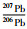2. 中国地质科学院矿产资源研究所,自然资源部成矿作用与资源评价重点实验室,北京 100037;
3. 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所,岩石圈演化国家重点实验室,北京 100029
2. MNR Key Laboratory of Metallogeny and Mineral Assessment, Institute of Mineral Resources, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Lithospheric Evolution, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China
胶东地区已累积探明黄金储量接近5000t(宋明春等,2019),是我国目前最大的金矿产区,也是环太平洋成矿系统的重要组成部分之一(Goldfarb et al., 2014; 范宏瑞等,2021)。该地区在中生代被卷入了复杂的构造演化过程,包括以下4期构造事件:(1)扬子板块与华北板块在三叠纪时期发生陆-陆碰撞及后续的大陆深俯冲作用,形成苏鲁超高压变质带(Li et al., 1993; Ye et al., 2000; Zheng, 2008);(2)郯庐断裂带自三叠纪以来发生了多次左旋走滑运动,引发构造-岩浆(流体)活动及成矿过程(邓军等,2000;朱光等,2009);(3)晚三叠世发生岩石圈的减薄(徐义刚等,2009;杨进辉和吴福元,2009;朱日祥等,2011;Wu et al., 2019);(4)至少在侏罗纪时期,中国东部就开始受到太平洋板块俯冲、回撤作用的影响(孙卫东等,2008; Jiang et al., 2010),胶东地区一系列白垩纪岩浆活动都与此有着密切的关系(Deng et al., 2017)。这些重大地质事件在胶东地区先后叠加,导致该区深部构造体制在中生代发生转换(邓军等,2006;宋明春,2014)、岩石圈地幔遭受破坏和改造(徐义刚等,2009;朱日祥等,2011;Wu et al., 2019),而同时期强烈的岩浆活动则是对整个构造演化的响应(霍腾飞等,2016)。
复杂的地质演化过程给讨论该地区金矿的物质来源及成矿过程提出了挑战,目前大多数学者认为该地区大规模成矿作用主要发生在110~130Ma(Yang and Zhou, 2001; 陈衍景等,2004;Deng et al., 2015; 朱日祥等,2015;范宏瑞等,2021)。然而,在胶东地区广泛发育的晚侏罗世花岗岩却与金矿有着密切的空间关系(Guo et al., 2013; Deng and Wang, 2016),是该区富产金矿的重要地质背景。例如,胶北玲珑型花岗岩是该区最主要的赋矿围岩之一(Wen et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2016a, b; Zhang et al., 2020)。前人对这些花岗岩的年代学、矿物学、地球化学等方面进行了大量的研究,对该期花岗岩的特征及成因进行了广泛深入的讨论(Wang et al., 1998; 苗来成等,1998; 郭敬辉等,2005; Hou et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014, 2018; Ma et al., 2013; 黄涛等,2014; 刘跃等,2014; Zhao et al., 2016; Deng et al., 2018; He et al., 2021)。已有的研究显示,这些岩体可能形成于相同的构造体制。胶东东部晚侏罗世花岗岩体中赋存的金矿数量明显少于胶北地体,因此前人对于成矿作用的研究主要集中在胶北金矿区,而对胶东东部出露的同期花岗岩体的研究相对较少。显然,开展胶东东部及西北部同一时期岩体的差异性研究,可对研究该区的金成矿作用提供重要的助力。
本文在前人研究的基础上,对胶东地区东部出露的两个晚侏罗世花岗岩体进行了锆石U-Pb和Hf同位素分析,并对比了出露在胶东几个不同构造单元内的同时代花岗岩体的继承锆石和Hf同位素特征,探讨了该期花岗岩的源区及成因,为研究胶东地区在侏罗纪时期的岩浆活动、构造演化及其对金成矿的贡献提供一定的制约。
1 区域地质背景及样品采集胶东地区位于华北克拉通的东南缘,西侧与鲁西地块界于郯庐断裂,南侧为苏鲁超高压变质带(图 1)。根据岩石和构造特征,胶东地区可分为三个构造单元:苏鲁超高压变质地体、胶北地体和胶莱盆地(张增奇等,2014;潘素珍等,2015)。
|
图 1 胶东地区地质简图(据李洪奎等,2011; Deng et al., 2015修改) Fig. 1 Geological sketch map of Jiaodong Peninsula (modified after Li et al., 2011; Deng et al., 2015) |
苏鲁超高压变质地体位于扬子板块北缘,形成于三叠纪华北板块与扬子板块陆-陆碰撞及后续的深俯冲作用。地体内广泛发育超高压变质岩,其原岩年龄在780~740Ma(Liu et al., 2006; 薛怀民等,2006; Zong et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2013; 高名迪等,2018)。胶北地体位于华北板块东南缘,基底岩石主要包括太古代TTG片麻岩和胶东岩群、古元古代荆山群和粉子山群以及新元古代蓬莱群(Tang et al., 2007; Tam et al., 2011; Shan and Zhai, 2020)。TTG片麻岩和胶东岩群的原岩年龄主要为~2.9Ga、~2.7Ga、~2.5Ga(Jahn et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2013),并普遍遭受~1.8Ga的角闪岩相区域变质作用(Tang et al., 2007)。荆山群和粉子山群,主要岩性为黑云斜长片麻岩、石榴夕线黑云片岩、黑云变粒岩、斜长角闪岩和大理岩等,直接覆盖在TTG片麻岩和胶东岩群之上(Wang et al., 1998)。蓬莱群为一套浅变质沉积岩,岩性主要为大理岩、板岩、石英岩、千枚岩和泥灰岩等,不整合覆盖在粉子山群之上(Li et al., 2007)。胶莱盆地是一个形成于中生代期间的伸展断陷盆地(张岳桥等,2008),盆地基底主要为新太古代胶东岩群、古元古代荆山群和粉子山群等变质岩系,盖层则主要由白垩系莱阳群、青山群及王氏群等陆相沉积岩及部分火山岩、火山碎屑岩等构成(邹为雷等,2010)。
中生代花岗岩在胶东地区发育广泛,根据锆石U-Pb年代学研究可将其分为三期:晚三叠世225~205Ma(Chen et al., 2003; 郭敬辉等,2005;曾令森等,2007)、晚侏罗世160~150Ma(苗来成等,1998;郭敬辉等,2005;Zhang et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012; Ma et al., 2013; Yang et al., 2014; He et al., 2021)和早白垩世130~110Ma(Hou et al., 2007; Goss et al., 2010; Li et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012; 李增达等,2018; Gao et al., 2019; 董学等,2020; 宋英昕等,2020)。晚三叠世花岗岩主要出露在苏鲁超高压变质地体中,岩性以碱性的正长花岗岩为主,是俯冲的扬子陆壳板片断离引发的岩石圈地幔部分融熔的结果(郭敬辉等,2005;曾令森等,2007;陈竟志和姜能,2011)。晚侏罗世花岗岩在该区最为发育,包括胶北地体的玲珑和栾家河岩体,胶东东部的昆嵛山、垛崮山和文登岩体。该期花岗岩主要包括偏铝质到过铝质黑云母花岗岩、二长花岗岩和花岗闪长岩,且含有中生代印支期变质锆石(200~250Ma)及少量前寒武纪继承锆石,属于地壳重熔花岗岩(郭敬辉等,2005; Zhang et al., 2010; Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014)。早白垩世花岗岩主要包括郭家岭型似斑状花岗闪长岩-二长花岗岩,伟德山型(或称艾山型)似斑状二长花岗岩,崂山型带晶洞碱长花岗岩-二长花岗岩。岩体局部可见暗色包体或团块,地球化学特征显示具有壳幔岩浆混合成因的特点(Hou et al., 2007; Goss et al., 2010; Yang et al., 2012; Yan and Shi, 2014; 李增达等,2018; Gao et al., 2019)。
本次研究的样品为出露在胶东东部的晚侏罗世花岗岩,包括位于苏鲁超高压地体内的文登岩体和位于苏鲁超高压地体与胶北地体交界处的垛崮山岩体(图 1b),所有样品均采自新鲜露头,未经历明显风化。其中文登岩体包括何家店花岗岩和架子山花岗岩。何家店花岗岩样品(SD06-10-01)为粗粒二长花岗岩,取自文登市东部的何家店采石场(N37°12′6″、E122°8′55″)。架子山花岗岩包括含斑中粗粒二长花岗岩(SD06-11-01)和正长花岗岩(SD06-11-05),取自文登市东南部的架子山(N37°9′5″、E122°6′17″)。垛崮山岩体包括弱片麻状花岗闪长岩(SD06-19-01)和呈脉状产出的正长花岗岩(SD06-19-04),二者均取自乳山市东南部的窗龙山(N36°53′14″、E121°44′45″)。
2 分析方法在野外观察和室内岩相学研究的基础上,选取新鲜的样品进行了锆石挑选和制靶,并在中国地质科学院离子探针中心进行锆石阴极发光(CL)图像的采集。锆石U-Pb定年是在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所岩石圈演化国家重点实验室的激光烧蚀等离子体质谱仪(LA-ICPMS)上完成。激光剥蚀系统采用GeoLasPlus型193nm ArF准分子激光器,ICPMS为Agilent7500a型四极杆等离子体质谱仪。激光束斑直径为32μm,年龄计算时以标准锆石91500和GJ-1为外标进行同位素比值校正,元素含量以国际标样NIST610为外标,Si为内标计算。测试数据采用204Pb进行普通铅校正,单个测试点的同位素比值误差均为1σ。详细的仪器运行条件和分析流程见谢烈文等(2008)。数据处理采用Glitter软件利用标准锆石91500线性内插的方式对分析时间相关的U-Th-Pb进行同位素比值校正。最后锆石的U-Pb谐和图和年龄加权平均计算均采用Isoplot软件(Ludwig, 2003)完成。
锆石Hf同位素测定是在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所岩石圈演化国家重点实验室的激光剥蚀多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICPMS)上完成。激光剥蚀系统为GeolasPlus型193nm ArF准分子激光器,多接收等离子体质谱仪为Neptune Plus。实验采用的束斑大小为40~50μm,直接覆盖在锆石U-Pb定年的测定部位,本次测试采用锆石标样Mud-Tank和FM0411为分析标样,仪器运行条件及详细分析过程见Wu et al. (2006a)。
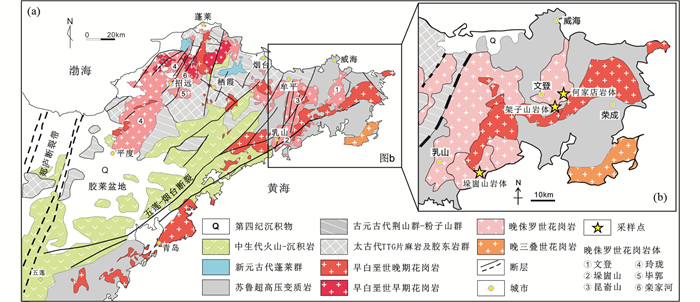
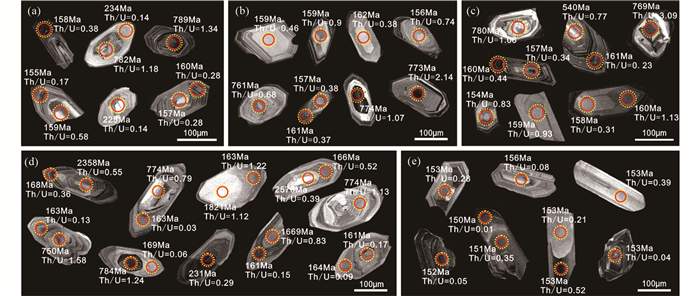
3 分析结果 3.1 锆石U-Pb年龄 3.1.1 文登岩体何家店二长花岗岩样品(SD06-10-01)中的锆石大部分为短柱状晶型,粒径50~150μm。阴极发光图像(图 2a)显示大部分锆石颗粒存在振荡环带,显示岩浆成因特点。部分锆石具有核-边结构,核部在形态和结构上与边部的新生岩浆锆石存在明显区别,为继承锆石。还有部分锆石的边部阴极发光为亮白色,无环带结构,显示出变质增生成因的特点。对样品中26颗锆石进行了31个点的测定,测定结果见表 1和图 3a。其中16个新生岩浆锆石分析点的U含量和Th/U比值分别为72×10-6~1413×10-6和0.26~1.13,谐和年龄范围在155~162Ma,加权平均为158±1Ma。5个继承锆石的U含量和Th/U比值分别为54×10-6~721×10-6和0.36~1.44,谐和年龄在770~789Ma,加权平均为782±9Ma。2个变质增生锆石的Th/U比值为0.14,谐和年龄为225±5Ma和234±4Ma。剩余的锆石测试点年龄不谐和,但均位于780~160Ma的U-Pb不一致线附近,为新元古代继承锆石在晚侏罗世岩浆热事件中发生Pb丢失造成。
|
图 2 代表性锆石的阴极发光图像及U-Pb定年结果 红色圆代表U-Pb定年位置,黄色圆代表Hf同位素测定位置 Fig. 2 Typical zircon CL images and the U-Pb ages Rounded circles indicate the locations of U-Pb (red circle) and Hf (yellow circle) analyses |
|
|
表 1 文登岩体和垛崮山岩体LA-ICPMS锆石U-Pb定年结果 Table 1 LA-ICPMS zircon U-Pb dating results for Wendeng and Duogushan plutons |
|
图 3 文登岩体和垛崮山岩体的锆石U-Pb谐和图 Fig. 3 U-Pb concordia diagrams of zircons from Wendeng and Duogushan plutons |
架子山二长花岗岩(SD06-11-01)样品中锆石大部分为短柱状晶型,粒径100~200μm。阴极发光图像(图 2b)显示大部分锆石颗粒具有振荡环带或板状环带,具有岩浆成因的特点。与何家店花岗岩中的锆石类似,一些锆石颗粒的核部也含有继承锆石。对样品中25颗锆石进行了30个点的测定,结果见表 1和图 3b、c。其中20个新生岩浆锆石分析点的U含量和Th/U比值分别为54×10-6~745×10-6和0.19~1.60,谐和年龄范围在147~167Ma,加权平均为159±2Ma。继承锆石的U含量和Th/U比值分别为68×10-6~672×10-6和0.34~2.14。其中5个继承锆石给出了773±8Ma的加权平均年龄,另有一个继承锆石谐和年龄为2535±37Ma。剩余锆石测试点的年龄不谐和,位于780~160Ma的U-Pb不一致线附近,为新元古代继承锆石在晚侏罗世岩浆热事件中发生Pb丢失造成。
架子山正长花岗岩(SD06-11-05)样品中锆石大部分为短柱状-长柱状晶型,粒径100~200μm。阴极发光图像(图 2c)显示大部分锆石颗粒具有振荡环带或板状环带,属于岩浆成因。部分新生岩浆锆石的内部也含有继承锆石核。对样品中的18颗锆石进行了24个点的测定,测定结果见表 1和图 3d。其中17个新生岩浆锆石分析点的U含量和Th/U比值为53×10-6~2091×10-6和0.19~1.13,谐和年龄范围在154~165Ma,加权平均为159±1Ma。3个继承锆石的U含量和Th/U比值为147×10-6~402×10-6和0.91~3.09,谐和年龄范围在769~784Ma,加权平均为776±11Ma。剩余锆石分析点的年龄不谐和,位于780~160Ma的U-Pb不一致线附近,是继承锆石在晚侏罗世岩浆热事件中发生Pb丢失造成。
3.1.2 垛崮山岩体垛崮山花岗闪长岩(SD06-19-01)中的锆石大部分为短柱状-长柱状,粒径150~250μm。阴极发光图像(图 2d)显示大部分锆石具有核-边结构,少数锆石还可识别出核-幔-边结构。锆石的边部具有较宽的振荡环带,显示岩浆成因特点。核部具有熔蚀结构,部分核部仍保留原始的环带结构。对样品中的34颗锆石进行了50个点的测定,测定结果见表 1和图 3e-g。其中23个新生岩浆锆石分析点的U含量和Th/U比值为77×10-6~3486×10-6和0.03~1.22,谐和年龄范围在160~169Ma,加权平均为164±2Ma。继承锆石的U含量和Th/U比值为56×10-6~3170×10-6和0.08~1.58。其中5颗继承锆石给出743~784Ma的谐和年龄,3颗继承锆石给出1669~1820Ma的谐和年龄,2个继承锆石测点给出了两个最老的谐和年龄分别为2358±20Ma和2576±39Ma。6个变质成因锆石测点的Th/U比值为0.08~0.26,其谐和年龄范围在224~243Ma,加权平均为230±7Ma。剩余锆石分析点的年龄不谐和,均位于谐和线右侧,应该是在中生代变质事件或岩浆事件时发生Pb丢失造成的。
垛崮山正长花岗岩(SD06-19-04)中的锆石大部分为长柱状晶型,粒径150~300μm。阴极发光显示它们具有振荡环带或板状环带(图 2e),为岩浆成因。对15颗岩浆锆石进行了17个点的测定,测定结果见表 1和图 3h。17个新生岩浆锆石分析点的U含量和Th/U比值分别为254×10-6~3048×10-6和0.01~1.01,谐和年龄范围在150~158Ma,加权平均为153±1Ma。
3.2 锆石Hf同位素|
|
表 2 文登岩体和垛崮山岩体锆石Hf同位素数据 Table 2 Hf isotopic data of zircons from Wendeng and Duogushan plutons |
|
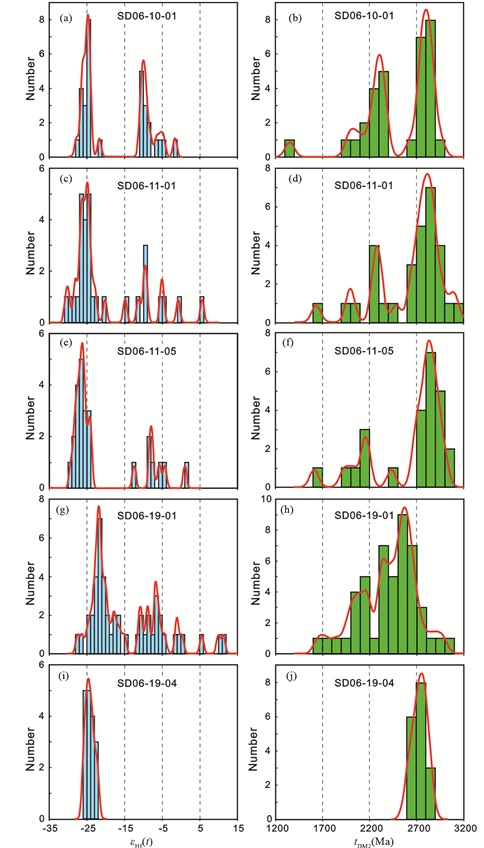
图 4 文登岩体和垛崮山岩体的锆石Hf同位素组成 Fig. 4 Zircon Hf isotopic compositions of Wendeng and Duogushan plutons |
何家店二长花岗岩(SD06-10-01)的新生岩浆锆石εHf(t)=-27.8~-24.1 (平均值-25.6,n=16),tDM2=2728~2961Ma。13颗继承锆石εHf(t)=-10.9~-4.7,tDM2=1978~2367Ma。2颗变质锆石εHf(t)=-24.9~-21.7,tDM2=2630~2837Ma。
架子山二长花花岗岩(SD06-11-01)的新生岩浆锆石εHf(t)=-30.7~-20.3(平均值-25.9,n=20),tDM2=2494~3145Ma。7颗继承锆石εHf(t)=-11.4~-0.7,tDM2=1626~2298Ma。另外1颗年龄为~2535Ma的继承锆石核测试点εHf(t)=5.7,tDM2=2675Ma。
架子山正长花岗岩(SD06-11-05)的新生岩浆锆石εHf(t)=-29.4~-24.1 (平均值-26.7,n=17),tDM2=2730~3059Ma。7个继承锆石测点εHf(t)=-12.5~1.0,tDM2=1616~2467Ma。
3.2.2 垛崮山岩体垛崮山花岗闪长岩(SD06-19-01)的新生岩浆锆石εHf(t)=-27.5~-17.9 (平均值-22.1,n=23),tDM2=2344~2947Ma。18颗继承锆石εHf(t)=-16.1~11.3,tDM2=1654~3021Ma。6颗变质锆石εHf(t)=-21.9~-9.2,tDM2=1845~2653Ma。
垛崮山正长花岗岩(SD06-19-04)的新生岩浆锆石εHf(t)=-25.9~-22.2 (平均值-24.2,n=17),tDM2=2606~2838Ma。
4 讨论 4.1 文登岩体和垛崮山岩体的形成时代本次研究获得文登岩体3个样品及垛崮山岩体花岗闪长岩样品的岩浆锆石年龄分别为158±1Ma、159±2Ma、159±1Ma和164±2Ma,表明文登岩体和垛崮山岩体均形成于晚侏罗世(~160Ma)。侵入到垛崮山花岗闪长岩体的正长花岗岩脉体(SD06-19-04)获得了较年轻的年龄(153±1Ma),与北部的昆嵛山岩体定年结果一致(郭敬辉等,2005;Zhao et al., 2016; He et al., 2021),代表稍晚一期花岗岩浆活动。郭敬辉等(2005)通过SHRIMP锆石U-Pb定年获得文登岩体和垛崮山岩体的年龄分别为160±3Ma和161±1Ma。Zhao et al.(2016)对文登东部花岗岩的锆石U-Pb定年获得的年龄较为年轻,为151±1Ma。本文的结果与郭敬辉等(2005)及Zhao et al.(2016)的结果在误差范围内一致,表明胶东地区东部在晚侏罗世也存在一期较强的岩浆作用。
4.2 晚侏罗世花岗岩的源区――继承锆石的U-Pb年龄证据花岗岩通常产生于深部地壳物质的重熔,因此岩石中常残留有难熔的壳源物质,尤其是锆石。因为锆石具有极高的矿物学稳定性,即使在经历多期热事件后,仍能够以继承锆石的形式存在于新生的岩石中,同时能够保留寄主岩石的一些信息(黄涛等,2014)。本次研究的文登岩体和垛崮山岩体中的继承锆石主要集中在新元古代以及三叠纪两个时期,此外还有部分继承锆石具有1700~1800Ma、~2400Ma、~2500Ma热事件的年龄记录。这些继承锆石的年龄数据,不仅能为两个岩体的源区提供限定,还可以为华北、扬子两个陆块的碰撞及演化提供重要的依据。
华北板块和扬子板块在中生代碰撞汇聚以前,各自经历了不同的岩浆-热事件(Bruguier et al., 1997; Hacker et al., 1998, 2000; Chen et al., 2003; Li et al., 2005a; Zheng et al., 2005, 2006; Tang et al., 2007)。新元古代是扬子板块所在的华南板块发生生长和再造的重要时代,并且扬子板块北缘广泛发育新元古代(750~820Ma)的岩浆活动(Zhou et al., 2002, 2006; Li et al., 2003a, b; Zheng et al., 2004; Wang et al., 2006; Wu et al., 2006b)。而在华北板块南缘则没有新元古代岩浆活动的记录,因此新元古代的岩浆岩年龄也是扬子板块区别于华北板块的一个重要特征(Hacker et al., 1998; 郑永飞,2003; Zheng et al., 2004; Tang et al., 2007, 2008)。文登岩体和垛崮山岩体均含有较多新元古代(700~800Ma)的继承锆石,这表明两个岩体的岩浆源区主要来自扬子板块。除新元古代年龄外,这两个岩体还含有许多三叠纪变质成因锆石,这与大别-苏鲁超高压变质带的变质峰期时代(~230Ma)(Liu et al., 2004, 2006; Wu et al., 2006c)相吻合,而且大别-苏鲁超高压变质岩的原岩年龄也是新元古代(740~780Ma)(Zheng et al., 2004; Tang et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2010)。样品中有部分核-边结构的锆石,它们核部的继承锆石为新元古代(~780Ma)的谐和年龄,边部变质锆石为三叠纪(~230Ma)的谐和年龄(图 2a),这与大别-苏鲁超高压变质岩中发现的核-边结构的锆石特征(Zheng, 2008)一致。这些锆石年代学特征表明,文登岩体和垛崮山岩体的主要源区物质是经历了超高压变质作用改造的扬子陆块。
华北板块前寒武纪基底岩石主要包括太古代花岗质片麻岩以及古元古代变质火山-沉积岩(Zhai et al., 2005; Zhao et al., 2005)。花岗质片麻岩的原岩年龄范围在2900~2500Ma,峰值范围是2900~2700Ma和2600~2500Ma(Zhai and Liu, 2003; Zhao et al., 2005),并主要经历了1900~1800Ma的区域角闪岩到麻粒岩相的变质作用(Zhai and Liu, 2003; Zhai et al., 2005; Santosh et al., 2007)。李江海等(2006)统计了华北板块近500件高精度的锆石U-Pb年龄数据,结果显示华北板块基底经历了多期次的构造热事件,大陆生长演化过程中重大的热事件幕为2700~2600Ma、2520Ma、2400Ma、2400~2250Ma、1950Ma、1840Ma,其中2520Ma、1840Ma分别对应于华北太古宙/元古宙和古元古代/中元古代地层界线,是最为显著的构造热事件。包括全岩Sm-Nd、锆石U-Pb等多种同位素年代学研究(Kröner et al., 1998; 金文山和管爱莲,1999; 李江海等,2000; 杨进辉等,2005)也证明~2500Ma和~1800Ma是华北板块地壳增生的两个主要时代,而且2400~2100Ma范围的热事件年龄,也仅在华北板块出现(路孝平等, 2004; Li et al., 2005b; Wan et al., 2006)。胶北地体的花岗质片麻岩同样显示有~2500Ma的热事件年龄(Tang et al., 2007; Jahn et al., 2008; Liu et al., 2013; 万渝生等,2017)。本次研究的文登岩体含有~2500Ma的继承锆石,垛崮山岩体含有~2500Ma和~2400Ma以及~1700Ma的继承锆石,表明文登和垛崮山两个岩体的岩浆源区有部分华北板块的物源贡献。
4.3 晚侏罗世花岗岩的源区――锆石Hf同位素证据文登岩体的三个花岗岩样品中具有非常一致的锆石Hf同位素特征:εHf(t)值和Hf模式年龄均具有双峰式分布,3个样品的εHf(t)值的两个峰值位于-25和-8,Hf两阶段模式年龄的两个峰值范围在2200~2400Ma和2700~2900Ma(图 4),表明三者来源于相同岩浆源区。垛崮山岩体的两阶段Hf模式年龄与文登岩体有所差异,Hf模式年龄变化范围较大,从1800~3000Ma,主要峰期在~2600Ma。其εHf(t)值也呈双峰式分布,峰值位于-21和-8,与文登岩体基本一致,只是变化范围更大。从Hf同位素特征来看垛崮山岩体与文登岩体的主要源区具有相似性,这与它们都具有新元古代和三叠纪的继承锆石年龄相吻合。但垛崮山岩体的εHf(t)值及Hf模式年龄较文登花岗岩体变化更大,这反应了二者的源区并不完全相同,应该还有其他源区的贡献,这也与我们在垛崮山获得了更多的华北板块继承锆石年龄结论相符合。值得注意的,本次文登岩体样品(SD06-11-01)中含有谐和年龄~2500Ma的继承锆石,其εHf(t)值为5.7,一阶段模式年龄为2623±32Ma与U-Pb年龄基本一致,表明~2500Ma的年龄记录了壳幔分异的年龄。同样地,垛崮山岩体样品(SD06-19-01)也含有2576±39Ma和2358±20Ma的继承锆石,其εHf(t)值分别为10.0和11.3,一阶段模式年龄为~2496Ma和~2259Ma,均与U-Pb年龄基本一致。这些壳幔分异年龄与华北地壳增生的时代记录一致(路孝平等,2004;Li et al., 2005b;Wan et al., 2006;Tang et al., 2007;Jahn et al., 2008;Liu et al., 2013;万渝生等,2017),也进一步证明了在两个岩体的源区中有华北板块的物源贡献。
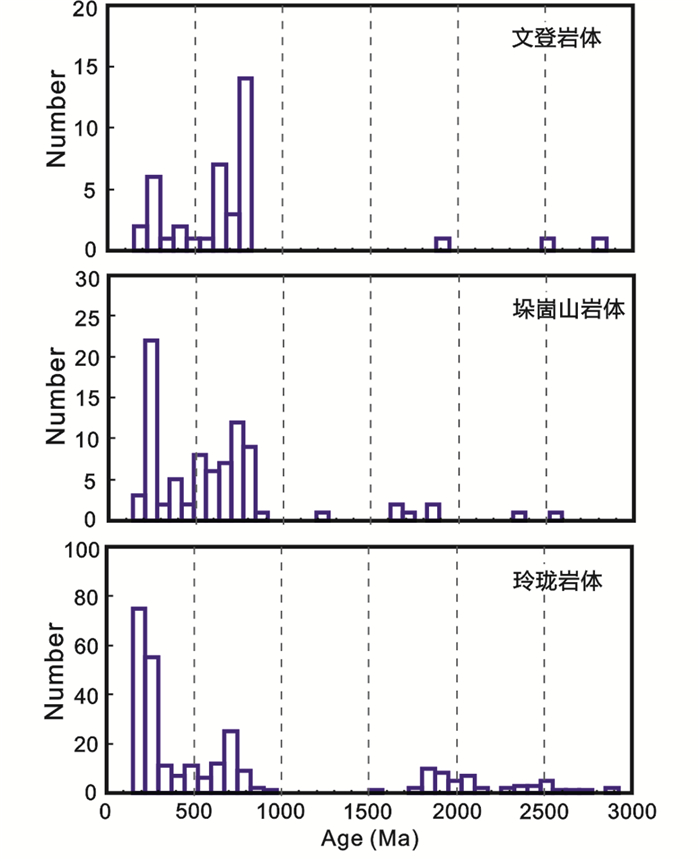
4.4 晚侏罗世花岗岩继承锆石及Hf同位素对胶东地区深部构造特征的制约为了更好地理解胶东地区晚侏罗世地质构造特征,本文统计了前人(Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014, 2018; Ma et al., 2013; 黄涛等, 2014; Zhao et al., 2016)发表的胶北地体中晚侏罗世玲珑岩体的继承锆石数据(图 5),进行对比研究。玲珑岩体中继承锆石的年龄包括三叠纪(~230Ma)、新元古代(~780Ma)、1750~2200Ma、~2500Ma、2700~2900Ma,其中最主要的年龄峰值在三叠纪和新元古代,表明玲珑岩体主要源区物质也来自于扬子板块。与文登岩体和垛崮山岩体不同的,玲珑岩体中与华北板块物源有关的继承锆石(1750~2200Ma、~2500Ma、2700~2900Ma)数量更多。从该地区大地构造格局来看,文登岩体所在的苏鲁超高压变质地体属于扬子板块,垛崮山岩体位于昆嵛山边界杂岩带,属华北板块与扬子板块交界处(Zhai et al., 2000; He et al., 2021),玲珑岩体地处的胶北地体属于华北板块。从文登岩体→垛崮山岩体→玲珑岩体,代表华北板块物源信息的继承锆石(~2500Ma、~1800Ma)逐渐增多,这与三个岩体所处的大地构造单元位置相符合。
|
图 5 胶东地区晚侏罗世花岗岩体中继承锆石年龄分布直方图 数据来源:文登岩体和垛崮山岩体来自本文和Zhao et al., 2016; 玲珑岩体引自Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014, 2018; Ma et al., 2013; 黄涛等,2014; Zhao et al., 2016 Fig. 5 Age distribution histograms of inherited zircons from Late Jurassic granites in Jiaodong area Data sources: the Wendong and Duogushan pluton from this study and Zhao et al., 2016; the Linglong pluton from Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014, 2018; Ma et al., 2013; Huang et al., 2014; Zhao et al., 2016 |
文登岩体处于苏鲁超高压变质地体内,其超高压变质岩的原岩是扬子板块的属性,因而在文登岩体中出现华北板块物源的记录有重要的构造意义。前人也在苏鲁超高压变质地体内发现多处太古代-古元古代的岩石具有华北板块的亲缘性(Zhang et al., 2006, 2014; Zhou et al., 2008)。目前普遍认为大别-苏鲁造山带的俯冲极性是扬子板块俯冲到华北板块的下部,如果在苏鲁超高压地体下部有华北板块的物质,而在胶北地体(传统上认为属于华北陆块)下部有扬子陆块的物质,那传统的单向俯冲构造样式就很难解释。而类似鳄鱼嘴式的重叠地壳构造模式(Li, 1994; 翟明国等,2000; Zhao et al., 2016)或许能更好的解释胶东地区晚侏罗世岩体中的继承锆石特征。
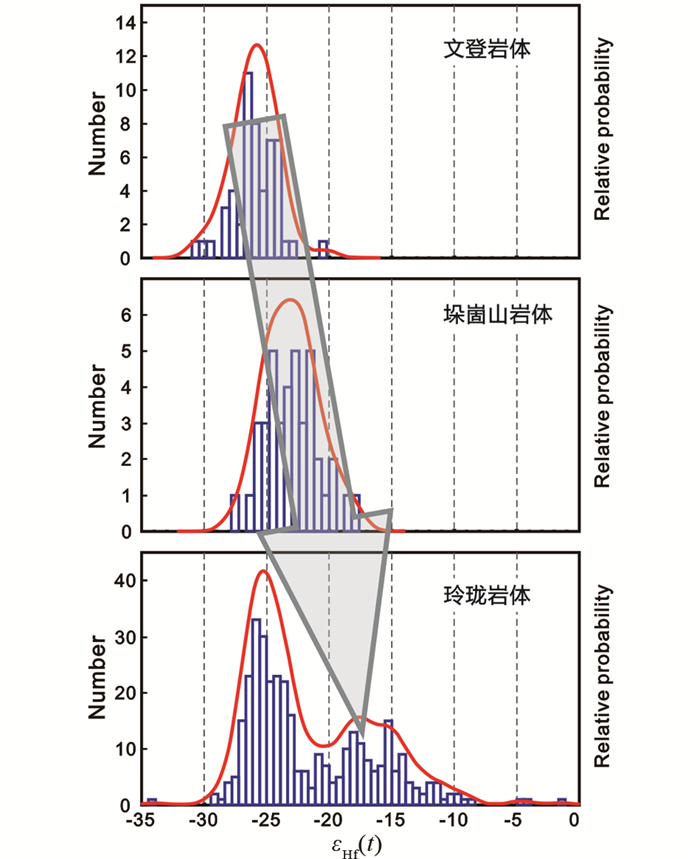
将文登岩体、垛崮山岩体和玲珑岩体中新生岩浆锆石(~160Ma)的Hf同位素特征进行对比(图 6),结果显示:文登岩体εHf(t)值在-30.7~-20.3之间,峰值集中在-26; 垛崮山岩体εHf(t)值在-27.5~-17.9之间,峰值集中在-23;而玲珑岩体εHf(t)值变化范围较大,主要集中在-29.3~-9.3之间,而且明显呈现两个峰值,分别在-25和-17。从整体上来看,从文登岩体→垛崮山岩体→玲珑岩体,εHf(t)值有略微增大的趋势(图 6)。在176Lu/177Hf对176Hf/177Hf图解中(图 7),玲珑岩体的Hf同位素组成也明显分成两个不同范围,即高εHf(t)值(玲珑岩体H)和低εHf(t)值(玲珑岩体L)的玲珑岩体能识别出两种不同的Hf同位素组成。文登岩体和垛崮山岩体的Hf同位素均与玲珑岩体中低εHf(t)值(玲珑岩体L)的特征一致,表明了三个岩体的源区具有一定的相似性。而玲珑岩体还具有高εHf(t)值(玲珑岩体H),这反映了胶北地体的地壳深部存在多个源区物质的混合,除了扬子板块物质、华北板块物质的重熔外,可能有部分幔源物质的加入,使锆石的εHf(t)值变大。Sr、Nd等同位素数据也表明,胶东地区晚侏罗世的岩浆活动主要来源于古老地壳融熔并伴随有幔源物质的加入(Deng et al., 2018)。此外,同样位于胶北地体内的早白垩世郭家岭岩体为壳幔混合成因(Yang et al., 2012, 2014; Wang et al., 2014; 宋英昕等,2020),高εHf(t)值的玲珑岩体与郭家岭岩体具有相似的锆石Hf同位素组成(图 7),这也表明这类玲珑岩体的形成可能具有幔源物质的参与。在胶东地区,从东到西(即文登岩体→垛崮山岩体→玲珑岩体)金矿床逐渐增多,而且大量的金矿集中产在玲珑岩体所处的胶北地体中。虽然从时间上来看,金成矿作用主要集中在130~110Ma(Yang and Zhou, 2001; 陈衍景等,2004;Deng et al., 2015, 2020; 朱日祥等,2015;范宏瑞等,2021),与晚侏罗世岩浆活动相隔至少30Ma,金成矿不可能由该期岩浆活动直接作用形成。但是,胶北地区晚侏罗世岩浆活动的多源区特点,尤其是幔源物质的加入能够促使金在深部预富集,为之后金在早白垩世短期巨量成矿提供了一个重要的物质条件。
|
图 6 晚侏罗世岩体中新生岩浆锆石的εHf(t)频率直方图 数据来源:文登岩体和垛崮山岩体数据来自本文;玲珑岩体数据引自Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014, 2018; Ma et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2016 Fig. 6 εHf(t) histogram of magmatic zircon from Late Jurassic granite plutons Data sources: Wendeng and Duogushan plutons from this study; Linglong pluton from Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014, 2018; Ma et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2016 |

|
图 7 新生岩浆锆石的176Lu/177Hf-176Hf/177Hf比值关系图 数据来源:文登岩体和垛崮山岩体数据来自本文; 玲珑岩体数据引自Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014, 2018; Ma et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2016; 郭家岭岩体数据引自Yang et al., 2012, 2014; Wang et al., 2014 Fig. 7 176Lu/177Hf vs. 176Hf/177Hf diagram of newly generated magmatic zircons Data sources: Wendeng and Duogushan plutons from this study; Linglong pluton from Jiang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2012, 2014, 2018; Ma et al., 2013; Zhao et al., 2016; Guojialing pluton from Yang et al., 2012, 2014; Wang et al., 2014 |
在晚侏罗世时期,郯庐断裂开始发生左行走滑活动(张长厚等,2001;朱光等,2009),该深达岩石圈地幔的断裂为壳/幔物质和能量交换提供了的重要场所(Zhao et al., 2012;杨立强等,2019)。与胶东地区东部相比,胶北地体更靠近郯庐断裂带,显然更容易受到其构造活动的影响。幔源岩浆底侵诱发加厚的下地壳拆沉并发生部分融熔,是晚侏罗世花岗岩形成的动力学机制之一(Hou et al., 2007; Ma et al., 2013; Yang et al., 2018)。这些幔源岩浆的入侵不仅促使了胶北地体太古宙-元古宙绿岩带地体强烈活化改造,使老地体中的金及成矿相关的元素被激活(李洪奎等,2011),而且相对富水、富金的幔源岩浆(Xia et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2020)还可以形成富含金及硫化物的角闪岩堆积体(Davidson et al., 2007; Hou et al., 2017),这些过程使金元素在下地壳深部完成初始富集,为之后在早白垩世爆发式金成矿提供了重要的物质基础(范宏瑞等,2021)。而胶东东部地区可能缺乏这种金的预富集机制,因而金矿较为贫乏。
5 结论(1) 胶东地区东部的文登岩体和垛崮山岩体均形成于晚侏罗世(~160Ma),与胶北金矿区的玲珑岩体形成时代一致。两个岩体中有较多的三叠纪(~230Ma)和新元古代(~780Ma)的继承锆石,表明它们的岩浆源区主要为经历了超高压变质作用的扬子板块。垛崮山岩体中还含有一定数量的华北板块物源的年龄记录,表明华北板块对其物质源区有重要的贡献。
(2) 文登岩体和垛崮山岩体的新生岩浆锆石εHf(t)值范围分别为-30.7~-20.3和-27.5~-17.9,玲珑岩体与东部这两个岩体相比,其新生岩浆锆石εHf(t)值的变化范围更大,在-29.3~-9.3之间,显示出源区更加复杂,εHf(t)值明显偏高暗示可能有更多地幔物质的影响。
(3) 胶东地区晚侏罗世花岗岩εHf(160Ma)值从东到西呈现增高的趋势,可能的成因是三叠纪扬子板块与华北板块碰撞后,加厚的地壳在晚侏罗世部分熔融,形成花岗岩。在此过程中胶北地体深部受到幔源物质的影响,从而对金及成矿相关元素产生一定的预富集作用。而同时期胶东东部地区未受到明显的地幔物质影响,可能是该区金矿产出较少的原因之一。
致谢 成文过程中,邓军教授对本文提出了许多建设性意见;两位审稿人对本文提出了十分宝贵的修改意见,提高了文章的质量;在此一并表示衷心的感谢!
Bruguier O, Lancelot JR and Malavieille J. 1997. U-Pb dating on single detrital zircon grains from the Triassic Songpan-Ganze flysch (Central China): Provenance and tectonic correlations. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 152(1-4): 217-231 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00138-6
|
Chen JF, Xie Z, Li HM, Zhang XD, Zhou TX, Park YS, Ahn KS, Chen DG and Zhang X. 2003. U-Pb zircon ages for a collision-related K-rich complex at Shidao in the Sulu ultrahigh pressure terrane, China. Geochemical Journal, 37(1): 35-46 DOI:10.2343/geochemj.37.35
|
Chen JZ and Jiang N. 2011. Petrogenesis of the Late-Triassic alkaline magmatism in the Jiaodong area: Evidence from U-Pb age, Hf-O isotopes of zircons. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(12): 3557-3574 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen YJ, Pirajno F, Lai Y and Li C. 2004. Metallogenic time and tectonic setting of the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(4): 907-922 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen YX, Zheng YF and Hu ZC. 2013. Synexhumation anatexis of ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks: Petrological evidence from granitic gneiss in the Sulu orogen. Lithos, 156-159: 69-96 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.10.008
|
Davidson J, Turner S, Handley H, Macpherson C and Dosseto A. 2007. Amphibole "sponge" in arc crust?. Geology, 35(9): 787-790 DOI:10.1130/G23637A.1
|
Deng J, Yang LQ, Fang Y, Ding SJ, Wang JP and Meng QF. 2000. Crust-mantle interaction and ore-forming effect of gold ore deposits concentrated area in Jiaodong, Shandong, China. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 35(1): 60-70 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Deng J, Yang LQ, Ge LS, Wang QF, Zhang J, Gao BF, Zhou YH and Jiang SQ. 2006. Coupling effects on gold mineralization of deep and shallow structures in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Progress in Natural Science, 16(5): 513-518 (in Chinese)
|
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Carranza EJM and Lu YJ. 2015. Cretaceous-Cenozoic tectonic history of the Jiaojia Fault and gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from zircon U-Pb, illite K-Ar, and apatite fission track thermochronometry. Mineralium Deposita, 50(8): 987-1006 DOI:10.1007/s00126-015-0584-1
|
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003
|
Deng J, Liu XF, Wang QF, Dilek Y and Liang YY. 2017. Isotopic characterization and petrogenetic modeling of Early Cretaceous mafic diking: Lithospheric extension in the North China Craton, eastern Asia. GSA Bulletin, 129(11-12): 1379-1407 DOI:10.1130/B31609.1
|
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Santosh M and Yao EY. 2018. Crustal architecture and metallogenesis in the south-eastern North China Craton. Earth-Science Reviews, 182: 251-272 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2018.05.001
|
Deng J, Qiu KF, Wang QF, Goldfarb R, Yang LQ, Zi JW, Geng JZ and Ma Y. 2020. In situ dating of hydrothermal monazite and implications for the geodynamic controls on ore formation in the Jiaodong gold province, eastern China. Economic Geology, 115(3): 671-685 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.4711
|
Dong X, Li DP, Zhao R, Wang XR and Wang QF. 2020. Zircon U-Pb chronology and petrogenesis of Zetou pluton in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Implications for regional petrogenesis and mineralization in the Aptian to Albian. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(5): 1501-1514 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.11
|
Fan HR, Lan TG, Li XH, Santosh M, Yang KF, Hu FF, Feng K, Hu HL, Peng HW and Zhang YW. 2021. Conditions and processes leading to large-scale gold deposition in the Jiaodong province, eastern China. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 51(9): 1504-1523 (in Chinese) DOI:10.1360/SSTe-2020-0335
|
Gao MD, Xu HJ, Zhang JF and Chen H. 2018. Incipient melt during partial melting of the deeply subducted continental crust: Evidence from leucosome of migmatite in Sulu ultra-high pressure terrane. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(3): 547-566 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Gao YJ, Niu YL, Duan M, Xue QQ, Sun P, Chen S, Xiao YY, Guo PY, Wang XH and Chen YH. 2019. The petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Early Cretaceous intraplate granites in eastern China: The Laoshan granite as an example. Lithos, 328-329: 200-211 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2019.01.031
|
Goldfarb RJ, Taylor RD, Collins GS, Goryachev NA and Orlandini OF. 2014. Phanerozoic continental growth and gold metallogeny of Asia. Gondwana Research, 25(1): 48-102 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.03.002
|
Goss SC, Wilde SA, Wu FY and Yang JH. 2010. The age, isotopic signature and significance of the youngest Mesozoic granitoids in the Jiaodong Terrane, Shandong Province, North China Craton. Lithos, 120(3-4): 309-326 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.019
|
Guo JH, Chen FK, Zhang XM, Siebel W and Zhai MG. 2005. Evolution of syn- to post-collisional magmatism from North Sulu UHP belt, eastern China: Zircon U-Pb geochronology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(4): 1281-1301 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Guo P, Santosh M and Li SR. 2013. Geodynamics of gold metallogeny in the Shandong Province, NE China: An integrated geological, geophysical and geochemical perspective. Gondwana Research, 24(3-4): 1172-1202 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.02.004
|
Hacker BR, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, Ireland T, Walker D and Dong SW. 1998. U/Pb zircon ages constrain the architecture of the ultrahigh-pressure Qinling-Dabie Orogen, China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 161(1-4): 215-230 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(98)00152-6
|
Hacker BR, Ratschbacher L, Webb L, McWilliams MO, Ireland T, Calvert A, Dong SW, Wenk HR and Chateigner D. 2000. Exhumation of ultrahigh-pressure continental crust in east central China: Late Triassic-Early Jurassic tectonic unroofing. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B6): 13339-13364 DOI:10.1029/2000JB900039
|
He JT, Li JJ, Fu C, Zhou HY, Li XZ, Dang ZC, Tian JP and Tang WL. 2021. Petrogenesis and tectonic implication of the Late Jurassic Kunyushan granitic complex in the Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Geological Journal, 56(6): 3275-3300 DOI:10.1002/gj.4101
|
Hou ML, Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Ling HF and Zhao KD. 2007. Contrasting origins of Late Mesozoic adakitic granitoids from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Implications for crustal thickening to delamination. Geological Magazine, 144(4): 619-631 DOI:10.1017/S0016756807003494
|
Hou ZQ, Zhou Y, Wang R, Zheng YC, He WY, Zhao M, Evans NJ and Weinberg RF. 2017. Recycling of metal-fertilized lower continental crust: Origin of non-arc Au-rich porphyry deposits at cratonic edges. Geology, 45(6): 563-566 DOI:10.1130/G38619.1
|
Huang T, Yang LQ, Liu XD, Li HL, Zhang BL, Wang JG, Zhao YF and Zhang N. 2014. Crustal evolution of the Jiaobei terrane: Evidence from U-Pb ages, trace element compositions and Hf isotopes of inherited zircons of the Linglong biotite granite. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2574-2594 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Huo TF, Yang DB, Shi JP, Xu WL and Yang HT. 2016. Petrogenesis of the Early Cretaceous alkali-rich intrusive rocks in the central North China Block: Constraints from zircon U-Pb chronology and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(3): 697-712 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Jahn BM, Liu DY, Wan YS, Song B and Wu JS. 2008. Archean crustal evolution of the Jiaodong Peninsula, China, as revealed by zircon SHRIMP geochronology, elemental and Nd-isotope geochemistry. American Journal of Science, 308(3): 232-269 DOI:10.2475/03.2008.03
|
Jiang N, Chen JZ, Guo JH and Chang GH. 2012. In situ zircon U-Pb, oxygen and hafnium isotopic compositions of Jurassic granites from the North China Craton: Evidence for Triassic subduction of continental crust and subsequent metamorphism-related 18O depletion. Lithos, 142-143: 84-94 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.02.018
|
Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Ling HF and Ni P. 2010. Petrogenesis and tectonic implications of Late Jurassic shoshonitic lamprophyre dikes from the Liaodong Peninsula, NE China. Mineralogy and Petrology, 100(3-4): 127-151 DOI:10.1007/s00710-010-0124-8
|
Jin WS and Guan AL. 1999. Isotopic age of the Archean rocks in Beijing area and their geological implications. Progress in Precambrian Research, 22(3): 1-13 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Kröner A, Cui WY, Wang SQ, Wang CQ and Nemchin AA. 1998. Single zircon ages from high-grade rocks of the Jianping complex, Liaoning Province, NE China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 16(5-6): 519-532 DOI:10.1016/S0743-9547(98)00033-6
|
Li HK, Li YF, Geng K, Zhuo CY, Zhang YB and Liang TT. 2011. Study on the orogenic type gold deposits in eastern Shandong Province. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 35(4): 533-542 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li JH, Qian XL, Huang XN and Liu SW. 2000. Tectonic framework of North China Block and its cratonization in the Early Precambrian. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 16(1): 1-10 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li JH, Niu XL, Cheng SH and Qian XL. 2006. The Early Precambrian tectonic evolution of continental craton: A case study from North China. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 31(3): 285-293 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li RW, Wan YS, Cheng ZY, Zhou JX, Li SY, Jin FQ, Meng QR, Li Z and Jiang MS. 2005a. Provenance of Jurassic sediments in the Hefei Basin, east-central China and the contribution of high-pressure and ultrahigh-pressure metamorphic rocks from the Dabie Shan. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 231(3-4): 279-294 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2004.12.021
|
Li SG, Xiao YL, Liou D, Chen YZ, Ge NJ, Zhang ZQ, Sun SS, Cong BL, Zhang R, Hart SR and Wang SS. 1993. Collision of the North China and Yangtse blocks and formation of coesite-bearing eclogites: Timing and processes. Chemical Geology, 109(1-4): 89-111 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(93)90063-O
|
Li SZ, Zhao GC, Sun M, Han ZZ, Luo Y, Hao DF and Xia XP. 2005b. Deformation history of the Paleoproterozoic Liaohe assemblage in the Eastern Block of the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 659-674 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2003.11.008
|
Li XC, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Yang KF, Lan TG, Liu YS and Yang YH. 2012. An evolving magma chamber within extending lithosphere: An integrated geochemical, isotopic and zircon U-Pb geochronological study of the Gushan granite, eastern North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 50: 27-43 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.01.016
|
Li XH, Li ZX, Ge WC, Zhou HW, Li WX, Liu Y and Wingate MTD. 2003a. Neoproterozoic granitoids in South China: Crustal melting above a mantle plume at ca. 825Ma?. Precambrian Research, 122(1-4): 45-83 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00207-3
|
Li XH, Chen FK, Guo JH, Li QL, Xie LW and Siebel W. 2007. South China provenance of the lower-grade Penglai Group north of the Sulu UHP orogenic belt, eastern China: Evidence from detrital zircon ages and Nd-Hf isotopic composition. Geochemical Journal, 41(1): 29-45 DOI:10.2343/geochemj.41.29
|
Li ZD, Yu XF, Wang QM, Du ZZ, Cao Q, Shi MY and Wang R. 2018. Petrogenesis of Sanfoshan granite, Jiaodong: Diagenetic physical and chemical conditions, zircon U-Pb geochronology and Sr-Nd isotope constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 34(2): 447-468 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li ZX. 1994. Collision between the North and South China blocks: A crustal-detachment model for suturing in the region east of the Tanlu fault. Geology, 22(8): 739-742 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0739:CBTNAS>2.3.CO;2
|
Li ZX, Li XH, Kinny PD, Wang J, Zhang S and Zhou H. 2003b. Geochronology of Neoproterozoic syn-rift magmatism in the Yangtze Craton, South China and correlations with other continents: Evidence for a mantle superplume that broke up Rodinia. Precambrian Research, 122(1-4): 85-109 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00208-5
|
Liu FL, Xu ZQ and Xue HM. 2004. Tracing the protolith, UHP metamorphism, and exhumation ages of orthogneiss from the SW Sulu terrane (eastern China): SHRIMP U-Pb dating of mineral inclusion-bearing zircons. Lithos, 78(4): 411-429 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.08.001
|
Liu FL, Gerdes A, Liou JG, Xue HM and Liang FH. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating from Sulu-Dabie dolomitic marble, eastern China: Constraints on prograde, ultrahigh-pressure and retrograde metamorphic ages. Journal of Metamorphic Geology, 24(7): 569-589 DOI:10.1111/j.1525-1314.2006.00655.x
|
Liu FL, Robinson PT, Gerdes A, Xue HM, Liu PH and Liou JG. 2010. Zircon U-Pb ages, REE concentrations and Hf isotope compositions of granitic leucosome and pegmatite from the north Sulu UHP terrane in China: Constraints on the timing and nature of partial melting. Lithos, 117(1-4): 247-268 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.03.002
|
Liu JH, Liu FL, Ding ZJ, Liu CH, Yang H, Liu PH, Wang F and Meng E. 2013. The growth, reworking and metamorphism of Early Precambrian crust in the Jiaobei terrane, the North China Craton: Constraints from U-Th-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic systematics, and REE concentrations of zircon from Archean granitoid gneisses. Precambrian Research, 224: 287-303 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.10.003
|
Liu Y, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Zhang C, Liu XD, Zheng XL and Wang XD. 2014. Zircon U-Pb age, Lu-Hf isotopes and petrogeochemistry of the monzogranites from Xincheng gold deposit, northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(9): 2559-2573 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Lu XP, Wu FY, Zhang YB, Zhao CB and Guo CL. 2004. Emplacement age and tectonic setting of the Paleoproterozoic Liaoji granites in Tonghua area, southern Jilin Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3): 381-392 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center Special Publications, 25-32
|
Ma L, Jiang SY, Dai BZ, Jiang YH, Hou ML, Pu W and Xu B. 2013. Multiple sources for the origin of Late Jurassic Linglong adakitic granite in the Shandong Peninsula, eastern China: Zircon U-Pb geochronological, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic evidence. Lithos, 162-163: 251-263 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.01.009
|
Miao LC, Luo ZK, Guan K and Huang JZ. 1998. The implication of the SHRIMP U-Pb age in zircon to the petrogenesis of the Linglong granite, East Shandong Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 14(2): 198-206 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Pan SZ, Wang FY, Zheng YP, Duan YL, Liu L, Deng XG, Song XH, Sun YN, Ma CJ and Li YQ. 2015. Crustal velocity structure beneath Jiaodong Peninsula and its tectonic implications. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(9): 3251-3263 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Santosh M, Wilde SA and Li JH. 2007. Timing of Paleoproterozoic ultrahigh-temperature metamorphism in the North China Craton: Evidence from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology. Precambrian Research, 159(3-4): 178-196 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.06.006
|
Shan HX and Zhai MG. 2020. Petrogenesis of Archean TTG-series rocks from the Jiaodong complex, eastern China: Implications for crustal evolution in the North China Craton. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 197: 104368 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2020.104368
|
Song MC. 2014. Jiaodong type gold deposit and its tectono-magmatic background. Mineral Deposits, 33(Suppl.1): 131-132 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Song MC, Song YX, Ding ZJ, Wei XF, Sun SL, Song GZ, Zhang JJ, Zhang PJ and Wang YG. 2019. The discovery of the Jiaojia and the Sanshandao giant gold deposits in Jiaodong Peninsula and discussion on the relevant issues. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(1): 92-110 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Song YX, Yu XF, Li DP, Geng K, Wei PF, Zuo XM and Wang XF. 2020. Petrogenesis of the Beijie pluton from the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints from zircon U-Pb age, petrogeochemistry and Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 36(5): 1477-1500 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2020.05.10
|
Sun WD, Ling MX, Wang FY, Ding X, Hu YH, Zhou JB and Yang XY. 2008. Pacific plate subduction and Mesozoic geological event in eastern China. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 27(3): 218-225 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Tam PY, Zhao GC, Liu FL, Zhou XW, Sun M and Li SZ. 2011. Timing of metamorphism in the Paleoproterozoic Jiao-Liao-Ji Belt: New SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of granulites, gneisses and marbles of the Jiaobei massif in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 19(1): 150-162 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.05.007
|
Tang J, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Gong B and Liu XM. 2007. Geochronology and geochemistry of metamorphic rocks in the Jiaobei terrane: Constraints on its tectonic affinity in the Sulu orogen. Precambrian Research, 152(1-2): 48-82 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.09.001
|
Tang J, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Gong B, Zha XP and Liu XM. 2008. Zircon U-Pb age and geochemical constraints on the tectonic affinity of the Jiaodong terrane in the Sulu orogen, China. Precambrian Research, 161(3-4): 389-418 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2007.09.008
|
Wan YS, Song B, Liu DY, Wilde SA, Wu JS, Shi YR, Yin XY and Zhou HY. 2006. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of Palaeoproterozoic metasedimentary rocks in the North China Craton: Evidence for a major Late Palaeoproterozoic tectonothermal event. Precambrian Research, 149(3-4): 249-271 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.06.006
|
Wan YS, Dong CY, Ren P, Bai WQ, Xie HQ, Liu SJ, Xie SW and Liu DY. 2017. Spatial and temporal distribution, compositional characteristics and formation and evolution of Archean TTG rocks in the North China Craton: A synthesis. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 33(5): 1405-1419 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang LG, Qiu YM, McNaughton NJ, Groves DI, Luo ZK, Huang JZ, Miao LC and Liu YK. 1998. Constraints on crustal evolution and gold metallogeny in the northwestern Jiaodong Peninsula, China, from SHRIMP U-Pb zircon studies of granitoids. Ore Geology Reviews, 13(1-5): 275-291 DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(97)00022-X
|
Wang XL, Zhou JC, Qiu JS, Zhang WL, Liu XM and Zhang GL. 2006. LA-ICP-MS U-Pb zircon geochronology of the Neoproterozoic igneous rocks from northern Guangxi, South China: Implications for tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research, 145(1-2): 111-130 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.014
|
Wang ZC, Cheng H, Zong KQ, Geng XL, Liu YS, Yang JH, Wu FY, Becker H, Foley S and Wang CY. 2020. Metasomatized lithospheric mantle for Mesozoic giant gold deposits in the North China Craton. Geology, 48(2): 169-173 DOI:10.1130/G46662.1
|
Wang ZL, Yang LQ, Deng J, Santosh M, Zhang HF, Liu Y, Li RH, Huang T, Zheng XL and Zhao H. 2014. Gold-hosting high Ba-Sr granitoids in the Xincheng gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Petrogenesis and tectonic setting. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 95: 274-299 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.03.001
|
Wen BJ, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Pirajno F and Yang KF. 2015. Genesis of two different types of gold mineralization in the Linglong gold field, China: Constrains from geology, fluid inclusions and stable isotope. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 643-658 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.03.018
|
Wu FY, Yang YH, Xie LW, Yang JH and Xu P. 2006a. Hf isotopic compositions of the standard zircons and baddeleyites used in U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 234(1-2): 105-126 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.05.003
|
Wu FY, Yang JH, Xu YG, Wilde SA and Walker RJ. 2019. Destruction of the North China Craton in the Mesozoic. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 47: 173-195 DOI:10.1146/annurev-earth-053018-060342
|
Wu RX, Zheng YF, Wu YB, Zhao ZF, Zhang SB, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006b. Reworking of juvenile crust: Element and isotope evidence from Neoproterozoic granodiorite in South China. Precambrian Research, 146(3-4): 179-212 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2006.01.012
|
Wu YB, Zheng YF, Zhao ZF, Gong B, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006c. U-Pb, Hf and O isotope evidence for two episodes of fluid-assisted zircon growth in marble-hosted eclogites from the Dabie orogen. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 70(14): 3743-3761 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2006.05.011
|
Xia QK, Liu J, Kovács I, Hao YT, Li P, Yang XZ, Chen H and Sheng YM. 2019. Water in the upper mantle and deep crust of eastern China: Concentration, distribution and implications. National Science Review, 6(1): 125-144 DOI:10.1093/nsr/nwx016
|
Xie LW, Zhang YB, Zhang HH, Sun JF and Wu FY. 2008. In situ simultaneous determination of trace elements, U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopes in zircon and baddeleyite. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(10): 1565-1573
|
Xu YG, Li HY, Pang CJ and He B. 2009. On the timing and duration of the destruction of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3379-3396
|
Xue HM, Liu FL and Meng FC. 2006. Major and trace element geochemistry of granitic gneisses from Sulu orogen, eastern Shandong Peninsula: Evidence for a Neoproterozoic active continental margin in the northern margin of the Yangtze Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 22(7): 1779-1790 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yan QS and Shi XF. 2014. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Cretaceous A-type granites in the Laoshan granitic complex, eastern China. Island Arc, 23(3): 221-235 DOI:10.1111/iar.12070
|
Yang JH and Zhou XH. 2001. Rb-Sr, Sm-Nd, and Pb isotope systematics of pyrite: Implications for the age and genesis of lode gold deposits. Geology, 29(8): 711-714 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(2001)029<0711:RSSNAP>2.0.CO;2
|
Yang JH, Wu FY, Liu XM and Xie LW. 2005. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes and their geological significance of the Miyun rapakivi granites from Beijing, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(6): 1633-1644 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang JH and Wu FY. 2009. Triassic magmatism and its relation to decratonization in the eastern North China Craton. Science in China (Series D), 52(9): 1319-1330 DOI:10.1007/s11430-009-0137-5
|
Yang KF, Fan HR, Santosh M, Hu FF, Wilde SA, Lan TG, Lu LN and Liu YS. 2012. Reactivation of the Archean lower crust: Implications for zircon geochronology, elemental and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic geochemistry of Late Mesozoic granitoids from northwestern Jiaodong Terrane, the North China Craton. Lithos, 146-147: 112-127 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.035
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Guo LN, Wang ZL, Li XZ and Li JL. 2016a. Origin and evolution of ore fluid, and gold-deposition processes at the giant Taishang gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 585-602 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.08.021
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Wang ZL, Zhang L, Goldfarb RJ, Yuan WM, Weinberg RF and Zhang RZ. 2016b. Thermochronologic constraints on evolution of the Linglong Metamorphic Core Complex and implications for gold mineralization: A case study from the Xiadian gold deposit, Jiaodong Peninsula, eastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 72: 165-178 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.07.006
|
Yang LQ, Dilek Y, Wang ZL, Weinberg RF and Liu Y. 2018. Late Jurassic, high Ba-Sr Linglong granites in the Jiaodong Peninsula, East China: Lower crustal melting products in the eastern North China Craton. Geological Magazine, 155(5): 1040-1062 DOI:10.1017/S0016756816001230
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Song MC, Yu XF, Wang ZL, Li RH and Wang SR. 2019. Structure control on formation and localization of giant deposits: An example of Jiaodong gold deposits in China. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 43(3): 431-446 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang QY, Santosh M, Shen JF and Li SR. 2014. Juvenile vs. recycled crust in NE China: Zircon U-Pb geochronology, Hf isotope and an integrated model for Mesozoic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula. Gondwana Research, 25(4): 1445-1468
|
Ye K, Cong BL and Ye DN. 2000. The possible subduction of continental material to depths greater than 200km. Nature, 407(6805): 734-736 DOI:10.1038/35037566
|
Zeng LS, Chen J, Chen ZY, Liu J, Liang FH and Gao LE. 2007. Emplacement depth of the Shidao granitic complex and the rapid exhumation of the Sulu ultrahigh pressure rocks: New constraints on the mechanisms for rapid exhumation. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(12): 3171-3179 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhai MG, Cong BL, Guo JH, Liu WJ, Li YG and Wang QC. 2000. Sm-Nd geochronology and petrography of garnet pyroxene granulites in the northern Sulu region of China and their geotectonic implication. Lithos, 52(1-4): 23-33 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(99)00082-1
|
Zhai MG, Guo JH, Wang QC, Ye K, Cong BL and Liu WJ. 2000. Division of petrological-tectonic units in the Northern Sulu ultra-high pressure zone: An example of thick-skin thrust of crystalline units. Scientia Geologica Sinica, 35(1): 16-26 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhai MG and Liu WJ. 2003. Palaeoproterozoic tectonic history of the North China craton: A review. Precambrian Research, 122(1-4): 183-199 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00211-5
|
Zhai MG, Guo JH and Liu WJ. 2005. Neoarchean to Paleoproterozoic continental evolution and tectonic history of the North China Craton: A review. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 24(5): 547-561 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2004.01.018
|
Zhang CH, Song HL, Wang GH, Yan DP and Sun WH. 2001. Mesozoic dextral strike-slip structural system in middle segment of intraplate Yanshan orogenic belt, northern China. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 26(5): 464-472 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang J, Zhao ZF, Zheng YF and Dai MN. 2010. Postcollisional magmatism: Geochemical constraints on the petrogenesis of Mesozoic granitoids in the Sulu orogen, China. Lithos, 119(3-4): 512-536 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.005
|
Zhang L, Weinberg RF, Yang LQ, Groves DI, Sai SX, Matchan E, Phillips D, Kohn BP, Miggins DP, Liu Y and Deng J. 2020. Mesozoic orogenic gold mineralization in the Jiaodong Peninsula, China: A focused event at 120±2Ma during cooling of pre-gold granite intrusions. Economic Geology, 115(2): 415-441 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.4716
|
Zhang RY, Liou JG, Tsujimori T and Maruyama S. 2006. Non-ultrahigh-pressure unit bordering the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane, eastern China: Transformation of Proterozoic granulite and gabbro to garnet amphibolite. In: Hacker BR, McClelland WC and Liou JG (eds. ). Ultrahigh-Pressure Metamorphism: Deep Continental Subduction. Special Paper of the Geological Society of America, 403: 169-207
|
Zhang SB, Tang J and Zheng YF. 2014. Contrasting Lu-Hf isotopes in zircon from Precambrian metamorphic rocks in the Jiaodong Peninsula: Constraints on the tectonic suture between North China and South China. Precambrian Research, 245: 29-50 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2014.01.006
|
Zhang YQ, Li JL, Zhang T, Dong SW and Yuan JY. 2008. Cretaceous to Paleocene tectono-sedimentary evolution of the Jiaolai Basin and the contiguous areas of the Shandong Peninsula (North China) and its geodynamic implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 82(9): 1229-1257 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang ZQ, Zhang CJ, Wang SJ, Liu SC, Wang LM, Du SX, Song ZY, Zhang SK, Yang EX, Cheng GS, Liu FC, Chen J and Chen C. 2014. Views on classification and contrast of tectonic units in strata in Shandong Province. Shandong Land and Resources, 30(3): 1-23 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA and Li SZ. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton: Key issues revisited. Precambrian Research, 136(2): 177-202 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002
|
Zhao R, Wang QF, Liu XF, Wang W and Pan RG. 2016. Architecture of the Sulu crustal suture between the North China Craton and Yangtze Craton: Constraints from Mesozoic granitoids. Lithos, 266-267: 348-361 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2016.10.018
|
Zhao Z, Zhao ZX and Xu JR. 2012. Velocity structure heterogeneity and tectonic motion in and around the Tan-Lu fault of China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 57: 6-14 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.05.019
|
Zheng YF. 2003. Neoproterozoic magmatic activity and global change. Chinese Science Bulletin, 48(16): 1639-1656 DOI:10.1360/03wd0342
|
Zheng YF, Wu YB, Chen FK, Gong B, Li L and Zhao ZF. 2004. Zircon U-Pb and oxygen isotope evidence for a large-scale 18O depletion event in igneous rocks during the Neoproterozoic. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 68(20): 4145-4165 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2004.01.007
|
Zheng YF, Zhou JB, Wu YB and Xie Z. 2005. Low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt: A passive-margin accretionary wedge deformed during continent subduction. International Geology Review, 47(8): 851-871 DOI:10.2747/0020-6814.47.8.851
|
Zheng YF, Zhao ZF, Wu YB, Zhang SB, Liu XM and Wu FY. 2006. Zircon U-Pb age, Hf and O isotope constraints on protolith origin of ultrahigh-pressure eclogite and gneiss in the Dabie orogen. Chemical Geology, 231(1-2): 135-158 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2006.01.005
|
Zheng YF. 2008. A perspective view on ultrahigh-pressure metamorphism and continental collision in the Dabie-Sulu orogenic belt. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(20): 3081-3104
|
Zhou JB, Wilde SA, Zhao GC, Zheng CQ, Jin W, Zhang XZ and Cheng H. 2008. Detrital zircon U-Pb dating of low-grade metamorphic rocks in the Sulu UHP belt: Evidence for overthrusting of the North China Craton onto the South China Craton during continental subduction. Journal of the Geological Society, 165(1): 423-433 DOI:10.1144/0016-76492007-040
|
Zhou MF, Yan DP, Kennedy AK, Li YQ and Ding J. 2002. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronological and geochemical evidence for Neoproterozoic arc-magmatism along the western margin of the Yangtze Block, South China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 196(1-2): 51-67 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(01)00595-7
|
Zhou MF, Ma YX, Yan DP, Xia XP, Zhao JH and Sun M. 2006. The Yanbian Terrane (southern Sichuan Province, SW China): A Neoproterozoic arc assemblage in the western margin of the Yangtze Block. Precambrian Research, 144(1-2): 19-38 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2005.11.002
|
Zhu G, Zhang L, Xie CL, Niu ML and Wang YS. 2009. Geochronological constraints on tectonic evolution of the Tan-Lu Fault Zone. Chinese Journal of Geology, 44(4): 1327-1342 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhu RX, Chen L, Wu FY and Liu JL. 2011. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(6): 789-797 DOI:10.1007/s11430-011-4203-4
|
Zhu RX, Fan HR, Li JW, Meng QR, Li SR and Zeng QD. 2015. Decratonic gold deposits. Science China (Earth Sciences), 58(9): 1523-1537 DOI:10.1007/s11430-015-5139-x
|
Zong KQ, Liu YS, Hu ZC, Kusky T, Wang DB, Gao CG, Gao S and Wang JQ. 2010. Melting-induced fluid flow during exhumation of gneisses of the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure terrane. Lithos, 120(3-4): 490-510 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.09.013
|
Zou WL, Yang JZ, Zeng QD, Li GM and Zhang LC. 2010. Geological characteristics and metallogenic geodynamic setting of interlayer-sliding tectonic breccia-type gold deposit in the margin of the Jiaolai Basin, Shandong Province. Acta Geologica Sinica, 84(4): 508-517 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
陈竟志, 姜能. 2011. 胶东晚三叠世碱性岩浆作用的岩石成因——来自锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf-O同位素的证据. 岩石学报, 27(12): 3557-3574. |
陈衍景, Pirajno F, 赖勇, 李超. 2004. 胶东矿集区大规模成矿时间和构造环境. 岩石学报, 20(4): 907-922. |
邓军, 杨立强, 方云, 丁式江, 王建平, 孟庆芬. 2000. 胶东地区壳-幔作用与金成矿效应. 地质科学, 35(1): 60-70. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.01.007 |
邓军, 杨立强, 葛良胜, 王庆飞, 张静, 高帮飞, 周应华, 江少卿. 2006. 胶东矿集区形成的构造体制研究进展. 自然科学进展, 16(5): 513-518. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2006.05.001 |
董学, 李大鹏, 赵睿, 王欣然, 王庆飞. 2020. 胶东泽头岩体锆石U-Pb年代学和岩石成因: 对区域早白垩世晚期成岩成矿作用的指示. 岩石学报, 36(5): 1501-1514. |
范宏瑞, 蓝廷广, 李兴辉, Santosh M, 杨奎锋, 胡芳芳, 冯凯, 胡换龙, 彭红卫, 张永文. 2021. 胶东金成矿系统的末端效应. 中国科学(地球科学), 51(9): 1504-1523. |
高名迪, 续海金, 章军锋, 陈辉. 2018. 深俯冲陆壳部分熔融初始熔体的厘定: 来自苏鲁超高压地体混合岩中浅色体证据. 岩石学报, 34(3): 547-566. |
郭敬辉, 陈福坤, 张晓曼, Siebel W, 翟明国. 2005. 苏鲁超高压带北部中生代岩浆侵入活动与同碰撞-碰撞后构造过程: 锆石U-Pb年代学. 岩石学报, 21(4): 1281-1301. |
黄涛, 杨立强, 刘向东, 李海林, 张炳林, 王建刚, 赵云峰, 张宁. 2014. 胶北地体地壳演化: 玲珑黑云母花岗岩继承锆石U-Pb年龄、微量元素和Hf同位素证据. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2574-2594. |
霍腾飞, 杨德彬, 师江朋, 许文良, 杨浩田. 2016. 华北地块中部早白垩世富碱侵入岩的成因: 锆石U-Pb年代学和Sr-Nd-Hf同位素制约. 岩石学报, 32(3): 697-712. |
金文山, 管爱莲. 1999. 北京地区太古宙岩石同位素年龄及其意义. 前寒武纪研究进展, 22(3): 1-13. |
李洪奎, 李逸凡, 耿科, 禚传源, 张玉波, 梁太涛. 2011. 山东鲁东碰撞造山型金矿成矿作用探讨. 大地构造与成矿学, 35(4): 533-542. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2011.04.007 |
李江海, 钱祥麟, 黄雄南, 刘树文. 2000. 华北陆块基底构造格局及早期大陆克拉通化过程. 岩石学报, 16(1): 1-10. |
李江海, 牛向龙, 程素华, 钱祥麟. 2006. 大陆克拉通早期构造演化历史探讨: 以华北为例. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 31(3): 285-293. |
李增达, 于晓飞, 王全明, 杜泽忠, 曹强, 师明元, 王然. 2018. 胶东三佛山花岗岩的成因: 成岩物理化学条件、锆石U-Pb年代学及Sr-Nd同位素约束. 岩石学报, 34(2): 447-468. |
刘跃, 邓军, 王中亮, 张良, 涨潮, 刘向东, 郑小礼, 王旭东. 2014. 胶西北新城金矿床二长花岗岩岩石地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及Lu-Hf同位素组成. 岩石学报, 30(9): 2559-2573. |
路孝平, 吴福元, 张艳斌, 赵成弼, 郭春丽. 2004. 吉林南部通化地区古元古代辽吉花岗岩的侵位年代与形成构造背景. 岩石学报, 20(3): 381-392. |
苗来成, 罗镇宽, 关康, 黄佳展. 1998. 玲珑花岗岩中锆石的离子质谱U-Pb年龄及其岩石学意义. 岩石学报, 14(2): 198-206. |
潘素珍, 王夫运, 郑彦鹏, 段玉玲, 刘兰, 邓晓果, 宋向辉, 孙一男, 马策军, 李怡青. 2015. 胶东半岛地壳速度结构及其构造意义. 地球物理学报, 58(9): 3251-3263. |
宋明春. 2014. 胶东型金矿及其成矿的构造岩浆背景. 矿床地质, 33(增1): 131-132. |
宋明春, 宋英昕, 丁正江, 魏绪峰, 孙绍立, 宋国政, 张军进, 张丕建, 王永国. 2019. 胶东焦家和三山岛巨型金矿床的发现及有关问题讨论. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(1): 92-110. |
宋英昕, 于学峰, 李大鹏, 耿科, 尉鹏飞, 左晓敏, 王秀凤. 2020. 胶东西北部北截岩体岩石成因: 锆石U-Pb年龄、岩石地球化学与Sr-Nd-Pb同位素制约. 岩石学报, 36(5): 1477-1500. |
孙卫东, 凌明星, 汪方跃, 丁兴, 胡艳华, 周继彬, 杨晓勇. 2008. 太平洋板块俯冲与中国东部中生代地质事件. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 27(3): 218-225. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2008.03.002 |
万渝生, 董春艳, 任鹏, 白文倩, 颉颃强, 刘守偈, 谢士稳, 刘敦一. 2017. 华北克拉通太古宙TTG岩石的时空分布、组成特征及形成演化: 综述. 岩石学报, 33(5): 1405-1419. |
谢烈文, 张艳斌, 张辉煌, 孙金凤, 吴福元. 2008. 锆石/斜锆石U-Pb和Lu-Hf同位素以及微量元素成分的同时原位测定. 科学通报, 53(2): 220-228. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2008.02.013 |
徐义刚, 李洪颜, 庞崇进, 何斌. 2009. 论华北克拉通破坏的时限. 科学通报, 54(14): 1974-1989. |
薛怀民, 刘福来, 孟繁聪. 2006. 苏鲁造山带胶东区段花岗片麻岩类的常量与微量元素地球化学: 扬子克拉通北缘新元古代活动大陆边缘的证据. 岩石学报, 22(7): 1779-1790. |
杨进辉, 吴福元, 柳小明, 谢烈文. 2005. 北京密云环斑花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 21(6): 1633-1644. |
杨进辉, 吴福元. 2009. 华北东部三叠纪岩浆作用与克拉通破坏. 中国科学(D辑), 39(7): 910-921. |
杨立强, 邓军, 宋明春, 于学峰, 王中亮, 李瑞红, 王偲瑞. 2019. 巨型矿床形成与定位的构造控制: 胶东金矿集区剖析. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(3): 431-446. |
曾令森, 陈晶, 陈振宇, 刘静, 梁凤华, 高利娥. 2007. 山东石岛花岗岩复合岩体的侵位深度与苏鲁超高压变质岩的快速折返机制及动力学效应. 岩石学报, 23(12): 3171-3179. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.12.009 |
翟明国, 郭敬辉, 王清晨, 叶凯, 从柏林, 刘文军. 2000. 苏鲁变质带北部的岩石构造单元及结晶块体推覆构造. 地质科学, 35(1): 16-26. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2000.01.002 |
张长厚, 宋鸿林, 王根厚, 颜丹平, 孙卫华. 2001. 燕山板内造山带中段近东西向中生代右行走滑构造系统. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 26(5): 464-472. |
张岳桥, 李金良, 张田, 董树文, 袁嘉音. 2008. 胶莱盆地及其邻区白垩纪-古新世沉积构造演化历史及其区域动力学意义. 地质学报, 82(9): 1229-1257. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2008.09.007 |
张增奇, 张成基, 王世进, 刘书才, 王来明, 杜圣贤, 宋志勇, 张尚坤, 杨恩秀, 程光锁, 刘凤臣, 陈军, 陈诚. 2014. 山东省地层侵入岩构造单元划分对比意见. 山东国土资源, 30(3): 1-23. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6979.2014.03.001 |
郑永飞. 2003. 新元古代岩浆活动与全球变化. 科学通报, 48(16): 1705-1720. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2003.16.001 |
朱光, 张力, 谢成龙, 牛漫兰, 王勇生. 2009. 郯庐断裂带构造演化的同位素年代学制约. 地质科学, 44(4): 1327-1342. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0563-5020.2009.04.019 |
朱日祥, 陈凌, 吴福元, 刘俊来. 2011. 华北克拉通破坏的时间、范围与机制. 中国科学(地球科学), 41(5): 583-592. |
朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 孟庆任, 李胜荣, 曾庆栋. 2015. 克拉通破坏型金矿床. 中国科学(地球科学), 45(8): 1153-1168. |
邹为雷, 杨金中, 曾庆栋, 李光明, 张连昌. 2010. 山东胶莱盆地边缘层间滑动角砾岩型金矿地质特征及成矿动力学背景. 地质学报, 84(4): 508-517. |
 2022, Vol. 38
2022, Vol. 38