2. 中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所, 岩石圈演化国家重点实验室, 北京 100029
2. State Key Laboratory of Lithospheric Evolution, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100029, China
榍石(CaTi[SiO4]O)是中酸性钙碱性-碱性岩浆岩和基性变质岩中常见的副矿物之一(Frost et al., 2000;向华等,2007;Kohn, 2017),另外在矽卡岩中也有产出(Li et al., 2010; 朱乔乔等,2014)。榍石通常含有中等含量的U(10×10-6~1000×10-6),其U-Pb同位素体系具有较高的封闭温度(660~700℃),因此可以进行U-Pb定年(Tilton and Grunenfelder, 1968; Cherniak, 1993; Scott and St-Onge, 1995; Aleinikoff et al., 2002; Amelin, 2009)。由于矿物晶体内元素的类质同象替代,榍石非常富集高场强元素(HFSE)和稀土元素(REE),榍石中Nd含量可以达到500×10-6~5000×10-6,且具有较低的Sm/Nd比值(一般 < 0.5),是进行激光原位Sm-Nd同位素分析的理想对象,榍石中Nd同位素体系封闭温度约为850~950℃(Cherniak, 1995),可以用来示踪岩浆或热液来源(Tiepolo et al., 2002; Gregory et al., 2009; Laurent et al., 2017)。与锆石或其他副矿物不同,榍石具有较强的活动性,易于与其他矿物或流体发生化学反应,因而其同位素体系和微量元素易随着多期的生长而发生变化,存在一定的成分环带。因此,原位获取榍石矿物内部Sm-Nd同位素组成空间变化的信息,结合微区的U-Pb年龄测定和微量元素分析,可以为矿物和岩石的成因演化提供重要的制约参数(Sun et al., 2010; Cao et al., 2015)。
近年来,四级杆/多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱(Quadrupole/Multi-Collector Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry, Q/MC-ICP-MS)结合激光剥蚀系统(Laser Ablation, LA)已成为榍石原位微区微量元素分析、U-Pb年代学和Sm-Nd同位素分析的重要技术手段(Willigers et al., 2002; Simonetti et al., 2006; Storey et al., 2006; Gao et al., 2012; 杨岳衡等,2016)。该方法不仅可以揭示矿物内部随空间变化的成分信息,同时也避免了冗长的化学前处理,分析效率明显提高。前人采用基体匹配的榍石作为外部标准物质,成功解决了成分不同的标样和样品之间存在的基体效应问题,极大地推进了榍石U-Pb年代学和Sm-Nd同位素体系的研究(Heaman, 2009; Kennedy et al., 2010; 孙金凤等,2012; Spandler et al., 2016; Ma et al., 2019)。
三江地区多金属成矿带是我国最具资源潜力的成矿带之一,其中,富碱斑岩型多金属成矿系统是其独具特色的成矿特征之一,矽卡岩型为最主要的矿化类型。这些矿床与新生代富碱侵入岩有密切的时空和成因关系,受到了国内外地质学家们的高度关注(侯增谦等,2004;Ge et al., 2009)。近三十年来,随着研究工作的不断深入,前人已取得了大量研究成果。其中,同位素年代学和地球化学的研究是三江地区富碱岩浆岩带和多金属成矿带自发现以来开展的重要工作之一,其目的是为了准确厘定成岩成矿时代,揭示岩浆和成矿物质来源,以及探讨成岩成矿关系(吕伯西等,1993;张玉泉和谢应雯,1997;Lu et al., 2013; Deng et al., 2014)。然而,目前对于成矿规律以及成矿作用过程中的元素迁移规律、控制因素和成矿物质来源等问题仍存在较大争议(邓军等,2010)。榍石在三江富碱侵入岩和相关矽卡岩矿床中广泛存在,多期生长榍石的原位微量元素、U-Pb年代学和Sm-Nd同位素等信息详细记录了其经历的岩浆或热液地质过程,对研究成岩成矿关系、元素迁移过程和物质来源具有重要意义,有助于揭示成矿规律,为进一步找矿提供理论依据。前人对三江地区富碱侵入岩和相关热液矿床中榍石已取得了一些研究成果,但已有的工作主要是基于溶液方法、激光微量元素和U-Pb年代学开展的,暂无Sm-Nd同位素的研究,因而一定程度损失了岩浆或成矿流体物质来源的信息(Zhang and Schärer, 1996, 1999; Xu et al., 2015; Fu et al., 2016, 2018)。
本文以哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩为研究对象,开展了榍石激光原位微区微量元素、U-Pb年代学和Sm-Nd同位素工作,识别了榍石成因类型。对比分析榍石U-Pb年龄和锆石等其他矿物年龄、榍石Sm-Nd同位素和全岩Sm-Nd同位素的异同,探讨了该地区富碱侵入岩形成时代和榍石Sm-Nd同位素的地质意义,为三江地区富碱岩石成岩成矿关系和物质来源研究提供了新的研究思路和研究手段。
1 地质背景与岩相学特征本文研究区位于三江地区哀牢山-红河富碱侵入岩带中段和南段。从地理上,三江地区是指怒江、澜沧江、金沙江所穿过的地区,包括川西、滇西、藏东以及青海省西南部玉树等地区,向南延伸到缅甸,老挝和越南,面积约为50万平方千米(Mo et al., 1994)(图 1a)。自65Ma印度-欧亚大陆碰撞以来,三江地区发生了强烈的陆内变形,形成了规模不同的微陆块和剪切带。在三江地区南部,由东向西包括扬子板块、印支地块和滇缅泰马地块,分别被哀牢山缝合带和昌宁-孟连缝合带分割开来;在三江地区北部,由北向南包括松潘甘孜地块、东羌塘地块和拉萨地块,分别为金沙江缝合带和班公湖-怒江缝合带所分割(Deng et al., 2014)。哀牢山-红河剪切带是三江地区东侧最主要的边界构造,是扬子板块和思茅地块(印支板块)的边界。三江地区新生代富碱侵入岩主要沿金沙江-哀牢山-红河剪切带及其两侧分布,主要由浅成相的富碱侵入岩组成,也包含大量火山喷发相的碱性火山岩,岩浆活动峰期为~35Ma(图 1b)。

|
图 1 三江地区构造单元划分和地理位置简图(a, 据Deng et al., 2014修改)及金沙江-哀牢山剪切带新生代富碱岩浆活动分布图(b, 据Lu et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2017修改) 各岩体文献年龄引自Chen et al., 2017及其中参考文献.IYZS-雅鲁藏布缝合带;BNS-班公湖-怒江缝合带;JSS-金沙江缝合带;CMS-昌宁-孟连缝合带;ASS-哀牢山缝合带;ARSZ-哀牢山-红河剪切带 Fig. 1 Simplified tectonic map of the Sanjiang Region showing the major continental blocks and suture zones (a, modified after Deng et al., 2014) and tectonic framework of the western Yangtze Craton and Simon Block, showing the distribution and ages of Cenozoic alkali-rich intrusions along the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone (b, modified after Lu et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2017) Ages within the rectangle from Chen et al., 2017, and references therein. IYZS-Indus-Yarlung Zangbo Suture Zone; BNS-Bangong-Nujiang Suture Zone; JSS-Jinsha Suture Zone; CMS-Changning-Menglian Suture Zone; ASS-Ailaoshan Suture Zone; ARSZ-Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone |
本文样品采自哀牢山-红河剪切带中段的桃花岩体、宁蒗-永胜岩体和南段的哈播岩体、铜厂岩体、十里村岩体(图 1b)。所采集样品均具有富碱(K2O+Na2O>8%)的特征(李晨,2019;武精凯等,2019),手标本均为灰色-肉红色,块状构造,副矿物有锆石、榍石、磷灰石等,镜下观察到榍石多数呈信封状,自形程度良好(图 2)。

|
图 2 三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩的镜下特征 Amp-角闪石; Bi -黑云母; Kfs-钾长石; Q-石英; Ttn-榍石 Fig. 2 The microscopic characteristics of the alkali-rich intrusion from the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone in the Sanjiang Region Amp-amphibole; Bi-biotite; Kfs-K-feldspar; Q-quartz; Ttn-titanite |
根据镜下观察鉴定,识别出四种岩石类型,分别是黑云二长斑岩、黑云角闪正长岩、正长斑岩和角闪正长斑岩。其中,桃花岩体(SG1708)和宁蒗-永胜岩体样品(YS1601、YS1612)均为黑云二长斑岩,斑状结构,斑晶约占整体的75%,主要为钾长石(30%~40%)、斜长石(30%~40%)、黑云母(10%~15%)及少量角闪石(图 2a, b)。样品SG1708肉眼可见黄铁矿和少量的黄铜矿,约占整体的10%。哈播岩体样品(LC1601、LC1605)为黑云角闪正长岩,中-粗粒结构,主要矿物为钾长石(40%~50%)、斜长石(15%~20%)、角闪石(10%~15%)和黑云母(10%~15%)(图 2c, d)。铜厂岩体样品(TCX1608)为正长斑岩,斑晶约占整体的70%,主要为钾长石(50%~60%)和斜长石(15%~20%),角闪石含量约为5%(图 2e)。十里村岩体样品(BSZ1604、BSZ1605)为角闪正长斑岩,斑晶约占整体的70%,主要为钾长石(40%~50%)、斜长石(20%~30%)和角闪石(10%~15%)(图 2f)。
2 测试方法榍石分选采用电磁法完成。将分选的待测榍石颗粒粘贴在双面胶上,将其放入环氧树脂中制成样品靶,对其进行抛光处理以露出颗粒中心,之后对榍石分别进行透射光、反射光和背散射(Backscattered electron, BSE)照相,检查榍石的内部结构,选择表面平整、无裂隙和包裹体的区域进行激光原位分析。
榍石激光原位微量元素分析和U-Pb定年在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱实验室完成,采用的仪器是美国Coherent公司生产的Geolas Pro 193nm ArF准分子激光剥蚀系统与美国Agilent公司的Agilent 7500a四级杆电感耦合等离子体质谱(Q-ICP-MS)。详细的仪器参数见相关文献(Ma et al., 2019)。本文中榍石微量元素和U-Pb定年分析测试采用点剥蚀方式,束斑直径为40μm,剥蚀频率为8Hz。每7个未知样品点插入2个微量元素标样(NIST 610)、2个榍石年龄主标样(MKED1)和2个榍石年龄副标样(BLR-1或OLT1),每个样品点总测试时间为90s,其中采集背景信号15s,激光剥蚀取样时间60s,冲洗样品池及管路时间15s。微量元素含量的计算采用Glitter 4.0软件(Griffin et al., 2008),以NIST610作为外标,以43Ca作为内标元素(CaO含量由电子探针分析获取)。U-Pb同位素分馏效应和质量歧视的校正计算采用Glitter 4.0软件,207Pb/206Pb、206Pb/238U、207Pb/235U(235U=238U/137.88)、208Pb/232Th的比值采用榍石标样MKED1作为外标进行校正,外标的相对标准偏差设定为2%,采用榍石BLR-1或OLT1作为副标样监测年龄准确性。数据投图采用Isoplot 3.0程序完成(Ludwig, 2003)。对含有普通铅的榍石,采用207Pb校正方法进行普通铅校正,其图形等价形式为Tera-Wasserburg(TW)图解。在TW图解中,样品普通铅组成和实测数据点连线的延长线与谐和线相交所获得的下交点对应的年龄即为样品207Pb校正后的206Pb/238U年龄。样品普通铅的组成由地球铅两阶段演化曲线计算获得(Stacey and Kramers, 1975)。
榍石激光原位Sm-Nd同位素分析同样在中国科学院地质与地球物理研究所多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱实验室完成,采用的仪器是美国Coherent公司生产的Geolas Pro 193nm ArF准分子激光剥蚀系统和Thermo Fisher公司生产的型号为Neptune的多接收电感耦合等离子体质谱(MC-ICP-MS)。详细的仪器参数见Ma et al.(2019)。在年龄测点附近进行Sm-Nd同位素分析,根据榍石样品Nd含量的高低,测试激光束斑直径在40~60μm之间,剥蚀频率为8Hz。使用146Nd/144Nd=0.7219及指数方程校正Nd同位素之间的质量歧视。使用147Sm/149Sm= 1.08680(Dubois et al., 1992)和指数方程校正Sm同位素间的质量分馏,并进一步利用144Sm/149Sm=0.22332(Isnard et al., 2005)校正144Sm对144Nd的同质异位素干扰(杨岳衡等,2008)。利用榍石外部标准BLR-1校正147Sm/144Nd的质量歧视和元素分馏。实验所测榍石副标样Ontario的147Sm/144Nd和143Nd/144Nd比值分别为0.1922±0.0030(2σ, n=38)和0.512807±0.000026(2σ, n=38),与参考值147Sm/144Nd=0.1928±0.0011(2σ, n=4)和143Nd/144Nd=0.512833±0.000008(2σ, n=4)(Ma et al., 2019)在误差范围内一致。激光分析测试获得的稳定同位素比值145Nd/144Nd和推荐值(0.348415, Wasserburg et al., 1981)在误差范围内一致,表明该校正方法可以准确校正Sm对Nd的同质异位素干扰,经过外部校正后,可以获得可靠的Sm-Nd同位素比值。
3 分析结果通过以上测试,本文共获得了8件富碱侵入岩样品中榍石的微量元素(见电子版附表 1)、U-Pb年龄(见电子版附表 2)和7件样品的Sm-Nd同位素(见电子版附表 3)结果。
|
|
附表 1 三江地区富碱侵入岩中榍石微量元素分析结果(× 10-6) Appendix Table 1 Trace elements compositions (× 10-6) of titanites in alkaline-rich intrusions in the Sanjiang Region |
|
|
附表 2 三江地区富碱岩石中榍石LA-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果 Appendix Table 2 LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of titanites in alkaline-rich intrusions in the Sanjiang Region |
|
|
附表 3 三江地区富碱岩石中榍石LA-MC-ICP-MS Sm-Nd同位素分析结果 Appendix Table 3 LA-MC-ICP-MS Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of titanites in alkaline-rich intrusions in the Sanjiang Region |
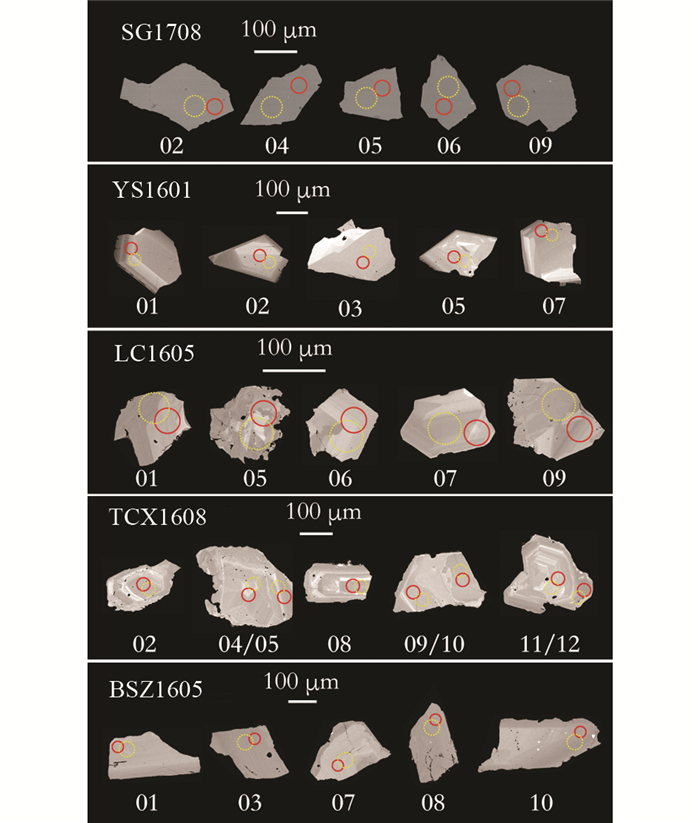
在BSE图像上,本文所测试的多数榍石样品内部结构具备规则的震荡环带和扇形分带(图 3),单个样品的微量元素含量变化范围不大(附表 1)。
|
图 3 三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩中榍石背散射图像 其中实线红色圆圈和虚线黄色圆圈分别代表U-Pb年龄激光剥蚀位置(直径40μm)和Sm-Nd同位素激光剥蚀位置(直径40~60μm) Fig. 3 Backscattered electron for titanites from the alkali-rich intrusions from the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone in the Sanjiang Region The red solid and yellow dashed circles refer to the locations of the laser ablation for titanite U-Pb analyses (diameter=40μm) and titanite Sm-Nd isotopic analyses (diameter=40~60μm), respectively |
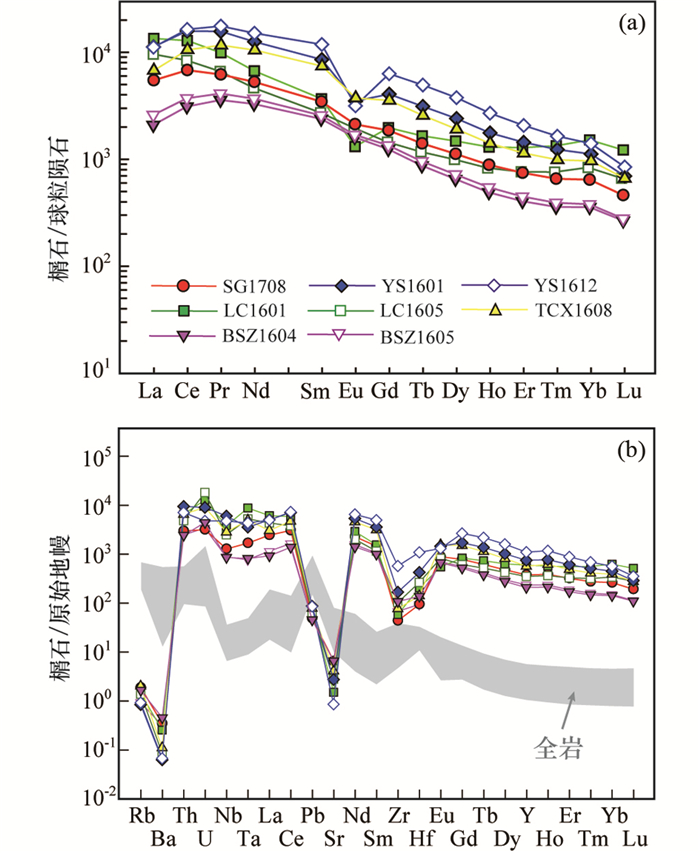
微量元素分析结果表明不同样品中榍石具有十分相似的稀土元素和微量元素特征,具有中等的轻重稀土分馏特征((La/Yb)N=8~17)。桃花岩体、十里村岩体和部分哈播岩体中榍石(SG1708、BSZ1604、BSZ1605、LC1605)基本无Eu异常(Eu/Eu*=0.83~1.08),宁蒗-永胜、哈播和铜厂岩体中榍石(YS1601、YS1612、LC1601、TCX1608)具有中等-弱的Eu负异常(Eu/Eu*=0.37~0.72)(图 4a)。与全岩微量元素相比,榍石亏损Rb、Ba、Pb、Sr等大离子亲石元素,富集Th、U、Nb、Ta、Zr和Hf等高场强元素和稀土元素(图 4b)。
|
图 4 三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩中榍石球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(a, 标准化值据Boynton, 1984)和原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(b, 标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) 全岩微量元素数据引自Lu et al. (2013), Chen et al. (2017), 韩美芝(2017), 李晨(2019), 武精凯等(2019) Fig. 4 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns (a, normalizing data from Boynton, 1984) and primitive mantle-normalized trace-element spidergrams (b, normalizing data from Sun and McDonough, 1989) of titanites from the alkali-rich intrusions from the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone in the Sanjiang Region The whole rock trace element data from Lu et al. (2013), Chen et al. (2017), Han (2017), Li (2019), Wu et al. (2019) |
本文三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩中榍石U-Pb年龄数据汇总于附表 2中。
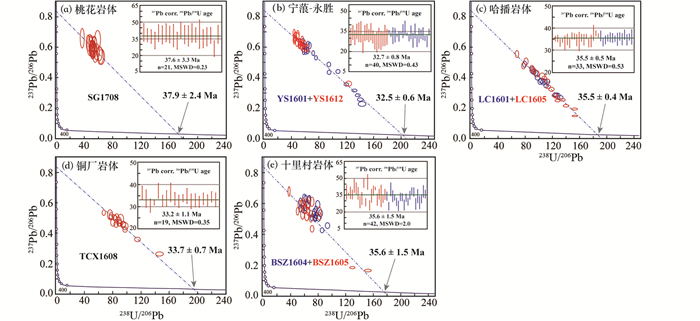
桃花岩体黑云二长斑岩SG1708取得21个榍石测点的207Pb校正的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为37.6±3.3Ma(2σ,n=21,MSWD=0.23)(图 5a)。Th/U比值为3.8±0.8(2SD,n=21),普通铅含量(f206=206Pb普通/206Pb实测,即普通206Pb占总206Pb的比例)较高,变化于0.62~0.77之间,因此单点年龄误差较大。宁蒗-永胜岩体黑云二长斑岩YS1601和YS1612两个样品取得40个榍石测点207Pb校正的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为32.7±0.8Ma(2σ,n=40, MSWD=0.43)。榍石YS1612的普通铅含量较高,f206=0.74±0.08(2SD,n=20);榍石YS1601普通铅变化范围较大,f206在0.23~0.75之间;数据点在TW图解中呈线性分布(图 5b)。哈播岩体黑云角闪正长岩LC1601和LC1605榍石的普通铅含量变化范围较大,f206变化在0.13~0.84之间,数据点在TW图解中呈线性分布,33个测点给出207Pb校正的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为35.5±0.5Ma(2σ,n=33, MSWD=0.53)(图 5c)。铜厂岩体正长斑岩TCX1608中榍石的Th/U比值为3.6±2.3(2SD,n=19)。普通铅含量较高且变化范围较大,f206=0.52±0.16(2SD,n=19)。获得207Pb校正的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为33.2±1.1Ma(2σ,n=19, MSWD=0.35)(图 5d)。十里村岩体角闪正长斑岩中榍石BSZ1604的Th/U比值为0.55±0.11(2SD,n=21),榍石BSZ1605的Th/U比值为0.52±0.25(2SD,n=21)。测点在TW图解中分布较为分散,2个样品共同获得207Pb校正的206Pb/238U加权平均年龄为35.6±1.5Ma(2σ,n=42, MSWD=2.0)(图 5e)。
|
图 5 三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩的榍石U-Pb年龄Tera-Wasserburg图解 (a)桃花岩体; (b)宁蒗-永胜岩体; (c)哈播岩体; (d)铜厂岩体; (e)十里村岩体 Fig. 5 U-Pb Tera Wasserburg diagrams of the titanites from alkali-rich intrusions from the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone in the Sanjiang Region (a) Taohua intrusion; (b)Ninglang-Yongsheng intrusion; (c) Habo intrusion; (d) Tongchang intrusion; (e) Shilicun intrusion |
本文总共对7件三江地区富碱侵入岩中的榍石进行了激光原位Sm-Nd同位素分析,数据结果列于附表 3和图 6中。从分析结果来看,各样品中榍石的Sm-Nd同位素组成比较均一,均具有富集的Nd同位素组成,桃花黑云二长斑岩中榍石(SG1708)的143Nd/144Nd实测值为0.512517±0.000035(2σ, n=19),εNd(t)为-2.74~-1.52;宁蒗-永胜黑云二长斑岩中榍石YS1601的143Nd/144Nd实测值为0.512465±0.000042(2σ, n=19),YS1612的143Nd/144Nd实测值为0.512479±0.000033(2σ, n=19),εNd(t)为-4.21~-2.64;哈播黑云角闪正长岩中榍石LC1601的143Nd/144Nd实测值为0.512429±0.000072(2σ, n=16),LC1605的143Nd/144Nd实测值为0.512453±0.000070(2σ, n=30),εNd(t)为-5.18~-2.07;铜厂岩体正长斑岩中榍石TCX1608的143Nd/144Nd实测值为0.512279±0.000051(2σ, n=21),εNd(t)为-7.34~-5.68;十里村角闪正长斑岩中榍石BSZ1605的143Nd/144Nd实测值为0.512407±0.000037(2σ, n=22),εNd(t)为-4.98~-4.25。

|
图 6 三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩中榍石激光原位LA-MC-ICP-MS Sm-Nd同位素分析结果 全岩数据后标a据李晨(2019);标b据武精凯等(2019) Fig. 6 Diagrams of Nd isotopic data of titanites from the alkali-rich intrusions from the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone in the Sanjiang Region using LA-MC-ICP-MS in this study Data symbol a after Li (2019); symbol b from Wu et al. (2019) |
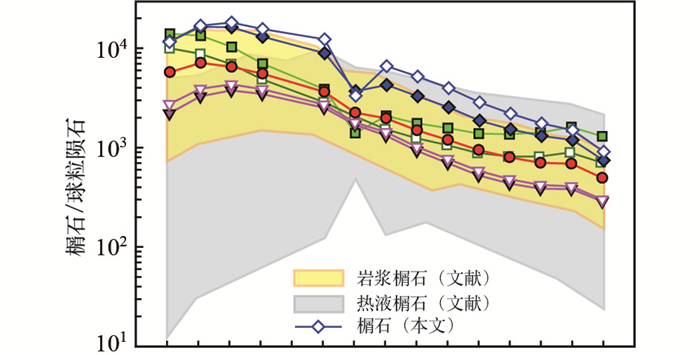
榍石稀土元素特征对榍石的成因具有一定的指示意义。一般情况下,岩浆成因的榍石具有明显的轻重稀土分异特征,稀土配分模式呈现明显右倾,不具有或具有弱的Eu负异常;而热液榍石的轻重稀土分异并不明显,Eu异常变化范围较大(图 7)。本文榍石样品的稀土配分图均呈现明显右倾,不具有或具有弱的Eu负异常,是典型的岩浆成因榍石特征。
|
图 7 岩浆榍石和热液榍石的球粒陨石标准化稀土元素图解 文献数据来自Li et al. (2010),Deng et al. (2015),Fu et al.(2016, 2018).本文榍石图例同图 4 Fig. 7 Chondrite-normalized REE patterns of titanites from igneous titanites and hydrothermal titanites Reference data from Li et al., 2010; Deng et al., 2015; Fu et al., 2016, 2018. Legends of titanites in this study are the same as Fig. 4 |
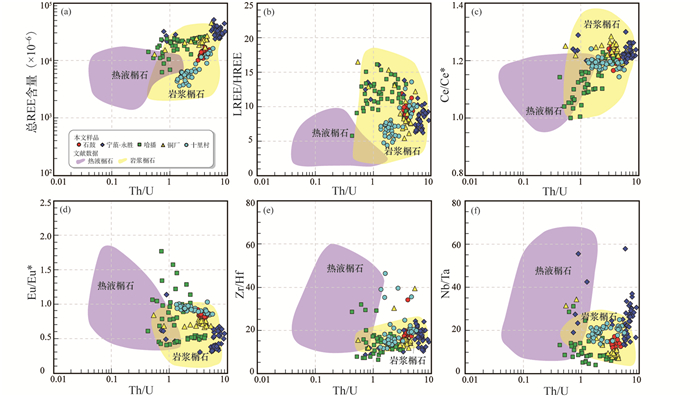
榍石的Th/U比值对于榍石的成因也具有指示意义。一般来说,热液榍石具有较低的Th/U比值,大多 < 1;而岩浆榍石的Th/U比值较高(Deng et al., 2015;Fu et al., 2016, 2018)。本文的榍石样品Th/U比值在0.4~9.1之间,大部分样品的Th/U比值大于1。同时,与典型的热液榍石相比,本文榍石的Th/U比值明显偏高(图 8),进一步表明其为岩浆成因。
|
图 8 三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱岩石中岩浆榍石和矽卡岩中热液榍石的Th/U对总REE含量(a)、LREE/HREE (b)、Ce/Ce* (c)、Eu/Eu* (d)、Zr/Hf (e)及Nb/Ta (f)二元图解 文献数据来自Li et al. (2010),Deng et al. (2015),Xu et al. (2015)和Fu et al.(2016, 2018) Fig. 8 Diagrams of Th/U against total REE (a), LREE/HREE (b), Ce/Ce* (c), Eu/Eu* (d), Zr/Hf (e) and Nb/Ta (f) of magmatic and hydrothermal titanites from the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone in the Sanjiang Region Reference data from Li et al. (2010), Deng et al. (2015), Xu et al. (2015), Fu et al.(2016, 2018) |
此外,与云南北衙、马厂箐矽卡岩矿床中的热液榍石相比,本文榍石在稀土元素组成上,具有较高的总REE含量、LREE/HREE、Ce/Ce*比值和较低的Eu/Eu*、Zr/Hf、Nb/Ta比值(图 8)。在岩浆体系中,Zr和Hf、Nb和Ta这样一些电价相同、离子半径相似的“双胞胎”元素通常比值变化较小(Green, 1995),然而当有流体参与作用时,这些元素比值将发生显著变化(Bau, 1996; Dostal and Chatterjee, 2000; Ballouard et al., 2016),这是由于在流体作用中,元素在矿物和熔体间的分配不再仅受离子半径和电价控制,更多是由化学络合作用控制(Irber, 1999)。榍石的Zr/Hf和Nb/Ta比值受到寄主岩浆化学组成的影响,岩浆成因榍石的Zr/Hf和Nb/Ta比值变化范围较小,而热液成因榍石的Zr/Hf和Nb/Ta比值受流体成分不同的影响变化范围较大。本文中榍石的Zr/Hf和Nb/Ta比值一般小于30(平均值:Zr/Hf = 16.5,Nb/Ta = 17.1),且变化范围较小;而北衙、马厂箐矿床热液榍石的Zr/Hf和Nb/Ta比值可以高达60,并且变化范围较广(图 8e, f),这种高的Zr/Hf、Nb/Ta比值特征反映了矿物形成时流体的特征。综上所述,本文三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩中榍石为岩浆成因。
和锆石相似,岩浆榍石和热液榍石中Ce/Ce*比值主要由氧逸度决定。Ce有Ce3+和Ce4+两种氧化态。Ce3+的半径为1.02Å,Ce4+的半径为0.87,氧化条件下Ce以+4价存在,不易置换Ca2+,从而较低的Ce/Ce*比值。Eu/Eu*的影响因素对于岩浆榍石来说主要为斜长石的分离结晶(Ballard et al., 2002; Bi et al., 2002),热液榍石中Eu/Eu*的影响因素主要是氧逸度(朱乔乔等,2014)。Eu有两种氧化态Eu2+和Eu3+,Eu3+的离子半径为0.95Å,与Ca2+的半径1.00Å相似,因此可以发生置换作用,而Eu2+的半径是1.17Å,难与Ca2+发生置换,氧化条件下,Eu以+3价存在,易置换Ca2+进入榍石,从而较高的Eu/Eu*比值。如图 8c和8d,文献中北衙和马厂箐矿床热液榍石与本文中岩浆榍石相比,具有更低的Ce/Ce*和更高的Eu/Eu*比值,表明北衙和马厂箐矿床形成于较高的氧逸度条件下,这与前人得到的结论一致(Bi et al., 2009; He et al., 2016; 沈阳等,2018;鲍新尚等,2019)。
4.2 榍石U-Pb年龄记录富碱侵入岩形成时代本文测定的富碱侵入岩中榍石U-Pb年龄为32.5~37.9Ma。与前人研究中采用锆石U-Pb等定年方法获得的结果在误差范围内一致。锆石U-Pb体系具有很高的封闭温度(>1000℃),因此其记录的年龄一般为岩石的形成年龄。与锆石相比,榍石U-Pb封闭温度较低,为600~750℃。据前人研究,三江地区富碱岩浆的温度明显高于榍石的U-Pb体系封闭温度(毕献武等,2005;Bi et al., 2009; 沈阳等,2018;鲍新尚等,2019),本文使用榍石Zr饱和温度计计算获得榍石的结晶温度在667~846℃之间(附表 1)(Hayden et al., 2008),也高于榍石的U-Pb封闭温度,因此榍石记录的年龄为岩浆冷却至封闭温度时的年龄。
本文通过收集前人数据,对比了各富碱岩体中锆石、榍石U-Pb年龄、全岩K-Ar年龄、全岩Rb-Sr年龄、黑云母K-Ar年龄(封闭温度为250~350℃)和长石K-Ar年龄(封闭温度为150~250℃),结果表明,这几种封闭温度不同的矿物定年结果在误差范围内一致(表 1),表明三江地区富碱岩浆冷却结晶是一个非常快速的过程,因此榍石的U-Pb年龄可以代表岩体形成时代。这些富碱岩体的形成时间与三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带及其附近新生代富碱岩浆活动高峰期(~35Ma)一致,属于青藏高原晚碰撞期岩浆作用的产物,是对印度-欧亚大陆碰撞作用的响应(Chung et al., 1997; 洪涛等,2015;徐恒等,2016)。
|
|
表 1 三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱岩石定年结果对比 Table 1 Comparison of dating results of alkali-rich intrusions from the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone in the Sanjiang Region |
榍石的Sm-Nd同位素组成代表了榍石结晶时富碱岩浆的同位素特征,而当岩浆同位素组成发生变化时,晶体的生长环带可以记录这一变化。因此,榍石的微区Sm-Nd同位素为示踪岩浆源区和演化过程提供了有效手段(孙金凤等,2009)。本文岩石样品中榍石颗粒的Nd同位素组成均一,没有随着生长环带发生明显改变,说明榍石结晶过程中寄主岩浆Nd同位素组成没有发生明显变化。各个富碱岩体之间的榍石Nd同位素组成变化范围不大(εNd(t)=-7.9~-2.1)。前人对三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩开展了详细的全岩Sr、Nd同位素地球化学研究,显示这些富碱侵入岩具有高的(87Sr/86Sr)i值(0.7056~0.7100)和低的εNd(t)值(-7.1~1.8),表明其源区具有富集地幔的地球化学特征(胥磊落等,2011; Lu et al., 2013; Chen et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2017, 2020; Xu et al., 2019; 武精凯等,2019)。本文与前人通过全岩同位素方法获得的结果一致(表 2、图 9)。因此,榍石的原位微区Sm-Nd同位素可以作为富碱侵入岩研究中有效的示踪手段之一。
|
|
表 2 三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带富碱侵入岩Sm-Nd同位素结果对比 Table 2 Sm-Nd isotopic compositions of alkali-rich intrusions from the Ailaoshan-Red River Shear Zone in the Sanjiang Region |
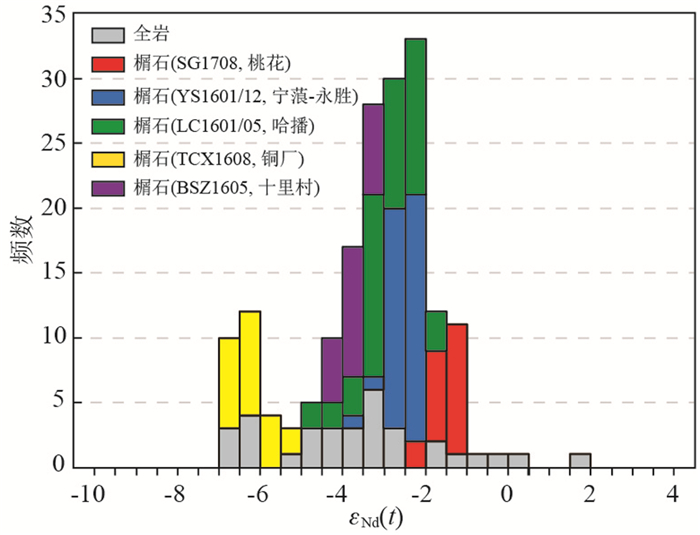
|
图 9 榍石和全岩εNd(t)值频率直方图榍石为本文数据,全岩数据来自表 2中参考文献 Fig. 9 Frequency histograms showing variations of εNd(t) for titanites (this study) and whole rocks Data of titanites from this study and whole rocks from references in Table 2 |
此外,在风化作用过程中,富碱岩石的Sm/Nd比值一般会发生不同程度的变化,而榍石的抗风化作用较强,它的原位Sm-Nd同位素基本代表了榍石结晶时岩浆的Nd同位素组成。因此,对于风化程度较高的的富碱岩石,我们可以通过分析榍石的Sm-Nd同位素组成来获取全岩的同位素信息。再者,榍石的原位微区Sm-Nd同位素分析和全岩同位素分析相比,分析更加经济,效率也大大提高。
5 结论(1) 本文研究的三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带新生代富碱侵入岩中榍石为岩浆成因。
(2) 榍石微区原位LA-Q-ICP-MS U-Pb定年结果表明,研究区富碱侵入岩中榍石结晶年龄在32.5~37.9Ma之间,代表了岩体形成时代,与三江地区哀牢山-红河剪切带及其附近新生代富碱岩浆活动高峰期(~35Ma)一致,属于青藏高原晚碰撞期岩浆作用的产物。
(3) 榍石微区原位LA-MC-ICP-MS Sm-Nd同位素分析结果表明,富碱岩体中榍石Nd同位素组成变化在-6.8~-2.1之间,与前人通过全岩Nd同位素方法获得的结果一致。榍石的Sm-Nd同位素可以代表榍石结晶时岩浆的Nd同位素组成,因此,榍石的原位微区Sm-Nd同位素可以作为富碱侵入岩研究中有效的示踪手段之一,与全岩同位素分析相比,分析效率大大提高。
致谢 审稿人和本刊编辑对本文提出诸多建设性修改建议,获益匪浅,在此表示诚挚感谢!
Aleinikoff JN, Wintsch RP, Fanning CM and Dorais MJ. 2002. U-Pb geochronology of zircon and polygenetic titanite from the Glastonbury Complex, Connecticut, USA:An integrated SEM, EMPA, TIMS, and SHRIMP study. Chemical Geology, 188(1-2): 125-147 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00076-1 |
Amelin Y. 2009. Sm-Nd and U-Pb systematics of single titanite grains. Chemical Geology, 261(1-2): 53-61 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.01.014 |
Ballard JR, Palin JM and Campbell IH. 2002. Relative oxidation states of magmas inferred from Ce(Ⅳ)/Ce(Ⅲ) in zircon:Application to porphyry copper deposits of northern Chile. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 144(3): 347-364 DOI:10.1007/s00410-002-0402-5 |
Ballouard C, Poujol M, Boulvais P, Branquet Y, Tartèse R and Vigneresse JL. 2016. Nb-Ta fractionation in peraluminous granites:A marker of the magmatic-hydrothermal transition. Geology, 44(3): 231-234 |
Bao XS, Yang LQ, He WY, Gao X and Li MM. 2019. Constraints of chemical compositions of biotite and zircon on crystallization conditions of magma:An example from the Beiya giant Au deposit, SW China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(5): 1447-1462 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.05.08 |
Bau M. 1996. Controls on the fractionation of isovalent trace elements in magmatic and aqueous systems:Evidence from Y/Ho, Zr/Hf, and lanthanide tetrad effect. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 123(3): 323-333 DOI:10.1007/s004100050159 |
Bi XW, Cornell DH and Hu RZ. 2002. REE composition of primary and altered feldspar from the mineralized alteration zone of alkaline intrusive rocks, western Yunnan Province, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 19(1-2): 69-78 DOI:10.1016/S0169-1368(01)00034-8 |
Bi XW, Hu RZ, Peng JT, Wu KX, Su WC and Zhan XZ. 2005. Geochemical characteristics of the Yao'an and Machangqing alkaline-rich intrusions. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 21(1): 113-124 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Bi XW, Hu RZ, Hanley JJ, Mungall JE, Peng JT, Shang LB, Wu KX, Yan SA, Li HL and Hu XY. 2009. Crystallisation conditions (T, P, fO2) from mineral chemistry of Cu-and Au-mineralised alkaline intrusions in the Red River-Jinshajiang alkaline igneous belt, western Yunnan Province, China. Mineralogy and Petrology, 96(1-2): 43-58 DOI:10.1007/s00710-009-0047-4 |
Boynton WV. 1984. Geochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed.). Rare Earth Element Geochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier
|
Cao MJ, Qing KZ, Li GM, Evans NJ and Jin LY. 2015. In situ LA-(MC)-ICP-MS trace element and Nd isotopic compositions and genesis of polygenetic titanite from the Baogutu reduced porphyry Cu deposit, Western Junggar, NW China. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 940-954 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.07.014 |
Chen B, Long XP, Wilde SA, Yuan C, Wang Q, Xia XP and Zhang ZF. 2017. Delamination of lithospheric mantle evidenced by Cenozoic potassic rocks in Yunnan, SW China:A contribution to uplift of the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Lithos, 284-285: 709-729 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2017.05.019 |
Cherniak DJ. 1993. Lead diffusion in titanite and preliminary results on the effects of radiation damage on Pb transport. Chemical Geology, 110(1-3): 177-194 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(93)90253-F |
Cherniak DJ. 1995. Sr and Nd diffusion in titanite. Chemical Geology, 125(3-4): 219-232 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(95)00074-V |
Chung SL, Lee TY, Lo CH, Wang PL, Chen CY, Yem NT, Hoa TT and Wu GY. 1997. Intraplate extension prior to continental extrusion along the Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone. Geology, 25(4): 311-314 |
Deng J, Yang LQ, Ge LS, Yuan SS, Wang QF, Zhang J, Gong QJ and Wang CM. 2010. Character and post-ore changes, modifications and preservation of Cenozoic alkali-rich porphyry gold metallogenic system in western Yunnan, China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 26(6): 1633-1645 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Deng J, Wang QF, Li GJ and Santosh M. 2014. Cenozoic tectono-magmatic and metallogenic processes in the Sanjiang region, southwestern China. Earth-Science Reviews, 138: 268-299 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2014.05.015 |
Deng XD, Li JW, Zhou MF, Zhao XF and Yan DR. 2015. In-situ LA-ICPMS trace elements and U-Pb analysis of titanite from the Mesozoic Ruanjiawan W-Cu-Mo skarn deposit, Daye district, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 65: 990-1004 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2014.08.011 |
Dostal J and Chatterjee AK. 2000. Contrasting behavior of Nb/Ta and Zr/Hf ratios in a peraluminous granitic pluton (Nova Scotia, Canada). Chemical Geology, 163(1-4): 207-218 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(99)00113-8 |
Dubois JC, Retali G and Cesario J. 1992. Isotopic analysis of rare earth elements by total vaporization of samples in thermal ionization mass spectrometry. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry and Ion Processes, 120(3): 163-177 DOI:10.1016/0168-1176(92)85046-3 |
Frost BR, Chamberlain KR and Schumacher JC. 2000. Sphene (titanite):Phase relations and role as a geochronometer. Chemical Geology, 172(1-2): 131-148 |
Fu Y, Sun XM, Zhou HY, Lin H and Yang TJ. 2016. In-situ LA-ICP-MS U-Pb geochronology and trace elements analysis of polygenetic titanite from the giant Beiya gold-polymetallic deposit in Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Ore Geology Reviews, 77: 43-56 DOI:10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.02.001 |
Fu Y, Sun XM, Hollings P, Li DF and Yang TJ. 2018. Geochronology and trace element geochemistry of titanite in the Machangqing Cu-Mo-dominated polymetallic deposit, Yunnan Province, Southwest China. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 158: 398-414 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2018.03.014 |
Gao XY, Zheng YF, Chen YX and Guo JL. 2012. Geochemical and U-Pb age constraints on the occurrence of polygenetic titanites in UHP metagranite in the Dabie orogen. Lithos, 136: 93-108 |
Ge LS, Deng J, Guo XD, Zou YL and Liu YC. 2009. Deep-seated structure and metallogenic dynamics of the Ailaoshan polymetallic mineralization concentration area, Yunnan Province, China. Science in China (Series D), 52(10): 1624-1640 DOI:10.1007/s11430-009-0136-6 |
Green T H. 1995. Significance of Nb/Ta as an indicator of geochemical processes in the crust-mantle system. Chemical Geology, 120(3-4): 347-359 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(94)00145-X |
Gregory CJ, McFarlane CRM, Hermann J and Rubatto D. 2009. Tracing the evolution of calc-alkaline magmas:In-situ Sm-Nd isotope studies of accessory minerals in the Bergell Igneous Complex, Italy. Chemical Geology, 260(1-2): 73-86 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.12.003 |
Griffin WL, Powell WJ, Pearson NJ and O'Reilly SY. 2008. GLITTER: Data reduction software for laser ablation ICP-MS. In: Sylvester P (ed.). Laser Ablation-ICP-MS in the Earth Sciences: Current Practices and Outstanding Issues. Mineralogical Association of Canada Short Course, 40: 308-311
|
Han MZ. 2017. Alkali-rich porphyry petrology and geochemistry in Jianchuan in Yunnan Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Hayden LA, Watson EB and Wark DA. 2008. A thermobarometer for sphene (titanite). Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 155(4): 529-540 DOI:10.1007/s00410-007-0256-y |
He WY, Mo XX, Yang LQ, Xing YL, Dong GC, Yang Z, Gao X and Bao XS. 2016. Origin of the Eocene porphyries and mafic microgranular enclaves from the Beiya porphyry Au polymetallic deposit, western Yunnan, China:Implications for magma mixing/mingling and mineralization. Gondwana Research, 40: 230-248 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.09.004 |
Heaman LM. 2009. The application of U-Pb geochronology to mafic, ultramafic and alkaline rocks:An evaluation of three mineral standards. Chemical Geology, 261(1-2): 43-52 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2008.10.021 |
Hong T, You J, Wu C and Xu XW. 2015. Archean-Paleoproterozoic zircons from a granite porphyry in the Taohua area, western Yunnan and their constrain on the basement of western margin of Yangtze Plate. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 31(9): 2583-2596 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hou ZQ, Zhong DL and Deng WM. 2004. A tectonic model for porphyry copper-molybdenum-gold metallogenic belts on the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geology in China, 31(1): 1-14 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Irber W. 1999. The lanthanide tetrad effect and its correlation with K/Rb, Eu/Eu*, Sr/Eu, Y/Ho, and Zr/Hf of evolving peraluminous granite suites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 63(3-4): 489-508 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00027-7 |
Isnard H, Brennetot R, Caussignac C, Caussignac N and Chartier F. 2005. Investigations for determination of Gd and Sm isotopic compositions in spent nuclear fuels samples by MC ICPMS. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 246(1-3): 66-73 DOI:10.1016/j.ijms.2005.08.008 |
Kennedy AK, Kamo SL, Nasdala L and Timms NE. 2010. Grenville skarn titanite:Potential reference material for SIMS U-Th-Pb analysis. The Canadian Mineralogist, 48(6): 1423-1443 DOI:10.3749/canmin.48.5.1423 |
Kohn MJ. 2017. Titanite petrochronology. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 83(1): 419-441 DOI:10.2138/rmg.2017.83.13 |
Laurent O, Zeh A, Gerdes A, Villaros A, Gros K and Słaby E. 2017. How do granitoid magmas mix with each other? Insights from textures, trace element and Sr-Nd isotopic composition of apatite and titanite from the Matok pluton (South Africa). Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 172(9): 80 DOI:10.1007/s00410-017-1398-1 |
Li C. 2019. Geochemistry and geochronology of Cenozoic alkali-rich porphyries in Nilang, Yunnan Province. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing) (in Chinese with English summary)
|
Li JW, Deng XD, Zhou MF, Liu YS, Zhao XF and Guo JL. 2010. Laser ablation ICP-MS titanite U-Th-Pb dating of hydrothermal ore deposits:A case study of the Tonglushan Cu-Fe-Au skarn deposit, SE Hubei Province, China. Chemical Geology, 270(1-4): 56-67 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2009.11.005 |
Liu JL, Chen XY, Tang Y, Song ZJ and Wang W. 2020. The Ailao Shan-Red River shear zone revisited:Timing and tectonic implications. GSA Bulletin, 132(5-6): 1165-1182 DOI:10.1130/B35220.1 |
Liu Z, Liao SY, Wang JR, Ma Z, Liu YX, Wang DB, Tang Y and Yang J. 2017. Petrogenesis of Late Eocene high Ba-Sr potassic rocks from western Yangtze Block, SE Tibet:A magmatic response to the Indo-Asian collision. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 135: 95-109 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.12.030 |
Lu YJ, Kerrich R, McCuaig TC, Li ZX, Hart CJR, Cawood PA, Hou ZQ, Bagas L, Cliff J, Belousova EA and Tang SH. 2013. Geochemical, Sr-Nd-Pb, and zircon Hf-O isotopic compositions of Eocene-Oligocene shoshonitic and potassic adakite-like felsic intrusions in western Yunnan, SW China:Petrogenesis and tectonic implications. Journal of Petrology, 54(7): 1309-1348 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egt013 |
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot/Ex, Version 3.00:A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley: Berkeley Geochronology Center
|
Lv BX, Wang Z, Zhang ND, Duan JZ, Gao ZY, Shen GF, Pan CY and Yao P. 1993. Sanjiang Granitoids and Their Metallogenic Specialization. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-12 (in Chinese)
|
Ma Q, Evans NJ, Ling XX, Yang JH, Wu FY, Zhao ZD and Yang YH. 2019. Natural titanite reference materials for in situ U-Pb and Sm-Nd isotopic measurements by LA-(MC)-ICP-MS. Geostandards and Geoanalytical Research, 43(3): 355-384 DOI:10.1111/ggr.12264 |
Mao XC, Yin FG and Liao SY. 2012. Zircon U-Pb geochronology of the Taohuacun porphyry, middle part of the Jinshajiang-Ailaoshan Shear Zone, and its geological significance. Journal of Mineralogy and Petrology, 32(3): 70-76 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Mo XX, Deng JF and Lu FX. 1994. Volcanism and the evolution of Tethys in Sanjiang area, southwestern China. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 9(4): 325-333 DOI:10.1016/0743-9547(94)90043-4 |
Scott DJ and St-Onge MR. 1995. Constraints on Pb closure temperature in titanite based on rocks from the Ungava orogen, Canada:Implications for U-Pb geochronology and P-T-t path determinations. Geology, 23(12): 1123-1126 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1995)023<1123:COPCTI>2.3.CO;2 |
Shen Y, Zheng YC, Ma R, Zhang AP, Xu PY, Wu CD and Wang ZX. 2018. Mineralogical characteristics of hornblendes and biotites in ore-forming porphyry from Machangqing Cu-Mo deposit in Yunnan Province and their significance. Mineral Deposits, 37(4): 797-815 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Simonetti A, Heaman LM, Chacko T and Banerjee NR. 2006. In situ petrographic thin section U-Pb dating of zircon, monazite, and titanite using laser ablation-MC-ICP-MS. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry, 253(1-2): 87-97 DOI:10.1016/j.ijms.2006.03.003 |
Spandler C, Hammerli J, Sha P, Hilbert-Wolf H, Hu Y, Roberts E and Schmitz M. 2016. MKED1:A new titanite standard for in situ analysis of Sm-Nd isotopes and U-Pb geochronology. Chemical Geology, 425: 110-126 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2016.01.002 |
Stacey JS and Kramers JD. 1975. Approximation of terrestrial lead isotope evolution by a two-stage model. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 26(2): 207-221 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(75)90088-6 |
Storey CD, Jeffries TE and Smith M. 2006. Common lead-corrected laser ablation ICP-MS U-Pb systematics and geochronology of titanite. Chemical Geology, 227(1-2): 37-52 DOI:10.1016/j.chemgeo.2005.09.003 |
Sun JF, Yang JH and Wu FY. 2009. Application of in-situ isotopic analysis to granite genesis. Earth Science Frontiers, 16(2): 129-139 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun JF, Yang JH, Wu FY, Li XH, Yang YH, Xie LW and Wilde SA. 2010. Magma mixing controlling the origin of the Early Cretaceous Fangshan granitic pluton, North China Craton:In situ U-Pb age and Sr-, Nd-, Hf-and O-isotope evidence. Lithos, 120(3-4): 421-438 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2010.09.002 |
Sun JF, Yang JH, Wu FY, Xie LW, Yang YH, Liu ZC and Li XH. 2012. In situ U-Pb dating of titanite by LA-ICPMS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 57(20): 2506-2516 DOI:10.1007/s11434-012-5177-0 |
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Tiepolo M, Oberti R and Vannucci R. 2002. Trace-element incorporation in titanite:Constraints from experimentally determined solid/liquid partition coefficients. Chemical Geology, 191(1-3): 105-119 DOI:10.1016/S0009-2541(02)00151-1 |
Tilton GR and Grunenfelder MH. 1968. Sphene:Uranium-lead ages. Science, 159(3822): 1458-1461 DOI:10.1126/science.159.3822.1458 |
Wasserburg GJ, Jacousen SB, DePaolo DJ, McCulloch MT and Wen T. 1981. Precise determination of Sm/Nd ratios, Sm and Nd isotopic abundances in standard solutions. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 45(12): 2311-2323 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(81)90085-5 |
Willigers BJA, Baker JA, Krogstad EJ and Peate DW. 2002. Precise and accurate in situ Pb-Pb dating of apatite, monazite, and sphene by laser ablation multiple-collector ICP-MS. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 66(6): 1051-1066 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(01)00838-9 |
Wu JK, Zhao ZD, Yang YY, Lei HS, Miao Z, Liu D, Zhu DC and Yu XH. 2019. Petrogenesis and geological implications of the alkali-rich porphyry in southern Ailaoshan-Red River shear zone. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 35(2): 485-504 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.18654/1000-0569/2019.02.14 |
Xia B, Lin QC and Zhang YQ. 2005. Zircon SHRIMP dating of diopside granite in Ailaoshan-Jinshajiang rock belt and its geological implications:Example for Yuzhaokuai, Matouwan and Shilicun diopside granites. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 29(1): 35-43 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiang H, Zhang L, Zhong ZQ, Zhou HW and Zeng W. 2007. Titanite:U-Pb dating and applications on defining P-T-t path of metamorphic rocks. Advances in Earth Science, 22(12): 1258-1267 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu H, Cui YL, Zhou JX, Zhang MH, Liang TX and Jiang YG. 2016. Geochemistry and zircon U-Pb age of the alkali-rich porphyry in the Fenshuiling ore district, Yongsheng City, Yunnan Province, and its geological implications. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 40(3): 614-624 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu LL, Bi XW, Su WC, Qi YQ, Li L, Chen YW, Dong SH and Tang YY. 2011. Geochemical characteristics and petrogenesis of the quartz syenite porphyry from Tongchang porphyry Cu (Mo-Au) deposit in Jinping County, Yunan Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(10): 3109-3122 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu LL, Bi XW, Hu RZ and Tang YY. 2015. LA-ICP-MS mineral chemistry of titanite and the geological implications for exploration of porphyry Cu deposits in the Jinshajiang-Red River alkaline igneous belt, SW China. Mineralogy and Petrology, 109(2): 181-200 DOI:10.1007/s00710-014-0359-x |
Xu LL, Bi XW, Hu RZ, Tang YY, Wang XS, Huang ML, Wang YJ, Ma R and Liu G. 2019. Contrasting whole-rock and mineral compositions of ore-bearing (Tongchang) and ore-barren (Shilicun) granitic plutons in SW China:Implications for petrogenesis and ore genesis. Lithos, 336-337: 54-66 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2019.03.031 |
Yang YH, Sun JF, Xie LW, Fan HR and Wu FY. 2008. In situ Nd isotopic measurement of natural geological materials by LA-MC-ICPMS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(7): 1062-1070 |
Yang YH, Yang JH, Wu FY, Xie LW and Huang C. 2016. New progresses in analytical methods of in situ Sm-Nd isotope measurement of natural geological samples by laser ablation multi-collector ICP mass spectrometry. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 35(3): 422-431 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang LS and Schärer U. 1996. Inherited Pb components in magmatic titanite and their consequence for the interpretation of U-Pb ages. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 138(1-4): 57-65 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(95)00237-7 |
Zhang LS and Schärer U. 1999. Age and origin of magmatism along the Cenozoic Red River shear belt, China. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 134: 67-85 DOI:10.1007/s004100050469 |
Zhang YQ and Xie YW. 1997. Geochronology of Ailaoshan-Jinshajiang alkali-rich intrusive rocks and their Sr and Nd isotopic characteristics. Science in China (Series D), 40(5): 524-529 DOI:10.1007/BF02877619 |
Zhu QQ, Xie GQ, Jiang ZS, Sun JF and Li W. 2014. Characteristics and in situ U-Pb dating of hydrothermal titanite by LA-ICPMS of the Jingshandian iron skarn deposit, Hubei Province. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(5): 1322-1338 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
鲍新尚, 杨立强, 和文言, 高雪, 李萌萌. 2019. 黑云母和锆石化学组分对岩浆结晶条件的约束:以滇西北衙超大型金矿床为例. 岩石学报, 35(5): 1447-1462. |
毕献武, 胡瑞忠, 彭建堂, 吴开兴, 苏文超, 战新志. 2005. 姚安和马厂箐富碱侵入岩体的地球化学特征. 岩石学报, 21(1): 113-124. |
邓军, 杨立强, 葛良胜, 袁士松, 王庆飞, 张静, 龚庆杰, 王长明. 2010. 滇西富碱斑岩型金成矿系统特征与变化保存. 岩石学报, 26(6): 1633-1645. |
韩美芝. 2017.云南剑川富碱斑岩的岩石学与地球化学.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学(北京)
|
洪涛, 游军, 吴楚, 徐兴旺. 2015. 滇西桃花花岗斑岩中新太古代-古元古代锆石年龄信息:对扬子板块西缘基底时代的约束. 岩石学报, 31(9): 2583-2596. |
侯增谦, 钟大赉, 邓万明. 2004. 青藏高原东缘斑岩铜钼金成矿带的构造模式. 中国地质, 31(1): 1-14. |
李晨. 2019.云南宁蒗新生代富碱斑岩地球化学和年代学.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学(北京)
|
吕伯西, 王增, 张能德, 段建中, 高子英, 沈敢富, 潘长云, 姚鹏. 1993. 三江地区花岗岩类及其成矿专属性. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-12.
|
毛晓长, 尹福光, 廖世勇. 2012. 金沙江-哀牢山构造带中段桃花村岩体的LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb定年及地质意义. 矿物岩石, 32(3): 70-76. |
沈阳, 郑远川, 马睿, 张爱萍, 徐培言, 吴昌炟, 王梓轩. 2018. 云南马厂箐铜钼矿成矿岩体的角闪石和黑云母矿物学特征及其意义. 矿床地质, 37(4): 797-815. |
孙金凤, 杨进辉, 吴福元. 2009. 原位微区同位素分析在花岗岩成因研究中的应用. 地学前缘, 16(2): 129-139. |
孙金凤, 杨进辉, 吴福元, 谢烈文, 杨岳衡, 刘志超, 李献华. 2012. 榍石原位微区LA-ICPMS U-Pb年龄测定. 科学通报, 57(18): 1603-1615. |
武精凯, 赵志丹, 杨逸云, 雷杭山, 苗壮, 刘栋, 朱弟成, 喻学惠. 2019. 云南哀牢山-红河断裂带南段新生代富碱斑岩岩石成因和地质意义. 岩石学报, 35(2): 485-504. |
夏斌, 林清茶, 张玉泉. 2005. 哀牢山-金沙江岩带透辉石花岗岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年龄及地质意义-以玉召块、马头湾和十里村岩体为例. 大地构造与成矿学, 29(1): 35-43. |
向华, 张利, 钟增球, 周汉文, 曾雯. 2007. 榍石:U-Pb定年及变质P-T-t轨迹的建立. 地球科学进展, 22(12): 1258-1267. |
徐恒, 崔银亮, 周家喜, 张苗红, 梁庭祥, 姜永果. 2016. 云南永胜分水岭矿区富碱斑岩地球化学、锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 大地构造与成矿学, 40(3): 614-624. |
胥磊落, 毕献武, 苏文超, 齐有强, 李亮, 陈佑纬, 董少花, 唐永永. 2011. 云南金平铜厂斑岩Cu(Mo-Au)矿床含矿石英正长斑岩地球化学特征及成因机制探讨. 岩石学报, 27(10): 3109-3122. |
杨岳衡, 孙金凤, 谢烈文, 范宏瑞, 吴福元. 2008. 地质样品Nd同位素激光原位等离子体质谱(LA-MC-ICPMS)测定. 科学通报, 53(5): 568-576. |
杨岳衡, 杨进辉, 吴福元, 谢烈文, 黄超. 2016. 激光原位LA-MC-ICP-MS测定地质样品Sm-Nd同位素方法新进展. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 35(3): 422-431. |
张玉泉, 谢应雯. 1997. 哀牢山-金沙江富碱侵入岩年代学和Nd、Sr同位素特征. 中国科学(D辑), 27(4): 289-293. |
朱乔乔, 谢桂青, 蒋宗胜, 孙金凤, 李伟. 2014. 湖北金山店大型矽卡岩型铁矿热液榍石特征和原位微区LA-ICPMS U-Pb定年. 岩石学报, 30(5): 1322-1338. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36