer over-thrust system within the Yangtze Block (South China). Tectonophysics, 361(3-4): 239-254 DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(02)00646-7
|
Ye XC, Huang YP, Liu QQ, Bai XH, Wu CZ, Yang YC and Li W. 2019. Geochemical characteristics and zircon U-Pb isotope chronology of the Bindong magnetite-rich hornblendite in Shimian County, Sichuan Province. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 38(6): 1177-1190 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yu SY, Song XY, Ripley EM, Li CS, Chen LM, She YW and Luan Y. 2015. Integrated O-Sr-Nd isotope constraints on the evolution of four important Fe-Ti oxide ore-bearing mafic-ultramafic intrusions in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China. Chemical Geology, 401: 28-42 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2015.02.020
|
Zhang ZC, Wang FS, Fan WM, Deng HL, Xu YG, Xu JF and Wang YJ. 2001. A discussion on some problems concerning the study of the Emeishan basalts. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 20(3): 239-246 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang ZC, Mao JW, Saunders AD, Ai Y, Li Y and Zhao L. 2009. Petrogenetic modeling of three mafic-ultramafic layered intrusions in the Emeishan large igneous province, SW China, based on isotopic and bulk chemical constraints. Lithos, 113(3-4): 369-392 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.023
|
Zhao HS, Wang QF, Groves DI and Deng J. 2019. A rare Phanerozoic amphibolite-hosted gold deposit at Danba, Yangtze Craton, China: Significance to fluid and metal sources for orogenic gold systems. Mineralium Deposita, 54(1): 133-152 DOI:10.1007/s00126-018-0845-x
|
Zhao JH and Zhou MF. 2008. Neoproterozoic adakitic plutons in the northern margin of the Yangtze Block, China: Partial melting of a thickened lower crust and implications for secular crustal evolution. Lithos, 104(1-4): 231-248 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.12.009
|
Zhao Z, Qi L, Huang ZL, Yan ZF and Xu C. 2012. Trace elements and Sr-Nd isotopic geochemistry and genesis of Jijie alkaline-ultramafic rocks, southern part of Panxi rift. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(6): 1915-1927 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhong H, Zhu WG, Chu ZY, He DF and Song XY. 2007. Shrimp U-Pb zircon geochronology, geochemistry, and Nd-Sr isotopic study of contrasting granites in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China. Chemical Geology, 236(1-2): 112-133 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.09.004
|
Zhong H, Zhu WG, Hu RZ, Xie LW, He DF, Liu F and Chu ZY. 2008. Zircon U-Pb age, elements and Sr-Nd-Hf isotope geochemistry of the Panzhihua A-type granite in the Emeishan Large Igneous Province. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 27(Suppl.1): 71-72 (in Chinese)
|
Zhou MF, Yan DP, Kennedy AK, Li YQ and Ding J. 2002. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronological and geochemical evidence for Neoproterozoic arc-magmatism along the western margin of the Yangtze block, South China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196(1-2): 51-67 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00595-7
|
Zhou MF, Robinson PT, Lesher CM, Keays RR, Zhang CJ and Malpas J. 2005. Geochemistry, petrogenesis and metallogenesis of the Panzhihua gabbroic layered intrusion and associated Fe-Ti-V oxide deposits, Sichuan Province, SW China. Journal of Petrology, 46(11): 2253-2280 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egi054
|
Zhou MF, Arndt NT, Malpas J, Wang CY and Kennedy AK. 2008. Two magma series and associated ore deposit types in the Permian Emeishan Large Igneous Province, SW China. Lithos, 103(3-4): 352-368 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2007.10.006
|
Zou XY, Jiang JL, Qin KZ, Zhang YG, Yang W and Li XH. 2021. Progress in the principle and application of zircon trace element. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 37(4): 985-999 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2021.04.03
|
代堰锫, 李同柱, 张惠华. 2021. 扬子陆块西缘江浪穹窿超基性岩的成因: 锆石U-Pb定年、岩石地球化学及Sr-Nd同位素. 沉积与特提斯地质, 41(4): 573-584. |
邓军, 王长明, 李文昌, 杨立强, 王庆飞. 2014. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用研究态势及启示. 地学前缘, 21(1): 52-64. |
宫江华, 王宗起, 王东升, 覃小锋. 2020. 对超基性-基性岩中锆石成因、来源及其U-Pb年龄的探讨——以江南造山带西段为例. 地质论评, 66(6): 1536-1554. |
胡瑞忠, 陶琰, 钟宏, 黄智龙, 张正伟. 2005. 地幔柱成矿系统: 以峨眉山地幔柱为例. 地学前缘, 12(1): 42-54. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2005.01.007 |
刘军平, 王晓峰, 王小虎, 杨爱平, 宋冬虎, 田素梅, 夏彩香, 张坤, 杨仕潘. 2020. 滇中甸中地区中二叠世晚期镁铁-超镁铁质岩体特征及其与峨眉地幔柱关系——来自锆石U-Pb年龄及岩石地球化学证据. 地质论评, 66(5): 1284-1298. |
罗雕, 侯通, 潘荣昊. 2020. 氧逸度对攀枝花岩体成岩成矿作用的制约: 来自锆石微量元素的证据. 岩石学报, 36(7): 2116-2126. |
马玉孝, 纪相田, 李金成, 黄明. 2003. 攀枝花矿产资源. 成都: 成都理工大学出版社, 1-275.
|
宋谢炎, 张成江, 胡瑞忠, 钟宏, 周美夫, 马润则, 李佑国. 2005. 峨眉火成岩省岩浆矿床成矿作用与地幔柱动力学过程的耦合关系. 矿物岩石, 25(4): 35-44. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2005.04.007 |
宋谢炎, 陈列锰, 于宋月, 陶琰, 佘宇伟, 栾燕, 张晓琪, 何海龙. 2018. 峨眉大火成岩省钒钛磁铁矿矿床地质特征及成因. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 37(6): 1003-1018. |
汤庆艳, 张铭杰, 余明, 王启立, 尚慧. 2013. 晚二叠世峨眉山地幔柱岩浆成矿作用. 岩石矿物学杂志, 32(5): 680-692. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2013.05.010 |
王登红, 李建康, 王成辉, 屈文俊, 付小方, 傅德明. 2007. 与峨眉地幔柱有关年代学研究的新进展及其意义. 矿床地质, 26(5): 550-556. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.05.007 |
吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589-1604. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 |
徐义刚, 钟孙霖. 2001. 峨眉山大火成岩省: 地幔柱活动的证据及其熔融条件. 地球化学, 30(1): 1-9. |
徐义刚, 何斌, 黄小龙, 罗震宇, 朱丹, 马金龙, 邵辉. 2007. 地幔柱大辩论及如何验证地幔柱假说. 地学前缘, 14(2): 1-9. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2007.02.001 |
叶小春, 黄玉蓬, 刘清强, 白新会, 吴春章, 杨友春, 李伟. 2019. 四川省石棉县滨东富磁铁矿角闪石岩的地球化学特征及锆石U-Pb年代学研究. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 38(6): 1177-1190. |
张招崇, 王福生, 范蔚茗, 邓海琳, 徐义刚, 许继峰, 王岳军. 2001. 峨眉山玄武岩研究中的一些问题的讨论. 岩石矿物学杂志, 20(3): 239-246. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2001.03.005 |
赵正, 漆亮, 黄智龙, 严再飞, 许成. 2012. 攀西裂谷南段鸡街碱性超基性岩微量元素和Sr-Nd同位素地球化学及其成因探讨. 岩石学报, 28(6): 1915-1927. |
钟宏, 朱维光, 胡瑞忠, 谢烈文, 何德锋, 刘峰, 储著银. 2008. 峨眉山大火成岩省中攀枝花A型花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄、元素及Sr-Nd-Hf同位素地球化学. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 27(增1): 71-72. |
邹心宇, 蒋济莲, 秦克章, 张毅刚, 杨蔚, 李献华. 2021. 锆石微量元素的理论基础及其应用研究进. 岩石学报, 37(4): 985-999. |
 2022, Vol. 38
2022, Vol. 38