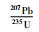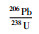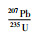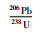2. 中国地质科学院, 北京 100037;
3. 中国地质调查局, 中国地质科学院地球深部探测中心, 北京 100037;
4. 河北省区域地质调查院, 廊坊 065000;
5. 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所, 北京 100081
2. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100037, China;
3. SinoProbe Center, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, China Geological Survey, Beijing 100037, China;
4. Hebei Regional Geological Survey Institute, Langfang 065000, China;
5. Institute of Geomechanics, Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, Beijing 100081, China
三江特提斯造山带位于欧亚板块、印度板块和太平洋板块的构造交汇处(Wang et al., 2018),一直以来以其独特的构造演化历史备受研究者的青睐(Tapponnier et al., 1990, 2001; Mo et al., 1994; 潘桂棠等, 2003; Jian et al., 2009a, b ; 莫宣学和潘桂棠, 2006; Deng et al., 2014)。三江特提斯造山带中,中特提斯及新特提斯构造事件的构造变形较为普遍,而古特提斯由于构造演化的复杂性和研究程度的局限性,在一些关键问题如洋盆闭合时代、岩浆岩在古特提斯演化中的位置等一直具有争议(张旗等, 1988; 钟大赉, 1998; Fan et al., 2010; 李龚健等, 2013; Xu et al., 2019)。
古特提斯主要包括两个分支:昌宁-孟连缝合带和金沙江-哀牢山缝合带(Metcalfe, 2006; Jian et al., 2009b)。金沙江-哀牢山缝合带连接了特提斯-喜马拉雅构造域和太平洋构造域,显示了华南板块和印支板块的地质亲缘关系,是了解古特提斯构造演化的关键区域(潘裕生, 1999; Xu et al., 2019)。目前,金山江缝合带碰撞型岩浆岩已有许多年代学和地球化学的报道,丰富了古特提斯演化的资料(高睿等, 2010; 杨喜安等, 2013; Zhu et al., 2011)。王保弟等(2011)测得德钦地区人支雪峰山组双峰式火山岩套中流纹岩LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄为249~247Ma,认为金沙江缝合带在早三叠世已进入后碰撞伸展时期。Zi et al. (2012)测得攀天阁组流纹岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为245~237Ma,结合Sr-Nd同位素,认为该火山岩为金沙江洋闭合造山后伸展作用的产物。相比之下,哀牢山构造带内可限制哀牢山洋闭合时限的岩浆岩的研究则略微不足。
位于哀牢山构造带中段的镇沅金矿酸性岩发育,前人研究主要集中于矿床地质特征、矿床成因等方面而忽视了矿区花岗斑岩的构造意义(胡云中和唐尚鹑, 1995; 何明友和胡瑞忠, 1996; Burnard et al., 1999; 黄智龙等, 1999; 薛传东等, 2002; 杨立强等, 2010, 2011; 梁业恒等, 2011; 邓碧平等, 2013; 邓军等, 2013; 赵凯等, 2013)。本文以矿区花岗斑岩为研究对象,通过系统分析其矿物学、地球化学、同位素年代学、Lu-Hf同位素特征,探讨其岩浆源区与岩石成因,进而对古特提斯洋的演化提供相关的信息。
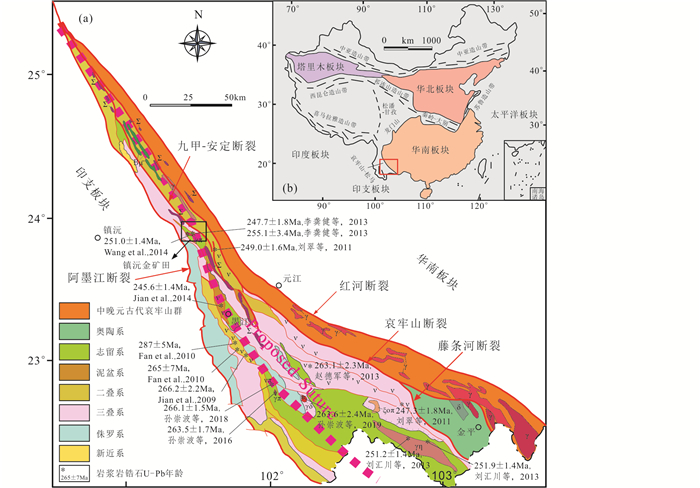
1 地质背景 1.1 区域地质概况三江古特提斯造山带是东特提斯构造域的一个重要分支,且保留了亚洲东南部特提斯构造域演化的记录(Wang et al., 2014a, b, 2015a, b, 2016)。构造上,哀牢山古特提斯造山带位于西南三江地区的东南,华南板块的西侧(邓军等, 2010; Deng et al., 2014, 2017; Wang et al., 2014c; 杨立飞等, 2016)。由于长期的构造演化,该变形变质带呈现扫帚状,位于扬子地块和思茅地块之间(Wang et al., 2015b, 2016; 杜斌等, 2016)。哀牢山造山带北西起于弥渡牛街,向南东于金平一带延伸出国外。该区处于三条断裂带间的构造-岩浆岩-变质带,北西窄而南东宽(图 1)。区内构造复杂,岩浆活动频繁,变质作用强烈,成矿流体、成矿物质和成矿作用活跃,显然是受控于三条构造断裂带。镇沅金矿、墨江金矿、大坪金矿和长安金矿等,都位于该构造带内。
|
图 1 哀牢山造山带区域地质图(a)及研究区在中国大地构造图中的位置(b)(据Zhao and Guo, 2012修改) Fig. 1 Geological map of the Ailaoshan orogenic belt (a) and the location of the study area in China's tectonic map (b) (modified after Zhao and Guo, 2012) |
出露地层以哀牢山断裂为界,北东为下元古界深变质带-哀牢山群;南西为古生界浅变质带,其上为中、新生界地层(王明亮等, 2014)。哀牢山岩群包括小羊街组(Pt1x)、阿龙组(Pt1a)、凤港组(Pt1f)、乌都坑组(Pt1w)。小羊街下部岩性主要为二云片岩、黑云变粒岩,上部岩性主要为黑云斜长片麻岩、黑云角闪石岩。阿龙组下部岩性主要为角闪斜长片麻岩、角闪变粒岩、透辉大理岩等,上部岩性主要为大理岩、黑云角闪变粒岩、斜长角闪岩。凤港组下部岩性主要为夕线黑云二长片麻岩、石榴黑云角闪岩、黑云斜长变粒岩、浅粒岩,中上部岩性主要为斜长角闪岩、石榴斜长角闪岩、大理岩。乌都坑组下部岩性主要为混合岩化黑云斜长片麻岩和黑云角闪斜长片麻岩、角闪岩、片岩,上部岩性主要为含石英片岩、石墨片岩、大理岩。
本区岩浆活动具有多期性和长期性的特点,从加里东期到喜马拉雅期均有;活动上既有喷发,又有侵入;既有热接触,又有冷接触;从超基性岩到碱性岩,岩石具多类型的特征。岩石的产出形态、规模和展布均受到三条深大断裂的制约和控制。酸性岩发育广泛,主要出露于哀牢山断裂之北东和南西两侧,其次沿九甲-阿墨江断裂分布。
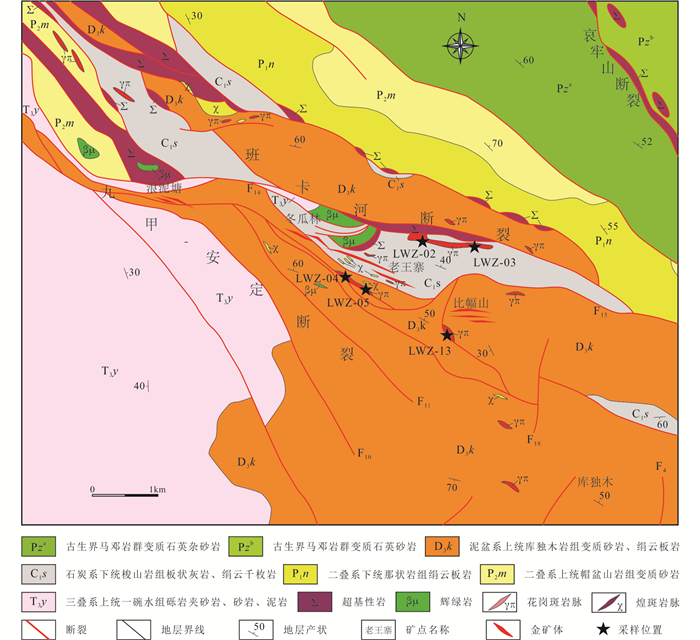
1.2 矿床特征镇沅金矿田位于哀牢山造山带中段。矿区出露地层为晚古生界、中生界及新生界地层(图 2)。泥盆系上统库独木组上段(D3k2),下部岩性主要为硅质板岩和绢云硅质板岩,中部岩性主要为含炭泥质灰岩;上部岩性主要为变质细粒石英杂砂岩,有大量石英斑岩、花岗斑岩、煌斑岩脉侵入,为冬瓜林矿段主要容矿地层(蔡飞跃等, 2010)。石炭系下统梭山岩组下段(C1s1)岩性主要为泥晶灰岩和含炭钙质板岩。石炭系下统梭山岩组上段(C1s2)岩性主要为含炭钙质板岩、含炭砂质绢云板岩、变质石英杂砂岩。二叠系下统那壮岩组(P1n)岩性主要为绢云千枚岩、变质石英杂砂岩、钙质板岩。三叠系上统一碗水组下段二层(T3y1-2)岩性主要为凝灰质粉砂岩、岩屑石英杂砂岩。第四系全新统(Qh)分布于河谷阶地、山坡及洼地,主要为冲洪积和残坡积。
|
图 2 镇沅金矿田地质简图(据林文信, 1992修改) Fig. 2 Sketch geological map of Zhenyuan gold ore field (modified after Lin, 1992) |
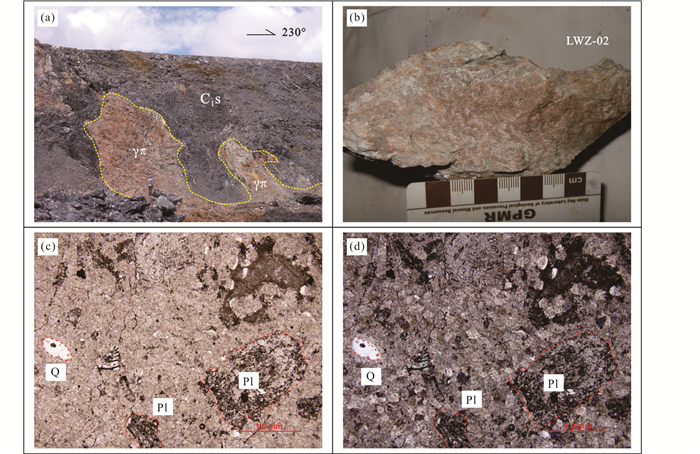
矿区岩浆岩发育,成群成带分布,冬瓜林、搭桥箐、比幅、库独木矿段以煌斑岩和中酸性岩脉为主,老王寨、浪泥塘以超基性岩、基性岩、玄武岩为主。超基性岩主要为橄榄辉石岩和斜辉辉橄岩,中酸性岩脉主要为花岗斑岩(图 3a, b)、石英斑岩、花岗闪长斑岩。

|
图 3 镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩野外与显微照片 (a)老王寨矿点花岗斑岩岩脉;(b)用于U-Pb测年的花岗斑岩(LWZ-02)手标本照片;(c、d)花岗斑岩斑晶以长石为主,次为石英,长石绢云母化,石英发生溶蚀. Q-石英;Pl-斜长石 Fig. 3 Field photos and hand specimen photograph of the granite porphyry in the Zhenyuan gold deposit (a) granite porphyry dike in Laowangzhai Mine; (b) hand specimen of granite porphyry (LWZ-02) used for U-Pb dating; (c, d) granite porphyry phenocryst is dominated by feldspar, secondly quartz, feldspar is sericitized, and the quartz is corroded. Q-quartz; Pl-plagioclase |
矿床处于北西向九甲-安定断裂带与近东西向班卡河断裂的斜接部位,以北西向构造为主,其次为东西向构造。构造以多期次推覆作用及继承性韧性剪切作用为特征,发生强烈糜棱岩化,无根褶皱、流劈理发育。北西向断裂较为发育,多为九甲-安定断裂带次级断裂,构成了倾向北东,上陡下缓的背驮式逆冲断裂带。东西向断裂为北西向断裂派生的共轭构造,以左行走滑剪切为特征。
2 样品采集和实验方法 2.1 样品采集及特征在野外详尽地质调查的基础上,在矿区的不同部位采集新鲜、弱蚀变样品5件进行分析测试。镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩呈浅灰色、灰白色,具斑状结构,块状构造。斑晶为钾长石、斜长石、石英、黑云母,斑晶粒径多为0.2~1mm。钾长石呈半自形-他形粒状,含量10%~15%;斜长石呈半自形-他形粒状,含量约10%;石英呈他形粒状,含量5%~10%;黑云母呈片状,含量2%~4%。基质具微晶-隐晶结构(图 3c, d),矿物成分为石英(16%~25%)、斜长石(30%~45%)、钾长石(15%~20%)、黑云母(3%~5%)和磁铁矿、榍石、锆石(1%)。
2.2 实验方法样品主量元素、稀土元素、微量元素分析工作由中国地质科学院地球物理地球化学研究所实验室完成。主量元素采用X荧光光谱仪3080E测试,执行标准为GB/B14506.28—1993,H 2O+执行标准为GB/T14506.2—1993,LOI标准为LY/T1253—1999,分析误差2%~8%;稀土元素和微量元素(Th、U、Hf、Ta)采用等离子质谱(ICP-MS)Excell测试,执行标准为DZ/T 0223—2001,微量元素Sr、Ba、Rb、Nb、Zr、Ga用X荧光光谱仪2100测试,执行标准为JY/T 016—1996,分析精度大多数为10-8,少数为10-6(Zr和Ba)和10-7(Hf、Nb),相对标准偏差小于10%。主量元素含量在归一化之后用于各种图解分析。
锆石分选在河北省区域地质调查院完成,样品经常规粉碎、磁选和重选,选出高纯度锆石,在双目镜下经人工挑选出纯度在99%以上的锆石。将挑选好的锆石粘贴在环氧树脂表面,打磨抛光后露出锆石的表面,制成靶样。锆石透、反射光及阴极荧光(CL)在北京锆年领航科技有限公司完成,锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素在中国地质调查局天津地质矿产研究所同位素实验室完成。
锆石测年采用激光烧蚀多接收器电感耦合等离子体质谱仪对锆石进行U-Pb同位素分析。锆石U-Pb分析采用193nm激光器对锆石进行剥蚀,激光剥蚀束斑直径为30μm,激光能量密度13~14J·cm-2,频率为8~10Hz,激光剥蚀物以氦为载气进入Neptune,利用动态变焦扩大色散可以同时接收质量数相差较大的U-Pb同位素。采用Plesovice(年龄为337±0.37Ma)(Sláma et al., 2008)作为外标样进行基体校正,普通铅校正采用ComPbCorr#3.17校正程序(Andersen, 2002)。对采集的数据采用中国地质大学刘勇胜博士研发的ICP-Ms DataCal程序和Kenneth R.Ludwig的Isoplot程序进行处理,并绘制谐和图等图件,置信度为95%。详细的仪器操作条件和数据处理方法件(Liu et al., 2010)。
锆石Hf同位素分析测试工作在激光剥蚀电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(LA-ICP-MS)上完成。LA-ICP-MS激光剥蚀系统为美国NewWave公司生产的UP193FX型193nm ArF准分子系统,激光器来自于德国ATL公司,ICP-MS为Agilent 7500a。激光器波长为193nm,脉冲宽度 < 4ns,束斑直径为35μm。采用锆石标样91500(176Hf/177Hf=0.282308±12(2σ))作为外标样进行基体校正(Goolaerts et al., 2004),数据计算和处理采用ICP-Ms DataCal程序完成(Liu et al., 2010)。
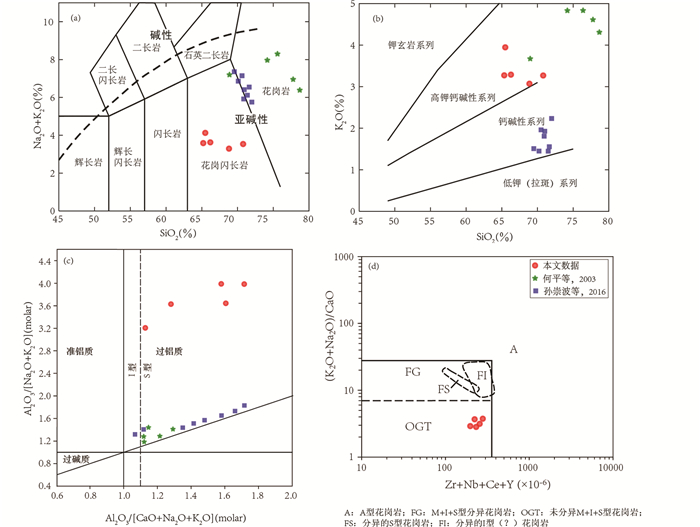
3 测试结果 3.1 主量元素花岗斑岩SiO2的含量为65.30%~70.79%,为中酸性岩石,Al2O3含量为13.42%~16.40%,全碱含量(K2O+Na2O)为3.28%~4.12%(表 1),与中国低钙花岗质岩石对比(史长义等, 2007),碱含量差异较小并偏低。结合图 3c, d,表明样品的K、Na等活动元素在蚀变作用下,可能发生了一定程度的迁移。因此,本文收集并整理研究区内及附近同时代具有相似地质意义的弱蚀变及未蚀变花岗岩数据共同进行岩石类型划分、铝饱和程度等判别(何平等, 2003; 孙崇波等, 2016)。在TAS图解(图 4a)中样品投点于花岗岩和花岗闪长岩范围,样品具亚碱性特征。在K2O-SiO2图解(图 4b)中样品投点于高钾钙碱性区域。岩石分异指数DI=Q+Or+Ab+Ne+Lc+Kp(CIPW计算数据),为65.58~74.67,同时岩石斑晶中含黑云母等暗色矿物,表明岩体不具有高分异特征,属于低分异系列岩石,铝饱和指数A/CNK为1.12~1.72,为强过铝质岩石(图 4c)。
|
|
表 1 镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩主量元素(wt%)、稀土和微量元素(×10-6)组成 Table 1 Major element (wt%), REE element and trace element (×10-6) compositions of the granite porphyry in the Zhenyuan gold deposit |
|
图 4 镇沅金矿田花岗岩类分类判别图解 (a) TAS分类图解(据Middlemost, 1994);(b) K2O-SiO2图解(据Middlemost, 1985);(c) A/NK-A/CNK图解(据Maniar and Piccoli, 1989);(d) A型花岗岩判别图解(据Whalen et al., 1987) Fig. 4 Classification and discriminant diagrams of granitoids in the Zhenyuan gold deposit (a) SiO2 vs. K2O+Na2O plot (Middlemost, 1994); (b) K2O vs. SiO2 plot (Middlemost, 1985); (c) A/NK vs. A/CNK plot (Maniar and Piccoli, 1989); (d) A-type granites classification plot (Whalen et al., 1987) |
花岗斑岩的主量元素组成表现出狭窄而集中的变化,其主量元素含量分别是:TiO2含量为0.22%~0.34%,FeOT含量为2.05%~2.99%,MnO含量为0.06%~0.12%,CaO含量为2.82%~4.69%,MgO含量为0.49%~1.35%,P2O5含量为0.11%~0.15%,K2O含量为3.04%~3.92%和Na2O含量为0.20%~0.34%(表 1)。在氧化物对SiO2的哈克图解中,Al2O3、K2O、MgO和TiO2等氧化物均与SiO2呈良好的负相关线性关系(图 5),暗示了可能存在钾长石、镁铁质矿物和铁-钛氧化物的结晶分异。

|
图 5 镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩哈克图解 Fig. 5 Harker diagrams for granite porphyry in the Zhenyuan gold deposit |
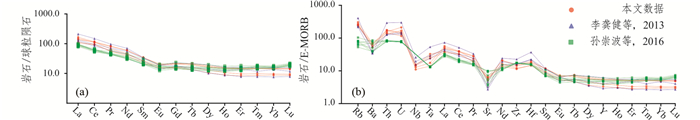
花岗斑岩稀土元素含量较低,∑REE含量123×10-6~168×10-6,平均为145×10-6;LREE含量112×10-6~152×10-6,平均为131×10-6;HREE含量10.1×10-6~16.3×10-6,平均为13.9×10-6;轻重稀土比值LREE/HREE为6.90~13.4,平均为9.78;(La/Yb)N为6.53~14.7,平均为10.6;重稀土亏损,轻稀土富集,轻重稀土分异程度较高。稀土元素配分曲线为右倾型(图 6a),δCe为0.92~1.14,平均为1.04,异常不明显,δEu为0.70~0.78,平均为0.76,具弱负异常。
|
图 6 镇沅金矿田花岗岩类球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分型式(a)和E-MORB标准化曲线(b) (标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989;成图软件据Yu et al., 2019) Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a) and E-MORB-normalized curves (b) for granite porphyry in the Zhenyuan gold deposit (a, normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989; Mapping software after Yu et al., 2019) |
花岗斑岩在E-MORB标准化曲线图解中,样品均显示Rb、U、K、La等大离子亲石元素(LILE)相对富集,Nb、Ta、Ti等高场强元素(HFSE)相对亏损,呈右倾(图 6b)。
3.4 锆石U-Pb年龄花岗斑岩用于测试的锆石自形程度良好,均呈自形短柱-长柱状,只有少数锥顶被溶蚀,呈次浑圆状,长约60~140μm,长宽比约1.5∶1~3∶1 (图 7)。阴极发光图像表明锆石发育震荡环带,具岩浆成因特征(Corfu et al., 2003)。选择不发育裂隙和包裹体的锆石进行年龄测试,在发育震荡环带的位置打点。锆石Th含量100.6×10-6~298.6×10-6,U含量218.3×10-6~741.6×10-6,Th/U为0.36~0.61>0.1(表 2),为典型岩浆锆石(Hoskin and Schaltegger, 2003; 吴元保和郑永飞, 2004)。样品中除12号测点偏差较大外,其他23个测点锆石206Pb/238U年龄分布在246.7~264.6Ma之间,加权平均年龄为253.3±2.0Ma(MSWD=2.4),表明岩体形成于晚二叠世(图 7)。
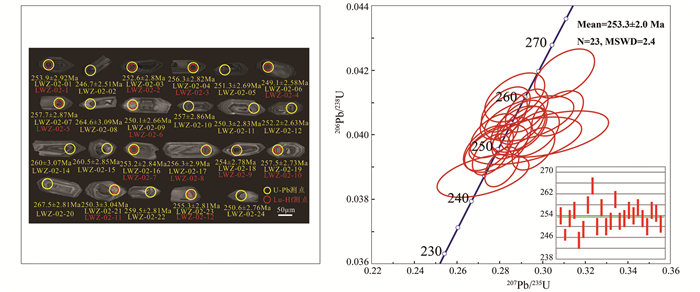
|
图 7 镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩(LWZ-02)锆石阴极发光照片及U-Pb年龄协和图 Fig. 7 Cathodoluminescence (CL) images of zircons and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb concordia diagram of the granite porphyry (LWZ-02) in the Zhenyuan gold deposit |
|
|
表 2 镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩(LWZ-02) LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb数据 Table 2 LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb data of the granite porphyry (LWZ-02) in the Zhenyuan gold deposit |
在进行U-Pb年龄测试的点位上挑选12个样品点完成锆石的Lu-Hf同位素测试,测试结果见表 3。
|
|
表 3 镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩(LWZ-02)锆石LA-ICP-MS Lu-Hf分析结果 Table 3 Zircon LA-ICP-MS Lu-Hf analysis results of granite porphyry (LWZ-02) in the Zhenyuan gold deposit |
花岗斑岩176Lu/177Hf比值为0.001381~0.002685,除7号测点外,其他测点的176Lu/177Hf比值小于0.002,表明锆石在形成后,仅具有少量的放射性成因Hf积累,因而可以用初始176Hf/177Hf比值代表形成时的Hf同位素组成(吴福元等, 2007)。锆石Hf同位素176Yb/177Hf比值为0.036415~0.065853,176Hf/177Hf比值为0.282593~0.282741,锆石fLu/Hf为-0.92~-0.96,εHf(t)为-1.0~+4.1,平均为+1.21;锆石Hf单阶段模式年龄(tDM)为739~945Ma,二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)为1.34~1.80Ga(图 8)。
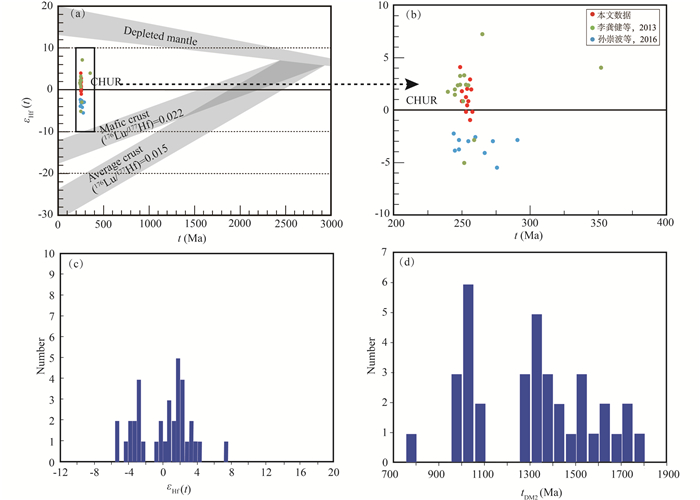
|
图 8 镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩锆石εHf(t)-t图(a、b)(底图据吴福元等, 2007)及εHf(t)值(c)与二阶段模式年龄(tDM2)直方图(d) Fig. 8 εHf(t) versus age diagram (a, b) (base map after Wu et al., 2007), histogram of εHf(t) values (c) and tDM2 values (d) for the granite porphyry in the Zhenyuan gold deposit |
矿区花岗斑岩形成时代前人研究较少。锆石U-Pb测年技术作为最成熟的同位素测年方法之一,当前已经成为同位素年代学研究中最常用且最有效的方法之一(吴元保和郑永飞, 2004)。锆石定年具有易挑选、稳定性强,同位素体系封闭温度高等特点(Lee et al., 1997)。本次工作获得镇沅花岗斑岩锆石206Pb/238U表面年龄加权平均值为253.3±2.0Ma(MSWD=2.4,N=23),与李龚健等(2013)测得的加权平均年龄251.7±2.1Ma较为一致,表明岩体形成于晚二叠世。
4.2 岩石成因和岩浆源区花岗岩分类方式较多,其中A型、S型、I型和M型分类应用较为广泛(Chappell, 1999)。研究区花岗斑岩SiO2含量均值为67%,低Rb/Sr(1.1~1.5)值,低分异指数(DI=65.58~74.67),高Zr/Hf(28~30,高分异花岗岩 < 25,Breiter et al., 2014),高Cr(4.6×10-6~9.3×10-6)的特点;在哈克图解中,主量元素部分随SiO2含量的升高而降低。
花岗斑岩镜下鉴定未见碱性暗色矿物,稀土配分曲线成右倾型,无明显Eu负异常,Zr含量为127.1×10-6~176.2×10-6,Zr+Nb+Ce+Y为213.0×10-6~280.6×10-6,与A型花岗岩含暗色矿物、稀土配分曲线成海鸥型、具明显Eu负异常、Zr>250×10-6及Zr+Nb+Ce+Y>350×10-6等特征明显不符(Collins et al., 1982);高的Ga/Al值是A型花岗岩的主要特征之一,绝大多数A型花岗岩的10000×Ga/Al值均大于2.6,平均值约在3.9左右(Eby, 1992),研究区花岗斑岩10000×Ga/Al值为1.83~1.98,明显低于2.5。在Zr+Nb+Ce+Y-(K2O+Na2O)/CaO图解中(图 4d),所有样品均落入非A型花岗岩中的未分异花岗岩区域,与岩石的低分异指数和高Zr/Hf值相一致。
研究区花岗斑岩SiO2含量65.30%~70.79%,变化范围窄,岩浆来自富SiO2的源岩,这种狭窄的成分范围是S型花岗岩不同于I型花岗岩的一个重要方面;花岗斑岩A/CNK为1.12~1.72>1.1,为强过铝质岩石,在A/NK-A/CNK判别图中,投入I-S型花岗岩分界的S型一侧(图 4c);CIPW标准矿物计算中C(标准刚玉分子)为2.06~7.68,无透辉石。以上特征与I型花岗岩特征明显不符,为S型花岗岩(Sylvester, 1998)。S型花岗岩多为沉积岩经部分熔融后产生的A/CNK>1.1的花岗岩(Chappell and White, 1974)。在部分熔融的过程中,如无外来物质加入Nb/Ta比值变化较小,同源岩浆Nb/Ta比值相同(Foley, 1984; Barth et al., 2000)。花岗斑岩Nb/Ta比值有较宽的变化范围(7.94~12.68),远小于地幔平均值(60),与地壳平均值相当(10)(Wedepohl, 1995),表明岩体的原始岩浆以壳源物质为主,受到了部分幔源岩浆的影响。
利用亲湿岩浆元素(H)与亲岩浆元素(M)的浓度比值对亲湿岩浆元素的浓度作图,平衡部分熔融的轨迹是一斜线,而分离结晶作用为一水平线。在La/Sm-La图解中,晚二叠世花岗岩类主要表现出与岩浆的分离结晶过程有关(图 9)。
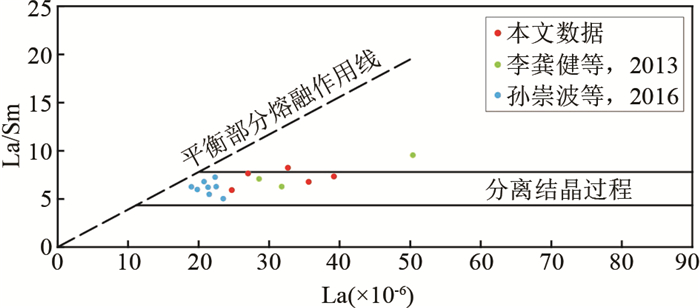
|
图 9 La/Sm-La图解反映的岩浆岩成岩过程(据Allègre and Minster, 1978) Fig. 9 Diagenesis process of magmatic rock shown in La/Sm vs. La diagram (after Allègre and Minster, 1978) |
在Rb/Ba-Rb/Sr图解中(图 10),样品点落入贫粘土源岩区,与实验计算的砂质来源熔体较为一致。以上分析说明研究区强过铝质花岗岩的源岩以砂质岩为主,泥质岩可能处于次要地位。砂质源岩为主的花岗岩反映了岩浆活动应发生于加厚地壳的构造背景下,地壳物源区熔融作用的结果。锆石εHf(t)为-1.0~4.1,以正值为主,投点介于亏损地幔演化线和地壳演化线之间。认为花岗斑岩岩浆源区是亏损地幔岩浆源与古老地壳物源的混合。花岗斑岩锆石fLu/Hf为-0.92~-0.96,明显小于大陆地壳(-0.72, Amelin et al., 1999),因此二阶段模式年龄可以真实反映其源区物质从亏损地幔被抽取的时间(即其源区物质在地壳的平均存留年龄)(Nebel et al., 2007)。锆石Hf单阶段模式年龄(tDM)为739~945Ma,二阶段模式年龄(tDMC)为1336~1795Ma。哀牢山构造带内的前寒武深变质岩系(哀牢山群等)的Nd同位素模式年龄集中在1600~1900Ma(朱炳泉等, 2001; 钟大赉, 1998),锆石Hf模式年龄与哀牢山群变质岩Nd模式年龄一致。翟明国和从柏林(1990)测得哀牢山群斜长角闪岩样品的TiO2含量为0.3%~1.3%,K2O+Na2O为2.4%~4%,具有中度富集的轻稀土(LREE)和较亏损的高场强元素,研究区花岗斑岩显示出相似的地球化学特征。结合岩石地球化学和锆石Hf同位素特征,推测镇沅金矿花岗斑岩的源岩可能是哀牢山群岩系中的变质砂岩,表明古老地壳物质可能来自于哀牢山岩群。
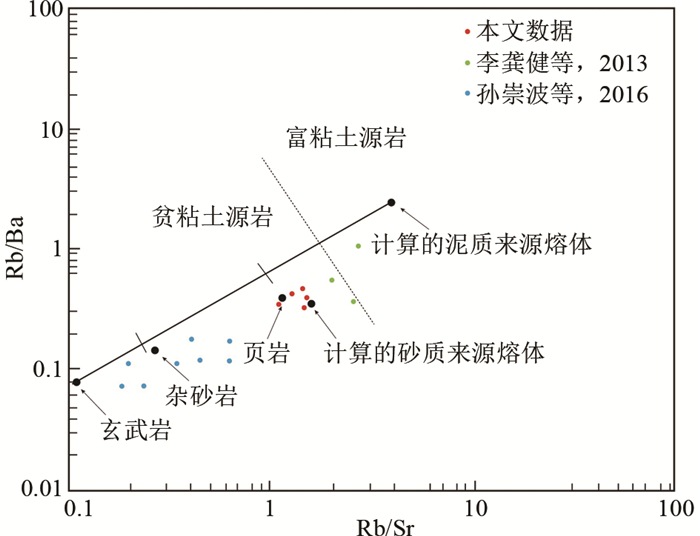
|
图 10 镇沅金矿田花岗斑岩Rb/Ba-Rb/Sr图解(据Collins et al., 1982) Fig. 10 Rb/Ba vs. Rb/Sr diagram for granite porphyry in the Zhenyuan gold deposit (after Collins et al., 1982) |
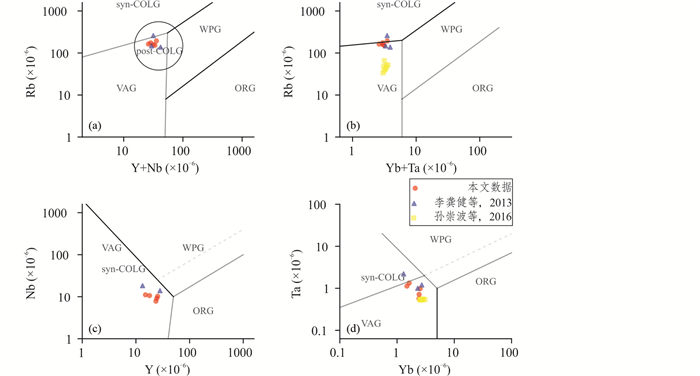
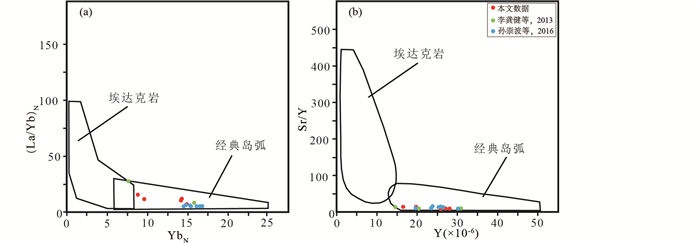
高场强元素(HFSE),如Nb、Ta、Th、Zr、Hf、HREE等,一般不受热液蚀变和低于角闪岩相变质作用的影响,能够有效判别岩石构造环境(Pearce and Cann, 1973)。Rb、Y(Yb)、Nb(Ta)是被选择区分大洋脊花岗岩(ORG)、火山弧花岗岩(VAG)、板内花岗岩(WPG)和碰撞带花岗岩(Syn-COLG)等大多数类型最为有效的判据(Pearce et al., 1984)。Rb-(Y+Nb)构造判别图解(图 11a)中样品投点于火山弧区域(Pearce et al., 1984)。Rb-(Yb+Ta)构造判别图解(图 11b)中样品投点于火山弧与同碰撞边界区域。Nb-Y构造判别图解(图 11c)中样品投点于火山弧与同碰撞构造环境。Ta-Yb构造判别图解(图 11d)中样品投点于火山弧构造环境,靠近与碰撞构造环境的边界区域。在(La/Yb)N-YbN和Sr/Y-Y图解中,样品点全部落入经典的岛弧花岗岩区域中(图 12)。
|
图 11 镇沅金矿田花岗岩类微量元素构造环境判别图解(底图据Pearce et al., 1984) (a) Rb-(Y+Nb)图解;(b) Rb-(Yb+Ta)图解;(c) Nb-Y图解;(d) Ta-Yb图解.Syn-COLD-同碰撞花岗岩;post-COLD-同碰撞花岗岩;VAG-火山岛弧花岗岩;WPG-板内花岗岩;ORG-洋脊花岗岩 Fig. 11 Tectonic discrimination diagrams for the granite porphyry in the Zhenyuan gold deposit (base map after Pearce et al., 1984) (a) Rb vs. (Y+Nb) diagram; (b) Rb vs. (Yb+Ta) diagram; (c) Rb vs. Y diagram; (d) Ta vs. Yb diagram. Syn-COLG-syn-collision granite; post-COLD-post-collision granite; VAG-volcanic arc granite; WPG-within plate granite; ORG-ocean ridge granite |
|
图 12 镇沅金矿田花岗岩类(La/Yb)N-YbN(a)和Sr/Y-Y(b)图解(底图据Defant and Drummond, 1990) Fig. 12 (La/Yb)N vs. YbN diagram and Sr/Y vs. Y diagram for the granite porphyry in the Zhenyuan gold deposit (base map after Defant and Drummond, 1990) |
哀牢山洋盆闭合的时限,即由洋陆俯冲转换为陆陆碰撞的时限,早期学者开展了大量的研究工作。哀牢山构造带内普遍发育三叠系一碗水组,钟大赉(1998)根据上三叠统一碗水组磨拉石角度不整合于哀牢山蛇绿混杂岩之上,认为碰撞发生于中三叠世。大龙凯地区斜长辉石岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄为245.6±1.4Ma,形成于后造山伸展背景产物,反映哀牢山洋早三叠世已经消亡(Jian et al., 2009a, b )。刘翠等(2011)测得的绿春流纹岩的锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄为247.3±1.8Ma,认为此时该地区已进入成熟岛弧向陆陆碰撞的过渡阶段。娘宗流纹斑岩锆石U-Pb年龄为263.1±2.3Ma,表明哀牢山洋闭合造山作用于晚二叠世发生(赵德军等, 2013)。Liu et al. (2013)揭示哀牢山变质带高压麻粒岩相在249~230Ma之间的变质事件,我们认为与晚二叠世-早三叠世的陆陆碰撞造山作用有关。李龚健等(2013)认为哀牢山洋的闭合时限开始于晚二叠世(~260Ma),碰撞造山作用可能一直持续至中三叠世。刘汇川等(2013)研究新安寨高钾过铝质二长花岗岩,认为该花岗岩体的构造环境为岛弧向陆陆碰撞转换或者同碰撞,岩浆为哀牢山群深熔作用成因,反映哀牢山洋闭合于晚二叠世-早三叠世;同时,新安寨花岗岩体被上三叠统高山寨组地层覆盖,说明扬子板块与思茅印支地块的碰撞一直持续到晚三叠世早期。Xu et al. (2019)报道了哀牢山缝合线两侧三叠系沉积岩碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素特征,研究表明缝合线两侧中三叠世沉积物源具有明显的相似性,表明陆陆碰撞发生在中三叠世之前。
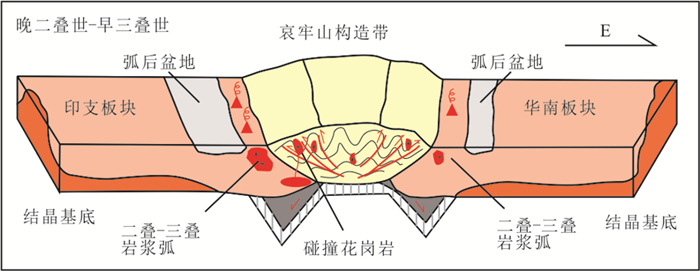
综上所述,认为哀牢山洋于晚二叠世(~255Ma)闭合,花岗斑岩形成于同碰撞构造环境。花岗斑岩的演化过程为:受印支构造事件的影响,晚二叠世末期,哀牢山洋盆闭合,哀牢山洋闭合造山作用产生的加厚地壳,受碰撞减压作用引发地幔物质熔融产生岩浆的底侵作用,地壳物质被加热,发生部分熔融,随着幔源岩浆与地壳物质的不断作用,形成混合岩浆,即花岗斑岩的母岩浆。岩浆沿构造薄弱部位上升侵位至地壳浅部,经历结晶分异作用,最终形成了花岗斑岩(图 13)。Hf同位素特征显示更多与印支板块的亲缘关系(Xu et al., 2019)。
|
图 13 晚二叠世-早三叠世哀牢山构造带区域构造模式图(据Xu et al., 2019修改) Fig. 13 Schematic cartoon showing the Ailaoshan tectonic zone during Late Permian-Early Triassic (modified after Xu et al., 2019) |
(1) 花岗斑岩为强过铝质亚碱性系列岩石,稀土配分曲线右倾,轻、重稀土分异程度略高,无明显Ce异常,具弱Eu负异常,大离子亲石元素富集,Nb、Ta负异常明显,类地壳稀土元素配分型式,S型花岗岩。微量元素给出的岩石大地构造环境判别表明花岗斑岩形成于陆陆碰撞的构造环境。
(2) 花岗斑岩锆石发育震荡环带,Th/U为1.65~2.78,锆石206Pb/238U年龄为246.7±2.51Ma~264.6±3.09Ma,加权平均年龄为253.3±2.0Ma,形成于晚二叠世。
(3) 花岗斑岩锆石fLu/Hf为-0.92~-0.96,εHf(t)为-1.0~4.1,Hf单阶段模式年龄(tDM)为739~945Ma,二阶段模式年龄(tDMC)为1336~1795Ma,岩浆源区主要来自于亏损地幔和古老地壳物质(哀牢山群)。
(4) 哀牢山洋于晚二叠世闭合,花岗斑岩限定了洋陆转换的时限。
致谢 野外工作受到了云南黄金有限责任公司王军平教授级高工和雷恒永高级工程师的支持和帮助;研究工作得到了中国地质大学(北京)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室狄永军副教授、王长明教授的指导和帮助;绘图工作得到了长春工程学院于秋野博士的大力帮助;审稿专家对论文提出了许多宝贵的意见和建议;在此一并致以衷心的感谢!
Allègre CJ and Minster JF. 1978. Quantitative methods of trace element behaviour in magmatic processes. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 38(1): 1-25 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(78)90123-1
|
Amelin Y, Lee DC, Halliday AN and Pidgeon RT. 1999. Nature of the earth's earliest crust from hafnium isotopes in single detrital zircons. Nature, 399(6733): 252-255 DOI:10.1038/20426
|
Andersen T. 2002. Correction of common lead in U-Pb analyses that do not report 204Pb. Chemical Geology, 192(1-2): 59-79 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00195-X
|
Barth MG, McDonough WF and Rudnick RL. 2000. Tracking the budget of Nb and Ta in the continental crust. Chemical Geology, 165(3-4): 197-213 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00173-4
|
Blichert-Toft J, Chauvel C and Albarède F. 1997. Separation of Hf and Lu for high-precision isotope analysis of rock samples by magnetic sector-multiple collector ICP-MS. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 127(3): 248-260 DOI:10.1007/s004100050278
|
Breiter K, Lamarão CN, Borges RMK and Dall'Agnol R. 2014. Chemical characteristics of zircon from A-type granites and comparison to zircon of S-type granites. Lithos, 192-195: 208-225 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.02.004
|
Burnard PG, Hu R, Turner G and Bi XW. 1999. Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in Ailaoshan gold deposits, Yunnan Province, China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(10): 1595-1604 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00108-8
|
Cai FY, Liu XF, Tao Z, Zhao FF and Cai YW. 2010. Petrography and element geochemical analysis of origin for Laowangzhai gold deposit. Mineral Exploration, 1(3): 215-222 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chappell BW and White AJR. 1974. Two contrasting granite types. Pacific Geology, 8: 173-174
|
Chappell BW. 1999. Aluminium saturation in I- and S-type granites and the characterization of fractionated haplogranites. Lithos, 46(3): 535-551 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00086-3
|
Collins WJ, Beams SD, White AJR and Chappell BW. 1982. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 80(2): 189-200 DOI:10.1007/BF00374895
|
Corfu F, Hanchar JM, Hoskin PWO and Kinny P. 2003. Atlas of zircon textures. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 469-500 DOI:10.2113/0530469
|
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662-665 DOI:10.1038/347662a0
|
Deng BP, Liu XF, Lu QX and Zhao FF. 2013. Isotope compositions and their geological implications of Laowangzhai gold deposit. Metal Mine, (7): 109-112, 117 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Deng J, Hou ZQ, Mo XX, Yang LQ, Wang QF and Wang CM. 2010. Superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis in Sanjiang Tethys. Mineral Deposits, 29(1): 37-42 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Deng J, Ge LS and Yang LQ. 2013. Tectonic dynamic system and compound orogeny: Additionally discussing the temporal-spatial evolution of Sanjiang orogeny, Southwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4): 1099-1114 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ, Li CS and Wang CM. 2014. Tethys tectonic evolution and its bearing on the distribution of important mineral deposits in the Sanjiang region, SW China. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 419-437 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.08.002
|
Deng J, Wang CM, Bagas L, Selvaraja V, Jeon H, Wu B and Yang LF. 2017. Insights into ore genesis of the Jinding Zn-Pb deposit, Yunnan Province, China: Evidence from Zn and in-situ S isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 90: 943-957 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.10.036
|
Du B, Wang CM, He XY, Yang LF, Chen JY, Shi KX, Luo Z and Xia JS. 2016. Advances in research of bulk-rock Nd and zircon Hf isotopic mappings: Case study of the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2555-2570 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Eby GN. 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Geology, 20(7): 641-644 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
|
Fan WM, Wang JY, Zhang AM, Zhang FF and Zhang YZ. 2010. Permian arc-back-arc basin development along the Ailaoshan tectonic zone: Geochemical, isotopic and geochronological evidence from the Mojiang volcanic rocks, Southwest China. Lithos, 119(3-4): 553-568 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.08.010
|
Foley SF. 1984. Liquid immiscibility and melt segregation in alkaline lamprophyres from Labrador. Lithos, 17: 127-137 DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(84)90013-6
|
Gao R, Xiao L, He Q, Yuan J, Ni PZ and Du JX. 2010. Geochronology, geochemistry and petrogenesis of granites in Weixi-Deqin, West Yunnan. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 35(2): 186-200 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.3799/dqkx.2010.019
|
Goolaerts A, Mattielli N, de Jong J, Weis D and Scoates JS. 2004. Hf and Lu isotopic reference values for the zircon standard 91500 by MC-ICP-MS. Chemical Geology, 206(1-2): 1-9 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2004.01.008
|
Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, Belousova E, Jackson SE, Van Achterbergh E, O'reilly SY and Shee SR. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle: LAM-MC-ICP MS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133-147 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9
|
He MY and Hu RZ. 1996. A Study on the Au-bearing fluid source and its properties of the Laowangzhai gold deposit, Yunnan Province, China. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 15(1): 36-39 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
He P, He MY, Liu F, Mao SD and Wang F. 2003. The elemental geochemistry features of the Laowangzhai gold field, Yunnan Province. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 22(3): 224-227 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Hoskin PWO and Schaltegger U. 2003. The composition of zircon and igneous and metamorphic petrogenesis. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 53(1): 27-62 DOI:10.2113/0530027
|
Hu YZ and Tang SC. 1995. Geology of Gold Deposits in Ailaoshan. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Huang ZL, Liu CQ, Zhu CM, Wang LK and Xiao HY. 1999. The Origin of Lamprohyres in the Laowangzhai Gold Field, Yunnan Province, and Their Relations with Gold Mineralization. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Jian P, Liu DY, Kröner A, Zhang Q, Wang YZ, Sun XM and Zhang W. 2009a. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in Southwest China (Ⅰ): Geochemistry of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks. Lithos, 113(3-4): 748-766 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.004
|
Jian P, Liu DY, Kröner A, Zhang Q, Wang YZ, Sun XM and Zhang W. 2009b. Devonian to Permian plate tectonic cycle of the Paleo-Tethys Orogen in Southwest China (Ⅱ): Insights from zircon ages of ophiolites, arc/back-arc assemblages and within-plate igneous rocks and generation of the Emeishan CFB province. Lithos, 113(3-4): 767-784 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.006
|
Lee JKW, Williams IS and Ellis DJ. 1997. Pb, U, Th diffusion in natural Zircon. Nature, 390(6656): 159-162 DOI:10.1038/36554
|
Li GJ, Wang QF, Yu L, Hu ZC, Ma N and Huang YH. 2013. Closure time of the Ailaoshan Paleo-Tethys Ocean: Constraints from the zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry of the Late Permian granitoids. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11): 3883-3900 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liang YH, Sun XM, Shi GY, Hu BM, Zhou F, Wei HX and Mo RW. 2011. Ore-forming fluid geochemistry and genesis of Laowangzhai large scale orogenic gold deposit in Ailaoshan gold belt, Yunnan Province. China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2533-2540 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Lin WX. 1992. Deformation characteristics and rock association of ductile metamorphic zone in Laowangzhai gold ore area. Yunnan Geology, 11(2): 153-161 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu C, Deng JF, Liu JL and Shi YL. 2011. Characteristics of volcanic rocks from Late Permian to Early Triassic in Ailaoshan tectono-magmatic belt and implications for tectonic settings. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(12): 3590-3602 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu FL, Wang F, Liu PH and Liu CH. 2013. Multiple metamorphic events revealed by zircons from the Diancang Shan-Ailao Shan metamorphic complex, southeastern Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Research, 24(1): 429-450 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.10.016
|
Liu HC, Wang YJ, Cai YF, Ma LY, Xing XW and Fan WM. 2013. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic composition of the Xin'anzhai granite along the Ailaoshan tectonic zone in West Yunnan Province. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 37(1): 87-98 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Zong KQ, Gao CG, Gao S, Xu J and Chen HH. 2010. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535-1546 DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4
|
Maniar PD and Piccoli PM. 1989. Tectonic discrimination of granitoids. GSA Bulletin, 101(5): 635-643 DOI:10.1130/0016-7606(1989)101<0635:TDOG>2.3.CO;2
|
Metcalfe I. 2006. Palaeozoic and Mesozoic tectonic evolution and palaeogeography of East Asian crustal fragments: The Korean Peninsula in context. Gondwana Research, 9(1-2): 24-46 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2005.04.002
|
Middlemost EAK. 1985. Magmas and Magmatic Rocks. London: Longman, 1-266
|
Middlemost EAK. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3-4): 215-224 DOI:10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9
|
Mo XX, Deng JF and Lu FX. 1994. Volcanism and the evolution of Tethys in Sanjiang area, southwestern China. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 9(4): 325-333 DOI:10.1016/0743-9547(94)90043-4
|
Mo XX and Pan GT. 2006. From the Tethys to the formation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: Constrained by tectono-magmatic events. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 43-51 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Nebel O, Nebel-Jacobsen Y, Mezger K and Berndt J. 2007. Initial Hf isotope compositions in magmatic zircon from Early Proterozoic rocks from the Gawler Craton, Australia: A test for zircon model ages. Chemical Geology, 241(1-2): 23-37 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.02.008
|
Pan GT, Xu Q, Hou ZQ, Wang LQ, Du DX, Mo XX, Li DM, Wang MJ, LI XZ, Jiang XS and Hu ZY. 2003. Archipelagic Orogenesis, Metallogenic Systems and Assessment of the Mineral Resources along the Nujiang-Lancangjiang-Jinshanjiang Area in Southwestern China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2003, 1-420 (in Chinese)
|
Pan YS. 1999. Formation and uplifting of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Earth Science Frontiers, 6(3): 153-163 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Pearce JA and Cann JR. 1973. Tectonic setting of basic volcanic rocks determined using trace element analyses. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 19(2): 290-300 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(73)90129-5
|
Pearce JA, Harris NBW and Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983 DOI:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956
|
Shi CY, Yan MC and Chi QH. 2007. Abundances of chemical elements of granitoids in different geotectonic units of China and their characteristics. Acta Geologica Sinica, 81(1): 47-59 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1007/s11707-007-0038-x
|
Sláma J, Košler J, Condon DJ, Crowley JL, Gerdes A, Hanchar JM, Horstwood MSA, Morris GA, Nasdala L, Norberg N, Schaltegger U, Schoene B, Tubrett MN and Whitehouse MJ. 2008. Plešovice zircon: A new natural reference material for U-Pb and Hf isotopic microanalysis. Chemical Geology, 249(1-2): 1-35 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2007.11.005
|
Söderlund U, Patchett PJ, Vervoort JD and Isachsen CE. 2004. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4): 311-324 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3
|
Sun CB, Li ZQ, Wang DY, Xu YP and Li YY. 2016. Petrogeochemistry and zircon U-Pb chronology of the Niuzhi monzonitic porphyry in southern segment of Ailao Mountain tectonic belt. Geology in China, 43(1): 111-119 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Sun CB, Li ZQ, Chen XD, Xie WH and Wang DY. 2018. Petrogeochemistry and zircon U-Pb chronology of the Fengbieshan felsophyre in southern section of Ailaoshan tectonic belt. Geological Review, 64(5): 1251-1262 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Sun CB, Li ZQ, Wang DY and Chen XD. 2019. Petrogeochemistry and zircon U-Pb age of the Mayu granodiorite in the southern section of Ailaoshan tectonic belt. Geological Bulletin of China, 38(2-3): 223-230 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic Basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345 DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
|
Sylvester PJ. 1998. Post-collisional strongly peraluminous granites. Lithos, 45(1-4): 29-44 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(98)00024-3
|
Tapponnier P, Lacassin R, Leloup PH, Schärer U, Zhong DL, Wu HW, Li XH, Jiang SC, Zhang LS and Zhong JY. 1990. The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt: Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China. Nature, 343(6257): 431-437 DOI:10.1038/343431a0
|
Tapponnier P, Xu ZQ, Roger F, Meyer B, Arnaud N, Wittlinger G and Yang JS. 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau. Science, 294(5547): 1671-1677 DOI:10.1126/science.105978
|
Wang BD, Wang LQ, Wang DB and Zhang WP. 2011. Zircons U-Pb dating of volcanic rocks from Renzhixueshan Formation in Shangdie rift basin of Sanjiang area and its geological implications. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 30(1): 25-33 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM and Lai XR. 2014a. Nature, diversity and temporal-spatial distributions of sediment-hosted Pb-Zn deposits in China. Ore Geology Reviews, 56: 327-351 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.06.004
|
Wang CM, Deng J, Carranza EJM and Santosh M. 2014b. Tin metallogenesis associated with granitoids in the southwestern Sanjiang Tethyan Domain: Nature, deposit types, and tectonic setting. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 576-593 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.05.005
|
Wang CM, Deng J, Lu YJ, Bagas L, Kemp AIS and McCuaig TC. 2015a. Age, nature, and origin of Ordovician Zhibenshan granite from the Baoshan terrane in the Sanjiang region and its significance for understanding Proto-Tethys evolution. International Geology Review, 57(5): 1922-1939
|
Wang CM, Deng J, Santosh M, Lu YJ, McCuaig TC, Carranza EJM and Wang QF. 2015b. Age and origin of the Bulangshan and Mengsong granitoids and their significance for post-collisional tectonics in the Changning-Menglian Paleo-Tethys Orogen. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 113: 656-676 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.05.001
|
Wang CM, Bagas L, Lu YJ, Santosh M, Du B and McCuaig TC. 2016. Terrane boundary and spatio-temporal distribution of ore deposits in the Sanjiang Tethyan Orogen: Insights from zircon Hf-isotopic mapping. Earth-Science Reviews, 156: 39-65 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2016.02.008
|
Wang ML, Zhang JG, Wang XW and Luan QL. 2014. Characteristics of paleotectonic stress filed the Ailaoshan structural belt. Journal of Geomechanics, 20(1): 82-93 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang QF, Deng J, Li CS, Li GJ, Yu L and Qiao L. 2014c. The boundary between the Simao and Yangtze blocks and their locations in Gondwana and Rodinia: Constraints from detrital and inherited zircons. Gondwana Research, 26(2): 438-448 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2013.10.002
|
Wang YJ, Qian X, Cawood PA, Li HC, Feng QL, Zhao GC, Zhang YH, He HY and Zhang PZ. 2018. Closure of the East Paleotethyan Ocean and amalgamation of the eastern Cimmerian and Southeast Asia continental fragments. Earth-Science Reviews, 186: 195-230 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2017.09.013
|
Wedepohl KH. 1995. The composition of the continental crust. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(7): 1217-1232 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(95)00038-2
|
Whalen JB, Currie KL and Chappell BW. 1987. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419 DOI:10.1007/BF00402202
|
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wu YB and Zheng YF. 2004. Genesis of zircon and its constraints on interpretation of U-Pb age. Chinese Science Bulletin, 49(16): 1554-1569
|
Xu J, Xia XP, Lai C, Long XP and Huang C. 2019. When did the Paleotethys Ailaoshan Ocean close: New insights from detrital zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopes. Tectonics, 38(5): 1798-1823 DOI:10.1029/2018TC005291
|
Xue CD, Liu X, Tan SC and Qin DX. 2002. Typomorphic characteristics of main minerals from Laowangzhai gold deposit, western Yunnan. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 22(3): 10-16 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang LF, Shi KX, Wang CM, Wu B, Du B, Chen JY, Xia JS and Chen J. 2016. Ore genesis of the Jinman copper deposit in the Lanping Basin, Sanjiang Orogen: constraints by copper and sulfur isotopes. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(8): 2392-2406 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang LQ, Liu JT, Zhang C, Wang QF, Ge LS, Wang ZL, Zhang J and Gong QJ. 2010. Superimposed orogenesis and metallogenesis: An example from the orogenic gold deposits in Ailaoshan gold belt, Southwest China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1723-1739 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang LQ, Deng J, Zhao K and Liu JT. 2011. Tectono-thermochronology and gold mineralization events of orogenic gold deposits in Ailaoshan orogenic belt, Southwest China: Geochronological constraints. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2519-2532 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang XA, Liu JJ, Han SY, Chen SY, Zhang HY, Li J and Zhai DG. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating and geochemistry of the Luchun volcanic rocks, and its geological implications in the Luchun Cu-Pb-Zn deposit, Yunnan, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(4): 1236-1246 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yu QY, Bagas L, Yang PH and Zhang D. 2019. GeoPyTool: A cross-platform software solution for common geological calculations and plots. Geoscience Frontiers, 10(4): 1437-1447 DOI:10.1016/j.gsf.2018.08.001
|
Zhai MG and Cong BL. 1990. Sm-Nd and Rb-Sr geochronology of metamorphic rocks from SW Yunnan orogenic zones, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 6(4): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang Q, Zhang KW, Li DZ and Wu HW. 1988. A preliminary study on Shuanggou ophiolite in Xinping County, Yunnan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 4(4): 37-46 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao DJ, Chen HD, Wang DY, Wang GZ and Li N. 2013. Disintegration of Niangzhong rock mass in the later period of the Middle Permian Epoch in the southern part of Ailaoshan Orogen. Geological Science and Technology Information, 32(3): 19-25 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao GC and Guo JH. 2012. Precambrian geology of China: Preface. Precambrian Research, 222-223: 1-12 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2012.09.018
|
Zhao K, Yang LQ, Li P and Xiong YQ. 2013. Morphology and chemistry composition of pyrite in the Laowangzhai gold deposit, Ailaoshan orogenic belt, SW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 29(11): 3937-3948 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhong DL. 1998. Paleo-Tethys Orogenic Belt in Western Yunnan and Sichuan. Beijing: Science Press: 1-231 (in Chinese)
|
Zhu BQ, Chang XY, Qiu HN, Wang JH and Deng SX. 2001. Geochronological study on formation and metamorphism of Precambrian basement and their mineralization in Yunnan, China. Progress in Precambrian Research, 24(2): 75-82 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhu JJ, Hu RZ, Bi XW, Zhong H and Chen H. 2011. Zircon U-Pb ages, Hf-O isotopes, and whole-rock Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic geochemistry of granitoids in the Jinshajiang suture zone, SW China: Constraints on petrogenesis and tectonic evolution of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Lithos, 126(3-4): 248-264 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.003
|
Zi JW, Cawood PA, Fan WM, Wang YJ, Tohver E, McCuaig TC and Peng TP. 2012. Triassic collision in the Paleo-Tethys Ocean constrained by volcanic activity in SW China. Lithos, 144-145: 145-160 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.04.020
|
蔡飞跃, 刘显凡, 陶专, 赵甫峰, 蔡永文. 2010. 老王寨金矿成因的岩相学和元素地球化学分析. 矿产勘查, 1(3): 215-222. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1674-7801.2010.03.005 |
邓碧平, 刘显凡, 卢秋霞, 赵甫峰. 2013. 老王寨金矿床同位素组成特征及其地质意义. 金属矿山, (7): 109-112, 117. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2013.07.030 |
邓军, 侯增谦, 莫宣学, 杨立强, 王庆飞, 王长明. 2010. 三江特提斯复合造山与成矿作用. 矿床地质, 29(1): 37-42. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.01.005action?journalTitle=西安交通大学学报(社会科学版)&year=2013&firstpage=96&issue=02 |
邓军, 葛良胜, 杨立强. 2013. 构造动力体制与复合造山作用——兼论三江复合造山带时空演化. 岩石学报, 29(4): 1099-1114. |
杜斌, 王长明, 贺昕宇, 杨立飞, 陈晶源, 石康兴, 罗政, 夏锦胜. 2016. 锆石Hf和全岩Nd同位素填图研究进展: 以三江特提斯造山带为例. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2555-2570. |
高睿, 肖龙, 何琦, 袁静, 倪平泽, 杜景霞. 2010. 滇西维西-德钦一带花岗岩年代学、地球化学和岩石成因. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 35(2): 186-200. |
何明友, 胡瑞忠. 1996. 云南老王寨金矿床合矿流体来源及其特性研究. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 15(1): 36-39. |
何平, 何明友, 刘峰, 毛世德, 王峰. 2003. 云南老王寨金矿田元素地球化学特征. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 22(3): 224-227. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2003.03.007 |
胡云中, 唐尚鹑. 1995. 哀牢山金矿地质. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
黄智龙, 刘丛强, 朱成明, 王联奎, 肖化云. 1999. 云南老王寨金矿区煌斑岩成因及其与金矿化的关系. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
李龚健, 王庆飞, 禹丽, 胡兆初, 马楠, 黄钰涵. 2013. 哀牢山古特提斯洋缝合时限: 晚二叠世花岗岩类锆石U-Pb年代学与地球化学制约. 岩石学报, 29(11): 3883-3900. |
梁业恒, 孙晓明, 石贵勇, 胡北铭, 周峰, 韦慧晓, 莫儒伟. 2011. 云南哀牢山老王寨大型造山型金矿成矿流体地球化学. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2533-2540. |
林文信. 1992. 老王寨金矿区韧性变质带变形特征和岩石组合. 云南地质, 11(2): 153-161. |
刘翠, 邓晋福, 刘俊来, 石耀霖. 2011. 哀牢山构造岩浆带晚二叠世-早三叠世火山岩特征及其构造环境. 岩石学报, 27(12): 3590-3602. |
刘汇川, 王岳军, 蔡永丰, 马莉燕, 邢晓婉, 范蔚茗. 2013. 哀牢山构造带新安寨晚二叠世末期过铝质花岗岩锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素组成研究. 大地构造与成矿学, 37(1): 87-98. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1552.2013.01.010 |
莫宣学, 潘桂棠. 2006. 从特提斯到青藏高原形成: 构造-岩浆事件的约束. 地学前缘, 13(6): 43-51. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.007 |
潘桂棠, 徐强, 侯增谦, 王立全, 杜德勋, 莫宣学, 李定谋, 汪名杰, 李兴振, 江新胜, 胡云中. 2003. 西南"三江"多岛弧造山过程成矿系统与资源评价. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-420.
|
潘裕生. 1999. 青藏高原的形成与隆升. 地学前缘, 6(3): 153-163. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.03.015 |
史长义, 鄢明才, 迟清华. 2007. 中国不同构造单元花岗岩类元素丰度及特征. 地质学报, 81(1): 47-59. |
孙崇波, 李忠权, 王道永, 许远平, 李友余. 2016. 哀牢山构造带南段扭只二长花岗斑岩地球化学特征及其锆石U-Pb年代学研究. 中国地质, 43(1): 111-119. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2016.01.008 |
孙崇波, 李忠权, 陈晓东, 谢万洪, 王道永. 2018. 哀牢山构造带南段风别山霏细斑岩地球化学特征及其锆石U-Pb年代学研究. 地质论评, 64(5): 1251-1262. |
孙崇波, 李忠权, 王道永, 陈晓东. 2019. 哀牢山构造带南段马玉花岗闪长岩地球化学特征及其锆石U-Pb年龄. 地质通报, 38(2-3): 223-230. |
王保弟, 王立全, 王冬兵, 张万平. 2011. 三江上叠裂谷盆地人支雪山组火山岩锆石U-Pb定年与地质意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 30(1): 25-33. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2011.01.003 |
王明亮, 张加桂, 汪新文, 栾秋雷. 2014. 哀牢山构造带古构造应力场特征. 地质力学学报, 20(1): 82-93. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2014.01.008 |
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. |
吴元保, 郑永飞. 2004. 锆石成因矿物学研究及其对U-Pb年龄解释的制约. 科学通报, 49(16): 1589-1604. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2004.16.002 |
薛传东, 刘星, 谈树成, 秦德先. 2002. 云南老王寨金矿床主要矿物的标型特征. 矿物岩石, 22(3): 10-16. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-6872.2002.03.003 |
杨立飞, 石康兴, 王长明, 吴彬, 杜斌, 陈晶源, 夏锦胜, 陈晶. 2016. 西南三江兰坪盆地金满铜矿床成因研究: 来自铜和硫同位素的联合约束. 岩石学报, 32(8): 2392-2406. |
杨立强, 刘江涛, 张闯, 王庆飞, 葛良胜, 王中亮, 张静, 龚庆杰. 2010. 哀牢山造山型金成矿系统: 复合造山构造演化与成矿作用初探. 岩石学报, 26(6): 1723-1739. |
杨立强, 邓军, 赵凯, 刘江涛. 2011. 哀牢山造山带金矿成矿时序及其动力学背景探讨. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2519-2532. |
杨喜安, 刘家军, 韩思宇, 陈思尧, 张红雨, 李娇, 翟德高. 2013. 云南鲁春铜铅锌矿床鲁春火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄、地球化学及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 29(4): 1236-1246. |
翟明国, 从柏林. 1990. 中国滇西南造山带变质岩的Sm-Nd和Rb-Sr同位素年代学. 岩石学报, 6(4): 1-11. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1990.04.001 |
张旗, 张魁武, 李达周, 吴海威. 1988. 云南新平县双沟蛇绿岩的初步研究. 岩石学报, 4(4): 37-46. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1000-0569.1988.04.005 |
赵德军, 陈洪德, 王道永, 王国芝, 李娜. 2013. 哀牢山造山带南段中二叠世晚期娘宗岩体厘定. 地质科技情报, 32(3): 19-25. |
赵凯, 杨立强, 李坡, 熊伊曲. 2013. 滇西老王寨金矿床黄铁矿形貌特征与化学组成. 岩石学报, 29(11): 3937-3948. |
钟大赉. 1998. 滇川西部古特提斯造山带. 北京: 科学出版社231.
|
朱炳泉, 常向阳, 邱华宁, 王江海, 邓尚贤. 2001. 云南前寒武纪基底形成与变质时代及其成矿作用年代学研究. 前寒武纪研究进展, 24(2): 75-82. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-4135.2001.02.002 |
 2021, Vol. 37
2021, Vol. 37