2. 中国地质大学(北京) 地球科学与资源学院, 北京 100083
2. School of Earth Science and Resources, China University of Geosciences, Beijing 100083, China
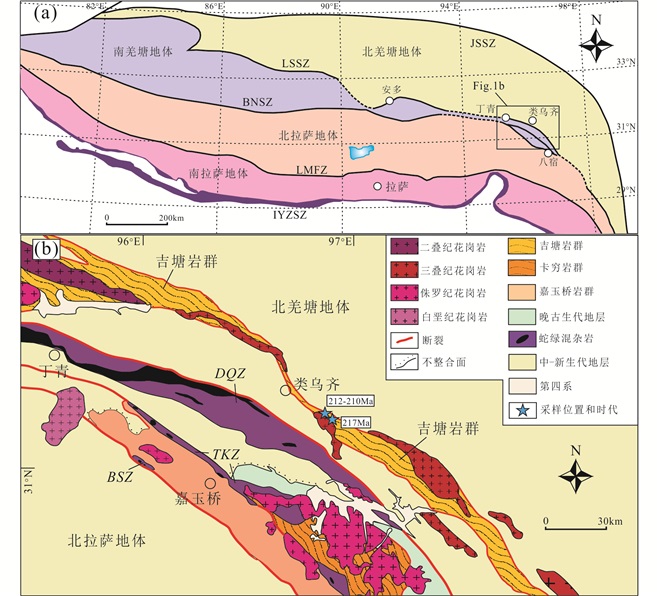
羌塘地体位于青藏高原中部,是青藏高原的重要组成部分,北部以金沙江缝合带为界与松潘-甘孜地体相连,南部以班公湖-怒江缝合带为界与拉萨地体相连(潘桂棠等, 2002; 莫宣学和潘桂棠, 2006; 许志琴等, 2007, 2011; 李才等, 2009a; Zhang et al., 2014)。以其内部的龙木措-双湖缝合带为界,羌塘地体又可划分为南、北羌塘两个地体(李才等, 2006, 2007, 2008; Zhai et al., 2010, 2016, 2017; 胡培远等, 2014; Xu et al., 2015)。羌塘地体中部和南缘分布大量的中生代岩浆岩,这些岩浆活动分别与龙木措-双湖古特提斯洋和班公湖-怒江洋的演化相关(Guynn et al., 2006; Zhai et al., 2011, 2013; Li et al., 2014, 2017a, b; Chen et al., 2016a, b; 吴浩, 2016; Wang et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2016)。但是在羌塘地体东部南缘地区,由于龙木措-双湖缝合带和班公湖-怒江缝合带空间位置的相近(图 1a),使该地区岩浆活动受龙木措-双湖古特提斯洋和班公湖-怒江洋演化叠加控制,导致该地区三叠纪岩浆岩的构造归属一直存在争议。
|
图 1 青藏高原中部构造纲要图(a, 据Chen et al., 2018)及羌塘地体东部类乌齐地区地质简图(b) JSSZ-金沙江缝合带;LSSZ-龙木措-双湖缝合带;BNSZ-班公湖-怒江缝合带;LMFZ-洛巴堆-米拉山断裂带;IYZSZ-印度-雅鲁藏布缝合带;DQZ-丁青蛇绿岩;TKZ-同卡蛇绿岩;BSZ-八宿蛇绿岩 Fig. 1 Tectonic outline of central Tibetan Plateau (a, after Chen et al., 2018) and geological map of Leiwuqi area, eastern Qiangtang terrane (b) |
羌塘地体东部类乌齐地区分布着大量的三叠纪岩浆岩,前人对该地区的花岗质岩石已进行了研究,初步确定了岩石类型和形成时代,并对岩石成因和构造背景进行了讨论(王保弟等, 2011; 沙绍礼等, 2012; 时超等, 2012; Hu et al., 2014; Tao et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2018)。目前对于花岗质岩石的构造归属仍存在不同的认识,一种观点认为形成在澜沧江洋闭合之后的碰撞或后碰撞环境下(王保弟等, 2011; Tao et al., 2014);另一种观点认为形成在龙木措-双湖古特提斯洋闭合之后的碰撞或后碰撞环境下(Hu et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2018)。但是以上认识都是基于对花岗质岩石的研究成果,对该地区出露的基性岩石却鲜有报道,基性岩石的形成时代、岩石成因和形成的构造背景尚不清楚,对该地区基性岩的研究,有助于揭示该地区不同类型岩浆岩的构造属性。本文选择羌塘地体东部类乌齐地区吉塘岩群内出露的变辉长岩为研究对象,对其开展岩石学、锆石U-Pb年代学、锆石Lu-Hf同位素以及岩石地球化学的研究,以限定变辉长岩形成时代,讨论岩石成因和形成的大地构造背景。
1 地质背景和样品本文的研究区位于青藏高原东部类乌齐地区,大地构造位置上位于羌塘地体东部(图 1a)。该地区出露的地层以中-新生代三叠系-白垩系地层为主,其中以三叠系和侏罗系地层发育最为广泛,三叠系地层为一套紫红色的砂砾岩、碎屑岩夹碳酸盐岩建造,侏罗系地层角度不整合于三叠系地层之上,为互层产出的砂岩、泥岩和灰岩。古生代地层在局部零星出露,主要由石炭系马查拉组的一套沉积于大陆边缘的浅海-海陆交互环境的含煤层沉积岩和二叠系莽措组灰岩组成。该地区构造复杂,北西-南东向的褶皱和脆、韧性断层比较发育(潘桂棠, 2004; 曾庆高等, 2010; 时超, 2011)。
类乌齐地区出露的变质岩被称为吉塘岩群,沿他念他翁山脉南侧呈北西向楔状分布。吉塘岩群普遍经历了绿片岩相-角闪岩相的变质,主要由正片麻岩、片岩、混合岩、斜长角闪岩和大理岩组成。吉塘岩群以往一直被认为是该地区的前寒武纪基底(李才等, 2009b; 何世平等, 2012; 邱军强等, 2015),近年来的研究发现吉塘岩群还经历了泛非期和印支期的岩浆活动以及印支期的变质作用(李才等, 2009b; 时超, 2011; Hu et al., 2014; 邱军强等, 2015),时超(2011)认为印支期的变质作用可以与藏东地区发育大规模印支期构造岩浆侵入事件相对应,是发生在古特提斯阶段“威尔逊旋回”中聚敛闭合期的事件。类乌齐地区岩浆岩以花岗质岩石为主,主要沿吉塘岩群两侧呈北西-南东向展布,与吉塘岩群呈断层或侵入接触,西北部发育早二叠世和早侏罗世二长花岗岩(潘桂棠, 2004; 曾庆高等, 2010),中部和南部出露晚三叠世的花岗岩和花岗闪长岩(Tao et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2018)。此外,在吉塘岩群中还发现原岩年龄为早三叠世和晚三叠世的正片麻岩(王保弟等, 2011; 沙绍礼等, 2012; 时超等, 2012; Hu et al., 2014)以及早二叠世的辉长岩(胡培远等, 2016)。
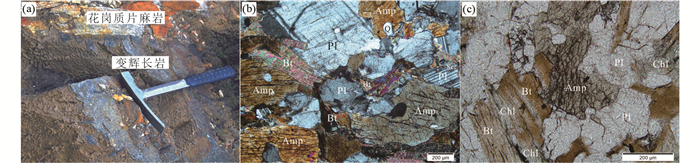
本次研究的变辉长岩样品采自类乌齐地区的吉塘岩群(图 1b),呈脉状侵入到花岗质片麻岩中(图 2a)。岩石为黑绿色,粒状变晶结构,块状构造,未见明显变形。主要矿物为斜长石(40%~45%)、角闪石(45%~50%)、黑云母(2%~5%)以及少量的石英、绢云母和绿泥石,未见辉石残留。斜长石呈板状自形-半自形晶,常发育聚片双晶,粒径在0.5~2mm之间,局部被绢云母交代(图 2b)。角闪石呈半自形柱状。黑云母呈片状,局部绿泥石化(图 2c)。
|
图 2 变辉长岩野外(a)和显微照片(b、c) 矿物代号:Amp-角闪石;Bt-黑云母;Pl-斜长石;Ser-绢云母;Q-石英;Chl-绿泥石 Fig. 2 Field photo (a) and microphotographs (b, c) of the metagabbro |
样品主量和微量元素(包括稀土)成分分析在中国地质科学院国家地质实验测试中心完成。主量元素采用XRF(X-ray fluorescence)方法测定(仪器型号Phillips 4400),检测限 < 0.01%,分析精度优于5%;FeO采用重铬酸钾滴定法测定;微量元素和稀土元素采用电感耦合等离子体质谱仪(ICP-MS)来测定(仪器型号PerkinElmer NexION 300D),检测限为1×10-6~0.05×10-6,分析误差为5%~10%。
锆石分选在河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所实验室完成。锆石阴极发光成像在中国地质科学院地质研究所北京离子探针中心完成。锆石U-Pb同位素LA-ICP-MS分析在武汉上谱分析科技有限责任公司完成,激光剥蚀系统为GeoLas 2005,激光斑束直径为32μm,频率为5Hz。ICP-MS仪器型号为Agilent 7700e。采用锆石91500和GJ-1作为标准样品。使用ICPMSDataCal(V10.7)软件对分析数据进行处理。详细的仪器操作条件和数据处理方法见Liu et al. (2010)。使用Isoplot软件(Ludwig, 2003)计算锆石加权平均年龄和绘制谐和图。
锆石Hf同位素测试在中国地质大学(武汉)地质过程与矿产资源国家重点实验室完成,使用的仪器为激光剥蚀多接收等离子体质谱仪(LA-MC-ICP-MS),激光剥蚀系统为德国Lamda Physik公司生产的Geolas 200M激光剥蚀仪器,MC-ICP-MS系统为德国Thermo Fisher Scientific公司生产的Neptune Plus仪器。实验过程中采用氦气作为剥蚀物质的载气。使用的激光剥蚀斑束直径为44μm,频率为8Hz。91500和GJ-1作为分析测试的标准锆石。详细的仪器状态和使用流程方法见Hu et al. (2015)。
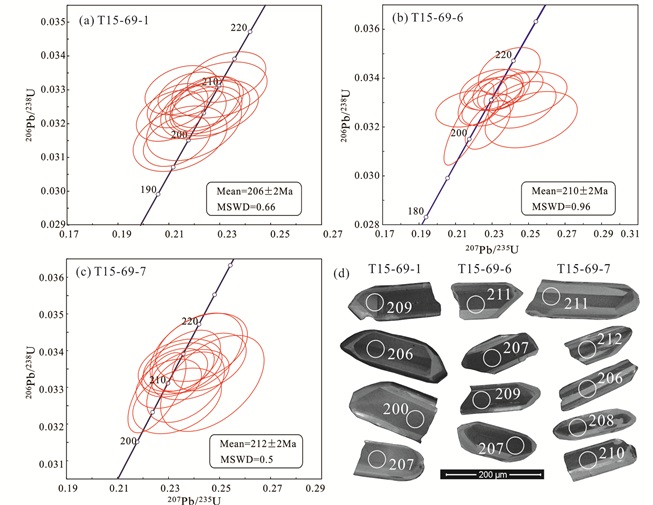
3 锆石U-Pb年代学和Lu-Hf同位素对3个变辉长岩样品(T15-69-1、T15-69-6、T15-69-7)进行锆石U-Pb同位素测年,测试结果见表 1。锆石为无色透明,自形-半自形柱状,长度为100~300μm。阴极发光(CL)图像显示,锆石颜色为灰-灰黑色,部分颗粒发育弱韵律环带或平行条带,变质边较窄或不发育(图 3d)。锆石Th和U含量分别为127×10-6~6413×10-6和418×10-6~4832×10-6,Th/U比值较大,介于0.30~1.32之间,表明其为岩浆成因锆石。3个样品锆石U-Pb年龄谐和度都较好,206Pb/238U加权平均年龄分别为206±2Ma、210±2Ma和212±2Ma(图 3a-c),该年龄代表了变辉长岩结晶年龄。
|
|
表 1 变辉长岩锆石U-Pb定年结果 Table 1 Zircon U-Pb dating data for the metagabbro |
|
图 3 类乌齐地区变辉长岩锆石U-Pb谐和图(a-c)和代表性锆石阴极发光图像(d, 含分析点位和相应年龄,单位Ma) Fig. 3 U-Pb concordia diagrams (a-c) and cathodoluminescence images (d) of representative zircon grains of the metagabbro in Leiwuqi area, showing the analytical spots and related ages (in Ma) |
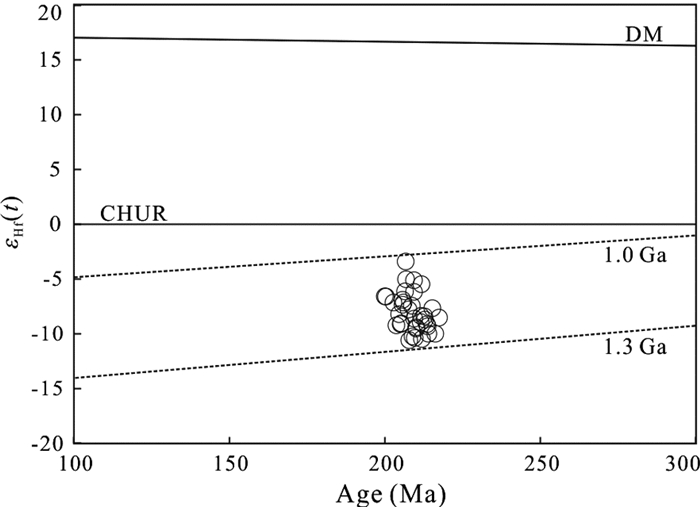
对以上3个样品进行锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析,测试结果见表 2。样品(176Hf/177Hf)i=0.282344~0.282552,εHf(t)的范围为-10.6~-3.2,单阶段模式年龄为tDM1=1034~1296Ma。
|
|
表 2 变辉长岩锆石Lu-Hf同位素分析结果 Table 2 Lu-Hf isotopic composition of the metagabbro |
类乌齐地区变辉长岩经历了变质作用,大离子亲石元素(如Rb、Ba、Cs、K等)在以上过程中容易发生改变,而高场强元素、稀土元素以及一些过渡金属元素则比较稳定(Winchester and Floyd, 1977; Humphris and Thompson, 1978)。为此,本文选取相对稳定的元素来进行变辉长岩地球化学特征的分析和讨论。
本文共选取了类乌齐地区6个变辉长岩样品进行了主、微量元素测试分析,分析结果见表 3。主量元素测试结果显示,样品SiO2含量为49.36%~52.82%,TiO2含量为1.28%~1.58%,Al2O3含量为17.10%~17.91%,FeOT为9.35%~9.95%,MgO含量为4.28%~7.17%,Mg#值为56~67。在SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图中投在了辉长岩区域(图 4a),在FeOT-(Na2O+K2O)-MgO图解中均落在了钙碱性系列区域(图 4b)。
|
|
表 3 变辉长岩主量元素(wt%)和微量(×10-6)元素分析结果 Table 3 Major (wt%) and trace (×10-6) element data for the metagabbro |

|
图 4 类乌齐地区变辉长岩SiO2-(Na2O+K2O)图解(a, 据Middlemost, 1994)和FeOT-(Na2O+K2O)-MgO图解(b, 据Irvine and Baragar, 1971) Fig. 4 SiO2 vs. (Na2O+K2O) (a, after Middlemost, 1994) and FeOT-(Na2O+K2O)-MgO (b, after Irvine and Baragar, 1971) classification diagrams of the metagabbro in Leiwuqi area |
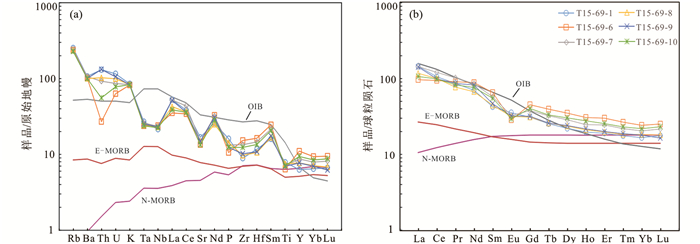
在原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图中,样品富集大离子亲石元素(如Rb、Ba、Th、U等),亏损高场强元素(如Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf、Ti等)(图 5a)。稀土元素含量较高,∑REE为157.7×10-6~193.4×10-6,LREE/HREE=4.45~7.05,(La/Yb)N=3.96~8.61,δEu=0.53~0.98。球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线为右倾型,轻、重稀土分馏明显,具有弱的负Eu异常(图 5b)。
|
图 5 类乌齐地区变辉长岩原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(a)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分曲线(b)(标准化值、OIB、E-MORB和N-MORB值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 5 Primitive-mantle normalized spider diagram (a) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns (b) for the metagabbro from Leiwuqi area (normalization, OIB, E-MORB and N-MORB values from Sun and McDonough, 1989) |
在早期的区域地质调查中,类乌齐地区已查明出露有三叠纪花岗质岩石。Tao et al. (2014)通过该地区花岗闪长岩和黑云母花岗岩锆石U-Pb同位素测年,获得~219Ma的岩浆年龄,Chen et al. (2018)也报道了吉塘岩群中片麻状花岗质岩石的锆石U-Pb年龄为213~208Ma。本文所研究的变辉长岩呈脉状侵入到花岗质片麻岩中,其结晶年龄为212~206Ma,稍晚于花岗质岩石。以上研究表明类乌齐地区不仅经历了晚三叠世的酸性岩浆事件,还经历了同时期的基性岩浆事件。
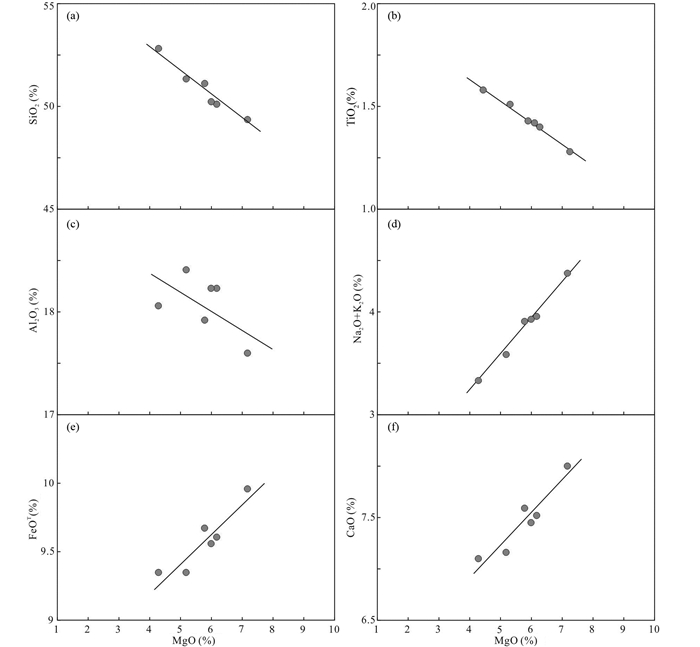
5.2 岩石成因类乌齐地区变辉长岩地球化学特征表明,SiO2、TiO2和Al2O3含量随MgO含量的增加而减少,呈现负相关性特征,而FeOT、CaO、(Na2O+K2O)含量和MgO具有良好的正相关性(图 6),表明岩石形成过程中岩浆发生了结晶分异作用。样品的Mg#值为56~67(表 3),低于初始岩浆的Mg#值(~70)(Wilson, 1989),也说明在成岩过程中岩浆发生了一定程度的结晶分异。Al2O3和MgO的负相关性以及Eu、Sr的负异常说明岩浆在演化过程中发生了斜长石分离结晶(图 5、图 6c)。CaO和MgO的正相关性表明岩浆可能发生了辉石的分离结晶(图 6f),(Na2O+K2O)含量和MgO的正相关性表明岩浆的碱性逐渐减弱(图 6d)。
|
图 6 类乌齐地区变辉长岩MgO与SiO2、TiO2、Al2O3、(Na2O+K2O)、FeOT和CaO图解 Fig. 6 Bivariate plots of MgO versus SiO2, TiO2, Al2O3, (Na2O+K2O), FeOT and CaO for the metagabbro in Leiwuqi area |
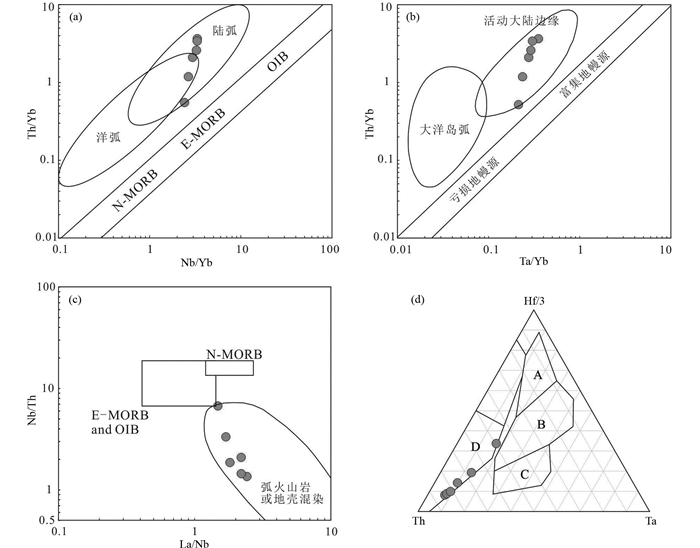
稀土和微量元素配分曲线特征显示,样品富集LREEs、Th、U和Ba,亏损Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf和Ti,具有岛弧火山岩的地球化学特征(Pearce, 2014)。样品具有较低的εHf(t)(-10.6~-3.2),单阶段模式年龄tDM1=1034~1296Ma(图 7),表明其岩浆来自中元古代岩石圈地幔部分熔融或富集地幔(Stern et al., 2004; Ishizuka et al., 2010)。样品较高的La/Nb比值(1.44~2.42)和低的La/Ba比值(0.03~0.05)也表明其具有受俯冲影响的大陆岩石圈地幔源区特征(Saunders et al., 1992)。微量元素Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf的亏损表明岩浆源区有俯冲带物质的加入,样品具有较高的Th(2.15×10-6~10.5×10-6)和LREE(135.7×10-6~167.1×10-6)含量以及Th/Yb和Th/Nb比值,也显示岩石源区有不同程度俯冲沉积物的加入(图 8a, b; Pearce and Peate, 1995; Woodhead et al., 1998; Aldanmaz et al., 2008)。
|
图 7 类乌齐地区变辉长岩锆石εHf(t)与U-Pb年龄图(据Chen et al., 2018) Fig. 7 Zircon εHf(t) values vs. U-Pb ages diagram (after Chen et al., 2018) of the metagabbro in Leiwuqi area |
|
图 8 类乌齐地区变辉长岩Nb/Yb-Th/Yb(a, 据Pearce, 2014)、Ta/Yb-Th/Yb(b, 据Pearce and Peate, 1995)、La/Nb-Nb/Th(c, 据Pearce, 1983)和Hf/3-Th-Ta(d, 据Wood, 1980)图解 A-亏损性洋中脊玄武岩;B-富集型洋中脊玄武岩和板内玄武岩;C-板内玄武岩;D-火山弧玄武岩 Fig. 8 Nb/Yb vs. Th/Yb (a, after Pearce, 2014), Ta/Yb vs. Th/Yb (b, after Pearce and Peate, 1995), La/Nb vs. Nb/Th (c, after Pearce, 1983) and Hf/3-Th-Ta (d, after Wood, 1980) diagrams for the metagabbro from Leiwuqi area |
类乌齐地区变辉长岩稀土和微量元素配分曲线特征明显区别于N-MORE、E-MORE和OIB的特征(图 5),样品富集LREEs、Th、U和Ba,亏损Nb、Ta、Zr、Hf和Ti,是典型的岛弧火山岩的地球化学特征(Pearce, 2014)。在Nb/Yb-Th/Yb构造判别图中,样品均落在大陆弧的范围内(图 8a);在Ta/Yb-Th/Yb图中,样品均落在了活动大陆边缘的区域内(图 8b);在La/Nb-Nb/Th图解中,样品也落在了弧火山岩或地壳混染岩浆源区域(图 8c);而在Hf/3-Th-Ta图解中,样品落在了火山弧区域(图 8d)。综上所述,类乌齐地区变辉长岩形成在大陆弧构造背景下。
类乌齐地区位于羌塘地体东部的南缘,由于龙木措-双湖缝合带和班公湖-怒江缝合带在该地区空间位置的相近(图 1a),使该地区成为龙木措-双湖古特提斯洋和班公湖-怒江洋叠加控制域,该地区三叠纪岩浆活动也主要与龙木措-双湖古特提斯洋和班公湖-怒江洋的演化相关(王保弟等, 2011; 时超等, 2012; Hu et al., 2014; Tao et al., 2014; Li et al., 2017a; Chen et al., 2018)。
关于龙木措-双湖古特提斯洋的演化历史,目前的研究认为其在中-晚寒武纪打开,形成了505~432Ma洋中脊蛇绿混杂岩(Wang et al., 2008; Zhai et al., 2010, 2016; 胡培远等, 2014; Xu et al., 2015),在晚泥盆世-中三叠世向北俯冲,在羌塘地体中部形成~243Ma蓝片岩-榴辉岩带以及375~246Ma的岛弧火山岩(Liu et al., 2011; Zhai et al., 2011, 2013, 2017; 江庆源等, 2014; 刘函等, 2015; 吴浩, 2016; Fan et al., 2016, 2017),至晚三叠世该大洋闭合,南、北羌塘地体碰撞,形成237~203Ma碰撞型花岗岩和高压变质带(李才等, 2006, 2007, 2008; Fan et al., 2017; Zhai et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2018; Wang et al., 2018)。前人对于类乌齐地区晚三叠世花岗质岩石的研究表明,岩石属于过铝质的超钾至高钾钙碱性的S型花岗岩,形成在碰撞环境(Tao et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2018),但是对于其构造归属仍存在分歧,Tao et al. (2014)认为其形成在澜沧江古特提斯洋闭合之后的后碰撞背景下,而Chen et al. (2018)则认为是形成在龙木措-双湖-丁青古特提斯洋闭合而导致的羌塘地体和同卡微陆块碰撞的构造环境下。本文所研究的变辉长岩形成在晚三叠世,形成的构造背景是俯冲环境下的大陆弧背景,而龙木措-双湖古特提斯洋在晚三叠世已经闭合,与该大洋演化相关的构造环境处于碰撞或后碰撞的背景,所以本文认为类乌齐地区变辉长岩的形成与龙木措-双湖古特提斯洋的演化无关。
关于班公湖-怒江特提斯洋的演化历史,最早的观点认为其打开时间在晚二叠世至早三叠世,在班公湖-怒江缝合带内形成255~248Ma的洋中脊蛇绿岩以及洋岛玄武岩和辉长岩(任纪舜和肖黎薇, 2004; 刘鸿飞和刘焰, 2009; Fan et al., 2015, 2017),通过对缝合带北侧羌塘地体内242~235Ma岛弧火山岩、高级变质岩和沉积盆地的研究,最早的向北初始俯冲的观点,认为其不晚于晚三叠世(段瑶瑶等, 2016; Chen et al., 2016a, b; Zhu et al., 2013; Zeng et al., 2016; Li et al., 2017b; Fan et al., 2018)。基于以上认识,本文所研究的变辉长岩的形成时代和构造背景与班公湖-怒江特提斯洋的演化更加吻合,所以,本文认为类乌齐地区晚三叠世变辉长岩是形成在班公湖-怒江特提斯洋向北俯冲在羌塘地体下的大陆弧背景下。
6 结论(1) 藏东类乌齐地区变辉长岩属于钙碱性系列,在成岩过程中岩浆发生了一定程度的结晶分异。
(2) 类乌齐地区变辉长岩结晶年龄为212~206Ma,为晚三叠世。岩浆来自中元古代岩石圈地幔部分熔融或富集地幔,源区有不同程度俯冲沉积物的加入。
(3) 类乌齐地区变辉长岩是形成在班公湖-怒江特提斯洋向北俯冲在羌塘地体下的大陆弧背景下。
致谢 感谢付长垒和袁月蕾对本文写作的帮助。感谢两位审稿人审阅全文并提出重要修改意见。
Aldanmaz E, Yaliniz MK, Güctekin A and Göncüolu MC. 2008. Geochemical characteristics of mafic lavas from the Neotethyan ophiolites in western Turkey:Implications for heterogeneous source contribution during variable stages of ocean crust generation. Geological Magazine, 145(1): 37-54 DOI:10.1017/S0016756807003986 |
Chen SS, Shi RD, Fan WM, Zou HB, Liu DL, Huang QS, Gong XH, Yi GD and Wu K. 2016a. Middle Triassic ultrapotassic rhyolites from the Tanggula Pass, southern Qiangtang, China:A previously unrecognized stage of silicic magmatism. Lithos, 264: 258-276 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2016.08.040 |
Chen SS, Shi RD, Yi GD and Zou HB. 2016b. Middle Triassic volcanic rocks in the Northern Qiangtang (Central Tibet):Geochronology, petrogenesis, and tectonic implications. Tectonophysics, 666: 90-102 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.10.017 |
Chen YF, Zhang ZM, Tian ZL, Dong X, Ding HX, Mu HC, Kang DY and Li YS. 2018. Early Mesozoic magmatism and tectonic evolution of east-central Tibet. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 107(8): 2767-2784 DOI:10.1007/s00531-018-1625-7 |
Duan YY, Li YL and Duan ZM. 2016. The discovery of the Early Triassic gabbro rocks of the Duolong accretionary complexes in southern Qiangtang terrane of Tibet and its geological significance. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(6): 887-893 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Fan JJ, Li C, Xie CM, Wang M and Chen JW. 2015. The evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Neo-Tethys Ocean:Evidence from zircon U-Pb and Lu-Hf isotopic analyses of Early Cretaceous oceanic islands and ophiolites. Tectonophysics, 655: 27-40 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2015.04.019 |
Fan JJ, Li C, Xie CM and Liu YM. 2016. Depositional environment and provenance of the upper Permian-Lower Triassic Tianquanshan Formation, northern Tibet:Implications for the Palaeozoic evolution of the Southern Qiangtang, Lhasa, and Himalayan terranes in the Tibetan Plateau. International Geology Review, 58(2): 228-245 DOI:10.1080/00206814.2015.1070108 |
Fan JJ, Li C, Xie CM, Liu YM, Xu JX and Chen JW. 2017. Remnants of Late Permian-Middle Triassic ocean islands in northern Tibet:Implications for the late-stage evolution of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Gondwana Research, 44: 7-21 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.10.020 |
Fan JJ, Li C, Wang M and Xie CM. 2018. Reconstructing in space and time the closure of the middle and western segments of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean in the Tibetan Plateau. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 107(1): 231-249 DOI:10.1007/s00531-017-1487-4 |
Guynn JH, Kapp P, Pullen A, Heizler M, Gehrels G and Ding L. 2006. Tibetan basement rocks near Amdo reveal "missing" Mesozoic tectonism along the Bangong suture, central Tibet. Geology, 34(6): 505-508 |
He SP, Li RS, Yu PS, Gu PY, Wang C, Yang YC and Zhang WJ. 2012. The age of Youxi formation of Jitang rock group in Taniantaweng mountains, Northern Qiangtang, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Acta Geologica Sinica, 86(6): 985-993 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu PY, Li C, Li J, Wang M, Xie CM and Wu YW. 2014. Zircon U-Pb-Hf isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry of gneissic granites from the Jitang complex in Leiwuqi area, eastern Tibet, China:Record of the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. Tectonophysics, 623: 83-99 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2014.03.018 |
Hu PY, Li C, Wu YW, Xie CM, Wang M and Li J. 2014. Opening of the Longmu Co-Shuanghu-Lancangjiang ocean:Constraints from plagiogranites. Chinese Science Bulletin, 59(25): 3188-3199 DOI:10.1007/s11434-014-0434-z |
Hu PY, Li C, Zhai QG, Wang M, Xie CM and Wu YW. 2016. The gabbros from the Leiwuqi area, eastern Tibet:Records of the Late Paleozoic break-up of the northern Gondwana. Geological Bulletin of China, 35(11): 1845-1854 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu ZC, Zhang W, Liu YS, Gao S, Li M, Zong KQ, Chen HH and Hu SH. 2015. "Wave" signal-smoothing and mercury-removing device for laser ablation quadrupole and multiple collector ICPMS analysis:Application to lead isotope analysis. Analytical Chemistry, 87(2): 1152-1157 DOI:10.1021/ac503749k |
Humphris SE and Thompson G. 1978. Trace element mobility during hydrothermal alteration of oceanic basalts. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 42(1): 127-136 DOI:10.1016/0016-7037(78)90222-3 |
Irvine TN and Baragar WRA. 1971. A guide to the chemical classification of the common volcanic rocks. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 8(5): 523-548 DOI:10.1139/e71-055 |
Ishizuka O, Yuasa M, Tamura Y, Shukuno H, Stern RJ, Naka J, Joshima M and Taylor RN. 2010. Migrating shoshonitic magmatism tracks Izu-Bonin-Mariana intra-oceanic arc rift propagation. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 294(1-2): 111-122 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2010.03.016 |
Jiang QY, Li C, Xie CM, Wang M, Hu PY, Wu H, Peng H and Chen JW. 2014. Geochemistry and LA-ICP-MS zircon U-Pb age of volcanic rocks of Wangguoshan Formation in the Gangmar Co area of Qiangtang, Tibet. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(11): 1702-1714 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C, Huang XP, Zhai QG, Zhu TX, Yu YS, Wang GH and Zeng QG. 2006. The Longmu Co-Shuanghu-Jitang plate suture and the northern boundary of Gondwanaland in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(4): 136-147 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C, Zhai QG, Dong YS, Zeng QG and Huang XP. 2007. Longmu Co-Shuanghu plate suture in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and records of the evolution of the Paleo-Tethyan Ocean in the Qiangtang area, Tibet, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(1): 13-21 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1109/TGRS.2007.894061 |
Li C, Zhai QG, Dong YS, Jiang GW, Xie CM, Wu YW and Wang M. 2008. Oceanic crust on the northern margin of Gondwana:Evidence from Early Paleozoic ophiolite in central Qiangtang, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(10): 1605-1612 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li C, Zhai GY, Wang LQ, Yin FG and Mao XC. 2009a. An important window for understanding the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau:A review on research progress in recent years of Qiangtang area, Tibet, China. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(9): 1169-1177 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1016/S1874-8651(10)60080-4 |
Li C, Xie YW, Dong YS, Qiangba ZX and Jiang GW. 2009b. Discussion on the age of Jitang Group around Leiwuqi area, eastern Tibet, China and primary understanding. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(9): 1178-1180 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Li HQ, Xu ZQ, Webb AAG, Li TF, Ma SW and Huang XM. 2017a. Early Jurassic tectonism occurred within the Basu metamorphic complex, eastern central Tibet:Implications for an archipelago-accretion orogenic model. Tectonophysics, 702: 29-41 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2017.02.016 |
Li S, Ding L, Guilmette C, Fu J, Xu Q and Yue Y. 2017b. The subduction-accretion history of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean:Constraints from provenance and geochronology of the Mesozoic strata near Gaize, central Tibet. Tectonophysics, 702: 42-60 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2017.02.023 |
Li SM, Zhu DC, Wang Q, Zhao ZD, Sui QL, Liu SA, Liu D and Mo XX. 2014. Northward subduction of Bangong-Nujiang Tethys:Insight from Late Jurassic intrusive rocks from Bangong Tso in western Tibet. Lithos, 205: 284-297 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2014.07.010 |
Liu H, Wang BD, Chen L, Li XB and Wang LQ. 2015. Early Carboniferous subduction of Lungmu Co-Shuanghu Paleo-Tethys Ocean:Evidence from island arc volcanic rocks in Riwanchaka, Central Qiangtang. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(2-3): 274-282 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu HF and Liu Y. 2009. Garnet glaucophane blueschist from Pana:Implications to Tibetan tectonic evolution. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 28(3): 199-214 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu Y, Santosh M, Zhao ZB, Niu WC and Wang GH. 2011. Evidence for Palaeo-Tethyan oceanic subduction within central Qiangtang, northern Tibet. Lithos, 127(1-2): 39-53 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2011.07.023 |
Liu YS, Hu ZC, Zong KQ, Gao CG, Gao S, Xu J and Chen HH. 2010. Reappraisement and refinement of zircon U-Pb isotope and trace element analyses by LA-ICP-MS. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(15): 1535-1546 DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-3052-4 |
Ludwig KR. 2003. Isoplot/Ex Version 3.00: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley Geochronology Center, Special Publication, No.4: 1-73
|
Middlemost EAK. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3-4): 215-224 DOI:10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9 |
Mo XX and Pan GT. 2006. From the Tethys to the formation of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau:Constrained by tectono-magmatic events. Earth Science Frontiers, 13(6): 43-51 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1007/s11442-006-0415-5 |
Pan GT, Li XZ, Wang LQ, Ding J and Chen ZL. 2002. Preliminary division of tectonic units of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its adjacent regions. Geological Bulletin of China, 21(11): 701-707 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Pan GT. 2004. Geological Map of Qinghai-Xizang (Tibet) Plateau and Adjacent Areas. Chengdu: Chengdu Cartographic Publishing House, 1-133 (in Chinese)
|
Pearce JA. 1983. Role of the sub-continental lithosphere in magma genesis at active continental margins. In: Hawkesworth CJ and Norry MJ (eds.). Continental Basalts and Mantle Xenoliths. Nantwich, Cheshire: Shiva Publications, 230-249
|
Pearce JA and Peate DW. 1995. Tectonic implications of the composition of volcanic arc magmas. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 23: 251-285 DOI:10.1146/annurev.ea.23.050195.001343 |
Pearce JA. 2014. Immobile element fingerprinting of ophiolites. Elements, 10(2): 101-108 DOI:10.2113/gselements.10.2.101 |
Qiu JQ, Qiangba ZX, Xie YW and Cui YQ. 2015. Tectostratigraphical division of the Jitang rock group in the Leiwuqi region of eastern Tibet, China and the main evidence. Journal of Geology, 39(1): 1-6 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Ren JS and Xiao LW. 2004. Lifting the mysterious veil of the tectonics of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau by 1:250000 geological mapping. Geological Bulletin of China, 23(1): 1-11 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1007/BF02873097 |
Saunders AD, Storey M, Kent RW and Norry MJ. 1992. Consequences of plume-lithosphere interactions. Geological Society London Special Publications, 68(1): 41-60 DOI:10.1144/GSL.SP.1992.068.01.04 |
Sha SL, Xie YW, Peng DP, Chen YM, Liu XL and Zhang N. 2012. A brief discussion of the Jitang Group in Eastern Tibet. Geology and Exploration, 48(4): 768-774 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Shi C. 2011. Study on the deformation features and the metamorphic-deformation stage of the Jitang rock group in the eastern segment of northern Qiangtang, Tibet. Master Degree Thesis. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 1-59 (in Chinese)
|
Shi C, Li RS, He SP, Wang C, Pan SJ, Zhang HD and Gu PY. 2012. Zircon U-Pb dating, geochemical and geological significances studies for gneissic biotite monzogranite in Riwoqe County, Tibet. Xinjiang Geology, 30(4): 456-464 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Stern RJ, Fouch MJ and Klemperer SL. 2004. An overview of the Izu-Bonin-Mariana subduction factory. In: Eiler J (ed.). Inside the Subduction Factory. Geophysical Monograph Series. Washington: AGU, 175-222
|
Sun SS and McDonough WF. 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Sanders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 42(1): 313-345
|
Tao Y, Bi XW, Li CS, Hu RZ, Li YB and Liao MY. 2014. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic significance of the Jitang granitic pluton in eastern Tibet, SW China. Lithos, 184-187: 314-323 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2013.10.031 |
Wang BD, Wang LQ, Qiangba ZX, Zeng QG, Zhang WP, Wang DB and Cheng WH. 2011. Early Triassic collision of northern Lancangjiang suture:Geochronological, geochemical and Hf isotope evidences from the granitic gneiss in Leiwuqi area, East Tibet. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 27(9): 2752-2762 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wang BD, Wang LQ, Chung SL, Chen JL, Yin FG, Liu H, Li XB and Chen LK. 2016. Evolution of the Bangong-Nujiang Tethyan Ocean:Insights from the geochronology and geochemistry of mafic rocks within ophiolites. Lithos, 245: 18-33 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.07.016 |
Wang LQ, Pan GT, Li C, Dong YS, Zhu DC, Yuan SH and Zhu TX. 2008. SHRIMP U-Pb zircon dating of Eopaleozoic cumulate in Guoganjianian Mt. from central Qiangtang area of northern Tibet:Considering the evolvement of Proto-and Paleo-Tethys. Geological Bulletin of China, 27(12): 2045-2056 |
Wang YX, Liang X, Wang GH, Yuan GL and Bons PD. 2018. Mayer Kangri metamorphic complexes in Central Qiangtang (Tibet, western China):Implications for the Triassic-Early Jurassic tectonics associated with the Paleo-Tethys Ocean. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 107(2): 757-776 DOI:10.1007/s00531-017-1526-1 |
Wilson BM. 1989. Igneous Petrogenesis: A Global Tectonic Approach. Netherlands: Springer, 11-40
|
Winchester JA and Floyd PA. 1977. Geochemical discrimination of different magma series and their differentiation products using immobile elements. Chemical Geology, 20: 325-343 DOI:10.1016/0009-2541(77)90057-2 |
Wood DA. 1980. The application of a Th-Hf-Ta diagram to problems of tectonomagmatic classification and to establishing the nature of crustal contamination of basaltic lavas of the British Tertiary volcanic province. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 50(1): 11-30 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(80)90116-8 |
Woodhead JD, Eggins SM and Johnson RW. 1998. Magma genesis in the New Britain Island Arc:Further insights into melting and mass transfer processes. Journal of Petrology, 39(9): 1641-1668 DOI:10.1093/petroj/39.9.1641 |
Wu H. 2016. Multiple stages of magmatism from ~375 to ~200Ma in central Qiangtang, Tibet: Constraints on subduction and the timing of closure of the Longmu Co-Shuanghu-Langcangjiang Ocean. Ph. D. Dissertation. Changchun: Jilin University, 1-153 (in Chinese)
|
Wu H, Xie CM, Li C, Wang M, Fan JJ and Xu WL. 2016. Tectonic shortening and crustal thickening in subduction zones:Evidence from Middle-Late Jurassic magmatism in Southern Qiangtang, China. Gondwana Research, 39: 1-13 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2016.06.009 |
Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Li HB, Zhang JX and Wu CL. 2007. Orogenic Plateau:Terrane Amalgamation, Collision and Uplift in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-458 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Xu ZQ, Yang JS, Li HB, Ji SC, Zhang ZM and Liu Y. 2011. On the tectonics of the India-Asia collision. Acta Geologica Sinica, 85(1): 1-33 (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI:10.1111/j.1755-6724.2011.00375.x |
Xu ZQ, Dilek Y, Cao H, Yang JS, Robinson P, Ma CQ, Li HQ, Jolivet M, Roger F and Chen XJ. 2015. Paleo-Tethyan evolution of Tibet as recorded in the East Cimmerides and West Cathaysides. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 105: 320-337 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2015.01.021 |
Zeng M, Zhang X, Cao H, Ettensohn FR, Cheng WB and Lang XH. 2016. Late Triassic initial subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean beneath Qiangtang revealed:Stratigraphic and geochronological evidence from Gaize, Tibet. Basin Research, 28(1): 147-157 DOI:10.1111/bre.12105 |
Zeng QG, Wang BD, Qiangba ZX, Nima CR and Li H. 2010. Zircon Cameca U-Pb dating of granitoid gneisses in the Leiwuqi area of the eastern Tibet, China, and its geological implication. Geological Bulletin of China, 29(8): 1123-1128 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai QG, Wang J, Li C and Su L. 2010. SHRIMP U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic analyses of Middle Ordovician meta-cumulate gabbro in central Qiangtang, northern Tibetan Plateau. Science China (Earth Sciences), 53(5): 657-664 DOI:10.1007/s11430-010-0063-6 |
Zhai QG, Jahn BM, Zhang RY, Wang J and Su L. 2011. Triassic subduction of the Paleo-Tethys in northern Tibet, China:Evidence from the geochemical and isotopic characteristics of eclogites and blueschists of the Qiangtang block. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 42(6): 1356-1370 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.07.023 |
Zhai QG, Jahn BM, Su L, Wang J, Mo XX, Lee HY, Wang KL and Tang SH. 2013. Triassic arc magmatism in the Qiangtang area, northern Tibet:Zircon U-Pb ages, geochemical and Sr-Nd-Hf isotopic characteristics, and tectonic implications. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 63: 162-178 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.08.025 |
Zhai QG, Jahn BM, Wang J, Hu PY, Chung SL, Lee HY, Tang SH and Tang Y. 2016. Oldest Paleo-Tethyan ophiolitic mélange in the Tibetan Plateau. GSA Bulletin, 128(3-4): 355-373 DOI:10.1130/B31296.1 |
Zhai QG, Jahn BM, Li XH, Zhang RY, Li QL, Yang YN, Wang J, Liu T, Hu PY and Tang SH. 2017. Zircon U-Pb dating of eclogite from the Qiangtang terrane, north-central Tibet:A case of metamorphic zircon with magmatic geochemical features. International Journal of Earth Sciences, 106(4): 1239-1255 DOI:10.1007/s00531-016-1418-9 |
Zhang ZM, Dong X, Santosh M and Zhao GC. 2014. Metamorphism and tectonic evolution of the Lhasa terrane, Central Tibet. Gondwana Research, 25(1): 170-189 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.08.024 |
Zhu DC, Zhao ZD, Niu YL, Dilek Y, Hou ZQ and Mo XX. 2013. The origin and pre-Cenozoic evolution of the Tibetan Plateau. Gondwana Research, 23(4): 1429-1454 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.02.002 |
段瑶瑶, 李亚林, 段志明. 2016. 西藏羌塘地体南部多龙增生杂岩早三叠世辉长岩的发现及其地质意义. 地质通报, 35(6): 887-893. |
何世平, 李荣社, 于浦生, 辜平阳, 王超, 杨永成, 张维吉. 2012. 青藏高原北羌塘他念他翁山吉塘岩群酉西岩组时代的确定. 地质学报, 86(6): 985-993. |
胡培远, 李才, 吴彦旺, 解超明, 王明, 李娇. 2014. 龙木错-双湖-澜沧江洋的打开时限:来自斜长花岗岩的制约. 科学通报, 59(20): 1992-2003. DOI:10.1360/csb2014-59-20-1992 |
胡培远, 李才, 翟庆国, 王明, 解超明, 吴彦旺. 2016. 藏东类乌齐地区辉长岩:冈瓦纳大陆北缘晚古生代裂解的记录. 地质通报, 35(11): 1845-1854. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2016.11.007 |
江庆源, 李才, 解超明, 王明, 胡培远, 吴浩, 彭虎, 陈景文. 2014. 藏北羌塘冈玛错地区望果山组火山岩地球化学特征及LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年龄. 地质通报, 33(11): 1702-1714. |
李才, 黄小鹏, 翟庆国, 朱同兴, 于远山, 王根厚, 曾庆高. 2006. 龙木错-双湖-吉塘板块缝合带与青藏高原冈瓦纳北界. 地学前缘, 13(4): 136-147. |
李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 曾庆高, 黄小鹏. 2007. 青藏高原龙木错-双湖板块缝合带与羌塘古特提斯洋演化记录. 地质通报, 26(1): 13-21. |
李才, 翟庆国, 董永胜, 蒋光武, 解超明, 吴彦旺, 王明. 2008. 冈瓦纳大陆北缘早期的洋壳信息——来自青藏高原羌塘中部早古生代蛇绿岩的依据. 地质通报, 27(10): 1605-1612. |
李才, 翟刚毅, 王立全, 尹福光, 毛晓长. 2009a. 认识青藏高原的重要窗口——羌塘地区近年来研究进展评述(代序). 地质通报, 28(9): 1169-1177. |
李才, 谢尧武, 董永胜, 强巴扎西, 蒋光武. 2009b. 藏东类乌齐一带吉塘岩群时代讨论及初步认识. 地质通报, 28(9): 1178-1180. |
刘函, 王保弟, 陈莉, 李小波, 王立全. 2015. 龙木错-双湖古特提斯洋俯冲记录——羌塘中部日湾茶卡早石炭世岛弧火山岩. 地质通报, 34(2-3): 274-282. |
刘鸿飞, 刘焰. 2009. 旁那石榴蓝闪片岩特征及其构造意义. 岩石矿物学杂志, 28(3): 199-214. |
莫宣学, 潘桂棠. 2006. 从特提斯到青藏高原形成:构造-岩浆事件的约束. 地学前缘, 13(6): 43-51. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2006.06.007 |
潘桂棠, 李兴振, 王立全, 丁俊, 陈智粱. 2002. 青藏高原及邻区大地构造单元初步划分. 地质通报, 21(11): 701-707. |
潘桂棠. 2004. 青藏高原及邻区地质图. 成都: 成都地图出版社, 1-133.
|
邱军强, 强巴扎西, 谢尧武, 崔永泉. 2015. 藏东类乌齐地区吉塘岩群的构造地层解析及主要依据. 地质学刊, 39(1): 1-6. |
任纪舜, 肖黎薇. 2004. 1:25万地质填图进一步揭开了青藏高原大地构造的神秘面纱. 地质通报, 23(1): 1-11. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2004.01.006 |
沙绍礼, 谢尧武, 彭道平, 陈应明, 刘学龙, 张娜. 2012. 略谈藏东吉塘群. 地质与勘探, 48(4): 768-774. |
时超. 2011.羌北东段吉塘岩群构造变形样式及变质变形期次.硕士学位论文.北京: 中国地质大学(北京), 1-59
|
时超, 李荣社, 何世平, 王超, 潘术娟, 张海迪, 辜平阳. 2012. 西藏类乌齐片麻状黑云二长花岗岩锆石U-Pb定年、地球化学特征及地质意义. 新疆地质, 30(4): 456-464. |
王保弟, 王立全, 强巴扎西, 曾庆高, 张万平, 王冬兵, 程万华. 2011. 早三叠世北澜沧江结合带碰撞作用:类乌齐花岗质片麻岩年代学、地球化学及hf同位素证据. 岩石学报, 27(9): 2752-2762. |
吴浩. 2016.青藏高原羌塘中部375~200Ma多期次岩浆作用.博士学位论文.长春: 吉林大学, 1-153
|
许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 张建新, 吴才来. 2007. 造山的高原:青藏高原的地休拼合、碰撞造山及隆升机制. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-458.
|
许志琴, 杨经绥, 李海兵, 嵇少丞, 张泽明, 刘焰. 2011. 印度-亚洲碰撞大地构造. 地质学报, 85(1): 1-33. |
曾庆高, 王保弟, 强巴扎西, 尼玛次仁, 李虎. 2010. 藏东类乌齐地区花岗质片麻岩锆石Cameca U-Pb定年及其地质意义. 地质通报, 29(8): 1123-1128. |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36