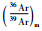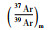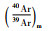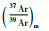2. 中国地质大学(北京)地球科学与资源学院, 北京 100083;
3. 灵宝金源矿业股份有限公司, 灵宝 472500
2. School of Earth Sciences and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China;
3. Lingbao Jinyuan Mining Co. Ltd., Lingbao 472500, China
位于河南和陕西境内的小秦岭金矿田是我国仅次于山东胶东金矿田的第二大黄金产地,区内发育石英脉型、蚀变碎裂岩型和蚀变千糜岩型等三种类型金矿床(胡正国等, 1994),其中石英脉型是金矿开采的主要类型。越来越多的成矿年代学研究工作表明,小秦岭金矿床主要形成于早白垩世(李绍儒等, 1998; 徐启东等, 1998; 李强之等, 2002; Wang et al., 2002; Li et al., 2012a; 强山峰等, 2013; Zhao et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020),其发育的伸展构造背景已基本达成共识(Mao et al., 2002; 王义天和毛景文, 2002; Li et al., 2012b; 朱日祥等, 2015)。而在2000年以前,一些研究者报道了陕西境内小秦岭的3个金矿床获得的三叠纪成矿年龄,包括东桐峪金矿床钾长石Rb-Sr等时线年龄208.2Ma(王秀璋等, 1992)、潼峪金矿床f5矿脉绢云母K-Ar年龄237.54±4.8Ma(胡正国等, 1994)及湘子岔金矿床黄铁矿40Ar-39Ar坪年龄208Ma(卢欣祥等, 1999),但是没有引起太多的注意。在此期间,小秦岭南缘与火成碳酸岩有关的黄龙铺钼铅矿床为三叠纪成矿得到了确认,依据是直接对辉钼矿开展的Re-Os定年结果(黄典豪等, 1994; Stein et al., 1997)。近十年来,陆续在小秦岭金矿田北缘的金矿床中发现了一些钼矿体,在南缘的黄龙铺周边发现了一些钼铅矿床、钼矿床和铀铌钼多金属矿床,对这些矿床(体)开展的以辉钼矿Re-Os定年为主的成矿年代学研究显示它们都形成于三叠纪(李厚民等, 2007; 李诺等, 2008; 王义天等, 2010; 袁海潮等, 2014; Jian et al., 2015; Zhao et al., 2019; 高龙刚等, 2019; 杜芷葳等, 2020; 王佳营等, 2020; 黄卉等, 2020; Zheng et al., 2020)。卢欣祥等(1999)最早提出了印支期是小秦岭-熊耳山地区乃至整个秦岭的一个重要的金、多金属成矿期的新认识;后来,卢欣祥等(2008)、陈衍景(2010)进一步指出印支期是秦岭造山带的重要成矿期。胡海珠等(2013)总结了秦岭地区三叠纪钼成矿作用的特征并探讨了找矿前景。毛景文等(2012)系统论述了我国三叠纪大规模成矿作用形成的主要矿种和矿床类型、基本特征、成矿动力学背景等,指出三叠纪金属矿产主要分布在昆仑-秦岭和红河-哀牢山两个主碰撞造山带及其邻区,另外在华南、东北和新疆三个地区的板内也发育一系列三叠纪多金属矿产。在上述地区,三叠纪矿产逐渐引起人们的关注,成为近年来的主要成矿研究对象和找矿对象。对于小秦岭金矿田三叠纪矿产的研究和勘查工作也不断深入,不过有关三叠纪成矿事件的构造背景研究尚属薄弱,还没有直接对这里的三叠纪构造变形开展过专题研究。为此,本次工作对小秦岭金矿田东端边缘发育的构造带开展了构造观察和测量,进而采用40Ar-39Ar年代学方法厘定构造变形时限,揭示小秦岭金矿田三叠纪成矿事件的构造背景,为进一步全面认识区内三叠纪多金属成矿作用特征和规律提供构造证据。
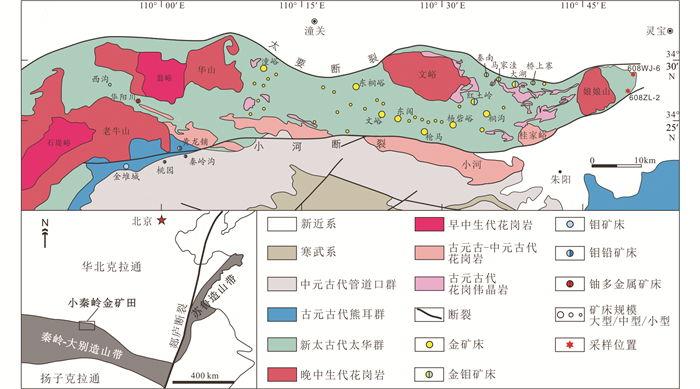
1 地质背景小秦岭金矿田在大地构造位置上属于华北克拉通南缘,位于沿太行山一带展布的华北克拉通中部造山带(Zhao et al., 2001)的南端,同时也是秦岭-大别复合型造山带的边缘组成部分(张国伟等, 1996),其北侧以太要断裂为界,南侧以小河断裂为界(图 1)。
|
图 1 小秦岭金矿田地质矿产简图 Fig. 1 Sketch map of geology and mineral resources in the Xiaoqinling goldfield |
小秦岭金矿田主体出露的地层为晚太古界太华群深变质火山-沉积岩系,金矿床及其他矿种主要产于太华群中。在小河断裂南侧出露的地层包括中元古界熊耳群浅变质中酸性火山岩系、中元古界官道口群碳酸盐岩-碎屑岩建造、以及寒武系和白垩系碎屑岩建造(图 1)。根据地层的变形-变质特征和空间产出关系,可将区内的岩石划分为刚性基底和盖层两部分,其中太华群构成了基底岩系,其它地层组成盖层岩系(胡正国等, 1994)。根据李继亮(1992, 2009)关于碰撞造山带的大地构造相分类方案,在秦岭碰撞造山带的形成过程中,太华群的基底岩系及其南部盖层属于仰冲基底相类(王义天和胡正国, 1999)。太华群地层为中深变质的角闪岩相,局部达麻粒岩相,岩性主要包括黑云斜长片麻岩、黑云角闪片麻岩、片麻状黑云斜长花岗岩、片麻状黑云石英闪长岩、斜长角闪岩、混合岩、石英岩、变粒岩、浅粒岩以及大理岩等。熊耳群不整合在太华群之上,以陆相喷发火山岩为主,岩性主要有玄武安山岩、安山岩、英安质或流纹质斑岩、火山角砾集块岩、碎屑熔岩、集块岩和沉凝灰岩等。官道口群为一套碎屑岩、化学沉积岩石组合,主要岩性为砂岩、页岩、白云岩、砂泥砾岩和泥板岩等。寒武系岩性以砂岩和白云岩为主,为碎屑-化学沉积产物。白垩系为一套红色岩系,岩性为紫红色粉砂质隐晶灰岩、含砾灰质白云岩、粉砂质粘土岩夹灰色砂砾岩及岩屑砂岩。
小秦岭金矿田南北两侧由两条大型断裂带所围限,奠定了小秦岭的基本构造格架(图 1)。北侧的太要断裂带呈近E-W向波状展布,整体产状向北陡倾;南侧的小河断裂带在走向上自西向东大致呈NE→近E-W→NE的变化,倾向南或南东。金矿田内部断裂和褶皱构造广泛发育。断裂构造以近E-W向为主,规模最大,其次为NW向、NE向和近S-N向,正是这些断裂控制了矿床的产出和分布,同时也控制了岩脉的产出。褶皱构造自北向南依次发育五里村背斜、七树坪向斜、老鸦岔背斜、庙沟向斜和上杨砦背斜,构成了一个近E-W向的复式背斜,其轴部位于大月坪-老鸦岔一线,横贯全区,向东西两端倾没围合。
小秦岭金矿田中岩浆岩十分发育,岩石类型以花岗岩类为主,同时发育基性岩和碱性岩岩脉。按照形成时代,花岗岩类大致可分为“一老一新”两组侵入岩体,老的包括元古代桂家峪岩体、张家坪岩体和小河岩体,以及多呈脉状或不规则岩株状的花岗伟晶岩;新的包括中生代的老牛山岩体、华山岩体、文峪岩体和娘娘山岩体(图 1)。桂家峪和张家坪岩体的岩性主要为角闪二长花岗岩、黑云角闪花岗岩、黑云二长花岗岩等,小河岩体的主要岩性为黑云二长花岗岩。中生代花岗岩呈巨大岩基产出,岩性以黑云二长花岗岩和黑云母花岗岩为主。基性岩脉的形成时期主要为古生代和中生代,主要岩性有辉绿岩、辉长辉绿岩、辉长辉绿玢岩和辉长玢岩等。碱性岩脉主要有正长斑岩、霓霞正长岩和火成碳酸岩等,主要形成于中生代。
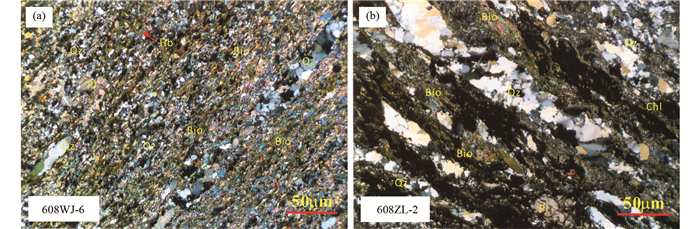
2 边缘构造带变形特征小秦岭金矿田南北两条边界断裂带早期表现为中深层次的韧性变形,中期为中上层次的韧脆性变形,晚期叠加浅层次的脆性变形而发育正断层和角砾岩带(胡正国等, 1994)。韧性变形的产物主要由长英质糜棱岩、绢英质糜棱岩、糜棱岩化片麻岩等组成,在断裂带中通常形成几米至上百米宽的糜棱岩带,糜棱岩面理的倾向大致与边缘构造带的整体走向垂直。本次工作对小秦岭东端武家山、庄里沟和柳沟一带的边缘构造带的变形特征进行了构造观察和测量,进而对构造岩样品开展构造年代学研究。构造带中发育糜棱岩化斜长角闪片麻岩、糜棱岩化黑云斜长片麻岩、长英质糜棱岩和绢英质糜棱岩等,其中绢英质糜棱岩中的石英脉少而小或无,主要表现为细的硅质条带。从露头尺度到显微尺度发育各种变形形迹。主要包括由长英质细脉和密集排列的云母类矿物构成的各种片内不对称无根褶皱、A型褶皱、褶曲等中尺度构造。例如,在庄里沟一带的露头,构造带的整体产状为150°∠40°,发育的不对称的、枢纽和轴面近水平的堆叠式层内揉皱(图 2a)、缓倾的层内褶曲(图 2b)、旋转碎斑系等变形形迹均指示了顺层滑脱变形。在小尺度上,矿物普遍拉长定向,发育透入性拉伸线理,整体产状130°∠20°。石英以韧性变形为主,多呈透镜体、扁豆体或细脉沿糜棱面理断续分布,长轴产状155°∠36°,还发育同构造压溶石英细脉;长石和少量的角闪石以脆韧性变形为主,形成σ型和δ型旋转碎斑,指示了顺层剪切变形;偶见绿泥石、绢云母。在显微尺度上,所有矿物均细粒化、定向排列,石英发育亚晶粒,具波状消光,还发育石英微细脉沿糜棱面理分布(图 3),石英和长石常呈小的扁豆体或σ型碎斑;黑云母为细小鳞片状,密集分布构成糜棱面理(图 3),常形成S-C组构,为变形变质的产物。不同尺度上的各种变形形迹和剪切运动学指向标志都表明,小秦岭金矿田东端构造带中的糜棱岩形成于中深层次的顺层剪切流变,是伸展滑脱构造的变形产物。

|
图 2 小秦岭金矿田东端边缘构造带庄里沟露头的滑脱变形构造 (a)层内揉皱;(b)层内褶曲 Fig. 2 Structures of extensional decollement deformation at the Zhuangligou outcrop within the marginal tectonic belt in the eastern end of the Xiaoqinling goldfield (a) intraformational crumple; (b) intraformational buckle |
|
图 3 小秦岭金矿田东端边缘构造带糜棱岩定年样品的正交偏光镜下显微特征 Qz-石英;Bio-黑云母;Pl-斜长石;Hb-角闪石;Chl-绿泥石 Fig. 3 Microscopic features of mylonite samples for dating from Wujiashan and Zhuangligou outcrops within the marginal tectonic belt in the eastern end of the Xiaoqinling goldfield (under cross-polarized light) Qz-quartz; Bio-biotite; Pl- plagioclase; Hb-hornblende; Chl-chlorite |
本次工作对采于武家山和庄里沟两个露头上的2件糜棱岩样品开展了黑云母单矿物40Ar-39Ar年代学研究,即直接对构造岩样品进行同位素定年。样品608WJ6(武家山,34°28′41″N、110°50′32″E)和608ZL2(庄里沟,34°27′19″N、110°50′28″E)均为黑云斜长质糜棱岩,镜下可见细小鳞片状的黑云母密集定向排列,形成糜棱面理,有的构成S-C组构;石英呈微细脉状、丝带状,发育波状消光、动态重结晶颗粒等;斜长石呈碎斑,偶见绿泥石(图 3)。
|
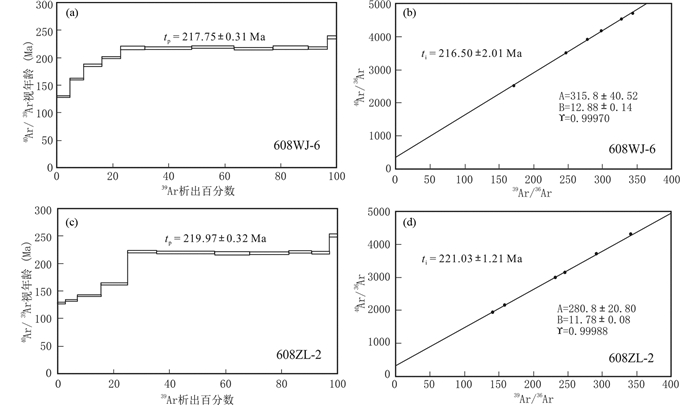
图 4 小秦岭金矿田东端边缘构造带糜棱岩样品的黑云母40Ar-39Ar坪年龄图(a、c)和等时线图(b、d) Fig. 4 Biotite 40Ar-39Ar plateau age diagrams (a, c) and isochron age diagrams (b, d) of the mylonite samples from the marginal tectonic belt in the eastern end of the Xiaoqinling goldfield |
构造岩样品经粉碎和重液分离后,在双目镜下挑选出新鲜的黑云母单矿物,纯度大于99%。单矿物样品在中国原子能科学研究院的49-2反应堆H8孔道进行快中子照射,样品608WJ6和608ZL2的照射参数分别为J=0.009898、J=0.011065。用于中子通量监测的标准样品是中国标样ZBH-25黑云母、国际标样BSP-1角闪石,它们的年龄分别为132.7±2.1Ma、2060±18.6Ma。照射后的样品在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所氩氩实验室的超高真空析氩系统中进行阶段加热,提纯后的氩用RGA-10气体源质谱仪进行静态氩同位素测定。对氩同位素质谱峰值进行了本底校正、质量歧视校正、分馏校正和记忆效应校正,对37Ar进行了衰变校正。钾钙诱发同位素校正因子分别为(40Ar/39Ar)K=3.048×10-3、(36Ar/37Ar)Ca=2.644×10-4、(39Ar/37Ar)Ca=6.868×10-4。年龄计算采用40K衰变常数λ=5.543×10-10/y,年龄误差为1σ。
4 测试结果样品608WJ6的黑云母重量为0.1065g,经过11个阶段的分步加热,加热温度区间为400~1400℃(表 1)。其中在780~1300℃的温度范围内,即第5~10的6个加热阶段获得的视年龄之间的差异极小,采用加权平均计算其坪年龄为217.75±0.31Ma(图 4a),39ArK的析出量为74%。采用线性回归计算其等时线年龄为216.50±2.01Ma(图 4b),相关系数为0.9997。初始40Ar/36Ar值为315.8±40.52,略大于标准尼尔值(295.5±5),指示样品中存在一定的过剩氩,但等时线年龄与坪年龄的测试结果具有极好的一致性,表明过剩氩的存在对所获年龄数据的可靠性影响不大。
|
|
表 1 小秦岭边缘构造带武家山糜棱岩(样品608WJ6)的黑云母40Ar-39Ar年龄分析结果 Table 1 Biotite 40Ar-39Ar dating analysis results of the Wujiashan mylonite (Sample 608WJ6) from the marginal tectonic belt in the eastern end of the Xiaoqinling goldfield |
样品608ZL2的黑云母重量0.1241g,也经过11个阶段的分步加热,加热温度区间为420~1400℃(表 2)。其中在800~1250℃的范围内,即第5~10的6个加热阶段获得了差异很小的一组视年龄,计算其坪年龄为219.97±0.32Ma(图 4c),39ArK的析出量为72.2%。计算其等时线年龄为221.03±1.21Ma(图 4d),相关系数为0.99988。初始40Ar/36Ar值为280.8±20.8,略小于标准尼尔值(295.5±5),指示样品中丢失了一定的氩,不过等时线的线性关系很好,说明中高温区各数据点(不同加热阶段的氩析出量对应于从矿物颗粒表面至颗粒内部的不同位置)的氩丢失均匀,因而等时线年龄具有更好的可靠性。
|
|
表 2 小秦岭边缘构造带庄里沟糜棱岩(样品608ZL2)的黑云母40Ar-39Ar年龄分析结果 Table 2 Biotite 40Ar-39Ar dating analysis results of the Zhuangligou mylonite (Sample 608ZL2) from the marginal tectonic belt in the eastern end of the Xiaoqinling goldfield |
在有关小秦岭金矿田中金矿床的三叠纪成矿年龄的最早报道中(表 3; 王秀璋等, 1992; 胡正国等, 1994; 卢欣祥等, 1999),由于文献中没有提供相关的样品描述、测试流程、分析数据表及图件、实验室等信息,所以这些年龄数据的可靠性无法判断。在后续的研究工作中,不同研究者采用多种精细的同位素定年方法测定了小秦岭代表性金矿床的成矿年龄,所有的数据都集中在早白垩世(李绍儒等, 1998; 徐启东等, 1998; 李强之等, 2002; Wang et al., 2002; Li et al., 2012b; 强山峰等, 2013; Zhao et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020)。因此,小秦岭金矿田中是否发育三叠纪金的成矿作用还有待于进一步研究。而越来越多的同位素年龄数据表明,在小秦岭金矿田南北边缘发育的钼、铅、铀等多金属矿床(图 1)主要形成于三叠纪(表 3)。钼矿是最发育的矿种,其中的泉家峪和车仓峪两个小型石英脉型钼矿床的辉钼矿Re-Os模式年龄为早白垩世(李厚民等, 2007; 赵海香等, 2015),除此以外其它钼矿床(体)的年龄都为三叠纪。在北缘,大型的大湖和红土岭、中型的马家洼石英脉型金矿床(图 1)的下部都发育石英脉型钼矿体,因此被称为金钼矿床,其中钼矿体的形成时代为三叠纪(表 3)。对红土岭金钼矿床的多种同位素定年研究结果显示,钼矿体的辉钼矿Re-Os等时线年龄为204.0±4.6Ma、独居石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄为203.5±8.1Ma(Zhao et al., 2019);金矿体的独居石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb年龄为130.4±5.3Ma(Zhao et al., 2019),矿化蚀变岩中的黑云母40Ar-39Ar等时线年龄为128.5±0.2Ma~126.7±0.2Ma(Wang et al., 2002)。推测与红土岭金钼矿床具有相似成矿特征的大湖和马家洼金钼矿床中的金矿体也形成于早白垩世。在南缘,发育多种三叠纪的矿产(图 1、表 3)。代表性的矿床包括黄龙铺、桃园、秦岭沟碳酸岩型钼铅矿床(黄典豪等, 1994, 2009; Stein et al., 1997; 王佳营等, 2020),西沟斑岩型钼矿床(袁海潮等, 2014; 杜芷葳等, 2020),华阳川碳酸岩型铀铌铅多金属矿床(高龙刚等, 2019; 王佳营等, 2020; 黄卉等, 2020; Zheng et al., 2020),Cai et al. (2020)认为华阳川多金属矿床发育两阶段成矿作用,分别发生在三叠纪和白垩纪。此外,在距小秦岭东缘60km左右的熊耳山地区,发育黄水庵碳酸岩型钼铅矿床,其辉钼矿Re-Os等时线年龄为208.4±3.6Ma(曹晶等,2014)。总之,除了大湖和马家洼金钼矿床的辉钼矿Re-Os年龄的部分数据误差较大以外,小秦岭金矿田钼、铅、铀多金属矿床的成矿年龄集中于222~200Ma(表 3),即晚三叠世,成矿作用与岩浆热液活动密切相关。
|
|
表 3 小秦岭金矿田三叠纪成岩成矿年龄数据 Table 3 Triassic age data of deposits and magmatic rocks in the Xiaoqinling goldfield |
近年来,采用精细的锆石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年方法对小秦岭金矿田中的花岗岩类岩体开展了许多研究工作,为厘定成岩年龄、揭示岩石成因提供了可靠依据。定年结果表明,老牛山、华山、文峪和娘娘山等四个岩基主要形成于早白垩世,同时在老牛山和华山岩体内部发现有三叠纪的岩石单元。Ding et al. (2011)、齐秋菊等(2012)、Li et al. (2020)报道了老牛山岩体的石堤峪二长花岗岩、石英闪长岩、石英二长岩、角闪二长岩等岩性的锆石U-Pb年龄为三叠纪,Hu et al. (2012)报道了华山的翁峪角闪二长花岗岩的锆石U-Pb年龄为三叠纪(图 1、表 3)。此外,早期报道有正长斑岩脉和钾长花岗岩脉的年龄为三叠纪(表 3; 胡正国等, 1994; 徐启东等, 1998)。总之,小秦岭金矿田中发育三叠纪的花岗岩体和碱性岩脉,成岩年龄集中于228~205Ma(表 3),亦即晚三叠世,略早于三叠纪多金属成矿作用。
5.2 三叠纪成矿事件的构造背景本次工作对小秦岭金矿田东端边缘构造带进行的构造观察和测量、以及构造年代学研究结果表明,这里发育伸展滑脱构造,构造变形时限为221~216Ma(图 4)。在南缘的桃园钼铅矿区中(图 1),NEE向控矿断裂带具有多次活动的特征,晚期发生近东西向水平剪切变形形成绢云母片岩,任富根等(2001)获得绢云母的K-Ar年龄为211Ma。如前所述,小秦岭金矿田钼、铅、铀多金属矿床形成于222~200Ma,三叠纪花岗岩体和碱性岩脉形成于228~205Ma(表 3)。显然,小秦岭金矿田三叠纪的构造变形、岩浆活动和成矿作用在时间上耦合,集中发育在晚三叠世228~200Ma期间;同时,多金属矿床在成因上都与岩浆热液活动相关。因此,小秦岭三叠纪成矿事件是在伸展构造背景中的构造-岩浆-流体活动的产物。
火成碳酸岩及相关的成矿作用常形成于伸展构造背景(Pirajno, 2015),毛景文等(2003, 2005)认为黄龙铺地区碳酸岩型钼铅矿床很可能是造山晚期地幔蠕动或脱气过程的一种成矿响应,黄典豪等(2009)、曹晶等(2014)认为黄龙铺和黄水庵碳酸岩形成于华北和扬子板块三叠纪碰撞造山后的伸展阶段。Zhao et al. (2019)提出红土岭金钼矿床中的钼矿体形成于秦岭造山带后碰撞阶段的岩石圈拆沉作用过程中。Ding et al. (2011)认为老牛山岩体中的印支期花岗岩类形成于秦岭造山带后碰撞伸展构造体制中,是碰撞后板片断离、软流圈上涌引起的。Hu et al. (2012)也认为华山岩体中的翁峪角闪二长花岗岩形成于同样的构造背景中。
三叠纪时期,秦岭造山带经历了从扬子克拉通向北俯冲,到最终与南秦岭地块沿勉略缝合带汇聚碰撞联为一体的演化过程,已成为目前的研究共识(Ames et al., 1993; 张国伟等, 1996, 2004; Meng and Zhang, 2000; Dong et al., 2011; Wang et al., 2013; Dong and Santosh, 2016)。而对于这一造山过程中不同构造演化阶段的时限还存在不同观点。高山等(1999)认为秦岭-大别造山带下地壳最后一次拆沉作用的时间可能为213~200Ma。张成立等(2008)认为西秦岭225~210Ma的花岗岩类是后碰撞阶段岩石圈拆沉作用的产物。Dong et al. (2011)、Dong and Santosh (2016)提出248~224Ma为俯冲阶段,碰撞发生在223~218Ma期间,随后进入后碰撞阶段。Wang et al. (2015)认为产于商丹缝合带中的三叠纪沙河湾奥长环斑花岗岩(Lu et al., 1996; 张宗清等, 1999)为高分异花岗岩,指示了217~209Ma时期为后碰撞阶段。陈衍景(2010)、Chen and Santosh (2014)认为扬子陆块与华北-秦岭联合大陆之间的碰撞始于230~200Ma,勉略洋作为古特提斯洋的一部分自东向西呈拉链式缝合的时间逐渐变晚。Chen et al. (2020)提出西秦岭三叠纪的造山过程为248~235Ma的俯冲阶段、235~225Ma碰撞阶段、225~195Ma后碰撞阶段,在后碰撞阶段俯冲板片断离,强烈的壳幔相互作用引发大规模岩浆活动及相关的成矿作用。
小秦岭金矿田位于华北克拉通南缘,是秦岭造山带的北缘组成部分,因此秦岭造山带三叠纪的构造演化过程会在研究区中得到响应并被记录下来。碰撞阶段的挤压构造作用可使地壳加厚,重力势能差增大。在碰撞峰期之后,随着水平挤压应力的减弱至消失,造山带进入松弛调整阶段,即从碰撞向后碰撞的转折时期,主应力轴由水平方向转为垂直方向,在重力作用下发育伸展滑脱构造,如在小秦岭金矿田东端边缘构造带中发育的枢纽和轴面近水平的堆叠式揉皱(图 2a)和缓倾的层内褶曲(图 2b)。因此,本次工作获得的构造年代学数据(221~216Ma)约束了小秦岭地区自碰撞向后碰撞转折的演化阶段时限,之后进入后碰撞阶段。
综合上述研究区内的三叠纪多金属成矿作用、构造变形和岩浆活动,以及区域上的构造研究成果表明,小秦岭金矿田三叠纪的成矿事件发生于伸展构造背景中,可以划分为两个阶段,早阶段的火成碳酸岩型钼铅、铀铌铅多金属矿床(221Ma左右)形成于碰撞向后碰撞转折阶段的重力滑脱构造环境中,晚阶段的石英脉型和斑岩型钼矿床(214~203Ma)形成于后碰撞阶段由俯冲板片断离或岩石圈拆沉作用等深部过程导致的区域伸展构造环境。
5.3 中生代两期伸展构造与成矿事件综合本次工作和前人的研究成果表明,小秦岭金矿田中生代经历了两期伸展构造活动,相应的发生了两次成矿事件。
(1) 晚三叠世伸展构造与成矿:伸展构造作用开始于由碰撞向后碰撞转折时期的重力滑脱构造,时限为221~216Ma,在此阶段形成酸岩型钼铅、铀铌铅多金属矿床。随后转入后碰撞阶段,在214~203Ma期间发育石英脉型和斑岩型钼矿床。
(2) 早白垩世伸展构造与成矿:这一时期在小秦岭金矿田中形成大量的石英脉型金矿床,前人对此已做了许多卓有成效的研究工作,认为在早白垩世时期中国东部发生大规模的岩石圈伸展减薄,软流圈物质上涌导致强烈的壳幔相互作用及相关的成矿作用(邓晋福等, 1999; Yang et al., 2003; 毛景文等, 2003, 2005),引发华北克拉通破坏(Yang et al., 2008; Li et al., 2012a; 朱日祥等, 2015; Li and Santosh, 2017)。在华北克拉通南缘,形成了一条近东西向的伸展构造走廊,发育骊山、小秦岭、崤山和熊耳山等变质核杂岩(Zhang and Zheng, 1999),小秦岭变质核杂岩(胡正国等, 1994; 胡正国和钱壮志, 1994; 石铨曾等, 1996; Zhang and Zheng, 1999; Wang et al., 2020; Li et al., 2020)是其中的典型代表,大规模的金成矿作用即发育在这一区域伸展构造背景中。
6 结论小秦岭金矿田三叠纪的成矿事件发生于晚三叠世的伸展构造背景,早阶段(221~216Ma)是在碰撞向后碰撞转折阶段的重力滑脱构造环境中,发育火成碳酸岩型钼铅、铀铌铅多金属矿床;晚阶段(214~203Ma)是在后碰撞阶段由俯冲板片断离或岩石圈拆沉作用等深部过程导致的区域伸展构造环境中,发育石英脉型和斑岩型钼矿床。在早白垩世,小秦岭金矿田大规模金的成矿作用构造背景是岩石圈大规模减薄的区域伸展构造。小秦岭中生代晚三叠世和早白垩世两期成矿事件都是在伸展构造背景中的构造-岩浆-流体活动的产物。
致谢 审稿人侯泉林教授和陈正乐研究员对本文提出了宝贵的意见和建议,谨致谢意!
第一作者于1996~1999年有幸师从李继亮老师攻读博士学位,先生博学多才、治学严谨,造诣深厚、卓尔不群,让我心生仰慕、如沐春风。在我三年的求学过程中,无论是专业学习,还是室内外研究工作,先生都循循善诱、耐心施教,将一个个概念、理论或构造现象的来龙去脉娓娓道来,仔细传授构造路线剖面的研究方法,甚至亲自带我去图书馆查阅文献。如今回首,这一切点点滴滴都历历在目,先生的学养精神和言传身教让我受益终身!在我毕业以后,先生仍然关心我的工作和生活,让我感受到了温暖和力量!永远怀念您,我的恩师!
Ames L, Tilton GR and Zhou GZ. 1993. Timing of collision of the Sino-Korean and Yangtse cratons: U-Pb zircon dating of coesite-bearing eclogites. Geology, 21(4): 339-342 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1993)021<0339:TOCOTS>2.3.CO;2
|
Cai JX, Yu LL, Xu DR, Gao C, Chen GW, Yu DS, Jiao QQ, Ye TW, Zou SH and Li LR. 2020. Multiple episodes of tectono-thermal disturbances in the Huayangchuan UNb-Pb polymetallic deposit in the Xiaoqinling region, central China and their significances on metallogeny. Ore Geology Reviews, 127: 103755 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103755
|
Cao J, Ye HS, Li HY, Li ZY, Zhang XK, He W and Li C. 2014. Geological characteristics and molybdenite Re-Os isotopic dating of Huangshuian carbonatite vein-type Mo (Pb) deposit in Songxian County, Henan Province. Mineral Deposit, 33(1): 53-69 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen SC, Wang YT, Yu JJ, Hu QQ, Zhang J, Wang RT, Gao WH and Wang CA. 2020. Petrogenesis of Triassic granitoids in the Fengxian-Taibai ore cluster, Western Qinling Orogen, central China: Implications for tectonic evolution and polymetallic mineralization. Ore Geology Reviews, 123: 103577 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103577
|
Chen YJ. 2010. Indosinian tectonic setting, magmatism and metallogenesis in Qinling Orogen, central China. Geology in China, 37(4): 854-865 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen YJ and Santosh M. 2014. Triassic tectonics and mineral systems in the Qinling Orogen, central China. Geological Journal, 49(4-5): 338-358 DOI:10.1002/gj.2618
|
Deng JF, Mo XX, Zhao HL, Luo ZH, Zhao GC and Dai SQ. 1999. The Yanshanian lithosphere-asthenosphere catastrophe and metallogenic environment in East China. Mineral Deposit, 18(4): 309-315 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Ding LX, Ma CQ, Li JW, Robinson PT, Deng XD, Zhang C and Xu WC. 2011. Timing and genesis of the adakitic and shoshonitic intrusions in the Laoniushan complex, southern margin of the North China Craton: Implications for post-collisional magmatism associated with the Qinling Orogen. Lithos, 126(3-4): 212-232 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.008
|
Dong YP, Zhang GW, Neubauer F, Liu XM, Genser J and Hauzenberger C. 2011. Tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, China: Review and synthesis. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 41(3): 213-237 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.03.002
|
Dong YP and Santosh M. 2016. Tectonic architecture and multiple orogeny of the Qinling Orogenic Belt, Central China. Gondwana Research, 29(1): 1-40 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.06.009
|
Du ZW, Ye HS, Mao JW, Meng F, Cao J, Wang P, Wei Z and Ding JH. 2020. Molybdenite Re-Os gochronology and isotope geochemical characteristics of Xigou molybdenum deposit in Shaanxi Province and its geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 39(4): 728-744 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Gao LG, Chen YW, Bi XW, Hu RZ, Gao C, Dong SH and Luo JC. 2019. Chronology and mineral chemistry of the uranium minerals in Huayangchuan uranium-niobium deposit, Shaanxi Province and its implications for uranium mineralization. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(9): 2273-2291 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Gao S, Zhang BR, Jin ZM and Kern H. 1999. Lower crustal delamination in the Qinling-Dabie orogenic belt. Science in China (Series D), 42(4): 423-433 DOI:10.1007/BF02874262
|
Hu HZ, Li N, Deng XH, Chen YJ and Li Y. 2013. Indosinian Mo mineralization in Qinling area and prospecting potential. Geology in China, 40(2): 549-565 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Hu J, Jiang SY, Zhao HX, Shao Y, Zhang ZZ, Xiao E, Wang YF, Dai BZ and Li HY. 2012. Geochemistry and petrogenesis of the Huashan granites and their implications for the Mesozoic tectonic settings in the Xiaoqinling gold mineralization belt, NW China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 56: 276-289 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.05.016
|
Hu ZG and Qian ZZ. 1994. A new idea of geological tectonics in the Xiaoqinling region. Geological Review, 40(4): 289-295 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Hu ZG, Qian ZZ, Yan GM, Chen ZL and Li MX. 1994. Detachment-Metamorphic Core Complex Tectonics and Gold Deposits in the Xiaoqinling. Xi'an: Shaanxi Science and Technology Press, 1-238 (in Chinese)
|
Huang DH, Wu CY, Du AD and He HL. 1994. Re-Os isotope ages of molybdenum deposits in East Qinling and their significance. Mineral Deposits, 13(3): 221-230 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Huang DH, Hou ZQ, Yang ZM, Li ZQ and Xu DX. 2009. Geological and geochemical characteristics, metallogenetic mechanism and tectonic setting of carbonatite vein-type Mo (Pb) deposits in the East Qinling molybdenum ore belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(12): 1968-1984 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Huang H, Pan JY, Hong BY, Kang QQ and Zhong FJ. 2020. EPMA chemical U-Th-Pb dating of uraninite in Huayangchuan U-polymetallic deposit of Shaanxi Province and its geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 39(2): 351-368 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Jian W, Lehmann B, Mao JW, Ye HS, Li ZY, He HJ, Zhang JG, Zhang H and Feng JW. 2015. Mineralogy, fluid characteristics, and Re-Os age of the Late Triassic Dahu Au-Mo deposit, Xiaoqinling region, Central China: Evidence for a magmatic-hydrothermal origin. Economic Geology, 110(1): 119-145 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.110.1.119
|
Li HM, Ye HS, Mao JW, Wang DH, Chen YC, Qu WJ and Du AD. 2007. Re-Os dating of molybdenites from Au (Mo) deposits in Xiaoqinling gold ore district and its geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 26(4): 417-424 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li JL. 1992. Tectonic Facies of Collisional Orogenic Belts. In: Li QB, Dai JX, Liu RQ and Li JL (eds.). Collection of Research on Modern Geology (Part Ⅰ). Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 9-22 (in Chinese)
|
Li JL. 2009. Global tectonic facies: A preclusive opinion. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(10): 1375-1381 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li JW, Bi SJ, Selby D, Chen L, Vasconcelos P, Thiede D, Zhou MF, Zhao XF, Li ZK and Qiu HN. 2012a. Giant Mesozoic gold provinces related to the destruction of the North China craton. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 349-350: 26-37 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2012.06.058
|
Li JW, Li ZK, Zhou MF, Chen L, Bi SJ, Deng XD, Qiu HN, Cohen B, Selby D and Zhao XF. 2012b. The Early Cretaceous Yangzhaiyu lode gold deposit, North China Craton: A link between craton reactivation and gold veining. Economic Geology, 107(1): 43-79 DOI:10.2113/econgeo.107.1.43
|
Li N, Sun YL, Li J, Xue LW and Li WB. 2008. Molybdenite Re-Os isotope age of the Dahu Au-Mo deposit, Xiaoqinling and the Indosinian mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(4): 810-816 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li QZ, Chen YJ, Zhong ZQ, Li WL, Li SR, Guo XD and Jin BY. 2002. 40Ar-39Ar ages of the ore-forming processes of the Dongchuang gold deposit in the Xiaoqinling district, China. Geological Review, 48(Suppl.1): 122-126 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li SR, Li QZ, Li WL and Guo XD. 1998. A new viewpoint of ore genesis in Xiaoqinling gold field. Gold Geology, 4(1): 41-49 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li SR and Santosh M. 2017. Geodynamics of heterogeneous gold mineralization in the North China Craton and its relationship to lithospheric destruction. Gondwana Research, 50: 267-292 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2017.05.007
|
Li YJ, Zhu G, Su N, Xiao SY, Zhang S, Liu C, Xie CL, Yin H and Wu XD. 2020. The Xiaoqinling metamorphic core complex: A record of Early Cretaceous backarc extension along the southern part of the North China Craton. GSA Bulletin, 132(3-4): 617-637 DOI:10.1130/B35261.1
|
Liu JC, Wang YT, Hu QQ, Wei R, Huang SK, Sun ZH and Hao JL. 2020. Ore genesis of the Fancha gold deposit, Xiaoqinling goldfield, southern margin of the North China Craton: Constraints from pyrite Re-Os geochronology and He-Ar, in-situ S-Pb isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 119: 103373 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103373
|
Lu XX, Dong Y, Chang QL, Xiao QH, Li XB, Wang XX and Zhang GW. 1996. Indosinian Shahewan rapakivi granite in Qinling and its dynamic significance. Science in China (Series D), 39(3): 266-272
|
Lu XX, Wei XD, Dong Y and Xuan SM. 1999. The metallogenetic epoch of gold deposits in Xiaoqinling-Xiong'ershan region. Gold Geology, 5(1): 11-16 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Lu XX, Li ML, Wang W, Yu ZP and Shi YZ. 2008. Indosinian movement and metallogenesis in Qinling orogenic belt. Mineral Deposits, 27(6): 762-773 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Mao JW, Goldfarb RJ, Zhang ZW, Xu WY, Qiu YM and Deng J. 2002. Gold deposits in the Xiaoqinling-Xiong'ershan region, Qinling Mountains, central China. Mineralium Deposita, 37(3): 306-325
|
Mao JW, Wang YT, Zhang ZH, Yu JJ and Niu BG. 2003. Geodynamic settings of Mesozoic large-scale mineralization in North China and adjacent areas. Science in China (Series D), 46(8): 838-851
|
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Zhang ZH, Li XF, Wang YT, Zhang CQ and Li YF. 2005. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic settings. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(1): 169-188 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Mao JW, Zhou ZH, Feng CY, Wang YT, Zhang CQ, Peng HJ and Yu M. 2012. A preliminary study of the Triassic large-scale mineralization in China and its geodynamic setting. Geology in China, 39(6): 1437-1471 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Meng QR and Zhang GW. 2000. Geologic framework and tectonic evolution of the Qinling orogen, Central China. Tectonophysics, 323(3-4): 183-196 DOI:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00106-2
|
Pirajno F. 2015. Intracontinental anorogenic alkaline magmatism and carbonatites, associated mineral systems and the mantle plume connection. Gondwana Research, 27(3): 1181-1216 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2014.09.008
|
Qi QJ, Wang XX, Ke CH and Li JB. 2012. Geochronology and origin of the Laoniushan complex in the southern margin of North China Block and their implications: New evidences from zircon dating, Hf isotopes and geochemistry. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 28(1): 279-301 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Qiang SF, Bi SJ, Deng XD, Guo LQ and Li JW. 2013. Monazite U-Th-Pb ages of the Qinnan gold deposit, Xiaoqinling district: Implications for regional metallogenesis and tectonic setting. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 38(1): 43-56 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.3799/dqkx.2013.005
|
Ren FG, Yin YJ, Li SB and Zhao JN. 2001. The coupling character between isotopic geochronology of Indosinian epoch in Xiong'er fault basin. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 20(4): 286-288 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Shi QZ, Wei XD and Li ML. 1996. Basic characteristics of metamorphic core complex in Xiaoqinling and its relationship with gold mineralization. In: Henan Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources (ed.). Papers on Geology, Mineral Resources and Environment in Henan Province. Beijing: China Environmental Science Press, 11-17 (in Chinese)
|
Stein HJ, Markey RJ, Morgan JW, Du A and Sun Y. 1997. Highly precise and accurate Re-Os ages for molybdenite from the East Qinling molybdenum belt, Shaanxi Province, China. Economic Geology, 92(7-8): 827-835 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.92.7-8.827
|
Wang JY, Li ZD, Zhang Q, Li C, Xie Y, Li GY, Zeng W and Ding N. 2020. Metallogenic epoch of the carbonatite-type Mo-U polymetallic deposit in East Qinling: Evidence from the monazite LA-ICP-MS U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os isotopic dating. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(10): 2946-2964 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang XX, Wang T and Zhang CL. 2013. Neoproterozoic, Paleozoic, and Mesozoic granitoid magmatism in the Qinling Orogen, China: Constraints on orogenic process. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 72: 129-151 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.11.037
|
Wang XX, Wang T and Zhang CL. 2015. Granitoid magmatism in the Qinling orogen, central China and its bearing on orogenic evolution. Science China (Earth Sciences), 58(9): 1497-1512 DOI:10.1007/s11430-015-5150-2
|
Wang XZ, Cheng JP, Zhang BG, Fan WL, Bai ZH and Liang HY. 1992. Geochemistry of the Reformed-type Gold Deposits in China. Beijing: Science Press, 1-177 (in Chinese)
|
Wang YT and Hu ZG. 1999. Geotectonic facies analysis of the Xiaoqinling gold deposit. In: Chen HH, Hou QL and Xiao WJ (eds.). A Study of Collisional Orogenic Belts in China. Beijing: China Ocean Press, 224-232 (in Chinese)
|
Wang YT and Mao JW. 2002. Mineralization in the post-collisional orogenic extensional regime: A case study of the Xiaoqinling gold deposit clustering area. Geological Bulletin of China, 21(8): 562-566 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang YT, Mao JW, Lu XX and Ye AW. 2002. 40Ar-39Ar dating and geological implication of auriferous altered rocks from the middle-deep section of Q875 gold-quartz vein in Xiaoqinling area, Henan, China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 47(20): 1750-1755 DOI:10.1007/BF03183322
|
Wang YT, Ye HS, Ye AW, Li YG, Shuai Y, Zhang CQ and Dai JZ. 2010. Re-Os age of molybdenite from the Majiawa Au-Mo deposit of quartz vein type in the northern margin of the Xiaoqinling gold area and its implication for metallogeny. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(2): 140-145 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang YT, Ye HS, Ye AW, Liu SL, Hao JL, Liu JC, Wei R, Huang SK and Sun ZH. 2020. Cooling and uplift history of the Niangniangshan granitic pluton in the Xiaoqinling goldfield, central China: Implications for tectonic evolution and gold mineralization. Geological Journal, 55(8): 5967-5977 DOI:10.1002/gj.3662
|
Wu FY, Lin JQ, Wilde SA, Zhang XO and Yang JH. 2005. Nature and significance of the Early Cretaceous giant igneous event in eastern China. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 233(1-2): 103-119 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2005.02.019
|
Xu QD, Zhong ZQ, Zhou HW, Yang FC and Tang XC. 1998. 40Ar/39Ar dating of the Xiaoqinling gold area in Henan Province. Geological Review, 44(3): 323-327 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang JH, Wu FY and Wilde SA. 2003. A review of the geodynamic setting of large-scale Late Mesozoic gold mineralization in the North China Craton: An association with lithospheric thinning. Ore Geology Reviews, 23(3-4): 125-152 DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(03)00033-7
|
Yang JH, Wu FY, Wilde SA, Belousova E and Griffin WL. 2008. Mesozoic decratonization of the North China block. Geology, 36(6): 467-470 DOI:10.1130/G24518A.1
|
Yuan HC, Wang RT, Jiao JG, Li WY, Liu WQ and Tan W. 2014. Re-Os isotopic ages of molybdenites from Xigou Mo deposit in Huaxian of East Qinling and their geological significance. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 36(1): 120-127 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang CL, Wang T and Wang XX. 2008. Origin and tectonic setting of the Early Mesozoic granitoids in Qinling orogenic belt. Geological Journal of China Universities, 14(3): 304-316 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang GW, Meng QR, Yu ZP, Sun Y, Zhou DW and Guo AL. 1996. Orogenesis and dynamics of the Qinling Orogen. Science in China (Series D), 39(3): 225-234
|
Zhang GW, Cheng SY, Guo AL, Dong YP, Lai SC and Yao AP. 2004. Mianlue paleo-suture on the southern margin of the Central Orogenic System in Qinling-Dabie: With a discussion of the assembly of the main part of the continent of China. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(9-10): 846-853 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang JJ and Zheng YD. 1999. Multistage extension and age dating of the Xiaoqinling metamorphic core complex, Central China. Acta Geologica Sinica, 73(2): 139-147 DOI:10.1111/j.1755-6724.1999.tb00821.x
|
Zhang ZQ, Zhang GW, Tang SH and Lu XX. 1999. The age of the Shahewan rapakivi granite in Qinling and its restriction on the end of main orogeny of Qinling orogenic belt. Chinese Science Bulletin, 44(9): 981-984 (in Chinese) DOI:10.1360/csb1999-44-9-981
|
Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Cawood PA and Sun M. 2001. Archean blocks and their boundaries in the North China Craton: Lithological, geochemical, structural and P-T path constraints and tectonic evolution. Precambrian Research, 107(1-2): 45-73 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(00)00154-6
|
Zhao HX, Dai BZ, Li B and Zhu ZY. 2015. Genesis of the Checangyu molybdenum deposit in the Xiaoqinling district: Constraints from the Re-Os dating of molybdenite and in situ trace element analysis of pyrite. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(3): 784-790 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao SR, Li JW, Lentz D, Bi SJ, Zhao XF and Tang KF. 2019. Discrete mineralization events at the Hongtuling Au-(Mo) vein deposit in the Xiaoqinling district, southern North China Craton: Evidence from monazite U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os dating. Ore Geology Reviews, 109: 413-425 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.04.025
|
Zheng H, Chen HY, Li DF, Wu C, Chen X and Lai CK. 2020. Timing of carbonatite-hosted U-polymetallic mineralization in the supergiant Huayangchuan deposit, Qinling Orogen: Constraints from titanite U-Pb and molybdenite Re-Os dating. Geoscience Frontiers, 11(5): 1581-1592 DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2020.03.001
|
Zhu RX, Fan HR, Li JW, Meng QR, Li SR and Zeng QD. 2015. Decratonic gold deposits. Science China (Earth Sciences), 58(9): 1523-1537 DOI:10.1007/s11430-015-5139-x
|
曹晶, 叶会寿, 李洪英, 李正远, 张兴康, 贺文, 李超. 2014. 河南嵩县黄水庵碳酸岩脉型钼(铅)矿床地质特征及辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄. 矿床地质, 33(1): 53-69. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2014.01.004 |
陈衍景. 2010. 秦岭印支期构造背景、岩浆活动及成矿作用. 中国地质, 37(4): 854-865. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2010.04.003 |
邓晋福, 莫宣学, 赵海玲, 罗照华, 赵国春, 戴圣潜. 1999. 中国东部燕山期岩石圈-软流圈系统大灾变与成矿环境. 矿床地质, 18(4): 309-315. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.1999.04.003 |
杜芷葳, 叶会寿, 毛景文, 孟芳, 曹晶, 王鹏, 魏征, 丁建华. 2020. 陕西西沟钼矿床辉钼矿Re-Os年代学和同位素地球化学特征及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 39(4): 728-744. |
高龙刚, 陈佑纬, 毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 高成, 董少花, 骆金诚. 2019. 陕西华阳川铀铌矿床中铀矿物的年代学与矿物化学研究及其对铀成矿的启示. 地质学报, 93(9): 2273-2291. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.09.012 |
高山, 张本仁, 金振民, Kern H. 1999. 秦岭-大别造山带下地壳拆沉作用. 中国科学(D辑), 29(6): 532-541. |
胡海珠, 李诺, 邓小华, 陈衍景, 李毅. 2013. 秦岭地区印支期钼矿化特征及找矿前景. 中国地质, 40(2): 549-565. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2013.02.019 |
胡正国, 钱壮志. 1994. 小秦岭地质构造新认识. 地质论评, 40(4): 289-295. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1994.04.001 |
胡正国, 钱壮志, 闫广民, 陈在劳, 李民贤. 1994. 小秦岭拆离-变质杂岩核构造与金矿. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 1-238.
|
黄典豪, 吴澄宇, 杜安道, 何红蓼. 1994. 东秦岭地区钼矿床的铼-锇同位素年龄及其意义. 矿床地质, 13(3): 221-230. |
黄典豪, 侯增谦, 杨志明, 李振清, 许道学. 2009. 东秦岭钼矿带内碳酸岩脉型钼(铅) 矿床地质-地球化学特征、成矿机制及成矿构造背景. 地质学报, 83(12): 1968-1984. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2009.12.012 |
黄卉, 潘家永, 洪斌跃, 康清清, 钟福军. 2020. 陕西华阳川铀-多金属矿床晶质铀矿电子探针U-Th-Pb化学定年及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 39(2): 351-368. |
李厚民, 叶会寿, 毛景文, 王登红, 陈毓川, 屈文俊, 杜安道. 2007. 小秦岭金(钼) 矿床辉钼矿铼-锇定年及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 26(4): 417-424. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2007.04.005 |
李继亮. 1992. 碰撞造山带大地构造相. 见: 李清波, 戴金星, 刘如琦, 李继亮编. 现代地质学研究文集(上). 南京: 南京大学出版社, 9-22
|
李继亮. 2009. 全球大地构造相刍议. 地质通报, 28(10): 1375-1381. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.10.002 |
李诺, 孙亚莉, 李晶, 薛良伟, 李文博. 2008. 小秦岭大湖金钼矿床辉钼矿铼锇同位素年龄及印支期成矿事件. 岩石学报, 24(4): 810-816. |
李强之, 陈衍景, 钟增球, 李文良, 李绍儒, 郭晓东, 金宝义. 2002. 小秦岭东闯金矿成矿作用的40Ar-39Ar年代学研究. 地质论评, 48(增1): 122-126. |
李绍儒, 李强之, 李文良, 郭晓东. 1998. 小秦岭金矿田矿床成因新认识. 黄金地质, 4(1): 41-49. |
卢欣祥, 尉向东, 董有, 轩慎民. 1999. 小秦岭-熊耳山地区金矿时代. 黄金地质, 5(1): 11-16. |
卢欣祥, 李明立, 王卫, 于在平, 时永志. 2008. 秦岭造山带的印支运动及印支期成矿作用. 矿床地质, 27(6): 762-773. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2008.06.009 |
毛景文, 张作衡, 余金杰, 王义天, 牛宝贵. 2003. 华北及邻区中生代大规模成矿的地球动力学背景: 从金属矿床年龄精测得到启示. 中国科学(D辑), 33(4): 289-299. |
毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 李晓峰, 王义天, 张长青, 李永峰. 2005. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景. 岩石学报, 21(1): 169-188. |
毛景文, 周振华, 丰成友, 王义天, 张长青, 彭惠娟, 于淼. 2012. 初论中国三叠纪大规模成矿作用及其动力学背景. 中国地质, 39(6): 1437-1471. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.06.001 |
齐秋菊, 王晓霞, 柯昌辉, 李金宝. 2012. 华北地块南缘老牛山杂岩体时代、成因及地质意义——锆石年龄、Hf同位素和地球化学新证据. 岩石学报, 28(1): 279-301. |
强山峰, 毕诗健, 邓晓东, 郭连巧, 李建威. 2013. 豫西小秦岭地区秦南金矿床热液独居石U-Th-Pb定年及其地质意义. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 38(1): 43-56. |
任富根, 殷艳杰, 李双保, 赵家农. 2001. 熊耳裂陷印支期同位素地质年龄耦合性. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 20(4): 286-288. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2001.04.022 |
石铨曾, 尉向东, 李明立. 1996. 小秦岭变质核杂岩基本特征及与金的成矿作用. 见: 河南省地质矿产厅编. 河南地质矿产与环境论文集. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 11-17
|
王佳营, 李志丹, 张祺, 李超, 谢瑜, 李光耀, 曾威, 丁宁. 2020. 东秦岭地区碳酸岩型钼-铀多金属矿床成矿时代: 来自LA-ICP-MS独居石U-Pb和辉钼矿Re-Os年龄的证据. 地质学报, 94(10): 2946-2964. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.10.011 |
王秀璋, 程景平, 张宝贵, 樊文苓, 白正华, 梁华英. 1992. 中国改造型金矿床地球化学. 北京: 科学出版社, 1-177.
|
王义天, 胡正国. 1999. 小秦岭金矿的大地构造相分析. 见: 陈海泓, 侯泉林, 肖文交编. 中国碰撞造山带研究. 北京: 海洋出版社, 224-232
|
王义天, 毛景文. 2002. 碰撞造山作用期后伸展体制下的成矿作用——以小秦岭金矿集中区为例. 地质通报, 21(8): 562-566. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2002.08.017 |
王义天, 叶会寿, 叶安旺, 李永革, 帅云, 张长青, 代军治. 2010. 小秦岭北缘马家洼石英脉型金钼矿床的辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及其意义. 地学前缘, 17(2): 140-145. |
徐启东, 钟增球, 周汉文, 杨发城, 唐学超. 1998. 豫西小秦岭金矿区的一组40Ar/39Ar定年数据. 地质论评, 44(3): 323-327. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.1998.03.014 |
袁海潮, 王瑞廷, 焦建刚, 李伍义, 刘文庆, 谭雯. 2014. 东秦岭华县西沟钼矿床Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义. 地球科学与环境学报, 36(1): 120-127. |
张成立, 王涛, 王晓霞. 2008. 秦岭造山带早中生代花岗岩成因及其构造环境. 高校地质学报, 14(3): 304-316. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.03.003 |
张国伟, 孟庆任, 于在平, 孙勇, 周鼎武, 郭安林. 1996. 秦岭造山带的造山过程及其动力学特征. 中国科学(D辑), 26(3): 193-200. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1006-9267.1996.03.001 |
张国伟, 程顺有, 郭安林, 董云鹏, 赖绍聪, 姚安平. 2004. 秦岭-大别中央造山系南缘勉略古缝合带的再认识——兼论中国大陆主体的拼合. 地质通报, 23(9-10): 846-853. |
张宗清, 张国伟, 唐索寒, 卢欣祥. 1999. 秦岭沙河湾奥长环斑花岗岩的年龄及其对秦岭造山带主造山期结束时间的限制. 科学通报, 44(9): 981-984. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.1999.09.020 |
赵海香, 戴宝章, 李斌, 朱志勇. 2015. 小秦岭车仓峪钼矿成因研究: 辉钼矿Re-Os年龄及黄铁矿微量元素制约. 岩石学报, 31(3): 784-790. |
朱日祥, 范宏瑞, 李建威, 孟庆任, 李胜荣, 曾庆栋. 2015. 克拉通破坏型金矿床. 中国科学(地球科学), 45(8): 1153-1168. |
 2021, Vol. 37
2021, Vol. 37