2. 华北地质科技创新中心, 天津 300170;
3. 河北省区域地质矿产调查研究所, 廊坊 065000
2. North China Center for Geoscience Innovation, Tianjin 300170, China;
3. Institute Regional Geology and Mineral Resources of Hebei Province, Langfang 065000, China
中亚造山带位于西伯利亚板块、塔里木板块和华北板块之间,是典型的显生宙增生造山带(Șengör et al., 1993;吴福元等, 1999;Jahn et al., 2000, 2004;Badarch et al., 2002;Xiao et al., 2003; 洪大卫等,2003),是古亚洲洋及其众多微陆块长期演化的结果(Șengör et al., 1993)。兴蒙造山带位于中亚造山带东南缘(图 1),分布着众多由前寒武纪变质岩系组成的古老块体(邵济安和张履桥,1990;Gordienko,1996;李述靖等,1998;任纪舜等,1999;刘正宏等,2000;Kuzmichev, 2001;Khain et al., 2002, 2003;Pisarevsky and Natapov, 2003;Li, 2006;Rojas-Agramonte, 2011;徐备等,2014),对造山带格局及其形成演化具有重要影响,是造山带研究的热点问题之一。
|
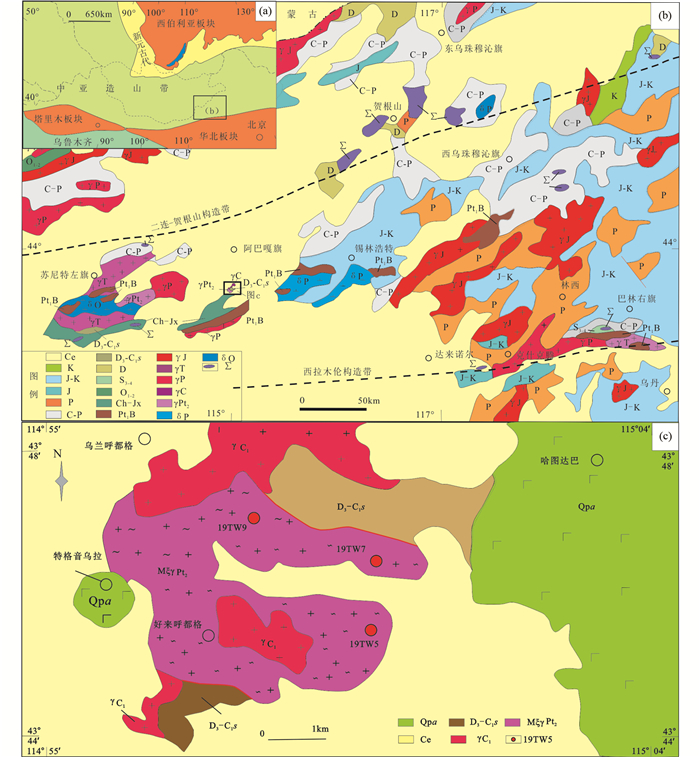
图 1 内蒙古中部地质简图(a, b, 据内蒙古自治区地质矿产局,1991修改)及采样位置(c) 图 1a, b中:Ce-新生界;K-白垩系陆相碎屑岩;J-K-侏罗-白垩系陆相火山岩夹碎屑岩;J-侏罗系碎屑岩;P-二叠系碎屑岩夹灰岩;C-P石炭-二叠系海相碎屑岩、灰岩夹火山岩;D3-C1s上泥盆统-下石炭统碎屑岩夹灰岩;D-泥盆系碎屑岩;S3-4-中-上志留统灰岩夹碎屑岩, O1-2-下-中奥陶统海相碎屑岩;Ch-Jx-长城-蓟县系碎屑岩夹含铁矿层;Pt1B-古元古代宝音图群石英岩、片岩、白云质大理岩;γJ-侏罗纪花岗岩;γT-三叠纪花岗岩;γP-二叠纪花岗岩;γPt2-中元古代花岗岩;δP-二叠纪闪长岩;δO-奥陶纪闪长岩;Σ-超基性岩.图 1c中:Qpa-新近系阿巴嘎玄武岩;D3-C1s-晚泥盆世-早石炭世碎屑岩夹灰岩;γC1-早石炭世花岗岩;MξγPt2-中元古代片麻状花岗岩;19TW5-样品号 Fig. 1 Geological sketch map of central Inner Mongolia (a, b, after BGMRN, 1991) and sampling location(c) |
内蒙古阿巴嘎旗地区位于中亚造山带东南缘,介于二连-贺根山构造带和索伦山-西拉木伦构造带之间(图 1a),大地构造上隶属于兴蒙造山带东段(内蒙古自治区地质矿产局,1991)。该地区是艾力格庙-锡林浩特微地块的主要残留区,为中亚造山带众多残存的微地块之一(邵济安和张履桥,1990;邵济安,1991;程裕琪,1994;李述靖等,1998;刘正宏等,2000;Li, 2006;徐备等,2014)。该地块发育绿片岩相-角闪岩相变质作用的中级变质岩系,主要岩石类型是石英岩、云母石英片岩、大理岩、黑云斜长片麻岩、长英质片麻岩等构成的表壳岩系,曾被称为“锡林郭勒杂岩”、或“宝音图群”(内蒙古自治区地质矿产局,1991)、“昌特敖包岩群”。其次还发育温都尔庙群,为经历蓝片岩相-绿片岩相变质的中浅变质岩系(内蒙古自治区地质矿产局,1996),主要岩石类型包括绢云石英片岩、绿泥石英片岩、蓝片岩、石英岩、含铁石英岩、变玄武岩、辉长岩和辉绿岩等,原岩以变质陆源碎屑-火山岩建造为主,形成时代为早古生代早期(徐备等,2016)。宝音图群作为锡林浩特地块的基底岩系,原岩形成时代为古元古代,角闪岩相变质作用发生在早古生代奥陶纪末期(内蒙古自治区地质矿产局,1991;李述靖和高德臻,1995;肖荣阁等,1995;刘敦一等,2003)。
该地区自中元古代至新生代岩浆活动频繁,发育大量花岗质岩石和火山岩。野外调查发现,其中一部分以片麻状花岗质岩石为主,经受区域变质作用改造,具有与宝音图群近于一致的片麻理构造,此类岩石变形、变质均较强烈,为地块结晶基底的组成之一。另一部分以变形弱、未变质变形的花岗岩、中酸性火山岩为主,多为早古生代岛弧和同碰撞岩浆岩、晚古生代岩浆岩和新生代大陆溢流玄武岩,其研究程度相对较高。
本区元古代岩浆活动鲜有发现,研究程度较低。近年来我们在苏尼特左旗地区片麻状花岗岩中获得了中元古代年龄(1.39~1.51Ga),反映锡林浩特地块存在中元古代裂解事件的岩浆记录(孙立新等, 2013, 2018)。笔者最新的野外调查发现,阿巴嘎旗南部同样分布着与苏尼特左旗一带相同的元古代片麻状正长花岗岩体,为了查明其时代和地球化学特征,笔者进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb年代学、岩石学、地球化学和锆石Hf同位素研究,并结合兴蒙造山带及前寒武纪研究的区域资料,探讨其岩石成因以及大地构造意义。
1 岩体地质特征阿巴嘎旗南部片麻状花岗岩体,位于阿巴嘎旗南部约35km处,中心地理坐标为N43°46′、E115°59′,出露面积约9.2km2;北东侧、西南侧与晚泥盆-早石炭世色日巴彦敖包组呈断层接触,周围被早石炭世花岗岩侵入(图 2e),其局部被第四系阿巴嘎玄武岩覆盖(图 1b)。

|
图 2 片麻状花岗岩野外(a、c、e)和正交显微镜下照片(b、d、f) (a)片麻状正长花岗岩露头照片;(b、d)片麻状正长花岗岩显微照片;(c)正长花岗岩不均一条带片麻状构造;(e)早石炭世花岗岩侵入中元古代片麻状正长花岗岩;(f)片麻状正长花岗岩中的条纹长石.Q-石英;Bi-黑云母;Mi-微斜长石;Per-条纹长石;Pl-斜长石 Fig. 2 Photographs of the outcrops (a, c, e) and photomicrographs of the samples (b, d, f) from gneissic granitiods |
片麻状花岗岩由浅红色弱片麻状中细粒正长花岗岩、混合花岗质片麻岩以及弱条带状片麻状中粗正长花岗岩等组成。露头上条带或片麻状正长花岗岩具有弱的混合岩化,普遍发育条带状片麻理构造(图 2a),由长英质石英和长石浅色条带与黑云母组成的暗色条带相间排列构成,长英质条带宽0.3~0.5cm,长10~30cm,边界模糊不清;暗色条带宽0.5~1.5cm, 长约30~50cm,具有变质分异条带特点(图 2a, c)。片麻理总体近东西向,产状近于直立。弱片麻状中粗粒二长花岗岩岩石相对均匀,局部发育弱的片麻状构造,不具有变质分异条带特征,岩石成分单一,主要为长英质成分,少量黑云母。
片麻状正长花岗岩:岩石新鲜面为浅红色,中粒-中粗粒半自形粒状结构(图 2b),局部可见似斑状结构,条纹状-弱片麻状构造。主要矿物为石英(25%~30%)、钾长石(微斜长石)(30%~40%)、条纹长石(15%~20%)、斜长石5%~10%,以及少量黑云母(约5%)。长石类矿物多为半自形板状,粒径2~3mm,其中,微斜长石则具有格子双晶特征(图 2d),微斜长石内部多发生了轻微的绢云母化蚀变。条纹长石具细条带状、叶脉状条纹结构(图 2f)。斜长石为半自形板状,发育聚片双晶和卡钠复合双晶结构,粒径多为1~2mm。石英多为他形粒状。黑云母为半自形片状,呈集合体。副矿物可见磷灰石、锆石、榍石等。
2 样品及分析方法 2.1 主量、微量元素本文对采自阿巴嘎旗(图 1)新鲜样品,进行了主量和微量元素测定,测试在天津地质调查中心实验室完成。主量元素采用PW4400/40X-射线荧光光谱法(XRF)测试,Fe2O3、FeO应用氢氟酸硫酸溶样、重铬酸钾滴定容量法测定,分析精度优于2%,微量元素使用Thermo Fisher X series-Ⅱ等离子体质谱仪(MC-ICP)测试,分析精度优于5%。
2.2 锆石U-Pb测年阿巴嘎旗片麻状花岗岩样品锆石挑选由河北省区域地质调查研究所实验室采用常规方法选取,制靶、锆石透射、反射、阴极发光照相天津地质调查中心实验室完成,锆石U-Pb年龄以及Lu-Hf同位素分析采用LA-MC-ICP-MS仪器,由New Wave的193nm激光器剥蚀系统和Thermo Fisher的Neptune型多接收等离子质谱仪完成,采用的激光剥蚀的束斑直径为35μm,进行锆石U-Pb同位素测定,采用TEMORA作为外部锆石年龄标准。利用NIST612玻璃标样作为外标计算锆石样品的Pb、U、Th含量,详细的实验原理和流程参见文献(Liu Y S et al., 2010)。采用ICP-MS DataCal程序和Isoplot(ver3.0)程序(Ludwig, 2003)进行数据处理。
2.3 锆石Hf同位素分析锆石Lu-Hf同位素测试在天津地质矿产研究所实验室完成,采用配有193nm的LA-MC-ICP-MS仪器上进行,分析时采用8~10Hz的激光频率、100mJ的激光强度和50μm的激光束斑直径。激光剥蚀物质以He为载气送入Neptune,采用GJ-1作为监控标样,具体测试过程见耿建珍等(2011)。为使Hf同位素分析与锆石U-Pb年龄分析相对应,锆石Hf分析点与锆石U-Pb年龄分析点位于同一颗粒相同锆石晶域内,计算Hf同位素的相关参数时,采用同一颗粒锆石测得的U-Pb年龄。在计算176Lu的衰变常数采用1.865×10-11/y(Scherer et al., 2001; Li et al., 2007)。球粒陨石的176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf的比值分别为0.0332和0.282772(Blichert-Toft and Albarède, 1997;吴福元等,2007),亏损地幔的176Lu/177Hf和176Hf/177Hf的比值分别为0.0384和0.28325(Griffin et al., 2000),二阶段模式年龄分别采用平均地壳的Lu/Hf=-0.55, (176Lu/177Hf)平均地壳为0.015(Griffin et al., 2002; Söderlund et al., 2004)。
3 测试结果 3.1 锆石U-Pb年龄本文对阿巴嘎旗南部片麻状花岗岩体中的3件样品进行了LA-ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年,采样位置(图 1c)分别为19TW5(N43°45.87′、E114°59.24′)、19TW07(N43°46.86′、E114°59.12′)和19TW9(N43°46.93′、E114°58.39′),测年分析结果见表 1。
|
|
表 1 片麻状花岗岩LA- ICP-MS锆石U-Pb测年数据 Table 1 Zircon LA-ICP-MS U-Pb data of gneissic granites |
片麻状正长花岗岩3件样品(19TW5、19TW7、19TW9)的锆石特征基本一致,多为无色或浅桔黄色的透明至半透明的短柱状、长柱状晶体,粒径多在150~200μm之间,晶面光滑,晶棱平直,长宽比2:1,锆石类型相对单一。阴极发光图像显示出清晰的环带结构(图 3),且锆石的Th/U为0.49~0.98,均大于0.4(表 1),指示它们为典型的岩浆结晶锆石。

|
图 3 片麻状花岗岩样品锆石阴极发光(CL)图像和锆石U-Pb同位素年龄谐和图 锆石CL图中实圆圈为锆石测年点、白点为锆石Hf同位素测点 Fig. 3 Zircon CL images and U-Pb concordia plots of the gneissic granites |
样品19TW5锆石共测得25个有效测试点数据(表 1),在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上(图 3b),绝大多数测点皆位于在谐和线上,25个测点的207Pb/206U年龄变化于1327~1414Ma之间,个别2个点偏离谐和线构成不一致线,计算获得207Pb/206Pb的统计权重平均值为1380±21Ma(MSWD=0.15),代表片麻状正长花岗岩形成的年龄。样品19TW7锆石共测得23个有效测试点数据(表 1),23个测点的207Pb/206U年龄变化于1352~1407Ma之间,在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上(图 3d),21个测点皆位于谐和线上,2个点偏离谐和线铅丢较为失严重,计算获得207Pb/206Pb的统计权重平均值为1385±14Ma(MSWD=0.46),可代表片麻状正长花岗岩形成的年龄。样品19TW9共测得锆石24个有效测试点数据(表 1),与19TW7年龄特征近于一致,锆石微区记录的207Pb/206Pb年龄变化于1349~1396Ma之间。在206Pb/238U-207Pb/235U谐和图上(图 3f),除1个点偏离谐和线外,其他点皆位于谐和线上或谐和线附近,去除谐和度不理想的1个点,23个分析点计算获得207Pb/206Pb的统计权重平均值为1377±10Ma(MSWD=0.32)(图 3),代表片麻状正长花岗岩的形成时代。
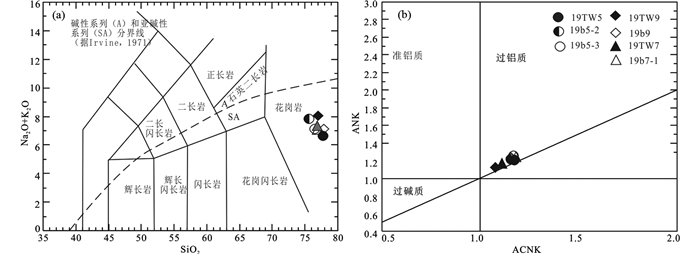
3.2 地球化学特征 3.2.1 主量元素阿巴嘎旗南部好来呼都格片麻状正长花岗岩7件样品的主元素和微量元素分析结果见表 2,其主量元素特征为:高SiO2(76.05%~78.16%)、低TiO2 (0.17%~0.23%)、低A12O3(10.99%~11.97%)和低MgO(0.08%~0.44%);FeO+Fe2O3为1.53%~2.82%;FeOT/MgO比值较高,为4.51~26.64,平均14.06;贫CaO(0.15%~0.37%)、Na2O(2.25%~3.49%)、K2O(3.36%~5.59%);高碱(K2O+Na2O=6.69%~8.04%),较高的K2O/Na2O (1.01~2.48),Na2O < K2O,岩石富钾,里特曼指数σ=1.28~1.88,大多数小于1.8,为钙性系列,碱性程度中等到强。片麻状花岗岩总体显示出高硅、富碱、贫钙、低镁的特征。在岩石分类TAS图(图 4a)中样品均落入花岗岩区,呈亚碱性。片麻花岗质岩石的铝饱和指数A/CNK为1.10~1.17,均大于1.1,为过铝质系列。在A/CNK-A/NK图中(图 4b)样品均落入过铝质区。
|
|
表 2 片麻状花岗岩主量(wt%)、微量和稀土元素(×10-6)含量 Table 2 Major (wt%) and trace element (×10-6) contents of gneissic granites |
|
图 4 片麻状花岗岩的化学分类TAS图(a, 据Middlemost, 1994)及A/CNK-A/NK图解(b, 据Chappell and White, 1974) Fig. 4 Chemical classification of gneissic granites (a, after Middlemost, 1994; b, after Chappell and White, 1974) |
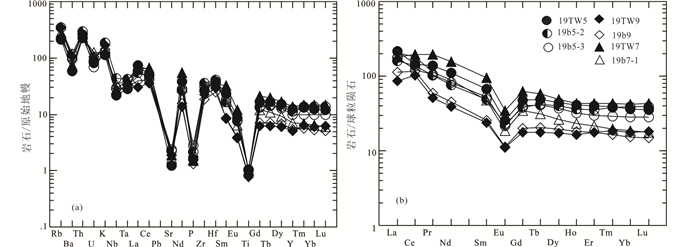
片麻状正长花岗岩微量元素(表 2)中的大离子亲石元素Rb、Ba含量较高,Rb为136×10-6~223×10-6、Ba含量为402×10-6~816×10-6、Rb/Sr=2.70~5.50,相对均一,变化不大。原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图中(图 5a)片麻状正长花岗岩表现出富集Rb、Th、U、La、Ce、Zr、Hf等高场强元素,亏损Ba、Sr、P、Eu和Ti的负异常特征(图 5a),其微量元素标准化图与铝质A型花岗岩较为一致,暗示了长石、磷灰石以及榍石、角闪石、黑云母等矿物的分离结晶作用。
|
图 5 片麻状花岗岩原始地幔标准化微量元素蛛网图(a)和球粒陨石标准化稀土元素配分图(b)(标准化值据Sun and McDonough, 1989) Fig. 5 Primitive mantle-normalized trace element spider diagrams (a) and chondrite-normalized REE patterns (b) (normalization values after Sun and McDonough, 1989) of gneissic granites |
片麻状正长花岗岩的稀土总量较高(表 2),∑REE(127.7×10-6~346.2×10-6),稀土分布曲线形状相似,都具有相近的轻稀土富集趋势(图 5b),LREE/HREE (5.35~9.40)为分异作用明显轻稀土富集型;δEu为(0.44~0.53)显示明显负异常。(La/Sm)N介于3.22~4.43,(La/Yb)N介于4.10~10.96,反映轻稀土分馏程度明显高于重稀土分馏程度。岩石稀土元素球粒陨石标准化配分图中呈相似的右倾稀土配分曲线(图 5b)。
3.2.3 锆石Lu-Hf同位素在LA-ICP-MS锆石定年基础上,选择19TW5、19TW9样品在每个测年点的锆石上进行了锆石微区Lu-Hf同位素分析,其结果列于表 3。表 3中绝大部分锆石的176Lu/177Hf值小于0.002,表明锆石没有放射性成因Hf的积累,所测样品的176Lu/177Hf值可以代表其形成时体系的Hf同位素组成(吴福元等,2007)。
|
|
表 3 样品Lu-Hf同位素分析数据和相关的特征参数 Table 3 Lu-Hf isotopic data and related parameters |
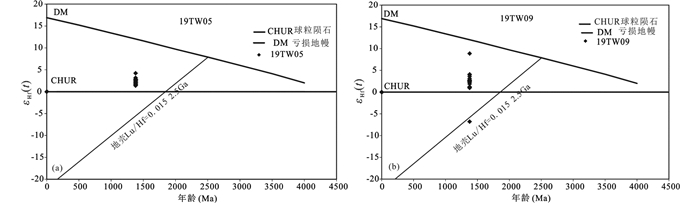
样品19TW5共分析了23个Hf同位素测点,所测锆石的176Yb/177Hf和176Lu/177Hf比值范围分别为0.0337~0.0747、0.0011~0.0021(表 3)。图 6a显示锆石点集中于球粒陨石演化线上方,样品19TW5所测23颗锆石的Hf同位素相对比较均一,其中176Hf/177Hf比值变化于0.281984~0.282058,加权平均值为0.2820198±0.000007;Hf同位素初始比值176Hf/177Hfi分布在0.281952~0.282028之间,平均值为0.281978;εHf(t)变化于1.4~4.6,平均为2.42,εHf(t)均为正值,指示来源于新生的年轻地壳。单阶段模式年龄tDM变化范围为1.69~1.81Ga,平均为1.76Ga。两阶段模式年龄t2DM变化范围为1.88~2.07Ga,t2DM远大于其形成年龄。样品19TW9共分析了20个点,所测锆石的176Yb/177Hf和176Lu/177Hf比值范围分别为0.0254~0.0721,0.0009~0.0026(表 3)。图 6b显示锆石点也集中于球粒陨石演化线上方,具有与19TW5样品相同的Lu-Hf同位素特征,Hf同位素初始比值176Hf/177Hfi分布在0.281938~0.282161之间,平均值为0.281975;除5号点外,其他锆石测点εHf(t)变化于0.5~8.9,平均为2.77,εHf(t)均为正值,指示岩浆可能来源于古元古代新增生地壳的部分熔融。单阶段模式年龄tDM变化范围为1.51~1.82Ga,平均为1.75Ga。两阶段模式年龄变化范围为1.58~2.08Ga。t2DM远大于其形成年龄,其中εHf(t)为最大正值8.9时,单阶段模式年龄和二阶段模式年龄与岩石形成年龄近于一致,表明在1.40Ga前后存在一次地壳增生事件。
|
图 6 片麻状花岗岩锆石U-Pb年龄与εHf(t)相关图 Fig. 6 Plots of zircon U-Pb age vs. εHf(t) for the gneissic granite |
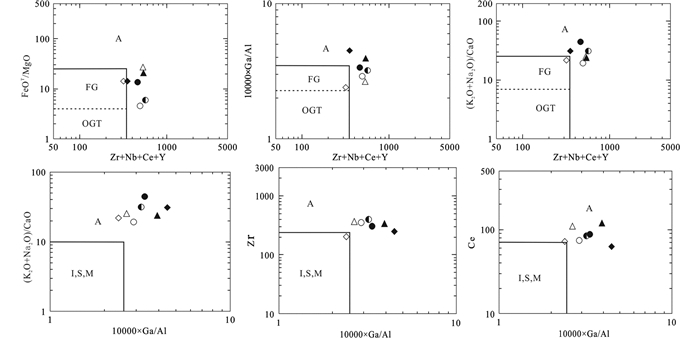
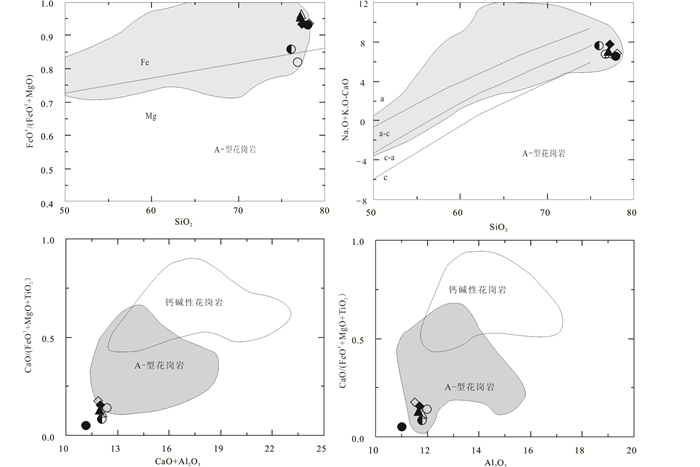
阿巴嘎旗南部中元古代片麻状正长花岗岩类为钙性过铝质岩石,矿物组合以石英、钾长石(条纹长石、微斜长石)和黑云母为主,其较高的SiO2和K2O+Na2O、低CaO、MgO、P2O5、TiO2和MnO,高场强元素(HFSE)如Th、U、Zr、Hf相对于大离子亲石元素(LILE)明显富集,富集Rb和REE等,明显亏损Ba、Sr、Ti、P、Eu等元素,显示A型花岗岩特征。铝饱和指数A/CNK值(1.10~1.17),显示为过铝质花岗岩;具有较高的Na2O+K2O=6.69%~8.04%、FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)比值和高Zr+Nb+Ce+Y含量、10000Ga/Al= 3.17~6.13,平均4.43高于A型花岗岩的平均值2.6,与King et al. (1997)定义的铝质A型花岗岩相似。这些地球化学特征显示其具有A型花岗岩特征。在Zr+Nb+Ce+Y和10000×Ga/Al的图解中(图 7),它们的投点均落入A型花岗岩区(Whalen et al., 1987;Frost and Frost, 2011)。同样在SiO2与FeOT/(FeOT+MgO)和Na2O+K2O-CaO图(Frost and Frost, 2011)以及CaO/(FeOT+MgO+TiO2)与(Al2O3+CaO)和Al2O3构建的判别图解中(Dall’Agnol和De Oliveira,2007),绝大部分投点也落入A型花岗岩区(图 8)。
|
图 7 片麻状花岗岩的A型花岗岩判别图解(据Whalen et al., 1987) 图 7-图 9样品图例同图 4.OGT代表未分异的I型,S型,M型,A型花岗岩; FG代表高分异的I型; A代表A型花岗岩 Fig. 7 Discrimination diagrams of A-type granite for gneissic granites (after Whalen et al., 1987) |
|
图 8 片麻状花岗岩全岩SiO2与FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) (a)和SiO2与Na2O+K2O-CaO图解(b)(据Frost and Frost, 2011)及CaO/(FeOT+MgO+TiO2)与(Al2O3+CaO)(c)和Al2O3图解(d)(据Dall’Agnol and De Oliveira,2007) Fig. 8 Whole-rock SiO2 vs. FeOT/(FeOT+MgO) (a) and SiO2 vs. Na2O+K2O-CaO (b) (after Frost and Frost, 2011), CaO/(FeOT+MgO+TiO2) vs.(Al2O3+CaO)(c) and CaO/(FeOT+MgO+TiO2) vs. Al2O3 (d) (after Dall'Agnol and De Oliveira, 2007) |
在成岩温度方面,A型花岗岩比I型和S型具有较高的成岩温度,锆石饱和温度计算出的结晶温度大于800℃(刘昌实等,2003),而岩石学实验表明其形成温度可能超过900℃。A型花岗岩具有高温属性,采用Watson and Harrison (1983)的方法估算了中元古代片麻状花岗岩的形成温度在826~890℃之间,平均为865℃(表 2)。
4.2 岩石源区花岗岩锆石原位Hf同位素组成,由于锆石极高的稳定性和封闭温度,使得其Lu-Hf同位素体系较少受后期构造热事件的影响,即便在麻粒岩相等高级变质条件下,所测锆石的176Hf/177Hf比值仍能很好反映其形成时体系的Hf同位素组成,甚至可记录岩浆源区不同源岩类型的特征(Scherer et al., 2001;Griffin et al., 2002;吴福元等,2007)。正的εHf(t)值代表来自亏损幔源物质或新生地壳的部分熔融,负的εHf(t)值指示来自于古老陆壳岩石源区,如果存在较大变化范围的εHf(t),可揭示其源区不同性质源岩物质存在的信息(Kröner et al., 2014)。本文片麻状正长花岗岩锆石具有较高的176Hf/177Hf比值(0.281987~0.282258),依形成年龄(1380Ma)计算获得的εHf(t)值均为正值(+0.5~+8.9),在t-εHf(t)图解上所有成分点落在球粒陨石演化线以上靠近亏损地幔演化线的区域(图 6a,b),其二阶段模式年龄tDM2 =1.5~2.08Ga,指示它们主要来自古元古代末期新生地壳物质的部分熔融。当εHf(t)为最大+8.9时,单阶段模式年龄t1DM和t2DM年龄近于一致,与岩石形成年龄相近,表明在~1.4Ga时存在一次地壳增生事件。
4.3 大地构造意义A-型花岗岩作为花岗岩的一种重要成因类型,其成因分类、岩浆起源、大地构造背景及其地球动力学意义备受关注(Loiselle et al., 1979;Collins et al., 1982;Whalen et al., 1987;Eby, 1990, 1992;胡受奚等,1991;洪大卫等,1995;Hong et al., 1996;刘昌实等,2003)。A型花岗岩为“非造山、碱性和贫水的花岗岩”,具有富碱、高Fe/(Fe+Mg)、Rb/Sr、HFSE,低Ca、Fe、Mg,强烈亏损Eu、Sr、Ba、P、Ti的特点(King et al., 1997;Collins et al., 1982);按成分特点分为铝质和过碱性两类,其成因观点多样(Collins et al., 1982;Bonin, 2007)。虽然两类A型花岗岩在岩石学和地球化学上各具特色,但其形成环境均与伸展作用有关(Frost and Frost, 1997,2011; Frost et al., 1999),常用于陆壳伸展环境的岩石学判据。其形成环境分非造山型和后造山型,前者主要包括地幔柱和板内裂谷等,形成于板内,其源岩接近于洋岛玄武岩;后者包括弧后伸展和造山后伸展等,形成于陆-陆碰撞的后造山环境,源岩接近于大陆壳或底侵垫托的下地壳侵入岩。
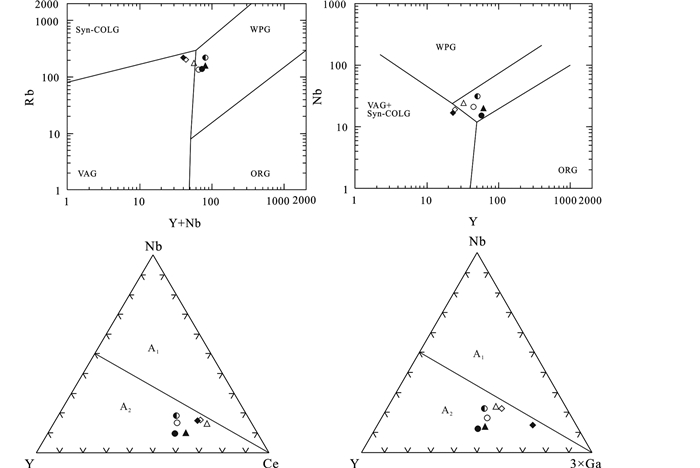
Eby (1992)将A型花岗岩划分为非造山与裂谷环境有关的A1型花岗岩和造山后构造环境形成的A2型花岗岩。在A1-A2分类判别图中(图 9),中元古代片麻状花岗岩类具有较高的Ce/Nb、Y/Nb和Yb/Ta比值,均落入A2区域,指示中元古代片麻状花岗岩类的形成构造背景与伸展作用密切相关。在Pearce et al. (1984)花岗岩Nb-Y和Rb-(Y+Nb)判别图解中落入与后碰撞花岗岩环境有关的区域(图 9)。
|
图 9 中元古代片麻状花岗岩的Rb-(Nb+Y)和Nb-Y (a, b, 据Pearce et al., 1984)及A1-A2分类(c, d, 据Eby, 1992)判别 WPG-板内花岗岩; ORG-洋脊花岗岩; VAG-火山弧花岗岩; syn-COLG and post-COLG-同碰撞/碰撞后花岗岩. A1型代表来源于幔源熔体的分离结晶; A2型代表来源于地壳部分熔源区 Fig. 9 Diagrams of Rb vs. (Nb+Y) and Nb vs. Y (a, b, after Pearce et al., 1984) and A1-A2 classification discriminant (c, d, after Eby, 1992) for the Mesoproterozoic gneissic granite |
中元古代的岩浆活动在全球范围分布十分广泛,由斜长岩-辉长岩及纹长二长岩与花岗岩类组成的“环斑花岗岩-斜长岩岩套”,从东端的西伯利亚及华北板块(1.70~1.60Ga左右)向西延至东欧板块和波罗的海地盾(1.65~1.54Ga),穿过格陵兰南部,直至北美大陆的拉布拉多地区及美国中西部(1.49~1.2Ga),在北半球组成一个近东西向的巨型岩带(Dickin et al., 1992; Åhäll and Connelly, 1998; Anderson and Cullers, 1999; Haapala and Rämö, 1999;Corrigan et al., 2000; Blein et al., 2003),包括被称之为1.4Ga的岩浆活动带,它沿着劳伦古陆(Laurentia)太古宙克拉通的外侧边缘地带分布(Nyman et al., 1994;胡霭琴等,2006)。在中亚造山带中多个微陆块内也存在1.4Ga岩浆事件,如哈萨克斯坦板块(Konopelko et al., 2012)、中天山地块(胡霭琴等,2006;施文翔等,2010; He et al., 2015;贺振宇等,2015)、阿拉善地块(史兴俊等,2016;王毛毛等,2019)、锡林浩特地块(孙立新等, 2013, 2018);在中亚造山带周缘克拉通中,东欧板块也具有该时期构造岩浆记录,如Sveco-Fennian, Trans-Scandinavian和Gothian等构造带(Cawood et al., 2007; Kuznetsov et al., 2010)。华北板块南北缘同样也存在该时期构造热事件的记录(邵济安等, 2002, 2005), 例如在高于庄组(李怀坤等,2009)和铁岭组斑脱岩夹层(苏文博等,2010)及下马岭组辉绿岩床(李怀坤等,2009;Zhang et al., 2012),都与中元古代燕辽裂陷槽形成的构造背景有关,也是Columbia超大陆中元古代裂解事件的响应(Lu et al., 2002; 翟明国和彭澎,2007; 翟明国等, 2014)。综上所述,~1.4Ga构造岩浆记录对揭示造山带微地块的来源及其形成的构造环境具有重要的意义。
目前,中元古代1.4Ga岩浆活动形成于两者截然不同的构造环境,一种形成于板缘挤压背景,具有造山作用的岩浆活动和变质作用特点(Dickin et al., 1992; Nyman et al., 1994);另一种形成于非造山构造背景,由大规模的地幔上涌导致拉斑质下地壳的部分熔融形成(Frost et al., 1997, 1999; Barnes et al., 2002; Vigneresse, 2005)。研究表明Columbia超大陆的汇聚可能是在2.1~1.8Ga发生的全球性碰撞造山事件中完成,而裂解可能开始于1.7Ga,结束于1.3~1.2Ga(Zhao et al., 2002, 2003a, b,2004, 2005),但全球不同块体的裂解历史有较大的差异,其间发生了大量中元古代造山后-非造山阶段的非造山岩浆活动及镁铁质岩墙群的侵入(Hou et al., 2008; Goldberg, 2010)。华北板块南、北缘已发现的辉绿岩岩床(1.35Ga; Zhang et al., 2009)、钾质斑脱岩(1.37Ga; Su et al., 2008)、正长岩(1.35Ga)及~1.31Ga的A型花岗岩和1.3~1.2Ga基性岩墙群(Hou et al., 2008)等,说明中元古代中期整个华北克拉通处于大陆伸展构造环境。而锡林浩特微地块苏尼特左旗、阿巴嘎旗一带中元古代(~1.4Ga前后) A型花岗岩的发现,进一步说明中元古代中期锡林浩特地块也存在伸展作用的岩浆记录,与Columbia超大陆裂解事件在时代上基本一致,岩石为中元古代时期大陆裂解过程中的产物,可能与Columbia超大陆裂解(1.5~1.3Ga)有关。
5 结论(1) 锆石U-Pb年代学结果表明本文报道的阿巴嘎旗中元古代片麻状花岗岩形成于1377~1385Ma.;Hf同位素结果表明其岩浆来源于古元古代新增生地壳的部分熔融。
(2) 中元古代片麻状花岗岩类具有高硅、高碱(K2O+Na2O)、富铁、贫镁、钙和富集高场强元素等特征,并具有较高的铝过饱和指数(ACNK=1.1~1.28)、较高的10000Ga/Al比值和较明显的δEu负异常等特征,表明岩石属于铝质A型花岗岩,岩石形成温度为826~890℃,平均865℃。
(3) 阿巴嘎旗一带中元古代A型花岗岩与中亚造山带中的中天山、阿拉善等微地块具有相同或基本一致的构造岩浆热事件,可能记录了哥伦比亚超大陆裂解事件的岩浆响应。
致谢 感谢中国地质科学院地质研究所任纪舜院士的支持和鼓励。同位素分析测试得到天津地质调查中心实验室周红英主任、郝爽、肖志斌高级工程师的大力帮助;匿名审稿人提出了宝贵的修改意见;在此一并致以诚挚的谢意!
Åhäll KI and Connelly J. 1998. Intermittent 1.53~1.13Ga magmatism in western Baltica:Age constraints and correlations within a postulated supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 92(1): 1-20 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(98)00064-3 |
Anderson JL and Cullers RL. 1999. Paleo- and Meso-Proterozoic granite plutonism of Colorado and Wyoming. Rocky Mountain Geology, 34(2): 149-164 DOI:10.2113/34.2.149 |
Badarch G, Cunningham WD and Windley BF. 2002. A new terrane subdivision for Mongolia:Implications for the Phanerozoic crustal growth of Central Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 21(1): 87-110 DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(02)00017-2 |
Barnes MA, Anthony EY, Williams I and Asquith GB. 2002. Architecture of a 1.38~1.34Ga granite-rhyolite complex as revealed by geochronology and isotopic and elemental geochemistry of subsurface samples from West Texas, USA. Precambrian Research, 119(1-4): 9-43 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00116-X |
Blein O, LaFlèche MR and Corriveau L. 2003. Geochemistry of the granulitic Bondy gneiss complex:A 1.4Ga arc in the Central Metasedimentary Belt, Grenville Province, Canada. Precambrian Research, 120(3-4): 193-217 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(02)00112-2 |
Blichert-Toft J and Albarède F. 1997. The Lu-Hf isotope geochemistry of chondrites and the evolution of the mantle-crust system. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 148(1-2): 243-258 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(97)00040-X |
Bonin B. 2007. A-type granites and related rocks:Evolution of a concept, problems and prospects. Lithos, 97(1-2): 1-29 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.12.007 |
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Nei Mongol Autonomous Region (BGMRN). 1991. Regional Geology of Nei Mongol (Inner Mongolia) Autonomous Region. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-657 (in Chinese)
|
Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources of Nei Mongol Autonomous region. 1996. Lithostratigraphic Units of of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 1-200 (in Chinese)
|
Cawood PA, Nemchin AA, Strachan R, PraveT and Krabbendam M. 2007. Sedimentary basin and detrital zircon record along East Laurentia and Baltica during assembly and breakup of Rodinia. Journal of the Geological Society, 164(2): 257-275 DOI:10.1144/0016-76492006-115 |
Chappell BW and White AJR. 1974. Two contrasting granite types. Pacific Geology, 8: 173-174 |
Cheng YQ. 1994. Introduction to Regional Geology in China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 70-85 (in Chinese)
|
Collins WJ, Beams SD, White AJR and Chappell BW. 1982. Nature and origin of A-type granites with particular reference to southeastern Australia. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 80(2): 189-200 DOI:10.1007/BF00374895 |
Corrigan D, Rivers T and Dunning G. 2000. U-Pb constraints for the plutonic and tectonometamorphic evolution of Lake Melville Terrane, Labrador and implications for basement reworking in the northeastern Grenville Province. Precambrian Research, 99(1-2): 65-90 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(99)00054-6 |
Dall'Agnol R and De Oliveira DC. 2007. Oxidized, magnetite-series, rapakivi-type granites of Carajás, Brazil:Implications for classification and petrogenesis of A-type granites. Lithos, 93(3-4): 215-233 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2006.03.065 |
Dickin AP and Higgins MD. 1992. Sm/Nd evidence for a major 1.5Ga crust-forming event in the central Grenville province. Geology, 20: 137-140 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0137:SNEFAM>2.3.CO;2 |
Eby GN. 1990. The A-type granitoids:A review of their occurrence and chemical characteristics and speculations on their petrogenesis. Lithos, 26(1-2): 115-134 DOI:10.1016/0024-4937(90)90043-Z |
Eby GN. 1992. Chemical subdivision of the A-type granitoids:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications. Geology, 20(7): 641-644 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1992)020<0641:CSOTAT>2.3.CO;2 |
Frost CD and Frost BR. 1997. Reduced rapakivi-type granites:The tholeiite connection. Geology, 25(7): 647-650 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0647:RRTGTT>2.3.CO;2 |
Frost CD, Frost BR, Chamberlain KR and Edwards BR. 1999. Petrogenesis of the 1.43Ga Sherman batholith, SE Wyoming, USA:A reduced, rapakivi-type anorogenic granite. Journal of Petrology, 40(12): 1771-1802 DOI:10.1093/petroj/40.12.1771 |
Frost CD and Frost BR. 2011. On ferroan (A-type) granitoids:Their compositional variability and modes of origin. Journal of Petrology, 52(1): 39-53 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egq070 |
Geng JZ, Li HK, Zhang J, Zhou HY and Li HM. 2011. Zircon Hf isotope analysis by means of LA-MC-ICP-MS. Geological Bulletin of China, 30(10): 1508-1513 |
Goldberg AS. 2010. Dyke swarms as indicators of major extensional events in the 1.9~1.2Ga Columbia supercontinent. Journal of Geodynamics, 50(3-4): 176-190 DOI:10.1016/j.jog.2010.01.017 |
Gordienko IV. 1996. Correlation of Pre-Jurassic sections of ancient continents and microcontinents in East Asia. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 13(3-5): 215-221 DOI:10.1016/0743-9547(96)00028-1 |
Griffin WL, Pearson NJ, Belousova E, Jackson SE, Van Achterberg E, O'Reilly SY and Shee SR. 2000. The Hf isotope composition of cratonic mantle:LA-MC-ICPMS analysis of zircon megacrysts in kimberlites. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 64(1): 133-147 DOI:10.1016/S0016-7037(99)00343-9 |
Griffin WL, Wang X, Jackson SE, Pearson NJ, O'Reilly SY, Xu XS and Zhou XM. 2002. Zircon chemistry and magma mixing, SE China:In-situ analysis of Hf isotopes, Tonglu and Pingtan igneous complexes. Lithos, 61(3-4): 237-269 DOI:10.1016/S0024-4937(02)00082-8 |
Haapla I and Rämö OT. 1999. Rapakivi grantes and related rocks:An introduction. Precambrian Research, 95(1-2): 1-7 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(98)00124-7 |
He ZY, Klemd R, Zhang ZM, Zong KQ, Sun LX, Tian ZL and Huang BT. 2015. Mesoproterozoic continental arc magmatism and crustal growth in the eastern Central Tianshan Arc Terrane of the southern Central Asian Orogenic Belt:Geochronological and geochemical evidence. Lithos, 236-237: 74-89 DOI:10.1016/j.lithos.2015.08.009 |
He ZY, Sun LX, Mao LJ, Zong KQ and Zhang ZM. 2015. Zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopic study of gneiss and granodiorite from the southern Beishan orogenic collage:Mesoproterozoic magmatism and crustal growth. Chinese Science Bulletin, 60(4): 389-399 (in Chinese) DOI:10.1360/N972014-00898 |
Hong DW, Wang SG, Han BF and Jin MY. 1995. Tectonic setting classifications and discrimination criteria for alkaline granites. Science in China (Series B), 25(4): 418-426 (in Chinese) |
Hong DW, Wang SG, Han BF and Jin MY. 1996. Post-orogenic alkaline granites from China and comparisons with anorogenic alkaline granites elsewhere. Journal of Southeast Asian Earth Sciences, 13(1): 13-27 DOI:10.1016/0743-9547(96)00002-5 |
Hong DW, Wang SG, XieXL, Zhang JS and Wang T. 2003. Correlation between continental crustal growth and the supercontinental cycle:Evidence from the granites with positive εNd in the central Asian orogenic belt. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(2): 203-209 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hou GT, Santosh M, Qian XL, Lister GS and Li JH. 2008. Tectonic constraints on 1.3~1.2Ga final breakup of Columbia supercontinent from a giant radiating dyke swarm. Gondwana Research, 14(3): 561-566 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2008.03.005 |
Hu AQ, Wei GJ, Deng WF, Zhang JB and Chen LL. 2006. 1.4Ga SHRIMP U-Pb age for zircons of granodiorite and its geological significance from the eastern segment of the Tianshan Mountains, Xinjiang, China. Geochimica, 35(4): 333-345 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Hu SX, Gu LX, Yan ZF, Hu ZH, Guo JH, Li HZ and Sun YD. 1991. Relationship of various types of granites with plate tectonics and their genesis and distribution regularity. In: Li ZT (ed.). Contributions on Granitiods and their Minerogenesis in Northern China. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 33-39 (in Chinese)
|
Jahn BM, Griffin WL and Windley B. 2000. Continental growth in the Phanerozoic:Evidence from Central Asia. Tectonophysics, 328(1-2): ⅶ-ⅹ |
Jahn BM, Windley B, Natal'in B and Dobretsov N. 2004. Phanerozoic continental growth in Central Asia. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 23(5): 599-603 DOI:10.1016/S1367-9120(03)00124-X |
Khain EV, Bibikova EV, Kröner A, Zhuravlev DZ, Sklyarov EV and Fedotova AA and Kravchenko-Berezhnoy IR. 2002. The most ancient ophiolite of the Central Asian fold belt:U-Pb and Pb-Pb zircon ages for the Dunzhugur complex, eastern Sayan, Siberia, and geodynamic implications. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 199(3-4): 311-325 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(02)00587-3 |
Khain EV, Bibikova EV, Salnikova EB, Kröner A, Gibsher AS, Didenko AN, Degtyarev KE and Fedotova AA. 2003. The Palaeo-Asian Ocean in the Neoproterozoic and Early Palaeozoic:New geochronologic data and palaeotectonic reconstructions. Precambrian Research, 122(1-2): 329-358 |
King PL, White AJR, Chappell BW and Allen LM. 1997. Characterization and origin of aluminous A-type granites from the Lachlan fold belt, southeastern Australia. Journal of Petrology, 38(3): 371-391 DOI:10.1093/petroj/38.3.371 |
Konopelko D, Kullerud K, Apayarov F, Sakiev K, Baruleva O, Ravna E and Lepekhina E. 2012. SHRIMP zircon chronology of HP-UHP rocks of the Makbal metamorphic complex in the Northern Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan. Gondwana Research, 22(1): 300-309 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2011.09.002 |
Kröner A, Kovach V, Belousova E, Hegner E, Armstrong R, Dolgopolova A, Seltmann R, Alexeiev DV, Hoffmann JE, Wong J, Sun MC, Wang T, Tong Y, Wilde SA, Degtyarev KE and Rytsk E. 2014. Reassessment of continental growth during the accretionary history of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Research, 25(1): 103-125 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2012.12.023 |
Kuzmichev AB, Bibikova EV and Zhuravlev DZ. 2001. Neoproterozoic (~800Ma) orogeny in the Tuva-Mongolia Massif (Siberia):Island arc-continent collision at the northeast Rodinia margin. Precambrian Research, 110(1-4): 109-126 DOI:10.1016/S0301-9268(01)00183-8 |
Kuznetsov LM, Natapov E, Belousova A, O'Reilly SY and Griffin WL. 2010. Geochronological, geochemical and isotopic study of detrital zircon suites from Late Neoproterozoic clastic strata along the NE margin of the East European Craton:Implications for plate tectonic models. Gondwana Reserch, 17: 583-601 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2009.08.005 |
Li HK, Lu SN, Li HM, Sun LX, Xiang ZQ, Geng JZ and Zhou HY. 2009. Zircon and beddeleyite U-Pb precision dating of basic rock sills intruding Xiamaling Formation, North China. Geological Bulletin of China, 28(10): 1396-1404 |
Li JY. 2006. Permian geodynamic setting of northeast China and adjacent regions:Closure of the Paleo-Asian Ocean and subduction of the Paleo-pacific plate. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 26(3-4): 207-224 DOI:10.1016/j.jseaes.2005.09.001 |
Li SJ and Gao DZ. 1995. New discoveries of geological structures in Sonid Zuoqi of Inner Mongolia and discussion on Tectonic features. Geoscience, 9(2): 130-141 (in Chinese) |
Li SJ, Zhang WJ, Geng MS and Gao DZ. 1998. An Overview of the Geological Structural Characteristics and Formation and Evolution of the Mongolian Arc. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1-145 (in Chinese)
|
Li XH, Liu Y, Yang YH, Chen FK, Tu XL and Qi CS. 2007. Rapid separation of Lu-Hf and Sm-Nd from a single rock dissolution and precise measurement of Hf-Nd isotopic ratios for nations rock standards. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 221-226 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu CS, Chen XM, Chen PR, Wang RC and Hu H. 2003. Subdivision, discrimination criteria and genesis for A-type rock suites. Geological Journal of China Universities, 9(4): 573-591 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu DY, Jian P, Zhang Q, Zhang FQ, Shi YR, Shi GH, Zhang LQ and Tao H. 2003. SHRIMP dating of adakites in the Tulingkai ophiolite, Inner Mongolia:Evidence for the Early Paleozoic subduction. Acta Geologica Sinica, 77(3): 317-327 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Liu YS, Gao S, Hu ZC, Gao CG, Zong KQ and Wang DB. 2010. Continental and oceanic crust recycling-induced melt-peridotite interactions in the Trans-North China Orogen:U-Pb dating, Hf isotopes and trace elements in zircons from mantle xenoliths. Journal of Petrology, 51(1-2): 537-571 DOI:10.1093/petrology/egp082 |
Liu ZH, Liu YQ and Feng BZ. 2000. The establishment and tectonic evolution of Proterozoic orogenic belt in the north margin of North China plate. Journal of Changchun University of Science and Technology, 30(2): 110-114 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Loiselle MC and Wones DR. 1979. Characteristics and origin of anorogenic granites. Geological Society of America, 11: 468 |
Lu SN, Yang CL, Li HK and Chen ZH. 2002. A group of rifting events in the terminal Paleoproterozoic in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 5(1): 123-131 DOI:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70896-0 |
Ludwig KR. 2003. User's Manual for Isoplot/EX Version3.0: A Geochronological Toolkit for Microsoft Excel. Berkeley, California, USA: Berkeley Geochronology Center, 1-70
|
Middlemost EAK. 1994. Naming materials in the magma/igneous rock system. Earth-Science Reviews, 37(3-4): 215-244 DOI:10.1016/0012-8252(94)90029-9 |
Nyman MW, Karlstrom KE, Kirby E and Graubard CM. 1994. Mesoproterozoic contractional orogeny in western North America:Evidence from ca. 1.4Ga plutons. Geology, 22(10): 901-904 DOI:10.1130/0091-7613(1994)022<0901:MCOIWN>2.3.CO;2 |
Pearce JA, Harris NBW and Tindle AG. 1984. Trace element discrimination diagrams for the tectonic interpretation of granitic rocks. Journal of Petrology, 25(4): 956-983 DOI:10.1093/petrology/25.4.956 |
Pisarevsky SA and Natapov LM. 2003. Siberia and Rodinia. Tectonophysics, 375(1-4): 221-245 DOI:10.1016/j.tecto.2003.06.001 |
Ren JS, Wang ZX, Chen BW, Jiang CF, Niu BG, Li JY, Xie GL, He ZJ and Liu ZG. 1999. The Tectonics of China from A Global View:A Guide to the Tectonic Maps of China and Adjacent Regions. Beijing: Geological publishing House, 1-32 (in Chinese)
|
Rojas-AgramonteY, KrönerA, Demoux A, Xia X, Wang W, DonskayaT, Liu DY and Sun M. 2011. Detrital and xenocrystic zircon ages from Neoproterozoic to Palaeozoic arc terranes of Mongolia:Significance for the origin of crustal fragments in the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Gondwana Research, 19(3): 751-763 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2010.10.004 |
Scherer E, Münker C and Mezger K. 2001. Calibration of the lutetium-hafnium clock. Science, 293(5530): 683-687 DOI:10.1126/science.1061372 |
Şengör AMC, Natal'in BA and BurtmanVS. 1993. Evolution of the Altaid tectonic collage and Palaeozoic crustal growth in Eurasia. Nature, 364(6435): 299-307 DOI:10.1038/364299a0 |
Shao JA and Zhang LQ. 1990. Ancient terranes in the Hinganling-Mongolia orogenic belt. In: Orogenic Belt, Basin, Pan-Pafic Tectonic International Continental Lithosphere Tectonic Evolution and Dynamics Symposium and the 3rd National Tectonic Conference Proceedings 1. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 16-21 (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
Shao JA. 1991. Crust Evolution in the Middle Part of the Northern Margin of Sino-Korean Plate. Beijing: Peking University Publishing House, 1-200 (in Chinese)
|
Shao JA, Zhang LQ and Li DM. 2002. Three Proterozoic extensional events in North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 18(2): 152-160 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Shao JA, Zhai MG, Zhang LQ and Li DN. 2005. Identification of 5 time-groups of dike swarms in Shanxi-Hebei-Inner Mongulia border area and its tectonic implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 79(1): 56-67 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Shi WX, Liao QA, Hu YQ and Yang ZF. 2010. Characteristics of Mesoproterozoic granites and their geological significances from Middle Tianshan Block, East Tianshan district, NW China. Geological Science and Technology Information, 29(1): 29-37 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Shi XJ, Zhang L, Wang T, Zhang JJ, Liu MH, Zhou HS and Yan YT. 2016. Zircon geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions for the Mesoproterozoic gneisses in Zongnaishan area, northern Alxa and its tectonic affinity. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 32(11): 3518-3536 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Söderlund U, Patchett PJ, Vervoort JD and Isachsen CE. 2004. The 176Lu decay constant determined by Lu-Hf and U-Pb isotope systematics of Precambrian mafic intrusions. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 219(3-4): 311-324 DOI:10.1016/S0012-821X(04)00012-3 |
Su WB, Zhang SH, Huff WD, Li HK, Ettensohn FR, Chen XY, Yang HM, HanYG, Song B and Santosh M. 2008. SHRIMP U-Pb ages of K-bentonite beds in the Xiamaling Formation:Implications for revised subdivision of the Meso- to Neoproterozoic history of the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 14(3): 543-553 DOI:10.1016/j.gr.2008.04.007 |
Su WB, Li HK, Huff WD, Ettensohn FR, Zhang SH, Zhou HY and Wan YS. 2010. SHRIMP U-Pb dating for a K-bentonite bed in the Tieling Formation, North China. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(29): 3312-3323 DOI:10.1007/s11434-010-4007-5 |
Sun LX, RenBF, Zhao FQ, Gu YC, Li YF and Liu H. 2013. Zircon U-Pb dating and Hf isotopic compositions of the Mesoporterozoic granitic gneiss in Xilinhot Block, Inner Mongolia. Geological Bulletin of China, 32(2-3): 327-340 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun LX, Ren BF, Wang SQ, Xu XY and Zhang Y. 2018. Petrogenesis of the Mesoproterozoic gneissic granite in the Sonid Left Banner area, Inner Mongolia, and its tectonic implications. Acta Geologica Sinica, 92(11): 2167-2189 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Sun SS and McDonough WF, 1989. Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD and Norry MJ (eds.). Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 42(1): 313-345
|
Vigneresse JL. 2005. The specific case of the Mid-Proterozoic rapakivi granites and associated suite within the context of the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 137(1-2): 1-34 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2005.01.001 |
Wang MM, Zhang L, Huo YJ, Shi XJ and Liu C. 2019. Tectonic affinity of the northern Longshoushan-Beidashan:Constraints from the zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotopic compositions of the Haisen Chulu gneiss. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 38(5): 631-645 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Watson EB and Harrison TM. 1983. Zircon saturation revisited:Temperature and composition effects in a variety of crustal magma types. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 64(2): 295-304 DOI:10.1016/0012-821X(83)90211-X |
Whalen JB, Currie KL and Chappell BW. 1987. A-type granites:Geochemical characteristics, discrimination and petrogenesis. Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology, 95(4): 407-419 DOI:10.1007/BF00402202 |
Wu FY, Sun DY and Lin QD. 1999. Petrogenesis of the Phanerozoic granites and crustal growth in northeast China. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 15(2): 181-189 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Wu FY, Li XH, Zheng YF and Gao S. 2007. Lu-Hf isotopic systematics and their applications in petrology. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(2): 185-220 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiao RG, Sui DC, Luo ZH, Zhang WJ and Li SJ. 1995. Discovery of Early Proterozoic metamorphic complex in North Inner Mongolia. Geoscience, 9(2): 142-148 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xiao WJ, Windley BF, Hao J and Zhai MG. 2003. Accretion leading to collision and the Permian Solonker suture, Inner Mongolia, China:Termination of the Central Asian Orogenic Belt. Tectonics, 22(6): 1069 |
Xu B, Zhao P, Bao QZ, Zhou YH, Wang YY and Luo ZW. 2014. Preliminary study on the pre-Mesozoic tectonic unit division of the Xing-Meng Orogenic Belt (XMOB). Acta Petrologica Sinica, 30(7): 1841-1857 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Xu B, Xu Y, Li J and Li QS. 2016. Age of the Ondor Sum Group in western Inner Mongolia and its position in the Central Asia Orogenic Belt. Earth Science Frontiers, 23(6): 120-127 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG, Hu B, Peng P and Zhao TP. 2014. Meso-Neoproterozoic magmatic events and multi-stage rifting in the NCC. Earth Science Frontiers, 21(1): 100-119 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhai MG and Peng P. 2016. Paleo-Proterozoic tectonic events of in the North China Craton. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 23(11): 2665-2682 (in Chinese with English abstract) |
Zhang SH, Zhao Y, Yang ZY, He ZF and Wu H. 2009. The 1.35Ga diabase sills from the northern North China Craton:Implications for breakup of the Columbia (Nuna) supercontinent. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 288(3-4): 588-600 DOI:10.1016/j.epsl.2009.10.023 |
Zhang SH, Zhao Y and Santosh M. 2012. Mid-Mesoproterozoic bimodal magmatic rocks in the northern North China Craton:Implications for magmatism related to breakup of the Columbia supercontinent. Precambrian Research, 222-223: 339-367 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2011.06.003 |
Zhao GC, Cawood PA, Wilde SA and Sun M. 2002. Review of global 2.1~1.8Ga orogens:Implications for a pre-Rodinia supercontinent. Earth-Science Reviews, 59(1-4): 125-162 DOI:10.1016/S0012-8252(02)00073-9 |
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA and Li SZ. 2003a. Assembly, accretion and breakup of the Paleo-Mesoproterozoic Columbia supercontinent:Records in the North China Craton. Gondwana Research, 6(3): 417-434 DOI:10.1016/S1342-937X(05)70996-5 |
Zhao GC, Sun M and Wilde SA. 2003b. Major tectonic units of the North China Craton and their Paleoproterozoic assembly. Science in China (Series D), 46(1): 23-38 DOI:10.1360/03yd9003 |
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA and Li SD. 2004. A Paleo-Mesoproterozoic supercontinent:Assembly, growth and breakup. Earth-Science Reviews, 67(1-2): 91-123 DOI:10.1016/j.earscirev.2004.02.003 |
Zhao GC, Sun M, Wilde SA and Li SD. 2005. Late Archean to Paleoproterozoic evolution of the North China Craton:Key issues revisited. Precambrian Research, 136(2): 177-202 DOI:10.1016/j.precamres.2004.10.002 |
程裕淇. 1994. 中国区域地质概论. 北京: 地质出版社, 70-85.
|
耿建珍, 李怀坤, 张健, 周红英, 李惠民. 2011. 锆石Hf同位素组成的LA-MC-ICP-MS测定. 地质通报, 30(10): 1508-1513. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2011.10.004 |
贺振宇, 孙立新, 毛玲娟, 宗克清, 张泽明. 2015. 北山造山带南部片麻岩和花岗闪长岩的锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素:中元古代的岩浆作用与地壳生长. 科学通报, 60(4): 389-399. |
洪大卫, 王式洸, 韩宝福, 靳满元. 1995. 碱性花岗岩的构造环境分类及其鉴别标志. 中国科学(B辑), 25(4): 418-426. |
洪大卫, 王式洸, 谢锡林, 张季生, 王涛. 2003. 从中亚正εNd值花岗岩看超大陆演化和大陆地壳生长的关系. 地质学报, 77(2): 203-209. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.02.008 |
胡受奚, 顾连兴, 严正富, 胡志宏, 郭继春, 李海章, 孙冶东. 1991.不同类型花岗岩与板块构造的关系及其形成和分布规律.见: 李之彤编.中国北方花岗岩及其成矿作用论文集.北京: 地质出版社, 33-39
|
胡霭琴, 韦刚健, 邓文峰, 张积斌, 陈林丽. 2006. 天山东段1.4Ga花岗闪长质片麻岩SHRIMP锆石U-Pb年龄及其地质意义. 地球化学, 35(4): 333-345. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2006.04.001 |
李怀坤, 陆松年, 李惠民, 孙立新, 相振群, 耿建珍, 周红英. 2009. 侵入下马岭组的基性岩床的锆石和斜锆石U-Pb精确定年——对华北中元古界地层划分方案的制约. 地质通报, 28(10): 1396-1404. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-2552.2009.10.005 |
李述靖, 高德臻. 1995. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗地区若干地质构造新发现及其构造属性的初步探讨. 现代地质, 9(2): 130-141. |
李述靖, 张维杰, 耿明山, 高德臻. 1998. 蒙古弧地质构造特征及形成演化概论. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-145.
|
李献华, 刘颖, 杨岳衡, 陈福坤, 涂湘林, 祁昌实. 2007. 同一岩石试样的Lu-Hf和Sm-Nd快速分离及国家岩石标准物质的Hf-Nd同位素比值精确测定. 岩石学报, 23(2): 221-226. |
刘昌实, 陈小明, 陈培荣, 王汝成, 胡欢. 2003. A型岩套的分类、判别标志和成因. 高校地质学报, 9(4): 573-591. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1006-7493.2003.04.011 |
刘敦一, 简平, 张旗, 张福勤, 石玉若, 施光海, 张履桥, 陶华. 2003. 内蒙古图林凯蛇绿岩中埃达克岩SHRIMP测年:早古生代洋壳消减的证据. 地质学报, 77(3): 317-327. DOI:10.3321/j.issn:0001-5717.2003.03.004 |
刘正宏, 刘雅琴, 冯本智. 2000. 华北板块北缘中元古代造山带的确立及其构造演化. 长春科技大学学报, 30(2): 110-114. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1671-5888.2000.02.002 |
内蒙古自治区地质矿产局. 1991. 内蒙古自治区区域地质志. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-657.
|
内蒙古自治区地质矿产局. 1996. 内蒙古自治区岩石地层. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 1-200.
|
任继舜, 王作勋, 陈炳蔚, 姜春发, 牛宝贵, 李锦轶, 谢广连, 和政军, 刘志刚. 1999. 从全球看中国大地构造——中国及邻区大地构造图简要说明. 北京: 地质出版社, 1-32.
|
邵济安, 张履桥. 1990.兴蒙造山带中的古地体.见: 《造山带·盆地·环太平洋构造》国际大陆岩石圈构造演化与动力学讨论会暨第三届全国构造会议论文集1.北京: 地质出版社, 16-21
|
邵济安. 1991. 中朝板块北缘中段地壳演化. 北京: 北京大学出版社, 1-200.
|
邵济安, 张履桥, 李大明. 2002. 华北克拉通元古代的三次伸展事件. 岩石学报, 18(2): 152-160. |
邵济安, 翟明国, 张履桥, 李大明. 2005. 晋冀蒙交界地区五期岩墙群的界定及其构造意义. 地质学报, 79(1): 56-67. |
施文翔, 廖群安, 胡远清, 杨再峰. 2010. 东天山地区中天山地块内中元古代花岗岩的特征及地质意义. 地质科技情报, 29(1): 29-37. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-7849.2010.01.005 |
史兴俊, 张磊, 王涛, 张建军, 刘明华, 周红升, 严育通. 2016. 阿拉善北部宗乃山地区片麻岩锆石U-Pb年龄、Hf同位素特征及其构造归属探讨. 岩石学报, 32(11): 3518-3536. |
苏文博, 李怀坤, Huff WD, Ettensohn FR, 张世红, 周红英, 万渝生. 2010. 铁岭组钾质斑脱岩锆石SHRIMP U-Pb年代学研究及其地质意义. 科学通报, 55(22): 2197-2206. |
孙立新, 任邦方, 赵凤清, 谷永昌, 李艳峰, 刘卉. 2013. 内蒙古锡林浩特地块中元古代花岗片麻岩的锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素特征. 地质通报, 32(2-3): 327-340. |
孙立新, 任邦方, 王树庆, 许新英, 张云. 2018. 内蒙古苏尼特左旗中元古代片麻状花岗岩的成因及大地构造意义. 地质学报, 92(11): 2167-2189. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.11.001 |
王毛毛, 张磊, 霍雨佳, 史兴俊, 刘翠. 2019. 龙首山-北大山北部的属性——来自海森楚鲁片麻岩锆石U-Pb年龄和Hf同位素的约束. 岩石矿物学杂志, 38(5): 631-645. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2019.05.003 |
吴福元, 孙德有, 林强东. 1999. 北地区显生宙花岗岩的成因与地壳增生. 岩石学报, 15(2): 181-189. |
吴福元, 李献华, 郑永飞, 高山. 2007. Lu-Hf同位素体系及其岩石学应用. 岩石学报, 23(2): 185-220. |
肖荣阁, 隋德才, 罗照华, 张维杰, 李述靖. 1995. 内蒙古北部早元古代变质岩系的发现及其岩石学研究. 现代地质, 9(2): 142-148. |
徐备, 赵盼, 鲍庆中, 周永恒, 王炎阳, 罗志文. 2014. 兴蒙造山带前中生代构造单元划分初探. 岩石学报, 30(7): 1841-1857. |
徐备, 徐严, 粟进, 李群生. 2016. 内蒙古西部温都尔庙群的时代及其在中亚造山带中的位置. 地学前缘, 23(6): 120-127. |
翟明国, 胡波, 彭澎, 赵太平. 2014. 华北中-新元古代的岩浆作用与多期裂谷事件. 地学前缘, 21(1): 100-119. |
翟明国, 彭澎. 2007. 华北克拉通古元古代构造事件. 岩石学报, 23(11): 2665-2682. DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1000-0569.2007.11.001 |
 2020, Vol. 36
2020, Vol. 36

