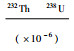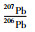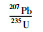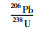2. 自然资源部矿产勘查技术指导中心, 北京 100083;
3. 东华理工大学核资源与环境国家重点实验室, 南昌 330013;
4. 河北省地矿局第三地质大队, 张家口 075000;
5. 中国地质大学(北京), 北京 100083;
6. 安徽省地质测绘技术院, 合肥 230022
2. Technical Guidance Center for Mineral Resources Exploration, Ministry of Natural Resources, Beijing 100083, China;
3. State Key Laboratory of Nuclear Resource and Environment, East China University of Technology, Nanchang, 330013, China;
4. The Third Geological Brigade of Hebei Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Zhangjiakou 075000, China;
5. School of Earth Science and Resources, China University of Geosciences (Beijing), Beijing 100083, China;
6. Institute of Geological Surveying and Mapping Technology of Anhui Province, Hefei 230022, China
华北克拉通是世界上最古老的克拉通之一(Zhao and Zhai, 2013),自元古代以来,华北克拉通北缘经历了漫长的大陆边缘演化过程,并保存了大陆裂解、被动大陆边缘转为活动大陆边缘等地质记录(Windley et al., 2007; 张晓晖和翟明国, 2010)。显生宙以来,华北克拉通北缘地区构造活动异常活跃,主要可分为四个阶段:早奥陶世到晚志留世古亚洲洋的俯冲削减和弧-陆碰撞阶段、早石炭世-早二叠世活动大陆边缘演化阶段、二叠纪末期至三叠纪微陆块碰撞合并阶段及侏罗纪-白垩纪的克拉通破坏阶段(Zhang et al., 2009a; 赵越等, 2017)。华北克拉通北缘有大量金矿床产出,主要呈近EW向沿阴山-燕山边缘隆起带展布,自西向东可分为大青山成矿区(包括哈达门沟、赛因乌素、瓦厂沟等金矿床)、张家口成矿区(包括东坪、小营盘、中山沟、大白阳等金矿床)、燕山成矿区(包括金厂峪、峪耳崖等金矿床)、辽西成矿区(包括金厂沟梁、排山楼等金矿床)和长白山成矿区(包括夹皮沟、五龙、小佟家堡子等金矿床)(Hart et al., 2002; Deng and Wang, 2016)。区内金矿化主要发生在~350Ma、~250Ma、~200Ma、~180Ma、~150Ma和~129Ma等6个时期,矿床往往经历了多期地质作用叠加,具有明显的继承性特点。
河北省张家口-宣化地区(张宣地区)位于华北克拉通北缘中段,区内自显生宙以来构造活动频繁,主要可分为四个阶段:早奥陶世至晚志留世古亚洲洋的俯冲削减和弧-陆碰撞阶段、早石炭世至早二叠世期间活动大陆边缘演化阶段、二叠纪末期至三叠纪期间各微陆块碰撞合并阶段及三叠纪-侏罗纪的克拉通破坏阶段(Zhang et al., 2009a; 赵越等, 2017)。早古生代时期,古亚洲洋开始向华北克拉通俯冲;泥盆纪时期,大量的碱性岩和少量的基性-超基性岩产出(Miao et al., 2002);早石炭世-早二叠世期间华北克拉通北缘为活动大陆边缘,古亚洲洋俯冲至华北板块这一过程使古老下地壳发生深熔作用;二叠纪末期至三叠纪期间各陆块碰撞合并,属于后碰撞/后造山的伸展环境;随后,华北克拉通岩石圈发生减薄,但减薄的开始时间尚存较大争议。中生代时期,由于古亚洲洋的闭合和太平洋的俯冲,中国东部近东西向的构造域向北北东向转换,并在燕山期达到顶峰,形成燕山运动(马寅生等, 2002)。张宣地区产出大量金矿床,主要集中在赤城、崇礼和宣化地区,被称为河北省的“金三角”,是我国重要的金产地之一。区内金矿床多以富含碲化物为特征,其中小营盘与东坪金矿床为大型矿床;后沟、韩家沟、中山沟和水晶屯等金矿床属于中型矿床;赵家沟、金家庄、西坪和大营盘等属于小型矿床。
虽然前人对张家口-宣化地区的岩浆岩进行了较多研究(Jiang, 2005; Jiang et al., 2007, 2009; Zhang et al., 2010; 包志伟等, 2003; 李长民等, 2014; 张招崇, 1995),但缺乏对古生代-中生代岩浆-构造-成矿系统的整体认识。为此,本文在收集前人研究成果的基础上,结合最新获得的区域构造、岩浆岩年龄、地球化学和Lu-Hf同位素数据,对张家口-宣化地区古生代-中生代岩浆活动的侵位序列、岩石成因和成岩构造背景进行综合分析,探究区内古生代-中生代岩浆-构造演化过程,探讨岩浆活动与成矿作用,建立成矿模型。该研究将为了解华北克拉通北缘岩浆-构造-成矿演化系统提供重要线索,并对区内的进一步找矿勘探实践提供重要的参考依据。
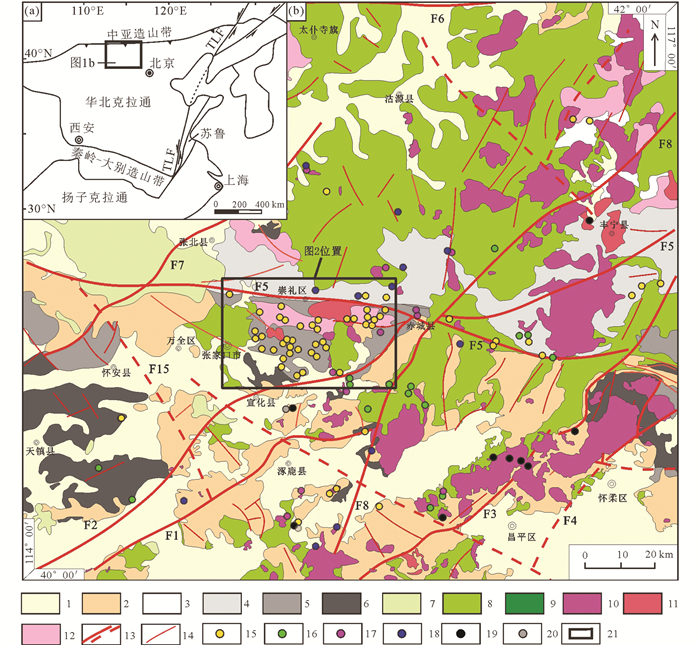
1 区域地质概况张宣地区位于华北克拉通北缘中段(图 1a),燕山山脉与大兴安岭-太行山脉交汇部位,北部与兴蒙造山带相邻。区内广泛发育前寒武纪麻粒岩相变质地体,主要为太古宙和古元古代角闪岩相-麻粒岩相变质岩系(刘敦一等, 1997)。其中,太古宇桑干岩群主要分布于尚义-崇礼-赤城断裂以南,由底端到顶端可划分为5个组,分别为西葛峪组、水地庄组、花家营组、涧沟河组和艾家沟组,岩性主要为斜长角闪片麻岩、斜长角闪岩、二辉麻粒岩、磁铁石英岩等角闪-麻粒岩相变质杂岩。该变质岩群由基性-酸性火山岩变质形成,变质程度深、退变质普遍(张招崇, 1995)。下元古界红旗营子群主要分布于尚义-崇礼-赤城断裂以北,可分为底部的大同营组和顶部的庙子沟组,岩性为含石墨斜长片麻岩、黑云变粒岩、斜长角闪岩、二云石英片岩、石英岩和大理岩等角闪岩相变质杂岩。中元古界长城系沉积建造出露甚少,仅分布于赤城-温泉以南的深大断裂内,与下伏红旗营子群为不整合接触,自下而上分常州沟组、串岭沟组、团山子组、大红峪组和高于庄组,岩性为砂砾岩、砂岩、黑色页岩和碳酸盐岩,部分地区发育“宣龙式铁矿”。上元古界蓟县系主要出露于赤城以南,龙关以东地区,与下伏长城系整合接触,自下而上分为杨庄组、雾迷山组、洪水庄组和铁岭组,主要为泻湖蒸发岩和滨海-浅海沉积岩。上侏罗统-下白垩统火山岩在区内分布广泛,以不整合形式覆盖在前寒武纪变质岩与水泉沟碱性杂岩体之上,自下而上分为白旗组和张家口组;白旗组以紫红色和砖红色凝灰质粉砂岩、凝灰质角砾岩、流纹质凝灰熔岩、紫灰-灰绿色安山岩和夹安山质角砾熔岩为主;张家口组火山岩在区内堆积厚度大,主要为砖红色-紫褐色流纹质凝灰角砾岩、棕褐色粗面岩、粉红色流纹质晶屑凝灰岩和砖红色凝灰质粉砂岩,总厚超6000m,属晚侏罗世-早白垩世陆相火山沉积建造(韦忠良等, 2008)。
|
图 1 张宣地区大地构造位置(a)及区域地质简图(b)(据甄世民等, 2019①) 1-第四系;2-古生代—中生代沉积岩系;3-古元古代变质岩系;4-新太古代变质岩系;5-中太古代变质岩系;6-古太古代变质岩系;7-喜马拉雅期火山岩;8-燕山期火山岩;9-印支期火山岩;10-燕山期侵入岩;11-印支期侵入岩;12-海西期侵入岩;13-实测(推断)深大断裂;14- 一般断裂;15-金矿;16-铜矿;17-银矿;18-铅锌矿;19-钼矿;20-钨矿;21-研究区范围;F1-桑干-平泉构造(结合)带南界深大断裂;F2-桑干-平泉构造(结合)带北界深大断裂;F3-紫荆关-灵山断裂带;F4-太行山山前断裂带;F5-尚义-崇礼-赤城断裂带;F6-康保-围场断裂带;F7-张北-沽源断裂带;F8-上黄旗-乌龙沟断裂带;F15-马市口-松枝口断裂 Fig. 1 Sketch maps of (a) geotectonic location and (b) tectonic-magmatic framework of the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area 1-Quaternary; 2-Paleozoic-Mesozoic sedimentary rocks; 3-Paleoproterozoic metamorphic rocks; 4-Neoarchean metamorphic rocks; 5-Mesoarchean metamorphic rocks; 6-Paleoarchean metamorphic rocks; 7-Himalayan volcanic rocks; 8-Yanshanian volcanic rocks; 9-Indosinian volcanic rocks; 10-Yanshanian intrusions; 11-Indosinian intrusions; 12-Hercynian intrusions; 13-measured (inferred) deep faults; 14-general faults; 15-gold deposit; 16-copper deposits; 17-silver deposits; 18-Pb-Zn deposits; 19-Mo deposits; 20-W deposits; 21-study district; F1-south deep fault of the Sanggan-Pingquan structure belt; F2-north deep fault of the Sanggan-Pingquan structure belt; F3-Zijingguan-Lingshan fault; F4-piedmont fault of the Taihang mountain; F5-Shangyi-Chongli-Chicheng fault; F6-Kangzhuang-Weichang fault; F7-Zhangbei-Guyuan fault; F8-Shanghuangqi-Wulonggou fault; F15-Mashikou-Songzhikou fault |
① 甄世民, 白海军, 贾儒雅, 姚磊, 张志辉, 陈辉, 陶文, 庞振山, 程志中, 薛建玲, 左群超. 2019. 河北省宣化-丰宁矿集区找矿预测子项目成果报告
区内构造活动频繁,断裂极为发育,且具有长期活动的特点。区域性一级断裂包括:(1)桑干-平泉构造(结合)带南界深大断裂,主体呈北东东向展布(图 1b),大部分被中元古代至第四纪地层角度不整合覆盖,线状或带状负地形特征明显,切穿多期变质变形叠加改造的糜棱岩;(2)桑干-平泉构造(结合)带北界深大断裂,主体呈北东-北东东向展布,局部呈北西西向展布(图 1b),出露宽度达0.5~3km,该深大断裂带最初形成于桑干构造运动,并在迁西、阜平、五台及吕梁等构造时期发生强烈活动;(3)尚义-崇礼-赤城断裂,走向东西,通过尚义、赤城、承德到平泉截止,全长470km(图 1b);该断裂具有复杂的演化历史,其形成于太古宙末期,至中新生代断裂活动依旧剧烈;该断裂导控元古代及古生代岩浆岩的侵位,并为成矿提供有利的构造环境(李少众和靳光成, 2000);据卫星遥感影像解译,尚义-崇礼-赤城断裂及其次级断裂控制着区内金矿床的分布,如NWW向的杨木洼-炮梁断裂控制着杨木洼、下两间房、后沟等金矿的分布,中山沟-上水泉断裂则控制着中山沟、王子府、东坪等金矿的分布,东坪金矿处于隐伏的NNE和NW向两组断裂构造的交汇部位;(4)上黄旗-乌龙沟断裂,是区域上大兴安岭-太行山断裂带的南部,走向北北东,由沫源经涿鹿、赤城、丰宁至上黄旗,全长470km;该断裂带形成于新太古代,新近纪仍有继承性活动,周边出露串珠状分布的燕山期花岗岩及火山岩,形成NNE向构造岩浆带(图 1b), 该深断裂带初始破裂时期为中侏罗世末或晚侏罗世初,剧烈变形时期为白垩纪。
区内二级断裂包括:(1)上太子城-温泉断裂,走向东西,长约27km,穿过水泉沟杂岩体、小张家口超基性岩体和温泉花岗岩体(图 2);(2)西三间房-沃麻坑断裂,走向东西,长约45km,与上太子城-温泉断裂近于平行,穿过水泉沟杂岩体和小张家口超基性岩体(图 2);(3)韩家沟-谷嘴子-场地断裂,走向北西-南东,长约30km,切过水泉沟杂岩体张家口组火山岩(图 2)。区内存在较多韧性剪切带,其经历了韧性变形→脆韧性变形→脆性变形的变形变质过程,海西期末-燕山期是韧性剪切带活化的主要阶段,明显的表现是以水泉沟杂岩体遭受了强烈的韧性剪切变形,形成了各种不同变形程度的糜棱岩。
|
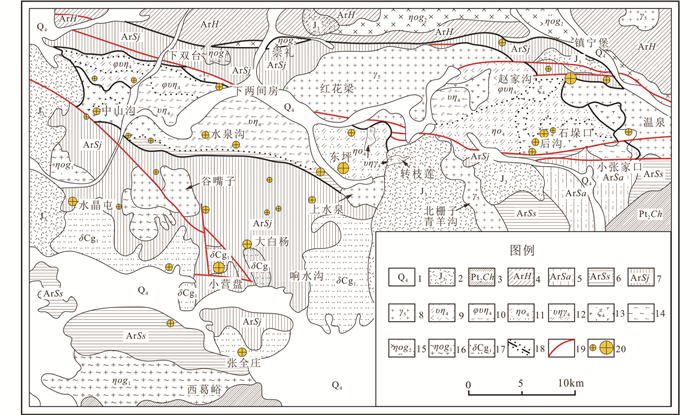
图 2 张宣地区地质矿产图(据Zhen et al., 2020) 1-第四系;2-侏罗系火山岩;3-长城系;4-红旗营子群;5-桑干群艾家沟组;6-桑干群水地庄组;7-桑干群涧沟河组;8-花岗岩;9-角闪二长岩;10-辉石角闪岩;11-石英二长岩;12-角闪二长花岗岩;13-正长岩;14-辉石岩;15-元古宇花岗片麻岩;16-太古宇花岗片麻岩;17-太古宇变质云英闪长岩;18-混合岩带;19-断裂带;20-小-大型金矿床 Fig. 2 Sketch map of geology and ore deposits of the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area (modified after Zhen et al., 2020) 1-Quaternary; 2-Jurassic volcanic rocks; 3-Changcheng System; 4-Hongqiyingzi Group; 5-Aijiagou Formation, Sanggan Group; 6- Shuidizhuang Formation, Sanggan Group; 7-Jiangouhe Formation, Sanggan Group; 8-granite; 9-hornblende monzonite; 10-pyroxene amphibolite; 11-quartz monzonite; 12-hornblende monzogranite; 13-syenite; 14-pyroxenite; 15-Proterozoic granitic gneiss; 16-Archean granitic gneiss; 17-Archean metamorphic tonalite; 18-migmatite belt; 19-faults; 20-small and large gold deposits |
区内褶皱构造主要发育于桑干群和红旗营子群。桑干群经历了三期褶皱变形:迁西运动期间形成了一系列束带状褶皱构造,由中等开阔的背向形构造相间组成,褶皱轴迹呈北西向至北东向展布;阜平运动期间,以同向挤压叠加为特征,使大部分已形成的束带状褶皱构造变成紧闭同斜褶皱,将前期褶皱翼部的不对称指向小褶皱多改造成片内无根褶皱,同时在部分地段也有一些同向宽缓的背向形褶皱构造形成;经过阜平运动同向挤压叠加的改造,桑干群进一步褶皱隆起,围绕桑干岩群呈半环带状分布,构成了怀安复式穹窿状褶皱隆起带的翼部。红旗营子群的褶皱变形相对较弱,可分为两期:五台运动期间,红旗营子群中的褶皱构造以继承大陆边缘盆地形成的大型至巨型复式向形构造为特征,由一系列束带状中等开阔的背向形构造相间组成,褶皱轴迹呈北西西向至近东西向展布;吕梁运动期间,以近南北向同向挤压叠加为特征,使部分已形成的中等开阔束带状褶皱构造变成紧闭褶皱、少数变成倒转同斜褶皱和平卧褶皱,并将前期褶皱的附属小褶皱改造成片内无根褶皱(张招崇, 1995; 甄世民等, 2019)。
区内岩浆岩具有多期次、分布广及岩石类型丰富的特点。太古宙侵入岩主要分布在尚义-赤城-隆化以南地区,岩性主要为橄榄岩、辉长岩、闪长岩及花岗岩等,如东营盘、八道河、大光顶、温泉和九神庙等岩体。显生宙以来,区内岩浆活动频繁,形成水泉沟碱性杂岩体、响水沟花岗岩、上水泉花岗岩及大面积张家口组火山岩等一系列岩浆岩(图 2; Jiang et al., 2007; 包志伟等, 2003),各岩浆岩地质特征见下文。
2 研究区古生代-中生代岩浆岩地质特征水泉沟碱性杂岩体呈岩基状侵位于太古宇桑干群涧沟河组变质岩中,岩体总体呈近东西向狭长带状出露,东西长约55km,南北宽5~8km,面积约340km2(图 2; 李长民等, 2014)。西部岩段以中粗粒辉石角闪岩、角闪正长岩、角闪二长岩类组合为主,主要见于中山沟、下双台、营盘地一带;中部岩段以含霓辉石的中细粒正长岩-细晶岩类组合为主(图 3a, b),主要见于水泉沟、西坪、东坪一带;东部岩段以含黑榴石的中细粒正长岩-石英正长岩类组合为主,部分地段可见碱长花岗岩小岩株或岩脉侵入于石英正长岩中,主要见于大南山、赵家沟、石垛口、后沟一带。岩体的西段和中段被上侏罗统张家口组酸性、中酸性火山熔岩和火山碎屑岩等不整合覆盖,其北部、东部和南部分别被红花梁、温泉和上水泉3个燕山期花岗岩所侵入(图 2)。杂岩体与围岩太古宇桑干群变质岩呈侵入接触关系,在岩体东段后沟一带,可见杂岩体与围岩呈断层接触,边缘混染带不发育。在岩体南侧的场地、东坪与岩体北侧的下双台、下两间房一带均存在数十米宽的混染带,岩体的边部含有围岩捕虏体和大小不一的包体(直径0.5~20cm),包体岩性为红旗营子群角闪斜长片麻岩和斜长角闪岩,岩体内部包体变小而趋于消失。杂岩体内不同岩性之间一般无明显界线,多为渐变过渡关系(如西段的中粗粒角闪正长岩与角闪二长岩即为渐变过渡关系),局部地段可见不同岩性之间为侵入接触关系(如东段后沟一带可见碱长花岗岩小岩株或岩脉与石英正长岩呈侵入接触关系)。

|
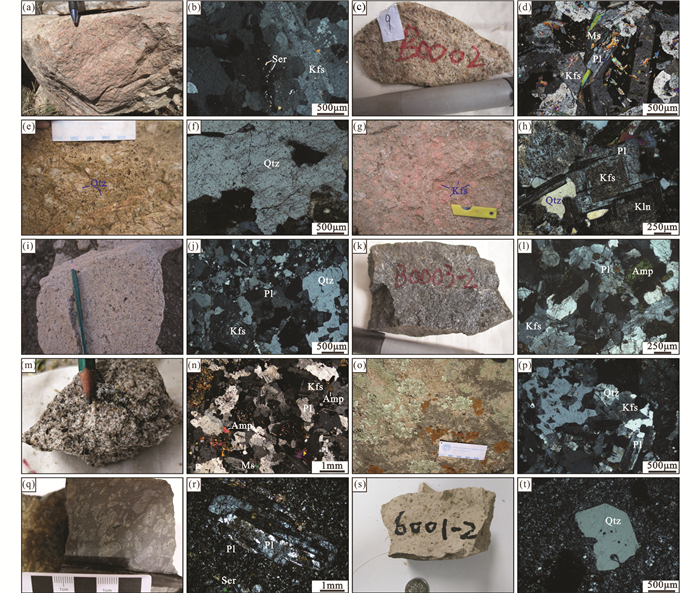
图 3 张宣地区岩浆岩野外及镜下照片 水泉沟正长岩野外照片(a)及镜下照片(b);红花梁二长花岗岩野外照片(c)及镜下照片(d);谷嘴子巨斑状花岗岩野外照片(e)及镜下照片(f);响水沟似斑状花岗岩野外照片(g)及镜下照片(h);上水泉花岗岩野外照片(i)及镜下照片(j);转枝莲闪长岩野外照片(k)及镜下照片(l);象山花岗闪长岩野外照片(m)及镜下照片(n);北栅子花岗岩野外照片(o)及镜下照片(p);井儿洼粗安岩野外照片(q)及镜下照片(r);张家口组流纹岩野外照片(s)及镜下照片(t). Amp-角闪石;Kfs-钾长石;Kln-高岭土;Ms-白云母;Pl-斜长石;Qtz-石英;Ser-绢云母 Fig. 3 Field photos and microphotographs of magmatic rocks in the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area Field photograph (a) and microphotograph (b) of the Shuiquangou syenite; field photograph (c) and microphotograph (d) of the Honghualiang monzogranite; field photograph (e) and microphotograph (f) of the Guzuizi giant porphyritic granite; field photograph (g) and microphotograph (h) of the Xiangshuigou porphyritic granite; field photograph (i) and microphotograph (j) of the Shangshuiquan granite; field photograph (k) and microphotograph (l) of the Zhuanzhilian diorite; field photograph (m) and microphotograph (n) of the Xiangshan granodiorite; field photograph (o) and microphotograph (p) of the Beishanzi granite; field photograph (q) and microphotograph (r) of the Jingerwa trachyandesite; field photograph (s) and microphotograph (t) of the Zhangjiakou formation rhyolite. Amp-amphibole; Kfs-K-feldspar; Kln-kaoline; Ms-muscovite; Pl-plagioclase; Qtz-quartz; Ser-sericite |
红花梁二长花岗岩分布在马丈子-新洞坑-张寺沟一带,近EW向展布(图 2),主要岩性为灰白色-肉红色细粒-中粗粒二长花岗岩(图 3c)。岩石呈花岗结构,主要成分为奥-中长石(< 40%)、碱性长石(>30%)、石英(>20%)及黑云母(< 5%)(图 3d)。岩体侵入桑干群变质岩和水泉沟正长岩中,局部被下白垩统张家口组覆盖。
谷嘴子巨斑状花岗岩分布在罗家营、谷嘴子一带,呈岩株状侵入太古宇桑干群(图 2)。岩石呈巨斑状结构(图 3e),斑晶主要为条纹长石,呈板状自形晶,多大于2cm,斑晶约占50%左右,基质为花岗结构(图 3f)。
响水沟似斑状花岗岩出露于响水沟村西南侧,地表出露似肾状,面积约1km2,略向南西倾斜,围岩为太古宇桑干群(图 2)。岩石呈肉红色,似斑状结构,基质为等粒花岗结构,块状构造(图 3g)。主要矿物由中-更长石、钾长石(条纹长石、微斜长石和少量正长石)、石英及黑云母组成(图 3h)。斑晶主要为条纹长石、石英以及少数中-更长石,含量达50%左右。条纹长石斑晶直径多大于1cm,呈板状,内部有斜长石包体;部分钾长石呈粗粒圆形,被斜长石包裹,具环斑结构;石英斑晶直径达1cm左右呈他形球粒状聚晶出现。
小张家口基性-超基性岩出露于小张家口-于家沟一带,尚义-崇礼-赤城断裂南部,岩体侵入长城系地层和水泉沟杂岩体中,呈东西向蝌蚪状分布,长约10km,宽0.15~1.5km(图 2)。岩性主要为透辉石岩、橄榄透辉石岩和纯橄榄岩,蛇纹石化强烈。辉石岩由单斜辉石(70%~90%)、斜方辉石(5%~15%)、钛-磁铁矿(< 5%)和磷灰石(< 5%)组成,堆晶结构常见。
上水泉花岗岩分布于窑子湾-上水泉一带,尚义-崇礼-赤城深大断裂带南侧,呈不规则的椭圆形,面积约15km2(图 2)。主要岩性为浅肉红色中粒-中粗粒黑云母花岗岩(图 3i),矿物成分为钾长石(25%~30%)、斜长石(35%~40%)、石英(25%~30%)、黑云母(< 5%)及萤石(< 5%)(图 3j)。岩石中晶洞发育,常见石英晶簇,且存在大量钾长花岗岩细脉。岩体侵入水泉沟碱性杂岩体和桑干群变质岩中。
转枝莲闪长岩分布于营岔一带,主要岩性组合为深灰色中细粒-中粒辉石闪长岩(图 2)。岩石呈深灰色(图 3k),半自形粒状结构,矿物主要为中长石65%、普通辉石10%~15%、紫苏辉石5%,黑云母4%~5%,石英4%~5%,副矿物有磁铁矿、磷灰石及金红石等(图 3l)。
象山花岗闪长岩主要分布于杨家营、关底一带,出露面积0.5km2,呈舌状侵入于长城系地层中(图 2)。岩石呈浅灰色,带褐绿色调,粗粒花岗结构,块状构造(图 3m),主要由斜长石(60%)、钾长石(15%)、石英(15%)、黑云母(5%)和角闪石(5%)组成(图 3n)。斜长石呈完好的自形柱体; 石英分布其间隙中,晶体发育受到限制,呈他形。岩体球状风化显著。
北栅子花岗岩分布于北栅子、青羊沟、老王沟一带,呈NW向带状展布,出露面积约3km2(图 2),主要岩性组合为浅肉红色中粒-中粗粒黑云母花岗岩(图 3o)。岩石呈花岗结构、文象结构,矿物有微斜条纹长石(45%)、更长石(25%)、石英(20%~25%)、黑云母(>5%),副矿物有锆石、磷灰石及磁铁矿等(图 3p)。岩体侵入桑干群变质岩和水泉沟杂岩体中,被张家口组不整合覆盖。
井儿洼粗安岩-英安岩分布于庞家堡北部,赵川镇乡东部(图 2),为一套粗面安山岩、安山岩、英安岩的一套火山岩,具明显斑状结构和粗面结构(图 3q),绿泥石化强烈,斑晶主要为长石和石英(图 3r)。井儿洼火山岩内发育象山铜矿床。
张家口组火山岩在区内广泛出露,为一套中酸性的火山岩、火山碎屑岩,岩性以英安岩、粗面岩和流纹岩为主。具明显流动构造及斑状结构、凝灰结构、粗面结构(图 3s)。斑晶主要为石英斑晶、长石斑晶,基质为隐晶质长石、石英及岩屑、玻屑等(图 3t)。
3 样品测试分析方法本文研究分别采集水泉沟正长岩、响水沟似斑状花岗岩、象山花岗闪长岩、青羊沟黑云母二长花岗岩、井儿洼粗安岩-英安岩及张家口组流纹岩样品进行锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素及主微量元素测试。
3.1 锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素分析方法锆石的U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素测试在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室利用LA-ICP-MS完成,采用GeoLas 2005激光剥蚀系统。本次测试的激光束斑和频率分别为32μm和5Hz分析,测试过采用20s左右的空白信号和50s左右的样品信号。采用数据处理软件ICPMSDataCal完成对空白信号及样品信号的选择、仪器灵敏度校正及年龄等的处理(Liu et al., 2008)。采用91500为标样做数据校正,利用软件Isoplot/Ex_ver3完成年龄谐和图的制作和年龄加权平均计算(Ludwig, 2003)。
锆石原位Hf同位素分析仪器为Geolas2005准分子激光剥蚀系统(LA-MC-ICP-MS)和Neptune PLUS多接收等离子质谱,剥蚀直径为44μm,分析点位于锆石U-Pb测年分析点附近。分析过程中锆石标准91500的176Hf/177Hf测试加权平均值为0.282308±30(2σ,n=4),在文献报道的误差范围内。数据处理采用ICPMSDataCal(Liu et al., 2008)。
3.2 岩石主微量元素分析方法主微量元素测试在北京大学造山带与地壳演化教育部重点实验室进行。主量元素应用XRF分析方法测定,仪器为美国ThermoElectron公司的ARLADVANTXP+扫描型波长色散X射线荧光光谱仪,测试精度在1%以内。微量元素和稀土元素采用高压釜酸溶法,应用ICP-MS分析方法测定,仪器为美国AGILENT科技有限公司的Agilent 7500Ce ICP-MS,测试精度为5%,Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf的精度为10%。详细分析流程参照刘颖等(1996)。
4 分析结果 4.1 锆石U-Pb年龄和Lu-Hf同位素对水泉沟正长岩、响水沟似斑状花岗岩、井儿洼粗安岩-英安岩、象山花岗闪长岩、青羊沟黑云母二长花岗岩和张家口组流纹岩样品进行锆石挑选,各样品锆石均较完整,破损小,CL图像具有明显震荡环带,为典型岩浆锆石(图 4)。各样品锆石U-Pb年龄和Lu-Hf同位素测试结果分别见表 1和表 2。
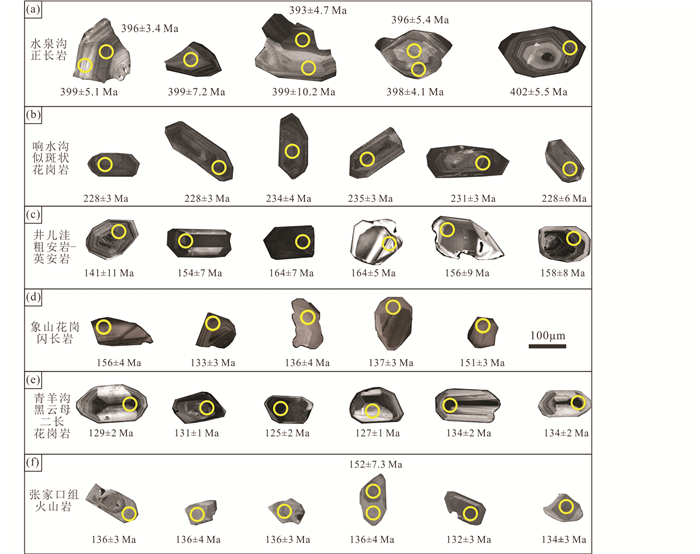
|
图 4 张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆岩锆石CL图像 Fig. 4 Zircon CL images of the Paleozoic-Mesozoic igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area |
|
|
表 1 张宣地区岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄 Table 1 Zircon U-Pb ages of igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area |
|
|
表 2 张宣地区岩浆岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素组成 Table 2 Zircon Lu-Hf isotope compositions of igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area |
水泉沟正长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为400±2Ma(MSWD=0.76,图 5a),与前人测试结果在误差范围内一致(Miao et al., 2002; Bao et al., 2014)。锆石176Lu/177Hf值为0.000173~0.001156,176Hf/177Hf值为0.281879~0.281970,εHf(t)为-22.9~-19.7,一阶模式年龄tDM为1900~1768Ma,二阶模式年龄tDMC为2833~2631Ma。
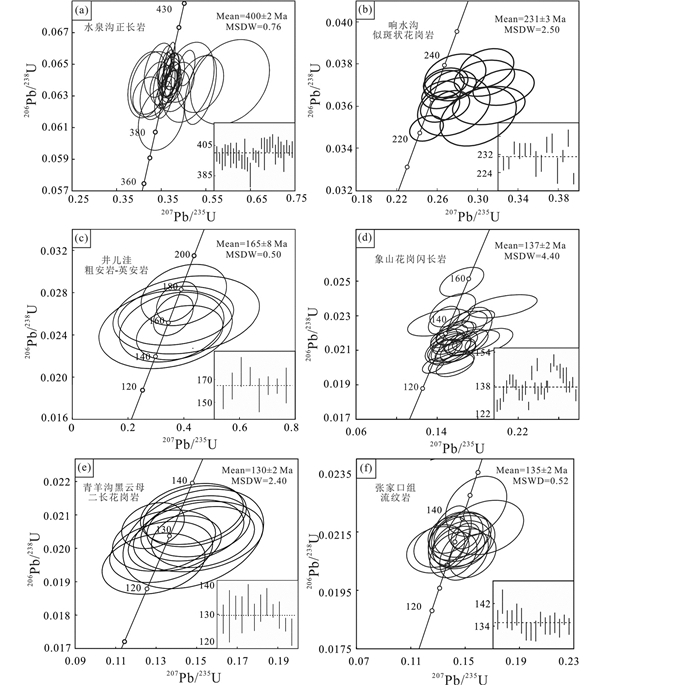
|
图 5 张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆岩锆石U-Pb年龄 Fig. 5 Zircon U-Pb ages of the PaleozoicMesozoic igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area |
响水沟似斑状花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为231±3Ma(MSWD=2.50,图 5b),与红花梁二长花岗岩(235±2Ma, Jiang et al., 2007)和谷嘴子巨斑状花岗岩(236±2Ma, Miao et al., 2002)年龄一致,表明其为同一岩浆活动下的产物。锆石176Lu/177Hf值为0.000544~0.001493,176Hf/177Hf比值为0.282142~0.282266,εHf(t)值为-17.4~-13.2,一阶模式年龄tDM为1554~1409Ma,二阶模式年龄tDMC为2361~2092Ma。
井儿洼粗安岩-英安岩锆石U-Pb年龄为165±8Ma(MSWD=0.50,图 5c),该年龄为首次在区内获得。锆石176Lu/177Hf值为0.001019~0.003179,176Hf/177Hf值为0.282271~0.282855,εHf(t)为-14.2~6.4,一阶模式年龄tDM为597~1399Ma,二阶模式年龄tDMC为811~2116Ma。
象山花岗闪长岩锆石U-Pb年龄为137±2Ma(MSWD=4.40,图 5d),表明其为燕山期侵位。锆石176Lu/177Hf值为0.000322~0.001152,176Hf/177Hf值为0.281980~0.282090,εHf(t)为-25.1~-21.1,一阶模式年龄tDM为1623~1787Ma,二阶模式年龄tDMC为2530~2776Ma。
青羊沟黑云母二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄为130±2Ma(MSWD=2.40,图 5e),与李创举和包志伟(2012)获得的北栅子岩体测试结果一致。锆石176Lu/177Hf值为0.001472~0.002272,176Hf/177Hf值为0.282047~0.282122,εHf(t)为-22.9~-20.3,一阶模式年龄tDM为1641~1726Ma,二阶模式年龄tDMC为2470~2636Ma。
张家口组流纹岩锆石U-Pb年龄为135±2Ma(MSWD=0.52,图 5f),锆石176Lu/177Hf值为0.000619~0.002535,176Hf/177Hf值为0.282225~0.282309,εHf(t)为-16.6~-13.4,一阶模式年龄tDM为1318~1509Ma,二阶模式年龄tDMC为2043~2241Ma。
4.2 全岩主微量特征水泉沟正长岩、响水沟似斑状花岗岩、象山花岗闪长岩、北栅子黑云母二长花岗岩和张家口组流纹岩全岩主微量元素测试结果见表 3。
|
|
表 3 张宣地区岩浆岩全岩主量(wt%)、微量(×10-6)元素组成 Table 3 Whole-rock major (wt%) and trace (×10-6) element compositions of igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area |
水泉沟正长岩具中等SiO2(63.60%~64.79%),高Al2O3(18.80%~19.02%)、K2O(4.98%~6.49%)和Na2O(6.00%~7.23%),K2O/Na2O比值为0.69~1.08。Fe2O3T、MgO和TiO2含量低,分别为1.31%~1.37%、0.06%~0.12%和0.11%~0.16%,Mg#为10~17。稀土总量为33.97×10-6~78.21×10-6,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素分布较平缓((La/Yb)N=2.22~22.01),轻稀土较富集((La/Sm)N=2.10~4.99),重稀土相对平稳且有富集趋势((Gd/Yb)N=0.75~2.17),无Ce、Eu异常(Ce/Ce*=1.05~1.16、Eu/Eu*=1.07~1.15,图 6a)。原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图显示水泉沟正长岩富集大离子亲石元素,如Rb、Ba、Sr和Pb,亏损高场强元素,如Nb、Ta(图 6b)。水泉沟碱性杂岩体中的辉石闪长岩、角闪二长岩和正长岩的稀土和微量元素分布模式一致(图 6a, b),其中辉石闪长岩的稀土元素总量稍高,表明其来源的一致性。细晶岩的稀土元素总量偏低,(La/Yb)N=0.78~2.57,明显低于其他岩性,表明细晶岩的演化程度高,可能形成于流体-熔体共存的高演化岩浆体系。
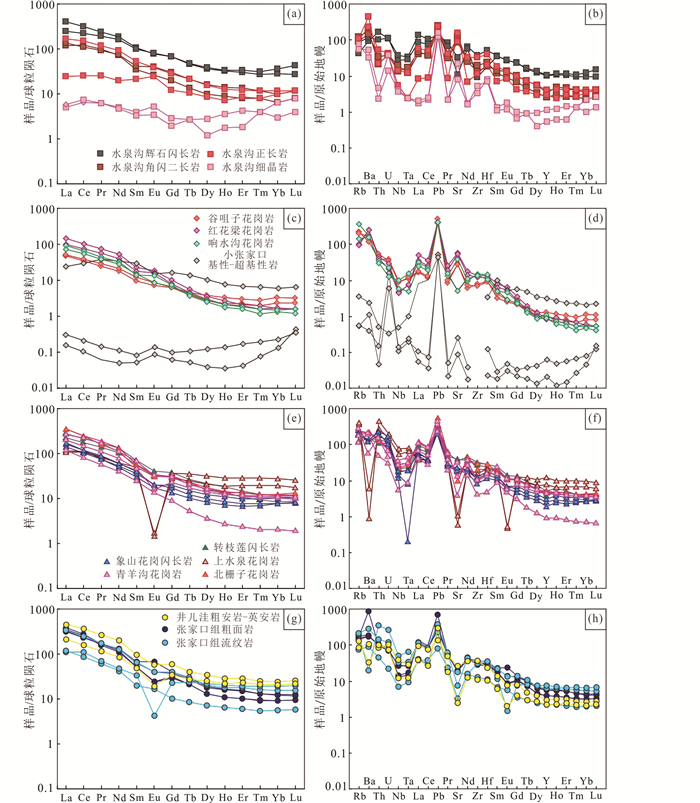
|
图 6 张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆岩球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) 数据据Jiang (2005)、Jiang et al.(2007, 2009)、张招崇(1995)、田伟等(2007)、李创举和包志伟(2012)和本文 Fig. 6 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns and primitive mantle-normalized element spider diagrams for the Paleozoic-Mesozoic igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) Data sources: Zhang (1995), Jiang (2005), Jiang et al.(2007, 2009), Tian et al. (2007), Li and Bao (2012), and this text |
响水沟似斑状花岗岩具有较高SiO2(61.36%~71.06%),高的Al2O3(15.94%~20.21%)、K2O(3.34%~3.81%)和Na2O(3.26%~6.89%)含量,K2O/Na2O比值为0.55~1.06。Fe2O3T和MgO含量低,分别为0.93%~1.37%、0.26%~0.33%,Mg#为36~39。稀土总量为36.70×10-6~80.25×10-6,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素分布呈右倾模式((La/Yb)N=12.51~49.64),轻稀土较富集((La/Sm)N=4.49~5.30),重稀土相对平稳((Gd/Yb)N=1.88~4.50),无Ce、Eu异常(Ce/Ce*=1.01~1.03、Eu/Eu*=0.86~1.28,图 6c)。样品富集大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素(图 6d)。同期岩浆岩的稀土元素组成一致(除小张家口基性-超基性岩,图 6c, d),表明其源区的一致性,但其微量元素比值,包括Rb/Sr=0.05~2.26、Ba/Rb=3.00~30.77、Ba/Sr=0.96~10.92、Nb/Ta=6.76~21.67的变化范围大,可能存在岩浆混合。
象山花岗闪长岩SiO2含量较高(67.19%~71.18%),具有中等Al2O3(11.83%~12.52%)、高的K2O(5.82%~7.18%)和低的Na2O(1.26%~1.49%),K2O/Na2O比值大,为4.04~5.70。Fe2O3T和MgO含量高,分别为4.10%~5.65%、2.48%~3.72%,Mg#为58~65。稀土总量为146.0×10-6~170.2×10-6,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素分布右倾((La/Yb)N=15.39~22.59),轻稀土富集((La/Sm)N=3.88~5.86),重稀土平稳((Gd/Yb)N=1.73~2.22),无Ce异常(Ce/Ce*=0.99~1.06),具轻微Eu负异常(Eu/Eu*=0.71~0.87,图 6e)。样品富集大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素(图 6f)。
青羊沟黑云母二长花岗岩具有高的SiO2(69.23%~74.30%),中等Al2O3(13.45%~15.21%),高的K2O(3.50%~5.51%)和Na2O(4.06%~5.63%),K2O/Na2O比值为0.62~1.28。Fe2O3T、MgO和TiO2含量低,分别为1.29%~2.41%、0.52%~1.23%、0.19%~0.44%,Mg#为41~58。稀土总量为109.3×10-6~314.3×10-6,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素分布右倾((La/Yb)N=18.05~58.38),轻稀土富集((La/Sm)N=3.98~4.97),重稀土平稳((Gd/Yb)N=1.97~4.49),无Ce异常(Ce/Ce*=0.97~1.06),Eu呈负异常(Eu/Eu*=0.38~0.90,图 6e)。样品富集大离子亲石元素,亏损高场强元素(图 6f)。同期岩浆岩的稀土和微量元素组成区别明显,表现为Eu是否具有负异常,表明该时期岩浆演化及成岩过程较复杂。
井儿洼粗安岩-英安岩SiO2含量变化大(53.55%~66.57%),较高Al2O3(13.53%~18.25%),中等K2O(2.97%~3.67%)和Na2O(1.47%~3.88%),K2O/Na2O比值为0.95~2.02。Fe2O3T和MgO含量高,分别为4.68%~7.59%、1.79%~2.67%,Mg#为35~57。稀土总量为229.8×10-6~502.4×10-6,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素分布右倾((La/Yb)N=10.29~19.08),轻稀土富集((La/Sm)N=4.36~4.78),重稀土平稳((Gd/Yb)N=1.67~2.47),无Ce异常(Ce/Ce*=1.01~1.05),具轻微Eu负异常(Eu/Eu*=0.48~0.77,图 6g)。
张家口组流纹岩具有高的SiO2(74.94%~78.91%),中等Al2O3(11.45%~15.50%)、K2O(1.88%~3.30%)和Na2O(0.10%~4.21%),K2O/Na2O比值为0.78~18.80。Fe2O3T、MgO和TiO2含量分别为0.66%~1.97%、0.09%~0.11%和0.15%~0.28%。稀土总量为116.3×10-6~147.1×10-6,球粒陨石标准化稀土元素右倾分布((La/Yb)N=5.78~20.70),轻稀土富集((La/Sm)N=3.29~5.96),重稀土平稳((Gd/Yb)N=1.20~1.78),无Ce异常(Ce/Ce*=1.01~1.25),不一致的Eu异常,其中一件样品具有明显Eu负异常(Eu/Eu*=0.16,图 6g)。原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图显示张家口组流纹岩富集大离子亲石元素,如Rb、Ba、Sr和Pb,亏损高场强元素,如Nb、Ta(图 6h)。
5 讨论 5.1 成岩年龄基于本次工作获得的岩浆岩年龄,结合前人工作,对张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆岩成岩年龄进行统计,见图 7。区内岩浆岩主要形成于三个时期,分别为海西期、印支期和燕山期。
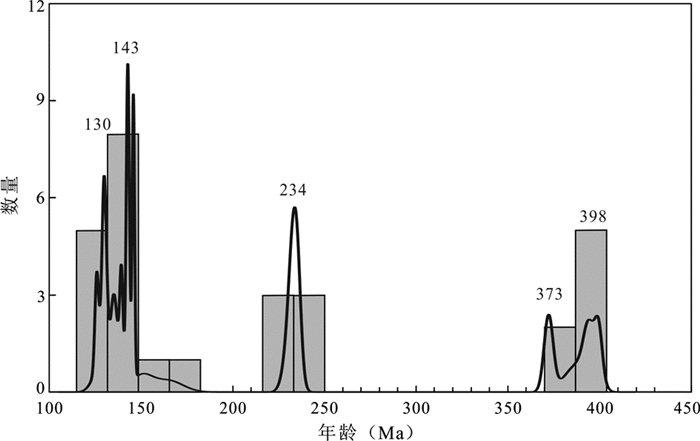
|
图 7 张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆岩成岩年龄统计图 年龄数据据Miao et al. (2002)、Jiang et al.(2007, 2009)、Cisse et al. (2017)、杨进辉(2006)、李创举和包志(2012)、陈(2013)、李长民(2014)及本文 Fig. 7 Statistical diagram of diagenetic ages for the PaleozoicMesozoic igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area Data sources: Miao et al. (2002), Yang et al. (2006), Jiang et al.(2007, 2009), Li and Bao (2012), Chen (2013), Li et al. (2014), Cisse et al. (2017) and this text |
海西期岩浆岩主要为水泉沟碱性杂岩体,为区内分布范围最大的岩体(图 2)。该杂岩性变化大,包括辉石闪长岩、角闪二长岩、正长岩和细晶岩等。不同岩性的成岩年龄跨度范围大,为410~370Ma,峰值为398Ma和373Ma(图 7),且具有东部年龄大、西部年龄小的特点(李长民等, 2014),表明水泉沟碱性杂岩体为多期次连续侵位形成,该特点在碱性杂岩体中普遍存在(Shangguan et al., 2016; Decrée et al., 2019)。
印支期岩浆岩包括红花梁花岗岩、谷嘴子花岗岩、响水沟花岗岩和小张家口基性-超基性岩,岩体侵位年龄集中,为240~220Ma,峰值为234Ma(图 7)。3个花岗岩体的年龄一致,矿物组成类似,且微量元素、锆石Hf及全岩Sr-Nd同位素组成一致(图 6c, d、图 8、图 9),表明三者为同一岩浆活动下的产物,小张家口基性-超基性岩的年龄为220Ma(田伟等, 2007),为本次岩浆活动的晚期侵位形成。

|
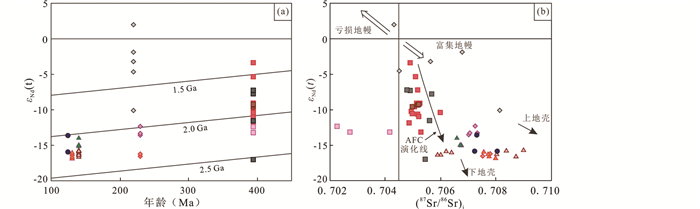
图 8 张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆岩Hf同位素分布图 白乃庙地区岩浆岩Hf同位素据Zhang et al. (2014a); 阿拉善地区岩浆岩Hf同位素据Liu et al. (2016);张宣地区岩浆岩Hf同位素据Jiang et al.(2007, 2009)、Cisse et al. (2017)、杨进辉等(2006)、田伟等(2007)、李创举和包志伟(2012)、李长民等(2014)及本文;岩浆岩标志、图例与图 6一致 Fig. 8 Scattergrams of Hf isotope compositions for the Paleozoic-Mesozoic igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area Data sources: the Bainaimiao magma Hf isotope compositions from Zhang et al. (2014a); the Alxa magma Hf isotope compositions from Liu et al. (2016); the Zhangjiakou magma Hf isotope compositions from Yang et al. (2006), Jiang et al.(2007, 2009), Tian et al. (2007), Li and Bao (2012), Li et al. (2014a), Cisse et al. (2017) and this text. Magmatite symbols are consistent with Fig. 6 |
|
图 9 张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆岩Sr-Nd同位素分布图 数据据Jiang (2005)、Jiang et al.(2007, 2009)、张招(1995)、包志伟(2003)、陈斌(2008)和李创举和包志伟(2012);岩浆岩标志、图例与图 6一致 Fig. 9 Scattergrams of Sr-Nd isotope compositions for the Paleozoic-Mesozoic igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area Data sources: Zhang (1995), Bao et al. (2003), Jiang (2005), Jiang et al.(2007, 2009), Li and Bao (2012) and Chen et al. (2008). Magmatite symbols are consistent with Fig. 6 |
燕山期岩浆岩在区内出露广泛,侵入岩包括转枝莲闪长岩、象山花岗闪长岩、上水泉花岗岩和北栅子花岗岩,火山岩包括井儿洼粗安岩-英安岩和张家口组火山岩。成岩年龄跨度大,集中在160~120Ma,峰值为143Ma和130Ma(图 7)。其中143Ma为侵入岩年龄,130Ma为火山岩年龄。井儿洼粗安岩-英安岩年龄165±8Ma是区内首次报道,表明中侏罗世时,该地区已存在岩浆活动,可能指示华北克拉通破坏初期。
5.2 岩石成因 5.2.1 海西期岩浆岩泥盆纪水泉沟碱性杂岩体岩性复杂,主要为辉石闪长岩、角闪二长岩、正长岩和细晶岩。张招崇和陈洪新(1997)认为水泉沟杂岩体存在两种演化趋势,分别为①辉石闪长岩→角闪二长岩→石英碱长正长岩→碱长花岗岩和②正长岩→霓辉正长岩→碱长正长岩。该杂岩体经历了强烈的后期蚀变作用,产出硅钛铈矿(Jiang, 2006)及稀土元素出现MW型的四分组效应(Zhao et al., 2010)。水泉沟碱性杂岩体不同岩性之间具有时空关联,且微量元素和同位素组成相近(图 6a, b、图 8b、图 9),表明具有一致的物质来源,因此可用哈克图解解释岩浆的演化过程。哈克图解中,TiO2、Fe2O3T、MgO随SiO2含量的增加而减少(图 10),指示岩浆经历了辉石、磁铁矿、钛铁矿等矿物的分离结晶。Al2O3与Na2O随SiO2含量的增加先增加后减少,且CaO随SiO2含量的增加减少(图 10),表明岩浆存在钾长石和单斜辉石的分离结晶。上述的分离结晶过程与各岩性矿物组成一致,表明水泉沟碱性杂岩体不同类型的岩石之间是一个演化序列。微量元素组成表明,细晶岩的演化程度高,为岩浆演化末期流体-熔体共存阶段的产物。

|
图 10 水泉沟碱性杂岩体哈克图解 数据据Jiang (2005)、Cisse et al. (2017)、张招崇(1995)和本文;岩性标志、图例与图 6一致 Fig. 10 Harker diagrams of the Shuiquangou alkaline complex Data sources: Zhang (1995), Jiang (2005), Cisse et al. (2017) and this text. Magmatite symbols are consistent with Fig. 6 |
碱性岩浆通常由以下三种方式形成:(1)下地壳的部分熔融(Huang and Wyllie, 1981);(2)地幔的部分熔融或碱性玄武岩分离结晶(Sutcliffe et al., 1990);(3)幔源岩浆与壳源岩浆混合(Riishuus et al., 2005)。水泉沟碱性杂岩体的εHf(t)、εNd(t)值变化范围大,落于1.5~3.0Ga下地壳演化线之间(图 8、图 9),因此其可能形成于下地壳的高压(>15kbar)部分熔融(Huang and Wyllie, 1981)。华北克拉通的下地壳主要由麻粒岩和片麻岩组成(Gao et al., 1998),实验岩石学表明该类地壳高压部分熔融会形成重稀土元素强烈亏损、Eu负异常明显的岩浆岩,与水泉沟REE分布特点不符(图 6)。岩体εNd(t)值范围为-13.2~-3.4(图 9),锆石εHf(t)的范围为-26.7~-8.9(图 8b),辉石闪长岩和角闪二长岩的锆石εHf(t)值明显高于正长岩和细晶岩。虽然张宣地区缺少大量泥盆纪基性岩,但在张家口西北部商都地区的三道沟和乌兰哈达侵入体产出大量基性-超基性岩,其Hf和Nd同位素组成与水泉沟碱性杂岩体一致(Zhang et al., 2018),因此,水泉沟碱性杂岩体的岩浆可能来源于富集岩石圈地幔。受俯冲作用影响的岩石圈地幔低程度的部分熔融可以形成碱性玄武质岩浆(Wyllie and Sekine, 1982),但水泉沟碱性杂岩体中富硅的正长岩和细晶岩表明有地壳物质的混入。水泉沟碱性杂岩体的εNd(t)随SiO2增加而减小(图 10i),表明岩浆中有壳源物质的加入,Eu异常不明显指示长石未分离结晶。Jiang (2005)认为水泉沟碱性杂岩体的岩浆经历了两个演化阶段,为早期橄榄石和辉石的结晶分异及晚期斜方辉石、角闪石及其他副矿物的结晶分异,两个阶段都存在壳源物质的混入。上述特征表明幔源岩浆在演化过程中经历了地壳的同化混染和分离结晶的共同作用(AFC, crustal assimilation and fractional crystallization; DePaolo, 1981)。水泉沟杂岩体东段岩性偏酸性,年龄~400Ma,εHf(t)值低,西段岩性偏基性,年龄~370Ma,εHf(t)值高,表明岩浆侵位初期壳源物质比例高,后期壳源物质减少,从而导致碱性岩和中酸性岩共存,进一步证实了碱性岩浆经历了AFC过程(Zhang et al., 2018; Decrée et al., 2019)。
碱性岩通常形成于碰撞后、裂谷或板内伸展构造背景(Eby, 1992; Whalen et al., 1987),可为区内岩浆构造的演化过程提供重要信息。华北克拉通北缘产出大量泥盆纪碱性岩,如赤峰的红山公园正长花岗岩(~387Ma, Shi et al., 2010)、车户沟正长花岗岩(~393Ma)、固阳的白采沟(~400Ma)、高家村(~396Ma)、三道沟碱性岩(~400Ma)等(Zhang et al., 2018)。早古生代时期,古亚洲洋向华北克拉通俯冲,形成470~440Ma的白乃庙岩浆岛弧带(Zhang et al., 2014a),但该时期岩浆岩很少在华北克拉通北缘产出。泥盆纪时期,古亚洲洋持续俯冲,华北克拉通北缘处于活动大陆边缘,白乃庙岛弧带和华北克拉通北缘发生弧陆碰撞,碰撞后的伸展导致岩石圈地幔的部分熔融,形成水泉沟碱性杂岩体(Zhang et al., 2010, 2018; 张晓晖和翟明国, 2010)。
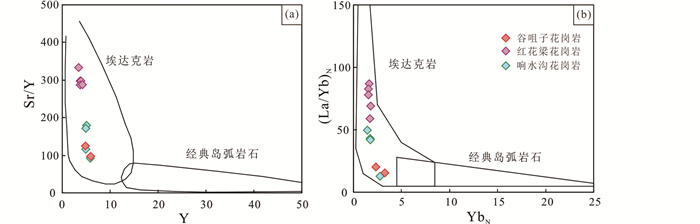
5.2.2 印支期岩浆岩张宣地区印支期岩浆岩包括基性-超基性岩和花岗岩,其中,小张家口基性-超基性岩的εHf(t)和εNd(t)值高,具有幔源特征,花岗岩εHf(t)和εNd(t)值较低,位于2.0~2.5Ga下地壳演化线之间(图 8和图 9)。区内三叠纪花岗岩具有高Sr低Y的特点,在Sr/Y-Y和(La/Yb)N-YbN图解上落在埃达克岩区域(图 11)。目前对埃达克质岩浆来源主要有以下观点:(1)洋壳板片部分熔融并混染地幔橄榄岩(Defant and Drummond, 1990);(2)高压环境下玄武质岩浆的部分熔融和分离结晶(Huang et al., 2008);(3)含水地幔橄榄岩部分熔融(Stern and Hanson, 1991);(4)地幔岩浆与地壳物质混合(Fu et al., 2012);(5)下地壳低压熔融,继承源区岩石的高Sr低Y特征(Ma et al., 2015)。
|
图 11 张宣地区三叠纪花岗岩埃达克岩判别图解(底图据Defant and Drummond, 1993) 数据据Jiang et al. (2007)和本文 Fig. 11 Discrimination diagrams of adakitic rocks for the Triassic granites from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area (base map after Defant and Drummond, 1993) Data from Jiang et al. (2007) and this text |
三叠纪时期,古亚洲洋的俯冲活动已结束,埃达克岩不可能产自俯冲洋壳的部分熔融。高的SiO2含量排除了地幔橄榄岩的富水熔融(Martin et al., 2005)。玄武质岩浆中角闪石的分离结晶会使中稀土元素含量减少,Sr/Y和La/Yb比值增高(Moyen, 2009),斜长石不同程度的分离结晶会使岩浆中Sr含量降低(Castillo et al., 1999),两者共同作用可形成埃达克质岩浆(Gao et al., 2012)。三叠纪埃达克岩的La/Yb、Dy/Yb与SiO2之间无明显线性关系,表明角闪石分离结晶不明显,Sr与SiO2无线性关系,且无Eu负异常等,表明斜长石未分离结晶,因此其不是由玄武质岩浆分离结晶形成。三叠纪埃达克岩中存在环斑结构(钾长石被斜长石包裹,图 3h),该现象多形成于酸性和基性岩浆的混合作用(Vernon, 2004)。当基性岩浆注入到碱性岩浆,早期结晶的钾长石由于在混合岩浆中不稳定,部分被溶解且圆化,基性岩浆在钾长石边缘快速结晶,使钾长石被斜长石包裹,形成环斑结构。其次,该岩浆岩主量元素和微量元素比值变化大(Rb/Sr=0.05~2.26、Ba/Rb=3.00~30.77、Ba/Sr=0.96~10.92、Nb/Ta =6.76~21.67),显示壳幔物质混合,以及与同时期的小张家口基性-超基性岩共存,表明三叠纪岩浆岩可能经历了一定程度的镁铁质岩浆和长英质岩浆的混合作用(Jiang et al., 2007; Ma et al., 2015; 杨进辉等, 2005)。
三叠纪岩浆岩中含有大量前寒武纪继承锆石,表明岩浆源区存在古地壳物质。Gao et al. (2012)认为继承锆石不能完全代表岩浆源区性质,其可能是岩浆上升过程中捕获的围岩中的锆石,但Jiang et al. (2007)研究发现区内三叠纪岩浆岩中的继承锆石与岩浆锆石具有相同的Hf同位素组成,证明了继承锆石为岩浆源区锆石,并且εHf(t)和εNd(t)值以及模式年龄均指示源区为古老下地壳(图 8和图 9)。综上所述,张宣地区三叠纪岩浆岩来源于地幔岩浆上涌引起的加厚下地壳的部分熔融,可能存在镁铁质岩浆和长英质岩浆的混合。
形成于岛弧环境中的埃达克岩可以指示板块俯冲过程,但形成于大陆内部埃达克岩的物质组成受源岩控制,不存在明确的构造意义(张超等, 2012)。华北克拉通北缘广泛存在三叠纪岩浆岩(Jiang et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2009b, 2014b; 田伟等, 2007),岩性主要为基性-超基性岩、闪长岩、花岗闪长岩、正长岩和花岗岩等。古亚洲洋在二叠纪-三叠纪期间闭合,各陆块相互碰撞合并(Jian et al., 2010; Li et al., 2014; 张超等, 2014),华北克拉通北缘属于碰撞后伸展环境。岩石圈的强烈伸展使热的地幔岩浆上涌,熔融下地壳形成酸性岩浆,岩浆上涌侵位形成大量花岗岩和基性-超基性岩。
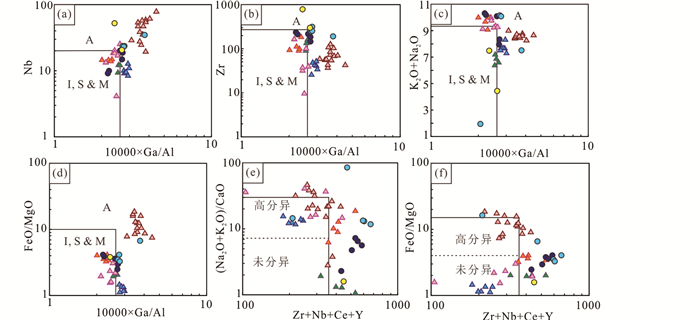
5.2.3 燕山期岩浆岩张宣地区燕山期岩浆岩岩性复杂,侵入岩有闪长岩、花岗闪长岩和花岗岩,火山岩有安山岩、粗面岩和流纹岩等。这些岩浆岩具有不同的地球化学组成,如转枝莲闪长岩具有高Sr低Y的埃达克岩特征,与三叠纪岩浆岩一致,而其他岩浆岩则偏向于弧岩浆岩,表明源区熔融条件存在差异(李创举和包志伟, 2012);上水泉花岗岩具低Al2O3、MgO,明显Eu负异常的特点(图 6e, f),在花岗岩分类图上落入A型花岗岩区域(图 12),其它岩浆岩的FeO/Al2O3值低,无明显Eu异常,在花岗岩分类图上落在I型、A型花岗岩边界处(图 12)。Jiang et al. (2009)认为上水泉花岗岩属于高分异花岗岩,而Yang et al. (2020)则将区内岩浆岩划为A型花岗岩。研究表明,高分异花岗岩与A型花岗岩具有相似的地球化学特征,表现为高的Ga/Al比和Zr+Nb+Ce+Y值(Chappell and White, 1992; 吴福元等, 2017),而A型花岗岩一个显著的特点是形成温度高,高分异花岗岩则不具备这一特征。晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆岩全岩锆饱和温度为750~850℃(表 3),低于A型花岗岩形成的最低温度(900℃;孙金凤和杨进辉, 2009),因此应属于高分异花岗岩。
|
图 12 张宣地区晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆岩A型花岗岩和高分异花岗岩判别图解(底图据Whalen et al., 1987) 数据据Jiang et al.(2007, 2009)、李创举和包志伟(2012)及本文;岩性标志与图 6一致 Fig. 12 Discrimination diagrams of A-type and highly-fractionated granites for the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous igneous rocks from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area (base map after Whalen et al., 1987) Data from Jiang et al.(2007, 2009), Li and Bao (2012) and this text. Magmatite symbols are consistent with Fig. 6 |
燕山期岩浆岩的εHf(t)值变化较大,其中,井儿洼的εHf(t)值为-14.3~6.4,而其他岩浆岩的εHf(t)值位于2.0~3.0Ga下地壳的演化线之间(图 8和图 9),结合(87Sr/86Sr)i值较分散(图 9b),可知该时期的岩浆来源于华北克拉通古老下地壳的部分熔融,侵位过程经历了不同程度的分离结晶及壳幔物质混染(Jiang et al., 2009; Zhang et al., 2014b)。侏罗纪至白垩纪期间华北克拉通发生大规模的破坏,约100多千米的岩石圈破坏减薄(吴福元等, 2008),导致大量岩浆活动(Yang et al., 2020; 翟明国, 2010; 赵越等, 2017)。目前华北克拉通岩石圈减薄开始的时间存在较大争议:具体表现为减薄事件开始于三叠纪或更早时期(Xu et al., 2009)、中侏罗世(Gao et al., 2004)、晚侏罗世(姜耀辉等, 2005)、早白垩世(吴福元等, 2008; Zhu et al., 2011)及晚白垩世(路凤香等, 2006)。Zhang et al. (2014b)研究表明,华北克拉通岩石圈减薄是穿时的,可能克拉通的东缘和北缘首先发生破坏。该时期,华北克拉通北缘受多重构造叠加,包括古亚洲洋闭合、蒙古-鄂霍次克洋闭合后伸展、古太平洋的西向俯冲及印度板块的北向俯冲等(翟明国和彭澎, 2007; Zhang et al., 2009c, 2012, 2014b),这些造山运动在华北克拉通岩石圈减薄作用中发挥了重要的作用。张宣地区晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆岩成岩年龄为165~120Ma,与辽东、胶东、苏北一带碱性岩和双峰式火山岩(孙金凤和杨进辉, 2009)年龄一致,均为华北克拉通破坏的产物。
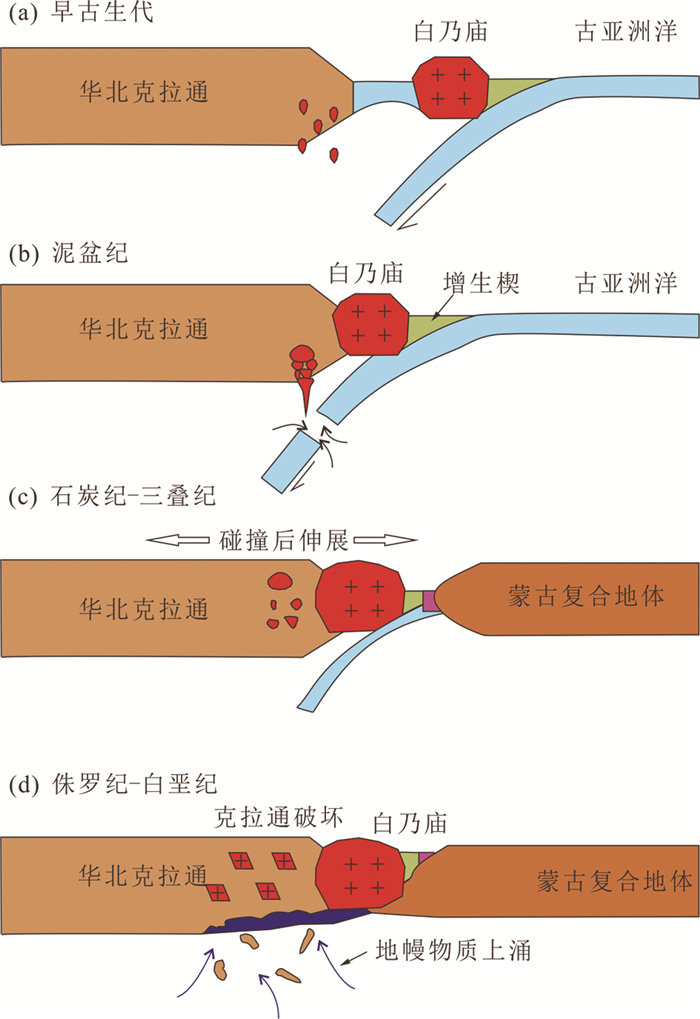
5.3 张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆-构造演化根据张宣地区岩浆岩时代、类型和范围等特点,结合区域构造演化过程,对区内古生代-中生代岩浆-构造演化过程进行总结。
早古生代开始,古亚洲洋板块向华北板块俯冲(Xiao et al., 2003; Windley et al., 2007),使华北克拉通岩石圈地幔脱水变质(Liu et al., 2010),形成白乃庙岛弧带(图 13a)。泥盆纪期间,岩浆岩在华北克拉通北缘大量出现,主要沿克拉通边缘的深大断裂带分布,包括张家口水泉沟碱性杂岩体(~400Ma)、承德大庙孤山二长闪长岩(~390Ma, Zhang et al., 2007)及赤峰红山公园钾长花岗岩(~387Ma, Shi et al., 2010)等。这些岩浆岩以高碱性为主,无或弱Eu负异常,低的初始87Sr/86Sr、负的εNd(t)和εHf(t)和老的Nd、Hf同位素模式年龄(Jiang, 2005; Zhang et al., 2007, 2010),与水泉沟碱性杂岩体地球化学特征一致,(Jiang et al., 2007; Zhang et al., 2007),形成于白乃庙岛弧带和华北克拉通北缘弧陆碰撞后的板片断离环境(图 13b, Zhang et al., 2010)。
|
图 13 张宣地区古生代-中生代岩浆-构造演化模式图 (a)早古生代,古亚洲洋板块向南俯冲到华北板块之下;(b)泥盆纪,与古亚洲洋俯冲有关的板片断离;(c)石炭纪-三叠纪,华北克拉通北缘处于碰撞后伸展环境;(d)侏罗纪-白垩纪,华北克拉通发生减薄 Fig. 13 Model of the Paleozoic-Mesozoic magmatic-tectonic evolution from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area (a) during Early Paleozoic, the Paleo-Asian ocean subducted southward beneath the NCC; (b) during Devonian, slab break off with the subduction of the Paleo-Asian ocean; (c) during Carboniferous-Triassic, the northern margin of the North China Craton was under a post-collision extensional setting; (d) during Jurassic-Cretaceous, lithosphere of the North China Craton was thinning |
古生代晚期到中生代早期,古亚洲洋与华北板块碰撞,在华北克拉通北缘形成大量东西向带状分布的岩浆岩(Zhang et al., 2007, 2009a, b )。如大石寨组双峰式火山岩(290~270Ma, 邵济安等, 2015)、冀东东湾子基性岩(308±4Ma, Zhao et al., 2007)和白云鄂博闪长岩-花岗岩(281±3Ma, 范宏瑞等, 2009)等。该时期岩浆岩SiO2含量变化大,以钙碱性-高钾钙碱性为主,部分表现为埃达克岩特征,与安第斯型大陆弧岩浆岩一致(Zhang et al., 2009a)。该时期岩浆岩在张宣地区不发育。
华北板块与蒙古微陆块的碰撞时间为300~250Ma,碰撞位置位于索伦科尔-林西缝合带(Xiao et al., 2003; Windley et al., 2007)。三叠纪时期华北克拉通北缘处于碰撞后伸展环境(图 13c),形成大量高碱、高钾性,具埃达克岩性质的岩浆岩,包括丰宁光岭山花岗岩(254±3Ma, Zhang et al., 2009c),辽西建平花岗岩(241±2Ma, Zhang et al., 2009c),张宣地区谷嘴子、红花梁和响水沟花岗岩等。该时期岩浆岩表现为高碱、高钾性,部分具有明显埃达克岩特征(Jiang et al., 2007)。Sr-Nd-Hf同位素组成变化大,εNd(t)和εHf(t)值较晚古生代到早中生代岩浆岩显著升高,表明幔源成分的增多。并且小张家口超基性岩体(200±5Ma, 田伟等, 2007)的出露也表明幔源岩浆的存在。热的幔源岩浆上升侵蚀下地壳,导致下地壳发生部分熔融,在经历MASH过程后(熔融、同化、储集和均一),上升到地表形成酸性岩体,而部分幔源熔体未经过MASH作用直接上升到地表形成基性-超基性岩。
侏罗纪-白垩纪,华北克拉通受多重构造叠加作用的影响发生减薄(图 13d),由克拉通边缘开始,逐渐向内部扩展(Zhang et al., 2009b),并在晚侏罗世出现大范围的高镁安山岩、英安岩和埃达克岩。侏罗纪早期岩浆活动在华北克拉通北缘出露少,主要发育于胶东半岛、辽东半岛和燕山褶皱带最东部(Yang et al., 2005),多为长英质岩石,仅在北京西山南大岭组有玄武岩的报道(李晓勇等, 2004)。晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆岩在张宣地区广泛分布,岩石类型和化学组成复杂,表明其形成过程中存在不同程度的分离结晶及上地壳混染(Yang et al., 2005; Zhu et al., 2012),指示华北克拉通破坏达到顶峰。
总结,张宣地区在古生代-中生代主要经历了古亚洲洋俯冲和克拉通破坏过程。早古生代,古亚洲洋南向俯冲到华北克拉通之下,形成白乃庙岛弧带和北缘地区少量的岩浆岩(辉绿岩中继承锆石);泥盆纪时期,张宣地区处于弧陆碰撞后的伸展环境,形成大量水泉沟正长岩类的碱性岩;二叠纪末期,古亚洲洋闭合,各微陆块相互碰撞,张宣地区处于陆陆碰撞后伸展环境,形成大量安第斯型大陆弧岩浆岩;三叠纪-白垩纪,华北克拉通破坏开始,破坏由边缘向内部逐步进行,在张宣地区形成大量高镁安山岩和埃达克岩,并形成面积巨大的张家口组火山岩。
5.4 张宣地区古生代-中生代成矿作用 5.4.1 矿床空间分布特征受古亚洲洋和古太平洋俯冲控制,华北克拉通北缘矿床在空间上具有明显成区、成带集中分布的特点,可划分为3条一级东西向成矿带与5条一级北东向成矿带。东西向成矿带自北向南依次为:围场-赤峰-阜新金银铜成矿带、崇礼-丰宁-凌源金银铜铅锌成矿带和昌平-兴隆-绥中金铜铅锌钼成矿带。北东向成矿带自北西向东依次为张家口-涿鹿金铅锌成矿带、围场-丰宁-来源金银铅锌钼成矿带、撰山子-承德-兴隆金银铜成矿带、金厂沟梁-凌源-迁西金铜铅锌成矿带和阜新-兴城-昌黎金银铜钼成矿带。各矿带之间呈等距性分布,在东西向矿带与北东向矿带的交汇部位,形成多金属矿化集中区(崔盛芹等, 2002)。
张宣地区位于崇礼-丰宁-凌源金银铜铅锌成矿带和张家口-涿鹿金铅锌成矿带的交汇部位,区内矿产资源丰富,形成大量金矿床(如东坪、小营盘、中山沟和张全庄等)、铅锌矿床(如蔡家营、三义庄和三道沟等)和银矿床(如彭家沟、孙家庄和金家庄等),少量铜矿床(象山铜矿)和钼矿床(张麻井和贾家营)。各矿种之间存在明显分区,金矿床明显集中产于宣化-崇礼-赤城三县(区)交界处,构成冀西北金矿集中区,而银铅锌多金属矿床则明显成群成带环绕金矿化集中区分布,形成兰闫-蔡家营-彭家沟-火石沟-相广巨大半环形银铅锌多金属矿成矿带(图 1)。矿床尺度中,金矿脉多成近东西分布,尤其是在近东西向断裂与近南北向、北东向、北西向断裂构造的交叉复合部位之中;银铅锌矿床产出部位多样,部分产于岩体内外接触带中,部分产于侏罗纪火山盆地之中,部分产于太古代变质岩地层之中,主要与燕山期岩浆活动有关。
5.4.2 矿床时间分布特征张宣地区作为华北克拉通北缘的一部分,两者在成矿时限上具有一致性,可以分为海西期成矿、印支期成矿和与燕山期成矿(江思宏等, 2018)。
海西期早期,古亚洲洋的俯冲作用引起岩石圈地幔的部分熔融,导致大面积碱性岩的侵位,并提供成矿物质及元素运移沉淀的能量。该时期形成大量与碱性岩有关的金矿床,包括张宣地区的中山沟和东坪等矿床(~380Ma; 王大钊等, 2020)、沿乌拉山-大青山南麓深大断裂分布的柳坝沟和哈达门沟金矿床(~380Ma; 侯万荣, 2011; Zhang et al., 2017)以及研究区北部的白乃庙金铜矿床(445Ma; Li et al., 2012)。
海西期晚期,古亚洲洋俯冲趋于结束,形成大量以钙碱性-高钾钙碱性为主的岩浆岩(Liu and Nie, 2015; Yang et al., 2016)。该时期金矿床与铜钼矿床共同产出,包括沿乌拉山-大青山-集宁深大断裂分布的十八顷壕、北腮忽洞、老羊壕、东伙房和后石花金矿床(282Ma; 王梁等, 2015)、毕力赫金矿床(261Ma; Yang et al., 2016)、赛因乌苏金矿床(253Ma; Hart et al., 2002)、准苏吉斑岩铜钼矿床(298.1Ma; 刘翼飞等, 2012)及好力宝斑岩铜钼矿床(265Ma; Zeng et al., 2013)等。该时期的岩浆岩在张宣地区不发育,相应矿床也尚未发现。
进入印支期,大量高碱高钾性岩浆岩侵位,在华北克拉通北缘形成大量250~220Ma的金矿床和钼矿床。金矿床包括金厂峪金矿床(223±5Ma; Song et al., 2016)、柏杖子金矿床、金厂沟梁金矿床(244~245Ma; 侯万荣, 2011)等。钼矿床如查干花钨钼矿床(243Ma; 蔡明海等, 2011b)、查干德尔斯钼铋矿床(243Ma; 蔡明海等, 2011a)、大苏计钼矿床(223Ma; 张彤等, 2009)和撒岱沟门钼矿床(237Ma; 张莉莉等, 2019)等。刘翼飞和江思宏(2017)研究发现,该时期在兴蒙造山带和华北板块北缘内各形成1条钼矿带,两者的岩浆源区均为岩石圈地幔,水化的岩石圈地幔的低程度批式脱水部分熔融形成富含成矿元素和挥发分的成矿岩浆,经历了多阶段结晶分异和同化混染,最终侵位成矿。古生代铜矿床和中生代钼矿床的成矿岩浆具有相似的特征,为大洋板块俯冲过程中古老岩石圈脱水熔融的产物(刘翼飞和江思宏, 2017)。该时期,张宣地区矿床发育少,但产出大量高碱高钾性岩浆岩,因此应存在成矿潜力。
燕山期华北克拉通北缘爆发大规模岩浆和成矿活动(毛景文等, 2003, 2005; 翟明国, 2010),以金矿床和钼矿床为多,如兰家沟钼矿床(182Ma; Han et al., 2009)、肖家营子钼矿床(166Ma; Dai et al., 2009)、鸡冠山钼矿床(155Ma; 曾庆栋等, 2009)、五龙金矿床(127Ma; Yu et al., 2020)、金厂沟梁金矿床(120Ma; 王建平等, 1992)、东坪金矿床(140Ma成矿叠加; Bao et al., 2014; Li et al., 2018; Fan et al., 2021)、蔡家营铅锌矿床及象山铜矿床(宋瑞先等, 2013)。
华北克拉通北缘地区,不同成矿期所形成的矿种存在差异,海西期早期主要为金成矿,晚期则出现大量铜钼矿床;印支期以钼成矿为主,存在少量金成矿;燕山期成矿爆发,主要为金、钼成矿和少量铅锌成矿。张宣地区存在海西期、印支期和燕山期的构造-岩浆活动及海西期和燕山期的成矿活动。虽然张宣地区印支期成矿尚未明确,但成矿潜力巨大。Zeng et al. (2021)研究华北克拉通北缘金成矿时间,发现自西向东,金矿床年龄存在逐渐减小的趋势。海西期早期金矿床主要分布在包头和张家口地区(哈达门沟和东坪金矿床),海西期晚期金矿床主要分布在包头地区,燕山早期金矿床主要分布在冀东地区,燕山晚期金矿床则分布广泛,张家口、冀东及辽宁地区均有产出,但包头地区并未发现该期金成矿事件。该趋势表明,古亚洲洋俯冲时期形成的金矿床受到古太平洋俯冲时期热液的叠加改造,而且东部叠加改造强烈,向西逐渐减弱。
5.4.3 张宣地区金成矿作用张宣地区金矿床(点)数量众多,包括东坪、黄土梁、中山沟、后沟、大白阳和小营盘等矿床。这些矿床主要分布在泥盆纪水泉沟碱性杂岩体和桑干群老变质岩中,其余地质体中无或很少存在金矿化(除金家庄金矿床产在小张家口基性-超基性岩中外)。区内金矿床沿尚义-崇礼-赤城深大断裂重新活动形成的NWW-SEE和NW-SE向次级断裂(包括上太子城-温泉断裂、西三间房-沃麻坑断裂和韩家沟-谷嘴子-场地断裂等,图 2)分布,如东坪和后沟金矿床受控于NWW-SEE向断裂,小营盘和大白阳金矿床则产在NW-SE向断裂附近,受褶皱控制。
5.4.3.1 金矿床地球化学特征张宣地区金矿床除在空间上具密切联系外,其还具有一些共同特点,如富含碲化物、硫化物的δ34S为负值(张全庄和金家庄除外)、矿床中硫化物含量少且黄铁矿中不含砷(Cook et al., 2009; Wang et al., 2020; 江思宏和聂凤军, 1998)。
张宣地区各金矿床H-O同位素分布见图 14a。各矿床H-O同位素重叠分布,δD集中在-1.7‰~8.9‰,δ18OH2O集中在-109.1‰~-50.5‰,位于岩浆水下方偏大气降水一侧。王时麟(1986)对桑干群浅粒岩中的石英进行H-O同位素测试,获得区内变质岩的δD和δ18OH2O范围为-111.3‰~-104.6‰和6.8‰~8.7‰。矿床中低的氢同位素可能是由于成矿流体与变质围岩发生水岩反应导致,而低的氧同位素归因于大气降水的加入。东坪和中山沟矿床的δ18OH2O较δD的分布范围广,表明其流体主要为岩浆水掺杂不同比例的大气降水;小营盘、大白阳和张全庄的δ18OH2O值较高且变化范围小,投点于岩浆水与桑干群变质岩之间,表明成矿流体与围岩发生强烈水岩反应,为岩浆水与变质水的混合流体,δD偏移较小,大气降水混合比例不高。
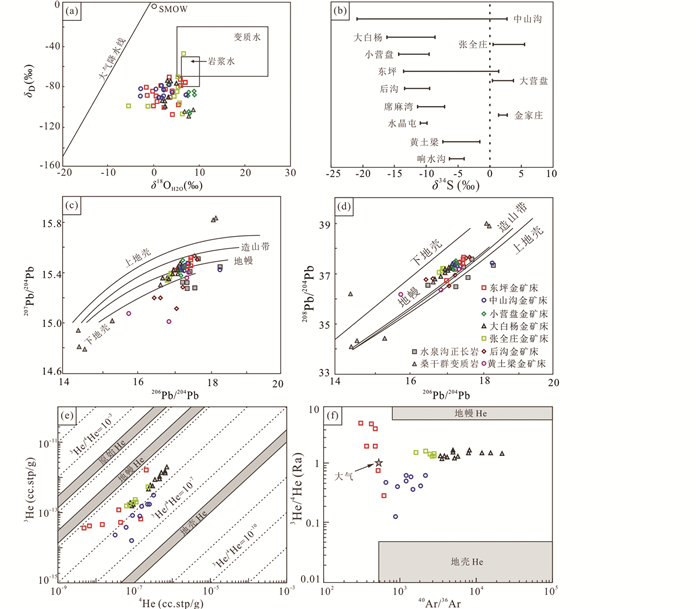
|
图 14 张宣地区金矿床H-O-S-Pb-He-Ar同位素组成(a, 底图据Taylor, 1974; c, d, 底图据Zartman and Doe, 1981;e, f, 底图据Mamyrin and Tolstikhin, 1984) 数据据Zhang and Mao (1995)、Nie (1998)、Fan et al. (2001)、Mao et al. (2003a)、Shen et al. (2020)、Zhen et al. (2020)、Wang et al. (2021)、王时麟(1986)、王郁等(1990)、李瑞(1992)、银剑钊和史红云(1995)、宋国瑞和赵振华(1996)、江思宏和聂凤军(1998)、刘海田(1999)、付方建(2007)、石来生等(2007)、吴姗姗(2009)、陈茜(2013)、陶利鑫等(2020)和甄世民等(2021) Fig. 14 H-O-S-Pb-He-Ar isotope compositions of gold deposits in the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area (a, after Taylor, 1974; c, d, after Zartman and Doe, 1981; e, f, after Mamyrin and Tolstikhin, 1984) Data sources: Wang (1986), Li (1992), Wang et al.(1990, 2021), Yin and Shi (1995), Zhang and Mao (1995), Song and Zhao (1996), Jiang and Nie (1998), Nie (1998), Liu (1999), Fan et al. (2001), Mao et al. (2003a), Fu (2007), Shi et al. (2007), Wu (2009), Chen (2013), Shen et al. (2020), Tao et al. (2020) and Zhen et al.(2020, 2021) |
张宣地区金矿床S同位素组成(图 14b)总体可分为三类:(1)以东坪和中山沟为代表,δ34S变化范围大;(2)以小营盘和大白阳等为代表,δ34S主要为负值,无正值出现;(3)以张全庄、大营盘和金家庄等为代表,δ34S为0附近的正值。硫化物的δ34S组成受控于硫的来源和流体的物理化学条件。张全庄、金家庄和大营盘的δ34S具有典型岩浆硫特征,而东坪、小营盘等矿床的负δ34S需要进行讨论。生物成因硫和变质岩中的硫都可能富集轻硫(Chaussidon and Lorand, 1990),导致硫化物的δ34S呈负值。张宣地区金矿床中的硫化物无生物成因的特征(如草莓状黄铁矿),水泉沟岩体的δ34S为1.9‰~3.5‰(Nie, 1998),桑干群变质杂岩的δ34S为-0.01‰~4.4‰(王郁等, 1990),因此东坪和小营盘等矿床中负的δ34S可以排除生物成因或岩浆硫与围岩硫混合形成。成矿流体的高氧逸度和沸腾作用会导致矿床中的硫发生分馏,形成负δ34S的硫化物和正δ34S的硫酸盐(Ohmoto, 1972; Scherbarth and Spry, 2006)。张宣地区金矿床发育大量赤铁矿、磁铁矿、金红石等氧化物和重晶石等硫酸盐(Bao et al., 2016; Wang et al., 2019a),表明成矿流体氧逸度高,且存在强烈硫同位素分馏,因此负δ34S应是由成矿流体的高氧逸度和硫的分馏形成,硫主要来源于岩浆硫。该现象在许多世界级浅成低温热液碲化物型金矿床中都有表现,如美国蒙大拿州的Golden Sunlight矿床(Spry et al., 1996)和斐济的Emperor矿床(Ahmad et al., 1987)等。东坪和中山沟部分样品具有正δ34S,可能是由于成矿流体物理化学条件变化或存在多期成矿导致(Bao et al., 2016; Li et al., 2018)。
张宣地区金矿床硫化物Pb同位素分布见图 14c, d。东坪206Pb/204Pb为17.088~18.200,中山沟206Pb/204Pb为17.096~18.321,比值相对较高,在206Pb/204Pb-207Pb/204Pb和206Pb/204Pb-208Pb/204Pb图解上,落在造山带和上地幔铅同位素演化线之间,表明铅主要来源于为岩浆岩;大白阳206Pb/204Pb为16.923~17.370,小营盘206Pb/204Pb为16.313~17.501,张全庄206Pb/204Pb为16.874~17.263,比值相对较低,主要落在上地幔和下地壳铅同位素演化线之间,表明为岩浆岩和桑干群变质岩的混合铅(银剑钊和史红云, 1995);后沟(206Pb/204Pb=16.524~17.721)和黄土梁(206Pb/204Pb=15.810~17.460)铅同位素变化范围很大,部分接近桑干群变质岩的铅同位素组成,表明铅来源复杂,且混合不均匀。
张宣地区金矿床He-Ar同位素分布见图 14e, f。各矿床3He/4He比值在0.13~5.2Ra之间,高于地壳(0.01~0.05Ra;Stuart et al., 1995)且小于地幔(6~7Ra;Burnard et al., 1999),表明成矿流体由壳源和幔源流体混合形成,不同矿床的混合比例存在差异(如东坪幔源比例高,而中山沟壳源比例高)。矿床40Ar/36Ar比值存在明显差异,东坪和中山沟40Ar/36Ar比值为309~2200,靠近大气Ar(296;Mark et al., 2011);大白阳和张全庄40Ar/36Ar比值高,为3489~21824,放射性40Ar*(40Ar*=(40Ar)样品-296×(36Ar)样品;Mark et al., 2011)占总Ar的比值达82%~98%,表明大部分的40Ar来源于富钾的变质围岩。
根据地质特征和同位素组成,可将张宣地区金矿床分为三类,分别为(1)“东坪式”,富碲化物,产于水泉沟杂岩体中,具有负δ34S和较低的40Ar/36Ar比值,成矿流体和成矿物质主要来源于岩浆岩,包括东坪、中山沟、黄土梁等矿床;(2)“小营盘式”,富碲化物,产于桑干群变质岩,具有负δ34S和较高的40Ar/36Ar比值,成矿流体和成矿物质主要为岩浆岩和变质岩的混合来源,包括小营盘、大白阳、水晶屯等矿床;(3)“张全庄式”,无碲化物,具有正δ34S,成矿流体和成矿物质主要为岩浆岩和变质岩的混合来源,包括张全庄、大营盘和金家庄等矿床。“东坪式”和“小营盘式”金矿床可能为同一成矿流体经历不同迁移沉淀过程形成,而“张全庄型”金矿床为不同成矿流体沉淀形成。
5.4.3.2 金成矿年龄前人对张宣地区金矿床成矿年龄进行了大量研究(图 15),如Hart et al. (2002)对东坪、中山沟和小营盘金矿床中的白云母和钾长石进行Ar-Ar测年,分别获得~153Ma、~241Ma和~354Ma的成矿年龄;宋国瑞和赵振华(1996)和卢德林等(1993)测得东坪含金石英脉中钾长石Ar-Ar年龄为177~157Ma;李长民等(2010a, b )测试东坪钾长石石英脉和钾质蚀变岩样品中的热液锆石,获得~140Ma的成矿年龄;Bao et al. (2014)和Li et al. (2018)在东坪含金石英脉中获得~380Ma和~140Ma的热液锆石,认为矿床形成于水泉沟碱性杂岩体的岩浆期后热液,并受到侏罗-白垩纪的热液叠加改造;Wang et al. (2019b)测试东坪辉钼矿Re-Os年龄为~400Ma和~380Ma,认为成矿与水泉沟杂岩体的岩浆活动关系密切;Fan et al. (2021)研究东坪热液石榴子石U-Pb年龄,获得142±5Ma到139±6Ma的年龄,认为金成矿与侏罗纪氧化性侵入岩有关。
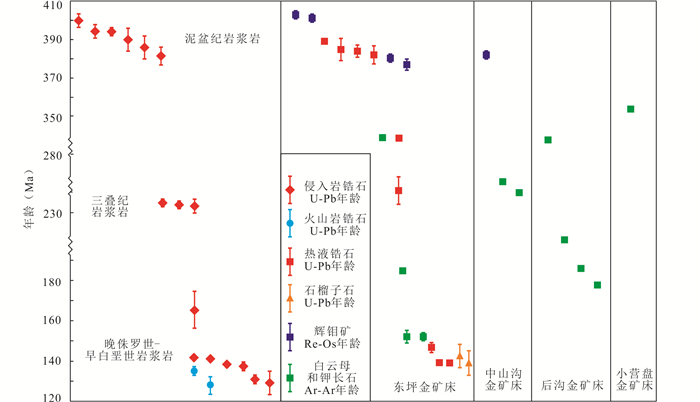
|
图 15 张宣地区成岩成矿年龄分布图 成岩年龄数据据Miao et al. (2002)、Jiang et al.(2007, 2009)、Cisse et al. (2017)、杨进辉等(2006)、李创举和包志伟(2012)、陈茜(2013)、李长民等(2014)及本文;成矿年龄数据据Hart et al. (2002)、Bao et al. (2014)、Li et al. (2018)、Wang et al. (2019b)、Fan et al. (2021)、王正坤等(1992)、江思宏和聂凤军(2000)、罗镇宽等(2000)和王大钊等(2020) Fig. 15 Distribution diagram of diagenetic and metallogenic ages from the Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area Diagenetic age data from Miao et al. (2002), Yang et al. (2006), Jiang et al.(2007, 2009), Li and Bao (2012), Chen (2013), Li et al. (2014), Cisse et al. (2017) and this text; Metallogenic age data from Wang et al.(1992, 2019b, 2020), Jiang and Nie (2000), Luo et al. (2000), Hart et al. (2002), Bao et al. (2014), Li et al. (2018) and Fan et al. (2021) |
张宣地区金成矿年龄复杂,表明其可能经历了多期次成矿及成矿叠加过程。通过统计区内金矿床成矿年龄(图 15),发现金矿化主要集中在400~380Ma的海西期和160~140Ma的燕山期,这两期年龄与区内泥盆纪和晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆活动对应很好,表明金成矿与两期岩浆活动存在密切成因联系。其他时期金矿床年龄较分散,表明成矿后存在强烈的后期扰动,使矿床重新活化叠加,与三叠纪岩浆岩相关。虽然区内尚未发现与三叠纪花岗岩有直接关系的金矿床,但产于三叠纪小张家口基性-超基性岩中的金家庄矿床应是该期岩浆活动的产物,这可能是“张全庄式”金矿床与“东坪式”、“小营盘式”金矿床在矿物组成和硫同位素上存在明显区别的原因。多期次成矿及成矿叠加是形成张宣地区大量金矿床的重要因素。
6 结论(1) 张家口-宣化地区古生代-中生代岩浆岩主要侵位于泥盆纪(峰值398Ma和373Ma)、三叠纪(峰值234Ma)和晚侏罗世-早白垩世(峰值143Ma和130Ma)。泥盆纪岩浆岩主要为碱性岩,来源于富集地幔,并在演化过程中经历了地壳的同化混染和分离结晶的共同作用;三叠纪基性岩与酸性岩共存,酸性岩具有埃达克岩特征,来源于地幔岩浆上涌引起的加厚下地壳的部分熔融,由镁铁质岩浆和长英质岩浆混合形成;晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆岩具有不同的地球化学特征,来源于幔源岩浆上涌导致克拉通岩石圈地幔的减薄熔融,岩浆侵位过程经历了不同程度的分离结晶及壳幔物质混染。
(2) 张家口-宣化地区在古生代-中生代经历了古亚洲洋俯冲、克拉通破坏及古太平洋俯冲过程。早古生代,古亚洲洋向华北克拉通俯冲,泥盆纪时期,张宣地区处于伸展环境,二叠纪末期-三叠纪,各微陆块相互碰撞,构造环境为碰撞后伸展阶段,侏罗纪时期,华北克拉通发生减薄,晚三叠世-早白垩世达到顶峰,张宣地区广泛发育岩浆活动,形成大范围的侵入岩和火山岩。
(3) 张宣地区产出大量金矿床、铅锌矿床、银矿床及少量铜矿床和钼矿床,金矿床集中产于宣化-崇礼-赤城交界处,而银铅锌多金属矿床则成群成带环绕金矿化集中区分布。成矿时间主要为海西期和燕山期,印支期成矿尚未明确,但成矿潜力巨大。
(4) 张宣地区金矿床根据地质特征和同位素组成可分为“东坪型”、“小营盘型”和“张全庄型”三类。古生代-中生代各时期岩浆活动均对金成矿有贡献,大部分金矿床与泥盆纪和晚侏罗世-早白垩世岩浆活动联系密切,多期次成矿及成矿叠加是形成张宣地区大量金矿床的重要因素。
Ahmad M, Solomon M and Walshe JL. 1987. Mineralogical and geochemical studies of the Emperor gold telluride deposit, Fiji. Economic Geology, 82(2): 345370
|
Bao ZW, Zhao ZH, Zhang PH and Wang YX. 2003. REE, Sr, Nd, and Pb isotopic evidence for the petrogenesis of the Shuiquangou syenite complex in NW Hebei Province, China. Geological Review, 49(6): 596-604 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Bao ZW, Sun WD, Li CJ and Zhao ZH. 2014. U-Pb dating of hydrothermal zircon from the Dongping gold deposit in North China: Constraints on the mineralization processes. Ore Geology Reviews, 61: 107-119 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.02.006
|
Bao ZW, Li CJ and Zhao ZH. 2016. Metallogeny of the syenite-related Dongping gold deposit in the northern part of the North China Craton: A review and synthesis. Ore Geology Reviews, 73: 198-210 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.04.002
|
Burnard PG, Hu R, Turner G and Bi XW. 1999. Mantle, crustal and atmospheric noble gases in ailaoshan gold deposits, Yunnan Province, China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(10): 1595-1604 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00108-8
|
Cai MH, Peng ZA, Qu WJ, He ZY, Feng G, Zhang SQ, Xu M and Chen Y. 2011a. Geological characteristics and Re-Os dating of molybdenites in Chagandeersi molybdenum deposit, western Inner Mongolia. Mineral Deposits, 30(3): 377-384 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Cai MH, Zhang ZG, Qu WJ, Peng ZA, Zhang SQ, Xu M, Chen Y and Wang XB. 2011b. Geological characteristics and Re-Os dating of the Chaganhua molybdenum deposit in Urad Rear Banner, western Inner Mongolia. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 32(1): 64-68 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Castillo PR, Janney PE and Solidum RU. 1999. Petrology and geochemistry of Camiguin Island, southern Philippines: Insights to the source of adakites and other lavas in a complex arc setting. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 134(1): 3351 DOI:10.1007/s004100050467
|
Chappell BW and White AJR. 1992. I- and S-type granites in the Lachlan Fold Belt. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of The Royal Society of Edinburgh, 83(1-2): 1-26 DOI:10.1017/S0263593300007720
|
Chaussidon M and Lorand JP. 1990. Sulphur isotope composition of orogenic spinel lherzolite massifs from Ariege (North-Eastern Pyrenees, France): An ion microprobe study. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 54(10): 2835-2846 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(90)90018-G
|
Chen B, Tian W and Liu AK. 2008. Petrogenesis of the Xiaozhangjiakou mafic-ultramafic complex, North Hebei: Constraints from petrological, geochemical and Nd-Sr isotopic data. Geological Journal of Chinese Universities, 14(3): 295-303 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Chen Q. 2013. Studies on fluid characteristics and mineralization mechanism of the Dabaiyang gold deposit, northwest of Hebei. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Cisse M, Lü XB, Algeo TJ, Cao XF, Li H, Wei M, Yuan Q and Chen M. 2017. Geochronology and geochemical characteristics of the Dongping ore-bearing granite, North China: Sources and implications for its tectonic setting. Ore Geology Reviews, 89: 1091-1106 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.07.006
|
Cook NJ, Ciobanu CL and Mao JW. 2009. Textural control on gold distribution in As-free pyrite from the Dongping, Huangtuliang and Hougou gold deposits, North China Craton (Hebei Province, China). Chemical Geology, 264(1-4): 101121
|
Dai JZ, Mao JW, Zhao CS, Xie GQ, Yang FQ and Wang YT. 2009. New U-Pb and Re-Os age data and the geodynamic setting of the Xiaojiayingzi Mo (Fe) deposit, western Liaoning Province, Northeastern China. Ore Geology Reviews, 35(2): 235-244 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2008.10.001
|
Decrée S, Demaiffe D, Tack L, Nimpagaritse G, De Paepe P, Boulvais P and Debaille V. 2019. The Neoproterozoic Upper Ruvubu alkaline plutonic complex (Burundi) revisited: Large-scale syntectonic emplacement, magmatic differentiation and late-stage circulations of fluids. Precambrian Research, 325: 150-171 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2019.02.023
|
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1990. Derivation of some modern arc magmas by melting of young subducted lithosphere. Nature, 347(6294): 662-665 DOI:10.1038/347662a0
|
Defant MJ and Drummond MS. 1993. Mount St. Helens: Potential example of the partial melting of the subducted lithosphere in a volcanic arc. Geology, 21(6): 547-550
|
Deng J and Wang QF. 2016. Gold mineralization in China: Metallogenic provinces, deposit types and tectonic framework. Gondwana Research, 36: 219-274 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2015.10.003
|
DePaolo DJ. 1981. Trace element and isotopic effects of combined wallrock assimilation and fractional crystallization. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 53(2): 189-202 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(81)90153-9
|
Eby GN. 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids: Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Geology, 20(7): 641-644 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2
|
Fan GH, Li JW, Deng XD, Gao WS and Li SY. 2021. Age and origin of the Dongping Au-Te deposit in the North China Craton revisited: Evidence from paragenesis, geochemistry, and in situ U-Pb geochronology of garnet. Economic Geology, 116(4): 963-985 DOI:10.5382/econgeo.4810
|
Fan HR, Xie YH and Zhai MG. 2001. Ore-forming fluids in the Dongping gold deposit, northwestern Hebei Province. Science in China (Series D), 44(8): 748-757 DOI:10.1007/BF02907204
|
Fan HR, Hu FF, Yang KF, Wang KY and Liu YS. 2009. Geochronology framework of Late Paleozoic dioritic-granitic plutons in the Bayan Obo area, Inner Mongolia, and tectonic significance. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(11): 2933-2938 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Fu FJ. 2007. The study of mineralization in Huangtuliang gold deposit, Northwest Hebei. Master Degree Thesis. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Fu LB, Wei JH, Kusky TM, Chen HY, Tan J, Li YJ, Shi WJ, Chen C and Zhao SQ. 2012. The Cretaceous Duimiangou adakite-like intrusion from the Chifeng region, northern North China Craton: Crustal contamination of basaltic magma in an intracontinental extensional environment. Lithos, 134-135: 273-288 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.01.007
|
Gao S, Luo TC, Zhang BR, Zhang HF, Han YW, Zhao ZD and Hu YK. 1998. Chemical composition of the continental crust as revealed by studies in East China. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 62(11): 1959-1975 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(98)00121-5
|
Gao S, Rudnick RL, Yuan HL, Liu XM, Liu YS, Xu WL, Ling WL, Ayers J, Wang XC and Wang QH. 2004. Recycling lower continental crust in the North China craton. Nature, 432(7019): 892-897 DOI:10.1038/nature03162
|
Gao YF, Santosh M, Hou ZQ, Wei RH, Ma GX, Chen ZK and Wu JL. 2012. High Sr/Y magmas generated through crystal fractionation: Evidence from Mesozoic volcanic rocks in the northern Taihang orogen, North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 22(1): 152168
|
Han CM, Xiao WJ, Zhao GC, Sun M, Qu WJ and Du AD. 2009. A Re-Os study of molybdenites from the Lanjiagou Mo deposit of North China Craton and its geological significance. Gondwana Research, 16(2): 264-271 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2009.01.001
|
Hart CJ, Goldfarb RJ, Qiu YM, Snee L, Miller LD and Miller ML. 2002. Gold deposits of the northern margin of the North China Craton: Multiple Late Paleozoic-Mesozoic mineralizing events. Mineralium Deposita, 37(3): 326-351 DOI:10.1007/s00126-001-0239-2
|
Hou WR. 2011. Constrast study on the Hadamengou gold deposit and Jinchanggouliang gold deposit, Inner Mongolia. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Huang F, Li SG, Dong F, He YS and Chen FK. 2008. High-Mg adakitic rocks in the Dabie orogen, central China: Implications for foundering mechanism of lower continental crust. Chemical Geology, 255(1-2): 1-13 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.02.014
|
Huang WL and Wyllie PJ. 1981. Phase relationships of S-type granite with H2O to 35kbar: Muscovite granite from Harney Peak, South Dakota. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 86(B11): 10515-10529 DOI:10.1029/JB086iB11p10515
|
Jian P, Liu DY, Kröner A, Windley BF, Shi YR, Zhang W, Zhang FQ, Miao LC, Zhang LQ and Tomurhuu D. 2010. Evolution of a Permian intraoceanic arc-trench system in the Solonker suture zone, Central Asian Orogenic Belt, China and Mongolia. Lithos, 118(1-2): 169-190 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.04.014
|
Jiang N. 2005. Petrology and geochemistry of the Shuiquangou syenitic complex, northern margin of the North China Craton. Journal of the Geological Society, 162(1): 203-215 DOI:10.1144/0016-764903-144
|
Jiang N. 2006. Hydrothermal alteration of chevkinite-(Ce) in the Shuiquangou syenitic intrusion, northern China. Chemical Geology, 227(1-2): 100-112 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.09.004
|
Jiang N, Liu YS, Zhou WG, Yang JH and Zhang SQ. 2007. Derivation of Mesozoic adakitic magmas from ancient lower crust in the North China craton. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 71(10): 2591-2608 DOI:10.1016/j.gca.2007.02.018
|
Jiang N, Zhang SQ, Zhou WG and Liu YS. 2009. Origin of a Mesozoic granite with A-type characteristics from the North China craton: Highly fractionated from I-type magmas?. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 158(1): 113-130 DOI:10.1007/s00410-008-0373-2
|
Jiang SH and Nie FJ. 1998. A comparison study on geological and geochemical features and ore genesis of the Xiaoyingpan and Dongping gold deposits, Hebei. Gold Geology, 4(4): 12-24 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Jiang SH and Nie FJ. 2000. 40Ar/39Ar geochronology of the Shuiquangou alkaline complex and related gold deposits, northwestern Hebei, China. Geological Review, 46(6): 621-627 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Jiang SH, Zhang LL, Liu YF, Liu CH, Kang H and Wang FX. 2018. Metallogeny of Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt and some related problems. Mineral Deposits, 37(4): 671-711 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Jiang YH, Jiang SY, Zhao KD, Ni P, Ling HF and Liu DY. 2005. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating for lamprophyre from Liaodong Peninsula: Constraints on the initial time of Mesozoic lithosphere thinning beneath eastern China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 50(22): 2612-2620 DOI:10.1360/982005-373
|
Li CJ and Bao ZW. 2012. Geochemical characteristics and geodynamic implications of the Early Cretaceous magmatisms in Zhangjiakou region, northwest Hebei Province, China. Geochimica, 41(4): 343-358 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li CM, Deng JF, Chen LH, Su SG, Li HM, Hu SL and Liu XM. 2010a. Two periods of zircon from Dongping gold deposit in Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area, northern margin of North China: Constraints on metallogenic chronology. Mineral Deposits, 29(2): 265-275
|
Li CM, Deng JF, Su SG, Li HM and Liu XM. 2010b. Two stage zircon U-Pb ages of the potash altered rock in the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province, and their geological implications. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 31(6): 843-852 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li CM, Deng JF., Su SG, Liu C and Liu XM. 2014. Zircon U-Pb chronology and Hf isotope in the western part of the Shuiquangou alkaline complex, northern Hebei Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(11): 3301-3314 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li H, Li JW, Algeo TJ, Wu JH and Cisse M. 2018. Zircon indicators of fluid sources and ore genesis in a multi-stage hydrothermal system: The Dongping Au deposit in North China. Lithos, 314-315: 463478
|
Li R. 1992. Geological-geochemical features and metallogenic pattern of the Hougou gold deposit. Geology and Exploration, (3): 46-50 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li SZ and Jin GC. 2000. Geological characteristics and structural ore-controlling role of the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 21(1): 44-51 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li WB, Zhong RC, Xu C, Song B and Qu WJ. 2012. U-Pb and Re-Os geochronology of the Bainaimiao Cu-Mo-Au deposit, on the northern margin of the North China Craton, Central Asia Orogenic Belt: Implications for ore genesis and geodynamic setting. Ore Geology Reviews, 48: 139-150 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.03.001
|
Li XY, Fan WM, Guo F, Wang YJ and Li CW. 2004. Modification of the lithospheric mantle beneath the northern North China Block by the Paleo-Asian Ocean: Geochemical evidence from mafic volcanic rocks of the Nandaling Formation in the Xishan area, Beijing. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 20(3): 557-566 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Li YL, Zhou HW, Brouwer FM, Xiao WJ, Wijbrans JR and Zhong ZQ. 2014. Early Paleozoic to Middle Triassic bivergent accretion in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt: Insights from zircon U-Pb dating of ductile shear zones in central Inner Mongolia, China. Lithos, 205: 84-111 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.06.017
|
Liu CH and Nie FJ. 2015. Permian magmatic sequences of the Bilihe gold deposit in central Inner Mongolia, China: Petrogenesis and tectonic significance. Lithos, 231: 3552
|
Liu DY, Geng YS and Song B. 1997. Late Archean crustal accetion and reworking in northwestern Hebei Province: Isochronology evidence. Acta Geoscientia Sinica, 18(3): 226-232 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu HT. 1999. Analysis of ore controlling factors of Huangtuliang gold deposit, Northwest Hebei Province. Journal of Precious Metallic Geology, 8(4): 209-216 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu Q, Zhao GC, Sun M, Han YG, Eizenhofer PR, Hou WZ, Zhang XR, Zhu YL, Wang B, Liu DX and Xu B. 2016. Early Paleozoic subduction processes of the Paleo-Asian Ocean: Insights from geochronology and geochemistry of Paleozoic plutons in the Alxa Terrane. Lithos, 262: 546-560 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2016.07.041
|
Liu Y, Liu HC and Li XH. 1996. Simultaneous and precise determination of 40 trace elements in rock samples using ICP-MS. Geochimica, 25(6): 552-558 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu YF, Nie FJ, Jiang SH, Hou WR, Liang QL, Zhang K and Liu Y. 2012. Geochronology of Zhunsujihua molybdenum deposit in Sonid Left Banner, Inner Mongolia, and its geological significance. Mineral Deposits, 31(1): 119-128 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu YF and Jiang SH. 2017. Mo mineralization in Xing'an-Mongolian orogen and north margin of Chinacraton: Review, question and a preliminary genetic model. Mineral Deposits, 36(3): 557-594 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Gao S, Günther D, Xu J, Gao CG and Chen HH. 2008. In situ analysis of major and trace elements of anhydrous minerals by LA-ICP-MS without applying an internal standard. Chemical Geology, 257(1-2): 34-43 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.08.004
|
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen: U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egp082
|
Lu DL, Luo XQ, Wang JJ, Zhang SH and Zheng BY. 1993. The metallogenic epoch of the Dongping gold deposit. Mineral Deposits, 12(2): 182-188 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Lu FX, Zheng JP, Shao JA, Zhang RS, Chen MH and Yu CM. 2006. Asthenospheric upwelling and lithospheric thinning in late Cretaceous-Cenozoic in eastern North China. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(2): 86-92 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center
|
Luo ZK, Miao LC and Guan K. 2000. Discussion on the metallogenetic epoch of gold deposit on north fringe of North China platform. Gold Geology, 6(2): 70-76 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Ma Q, Zheng JP, Xu YG, Griffin WL and Zhang RS. 2015. Are continental "adakites" derived from thickened or foundered lower crust?. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 419: 125-133 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2015.02.036
|
Ma YS, Cui SQ, Zhao Y, Zeng QL and Wu ML. 2002. The transformation process of Mesozoic-cenozoic tectonic regime in the north of North China. Journal of Geomechanics, 8(1): 15-25 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Mao JW, Li YQ, Goldfarb R, He Y and Zaw K. 2003. Fluid inclusion and noble gas studies of the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province, China: A mantle connection for mineralization?. Economic Geology, 98(3): 517-534
|
Mao JW, Wang YT, Zhang ZH, Yu JJ and Niu BG. 2003. Geodynamic settings of Mesozoic large-scale mineralization in North China and adjacent areas: Implication from the highly precise and accurate ages of metal deposits. Science in China (Series D), 46(8): 838-851
|
Mao JW, Xie GQ, Zhang ZH, Li XF, Wang YT, Zhang CQ and Li YF. 2005. Mesozoic large-scale metallogenic pulses in North China and corresponding geodynamic setting. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(1): 169-188 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Mark DF, Stuart FM and de Podesta M. 2011. New high-precision measurements of the isotopic composition of atmospheric argon. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(23): 74947501
|
Martin H, Smithies RH, Rapp R, Moyen JF and Champion D. 2005. An overview of adakite, tonalite-trondhjemite-granodiorite (TTG), and sanukitoid: Relationships and some implications for crustal evolution. Lithos, 79(1-2): 1-24 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2004.04.048
|
Miao LC, Qiu YM, McNaughton N, Luo ZK, Groves D, Zhai YS, Fan WM, Zhai MG and Guan K. 2002. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon geochronology of granitoids from Dongping area, Hebei Province, China: Constraints on tectonic evolution and geodynamic setting for gold metallogeny. Ore Geology Reviews, 19(3-4): 187-204 DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(01)00041-5
|
Moyen JF. 2009. High Sr/Y and La/Yb ratios: The meaning of the "adakitic signature". Lithos, 112(3-4): 556-574 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.04.001
|
Nie FJ. 1998. Geology and origin of the Dongping alkalic-type gold deposit, Northern Hebei province, People's Republic of China. Resource Geology, 48(3): 139-158 DOI:10.1111/j.1751-3928.1998.tb00013.x
|
Ohmoto H. 1972. Systematics of sulfur and carbon isotopes in hydrothermal ore deposits. Economic Geology, 67(5): 551-578 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.67.5.551
|
Riishuus MS, Peate DW, Tegner C, Wilson JR, Brooks CK and Waight TE. 2005. Petrogenesis of syenites at a rifted continental margin: Origin, contamination and interaction of alkaline mafic and felsic magmas in the Astrophyllite Bay Complex, East Greenland. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 149(3): 350-371 DOI:10.1007/s00410-005-0655-x
|
Scherbarth NL and Spry PG. 2006. Mineralogical, petrological, stable isotope, and fluid inclusion characteristics of the Tuvatu gold-silver telluride deposit, Fiji: Comparisons with the emperor deposit. Economic Geology, 101(1): 135-158 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.101.1.135
|
Shangguan S, Peate IU, Tian W and Xu Y. 2016. Re-evaluating the geochronology of the Permian Tarim magmatic province: Implications for temporal evolution of magmatism. Journal of the Geological Society, 173(1): 228-239 DOI:10.1144/jgs2014-114
|
Shao JA, He GQ and Tang KD. 2015. The evolution of Permian continental crust in northern part of North China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(1): 47-55 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Shen JF, Santosh M, Li SR., Li CP, Zhang JQ, Zhang SQ, Alam M, Wang YH and Xu KX. 2020. He-Ar, S, Pb and O isotope geochemistry of the Dabaiyang gold deposit: Implications for the relationship between gold metallogeny and destruction of the North China Craton. Ore Geology Reviews, 116: 103229 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2019.103229
|
Shi LS, Rao YX, Song RX and Wen JH. 2007. Geological characteristics of isotopes and inclusions in gold accumulated area of Zhangjiakou, Hebei Province. Mineral Resources and Geology, 21(3): 219-227 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Shi YR, Liu DY, Miao LC, Zhang FQ, Jian P, Zhang W, Hou KJ and Xu JY. 2010. Devonian A-type granitic magmatism on the northern margin of the North China Craton: SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating and Hf-isotopes of the Hongshan granite at Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, China. Gondwana Research, 17(4): 632641
|
Song GR and Zhao ZH. 1996. Geology of Dongping Alkaline Complex-Hosted Gold Deposit in Hebei Province. Beijing: Seismological Press (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Song RX, Wei MH and Wang JS, et al. 2013. Geology and Ores in the Zhangjiakou District. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Song Y, Jiang SH, Bagas L, Li C, Hu JZ, Zhang Q, Zhou W and Ding HY. 2016. The geology and geochemistry of Jinchangyu gold deposit, North China Craton: Implications for metallogenesis and geodynamic setting. Ore Geology Reviews, 73: 313-329 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.10.031
|
Spry PG, Paredes MM, Foster F, Truckle JS and Chadwick TH. 1996. Evidence for a genetic link between gold-silver telluride and porphyry molybdenum mineralization at the Golden Sunlight deposit, Whitehall, Montana: Fluid inclusion and stable isotope studies. Economic Geology, 91(3): 507-526 DOI:10.2113/gsecongeo.91.3.507
|
Stern RA and Hanson GN. 1991. Archean high-Mg granodiorite: A derivative of light rare earth element enriched monzodiorite of mantle origin. Journal of Petrology, 32(1): 201238
|
Stuart FM, Burnard PG, Taylor RP and Turner G. 1995. Resolving mantle and crustal contributions to ancient hydrothermal fluids: He-Ar isotopes in fluid inclusions from Dae Hwa W-Mo mineralisation, South Korea. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 59(22): 46634673
|
Sun JF and Yang JH. 2009. Early Cretaceous A-type granites in the Eastern North China Block with relation to destruction of the craton. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 34(1): 137-147 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.3799/dqkx.2009.013
|
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345 DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1989.042.01.19
|
Sutcliffe RH, Smith AR, Doherty W and Barnett RL. 1990. Mantle derivation of Archean Amphibole-bearing granitoid and associated mafic rocks: Evidence from the Southern Superior Province, Canada. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 105(3): 255-274 DOI:10.1007/BF00306538
|
Tao LX, Zhen SM, Bai HJ, Wang J, Wang DZ and Zha ZJ. 2020. Pyrite trace element composition and S-Pb isotope characters of the Dabaiyang gold deposit, Hebei Province. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition), 50(5): 1582-1598 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Tian W, Chen B, Liu CQ and Zhang HF. 2007. Zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic composition of the Xiaozhangjiakou ultramafic pluton in northern Hebei. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(3): 583-590 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Vernon RH. 2004. A Practical Guide to Rock Microstructure. New York: Cambridge University Press
|
Wang DZ, Liu JJ, Zhai DG, Carranza EJM, Wang YH, Zhen SM, Wang J, Wang JP, Liu ZJ and Zhang FF. 2019a. Mineral paragenesis and ore-forming processes of the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province, China. Resource Geology, 69(3): 287-313 DOI:10.1111/rge.12202
|
Wang DZ, Liu JJ, Zhai DG, Zhen SM, Wang J and Yang XA. 2019b. New discovery of molybdenite in the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei province, China and its Re-Os geochronological implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 93(3): 769-770 DOI:10.1111/1755-6724.13841
|
Wang DZ, Liu JJ, Zhai DG, de Fourestier J, Wang YH, Zhen SM, Wang JP, Liu ZJ and Zhang FF. 2020. Textures and formation of microporous gold in the Dongping gold deposit, Hebei Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 120: 103437 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103437
|
Wang DZ, Liu JJ, Zhai DG, Zhen SM and Wang J. 2020. Study on molybdenite Re-Os and zircon U-Pb ages of the Dongping tellurium-gold deposit in Hebei Province. Earth Science Frontiers, 27(2): 405-419 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang DZ, Zhen SM, Liu JJ, Carranza EJM, Wang J, Zha ZJ, Li YS and Bai HJ. 2021. Mineral paragenesis and hydrothermal evolution of the Dabaiyang tellurium-gold deposit, Hebei Province, China: Constraints from fluid inclusions, H-O-He-Ar isotopes, and physicochemical conditions. Ore Geology Reviews, 130: 103904 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103904
|
Wang JP, Liu YS, Dong XF, Li ZJ, Peng H, Wang LJ, Ding YC, Yang YD, Meng XG, Jia HJ, Liu ZB, Liu JM and Wang HC. 1992. Study on Ore-Controlling Tectonics of Jinchanggouliang Gold Deposit, Inner Mongolia. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang L, Wang GH, Lei SB, Chang CJ, Hou WR, Jia LQ, Zhao GM and Chen HJ. 2015. Re-Os dating of molybdenites from the Houshihua gold deposit in Wuchuan County, Inner Mongolia and its geological significance. Geology and Exploration, 51(3): 422-431 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang SL. 1986. Study of the genesis of Zhangjiakou gold deposit. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium, Universitatis Pekinensis, (4): 81-89 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang Y, Jiang XM and Wang ZK. 1990. Characteristics of lead and sulfur isorope of the gold deposits in Zhangjiakou Xuanhua area Hebei Province. Contributions to Geology and Mineral Resources Research, 5(2): 66-75 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wang ZK, Jiang XM, Wang Y and Shang MY. 1992. A comparative analysis on geological-geochemical features of the Xiaoyingpan and Dongping gold deposits, Hebei. Geology and Exploration, (7): 14-20 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wei ZL, Zhang H, Liu XM and Zhang YQ. 2008. LA-ICP-MS dating and geological meaning of the Zhangjiakou Formation volcanic rocks, Zhangjiakou area. Progress in Natural Science, 18(5): 523-530 (in Chinese) DOI:10.1016/j.pnsc.2007.12.005
|
Whalen JB, Currie KL and Chappell BW. 1987. A-type granites: Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419 DOI:10.1007/BF00402202
|
Windley BF, Alexeiev D, Xiao WJ, Kroner A and Badarch G. 2007. Tectonic models for accretion of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Journal of the Geological Society, 164: 31-47 DOI:10.1144/0016-76492006-022
|
Wu FY, Xu YG, Gao S and Zheng JP. 2008. Lithospheric thinning and destruction of the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 24(6): 1145-1174 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Wu FY, Liu XC, Ji WQ, Wang JM and Yang L. 2017. Highly fractionated granites: Recognition and research. Science China (Earth Sciences), 60(7): 1201-1219 DOI:10.1007/s11430-016-5139-1
|
Wu SS. 2009. Research on ore-formation and ore-controlling structure of Zhongshangou gold deposit in Chongli County, Hebei Province. Master Degree Thesis. Shijiazhuang: Shijiazhuang University of Economics (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Wyllie PJ and Sekine T. 1982. The formation of mantle phlogopite in subduction zone hybridization. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 79(4): 375-380 DOI:10.1007/BF01132067
|
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Hao J and Zhai MG. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China: Termination of the central Asian orogenic belt. Tectonics, 22(6): 1069
|
Xu YG, Li HY, Pang CJ and He B. 2009. On the timing and duration of the destruction of the North China Craton. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(19): 3379-3396
|
Yang F, Santosh M, Kim SW, Zhou HY and Jeong YJ. 2020. Late Mesozoic intraplate rhyolitic volcanism in the North China Craton: Far-field effect of the westward subduction of the Paleo-Pacific Plate. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 132(1-2): 291-309 DOI:10.1130/B35123.1
|
Yang JH, Wu FY, Chung SL, Wilde SA, Chu MF, Lo CH and Song B. 2005. Petrogenesis of Early Cretaceous intrusions in the Sulu ultrahigh-pressure orogenic belt, East China and their relationship to lithospheric thinning. Chemical Geology, 222(34): 200231
|
Yang JH, Wu FY, Liu XM and Xie LW. 2005. Zircon U-Pb ages and Hf isotopes and their geological significance of the Miyun rapakivi granites from Beijing, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(6): 1633-1644 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang JH, Wu FY, Shao JA, Xie LW and Liu XM. 2006. In-situ U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic analyses of zircons from volcanic rocks of the Houcheng and Zhangjiakou Formations in the Zhang-Xuan area, Northeast China. Earth Science (Journal of China University of Geosciences), 31(1): 71-80 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Yang ZM, Chang ZS, Hou ZQ and Meffre S. 2016. Age, igneous petrogenesis, and tectonic setting of the Bilihe gold deposit, China, and implications for regional metallogeny. Gondwana Research, 34: 296314
|
Yin JZ and Shi HY. 1995. Geology of Gold Ore Deposits in Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua Region, Hebei Province, China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House (in Chinese)
|
Yu B, Zeng QD, Frimmel HE, Qiu HC, Li QL, Yang JH, Wang YB, Zhou LL, Chen PW and Li JP. 2020. The 127Ma gold mineralization in the Wulong deposit, Liaodong Peninsula, China: Constraints from molybdenite Re-Os, monazite U-Th-Pb, and zircon U-Pb geochronology. Ore Geology Reviews, 121: 103542 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103542
|
Zeng QD, Liu JM, Zhang ZL, Qin F, Chen WJ, Zhang RB, Yu CM and Ye J. 2009. Ore-forming time of the Jiguanshan porphyry molybdenum deposit, northern margin of North China Craton and the Indosinian mineralization. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 25(2): 393-398 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zeng QD, Sun Y, Duan XX and Liu JM. 2013. U-Pb and Re-Os geochronology of the Haolibao porphyry Mo-Cu deposit, NE China: Implications for a Late Permian tectonic setting. Geological Magazine, 150(6): 975-985 DOI:10.1017/S0016756813000186
|
Zeng QD, Wang YB, Yang JH, Guo YP, Yu B, Zhou LL and Qiu HC. 2021. Spatial-temporal distribution and tectonic setting of gold deposits in the northern margin gold belt of the North China Craton. International Geology Review, 63(8): 941-972 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2020.1737839
|
Zhai MG and Peng P. 2007. Paleoproterozoic events in the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11): 2665-2682 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhai MG. 2010. Tectonic evolution and metallogenesis of North China Craton. Mineral Deposits, 29(1): 24-36 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang C, Ma CQ and Holtz F. 2012. Partial melting of hydrous lower continental crust: Discussion on the petrogenesis of C-type adakites from the Dabie Orogen. Geological Journal of China Universities, 18(1): 41-51 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang C, Guo W, Xu ZY, Liu ZH, Liu YJ and Lei CC. 2014. Study on geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic implications of monzogranite from the Yanbian area, eastern Jilin Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(2): 512-526 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang LL, Jiang SH, Li HM, Wu D and Kang H. 2019. Metallogenic and petrogenic geochronology and geochemical features of the ore-related granite in the Sadaigoumen Mo Deposit, Fengning, Hebei Province. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 40(5): 708-724 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang QQ, Zhang SH, Zhao Y and Liu JM. 2018. Devonian alkaline magmatic belt along the northern margin of the North China Block: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Lithos, 302-303: 496-518 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2018.01.019
|
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Song B and Liu DY. 2007. Petrogenesis of the Middle Devonian Gushan diorite pluton on the northern margin of the North China block and its tectonic implications. Geological Magazine, 144(3): 553-568 DOI:10.1017/S0016756807003275
|
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Kröner A, Liu XM, Xie LW and Chen FK. 2009a. Early Permian plutons from the northern North China Block: Constraints on continental arc evolution and convergent margin magmatism related to the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 98(6): 1441-1467 DOI:10.1007/s00531-008-0368-2
|
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Liu XC, Liu DY, Ch en, F K, Xie LW and Chen HH. 2009b. Late Paleozoic to Early Mesozoic mafic-ultramafic complexes from the northern North China Block: Constraints on the composition and evolution of the lithospheric mantle. Lithos, 110(1-4): 229-246 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2009.01.008
|
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Song B, Hu JM, Liu SW, Yang YH, Chen FK, Liu XM and Liu J. 2009c. Contrasting Late Carboniferous and Late Permian-Middle Triassic intrusive suites from the northern margin of the North China craton: Geochronology, petrogenesis, and tectonic implications. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 121(1-2): 181-200
|
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Ye H, Hou KJ and Li CF. 2012. Early Mesozoic alkaline complexes in the northern North China Craton: Implications for cratonic lithospheric destruction. Lithos, 155: 1-18 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.08.009
|
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Ye H, Liu JM and Hu ZC. 2014a. Origin and evolution of the Bainaimiao arc belt: Implications for crustal growth in the southern Central Asian orogenic belt. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 126(9-10): 1275-1300 DOI:10.1130/B31042.1
|
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Davis GA, Ye H and Wu F. 2014b. Temporal and spatial variations of Mesozoic magmatism and deformation in the North China Craton: Implications for lithospheric thinning and decratonization. Earth-Science Reviews, 131: 49-87 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2013.12.004
|
Zhang T, Chen ZY, Xu LQ and Chen ZH. 2009. The Re-Os isotopic dating of molybdenite from the Dasuji molybdenum deposit in Zhuozi County of Inner Mongolia and its geological significance. Rock and Mineral Analysis, 28(3): 279-282 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang XH and Zhai MG. 2010. Magmatism and its metallogenetic effects during the Paleozoic continental crustal construction in northern North China: An overview. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(5): 1329-1341 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhang XH, Zhang HF, Jiang N, Zhai MG and Zhang YB. 2010. Early Devonian alkaline intrusive complex from the northern North China craton: A petrological monitor of post-collisional tectonics. Journal of the Geological Society, 167(4): 717-730 DOI:10.1144/0016-76492009-110
|
Zhang YM, Gu XX, Xiang ZL, Liu RP, Cheng WB and Wang XL. 2017. Magmatic hydrothermal origin of the Hadamengou-Liubagou Au-Mo deposit, Inner Mongolia, China: Constrains on geology, stable and Re-Os isotopes. Ore Geology Reviews, 86: 172-195 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2017.01.029
|
Zhang ZC. 1995. Origin of Shuiquangou complex in Northern Hebei Province and a study of its relation to the gold mineralization. Ph. D. Dissertation. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Zhang ZC and Mao JW. 1995. Geology and geochemistry of the Dongping gold telluride deposit, Heibei Province, North China. International Geology Review, 37(12): 1094-1108 DOI:10.1080/00206819509465441
|
Zhang ZC and Chen HX. 1997. Geology and petrology of Shuiquangou complex, northern Hebei Province. 6(2): 81-92 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao GC, Wilde SA, Li SZ, Sun M, Grant ML and Li XP. 2007. U-Pb zircon age constraints on the Dongwanzi ultramafic-mafic body, North China, confirm it is not an Archean ophiolite. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 255(1-2): 85-93 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2006.12.007
|
Zhao GC and Zhai MG. 2013. Lithotectonic elements of Precambrian basement in the North China Craton: Review and tectonic implications. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1207-1240 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.08.016
|
Zhao Y, Zhai MG, Chen H and Zhang SH. 2017. Paleozoic-early Jurassic tectonic evolution of North China Craton and its adjacent orogenic belts. Geology in China, 44(1): 44-60 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhao ZH, Bao ZW and Qiao YL. 2010. A peculiar composite M- and W-type REE tetrad effect: Evidence from the Shuiquangou alkaline syenite complex, Hebei Province, China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(22): 2684-2696
|
Zhen SM, Wang QF, Wang DZ, Carranza EJM, Liu J, Pang Z, Cheng Z, Xue J, Wang J and Zha ZJ. 2020. Genesis of the Zhangquanzhuang gold deposit in the northern margin of North China Craton: constraints from deposit geology and ore isotope geochemistry. Ore Geology Reviews, 122: 103511 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2020.103511
|
Zhen SM, Zha ZJ, Wang DZ, Liu JJ, Pang ZS, Cheng ZZ, Xue JL, Wang J, Bai HJ, Li Y, Chen C. 2021. Characteristics of ore-forming fluids of the Zhongshangou gold deposit, Zhangjiakou-Xuanhua area, Hebei Province, and its limitation on the intrusive rock related telluride-gold deposits. Geology in China: 1-27 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Zhu RX, Chen L, Wu FY and Liu JL. 2011. Timing, scale and mechanism of the destruction of the North China Craton. Science China (Earth Sciences), 54(6): 789-797 DOI:10.1007/s11430-011-4203-4
|
Zhu RX, Yang JH and Wu FY. 2012. Timing of destruction of the North China Craton. Lithos, 149: 51-60 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2012.05.013
|
包志伟, 赵振华, 张佩华, 王一先. 2003. 张家口水泉沟正长岩杂岩体成因的REE和Sr、Nd、Pb同位素证据. 地质论评, 49(6): 596-604. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2003.06.006 |
蔡明海, 彭振安, 屈文俊, 贺钟银, 冯罡, 张诗启, 徐明, 陈艳. 2011a. 内蒙古乌拉特后旗查干德尔斯钼矿床地质特征及Re-Os测年. 矿床地质, 30(3): 377-384. |
蔡明海, 张志刚, 屈文俊, 彭振安, 张诗启, 徐明, 陈艳, 王显彬. 2011b. 内蒙古乌拉特后旗查干花钼矿床地质特征及Re-Os测年. 地球学报, 32(1): 64-68. |
陈斌, 田伟, 刘安坤. 2008. 冀北小张家口基性-超基性杂岩的成因: 岩石学、地球化学和Nd-Sr同位素证据. 高校地质学报, 14(3): 295-303. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2008.03.002 |
陈茜. 2013. 冀西北大白阳金矿成矿流体及成矿机制研究. 硕士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质大学(北京)
|
范宏瑞, 胡芳芳, 杨奎锋, 王凯怡, 刘勇胜. 2009. 内蒙古白云鄂博地区晚古生代闪长质-花岗质岩石年代学框架及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 25(11): 2933-2938. |
付方建. 2007. 冀西北黄土梁金矿成矿规律研究. 硕士学位论文. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院
|
侯万荣. 2011. 内蒙古哈达门沟金矿床与金厂沟梁金矿床对比研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质科学院
|
江思宏, 聂凤军. 1998. 河北小营盘与东坪金矿地质地球化学特征对比及矿床成因探讨. 黄金地质, 4(4): 12-24. |
江思宏, 聂凤军. 2000. 冀西北水泉沟杂岩体及与其有关金矿床的40Ar/39Ar同位素年代学研究. 地质论评, 46(6): 621-627. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0371-5736.2000.06.010 |
江思宏, 张莉莉, 刘翼飞, 刘春花, 康欢, 王丰翔. 2018. 兴蒙造山带成矿规律及若干科学问题. 矿床地质, 37(4): 671-711. |
姜耀辉, 蒋少涌, 赵葵东, 倪培, 凌洪飞, 刘敦一. 2005. 辽东半岛煌斑岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其对中国东部岩石圈减薄开始时间的制约. 科学通报, 50(19): 2161-2168. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0023-074X.2005.19.016 |
李创举, 包志伟. 2012. 冀西北早白垩世岩浆岩的地球化学特征及其地球动力学背景. 地球学报, 41(4): 343-358. |
李长民, 邓晋福, 陈立辉, 苏尚国, 李惠民, 胡森林, 刘新秒. 2010a. 华北北缘张宣地区东坪金矿中的两期锆石: 对成矿年龄的约束. 矿床地质, 29(2): 265-275. |
李长民, 邓晋福, 苏尚国, 李惠民, 刘新秒. 2010b. 河北省东坪金矿钾质蚀变岩中的两期锆石年代学研究及意义. 地球学报, 31(6): 843-852. |
李长民, 邓晋福, 苏尚国, 刘翠, 刘新秒. 2014. 冀北水泉沟岩体西段锆石U-Pb年代学及Hf同位素研究. 岩石学报, 30(11): 3301-3314. |
李瑞. 1992. 后沟金矿地质地球化学特征及其成矿模式初步探讨. 地质与勘探, (3): 46-50. |
李少众, 靳光成. 2000. 东坪金矿床地质特征及构造控矿作用. 地球学报, 21(1): 44-51. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1006-3021.2000.01.007 |
李晓勇, 范蔚茗, 郭锋, 王岳军, 李超文. 2004. 古亚洲洋对华北陆缘岩石圈的改造作用: 来自于西山南大岭组中基性火山岩的地球化学证据. 岩石学报, 20(3): 557-566. |
刘敦一, 耿元生, 宋彪. 1997. 冀西北地区晚太古代大陆地壳的增生和再造——同位素年代学证据. 地球学报, 18(3): 226-232. |
刘海田. 1999. 冀西北黄土梁金矿控矿因素分析. 贵金属地质, 8(4): 209-216. |
刘颖, 刘海臣, 李献华. 1996. 用ICP-MS准确测定岩石样品中的40余种微量元素. 地球化学, 25(6): 552-558. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.1996.06.004 |
刘翼飞, 聂凤军, 江思宏, 侯万荣, 梁清玲, 张可, 刘勇. 2012. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗准苏吉花钼矿床成岩成矿年代学及其地质意义. 矿床地质, 31(1): 119-128. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2012.01.010 |
刘翼飞, 江思宏. 2017. 兴蒙造山带及华北板块北缘钼矿化: 进展、规律、问题与成因初探. 矿床地质, 36(3): 557-594. |
卢德林, 罗修泉, 汪建军, 张思红, 郑宝英. 1993. 东坪金矿成矿时代研究. 矿床地质, 12(2): 182-188. |
路凤香, 郑建平, 邵济安, 张瑞生, 陈美华, 余淳梅. 2006. 华北东部中生代晚期-新生代软流圈上涌与岩石圈减薄. 地学前缘, 13(2): 86-92. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.02.007 |
罗镇宽, 苗来成, 关康. 2000. 华北地台北缘金矿床成矿时代讨论. 黄金地质, 6(2): 70-76. |
马寅生, 崔盛芹, 赵越, 曾庆利, 吴满路. 2002. 华北北部中新生代构造体制的转换过程. 地质力学学报, 8(1): 15-25. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2002.01.002 |
毛景文, 张作衡, 余金杰, 王义天, 牛宝贵. 2003. 华北及邻区中生代大规模成矿的地球动力学背景: 从金属矿床年龄精测得到启示. 中国科学(D辑), 33(4): 289-299. |
毛景文, 谢桂青, 张作衡, 李晓峰, 王义天, 张长青, 李永峰. 2005. 中国北方中生代大规模成矿作用的期次及其地球动力学背景. 岩石学报, 21(1): 169-188. |
邵济安, 何国琦, 唐克东. 2015. 华北北部二叠纪陆壳演化. 岩石学报, 31(1): 47-55. |
石来生, 饶玉学, 宋瑞先, 温建华. 2007. 河北省张家口金矿集区同位素及包裹体地质特征. 矿产与地质, 21(3): 219-227. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1001-5663.2007.03.001 |
宋国瑞, 赵振华. 1996. 河北省东坪碱性杂岩金矿地质. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
宋瑞先, 魏明辉, 王金锁, 等. 2013. 张家口地质矿产. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
孙金凤, 杨进辉. 2009. 华北东部早白垩世A型花岗岩与克拉通破坏. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 34(1): 137-147. |
陶利鑫, 甄世民, 白海军, 王江, 王大钊, 查钟健. 2020. 河北大白阳金矿床黄铁矿微量元素及S-Pb同位素地球化学特征. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 50(5): 1582-1598. |
田伟, 陈斌, 刘超群, 张华峰. 2007. 冀北小张家口超基性岩体的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素组成. 岩石学报, 23(3): 583-590. |
王大钊, 刘家军, 翟德高, 甄世民, 王江. 2020. 河北东坪碲金矿床辉钼矿Re-Os及锆石U-Pb年龄研究. 地学前缘, 27(2): 405-419. |
王建平, 刘永山, 董法先, 李中坚, 彭华, 王连捷, 丁原辰, 杨玉东, 孟宪刚, 贾宏杰, 刘志斌, 刘建民, 王红才. 1992. 内蒙古金厂沟梁金矿构造控矿分析. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
王梁, 王根厚, 雷时斌, 常春郊, 侯万荣, 贾丽琼, 赵广明, 陈海舰. 2015. 内蒙武川后石花金矿床辉钼矿Re-Os同位素年龄及其地质意义. 地质与勘探, 51(3): 422-431. |
王时麟. 1986. 张家口金矿的成因研究. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), (4): 81-89. |
王郁, 蒋心明, 王正坤. 1990. 河北省张-宣地区金矿床的硫、铅同位素地质研究. 地质找矿论丛, 5(2): 66-75. |
王正坤, 蒋心明, 王郁, 商木元. 1992. 张宣地区小营盘、东坪金矿的地质地球化学对比. 地质与勘探, (7): 14-20. |
韦忠良, 张宏, 柳小明, 张晔卿. 2008. 张家口地区张家口组火山岩的LA-ICP-MS测年及其地质意义. 自然科学进展, 18(5): 523-530. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1002-008X.2008.05.006 |
吴福元, 徐义刚, 高山, 郑建平. 2008. 华北岩石圈减薄与克拉通破坏研究的主要学术争论. 岩石学报, 24(6): 1145-1174. |
吴福元, 刘小驰, 纪伟强, 王佳敏, 杨雷. 2017. 高分异花岗岩的识别与研究. 中国科学(地球科学), 47(7): 745-765. |
吴姗姗. 2009. 河北崇礼中山沟金矿成矿控矿构造研究. 硕士学位论文. 石家庄: 石家庄经济学院
|
杨进辉, 吴福元, 柳小明, 谢烈文. 2005. 北京密云环斑花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素及其地质意义. 岩石学报, 21(6): 1633-1644. |
杨进辉, 吴福元, 邵济安, 谢烈文, 柳小明. 2006. 冀北张-宣地区后城组、张家口组火山岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 31(1): 71-80. |
银剑钊, 史红云. 1995. 张家口-宣化地区金矿地质. 北京: 地质出版社.
|
曾庆栋, 刘建明, 张作伦, 覃锋, 陈伟军, 张瑞斌, 于昌明, 叶杰. 2009. 华北克拉通北缘鸡冠山斑岩钼矿床成矿年代及印支期成矿事件. 岩石学报, 25(2): 393-398. |
翟明国, 彭澎. 2007. 华北克拉通古元古代构造事件. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2665-2682. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.001 |
翟明国. 2010. 华北克拉通的形成演化与成矿作用. 矿床地质, 29(1): 24-36. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2010.01.004 |
张超, 马昌前, Holtz F. 2012. 含水大陆下地壳的部分熔融: 大别山C型埃达克岩成因探讨. 高校地质学报, 18(1): 41-51. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2012.01.004 |
张超, 郭巍, 徐仲元, 刘正宏, 刘永江, 雷聪聪. 2014. 吉林东部延边地区二长花岗岩年代学、岩石成因学及其构造意义研究. 岩石学报, 30(2): 512-526. |
张莉莉, 江思宏, 李红梅, 吴迪, 康欢. 2019. 河北丰宁撒岱沟门钼矿床成岩成矿年代学及成矿岩体地球化学特征. 地球学报, 40(5): 708-724. |
张彤, 陈志勇, 许立权, 陈郑辉. 2009. 内蒙古卓资县大苏计钼矿辉钼矿铼-锇同位素定年及其地质意义. 岩矿测试, 28(3): 279-282. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0254-5357.2009.03.017 |
张晓晖, 翟明国. 2010. 华北北部古生代大陆地壳增生过程中的岩浆作用与成矿效应. 岩石学报, 26(5): 1329-1341. |
张招崇. 1995. 冀北水泉沟杂岩体的成因机制及其与金的成矿作用关系的研究. 博士学位论文. 北京: 中国地质科学院
|
张招崇, 陈洪新. 1997. 水泉沟杂岩体的地质学和岩石学研究. 贵金属地质, 6(2): 81-92. |
赵越, 翟明国, 陈虹, 张拴宏. 2017. 华北克拉通及相邻造山带古生代-侏罗纪早期大地构造演化. 中国地质, 44(1): 44-60. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1672-6995.2017.01.011 |
甄世民, 查钟健, 王大钊, 刘家军, 庞振山, 程志中, 薛建玲, 王江, 白海军, 李阳, 陈超. 2021. 河北张宣地区中山沟金矿成矿流体特征及其对侵入岩型碲金矿床的限定. 中国地质: 1-27. |
 2021, Vol. 37
2021, Vol. 37