2. 山东省地质科学研究院,自然资源部金矿成矿过程与资源利用重点实验室,山东省金属矿产成矿地质过程与资源利用重点实验室,济南 250013;
3. 东华理工大学,核资源与环境国家重点实验室,南昌 330013
2. Shandong Institute of Geological Sciences, MNR Key Laboratory of Gold Mineralization Processes and Resources Utilization, Key Laboratory of Metallogenic-Geologic Processes and Comprehensive Utilization of Minerals Resources in Shandong Province, Jinan 250013, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resource and Environment, East China University of Technology, Nanchang 330013, China
胶东地区目前是中国最重要的黄金产区,拥有超过5000t的黄金资源(Deng et al., 2020b)。胶东金矿床赋存于前寒武纪变质基底中,主要分为浸染状细脉-网脉型(“焦家型”)和石英-硫化物脉型(“玲珑型”)矿床(Deng et al., 2020a)。焦家型金矿床产于区域性断裂的蚀变带中,玲珑型金矿床分布在区域性断裂的次级断层中(Yang et al., 2016b)。经过几十年的研究,关于胶东地区金的来源、超级富集机制以及矿床成因模式仍然存在激烈的争论。胶东金矿因其矿床的线性构造分布、矿化类型、围岩蚀变、流体成分和稳定同位素组成等(Goldfarb and Santosh, 2014)与造山型金矿特征(Goldfarb et al., 2019; Qiu et al., 2020a)相似,一般被归类为造山型金矿。由于胶东金矿床的构造环境和变质背景相对于传统造山型金矿成矿模式(Groves et al., 1998)具有独特性,故很难将其纳入经典造山型金矿。胶东金矿应划分为一类独特的胶东型金矿(Zhai and Santosh, 2013),或一种独特的造山型金矿(Goldfarb and Santosh, 2014),即胶东型造山型金矿(Deng et al., 2020b)。玲珑金矿区位于胶东西北部,招远-平度断裂带北部,以石英-硫化物脉为特征的玲珑型金矿床而闻名于世,整个矿区预计超过1000t以上的黄金资源量(Qiu et al., 2020b)。玲珑金矿区部分矿段产出高品位的明金矿石,大颗粒自然金的超级富集机制是备受瞩目的科学问题。
在热液金矿床中,铋-硫族化合物(硫族主要为S和Te)常与金紧密共生。铋、碲矿物在国内外金矿床中均有发现,例如罗马尼亚Sacarimb(Cook and Ciobanu, 2004),美国Golden Sunlight(Spry et al., 1997),菲律宾Acupan(Cooke and McPhail, 2001)等,以及中国的河北东坪(Cook et al., 2009a)等。许多研究表明铋-碲熔体在金的运移和沉淀机制中起着关键作用,可作为热液中金的关键吸附剂(Cabri, 1965;Frost et al., 2002;Törmänen and Koski, 2005;Ciobanu et al., 2006;Plotinskaya et al., 2006;Tomkins et al., 2007;Tooth et al., 2008, 2011;Cook et al., 2009a, b;Voudouris et al., 2013)。并且由于碲化物对硫逸度、碲逸度、pH值、温度等条件的高度敏感性,使其成为限制金沉淀时物理化学条件的重要指标。因此,对碲化物的研究有助于我们了解金的成矿过程及成矿时的物理化学条件。
玲珑金矿区明金矿石中存在大量与自然金共生的碲化物。本文通过显微岩相学观察、扫描电镜及电子探针分析,对玲珑金矿区碲化物的矿物组合特征及化学成分等进行研究;在此基础上,确定了碲化物的种类及成分特征,探讨共生矿物的成矿条件,并对成矿物质来源以及自然金的富集机制等问题进行了论述。本文是关于玲珑金矿区自然金共生碲化物的首次详细报道,在查明碲化物种类及特征的同时,阐明了碲化物产出的地质意义。
1 区域地质背景胶东半岛位于华北克拉通东南缘,西部以岩石圈尺度的郯庐断裂带为界(Deng et al., 2018)(图 1a),北临渤海,东部和南部被黄海所包围(图 1b)。胶东半岛被认为是三叠纪扬子板块和华北板块碰撞拼合后形成的(Liu et al., 2006),被五莲-烟台断裂分成东南部的苏鲁地体和西北部的胶北地体(魏瑜吉等,2020),胶北地体可进一步分为胶北地块和胶莱盆地(何登洋等,2020;图 1b)。胶东金矿床大多位于胶莱盆地北部,受NNE-NE向断裂控制(Zhang et al., 2020)。胶东地区广泛分布着前寒武纪基底变质岩,主要包括胶北地块的以TTG(奥长花岗岩-英云闪长岩-花岗闪长岩)片麻岩为主的新太古代胶东群,以变质沉积岩为主的元古宙景山群、粉子山群和蓬莱群(Tang et al., 2008)以及苏鲁地体的三叠纪超高压变质岩(图 1b)。

|
图 1 胶东大地构造位置简图(a)和胶东金成矿省区域地质图(b)(据Zhang et al., 2020修编) Fig. 1 Simplified geologic map of the tectonic situation of Jiaodong (a) and geological map of Jiaodong gold province (b) (modified after Zhang et al., 2020) |
胶东地区中生代侵入岩十分发育,主要包括玲珑花岗岩、郭家岭花岗闪长岩、艾山花岗岩以及广泛分布的镁铁质岩脉。玲珑花岗岩以玲珑黑云母花岗岩和栾家河二长花岗岩为主,LA-ICP-MS测得锆石U-Pb年龄主要在166~149Ma(Zhao et al., 2019),玲珑花岗岩来源于新太古代下地壳的部分熔融(Yang et al., 2018)。郭家岭花岗岩主要由斑状花岗闪长岩和石英二长岩组成,锆石U-Pb年龄显示其侵位时间为133~126Ma(Yang et al., 2014b),由下地壳前寒武纪变质基底部分熔融形成(Hou et al., 2007),并在上升过程中受到上地壳的混染(Wang et al., 2014)。艾山花岗岩主要出露在胶东半岛东部,由未变形的碱性花岗岩组成,锆石U-Pb年龄显示艾山花岗岩主要侵位于120~108Ma(Tang et al., 2014),具有壳幔混合成因特点(Charles et al., 2013)。胶东半岛的镁铁质岩脉分布广泛,但体积通常较小,SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄显示基性岩脉侵位时间在130~110Ma(Deng et al., 2017),主要来源于岩石圈地幔的低程度部分熔融(Deng et al., 2017)。玲珑花岗岩和郭家岭花岗岩为胶东地区金矿床的主要赋矿围岩(Yang et al., 2014a)。
胶东地区主要存在EW向和NNE-NE向两组构造体系(图 1b)。EW向构造主要为古老基底褶皱(Sai et al., 2020),其形成与中生代华北板块与扬子板块陆陆碰撞造成的南北向挤压作用有关(杨立强等,2014; Goldfarb et al., 2021)。NNE-NE向区域断裂及其次级断裂是胶东半岛的主要控矿构造(Guo et al., 2013;图 1b)。其中郯庐断裂和五莲-烟台断裂是区域一级断裂,NNE-NE向的二级和三级断裂被认为是郯庐断裂和五莲-烟台断裂的次级断裂(Goldfarb et al., 2001)。自西到东主要有五条断裂带,依次为三山岛-仓上断裂带、焦家断裂带、招远-平度断裂带、蓬莱-栖霞断裂带和牟平-乳山断裂带(赛盛勋和邱昆峰,2020),区域内金矿床的分布严格受这些断裂控制(Deng et al., 2020c; 图 1b)。
2 玲珑金矿区地质特征玲珑金矿区位于胶东半岛西北部,招远-平度断裂带北段,以石英-硫化物脉为特征的玲珑型金矿而闻名。矿区由西山、东山、九曲、大开头、台上、罗山、阜山、东风等金矿床组成(图 2),金资源总量超过1000t,属于世界级超大型金矿区。矿区出露的地层主要为新太古代胶东群变质岩和第四纪沉积物。新太古代胶东群变质岩主要出露于矿区以东,也有一些呈透镜状分布于中生代花岗岩中,主要由黑云斜长片麻岩和斜长角闪岩组成(孙华山等,2016)。矿区内中生代岩浆岩十分发育,主要为晚侏罗世玲珑花岗岩和早白垩世郭家岭花岗闪长岩。晚侏罗世玲珑花岗岩可分为玲珑黑云母花岗岩和栾家河二长花岗岩(Yang et al., 2012),在破头青断裂两侧分布广泛(图 2)。早白垩世郭家岭花岗岩通常产于矿区西北部。矿区内中基性岩脉十分发育,由煌斑岩、闪长玢岩、石英闪长玢岩组成(Wen et al., 2015),在空间上与金矿体有局部联系。
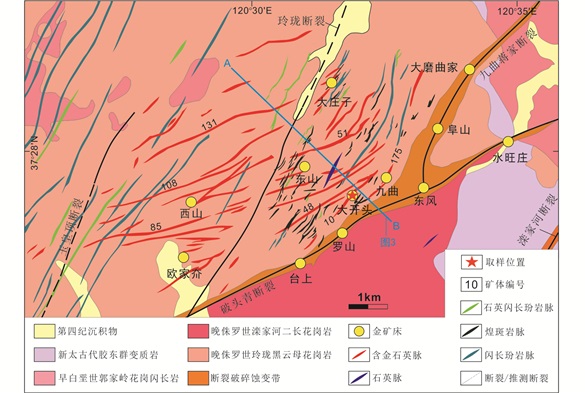
|
图 2 玲珑金矿区地质简图(据Guo et al., 2020修编) Fig. 2 Sketch geologic map of Linglong gold district (modified after Guo et al., 2020) |
矿区内主要发育三条断裂构造,包括破头青断裂、玲珑断裂和九曲蒋家断裂(图 2)。破头青断裂属于招远-平度断裂的北段,位于矿区东南部,沿玲珑花岗岩和滦家河花岗岩接触带分布。破头青断裂为成矿前或成矿期形成的主要控矿断裂带,走向为50°~80°,倾向SE,倾角30°~60°,控制着台上、罗山、东风和水旺庄等超大型浸染状细脉-网脉型金矿床。沿断裂带发育花岗质碎屑岩和断层泥,断裂带周围有宽阔的热液蚀变带(Guo et al., 2017)。九曲蒋家断裂带走向35°左右(申俊峰等,2013),倾向SE,倾角40°左右,由位于破头青断裂下盘的一系列次级断裂组成。玲珑断裂走向20°~30°,倾向SE和NW,倾角65°~85°,为成矿后断裂,切割玲珑金矿区中部和破头青断裂。玲珑断裂沿断裂发育花岗质碎屑岩、角砾岩、糜棱岩和少量的断层泥,热液蚀变作用相对较弱(Guo et al., 2017)。矿区内的二级断裂长度一般为数百至数千米,宽度一般为数米至数十米,走向NNE-NEE,倾向NW和SE,倾角50°~75°,是矿区内控制中基性岩脉和含金石英-硫化物脉产状的主要构造(Guo et al., 2020),产出有东山、西山、九曲、阜山、大开头等玲珑型石英-硫化物脉金矿床。
玲珑矿区内的矿体主要产于玲珑花岗岩和滦家河花岗岩岩体中(张祖青等,2007;Li et al., 2008),玲珑花岗岩中热液蚀变较发育,主要有钾长石化、绢英岩化、硅化、碳酸盐化等,蚀变带一般沿矿脉两侧呈对称分布(申俊峰等,2013)。矿区内已探明金矿脉超过500条,具有经济价值的矿脉约30条,主要为9、36、47、51、55、56、108和175号矿脉等(图 2、图 3),这些脉状矿体一般走向30°~75°,倾向NW,延伸几百米到几千米,宽度从几十厘米到几米不等。其中108号矿脉是石英-硫化物脉型金矿的最具代表性矿体,矿脉长约5500m,走向45°~65°,倾向NW,倾角50°~70°,是玲珑矿区已知的最大石英-硫化物脉矿体,由宽度0.3~3m不等的含金石英-硫化物脉组成,周围发育钾长石蚀变和局部绢英岩蚀变,蚀变宽度在1~8m之间(Guo et al., 2020)。含金石英-硫化物脉的品位通常从几克/吨到十几克/吨不等,最高可达数百克/吨。主要的矿石矿物为自然金、银金矿和黄铁矿,其次是黄铜矿、方铅矿和闪锌矿。主要的脉石矿物有石英、绢云母、长石、方解石和绿泥石等。
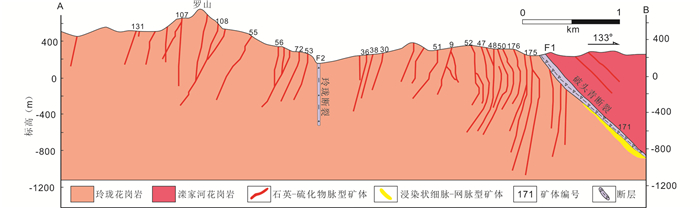
|
图 3 玲珑金矿区剖面图(据Wen et al., 2015修编) Fig. 3 Geological profile crossing Linglong gold district (modified after Wen et al., 2015) |
玲珑金矿区成矿作用可分为4个成矿阶段:黄铁矿-石英阶段、石英-黄铁矿阶段、石英-多金属硫化物阶段和石英-碳酸盐岩阶段(范宏瑞等,2005)。黄铁矿-石英阶段为成矿早阶段,基本不含金。石英-黄铁矿阶段和石英-多金属硫化物阶段是金的主成矿阶段。石英-碳酸盐岩阶段为成矿晚阶段偶见少量的自然金产出。
3 样品描述与分析方法含明金的高品位石英-硫化物脉样品采自玲珑矿区大开头矿段,为石英-黄铁矿阶段的样品。矿石手标本可见自然金呈浸染状或不规则树枝状集合体赋存于石英-硫化物脉中,自然金与暗色碲化物共生(图 4)。对12个代表性矿石样品进行切面磨制标准探针片进行研究,矿石探针片在廊坊市地科勘探技术服务有限公司完成。

|
图 4 玲珑金矿区含明金石英-硫化物脉样品照片 Au-自然金;Tel-碲化物;Qz-石英;Py-黄铁矿 Fig. 4 Photographs of gold-bearing quartz-sulfide vein samples from Linglong gold district Au-native gold; Tel-tellurides; Qz-quartz; Py-pyrite |
选取的探针片经表面喷碳处理,增强导电性后进行扫描电镜和X射线能谱及电子探针分析。扫描电镜-能谱分析(SEM-EDS)在核工业北京地质研究院地质矿产研究所岩矿鉴定实验室完成。使用的仪器为TESCAN VEGA3型扫描电子显微镜,元素面分布(EDS-Mapping)分析采用X射线能谱仪,工作电压为15kV,工作距离为12mm。
电子探针测试工作在山东省地质科学研究院自然资源部金矿成矿过程与资源利用重点实验室完成,仪器型号为日本电子公司生产的(JEOL)JXA-8230,所用标准样品均为加拿大Astimex系列金属和矿物标样,具体如下:金(Au)、银(Ag)、黄铁矿(S、Fe)、方铅矿(Pb)、闪锌矿(Zn)、赤铜矿(Cu)、毒砂(As)、辰砂(Hg)、硒化铋(Bi、Se)、镍黄铁矿(Ni)、辉碲矿(Sb)、钴(Co)等。波谱分析所用加速电压为20kV,电流20nA,束斑直径1μm。实验室温度22℃、湿度30%。相对误差0.01%。
4 分析结果 4.1 自然金矿物学和地球化学自然金呈金黄色,反射率明显高于碲化物和黄铁矿、方铅矿,粒径变化较大,从数微米到数毫米不等。自然金通常与碲化物共生,形成平滑的共结边结构(图 5)。自然金主要有三种赋存状态:(1)裂隙金:自然金呈不规则粒状和脉状,赋存于石英和黄铁矿的裂隙中(图 5a-b,d);(2)包体金:自然金多呈不规则粒状、浑圆状赋存于黄铁矿中(图 5c),少数赋存于石英中;(3)粒间金:多呈不规则状赋存于矿物之间的空隙中,如黄铁矿和石英的间隙(图 5d)。
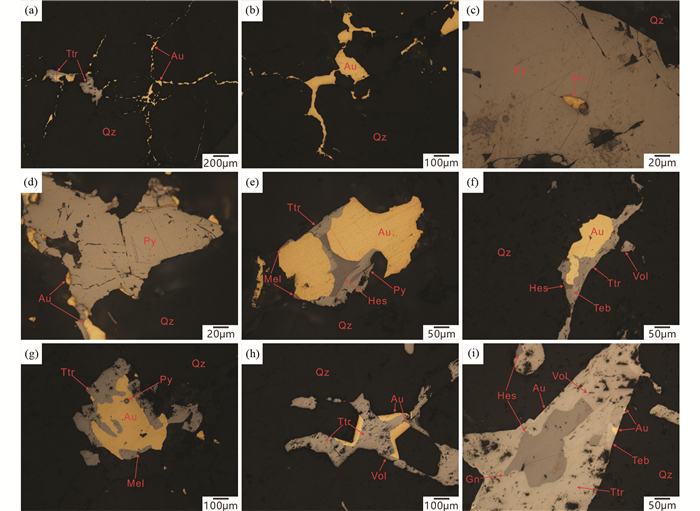
|
图 5 玲珑金矿区自然金赋存状态及共生矿物组合显微照片 (a)自然金呈细脉状分布于石英中;(b)石英中不规则状自然金;(c)黄铁矿中的包体金;(d)自然金分布于黄铁矿裂隙及黄铁矿-石英间隙中;(e-i)自然金及碲化物的共生关系. Ttr-辉碲铋矿;Teb-碲铋矿;Mel-碲镍矿;Hes-碲银矿;Vol-碲铋银矿;Gn-方铅矿 Fig. 5 Reflected light photomicrographs showing native gold occurrence and symbiotic mineral assemblages in Linglong gold district (a) veinlet gold in quartz; (b) irregular gold in quartz; (c) inclusion gold in pyrite; (d) native gold is distributed in pyrite fractures and in pyrite-quartz intersections; (e-i) symbiosis between native gold and tellurides. Ttr-tetradymite; Teb-tellurobismuthite; Mel-melonite; Hes-hessite; Vol-volynskite; Gn-galena |
电子探针成分分析显示自然金中Au含量为88.93%~91.06%,Ag含量为9.38%~11.83%(表 1)。对自然金电子探针数据进行统计,采用目前流行的Au/(Au+Ag)×1000的计算方法来确定金成色,玲珑矿区自然金成色较高,平均成色为894。根据金银系列矿物的分类,玲珑金矿区自然金属于含银自然金。
|
|
表 1 自然金电子探针分析结果(wt%) Table 1 Compositions of native gold detected by EMPA (wt%) |
根据显微鉴定及电子探针成分分析(表 2),共发现了五种碲化物,包括辉碲铋矿、碲铋矿、碲银矿、碲铋银矿和碲镍矿(图 5),为玲珑金矿区首次较为详细的碲化物报道。其中辉碲铋矿含量最多,分布最广泛。碲化物与自然金共生,为主成矿阶段产物。
|
|
表 2 碲化物电子探针分析结果(wt%) Table 2 Compositions of telluride minerals detected by EMPA (wt%) |
(1) 辉碲铋矿:反射色呈铅灰色,与自然金共生,形成平滑共结边结构。本研究测得辉碲铋矿中铋元素含量为58.69%~61.72%,碲元素含量为34.53%~35.79%,硫元素含量为3.83%~4.43%,含有微量的金、银、铁等元素。与标准辉碲铋矿(Bi2Te2S:Bi 59.21%,Te 36.26%,S 4.53%)对比,相对贫碲、硫,富铋。辉碲铋矿为样品中分布最为广泛,含量最高的碲化物。
(2) 碲铋矿:反射色呈浅灰白色,反射率略高于辉碲铋矿,与辉碲铋矿及自然金共生。本研究测得碲铋矿中铋元素含量为49.35%~53.88%,碲元素含量为45.52%~47.23%,含微量的金、银等元素。与标准的碲铋矿(Bi2Te3:Bi 52.20%,Te 47.80%)对比,相对贫碲。
(3) 碲银矿:反射色呈暗灰色,与自然金及其他碲化物共生。本研究测得碲银矿中银元素含量为59.52%~63.63%,碲元素含量为35.60%~40.80%,含有微量的金、镉等元素。与标准碲银矿(Ag2Te:Ag 62.86%,Te 37.14%)对比,除个别样品外,轻微富银。
(4) 碲铋银矿:反射色呈浅暗灰色,反射色相较于辉碲铋矿较暗,介于辉碲铋矿和碲银矿之间,常与碲银矿共生(图 6)。本研究测得碲铋银矿中碲元素含量为43.86%~47.70%,铋元素含量为37.78%~43.07%,银元素含量为10.77%~19.14%。与标准碲铋银矿(AgBiTe2:Te 44.61%,Bi 36.53%,Ag 18.86%)对比,相对富铋,个别样品中贫银。

|
图 6 自然金共生碲化物元素扫面图 (a)自然金及碲化物BSE图像;(b-f)Au、Ag、Te、Bi、S元素X射线能谱扫面图 Fig. 6 X-ray mapping of telluride minerals associated with native gold (a) BSE image of native gold and tellurides; (b-f) X-ray mapping of Au, Ag, Te, Bi, S elements |
(5) 碲镍矿:相对于其他碲化物含量较低,仅在个别样品中发现,反射色呈淡玫瑰色。本研究测得碲镍矿中碲元素含量为81.00%~82.06%,镍元素含量为18.18%~18.29%。与标准碲镍矿(NiTe2:Te 81.30%,Ni 18.70%)对比,轻微富碲贫镍。
5 讨论 5.1 碲化物形成条件碲逸度、硫逸度和温度对碲化物的形成起了至关重要的作用。在一定的碲逸度条件下低温有利于碲化物的形成,在相同的温度下高碲逸度对碲化物形成有利(涂光炽,2000;刘家军等,2013)。碲化物对成矿流体的硫逸度、碲逸度、pH值、温度等条件的高度敏感性,可以作为限制金沉淀时物理化学条件的重要指标(Afifi et al., 1988;McPhail, 1995;Cook and Ciobanu, 2004;Tombros et al., 2010),有助于我们了解金成矿时的物理化学条件。
玲珑金矿区明金矿石中的自然金和碲化物产出于石英-黄铁矿阶段,该阶段流体包裹体均一温度平均为260℃(李碧乐等,2009;Wen et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2016a; Guo et al., 2017)。结合矿物共生组合和成矿温度,可对碲化物形成时的硫逸度和碲逸度条件进行计算。成矿流体的碲逸度和硫逸度范围通过Afifi et al.(1988)建立的logfTe2-logfS2图解来约束。根据与自然金共生的碲银矿、碲铋矿、辉碲铋矿、碲镍矿、碲铋银矿、及少量黄铁矿和方铅矿等矿物,而没有出现碲金矿、碲铅矿和磁黄铁矿等矿物,初步判定玲珑金矿区碲化物形成时期的碲逸度的范围为-12.6 < logfTe2 < -9.1,硫逸度的范围为-13.6 < logfS2 < -9.6(图 7)。White et al.(1957)根据实验得出自然金中银含量和温度的关系式,Afifi et al.(1988)基于此关系式提出可通过共生的碲银矿和银金矿来计算成矿流体的碲逸度,其公式为:logfTe2=(1/4.576T){-50197+16.32T-18.302TlogXAg+4(1-XAg)2[5650-1600(1-XAg)-1.375T]},其中XAg为Ag在金银固溶体中的质量分数,T为开氏温度。应用该公式,要求体系中除碲银矿外,不能出现其他的金银系列碲化物,以排除早期析出的矿物相在低温状态下分解出碲金矿、碲金银矿等金银系列碲化物的情况。玲珑金矿区除碲银矿外,未发现与自然金共生的其他碲金银系列矿物,可应用该关系式。根据玲珑金矿区自然金中Ag的质量分数(表 1)和成矿温度260℃,大致可计算得出成矿流体碲逸度logfTe2=-9.52,与logfTe2-logfS2图解得到的碲逸度范围较为一致。
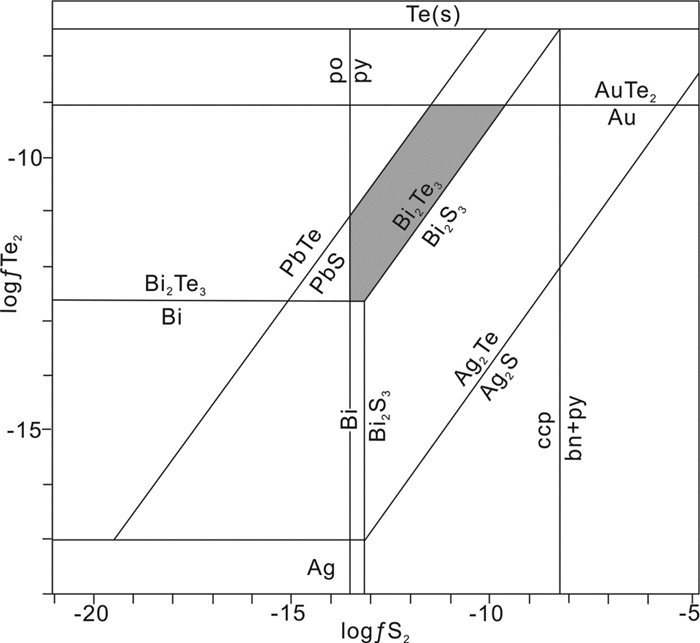
|
图 7 260℃条件下logfTe2-logfS2相图(据Afifi et al., 1988) po-磁黄铁矿;bn-斑铜矿;ccp-黄铜矿 Fig. 7 logfTe2 vs. logfS2 phase diagram at 260℃ (after Afifi et al., 1988) po-pyrrhotite; bn-bornite; ccp-chalcopyrite |
通常在一定的碲逸度条件下,低温有利于碲化物的形成。在相同的温度下,高fTe2/fS2对碲化物形成有利。在玲珑金矿区石英-硫化物脉矿体中,仅在石英-黄铁矿阶段发现碲化物大量产出。自然金及共生碲化物赋存于石英及黄铁矿裂隙及间隙中(图 8),自然金及碲化物的形成晚于黄铁矿。推测是由于黄铁矿的形成,消耗了热液体系中的硫,硫逸度下降,fTe2/fS2升高,导致碲化物形成。

|
图 8 自然金共生碲化物及黄铁矿接触关系显微照片 (a)自然金及碲化物分布于黄铁矿裂隙中;(b)碲化物溶蚀黄铁矿;(c、d)自然金和碲化物的固溶体分离结构 Fig. 8 Reflected light photomicrographs of contact relationship between native gold co-occurrence tellurides and pyrite (a) native gold and tellurides are distributed in the cracks of pyrite; (b) tellurides corrode pyrite; (c, d) solid solution separation structure of native gold and tellurides |
铋为亲地核地幔元素,在地壳中丰度较低(0.16×10-6)(Rudnick and Gao, 2014)。玲珑金矿区大量碲、铋矿物的出现,指示成矿物质源区可能需要有较高的碲和铋含量。研究表明玲珑金矿区与矿体时空关系较为密切的基性岩脉及围岩花岗岩中铋含量也很低(胡宝群等,2014),与地壳中铋的丰度相近。因此,玲珑金矿区铋矿物的大量富集可能指示成矿物质具有深成源区。碲同样是亲地核地幔元素,在地壳中丰度极低(5×10-9)(Wedepohl, 1995),与碲相关的热液矿床多与地幔或者深部岩浆活动有着密切的联系(Mao et al., 1995;毛景文和魏家秀,2000)。此外Hein et al.(2003)分析了大量洋底沉积物中的铁锰结核发现其中碲的含量具有极高的异常值(0.06×10-6~205×10-6)。据估计洋底铁锰结合中的碲资源量可达全球陆地的1.6倍(Hein et al., 2020)。结合其他稳定同位素等证据,本文认为洋壳俯冲过程中,富碲的洋底沉积物部分熔融可能是玲珑金矿区富碲的重要原因(Cook et al., 2009b; Harris et al., 2013)。这与Goldfarb and Santosh (2014)提出的胶东地区金矿床成矿物质来源与古太平洋板块俯冲作用有关的观点一致。
玲珑金矿区流体包裹体研究表明,其成矿期流体性质具有富CO2、中温、低盐度H2O-CO2-NaCl±CH4体系的特征(李碧乐等,2009;Wen et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2016a; Guo et al., 2017)。在这类性质流体中,金最有可能以金硫络合物如Au(HS)2-的形式运移(Pokrovski et al., 2009;Williams et al., 2009;Phillips and Powell, 2010)。由于物理化学条件变化,造成Au(HS)2-络合物的失稳导致金沉淀。但是Au(HS)2-在流体中的溶解度较低,流体中金络合物赋金能力是有限的,要形成明金尺度的大颗粒金是极其困难的,难以解释玲珑金矿区明金矿石中大颗粒自然金的成因。玲珑金矿区明金样品中的自然金普遍与碲-铋矿物紧密共生,自然金与碲-铋矿物形成平滑共结边或固溶体分离结构(图 8),Te、Bi等元素与金的成矿过程是密切相关的。金虽然有较高的熔点(1064℃),但在有低熔点亲硫元素(LMCE)的参与下,他们所形成的多金属熔体往往具有较低的熔点(Frost et al., 2002)。以Bi元素为例,自然铋具有低熔点(271℃),并且Bi熔体对Au具有极强的吸附能力。在含约13% Au的金-铋熔体中,其熔点可低至241℃(Törmänen and Koski, 2005)。在Au-Ag-Te体系中,当熔体中含有50% Au、15% Ag、和35% Te时,共晶熔体的熔点低至300℃左右(Cabri, 1965)。玲珑金矿区石英-黄铁矿阶段成矿温度或可满足体系中多金属熔点的要求。并且在较低氧逸度或富含CH4还原性热液体系中,铋熔体可与载金流体共存, 而金可有效地从热液流体分配进入到铋熔体相中(Tooth et al., 2008)。热力学模拟实验表明,含有约20×10-9的金热液流体可与含42%金的金-铋熔体共存。即使在含有0.2×10-9金的热液中,也将与含有约5%金的熔体共存(Tooth et al., 2011)。因此,即便金在流体中不饱和,在含有铋等LMCE存在的情况下,也可以形成有经济开采价值的矿床,可见LMCE熔体的赋金能力远超过含金热液流体的赋金能力(Ciobanu et al., 2009)。玲珑金矿区的成矿物理化学条件均满足低熔点多金属熔体的要求,结合观察到的与自然金共生的大量碲铋矿物,意味着金-银-碲-铋熔体是导致大颗粒可见金富集的关键。
玲珑金矿区明金矿石自然金成色较高,平均为894(表 1),通过对比发现玲珑金矿区自然金成色要略高于胶东其他金矿床自然金成色(表 3)。研究中发现大量与自然金共生的碲银矿、碲铋银矿,可能是由于含银碲化物的形成消耗了体系中的银含量(图 6),提高了自然金的成色。
|
|
表 3 胶东地区金矿床中自然金成色 Table 3 Gold fineness of gold deposits in Jiaodong gold province |
综上,玲珑金矿区碲、铋的来源与地幔具有较密切关系,与金共生的碲铋矿物大量出现显示了成矿物质深成、幔源的成因信息。碲、铋等元素在金的超级富集机制方面起到了不可忽视的作用,玲珑金矿区的大颗粒自然金的富集可能与金及碲、铋等元素形成低熔点多金属熔体有关。含银碲化物消耗了体系中Ag的含量,提高了自然金的成色。
6 结论(1) 玲珑金矿区明金矿石中的金矿物为含银自然金,主要以裂隙金、粒间金、包体金形式赋存,金成色整体较高,平均为894。共发现了五种与自然金共生的碲化物,分别是辉碲铋矿、碲铋矿、碲银矿、碲铋银矿和碲镍矿,其中辉碲铋矿含量最多。
(2) 碲、铋元素的大量富集,揭示了成矿物质来源具有深成幔源的信息,胶东地区碲、铋等物质来源与古太平洋板块俯冲相关。碲化物形成时成矿流体中碲逸度的范围为-12.6 < logfTe2 < -9.1,硫逸度的范围为-13.6 < logfS2 < -9.6。
(3) 玲珑矿区大颗粒自然金的富集,与碲、铋等元素结合形成低熔点金属熔体有关,含银碲化物的形成提高了自然金的成色。
致谢 论文的完成得益于邓军院士的指导。感谢俞良军老师对本文细心的审阅;感谢两位匿名审稿人对本文提出了详细的建设性意见。野外工作得到了山东黄金矿业(玲珑)有限公司的帮助和支持;核工业北京地质研究院邱林飞高级工程师、山东省地质科学研究院李增胜高级工程师和舒磊高级工程师在样品分析测试方面提供了帮助和支持,在此一并致谢。
Afifi AM, Kelly WC and Essene EJ. 1988. Phase relations among tellurides, sulfides, and oxides: I. Thermochemical data and calculated equilibria. Economic Geology, 83(2): 377-394
|
Cabri LJ. 1965. Phase relations in the Au-Ag-Te systems and their mineralogical significance. Economic Geology, 60(8): 1569-1606 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.60.8.1569
|
Charles N, Augier R, Gumiaux C, Monié P, Chen Y, Faure M and Zhu RX. 2013. Timing, duration and role of magmatism in wide rift systems: Insights from the Jiaodong Peninsula (China, East Asia). Gondwana Research, 24(1): 412-428 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.10.011
|
Ciobanu CL, Cook NJ, Damian F and Damian G. 2006. Gold scavenged by bismuth melts: An example from Alpine shear-remobilizates in the Highis Massif, Romania. Mineralogy and Petrology, 87(3-4): 351-384 DOI:10.1007/s00710-006-0125-9
|
Ciobanu CL, Cook NJ, Pring A, Brugger J, Danyushevsky LV and Shimizu M. 2009. 'Invisible gold' in bismuth chalcogenides. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(7): 1970-1999 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2009.01.006
|
Cook NJ and Ciobanu CL. 2004. Bismuth tellurides and sulphosalts from the Larga hydrothermal system, Metaliferi Mts., Romania: Paragenesis and genetic significance. Mineralogical Magazine, 68(2): 301-321 DOI:10.1180/0026461046820188
|
Cook NJ, Ciobanu CL and Mao JW. 2009a. Textural control on gold distribution in As-free pyrite from the Dongping, Huangtuliang and Hougou gold deposits, North China Craton (Hebei Province, China). Chemical Geology, 264(1-4): 101-121 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.02.020
|
Cook NJ, Ciobanu CL, Spry PG, Voudouris P and the Participants of IGCP-486. 2009b. Understanding gold-(silver)-telluride-(selenide) mineral deposits. Episodes, 32(4): 249-263 DOI:10.18814/epiiugs/2009/v32i4/002
|
Cooke DR and McPhail DC. 2001. Epithermal Au-Ag-Te mineralization, Acupan, Baguio district, Philippines: Numerical simulations of mineral deposition. Economic Geology, 96(1): 109-131
|
Deng J, Wang JG, Wei YG, Zhang ZQ, Lin JZ and Yan SL. 2007. Ores and gold-bearing characteristics in Xiejiagou gold deposit, Shandong Province. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 32(3): 373-380 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Dilek Y and Liang YY. 2017. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking: Lithospheric extension in the North China Craton, eastern Asia. GSA Bulletin, 129(11-12): 1379-1407 DOI:10.1130/B31609.1
|
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Santosh M and Yao EY. 2018. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Science Reviews, 182: 251-272 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.001
|
Deng J, Wang QF, Santosh M, Liu XF, Liang YY, Yang LQ, Zhao R and Yang L. 2020a. Remobilization of metasomatized mantle lithosphere: A new model for the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Mineralium Deposita, 55(2): 257-274 DOI:10.1007/s00126-019-00925-0
|
Deng J, Yang LQ, Groves DI, Zhang L, Qiu KF and Wang QF. 2020b. An integrated mineral system model for the gold deposits of the giant Jiaodong province, eastern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 208: 103274 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2020.103274
|
Deng J, Qiu KF, Wang QF, Goldfarb RJ, Yang LQ, Zi JW, Geng JZ and Ma Y. 2020c. In situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications for the geodynamic controls on ore formation in the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Economic Geology, 115(3): 671-685 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.4711
|
Du XJ and Zheng RH. 1989. The genetic implication and typomorphics of gold minerals in "Jiaojia-type" gold deposit. Gold, 10(11): 4-12 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Fan HR, Hu FF, Yang JH, Shen K and Zhai MG. 2005. Fluid evolution and large-scale gold metallogeny during Mesozoic tectonic transition in the eastern Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(5): 1317-1328 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Frost BR, Mavrogenes JA and Tomkins AG. 2002. Partial melting of sulfide ore deposits during medium- and high-grade metamorphism. The Canadian Mineralogist, 40(1): 1-18 DOI:10.2113/gscanmin.40.1.1
|
Goldfarb RJ, Groves DI and Gardoll S. 2001. Orogenic gold and geologic time: A global synthesis. Ore Geology Reviews, 18(1-2): 1-75
|
Goldfarb RJ and Santosh M. 2014. The dilemma of the Jiaodong gold deposits: Are they unique?. Geoscience Frontiers, 5(2): 139-153 DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2013.11.001
|
Goldfarb RJ, Qiu KF, Deng J, Chen YJ and Yang LQ. 2019. Orogenic gold deposits of China. SEG Special Publications, 22: 263-324
|
Goldfarb RJ, Mao JW, Qiu KF and Goryachev N. 2021. The great Yanshanian metallogenic event of eastern Asia: Consequences from one hundred million years of plate margin geodynamics. Gondwana Research, 100: 223-250 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2021.02.020
|
Groves DI, Goldfarb RJ, Gebre-Mariam M, Hagemann SG and Robert F. 1998. Orogenic gold deposits: A proposed classification in the context of their crustal distribution and relationship to other gold deposit types. Ore Geology Reviews, 13(1-5): 7-27 DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00012-7
|
Guo LN, Goldfarb RJ, Wang ZL, Li RH, Chen BH and Li JL. 2017. A comparison of Jiaojia- and Linglong-type gold deposit ore-forming fluids: Do they differ?. Ore Geology Reviews, 88: 511-533 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.12.003
|
Guo LN, Deng J, Yang LQ, Wang ZL, Wang SR, Wei YJ and Chen BH. 2020. Gold deposition and resource potential of the Linglong gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula: Geochemical comparison of ore fluids. Ore Geology Reviews, 120: 103434 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103434
|
Guo P, Santosh M and Li SR. 2013. Geodynamics of gold metallogeny in the Shandong Province, NE China: An integrated geological, geophysical and geochemical perspective. Gondwana Research, 24(3-4): 1172-1202 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.004
|
Hai DJ. 2013. Genetic mineralogy and deep ore prospecting of the Songjiazhuang gold deposit in Rushan County, Shandong Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 1-65 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Harris CR, Pettke T, Heinrich CA, Rosu E, Woodland S and Fry B. 2013. Tethyan mantle metasomatism creates subduction geochemical signatures in non-arc Cu-Au-Te mineralizing magmas, Apuseni Mountains (Romania). Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 366: 122-136 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2013.01.035
|
He DY, Qiu KF, Yu HC, Huang YQ, Ding ZJ and Shen Y. 2020. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous trachy-dacite from Mashan in the Jiaolai Basin, North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(12): 3705-3720 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.12.09
|
Hein JR, Koschinsky A and Halliday AN. 2003. Global occurrence of tellurium-rich ferromanganese crusts and a model for the enrichment of tellurium. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 67(6): 1117-1127 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(02)01279-6
|
Hein JR, Koschinsky A and Kuhn T. 2020. Deep-ocean polymetallic nodules as a resource for critical materials. Nature Reviews Earth & Environment, 1(3): 158-169
|
Hou ML, Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Ling HF and Zhao KD. 2007. Contrasting origins of Late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Implications for crustal thickening to delamination. Geological Magazine, 144(4): 619-631 DOI:10.1017/S0016756807003494
|
Hu BQ, Gao HD, Shen YK, Guo T, Lyu GX and Wu JC. 2014. Bi anomaly of the Dakaitou ore district in the Linglong gold mine and its indication significance. Geophysical and Geochemical Exploration, 38(6): 1134-1139 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Hu HL and Fan HR. 2018. The effect of water/rock interaction for the gold fineness of Jiaojia gold deposit. Gold Science and Technology, 26(5): 559-569 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li BL, Wang L, Huo L and Zhang H. 2009. Characteristics and genesis of ore-forming fluid in 52# vein group in Linglong gold mine, Jiaodong. Progress in Natural Science, 19(1): 51-60 (in Chinese)
|
Li HK, Zhuo CY, Shan W, Geng K and Liang TT. 2015. Mineral characterisitcs and its significance of Jiudian gold deposit in Shandong Province. Shandong Land and Resources, 31(8): 1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li QL, Chen FK, Yang JH and Fan HR. 2008. Single grain pyrite Rb-Sr dating of the Linglong gold deposit, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 34(3): 263-270 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2007.10.003
|
Liang YY, Liu XF, Liu LL, Zhou M, Li Y and He B. 2015. The micro-geochemical characteristics of gold from 'altered fracture-type' gold deposit in Jiaodong Peninsula. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(11): 3441-3454 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu JJ, Yang LB, Zhai DG and Wu J. 2013. Characteristics of some selenides and the physical-chemical condition of selenides and tellurides in the Jílové gold metallogenic concentration area, Czech Republic. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(1): 166-181 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu S, Zou HB, Hu RZ, Zhao JH and Feng CX. 2006. Mesozoic mafic dikes from the Shandong Peninsula, North China Craton: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Geochemical Journal, 40(2): 181-195 DOI:10.2343/geochemj.40.181
|
Mao JW, Chen YC and Wang PA. 1995. Geology and geochemistry of the Dashuigou tellurium deposit, western Sichuan, China. International Geology Review, 37(6): 526-546 DOI:10.1080/00206819509465416
|
Mao JW and Wei JX. 2000. Helium and argon isotopic components of fluid inclusions and tracing to the source of metallogenic fluids in the Dashuigou tellurium deposit of Sichuan Province. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 21(1): 58-61 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
McPhail DC. 1995. Thermodynamic properties of aqueous tellurium species between 25 and 350°. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(5): 851-866
|
Peng HW, Fan HR, Liu X, Wen BJ, Zhang YW and Feng K. 2021. New insights into the control of visible gold fineness and deposition: A case study of the Sanshandao gold deposit, Jiaodong, China. American Mineralogist, 106(1): 135-149 DOI:10.2138/am-2020-7475
|
Phillips GN and Powell R. 2010. Formation of gold deposits: A metamorphic devolatilization model. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 28(6): 689-718 DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2010.00887.x
|
Plotinskaya OY, Kovalenker VA, Seltmann R and Stanley CJ. 2006. Te and Se mineralogy of the high-sulfidation Kochbulak and Kairagach epithermal gold telluride deposits (Kurama Ridge, Middle Tien Shan, Uzbekistan). Mineralogy and Petrology, 87(3-4): 187-207 DOI:10.1007/s00710-006-0130-z
|
Pokrovski GS, Tagirov BR, Schott J, Hazemann JL and Proux O. 2009. A new view on gold speciation in sulfur-bearing hydrothermal fluids from in situ X-ray absorption spectroscopy and quantum-chemical modeling. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 73(18): 5406-5427 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2009.06.007
|
Qiu KF, Yu HC, Deng J, McIntire D, Gou ZY, Geng JZ, Chang ZS, Zhu R, Li KN and Goldfarb RJ. 2020a. The giant Zaozigou orogenic Au-Sb deposit in West Qinling, China: Magmatic or metamorphic origin?. Mineralium Deposit, 55(2): 345-362 DOI:10.1007/s00126-019-00937-w
|
Qiu KF, Goldfarb RJ, Deng J, Yu HC, Gou ZY, Ding ZJ, Wang ZK and Li DP. 2020b. Gold deposits of the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. SEG Special Publications, 23: 753-773
|
Rudnick RL and Gao S. 2014. Composition of the continental crust. In: Holland HD and Turekian KK (eds. ). Treatise on Geochemistry, Vol. 3. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1-64
|
Sai SX and Qiu KF. 2020. Ore-forming processes of the Rushan gold deposit, Jiaodong: Fluid immiscibility induced by episodic fluid pressure fluctuations. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(5): 1547-1566 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.14
|
Sai SX, Deng J, Qiu KF, Miggins DP and Zhang L. 2020. Textures of auriferous quartz-sulfide veins and 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Rushan gold deposit: Implications for processes of ore-fluid infiltration in the eastern Jiaodong gold province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 117: 103254 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103254
|
Shen JF, Li SR, Ma GG, Liu Y, Yu HJ and Liu HM. 2013. Typomorphic characteristics of pyrite from the Linglong gold deposit: Its vertical variation and prospecting significance. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(3): 55-75 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Song MC, Song YX, Cui SX, Jiang HL, Yuan WH and Wang HJ. 2011. Characteristic comparison between shallow and deep-seated gold ore bodies in Jiaojia superlarge gold deposit, northwestern Shandong Peninsula. Mineral Deposits, 30(5): 923-932 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Spry PG, Foster F, Truckle JS and Chadwick TH. 1997. The mineralogy of the Golden Sunlight gold-silver telluride deposit, Whitehall, Montana, U. S.A. Mineralogy and Petrology, 59(3-4): 143-164 DOI:10.1007/BF01161857
|
Sun HS, Han JB, Shen YK, Liu L, Leng SL, Xu C, Yang QM, Ge FJ, Ouyang SB and Deng X. 2016. Zircon (U-Th)/He age and its implication for post-mineralization exhumation degree of Linglong and Jiaojia goldfields, Northwest Jiaodong, China. Earth Science, 41(4): 644-654 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Tang HY, Zheng JP, Yu CM, Ping XQ and Ren HW. 2014. Multistage crust-mantle interactions during the destruction of the North China Craton: Age and composition of the Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Jiaodong Peninsula. Lithos, 190-191: 52-70 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.12.002
|
Tang J, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Gong B, Zha XP and Liu XM. 2008. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemical constraints on the tectonic affinity of the Jiaodong terrane in the Sulu orogen, China. Precambrian Research, 161(3-4): 389-418 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.09.008
|
Tombros S, Seymour KS and Williams-Jones AE. 2010. Controls on tellurium in base, precious, and telluride minerals in the Panormos bay Ag-Au-Te deposits, Tinos Island, Cyclades, Greece. Economic Geology, 105(6): 1097-1111 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.105.6.1097
|
Tomkins AG, Pattison DRM and Frost BR. 2007. On the initiation of metamorphic sulfide anatexis. Journal of Petrology, 48(3): 511-535
|
Tooth B, Brugger J, Ciobanu C and Liu WH. 2008. Modeling of gold scavenging by bismuth melts coexisting with hydrothermal fluids. Geology, 36(10): 815-818 DOI:10.1130/G25093A.1
|
Tooth B, Ciobanu CL, Green L, O'Neill B and Brugger J. 2011. Bi-melt formation and gold scavenging from hydrothermal fluids: An experimental study. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(19): 5423-5443 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2011.07.020
|
Törmänen TO and Koski RA. 2005. Gold enrichment and the Bi-Au association in pyrrhotite-rich massive sulfide deposits, Escanaba trough, Southern Gorda Ridge. Economic Geology, 100(6): 1135-1150 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.100.6.1135
|
Tu GC. 2000. A preliminary discussion on the mineralization of tellurium. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 19(4): 211-214 (in Chinese)
|
Voudouris PC, Spry PG, Mavrogonatos C, Sakellaris GA, Bristol SK, Melfos V and Fornadel AP. 2013. Bismuthinite derivatives, lillianite homologues, and bismuth sulfotellurides as indicators of gold mineralization in the Stanos shear-zone related deposit, Chalkidiki, Northern Greece. The Canadian Mineralogist, 51(1): 119-142 DOI:10.3749/canmin.51.1.119
|
Wang ZL, Yang LQ, Deng J, Santosh M, Zhang HF, Liu Y, Li RH, Huang T, Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2014. Gold-hosting high Ba-Sr granitoids in the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 95: 274-299 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.03.001
|
Wedepohl KH. 1995. The composition of the continental crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(7): 1217-1232 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
|
Wei YJ, Qiu KF, Guo LN, Liu XD, Tang L, Shi QF and Gao XK. 2020. Characteristics and evolution of ore-fluids of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit, Jiaodong gold province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(6): 1821-1832 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.06.11
|
Wen BJ, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Pirajno F and Yang KF. 2015. Genesis of two different types of gold mineralization in the Linglong gold field, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and stable isotope. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 643-658 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.03.018
|
White JL, Orr RL and Hultgren R. 1957. The thermodynamic properties of silver-gold alloys. Acta Metallurgica, 5(12): 747-760 DOI:10.1016/0001-6160(57)90078-0
|
Williams-Jones AE, Bowell RJ and Migdisov AA. 2009. Gold in solution. Elements, 5(5): 281-287 DOI:10.2113/gselements.5.5.281
|
Yang HY, Wang SH, Song XL, Pan HD and Ma PC. 2011. Gold occurrence of Jiaojia gold mine in Shandong Province. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 21(9): 2072-2077 DOI:10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60975-8
|
Yang KF, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Wilde SA, Lan TG, Lu LN and Liu YS. 2012. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of Late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton. Lithos, 146-147: 112-127 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.035
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang J, Gao BF and Wang ZL. 2014a. 40Ar/39Ar geochronological constraints on the formation of the Dayingezhuang gold deposit: New implications for timing and duration of hydrothermal activity in the Jiaodong gold province, China. Gondwana Research, 25(4): 1469-1483 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.07.001
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Guo LN, Song MC and Zheng XL. 2014. Mesozoic gold metallogenic system of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2447-2467 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Li XZ and Li JL. 2016a. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 585-602 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.08.021
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Guo LN, Li RH, Groves DI, Danyushevsky LV, Zhang C, Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2016b. Relationships between gold and pyrite at the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Implications for gold source and deposition in a brittle epizonal environment. Economic Geology, 111(1): 105-126 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.111.1.105
|
Yang LQ, Dilek Y, Wang ZL, Weinberg RF and Liu Y. 2018. Late Jurassic, high Ba-Sr Linglong granites in the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Lower crustal melting products in the eastern North China Craton. Geological Magazine, 155(5): 1040-1062 DOI:10.1017/S0016756816001230
|
Yang QY, Santosh M, Shen JF and Li SR. 2014b. Juvenile vs. recycled crust in NE China: Zircon U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotope and an integrated model for Mesozoic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula. Gondwana Research, 25(4): 1445-1468
|
Zeng QW, Ma XH, Zhang XY and Shu QH. 2020. Mineralogical characteristics of gold-bearing minerals and occurrence state of gold in the Qilishan gold deposit in the Jiaodong Peninsula, Shandong Province, China. Acta Mineralogica Sinica, 40(6): 714-722 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhai MG and Santosh M. 2013. Metallogeny of the North China Craton: Link with secular changes in the evolving Earth. Gondwana Research, 24(1): 275-297 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.007
|
Zhang L, Weinberg RF, Yang LQ, Groves DI, Sai SX, Matchan E, Phillips D, Kohn BP, Miggins DP, Liu Y and Deng J. 2020. Mesozoic orogenic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A focused event at 120±2Ma during cooling of pregold granite intrusions. Economic Geology, 115(2): 415-441 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.4716
|
Zhang QB, Zhang P, Xu ZH, Liu XD, Zhang LL, Wang B and Wang SS. 2018. Geological characteristics and genesis of Yanjiatuan gold deposit in Muping, Shandong Province. Gold Science and Technology, 26(3): 279-288 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang ZQ, Lai Y and Chen YJ. 2007. Fluid inclusion study of the Linglong gold deposit, Shandong Province, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(9): 2207-2216 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao R, Wang QF, Deng J, Santosh M, Liu XF, Liang YY and Cheng HY. 2019. Characterizing episodic orogenesis and magmatism in eastern China based on detrital zircon from the Jiaolai Basin. American Journal of Science, 319(6): 500-525 DOI:10.2475/06.2019.03
|
邓军, 王建国, 韦延光, 张志启, 林吉照, 闫顺玲. 2007. 山东谢家沟金矿床矿石与金矿物特征. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 32(3): 373-380. |
杜心君, 郑若惠. 1989. "焦家式"金矿床金矿物的标型特征及成因意义. 黄金, 10(11): 4-12. |
范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨进辉, 沈昆, 翟明国. 2005. 胶东中生代构造体制转折过程中流体演化和金的大规模成矿. 岩石学报, 21(5): 1317-1328. |
海东婧. 2013. 山东乳山宋家庄金矿成因矿物学与深部远景研究. 硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-65
|
何登洋, 邱昆峰, 于皓丞, 黄雅琪, 丁正江, 申颖. 2020. 华北克拉通胶莱盆地马山地区早白垩世粗面英安岩岩石成因. 岩石学报, 36(12): 3705-3720. DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.12.09 |
胡宝群, 高海东, 申玉科, 郭涛, 吕古贤, 武际春. 2014. 玲珑金矿大开头矿区Bi特征及指示意义. 物探与化探, 38(6): 1134-1139. |
胡换龙, 范宏瑞. 2018. 水/岩相互作用对焦家金矿金成色的影响. 黄金科学技术, 26(5): 559-569. |
李碧乐, 王力, 霍亮, 张晗. 2009. 胶东玲珑金矿52#脉群成矿流体特征及成因. 自然科学进展, 19(1): 51-60. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2009.01.007 |
李洪奎, 禚传源, 单伟, 耿科, 梁太涛. 2015. 山东旧店金矿金矿物特征及其意义. 山东国土资源, 31(8): 1-6. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2015.08.002 |
梁亚运, 刘学飞, 刘龙龙, 周勉, 李, 何碧. 2015. 胶东蚀变岩型金矿金矿物微区地球化学特征. 岩石学报, 31(11): 3441-3454. |
刘家军, 杨隆勃, 翟德高, 吴杰. 2013. 捷克Jílové金矿集区中硒矿物的特征与硒化物-碲化物的形成物理化学条件. 地学前缘, 20(1): 166-181. |
毛景文, 魏家秀. 2000. 大水沟碲矿床流体包裹体的He、Ar同位素组成及其示踪成矿流体的来源. 地球学报, 21(1): 58-61. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.01.009 |
赛盛勋, 邱昆峰. 2020. 胶东乳山金矿床成矿过程: 周期性压力波动诱发的流体不混溶. 岩石学报, 36(5): 1547-1566. |
申俊峰, 李胜荣, 马广钢, 刘艳, 于洪军, 刘海明. 2013. 玲珑金矿黄铁矿标型特征及其大纵深变化规律与找矿意义. 地学前缘, 20(3): 55-75. |
宋明春, 宋英昕, 崔书学, 姜洪利, 袁文花, 王化江. 2011. 胶东焦家特大型金矿床深、浅部矿体特征对比. 矿床地质, 30(5): 923-932. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2011.05.013 |
孙华山, 韩静波, 申玉科, 刘浏, 冷双良, 许冲, 杨巧梅, 葛风建, 欧阳淑冰, 邓旭. 2016. 胶西北玲珑、焦家金矿田锆石(U-Th)/He年龄及其对成矿后剥露程度的指示. 地球科学, 41(4): 644-654. |
涂光炽. 2000. 初论碲的成矿问题. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 19(4): 211-214. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2000.04.001 |
魏瑜吉, 邱昆峰, 郭林楠, 刘向东, 汤磊, 史启发, 高学坎. 2020. 胶东大尹格庄金矿床成矿流体特征与演化. 岩石学报, 36(6): 1821-1832. |
杨立强, 邓军, 王中亮, 张良, 郭林楠, 宋明春, 郑小礼. 2014. 胶东中生代金成矿系统. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2447-2467. |
曾庆文, 马星华, 张馨月, 舒启海. 2020. 胶东七里山金矿床载金矿物的矿物学特征和金赋存状态. 矿物学报, 40(6): 714-722. |
张琪彬, 张朋, 徐忠华, 刘向东, 张亮亮, 王斌, 王珊珊. 2018. 山东牟平阎家疃金矿床地质特征及成因探讨. 黄金科学技术, 26(3): 279-288. |
张祖青, 赖勇, 陈衍景. 2007. 山东玲珑金矿流体包裹体地球化学特征. 岩石学报, 23(9): 2207-2216. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.09.019 |
 2022, Vol. 38
2022, Vol. 38


